Advances with RNAi-Based Therapy for Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HBV Replication
3. Goals of Treating Chronic Infection with HBV
4. Currently Licensed Treatment for HBV
5. New HBV Drugs under Development
5.1. Rationale for Advancing RNAi-Based Anti-HBV Therapy
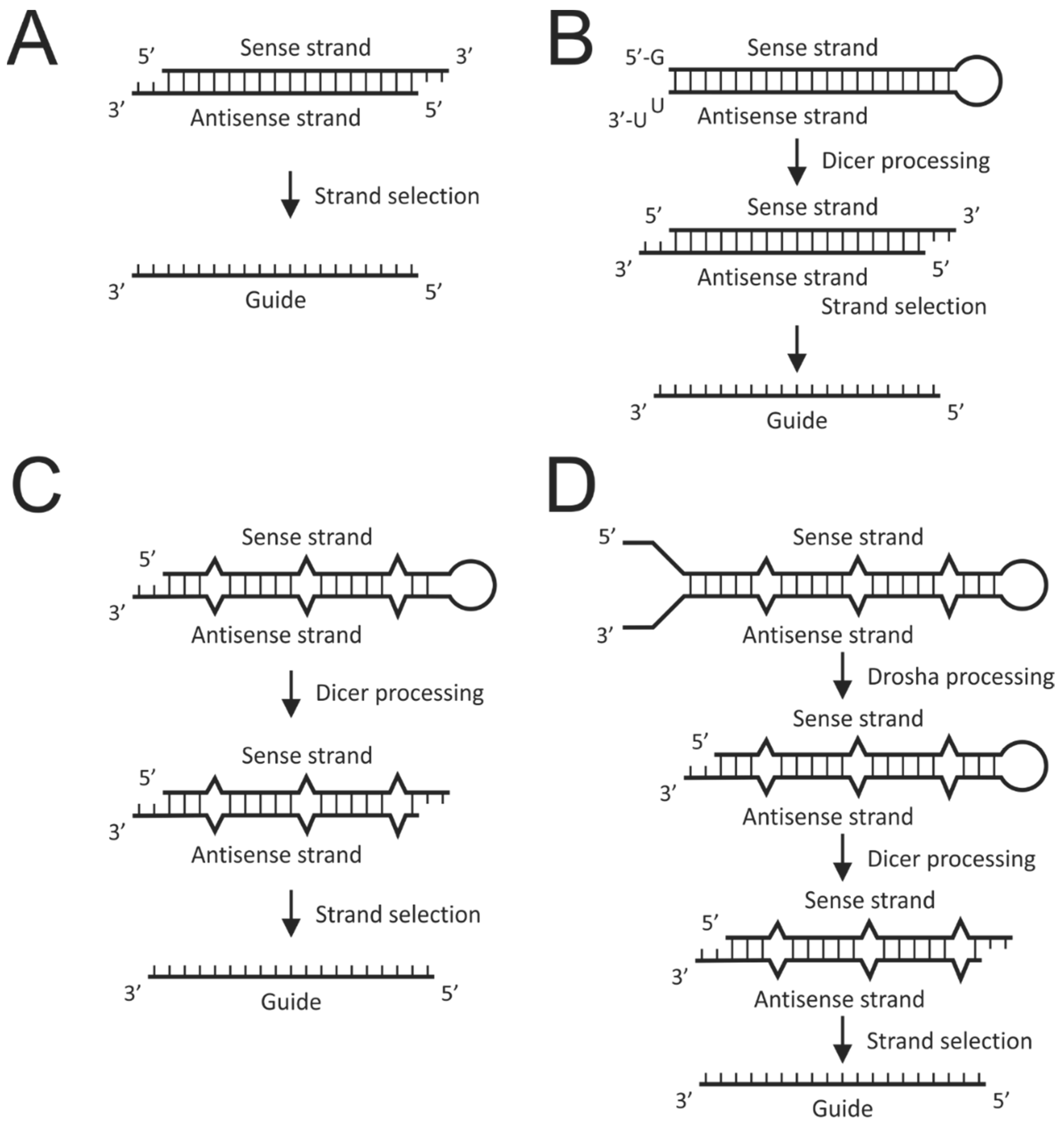
5.2. The RNAi Pathway
5.3. RNAi Activators
5.4. Significance of Genotype Variability for Advancing RNAi-Based HBV Therapy
6. Models of HBV Infection
7. Delivery of HBV-Targeting Gene Silencers
7.1. Non-Viral Vectors
7.2. Viral Vectors
7.3. Clinical Trials Evaluating RNAi-Based Treatment for HBV Infection
8. Future of the Field
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Revill, P.A.; Chisari, F.V.; Block, J.M.; Dandri, M.; Gehring, A.J.; Guo, H.; Hu, J.; Kramvis, A.; Lampertico, P.; Janssen, H.L.A.; et al. A global scientific strategy to cure hepatitis B. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovila, A.P.; Eder, A.M.; Fuller, S.D. Hepatitis B surface antigen assembles in a post-ER, pre-Golgi compartment. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 118, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, A.C.; Conway, J.F.; Cheng, N.; Watts, N.R.; Belnap, D.M.; Harris, A.; Stahl, S.J.; Wingfield, P.T. Structure, assembly, and antigenicity of hepatitis B virus capsid proteins. Adv. Virus Res. 2005, 64, 125–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maupas, P.; Goudeau, A.; Coursaget, P.; Drucker, J.; Bagros, P. Immunisation against hepatitis B in man. Lancet 1976, 1, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, R.H.; Gerin, J.L. Hepatitis B subunit vaccine: A preliminary report of safety and efficacy tests in chimpanzees. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1975, 270, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmuness, W.; Stevens, C.E.; Harley, E.J.; Zang, E.A.; Oleszko, W.R.; William, D.C.; Kellner, A. Hepatitis B vaccine: Demonstration of efficacy in a controlled clinical trial in a high-risk population in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 303, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureau, C.; Salisse, J. A conformational heparan sulfate binding site essential to infectivity overlaps with the conserved hepatitis B virus a-determinant. Hepatology 2013, 57, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Falth, M.; Stindt, J.; Koniger, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Saso, W.; Nishioka, K.; Ohashi, H.; Sugiyama, R.; Ryo, A.; Ohki, M.; Yun, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Ohshima, T.; et al. The machinery for endocytosis of epidermal growth factor receptor coordinates the transport of incoming hepatitis B virus to the endosomal network. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Saso, W.; Sugiyama, R.; Ishii, K.; Ohki, M.; Nagamori, S.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ryo, A.; Yun, J.H.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor is a host-entry cofactor triggering hepatitis B virus internalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8487–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Ou, J.H. Phosphorylation and nuclear localization of the hepatitis B virus core protein: Significance of serine in the three repeated SPRRR motifs. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koniger, C.; Wingert, I.; Marsmann, M.; Rösler, C.; Beck, J.; Nassal, M. Involvement of the host DNA-repair enzyme TDP2 in formation of the covalently closed circular DNA persistence reservoir of hepatitis B viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4244–E4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, K.; Que, L.; Shimadu, M.; Koura, M.; Ishihara, Y.; Wakae, K.; Nakamura, T.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T.; Muramatsu, M. Flap endonuclease 1 is involved in cccDNA formation in the hepatitis B virus. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asabe, S.; Wieland, S.F.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Roederer, M.; Engle, R.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. The size of the viral inoculum contributes to the outcome of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9652–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilbert, A.R.; Miller, D.S.; Scougall, C.A.; Turnbull, H.; Burrell, C.J. Kinetics of duck hepatitis B virus infection following low dose virus inoculation: One virus DNA genome is infectious in neonatal ducks. Virology 1996, 226, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorsière, A.; Mueller, H.; Van Breugel, P.C.; Abdul, F.; Gerossier, L.; Beran, R.K.; Livingston, C.M.; Niu, C.; Fletcher, S.P.; Hantz, O. Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor. Nature 2016, 531, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolla, N.; Kew, M.; Arbuthnot, P. Regulatory elements of hepatitis B virus transcription. J. Viral. Hepat. 2002, 9, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne, R.J.; Bagga, S.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B virus molecular biology and pathogenesis. Hepatoma Res. 2016, 2, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testoni, B.; Lebosse, F.; Scholtes, C.; Berby, F.; Miaglia, C.; Subic, M.; Loglio, A.; Facchetti, F.; Lampertico, P.; Levrero, M.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) correlates with covalently closed circular DNA transcriptional activity in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, B.; Valdes, J.D.; Sun, J.; Guo, H. Serum Hepatitis B Virus RNA: A New Potential Biomarker for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhou, L.; Chen, E.; Liu, C.; Tang, X.; Jiang, W.; Han, N.; Li, H.; Tang, H. Present and Future Therapies for Chronic Hepatitis B. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1179, 137–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ely, A.; Moyo, B.; Arbuthnot, P. Progress With Developing Use of Gene Editing To Cure Chronic Infection With Hepatitis B Virus. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijampatnam, B.; Liotta, D.C. Recent advances in the development of HBV capsid assembly modulators. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 50, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripon, P.; Cannie, I.; Urban, S. Efficient inhibition of hepatitis B virus infection by acylated peptides derived from the large viral surface protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Mier, W.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Volz, T.; von Weizsacker, F.; Haberkorn, U.; Fischer, L.; Pollok, J.M.; Erbes, B.; et al. Prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in vivo by entry inhibitors derived from the large envelope protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; Ben, M.M.; Warlich, M.; Lohse, A.W.; Pollok, J.M.; Alexandrov, A.; Urban, S.; Petersen, J.; Lutgehetmann, M.; et al. The entry inhibitor Myrcludex-B efficiently blocks intrahepatic virus spreading in humanized mice previously infected with hepatitis B virus. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiber, T.; Treiber, N.; Meister, G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, E.; Caudy, A.A.; Hammond, S.M.; Hannon, G.J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 2001, 409, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, G.; Landthaler, M.; Patkaniowska, A.; Dorsett, Y.; Teng, G.; Tuschl, T. Human Argonaute2 Mediates RNA Cleavage Targeted by miRNAs and siRNAs. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Carmell, M.A.; Rivas, F.V.; Marsden, C.G.; Thomson, J.M.; Song, J.J.; Hammond, S.M.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Hannon, G.J. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science 2004, 305, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, S.; Izaurralde, E. Towards a molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamore, P.D.; Tuschl, T.; Sharp, P.A.; Bartel, D.P. RNAi: Double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 2000, 101, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Yalcin, A.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 411, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.S.; Dohjima, T.; Bauer, G.; Li, H.; Li, M.J.; Ehsani, A.; Salvaterra, P.; Rossi, J. Expression of small interfering RNAs targeted against HIV-1 rev transcripts in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummelkamp, T.R.; Bernards, R.; Agami, R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 2002, 296, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giladi, H.; Ketzinel-Gilad, M.; Rivkin, L.; Felig, Y.; Nussbaum, O.; Galun, E. Small interfering RNA inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in mice. Mol. Ther. 2003, 8, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, K.; Nakao, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Eguchi, K. Short interfering RNA-directed inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication. FEBS Lett. 2003, 543, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Bock, C.T.; Wedemeyer, H.; Wustefeld, T.; Locarnini, S.; Dienes, H.P.; Kubicka, S.; Manns, M.P.; Trautwein, C. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in vivo by nucleoside analogues and siRNA. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M.; Wu, C.H.; Wu, G.Y. Inhibition of HBV replication by siRNA in a stable HBV-producing cell line. Hepatology 2003, 38, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.K.; Xuan, B.Q.; Min, T.S.; Xu, J.F.; Li, L.; Huang, W.D. Cost-effective method of siRNA preparation and its application to inhibit hepatitis B virus replication in HepG2 cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Martinez, J.; Patkaniowska, A.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Functional anatomy of siRNAs for mediating efficient RNAi in Drosophila melanogaster embryo lysate. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6877–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, D.V.; Blanchard, K.; Shaw, L.; Jensen, K.; Lockridge, J.A.; Dickinson, B.; McSwiggen, J.A.; Vargeese, C.; Bowman, K.; Shaffer, C.S; et al. Activity of stabilized short interfering RNA in a mouse model of hepatitis B virus replication. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, D.V.; Lockridge, J.A.; Shaw, L.; Blanchard, K.; Jensen, K.; Breen, W.; Hartsough, K.; Machemer, L.; Radka, S.; Jadhav, V.; et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hean, J.; Crowther, C.; Ely, A.; Ul Islam, R.; Barichievy, S.; Bloom, K.; Weinberg, M.S.; van Otterlo, W.A.; de Koning, C.B.; Salazar, F.; et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in vivo using lipoplexes containing altritol-modified antiviral siRNAs. Artif. DNA PNA XNA 2010, 1, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimani, M.D.; Ely, A.; Buff, M.C.; Bernhardt, S.; Engels, J.W.; Arbuthnot, P. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in cultured cells and in vivo using 2’-O-guanidinopropyl modified siRNAs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6145–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimani, M.D.; Ely, A.; Buff, M.C.; Bernhardt, S.; Engels, J.W.; Scherman, D.; Escriou, V.; Arbuthnot, P. Inhibition of replication of hepatitis B virus in transgenic mice following administration of hepatotropic lipoplexes containing guanidinopropyl-modified siRNAs. J. Control Release 2015, 209, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaffrey, A.P.; Nakai, H.; Pandey, K.; Huang, Z.; Salazar, F.H.; Xu, H.; Wieland, S.F.; Marion, P.L.; Kay, M.A. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus in mice by RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, D.; Streetz, K.L.; Jopling, C.L.; Storm, T.A.; Pandey, K.; Davis, C.R.; Marion, P.; Salazar, F.; Kay, M.A. Fatality in mice due to oversaturation of cellular microRNA/short hairpin RNA pathways. Nature 2006, 441, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomai, A.; Shaul, Y. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus expression and replication by RNA interference. Hepatology 2003, 37, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, V.; Ely, A.; Bloom, K.; Weinberg, M.; Arbuthnot, P. tRNA Lys3 promoter cassettes that efficiently express RNAi-activating antihepatitis B virus short hairpin RNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, A.; Naidoo, T.; Mufamadi, S.; Crowther, C.; Arbuthnot, P. Expressed anti-HBV primary microRNA shuttles inhibit viral replication efficiently in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, A.; Naidoo, T.; Arbuthnot, P. Efficient silencing of gene expression with modular trimeric Pol II expression cassettes comprising microRNA shuttles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, S.; Ely, A.; Crowther, C.; Moolla, N.; Salazar, F.H.; Marion, P.L.; Ferry, N.; Weinberg, M.S.; Arbuthnot, P. Effective inhibition of HBV replication in vivo by anti-HBx short hairpin RNAs. Mol. Ther. 2006, 13, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprichard, S.L.; Boyd, B.; Althage, A.; Chisari, F.V. Clearance of hepatitis B virus from the liver of transgenic mice by short hairpin RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivacik, D.; Ely, A.; Ferry, N.; Arbuthnot, P. Sustained inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in vivo using RNAi-activating lentiviruses. Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maepa, M.B.; Ely, A.; Grayson, W.; Arbuthnot, P. Sustained Inhibition of HBV Replication In Vivo after Systemic Injection of AAVs Encoding Artificial Antiviral Primary MicroRNAs. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramvis, A. Genotypes and genetic variability of hepatitis B virus. Intervirology 2014, 57, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatematsu, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Kurbanov, F.; Sugauchi, F.; Mano, S.; Maeshiro, T.; Nakayoshi, T.; Wakuta, M.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mizokami, M. A genetic variant of hepatitis B virus divergent from known human and ape genotypes isolated from a Japanese patient and provisionally assigned to new genotype J. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10538–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbi, G.C.; Kramvis, A.; Kew, M.C. Distinctive sequence characteristics of subgenotype A1 isolates of hepatitis B virus from South Africa. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.L.; Hui, A.; Wong, M.; Tse, A.M.; Hung, L.C.; Wong, V.W.; Sung, J.J. Genotype C hepatitis B virus infection is associated with an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2004, 53, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A.; Kew, M. Relationship of genotypes of hepatitis B virus to mutations, disease progression and response to antiviral therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2005, 12, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, A.; Blondin, D.; Hauck, K.; Sagir, A.; Kohnle, T.; Heintges, T.; Häussinger, D. Response to interferon alfa is hepatitis B virus genotype dependent: Genotype A is more sensitive to interferon than genotype D. Gut 2005, 54, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Gómez, J.Á.; Lozano-Serrano, A.B.; Cabezas-Fernández, M.T.; Soriano-Pérez, M.J.; Vázquez-Villegas, J.; Estévez-Escobar, M.; Cabeza-Barrera, I.; Salas-Coronas, J. Chronic hepatitis B genotype E in African migrants: Response to nucleos (t) ide treatment in real clinical practice. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sozzi, V.; Revill, P.A.; Liu, J.; Gao, L.; Yang, G.; Lu, M.; Sutter, K.; et al. Hepatitis B virus sensitivity to interferon-α in hepatocytes is more associated with cellular interferon response than with viral genotype. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1237–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A.; Kostaki, E.-G.; Hatzakis, A.; Paraskevis, D. Immunomodulatory function of HBeAg related to short-sighted evolution, transmissibility, and clinical manifestation of hepatitis B virus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Bai, S.; Ding, N.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L.; Mao, P.; Zoulim, F.; et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype and basal core promoter/precore mutations are associated with hepatitis B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure without pre-existing liver cirrhosis. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Rösler, C.; Kidd-Ljunggren, K.; Nassal, M. Quantitative assessment of the antiviral potencies of 21 shRNA vectors targeting conserved, including structured, hepatitis B virus sites. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Cheng, T.; Cai, Y.-J.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, T.; Xia, D.-Z.; Li, R.-Y.; Yang, L.-W.; Wang, Y.-B. RNA Interference inhibits hepatitis B virus of different genotypes in vitro and in vivo. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glebe, D.; Urban, S. Viral and cellular determinants involved in hepadnaviral entry. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Le Seyec, J.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillouzo, A.; Corlu, A.; Aninat, C.; Glaise, D.; Morel, F.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. The human hepatoma HepaRG cells: A highly differentiated model for studies of liver metabolism and toxicity of xenobiotics. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 168, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Replicative intermediates of hepatitis B virus in HepG2 cells that produce infectious virions. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschman, S.Z.; Price, P.; Garfinkel, E.; Christman, J.; Acs, G. Expression of cloned hepatitis B virus DNA in human cell cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 5507–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, S.K.; Otto, M.J.; Barker, C.S.; Zaifert, K.; Wang, G.H.; Guo, J.T.; Seeger, C.; King, R.W. Inducible expression of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) in stably transfected hepatoblastoma cells: A novel system for screening potential inhibitors of HBV replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huch, M.; Dorrell, C.; Boj, S.F.; van Es, J.H.; Li, V.S.; van de Wetering, M.; Sato, T.; Hamer, K.; Sasaki, N.; Finegold, M.J; et al. In vitro expansion of single Lgr5+ liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration. Nature 2013, 494, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebe, T.; Sekine, K.; Enomura, M.; Koike, H.; Kimura, M.; Ogaeri, T.; Zhang, R.R.; Ueno, Y.; Zheng, Y.W.; Koike, N.; et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature 2013, 499, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.L.; Althage, A.; Chung, J.; Chisari, F.V. Hydrodynamic injection of viral DNA: A mouse model of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13825–13830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Hirsch, M.L.; Zhang, L.; Samulski, R.J.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Adeno-associated virus vector mediated delivery of the HBV genome induces chronic hepatitis B virus infection and liver fibrosis in mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, P.; Salazar, F.; Liittschwager, K.; Bordier, B.; Seeger, C.; Winters, M.; Cooper, A.; Cullen, J. A transgenic mouse lineage useful for testing antivirals targeting hepatitis B virus. In Frontiers in Viral Hepatitis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.N.; Zhu, B.; Ai, L.; Yang, D.L.; Wang, B.J. Animal models for the study of hepatitis B virus infection. Zool Res. 2018, 39, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Von Weizsäcker, F.; Kock, J.; MacNelly, S.; Ren, S.; Blum, H.E.; Nassal, M. The tupaia model for the study of hepatitis B virus: Direct infection and HBV genome transduction of primary tupaia hepatocytes. Methods Mol. Med. 2004, 96, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Wieland, S.F. The chimpanzee model for hepatitis B virus infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Med. 2015, 5, a021469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burwitz, B.J.; Wettengel, J.M.; Muck-Hausl, M.A.; Ringelhan, M.; Ko, C.; Festag, M.M.; Hammond, K.B.; Northrup, M.; Bimber, B.N.; Jacob, T.; et al. Hepatocytic expression of human sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide enables hepatitis B virus infection of macaques. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kanasty, R.L.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Vegas, A.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Anderson, D.G. Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, S.; Jorgensen, M.R.; Kolli, S.; Crowther, C.; Salazar, F.H.; Marion, P.L.; Fujino, M.; Natori, Y.; Thanou, M.; Arbuthnot, P.; et al. Controlling HBV replication in vivo by intravenous administration of triggered PEGylated siRNA-nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rensen, P.C.; van Leeuwen, S.H.; Sliedregt, L.A.; van Berkel, T.J.; Biessen, E.A. Design and synthesis of novel N-acetylgalactosamine-terminated glycolipids for targeting of lipoproteins to the hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5798–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Rozema, D.B.; Hossbach, M.; John, M.; Hamilton, H.L.; Chu, Q.; Hegge, J.O.; Klein, J.J.; Wakefield, D.H.; Oropeza, C.E.; et al. Hepatocyte-targeted RNAi therapeutics for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluep, T.; Lickliter, J.; Hamilton, J.; Lewis, D.L.; Lai, C.L.; Lau, J.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Gish, R.G.; Given, B.D. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of ARC-520 Injection, an RNA Interference-Based Therapeutic for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection, in Healthy Volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2017, 6, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Yuen, M.F.; Chan, H.L.; Gish, R.G.; Locarnini, S.A.; Chavez, D.; Ferrari, C.; Given, B.D.; Hamilton, J.; Kanner, S.B.; et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.K.; Willoughby, J.L.; Chan, A.; Charisse, K.; Alam, M.R.; Wang, Q.; Hoekstra, M.; Kandasamy, P.; Kel’in, A.V.; Milstein, S.; et al. Multivalent N-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated siRNA localizes in hepatocytes and elicits robust RNAi-mediated gene silencing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16958–16961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.K.; Attarwala, H.; Sehgal, A.; Wang, Q.; Aluri, K.; Zhang, X.; Gao, M.; Liu, J.; Indrakanti, R.; Schofield, S.; et al. Impact of enhanced metabolic stability on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of GalNAc-siRNA conjugates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 10969–10977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.J.; Brown, C.R.; Shaikh, S.; Trapp, C.; Schlegel, M.K.; Qian, K.; Sehgal, A.; Rajeev, K.G.; Jadhav, V.; Manoharan, M.; et al. Advanced siRNA Designs Further Improve In Vivo Performance of GalNAc-siRNA Conjugates. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, M.R.; Turanov, A.A.; Alterman, J.F.; Haraszti, R.A.; Coles, A.H.; Osborn, M.F.; Echeverria, D.; Nikan, M.; Salomon, W.E.; Roux, L.; et al. Comparison of partially and fully chemically-modified siRNA in conjugate-mediated delivery in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Schiefke, I.; Yoon, J.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Heo, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lik Yuen Chan, H.; Yoon, K.T.; Klinker, H.; Manns, M.; et al. RNA Interference Therapy With ARC-520 Results in Prolonged Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Response in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Hepatology 2020, 72, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kootstra, N.A.; Verma, I.M. Gene therapy with viral vectors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 413–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nault, J.C.; Datta, S.; Imbeaud, S.; Franconi, A.; Mallet, M.; Couchy, G.; Letouze, E.; Pilati, C.; Verret, B.; Blanc, J.F.; et al. Recurrent AAV2-related insertional mutagenesis in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, G.J.; Dane, A.P.; Hallwirth, C.V.; Smyth, C.M.; Wilkie, E.E.; Amaya, A.K.; Zhu, E.; Khandekar, N.; Ginn, S.L.; Liao, S.H.Y; et al. Identification of liver-specific enhancer-promoter activity in the 3’ untranslated region of the wild-type AAV2 genome. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, J.M., 2nd; Hu, P.; Caballero, S.; Moldovan, L.; Verma, A.; Oudit, G.Y.; Li, Q.; Grant, M.B. Adeno-Associated Virus Overexpression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 Reverses Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 1 Diabetes in Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassner, U.; Hollstein, T.; Grenkowitz, T.; Wuhle-Demuth, M.; Salewsky, B.; Demuth, I.; Dippel, M.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E. Gene Therapy in Lipoprotein Lipase Deficiency: Case Report on the First Patient Treated with Alipogene Tiparvovec Under Daily Practice Conditions. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castle, M.J.; Turunen, H.T.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Wolfe, J.H. Controlling AAV Tropism in the Nervous System with Natural and Engineered Capsids. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1382, 133–149. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, D.M.; Monahan, P.E.; Samulski, R.J. Self-complementary recombinant adeno-associated virus (scAAV) vectors promote efficient transduction independently of DNA synthesis. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michler, T.; Grosse, S.; Mockenhaupt, S.; Roder, N.; Stuckler, F.; Knapp, B.; Ko, C.; Heikenwalder, M.; Protzer, U.; Grimm, D. Blocking sense-strand activity improves potency, safety and specificity of anti-hepatitis B virus short hairpin RNA. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnyandu, N.; Arbuthnot, P.; Maepa, M.B. In vivo delivery of cassettes encoding anti-hbv primary micrornas using an ancestral adeno-associated viral vector. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2115, 171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hosel, M.; Lucifora, J.; Michler, T.; Holz, G.; Gruffaz, M.; Stahnke, S.; Zoulim, F.; Durantel, D.; Heikenwalder, M.; Nierhoff, D.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection enhances susceptibility toward adeno-associated viral vector transduction in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Kan, F.; Yan, T.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, W. Enhanced antiviral and antifibrotic effects of short hairpin RNAs targeting HBV and TGF-beta in HBV-persistent mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Sun, C.P.; Ma, H.I.; Fang, C.C.; Wu, P.Y.; Xiao, X.; Tao, M.H. Comparative study of anti-hepatitis B virus RNA interference by double-stranded adeno-associated virus serotypes 7, 8, and 9. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mockenhaupt, S.; Grosse, S.; Rupp, D.; Bartenschlager, R.; Grimm, D. Alleviation of off-target effects from vector-encoded shRNAs via codelivered RNA decoys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4007–E4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcedo, R.; Morizono, H.; Wang, L.; McCarter, R.; He, J.; Jones, D.; Batshaw, M.L.; Wilson, J.M. Adeno-associated virus antibody profiles in newborns, children, and adolescents. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1586–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, C.S.; Pierce, G.F.; Arruda, V.R.; Glader, B.; Ragni, M.; Rasko, J.J.; Ozelo, M.C.; Hoots, K.; Blatt, P.; Konkle, B.; et al. Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, Z.; Leborgne, C.; Barbon, E.; Masat, E.; Ronziti, G.; van Wittenberghe, L.; Vignaud, A.; Collaud, F.; Charles, S.; Sola, M.; et al. Influence of Pre-existing Anti-Capsid Neutralizing and Binding Antibodies on AAV Vector Transduction. Mol. Ther. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowski, L.; Dane, A.P.; Chu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cunningham, S.C.; Wilson, E.M.; Nygaard, S.; Grompe, M.; Alexander, I.E.; Kay, M.A. Selection and evaluation of clinically relevant AAV variants in a xenograft liver model. Nature 2014, 506, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Ortiz, J.; Ojala, D.S.; Westesson, O.; Weinstein, J.R.; Wong, S.Y.; Steinsapir, A.; Kumar, S.; Holmes, I.; Schaffer, D.V. AAV ancestral reconstruction library enables selection of broadly infectious viral variants. Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinn, E.; Pacouret, S.; Khaychuk, V.; Turunen, H.T.; Carvalho, L.S.; Andres-Mateos, E.; Shah, S.; Shelke, R.; Maurer, A.C.; Plovie, E.; et al. In Silico Reconstruction of the Viral Evolutionary Lineage Yields a Potent Gene Therapy Vector. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Albright, B.; Hirsch, M.; Li, W.; Tseng, Y.S.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; McPhee, S.; Asokan, A.; Samulski, R.J. Development of Patient-specific AAV Vectors After Neutralizing Antibody Selection for Enhanced Muscle Gene Transfer. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mingozzi, F.; Anguela, X.M.; Pavani, G.; Chen, Y.; Davidson, R.J.; Hui, D.J.; Yazicioglu, M.; Elkouby, L.; Hinderer, C.J.; Faella, A.; et al. Overcoming preexisting humoral immunity to AAV using capsid decoys. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 194ra92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.M.; Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Nio, K.; Reszka-Blanco, N.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Su, L. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Promotes Degradation of SMC5/6 to Enhance HBV Replication. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| siRNA Activator | Delivery | Company | Phase | Identifier (Clinicaltrials.Gov) | End Date | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JNJ-3989 (ARO-HBV) | GalNAc | Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals | I/IIa | NCT03365947 NCT03982186 NCT04129554 | September 2020 | - |
| ARC-520 | GalNAc | Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals | I, IIb | NCT01872065 NCT02065336 NCT02604199 NCT02604212 | Completed/terminated | [96,97,102] |
| ARC-521 | GalNAc | Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals | I | NCT02797522 | Terminated | - |
| VIR-2218 (ALN-HBV02) | GalNAc | Alnylam Pharmaceuticals/ Vir Biotechnology | I/II | NCT03672188 NCT02826018 | March 2021 | - |
| ARB-1467 | LNP | Arbutus Biopharma | IIa | NCT02631096 | Completed | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van den Berg, F.; Limani, S.W.; Mnyandu, N.; Maepa, M.B.; Ely, A.; Arbuthnot, P. Advances with RNAi-Based Therapy for Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080851
van den Berg F, Limani SW, Mnyandu N, Maepa MB, Ely A, Arbuthnot P. Advances with RNAi-Based Therapy for Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Viruses. 2020; 12(8):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080851
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan den Berg, Fiona, Shonisani Wendy Limani, Njabulo Mnyandu, Mohube Betty Maepa, Abdullah Ely, and Patrick Arbuthnot. 2020. "Advances with RNAi-Based Therapy for Hepatitis B Virus Infection" Viruses 12, no. 8: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080851
APA Stylevan den Berg, F., Limani, S. W., Mnyandu, N., Maepa, M. B., Ely, A., & Arbuthnot, P. (2020). Advances with RNAi-Based Therapy for Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Viruses, 12(8), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080851





