Wear Measurements in Cylindrical Telescopic Crowns Using an Active Piezoresistive Cantilever with an Integrated Gold Microsphere Probe
Abstract
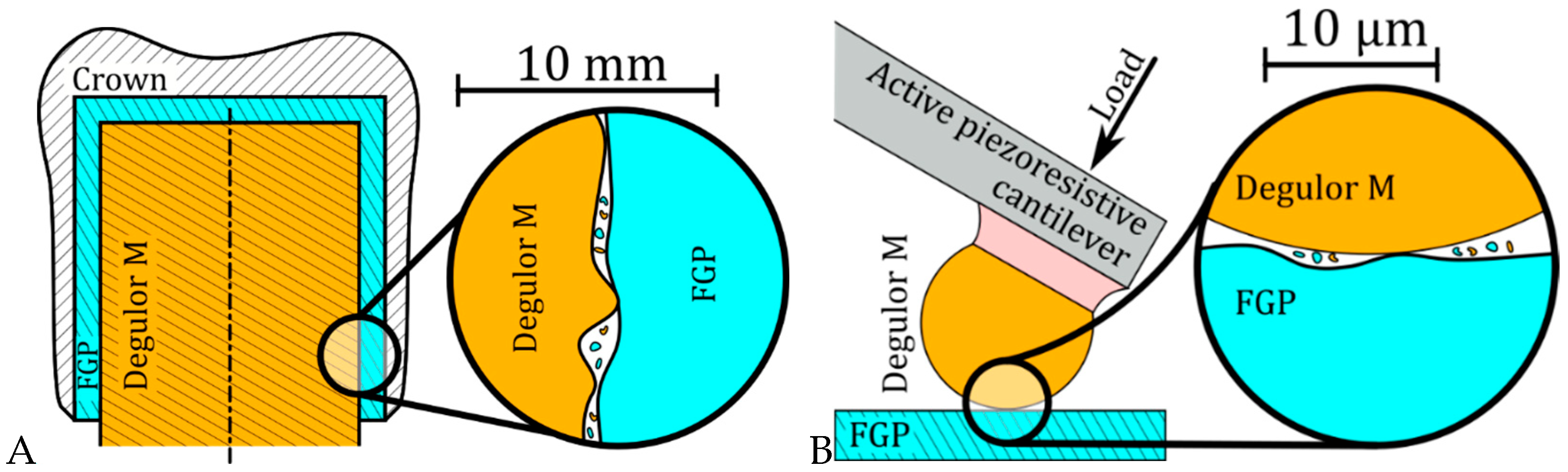
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
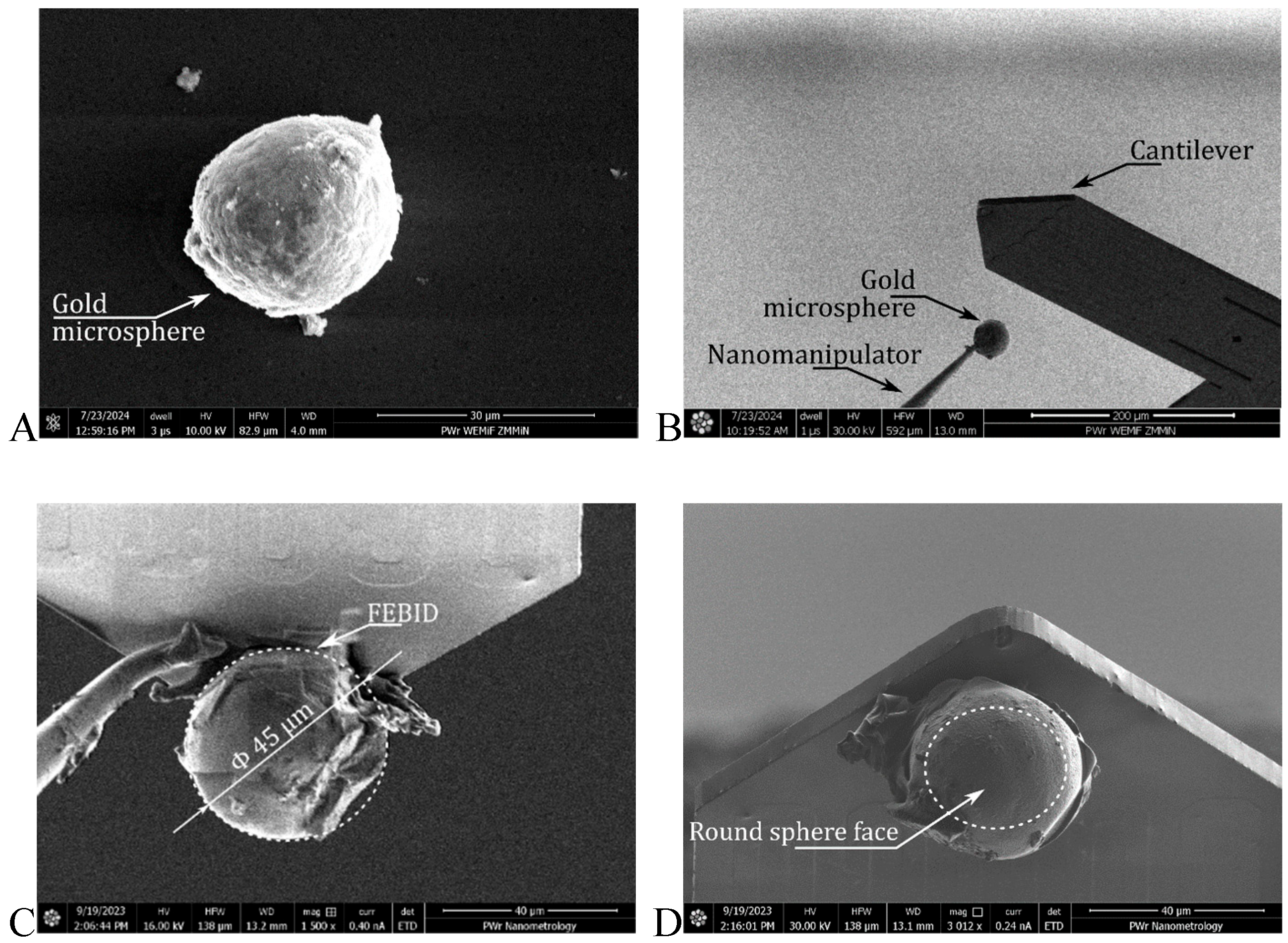
2.1. Gold Microsphere Fabrication
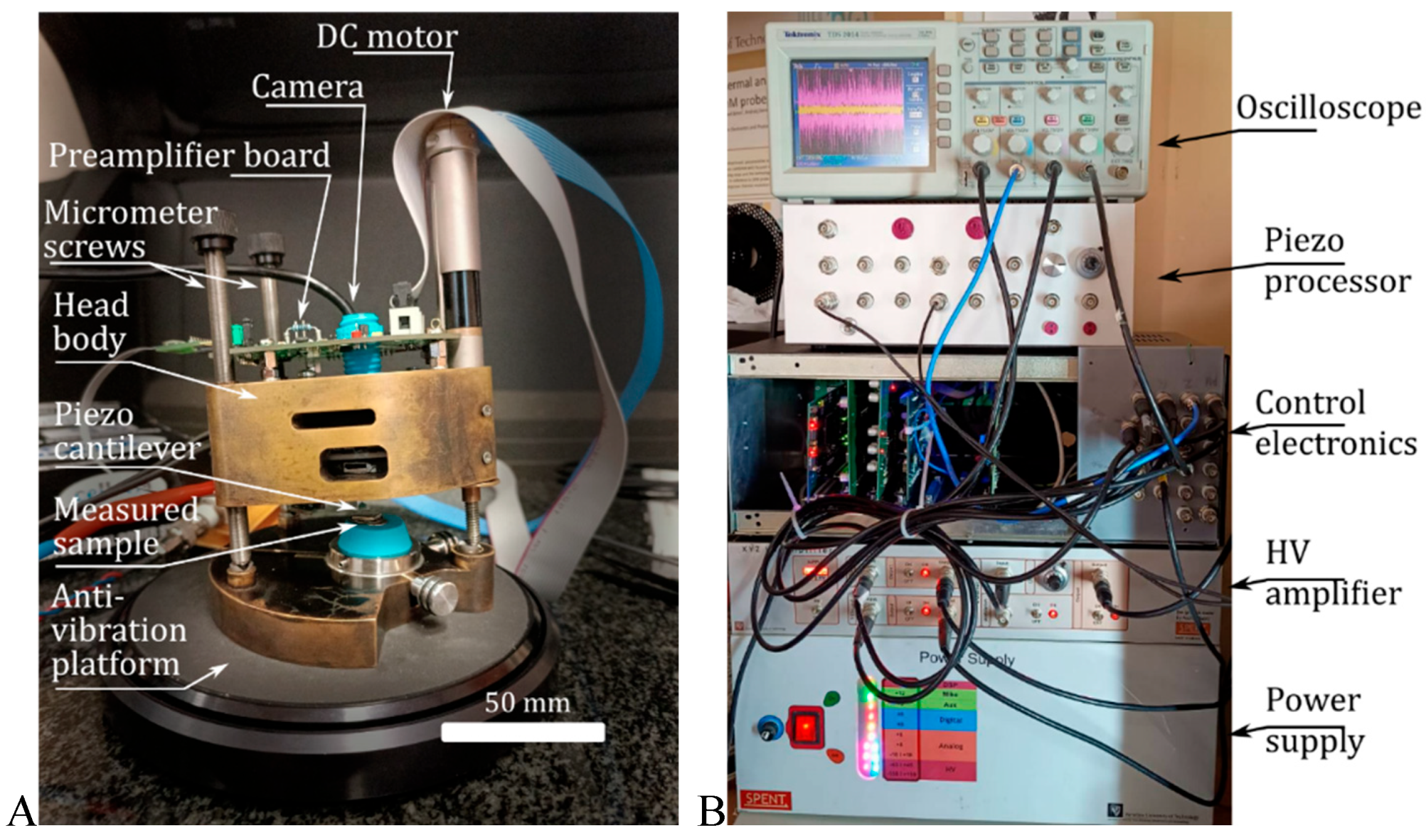
2.2. AFM System
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mass Determination of a Gold Microsphere
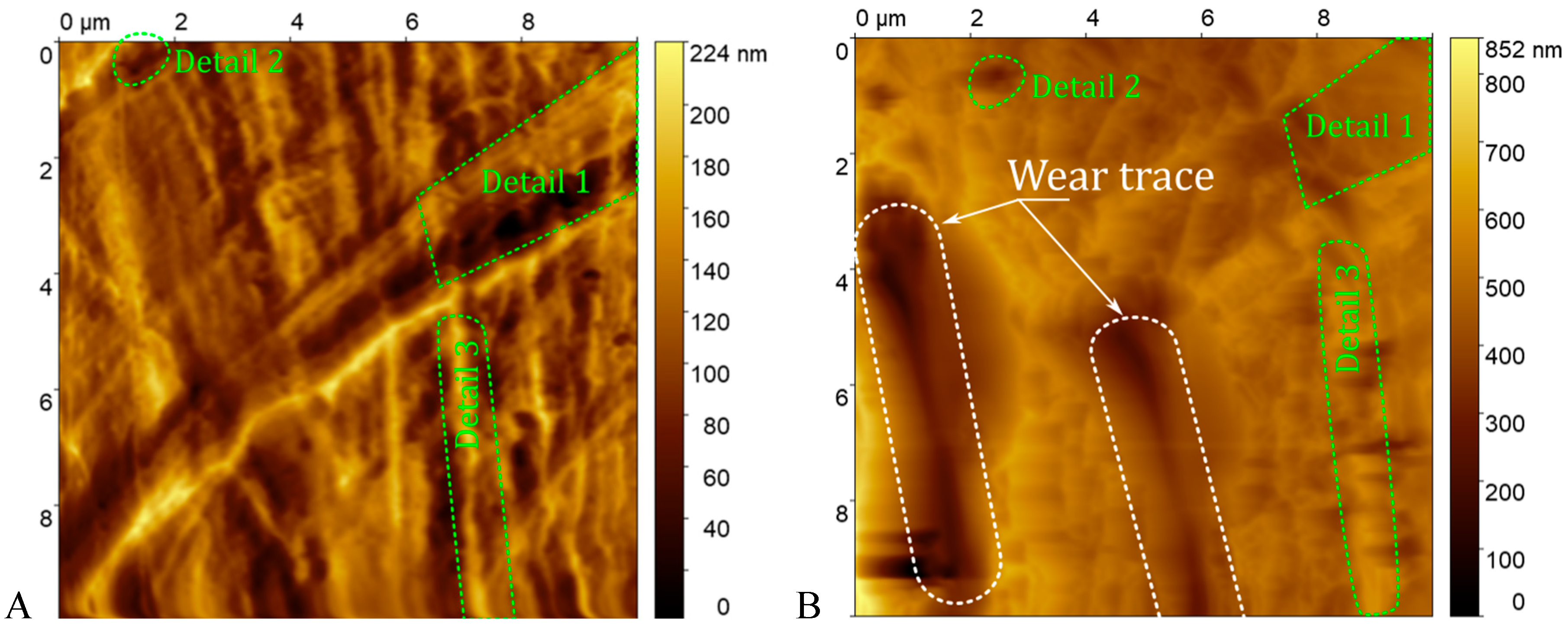
3.2. Sample Investigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, D.K.; Verma, R.K.; Singh, V.P.; Mishra, S. Production and Tribological Performance under Sliding Contact Conditions of Zirconia and Reduced Graphene Oxide Loaded Polymer Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 8097–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobena, S.T.; Woldeyohannes, A.D. Assessments and Investigation of Process Parameter Impacts on Surface Roughness, Microstructure, Tensile Strength, and Porosity of 3D Printed Polyetherether Ketone (PEEK) Materials. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Kiran, K.U.V.; Zhang, X.; Hou, X.; Roy, S. Investigating the Tribological and Corrosion Behavior of Co–Cr Alloy as an Implant Material for Orthodontic Applications. Wear 2023, 523, 204755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rojas, F.; Sánchez-González, E.; Borrero-López, Ó.; Hoffman, M. In-Vitro Study of the Sliding-Wear of CAD/CAM Dental Composite Materials. Tribol. Int. 2025, 202, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrzycki, J.; Klepka, T.; Marchewka, M.; Zubrzycki, R. Tests of Dental Properties of Composite Materials Containing Nanohybrid Filler. Materials 2023, 16, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageib, F.Y.; Fouad, R.A.; El-Sayed Seleman, M.M. A Study on the Influence of Nano-c-BN on the Physical and Mechanical Characteristics of PMMA Biocomposites Used in Dental Prosthetics. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Cong, M.; Liu, D.; Ren, X. A Robotic Chewing Simulator Supplying Six-Axis Mandibular Motion, High Occlusal Force, and a Saliva Environment for Denture Tests. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H 2021, 235, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, V.; Pospiech, P.; Schurig, A.; Schmitter, M. In Vitro Investigations on Retention Force Behavior of Conventional and Modern Double Crown Systems. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowa, T.; Dobrowolska, A.; Wieleba, W. The Role of Friction in the Mechanism of Retaining the Partial Removable Dentures with Double Crown System. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2013, 15, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabor, D. Surface Effects in Adhesion, Friction, Wear and Lubrication; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; ISBN 0-444-41966-7. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D. Wear: Treatise on Materials Science and Technology, Volume 13; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 13, ISBN 1483218228. [Google Scholar]
- Charitidis, C.A.; Logothetidis, S. Effects of Normal Load on Nanotribological Properties of Sputtered Carbon Nitride Films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Han, R.; Ren, J.; Li, L.; Han, N.; Xing, F.; Zhu, J. A Review on the Mechanical Properties for Thin Film and Block Structure Characterised by Using Nanoscratch Test. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2019, 8, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Koinkar, V.N. Tribological Studies of Silicon for Magnetic Recording Applications (Invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 75, 5741–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charitidis, C.A. Nanomechanical and Nanotribological Properties of Carbon-Based Thin Films: A Review. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2010, 28, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; VanLandingham, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; He, T. Direct Measurement of Plowing Friction and Wear of a Polymer Thin Film Using the Atomic Force Microscope. J. Mater. Res. 2001, 16, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi-Jamal, M.R.; Kaupp, G. New Nanoindentation and Nanoscratching Parameters of Thermoplastics. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 274, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöfer, J.; Santner, E. Quantitative Wear Analysis Using Atomic Force Microscopy. Wear 1998, 222, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohr, R.; Schug, C.; Wahl, M.; Wienss, A.; Hilgers, H.; Mahrholz, J.; Willich, P.; Jung, T. Analytical Characterization of Thin Carbon Films. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencl, A.; Mazeran, P.E.; Bellafkih, S.; Noël, O. Assessment of Wear Behaviour of Copper-Based Nanocomposite at the Nanoscale. Wear 2018, 414–415, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, F. Study of Friction and Wear with AFM in CMP Process of Selective Layer. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2013, 7, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrak, R.; Ivanov, T.; Ivanova, K.; Gotszalk, T.; Abedinov, N.; Rangelow, I.W.; Edinger, K.; Tomerov, E.; Schenkel, T.; Hudek, P. Micromachined Atomic Force Microscopy Sensor with Integrated Piezoresistive Sensor and Thermal Bimorph Actuator for High-Speed Tapping-Mode Atomic Force Microscopy Phase-Imaging in Higher Eigenmodes. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2003, 21, 3102–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majstrzyk, W.; Ahmad, A.; Ivanov, T.; Reum, A.; Angelow, T.; Holz, M.; Gotszalk, T.P.; Rangelow, I.W. Thermomechanically and Electromagnetically Actuated Piezoresistive Cantilevers for Fast-Scanning Probe Microscopy Investigations. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 276, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotszalk, T.; Jóźwiak, G.; Radojewski, J.; Fröhlich, T.; Füssl, R.; Manske, E.; Holz, M.; Ivanov, T.; Ahmad, A.; Rangelow, I.W. Tip-Based Nano-Manufacturing and -Metrology. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2019, 37, 030803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Egberts, P.; Ye, Z.; Carpick, R.W.; Martini, A. Correlation between Probe Shape and Atomic Friction Peaks at Graphite Step Edges. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 50, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Deng, J.; Dong, J.; Cohen, P.H. Study of Tip Wear for AFM-Based Vibration-Assisted Nanomachining Process. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 50, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melngailis, J. Focused Ion Beam Microfabrication. In Proceedings of the Electron-Beam, X-Ray, and Ion Beam Technology: Submicrometer Lithographies VII, San Jose, CA, USA, 31 January–5 February 1988; Volume 0923, pp. 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübbe, J.; Temmen, M.; Rahe, P.; Kühnle, A.; Reichling, M. Determining Cantilever Stiffness from Thermal Noise. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świadkowski, B.; Piasecki, T.; Rudek, M.; Świątkowski, M.; Gajewski, K.; Majstrzyk, W.; Babij, M.; Dzierka, A.; Gotszalk, T.P. ARMScope—The Versatile Platform for Scanning Probe Microscopy Systems. Metrol. Meas. Syst. 2020, 27, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopiec, D.; Majstrzyk, W.; Pruchnik, B.; Gacka, E.; Badura, D.; Sierakowski, A.; Janus, P.; Gotszalk, T.P. Metrology and Control of Electromagnetically Actuated Cantilevers Using Optical Beam Deflection Method. Metrol. Meas. Syst. 2021, 28, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Klapetek, P. Gwyddion: An Open-Source Software for SPM Data Analysis. Open Phys. 2012, 10, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowa, T.; Badura, D.; Pruchnik, B.; Gacka, E.; Kopczyński, W.; Mikulewicz, M.; Gotszalk, T.; Kijak, E. Correlation between Friction and Wear in Cylindrical Anchorages Simulated with Wear Machine and Analyzed with Scanning Probe and Electron Microscope. Materials 2023, 16, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, M.S.E.; Picton, D.C.A. A Study of Pressures Exerted by the Lips and Cheeks on the Teeth of Subjects with Normal Occlusion. Arch. Oral Biol. 1964, 9, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, A.P.; Soemardi, T.P.; Widjajalaksmi, K.; Reksoprodjo, A.H.S. Tensile and Flexural Strength of Ramie Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites for Socket Prosthesis Application. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2011, 6, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Barwell, F.T. Wear of Metals. Wear 1958, 1, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksar, H.; Ma, C.; Janiszewska, N.; Awsiuk, K.; Budkowski, A.; Gnecco, E. Nanoscale Wear Evolution on a Polystyrene/Poly (n-Butyl Methacrylate) Blend. Wear 2024, 536–537, 205160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, N.; Espejo, C.; Morina, A.; Emami, N. Tribological Performance of 3D Printed Neat and Carbon Fiber Reinforced PEEK Composites. Tribol. Int. 2024, 193, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Roy Chowdhury, S.K.; Sarangi, M. Effects of Non-Gaussian Counter-Surface Roughness Parameters on Wear of Engineering Polymers. Wear 2015, 332–333, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, K.; Gao, T.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Ye, J. The Unrecognized Importance of Roughness Directionality to Polymer Wear. Wear 2021, 486–487, 204084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, B.; Singh, R.; Pabla, B.S. On the Fabrication of Functionally Graded Prototypes with Laser Powder Bed Fusion from Reused Ni-625 and 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Powder. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muwafi, M.A.R.; Alafandy, M.H.; Thabet, Y.G. Evaluation of Accuracy and Wear of Two Different Materials in Digitally-Designed Telescopic Removable Partial Dentures. J. Stomatol. 2022, 75, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linek, W.; Richter, G.; Raedel, M.; Walter, M.; Reitemeier, B. In Vitro Analysis of the Tribological Behaviour of Different Material Combinations for Telescopic Crowns. Metals 2016, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Miao, Q.; Ding, W.; Li, H. A Short Review on the Influence of Mechanical Machining on Tribological and Wear Behavior of Components. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; He, C.G.; Zhao, X.J.; Guo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, Q.Y.; Jin, X.S. Study on Wear and Rolling Contact Fatigue Behaviors of Wheel/Rail Materials under Different Slip Ratio Conditions. Wear 2016, 366–367, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guarneros, M.A.; Domínguez-Cabrera, B.A.; Quinto-Saure, C.; Farfan-Cabrera, L.I.; Santander-Reyes, J.N.; Gallardo-Hernández, E.A. Investigating the Erosive Wear Caused by Dry-Ice Blasting in Paint Stripping Process. Mater. Lett. 2022, 308, 131203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahemi, N.; Liza, S.; Abbas, A.A.; Merican, A.M. Long-Term Wear Failure Analysis of Uhmwpe Acetabular Cup in Total Hip Replacement. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mory, N.; Cascos, R.; Celemín-Viñuela, A.; Gómez-Polo, C.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Gómez-Polo, M. Comparison of the Surface Roughness of CAD/CAM Metal-Free Materials Used for Complete-Arch Implant-Supported Prostheses: An In Vitro Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Busscher, H.J.; van der Mei, H.C.; Ren, Y. Influence of Surface Roughness on Streptococcal Adhesion Forces to Composite Resins. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Balani, K. Adhesion Force of Staphylococcus aureus on Various Biomaterial Surfaces. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 65, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

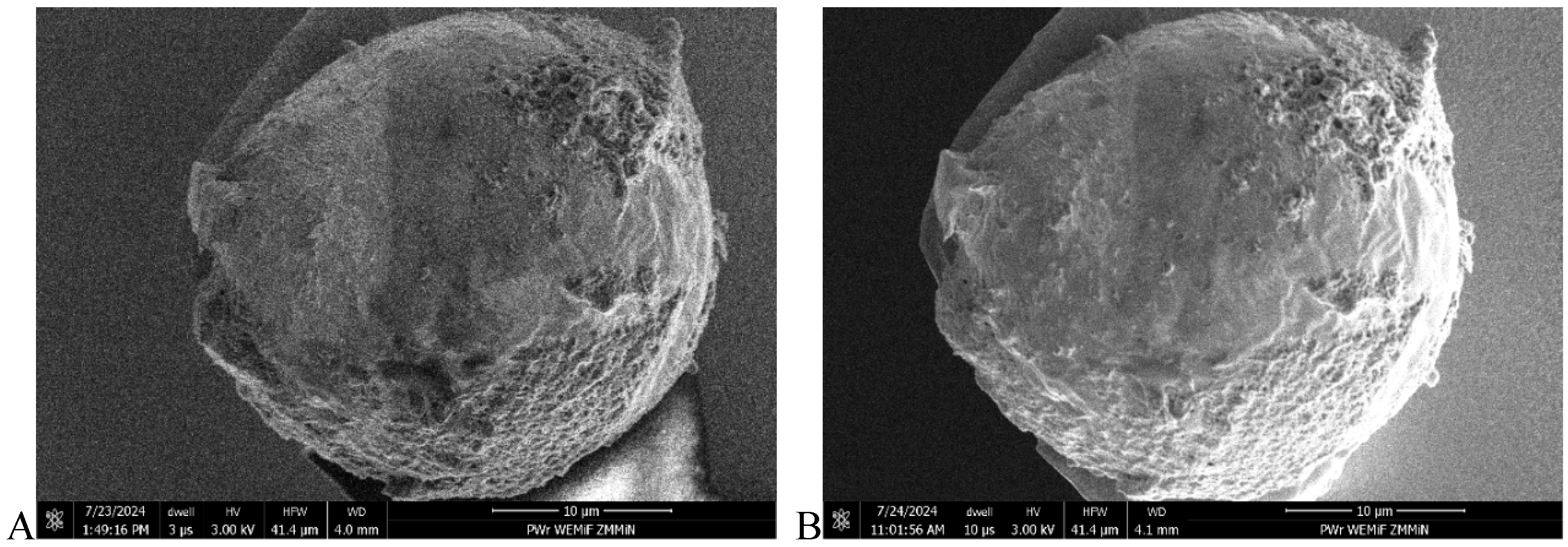
| Sample | FGP Congealed (Sa#1) | FGP Polished (Sa#2) | FGP Formed (Sa#3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample image | 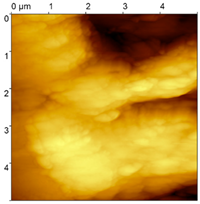 | 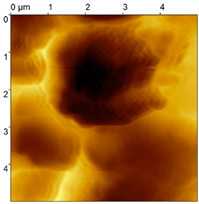 |  |
| Roughness Rq | Rq = 285.5 nm | Rq = 111.6 nm | Rq = 73.4 nm |
| Roughness Ra | Ra = 232.0 nm | Ra = 93.0 nm | Ra = 57.1 nm |
| Parameter | Degulor M | FGP |
|---|---|---|
| Young modulus (GPa) | 102.0 | 6.49 |
| Poisson ratio (-) | 0.4 | 0.33 |
| Diameter (μm) | 45 | - |
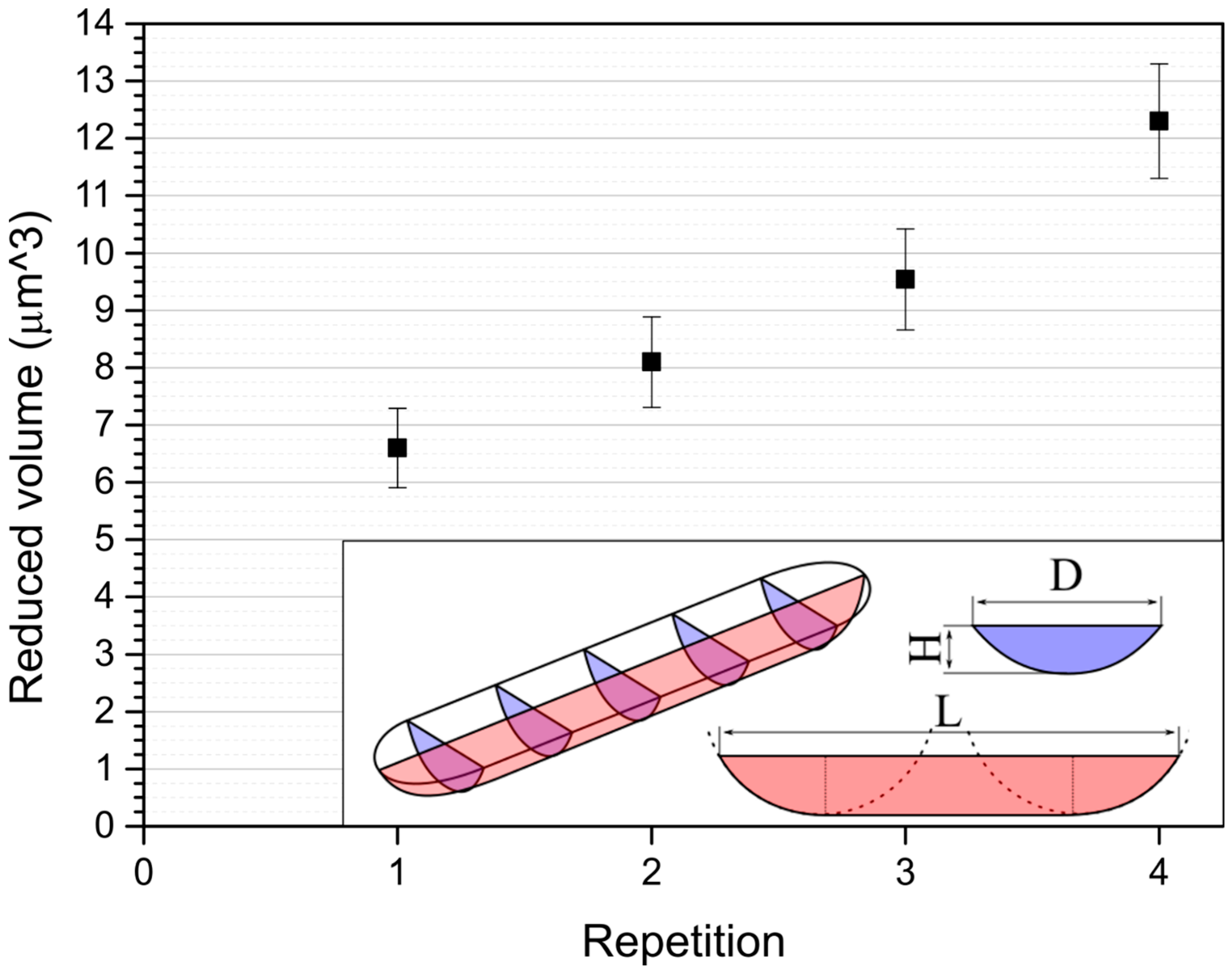
| Repetition: | Rq (nm): ± 5% | Ra (nm): ± 5% | H (μm): ± 0.022 μm | L (μm): ± 0.1 μm | D (μm): ± 0.1 μm | Reduced Volume (μm3): |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGP as-given | 31.86 | 25.51 | - | - | - | - |
| FGP after the 1st repetition | 101.2 | 77.1 | 0.55 | 8.11 | 2.8 | 6.60 ± 0.69 |
| FGP after the 2nd repetition | 45.67 | 36.23 | 0.56 | 8.51 | 3.2 | 8.10 ± 0.79 |
| FGP after the 3rd repetition | 138.5 | 107.1 | 0.59 | 8.94 | 3.4 | 9.54 ± 0.88 |
| FGP after the 4th repetition | 114.8 | 92.8 | 0.70 | 9.17 | 3.6 | 12.30 ± 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dąbrowa, T.; Badura, D.; Pruchnik, B.; Kopczyński, W.; Rangelow, I.W.; Kijak, E.; Gotszalk, T. Wear Measurements in Cylindrical Telescopic Crowns Using an Active Piezoresistive Cantilever with an Integrated Gold Microsphere Probe. Materials 2025, 18, 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194624
Dąbrowa T, Badura D, Pruchnik B, Kopczyński W, Rangelow IW, Kijak E, Gotszalk T. Wear Measurements in Cylindrical Telescopic Crowns Using an Active Piezoresistive Cantilever with an Integrated Gold Microsphere Probe. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194624
Chicago/Turabian StyleDąbrowa, Tomasz, Dominik Badura, Bartosz Pruchnik, Władysław Kopczyński, Ivo W. Rangelow, Edward Kijak, and Teodor Gotszalk. 2025. "Wear Measurements in Cylindrical Telescopic Crowns Using an Active Piezoresistive Cantilever with an Integrated Gold Microsphere Probe" Materials 18, no. 19: 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194624
APA StyleDąbrowa, T., Badura, D., Pruchnik, B., Kopczyński, W., Rangelow, I. W., Kijak, E., & Gotszalk, T. (2025). Wear Measurements in Cylindrical Telescopic Crowns Using an Active Piezoresistive Cantilever with an Integrated Gold Microsphere Probe. Materials, 18(19), 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194624







