Abstract
The muddy limestone in the Lei32 sub-member of the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in the well Chongtan 1 (CT1) of the Sichuan Basin has yielded promising industrial oil and gas production. This discovery has the potential to become a significant strategic reservoir in the future for oil and gas exploration in the Sichuan Basin. However, the understanding of hydrocarbon accumulation in the muddy limestone of the Lei32 sub-member remains insufficient, which poses limitations on further exploration selection and deployment strategies. This study focuses on the analysis of core samples and laboratory data in the wells CT1 and Jianyang 1 (JY1), aiming to investigate the source rock and reservoir characteristics of the muddy limestone in the Lei32 sub-member, as well as the primary controlling factors influencing the development of the source rock and reservoir. The results show that the Lei32 sub-member in the Central Sichuan Basin is an evaporated lagoon deposition; the tight argillaceous limestone and limy mudstone exhibit the characteristic of source–reservoir integration, belonging to a new type of unconventional oil and gas reservoir. The reservoir space of the argillaceous limestone and limy mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member primarily consists of inorganic and organic micro–nanopores and microfractures. The average porosity and permeability are 2.7% and 0.19 mD, indicating a low-porosity and low-permeability unconventional reservoir. The clay minerals and gypsum content are the important factors influencing reservoir porosity, and the fractures are key factors influencing permeability. This study will elucidate the specific features of hydrocarbon accumulation in the muddy limestone reservoirs of the Lei32 sub-member and provide insights into its exploration potential.
1. Introduction
The Triassic Leikoupo Formation in the Sichuan Basin has been a significant target for natural gas exploration, characterized by the high-quality dolomite reservoirs (average porosity: 3.22%; average permeability: 1.65 mD) and evaporite cap rocks [1,2]. However, despite exploration efforts over the past 50 years, conventional gas fields discovered in the Leikoupo Formation, such as Moxi, Longgang, Zhongba, and Pengzhou, have not been able to form large-scale reserves as expected [1,2,3]. To address this challenge, the focus has shifted towards unconventional oil and gas resources in the region [3]. In recent years, unconventional reservoirs, such as mudstone and limestone, have been discovered in the Lower Permian Maokou Formation in the Sichuan Basin [4]. These discoveries in the Maokou Formation represent a significant development for the exploration of unconventional oil and gas resources in the Sichuan Basin. As unconventional reservoirs gain attention worldwide, they are increasingly seen as important prospects for future global oil and gas exploration [3]. Notably, the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 in the Central Sichuan Basin has shown promising oil and gas displays. The reservoir in the Lei32 sub-member consists of argillaceous limestone and limy mudstone with a thickness of up to 31.3 m, an average porosity of 2.7%, and an average permeability of 0.17 mD [5]. This unconventional reservoir has achieved a breakthrough in the exploration of marine argillaceous limestone and limy mudstone resources, producing approximately 10.87 × 104 m3/day of natural gas and 47.04 m3/day of oil [3].
The argillaceous limestone and limy mudstone developed in the lagoon facies in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan Basin have the characteristics of wide distribution (Figure 1a); source–reservoir integration, with the roof and floor sealed by gypsum salt rock (Figure 1b); and in situ hydrocarbon generation, storage, and capping [3,6]. This new unconventional oil and gas accumulation system with high exploration potential is a new area for exploration and worth exploring [6,7].
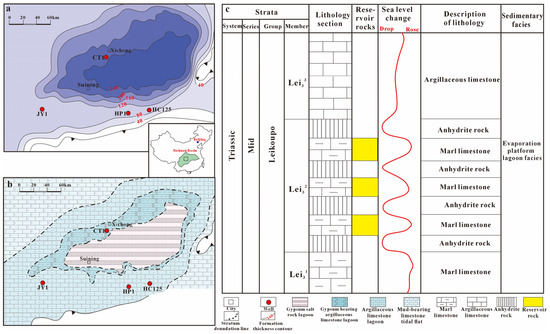
Figure 1.
(a) Residual formation thickness; (b) sedimentary facies; (c) stratigraphic columns of the Lei32 member in Central Sichuan Basin.
Previous studies have been conducted on the deposition and reservoir characteristics of the Leikoupo Formation [4,8]. Xin et al. concluded that during the Middle Triassic Leikoupo depositional period, the Central Sichuan Basin exhibited a barrier carbonate platform characterized by shallow water bodies with high and variable salinity [8]. The platform primarily consisted of platform margins, intra-platform beaches, lagoons, and mixed tidal flats. It is widely accepted that high-quality carbonate source rocks formed in an anoxic environment, with the oil-bearing rocks mainly comprising muddy limestone or limy mudstone [9,10,11].
The carbon and oxygen isotope composition of carbonate rocks serves as an essential environmental parameter [12]. However, there is currently limited systematic research and discussion regarding the carbonate source rocks of restricted platforms and their association with evaporates [13]. Controversies remain regarding the genetic mechanisms and controlling factors of lagoon facies carbonate reservoirs in the Lei32 sub-member [8]. Consequently, a key challenge lies in the unclear understanding of reservoir accumulation and enrichment in muddy limestone, as well as the lack of clarity regarding favorable zones. These limitations hamper effective exploration strategies and deployment in the region [6].
This study focuses on analyzing core samples of argillaceous limestone and limy mudstone from the Lei32 sub-member, obtained from key wells such as JY1, CT1, Hechuan125, and Heping1 (Figure 1b). The analysis aims to investigate the geochemical characteristics, mineral compositions, physical properties, and lithological types of the carbonate rocks. Additionally, the study examines the source rock characteristics and reservoir properties, while also identifying the factors that control the development of source rocks and reservoirs in this region. The findings of this research endeavor can contribute to a better understanding of the reservoir characteristics and aid in the development of effective exploration strategies in the Lei32 sub-member.
2. Geologic Settings
The Sichuan Basin, located within the Yangtze craton, underwent geological changes during the Leikoupo sedimentation period in the Triassic [14,15]. The Indosinian movement caused the uplift of the carbonate platform as a whole, leading to a pattern of uplift and depression within the basin [15]. The eastern part of the Sichuan Basin experienced uplift, forming the Luzhou–Kaijiang ancient uplift, while the western part formed the Western Sichuan Basin [16]. This paleogeographic pattern influenced the deposition environment of the Sichuan Basin during the Leikoupo sedimentation period, resulting in an evaporitic and restricted platform facies [6,16]. The Leikoupo Formation, which represents the Middle Triassic, displays distinct characteristics across the basin. It is thicker in the west and thinner in the east, with the stratigraphic layers gradually thinning out from west to east. The uplifted areas experienced significant erosion processes [4]. The formation primarily consists of interbedded limestone and gypsum deposits. At the top, it unconformably contacts the terrestrial clastic rocks of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, and it underlies the Lower Triassic Jialingjiang Formation (Figure 1a).
The Leikoupo Formation can be divided into four units, which are the first member of the Leikoupo Formation (Lei1), the second member of the Leikoupo Formation (Lei2), the third member of the Leikoupo Formation (Lei3), and the fourth member of the Leikoupo Formation (Lei4), with a cumulative thickness ranging from 0 to 1200 m [6]. The Lei3 member can be further subdivided into three sub-members, which are the Lei31 sub-member, the Lei32 sub-member, and the Lei33 sub-member (Figure 1c). In the Central Sichuan Basin, the lithology in the Lei31 sub-member is mainly composed of argillaceous limestone, while the lithology in the Lei32 sub-member consists of interbedded gypsum and argillaceous limestone, and the Lei33 sub-member is primarily composed of argillaceous limestone [3,5].
In the Central Sichuan Basin, the sedimentation of the Lei32 sub-member is primarily characterized by lagoon deposits. The hydrodynamic conditions in this area are relatively weak, indicating low-energy environments [6]. The lithology of the Lei32 sub-member is dominated by gypsum and mudstone deposits, which are indicative of high-salinity conditions in deeper water bodies. The mudstone and marly mudstone within the Lei32 sub-member exhibit slightly horizontal bedding, suggesting relatively calm depositional conditions [5]. These rock types also possess a strong hydrocarbon generation potential. The thickness distribution of the Lei32 sub-member follows a pattern of being thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges of the lagoon. Around the lagoon, there are successive deposits of marly mudstone and mudstone (Figure 1b). As we move towards the outermost region, mudstone deposits become more prominent. Additionally, the content of gypsum and mudstone gradually decreases from the center of the lagoon to the outermost region [3].
3. Materials and Methods
In this study, about 20 samples were collected from the Lei32 sub-member in the wells CT1 (7 samples), JY1 (12 samples), and HP1 (1 sample). Detailed observations and systematic sampling of the carbonate cores of the wells were carried out, and systematic total organic carbon (TOC), X-ray diffraction (XRD), automatic overburden porosity and permeability measurement, scanning electron microscope (SEM), carbon and oxygen isotopic composition, and major and trace element analyses were performed.
3.1. TOC and XRD Analysis
The TOC content was determined by the LECO CS-400 analyzer in the State Key Laboratory of the China University of Petroleum (Beijing, China). The testing precision was set at ±0.5%. The sample underwent multiple ultrasonic rinses with deionized water, followed by drying. Subsequently, it was ground to 80 mesh using an agate mortar and pestle. A 100 mg portion was weighed, immersed in 5% hydrochloric acid for 24 h to eliminate inorganic carbon, and then subjected to the machine to determine the organic carbon content.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed to obtain the whole-rock mineral compositions using an X’pert PRO X-ray diffractometer (PANalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands) with the following properties: scanning range (2θ): 5° to 45°; scanning speed: 2θ was 4°/min; sampling step width: 2θ was 0.013°; the uncertainty of diffraction peak position was 0.002 Å.
3.2. Porosity and Permeability Tests and Electron Microscopy Observation
The porosity and permeability of the samples were measured by automatic overburden porosity and permeability measurement and pressure pulse attenuation measurement. A PHI-220 helium automatic porosity tester (Hai’an Petroleum Scientific Research Instrument Co., Ltd., Nantong, Jiangsu, China) was used to measure porosity. Porosity measurement ranged from 0.1% to 100%, with measurement error (relative) ≤0.5%. A PDP-200 pressure pulse attenuation permeability tester (Core Lab, Houston, TX, USA) was used to implement the pressure pulse attenuation method and measure the permeability of tight rock samples (test pressure: 1000 psi, confining pressure: 1500~10,000 psi, permeability test range: 0.00001~0.1 mD, test medium: nitrogen).
The main reservoir space was determined using SEM and X-CT. The SEM model used was the ZEISS Sigma 300 (resolution: 1.2 nm@15 kv 2.2 nm@1 kv; magnification: 10~1,000,000 times). A Zeiss Xradia 510 three-dimensional X-ray microscope was used for X-CT. The testing process involved sample preparation, CT scanning, image reconstruction, material phase definition (including de-noising and segmentation), 3D model reconstruction, and calculation of parameters such as porosity.
3.3. C-O Isotopic Compositions and Major–Trace Elements
For carbon and oxygen isotopic measurement, the phosphoric acid method was used; this program was conducted in the Analytical Laboratory of BRIUG with the MF-ISOPRIME Complete Spectrometer. The standard sample GBW0445 was used to ensure the accuracy of the test, and the unit standard was V-PDB. Based on repeated tests, the error for the value of carbon and oxygen isotopes obtained in the paper was below 0.1%.
Major and trace element analysis was carried out at the Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology. Major element determination utilized X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (GB/T14506.28-2010) with a Philips PW2404 fluorescence spectrometer. For the trace element analysis, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (GB/T14506.30-2010) was performed using the Element XR instrument model.
4. Results
4.1. Lithological Characteristics
The Lei32 sub-member in the Central Sichuan Basin is characterized by lagoon sedimentation, and it exhibits a diverse lithology primarily composed of carbonate rocks and evaporites. The carbonate rocks within the Lei32 sub-member can be classified into three major categories based on their structures: laminated, homogeneous nodular, and heterogeneous nodular structures (Figure 2). The laminated structures consist mainly of dark organic-rich mudstone interbedded with light mud-crystal/argillaceous limestone, forming rhythmic layers of varying thickness. Examples of lithologies within this category include laminated calcareous shale and laminated argillaceous limestone. These laminated structures display alternating layers of different compositions (Figure 2a–d). The homogeneous nodular structures exhibit a uniform distribution of different components, such as homogeneous calcareous mudstone, homogeneous mud-crystal limestone, homogeneous mud-crystal dolomite, and homogeneous mud-crystal dolomitic limestone. These lithologies have a cohesive appearance with consistent composition throughout (Figure 2e,f). In contrast, the heterogeneous nodular structures show a non-uniform distribution of various components, characterized by variations in mineral and clastic grain sizes. Notable lithologies within this category include nodular dolomitic limestone/dolomite and nodular fossiliferous limestone/dolomite. These structures exhibit variations in mineral composition and grain sizes within individual nodules (Figure 2g,h).
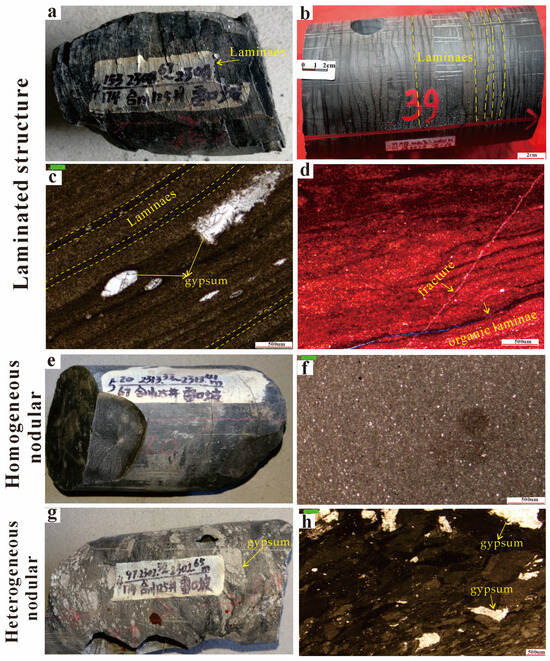
Figure 2.
The lithological characteristics in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan Basin. (a) Well Hechuan 125, 2308.67 m, the laminated developed shale. (b) Well Pengyang 3, the dark grey centimetric scale muddy limestone interbedded with millimeter-scale limy mudstone. (c) Well Hechuan 125, 2304.52 m, the horizontally laminated gypsum-bearing and mud-bearing limestone. (d) Jianyang 1, the laminar-like gypsum-bearing and muddy limestone, muddy layer, organic layer. (e) Well Hechuan 125, the homogeneous nodular muddy limestone. (f) Well Hechuan 125, 2306.23 m, muddy limestone. (g) Well Hechuan 125, 2302.5 m, the lumpiness gypsum-bearing muddy limestone. (h) Well Hechuan 125, 2302.5 m, the gypsum intercalated muddy layer.
The Lei32 sub-member also contains evaporites, primarily gypsum and rock salt. Gypsum rocks commonly display layered and nodular structures. The occurrence of gypsum and selenite is observed as agglomerates forming nodules, with a predominant diameter range of 1–5 mm. Overall, the Lei32 sub-member demonstrates a complex sedimentary succession of carbonate rocks and evaporites, showcasing distinct lithological variations and sedimentary structures (Figure 2).
4.2. Source Rock Characteristics
The measured TOC results of the five different carbonate rocks in the Lei32 sub-member indicate that the TOC content in the argillaceous limestone, gypsiferous argillaceous limestone, and calcareous mudstone ranges from 0.34% to 1.98%, generally exceeding 0.3% (Figure 3b and Table 1). Among them, the TOC content in the calcareous mudstone is the highest, ranging from 0.86% to 1.98%, with an average of 1.21%, indicating the best hydrocarbon source rock (Figure 3a). The gypsiferous argillaceous limestone follows, with a TOC content ranging from 0.81% to 0.91%, averaging 0.86%. The TOC content of argillaceous limestone ranges from 0.34% to 0.96%, with an average of 0.69%. The TOC content of limestone and mudstone is between 0.07% and 0.23%, below 0.3%, indicating that they are not hydrocarbon source rocks. The TOC content in the gypsiferous salt rock from well CT1 is between 0% and 0.2%, indicating that the salt rock is not an effective hydrocarbon source rock. Therefore, the main effective hydrocarbon source rocks in the Lei32 sub-member are argillaceous limestone, gypsiferous argillaceous limestone, and calcareous mudstone. Among them, the TOC content in the gypsiferous mud shale is the highest, reaching 4.0% (Figure 3a).
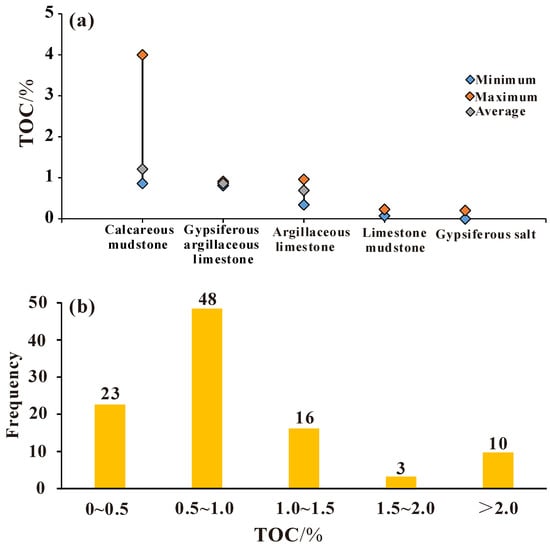
Figure 3.
The TOC content in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan Basin.

Table 1.
The TOC content and mineral composition in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan Basin.
The measured S1 of the mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member in well CT1 reaches a maximum of 0.28 mg/g, with an average of 0.19 mg/g, indicating a favorable oil and gas potential in the carbonate source rock. The S2 has an average value of 0.21 mg/g and can reach a maximum of 0.30 mg/g, indicating that the hydrocarbon source rock has the ability to generate hydrocarbons through thermal decomposition. The S1 + S2 ranges from 0.25 to 0.58 mg/g, with an average of 0.40 mg/g, indicating a significant hydrocarbon generation potential in the source rock.
The organic matter micro-components of source rock in the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 are primarily composed of sapropel and vitrinite. In the sapropel component, the majority of algal bodies have undergone degradation, forming micro granules, with a small amount preserving their original structure. It contains a small proportion of vitrinite and inertinite, with the vitrinite component mainly consisting of fragmented vitrinite particles. The carbon isotope of kerogen (δ13C) is −27.8‰ to −28.6‰, indicating that the organic matter type of the mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 belongs to Type II humic sapropelic kerogen. In comparison, the δ13C in well JY1 is relatively lighter, ranging from −29.6‰ to −27.1‰, indicating Type II organic matter with a higher oil-prone component.
The measured vitrinite reflectance (Ro) of the mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 ranges from 1.59% to 1.63%. This indicates that the mudstone is in a highly mature stage and falls within the range of generating condensate oil and wet gas. The Ro of the mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member of well JY1 is between 1.92% and 2.04%. This suggests an increased Ro value in the southern part of the Central Sichuan Basin.
4.3. Reservoir Characteristics
The reservoir space of argillaceous limestone and marly mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member primarily comprises inorganic micro–nanopores, organic micro–nanopores, and microfractures. The porosity ranges from 2.00% to 8.51%, with an average value of 2.7%. The permeability ranges from 0.00076 to 1.68 mD, with an average value of 0.19 mD (Figure 4 and Figure 5). These characteristics classify it as a low-porosity, low-permeability unconventional reservoir. From a lithological perspective, mud shale and dolomite exhibit superior physical properties compared to limestone. The average porosity of calcareous mudstone is 2.11%, while the average porosity of limestone is 1.6%. Dolomite demonstrates an average porosity of 2.18%. Overall, there is a positive relationship between porosity and permeability in these core samples (Figure 4). Due to the development of microfractures and bedding in the argillaceous limestone, there is an occurrence of low porosity and high permeability in certain datasets.
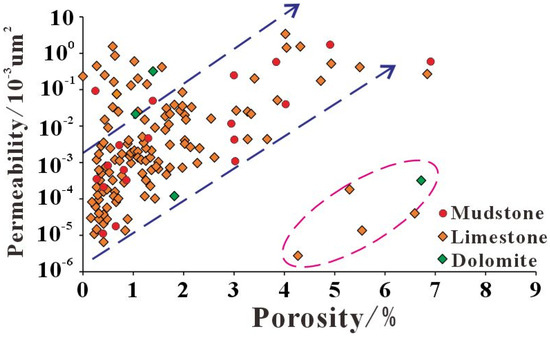
Figure 4.
The intersection diagram of porosity and permeability in the Lei32 sub-member.
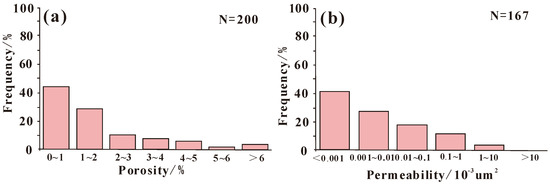
Figure 5.
The distribution histogram of porosity and permeability in the Lei32 sub-member.
In the Lei32 sub-member, the reservoir pore type mainly comprises nanopores, indicating small-scale pore spaces. The macro pores and fractures within the reservoir are generally undeveloped, suggesting limited larger-scale pore spaces. However, there are some notable macro pores and fractures present, including structural fractures, structural dissolution pores, and bedding/layering fractures (Figure 6 and Figure 7). Structural fractures exhibit a reticulate pattern and have high-angle openings. They can be either fully or partially filled, and localized dissolution phenomena may be observed. These structural fractures significantly enhance the storage capacity and permeability of the tight reservoir, potentially contributing to the observed high oil and gas production in well CT1 (Figure 6A,B). Bedding/layering fractures are primarily observed in calcareous mud shale or laminated mudstone. These fractures are partially filled with incompletely cemented calcite. While their presence may contribute to increased permeability and fluid flow within the reservoir, their overall impact on storage capacity and production potential may be less significant compared to structural fractures (Figure 6C,D).

Figure 6.
The reservoir characteristic in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan Basin. (A) Well CT1, 3567.56 m, the high-angle structural fractures and reticular fractures developed. (B) Well Hechuan 125, 2290 m, the interlayer joints are developed in the muddy limestone and are in the filling state. (C) Well Hechuan 125, carbonaceous mudstone with developed laminated fractures. (D) Well Hechuan 125, 2296.53 m, muddy crystal limestone filling fractures and weak dissolution.
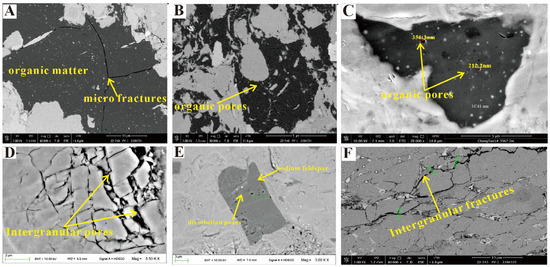
Figure 7.
The reservoir characteristic in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan Basin. (A) Well CT1, the shrinkage cracks developed within organic matter. (B) Well CT1, small amount of nanopores developed within the organic matter. (C) Well CT1, 3567.2 nm, organic matter with a small amount of circular pores, pore size approximately 31–354 nm. (D) Well CT1, 3566.61 m, the mud crystal calcite developed intergranular pores. (E) Well CT1, 3566.80–3567.06 m, the sodium feldspar developed dissolution pores. (F) Well CT1, the calcite intergranular pores are filled with clay minerals and rock salt, and with good pore connectivity.
The micro–nanopores in the reservoirs of the Lei32 sub-member include intergranular/intragranular pores (Figure 7D,F), dissolution pores (Figure 7E), and organic pores (Figure 7A–C). Electron microscopy reveals the presence of abundant intergranular pores formed by calcite, dolomite, pyrite, and clay minerals, which constitute the primary reservoir space types in the Lei32 sub-member. Dissolution pores develop within or between particles of calcite, dolomite, and sodium feldspar, with pore sizes mainly ranging from 100 to 1000 nm (Figure 7E). Organic matter pores, on the other hand, are not the dominant reservoir space type. They are found within or along the edges of some blocky organic matter, exhibiting circular or irregular-shaped pores with sizes primarily ranging from 20 to 500 nm (Figure 7A–C).
4.4. Oil and Gas Characteristics
The density of crude oil in the CT1 well ranges from 0.72 to 0.75 g/cm3, with an average of 0.74 g/cm3, indicating light oil. The viscosity of crude oil ranges from 0.67 to 0.91 mPa·s, with an average of 0.76 mPa·s. The initial boiling point is between 26 °C and 29 °C, and the distillate yield at 300 °C ranges from 72.5 to 87.0 mL, indicating it is a condensate oil. Based on the diamondoid identification, the maturity (Ro) of the condensate oil in the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 is 1.65%. Utilizing the methylphenanthrene index, the Ro is determined to be between 1.76% and 1.86%. This suggests that the condensate oil from the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 is in a high maturity stage. In the Central Sichuan Basin, the methane content in the Lei32 sub-member ranges from 85.82% to 88.15%; the ethane content, 5.51~7.76%; the propane content, 1.79~3.2%; and the dryness coefficient, 0.871 to 0.924. The gas does not contain hydrogen sulfide and can be classified as wet gas. The oil and gas in the well CT1 are self-generated and self-stored, locally accumulated, and the crude oil in the Lei32 sub-member originates from the humic-type mudstone source rock. The natural gas mainly comes from the organic-rich mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member [6].
5. Discussion
5.1. Effect of Evaporated Lagoon Sedimentation on Source Rocks
5.1.1. Paleo-Salinity and Closure
The analysis of carbon and oxygen isotopes (δ18O) provides insights into paleo-salinity and evaporation conditions, while carbon isotopes (δ13C) are indicative of the redox state or residence time of the basin [17,18,19,20]. In the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1, the carbonate rocks exhibit δ13C values ranging from 1.42‰ to 2.12‰, indicating a predominantly anaerobic reducing environment during deposition (Table 2). This is consistent with the presence of pyrite within the carbonate rocks, which further confirms the reducing conditions. The δ18O values range from −3.55‰ to −4.46‰, suggesting a higher salinity compared to normal seawater (Table 2). The presence of gypsum within the carbonate rocks in well JY1 also indicates a relatively high-salinity environment.

Table 2.
The carbon and oxygen isotope compositions and Z values in the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1.
Comparing the δ13C values of the calcareous mudstone and argillaceous limestone in well CT1, it can be observed that the calcareous mudstone has lower δ13C values (ranging from 1.42‰ to 1.63‰) compared to the argillaceous limestone (ranging from 2.02‰ to 2.12‰). This suggests that the water body during the deposition of the calcareous mudstone was possibly deeper and had a lower oxidation level. The lower δ13C values indicate a higher organic carbon content or a different carbon source in the deeper water environment. Overall, the carbon and oxygen isotope analysis of the Lei32 sub-member in well CT1 provides valuable information about the paleo-sedimentary environment, indicating a predominantly anaerobic reducing environment with higher salinity conditions compared to normal seawater [18].
In Figure 7, the casting points of carbon and oxygen isotopes in the closed lake system are in the first and second quadrants, like those of the Great Salt Lake, Turkana Lake, and Natron–Magadi Lake [19]. In the Lei32 sub-member, all the carbon and oxygen isotope casting points are in the second quadrant. In other words, the casting points fall into the closed lake system, indicating that the Lei32 sub-member is basically in a closed lake system, just like the Great Salt Lake (Figure 8).
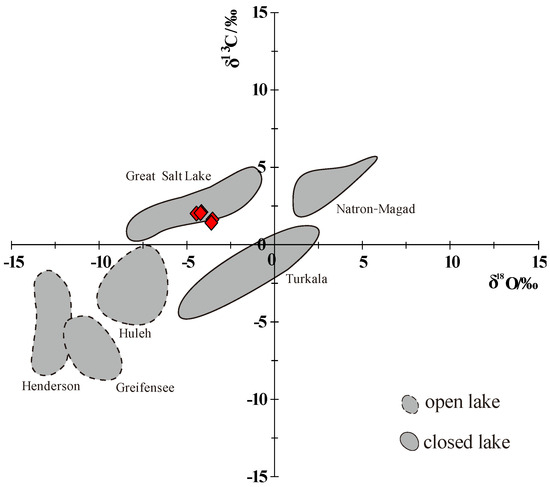
Figure 8.
Cross plot of the δ13C and δ18O values of Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan Basin (after Talbot and Kelts [19]).
Many scholars confirmed that there was a positive correlation between salinity and carbon–oxygen isotope [21,22]. Keith and Weber combined δ13C and δ18O to investigate the paleo-salinity; the formula is as follows [23]:
In Formula (1), the Z value represents the paleo-salinity parameter, both δ13C and δ18O are PDB standards. The Z value varies between 128.4 and 129.6 with an average of 129.1 in the Lei32 sub-member, indicating the study area is basically in a saline depositional environment (Table 2).
In addition, trace element values are commonly used to distinguish paleo-salinity. Generally, Sr/Cu ratios between 1.3 and 5.0 indicate low salinity or a warm humid climate, whereas a ratio greater than 5.0 points to high salinity or a hot arid climate [24,25]. The Sr/Cu ratios of the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 are generally high, almost exceeding 5.0 for the entire section, indicating that it was mainly deposited in a high-salinity environment under an arid climate (Figure 9). This is also consistent with the results obtained from carbon and oxygen isotope analysis.
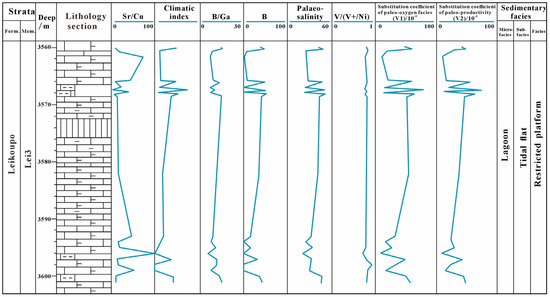
Figure 9.
Element markers and paleo-environmental characteristics of the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 in the Central Sichuan Basin.
5.1.2. Paleo-Sedimentary Environment
This study presents a detailed discussion of the main controlling factors for the development of carbonate source rocks in the restricted platform of the Lei32 sub-member in the Central Sichuan Basin. Identifying paleo-redox conditions is crucial in understanding the geological history of sediments [26]. Under the microscope, the mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member exhibits horizontal mud laminae and berry-shaped pyrite, indicating a relatively deep water, low energy, and reducing depositional environment. In addition, V/(V + Ni) is an important redox geochemical index, with a value greater than 0.5 indicating a hypoxic environment [26]. The V/(V + Ni) values of the Lei32 sub-member of well CT1 tend to approach 1.0. Combined with other trace element geochemistry indices and the high TOC content of the carbonate rocks in the Lei32 sub-member, it comprehensively indicates a high organic matter productivity in the evaporative environment of the Lei32 sub-member in the Central Sichuan Basin, with the water body being hypoxic to anoxic (Figure 9).
The Lei32 sub-member in the brackish lake has a high salinity, and under the influence of gravity, seawater easily forms salinity stratification. It can be divided into surface water and bottom water based on the normal wave base [6]. The surface water has a lower salinity, which is suitable for the survival of euryhaline and halophilic planktonic organisms. The bottom water in the deeper parts has a higher salinity and lacks dissolved oxygen, making it suitable for the enrichment and preservation of organic matter. However, the excessively high salinity in the central part of the brackish lake can inhibit the reproduction of organisms. Although brackish lakes with lower salinity in mudstone and limestone have a considerable number of organisms, they are prone to decay. Only brackish lakes with moderate salinity and gypsum content are more favorable for the formation of hydrocarbon source rocks with high organic matter abundance (Figure 10) [8,27].
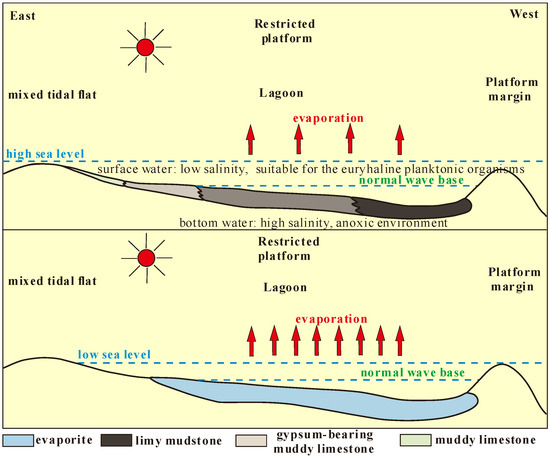
Figure 10.
Sedimentary environment model of the lagoon facies muddy limestone source rock in the Lei32 sub-member.
During the Lei32 sub-member period, the brackish lake depositional environment had a higher organic matter productivity, and the water body was characterized as hypoxic to anoxic, which is conducive to the development of mudstone hydrocarbon source rocks. Excessively high salinity inhibits the reproduction of organisms. In the Lei32 sub-member period, brackish lakes with moderate salinity and gypsum content were more favorable for the formation of hydrocarbon source rocks with high organic matter abundance [18].
5.1.3. Clay Mineral for Carbonate Source Rock
Carbonate rocks lacking clay minerals are unlikely to serve as source rocks. Only carbonate rocks with a higher proportion of clay minerals can become effective source rocks [28]. The analytical results also indicate that the clay mineral content is the primary factor influencing the TOC content of carbonate rocks in the Lei32 sub-member. Clay minerals are rich in organic matter, and with the clay mineral content increasing, the organic matter content also increases. There is a positive correlation between clay mineral and TOC contents (Figure 11). As the clay minerals increase, the transition from pure limestone to argillaceous limestone and mudstone, the TOC increases from 0.07% to 1.98%, with an average TOC increase from 0.07% to 1.21%. The impact of increasing clay mineral content on TOC content is evident.
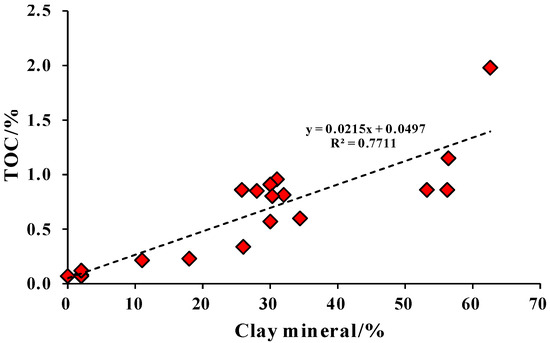
Figure 11.
Relationship between clay mineral content and TOC in the Lei32 sub-member.
5.2. Effect of Evaporated Lagoon Sedimentation on Reservoirs
Controlling Factors for Reservoir Development
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an important technique for characterizing fluid mobility in tight reservoirs [29]. In the Lei32 sub-member of wells JY1 and CT1, the NMR porosity of argillaceous limestone and mudstone ranges from 0.70% to 3.94%, with an average of 2.02%. However, the NMR porosity of mudstone with crystalline limestone ranges from 0.31% to 2.88%, with an average of only 0.84%. The NMR porosity shows a positive correlation with clay mineral content (Figure 12a) and a negative correlation with calcite content (Figure 12b), indicating that the mudstone reservoirs have more developed porosity compared to the limestone reservoirs. The clay mineral and gypsum contents in the rocks are important factors that influence reservoir porosity [30]. Reservoirs with high clay mineral and gypsum contents tend to have higher porosity. Fractures also play a crucial role in determining permeability, which affects the flow of fluids within the reservoir (Figure 12a).
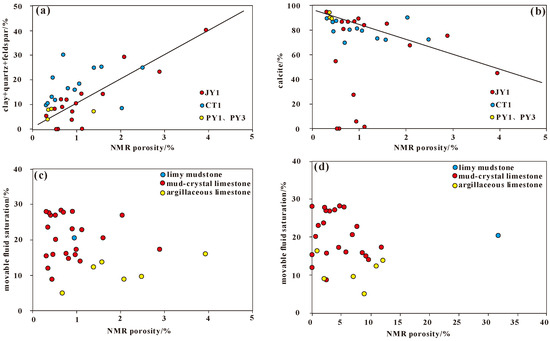
Figure 12.
Relationship between NMR porosity and mineral content in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan (a,b). Relationship between NMR movable fluid saturation and NMR porosity (c,d).
The NMR movable fluid saturation in the saturated samples of the Lei32 sub-member tight reservoir ranges primarily from 5% to 30%, with an average of only 18.1%. This indicates that the tight reservoirs in the Lei32 sub-member have poor fluid mobility in the absence of developed fractures (Figure 12c,d). Overall, the movable fluid saturation tends to decrease with increasing clay mineral content. This trend may be related to the water sensitivity of clay minerals. Therefore, reservoirs with higher clay mineral content, such as mudstone, may have slightly higher porosity compared to limestone, but they may not be favorable for the production of tight oil.
The development of pore space in the Lei32 sub-member is closely related to the content of clay minerals and organic matter and the dolomitization degree. There is a certain degree of positive correlation between porosity and TOC content, clay mineral content, and dolomite content (Figure 13). As the dolomite content increases, the porosity initially increases and then decreases. Samples with dolomite content ranging from 40% to 70% generally exhibit higher porosity, while samples with dolomite content exceeding 80% mostly have porosity below 2.0, indicating that pure mudstone limestone is not conducive to pore development. Therefore, the main controlling factors for pore development in the Lei32 sub-member include weak dolomitization, which generates intercrystalline pores, clay mineral transformation leading to intercrystalline fracture development, the generation of organic pores through the generation and expulsion of hydrocarbons as organic matter matures, and the dissolution of dolomite by organic acids derived from immature to low-maturity hydrocarbon source rocks, leading to the formation of dissolution micropores in plagioclase feldspar.
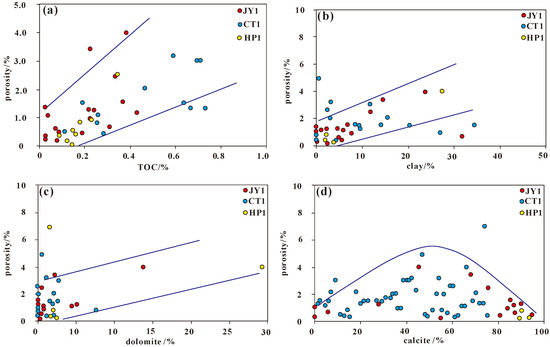
Figure 13.
Relationship between porosity and TOC content (a). Relationship between porosity and mineral content (b–d) in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan Basin.
The technique of CT scanning plays a crucial role in analyzing and understanding the three-dimensional arrangement of reservoir pores [31]. It facilitates the three-dimensional reconstruction of different lithology pore structures in the Lei32 sub-member using nanometer CT. The results show a relatively uniform distribution of pore space. With an increase in clay mineral content, the porosity and pore size of the three samples show an increasing trend (Figure 14).
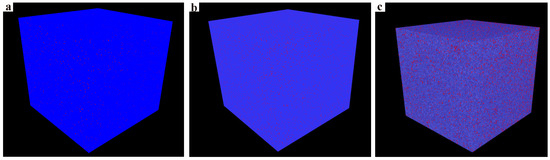
Figure 14.
The nanometer CT scanning pore structure characteristic of the tight reservoir in the Lei32 sub-member of Central Sichuan. (a) Well JY1, 2639.08 m, muddy limestone, porosity: 1.03%, clay content: 5%. (b) Well CT1, 3566 m, muddy limestone, porosity: 2.32%, clay content: 28%. (c) Well CT1, 3568 m, limy mudstone, porosity: 4.53%, clay content: 53%.
6. Conclusions
(1) The carbonate rocks within the Lei32 sub-member can be classified into laminated, homogeneous nodular, and heterogeneous nodular structures. The main effective hydrocarbon source rocks in the Lei32 sub-member are calcareous mudstone (1.21%), gypsiferous argillaceous limestone (0.86%), and argillaceous limestone (0.69%).
(2) The reservoir space of the argillaceous limestone and limy mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member primarily consists of inorganic and organic micro–nanopores and microfractures. The average porosity and permeability are 2.7% and 0.19 mD, indicating a low-porosity and low-permeability unconventional reservoir.
(3) The oil and gas in the well CT1 are self-generated and self-stored, exhibiting source–reservoir integration, and the crude oil in the Lei32 sub-member originates from the humic-type mudstone source rock. The natural gas mainly comes from the organic-rich argillaceous limestone and limy mudstone in the Lei32 sub-member, belonging to a new type of unconventional oil and gas reservoir.
(4) The Lei32 sub-member was basically in a closed lake system, like the Great Salt Lake. The average Z value is 129.1 in the Lei32 sub-member, indicating a saline and reducing depositional environment. The clay mineral content is the primary factor influencing the TOC content of carbonate rocks in the Lei32 sub-member.
(5) The clay mineral and gypsum contents are the important factors influencing reservoir porosity, and the fractures are key factors influencing permeability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.X. and W.L.; formal analysis, Y.X., W.L. and X.F.; investigation, H.T. and Z.X.; methodology, Y.X., W.L. and H.Z.; project administration, Y.X.; resources, H.T.; software, H.Z., H.T. and X.F.; supervision, Z.X.; writing—original draft, Y.X., W.L. and H.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.X. and W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the research on large-scale storage and production of marine carbonate oil and gas and exploration and development technology (Grant No. 2023ZZ16YJ01).
Data Availability Statement
The research created experimental data that can be found in the tables and figures presented in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge previous research findings related to the study.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Wenzheng Li and Xiaodong Fu were employed by the China National Petroleum Corporation. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Zhou, J.G.; Xin, Y.G.; Gu, M.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, G.J.; Lü, Y.Z. Direction of gas exploration in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation of the Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2010, 30, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Sun, W.; Song, J.M.; Yong, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, C. The key geological problems of natural gas exploration in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 151–167. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, J.R.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wen, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H. Characteristics and exploration potential of unconventional Middle Triassic Lei32 reservoirs in the central Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2022, 42, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Su, C.P.; Shi, G.S.; Jia, H.F.; Li, S.H.; Yu, Y. The genesis of nodular limestone reservoirs of the first period of Maokou Formation of Permian in southern Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2021, 32, 806–815. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Wang, G.W.; Duan, S.F.; Xin, Y.G.; Zhang, H. Reservoir characteristics and exploration target of the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in Sichuan Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2021, 26, 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Xin, Y.G.; Zhang, H.; Tian, H.; Zhu, X.J.; Chen, W. A new unconventional gas reservoir type Source-reservoir integrated carbonate gas reservoir from evaporated lagoon facies in Lei32 sub-member in Central Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 34, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Song, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Sealing Mechanism of the Roof and Floor for the Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale Gas in the Southern Sichuan Basin. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 6999–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.G.; Zhou, J.G.; Ni, C.; Gu, M.F.; Gong, Q.S.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.J. Sedimentary facies features and favorable lithofacies distribution of Middle Triassic Leikoupo barriered carbonate platform in Sichuan Basin. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2013, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tissot, B.P. Recent advances in petroleum geochemistry applied to hydrocarbon exploration. AAPG Bull. 1984, 68, 545–563. [Google Scholar]
- Palacas, J.G.; Anders, D.E.; King, J.D. South Florida basin—A prime example of carbonate source rocks of petroleum. In Petroleum Geochemistry and Source Rock Potential of Carbonate Rocks; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.M. Hydrocarbon potential of source rocks in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in the Western Sichuan Depression. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2016, 38, 366–374. [Google Scholar]
- Moldovanyi, E.P.; Lohmann, K.C. Isotopic and petrographic record of phreatic diagenesis; Lower Cretaceous Sligo and Cupido formations. J. Sediment. Res. 1984, 54, 972–985. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Esrafili-Dizaji, B.; Tavakoli, V. Dolomitization and anhydrite precipitation in permo-triassic carbonates at the South Pars gasfield, offshore Iran: Controls on reservoir quality. J. Pet. Geol. 2010, 33, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Zuo, Y.H.; Wen, H.G.; Li, D.M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Yang, M.H.; Zeng, J.C. Natural gas characteristics and gas-source comparisons of the lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation, Eastern Sichuan Basin. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 1458–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Zuo, Y.H.; Yang, M.H.; Huang, W.M.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Zeng, J.C. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion histories of the Upper Permian Longtan Formation in the Eastern Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 19329–19340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Zuo, Y.H.; Wen, H.G.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhou, G.; Xu, L.; Sun, H.F.; Yang, M.H.; Yan, K.N.; Zeng, J.C. Natural gas characteristics and gas-source comparisons of the lower Triassic Jialingjiang formation, Eastern Sichuan basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2023, 221, 111165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, M.J.; Marshall, J.D. Palaeoclimate interpretation of stable isotope data from lake sediment archives. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2004, 23, 811–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Song, Y.; Pang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, H. Effects of paleo sedimentary environment in saline lacustrine basin on organic matter accumulation and preservation: A case study from the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 185, 106669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, M.R.; Kelts, K. Paleolimnological Signatures from Carbon and Oxygen Isotopic Ratios in Carbonates, from Organic Carbon-Rich Lacustrine Sediments: Chapter 6. In Lacustrine Basin Exploration: Case Studies and Modern Analogs; AAPG MEMOIR; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1990; pp. 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.C.; Ku, T.L. δ13C-δ18C covariance as a paleo hydrological indicator for closed-basin lakes. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1997, 133, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.; Mayeda, T. Variation of 18O content of waters from natural sources. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1953, 4, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.T.; Cheng, R.H.; Liu, C.L. Review of paleo salinity recovering methods. Glob. Geol. 2002, 21, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, M.L.; Weber, J.D. Isotopic composition and environment classification of selected limestones and fossils. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 1964, 23, 1796–1816. [Google Scholar]
- Leila, M.; Moscariello, A.; Šegvić, B. Geochemical constraints on the provenance and depositional environment of the Messinian sediments, onshore Nile Delta, Egypt: Implications for the late Miocene paleogeography of the Mediterranean. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 143, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.T.; Liu, Z.J.; Bruch, A.A.; Liu, R.; Hu, F. Palaeoclimatic evolution during Eocene and its influence on oil shale mineralisation, Fushun basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 45, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, D.; Wagreich, M.; Fathi, E.; Ahmed, M.S.; Leila, M.; Sami, M. Maastrichtian Anoxia and Its Influence on Organic Matter and Trace Metal Patterns in the Southern Tethys Realm of Egypt during Greenhouse Variability. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 19603–19612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.F.; Luo, B.; Wen, L.; Wang, J.X.; Zhou, G.; Wen, H.G.; Huo, F.; Dai, X.; He, C.L. The first discovery of organic-rich shale in Leikoupo Formation and new areas of subsalt exploration, Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2021, 32, 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.W. Comparison of carbonate and shale source rocks. AAPG Bull. 2019, 68, 494. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Tan, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiao, L. Nuclear magnetic resonance pore radius transformation method and fluid mobility characterization of shale oil reservoirs. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 221, 211403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lü, X.; Quan, H.; Qian, W.; Mu, X.; Chen, K.; Bai, Z. Influence factors and an evaluation method about breakthrough pressure of carbonate rocks: An experimental study on the Ordovician of carbonate rock from the Kalpin area, Tarim Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 104, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shen, J.; Liu, S.; Jiang, C.; Qin, X. Three-dimensional modeling and analysis of macro-pore structure of coal using combined X-ray CT imaging and fractal theory. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 123, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).