Abstract
Chinese cities are pursuing an energy transition to decouple energy-related carbon emissions (ERCEs) from economic growth. Despite numerous studies focusing on the factors influencing carbon emissions, few have quantitatively analyzed their respective contribution rates, thus leaving a gap in effectively guiding policies. This study took 16 cities in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) as the study area. The decoupling between ERCEs and economic growth was analyzed during 2000–2020, and the contribution rates of different factors were explored. The results showed that the total ERCEs increased from 413.40 million to 1265.86 million tons during 2000–2020, increasing by over three times. Coal and oil were the dominant energy sources in most cities, but natural gas consumption increased from 0.15% to 5.96%. Moreover, 14 cities showed a decoupling status, indicating a certain win–win situation between economic growth and ERCE reduction. Economic growth greatly increased ERCEs, with its contribution rate ranging from 114.65% to 493.27% during 2000–2020. On the contrary, energy structure and energy intensity both contributed to reducing ERCEs in most cities, and their maximum contribution rates reached −32.29% and −449.13%, respectively, which were the main forces for the win–win situation. Finally, carbon reduction proposals are put forward, which provide theoretical support for achieving the “Double Carbon” goal in the YRD.
1. Introduction
Carbon emissions from fossil fuels and unsustainable energy burning are reported as the primary drivers of global warming, causing the current global average temperature to rise 1.1 °C above pre-industrial levels [1]. Consequently, there has been a growing consensus among the international community to reduce carbon emissions [2,3,4]. Over the past few decades, China has witnessed an astonishing pace of industrialization and urbanization, with its GDP growing at an annual rate of 9% [5,6]. However, this rapid economic growth has been accompanied by a significant surge in energy consumption, resulting in massive energy-related carbon emissions (ERCEs) [7,8]. In 2021, China contributed a substantial 33% share of the world’s total carbon emissions [9], making it the highest carbon emitter. To address this, the Chinese government has set forth the ambitious “Double Carbon” goal, aiming to achieve a carbon emission peak by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. Chinese cities are thus facing the dual pressure of maintaining rapid economic growth while reducing carbon emissions. Understanding the relationship between these two objectives is essential and can provide crucial insights for promoting sustainable development in China.
Scholars have pointed out that economic growth exhibits varying relationships with carbon emissions, depending on the specific region and time period [10,11]. For instance, Mireille et al. found that economic growth in resource-rich countries was more carbon-intensive than that in resource-poor countries [12]. Due to the availability of energy consumption data, previous research has primarily focused on the national level [13] and provincial levels [14,15]. For instance, Magazzino [16] and Lenzen et al. [17] conducted studies on carbon emissions in Israel and Brazil, respectively. Previous studies have significantly influenced the formulation of economic policies [18], carbon reduction strategies [19], and environmental planning [20,21] in different countries and provinces. In 2018, China surpassed its 2020 national carbon intensity reduction target through collective societal efforts [22]. The next phase of carbon reduction will be more challenging and necessitates targeted policies for smaller-scale regions. Studies on a national and provincial scale can no longer meet demand. Shan et al. pointed out that cities are the key zones for implementing the “Dual Carbon” strategy, given that cities have become the spatial carriers for socio-economic development in China [23]. Therefore, the city-level relationship between economic growth and ERCEs should be emphasized, thereby helping set strategies for a win–win situation in Chinese cities.
Chinese cities are striving to reduce ERCEs while maintaining robust economic growth [24]. Energy transition is a multi-faceted approach encompassing optimizing energy intensity, altering energy structure, and developing sustainable clean energy. It has been a widely pursued strategy in many cities [25,26]. Scholars have also extensively examined the influence of energy transition, economic growth, and other variables on ERCEs [27,28,29]. For instance, Zeng et al. pointed out that carbon emission efficiency was positively correlated with factors like industrial structure and external development while being negatively related to energy intensity [30]. However, previous research has mainly focused on identifying influencing factors, overlooking the quantitative analysis of their respective contribution rates. This gap makes it challenging to formulate effective policy guidance. There is a need to further clarify the contribution rates of different factors, thus identifying the main cause of carbon emissions [31,32]. This clarification would enable the formulation of targeted recommendations for cities with diverse carbon emission characteristics.
The Yangtze River Delta (YRD) has witnessed remarkable economic growth in the past few decades, which also makes it a hot spot for carbon emissions [33,34]. Given that fossil fuels remain the primary energy source in the YRD, cities in this region have actively pursued measures to reduce energy-related carbon emissions (ERCEs), including reducing energy intensity and optimizing energy structures. Against this background, assessing the coupling between ERCEs and economic growth and exploring their underlying mechanisms is crucial for formulating effective carbon reduction policies. In this study, involving 16 cities in the core area of the YRD as the study area, the spatio-temporal dynamics of ERCEs and their decoupling relationship with economic growth at the city level were evaluated. According to the characteristics of the YRD, the driving forces of ERCEs were decomposed into economic growth, population size, energy structure, and energy intensity. After that, the contribution rates of them were identified, and the proposals for carbon reduction were put forward. The main objectives were: (1) to examine whether economic growth has decoupled with ERCEs and (2) to determine the contribution rate of different carbon emission drivers and provide strategies for carbon reduction for the core area of the YRD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study took 16 cities in the YRD as the study area, including Shanghai, seven cities in Zhejiang, and eight cities in Jiangsu (Figure 1). According to the Regional Planning of the Yangtze River Delta issued by the State Council in 2010, these 16 cities serve as the core areas of the YRD, with them aiming to drive and coordinate the development of cities in the YRD. As a rapidly urbanized region, the YRD is home to 7.5% of China’s total population and contributes 15.9% of its GDP, despite occupying only 1.1% of the country’s land area [34]. However, this rapid economic growth has been paralleled by a substantial surge in energy consumption, making the YRD one of the top carbon emitters in China. In pursuit of balancing economic growth with carbon reduction, cities in the YRD are actively pursuing energy transitions [35]. Thus, it is essential to explore the decoupling between economic growth and ERCEs, along with their influencing factors, which may help to promote a low-carbon economy in the YRD.
Figure 1.
Study area.
2.2. Data Sources
The following data were utilized in our paper: (1) energy consumption and socio-economic data were obtained from the Statistical Yearbook of Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Shanghai, China Energy Statistical Yearbook; (2) population data and GDP data were obtained from the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center [36]; and (3) administrative boundary data were obtained from the National Geographic Information Public Service Platform [37].
2.3. Evaluation of Energy-Related Carbon Emission
Based on the statistical yearbook, the main energy sources in the YRD are coke, coal, gasoline, crude oil, kerosene, fuel oil, diesel, and natural gas. The IPCC has proposed a standard formula for the carbon dioxide emission calculation formula [1,38]. Referring to the IPCC, this study divided them into three categories, i.e., coal (including coke and coal), oil (including gasoline, crude oil, kerosene, fuel oil, and diesel), and natural gas. The ERCEs were calculated as Equation (1) [1,38].
where is the total amount of ERCEs; represents the consumption amount of energy type k; is the conversion factor for standard coal of energy type k; is the carbon emission coefficient of energy type k; 44/12 is the molecular weight of carbon dioxide. The conversion factors for standard coal and carbon emission coefficients for each energy source were set according to the IPCC [1,38].
2.4. Tapio Decoupling Analysis
Decoupling is commonly applied to represent variables that are no longer related to each other [39]. If economic growth is decoupled with ERCEs, this indicates economic growth is achieved without an accompanying increase in ERCEs, and ERCE reduction can be achieved along with economic growth [40]. The Tapio model, as a widely used method in decoupling measurement [41,42,43], can calculate the decoupling elastic coefficient by utilizing the ratio of the change rate in carbon emissions to that in GDP [44].
where is the decoupling elastic coefficient; represents the carbon emissions; is the carbon emission changes; indicates the GDP change. According to the elastic coefficient, and , the decoupling status can be divided into eight types (Table 1). In the 16 cities in the YRD, is always greater than 0; thus, only four types appeared, that is, expansive negative decoupling, expansive coupling, strong decoupling, and weak decoupling.

Table 1.
Classification of decoupling status based on carbon emission change, economic growth, and elastic coefficient [44].
2.5. LMDI Factor Decomposition Model
The logarithmic mean divisor index method (LMDI), as an effective approach to identifying influencing factors, enables the breakdown of total change into several comprehensible factors for ease of interpretation [45]. The LMDI model offers a straightforward calculation process and is aptly suited for conducting time series analysis involving multiple influencing factors [46], with it being a widely used method in driver decomposition [32,47]. Due to the fact that the YRD has the most rapid economic growth and the most densely populated population in China, economic growth and population size were considered to be the typical factors of ERCEs in the YRD. Meanwhile, according to the characteristics of energy consumption in the YRD and previous studies [48,49], energy structure and energy intensity were taken into account. Finally, LDMI was applied in this study, and four factors were considered as the driving forces behind ERCEs: economic growth, population size, energy intensity, and energy structure. The specific formula can be expressed as [46]:
where C is energy-related carbon emissions; is the carbon emissions of energy i; represents the consumption of the energy i; G represents GDP; P is population; is carbon emission intensity; is energy intensity; is energy structure; Y is per capita GDP, indicating economic growth; P is population size.
This study assumed that represents the carbon emissions for the base year, represents the carbon emissions for year t, and ΔC represents the carbon emission change from the base year to year t. In the LMDI model, the total effect can be decomposed into energy structure effect (ΔCM), energy intensity effect (ΔCI), economic growth effect (ΔCY) and population size effect (ΔCP). The decomposition effect of each driver was calculated as follows:
Finally, the comprehensive effect of carbon emission changes is shown as Equation (9). The contribution rate of energy structure (, energy intensity (), economic growth (), and population size () can be expressed as Equation (10), respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of ERCEs
During 2000–2020, the total amount of ERCEs rose significantly from 413.40 million tons to 1265.86 million tons in 16 cities in the YRD. In 2000, Zhoushan generated 2.20 million tons of ERCEs, ranking the least among all of the cities, while Shanghai ranked the top, with 104.21 million tons. In 2020, Yangzhou became the city producing the least ERCEs, with a total amount of 28.40 million tons, while Shanghai remained the largest emitter, generating 187.35 million tons of ERCEs. During 2000–2020, ERCEs increased in all of the cities (Figure 2). In detail, Zhoushan was the city with the largest growth rate in ERCEs, and it rose by 44 times from 2000 to 2020. Shanghai was the city with the slowest growth rate, but its ERCEs still increased by 80% from 2000 to 2020. Among the 16 cities, the ERCEs of Hangzhou, Ningbo, and Yangzhou showed a trend of increasing first and then stabilizing during the study period; that of Shanghai, Nantong, and Zhenjiang also increased first but then decreased; and in the remaining 10 cities, the ERCEs showed a continuous increase, with different growth rates. In the early period, Jiaxing, Taizhou (in Zhejiang), Changzhou, and Suzhou experienced rapid growth of ERCEs while in the later period, Zhoushan underwent a faster growth rate.
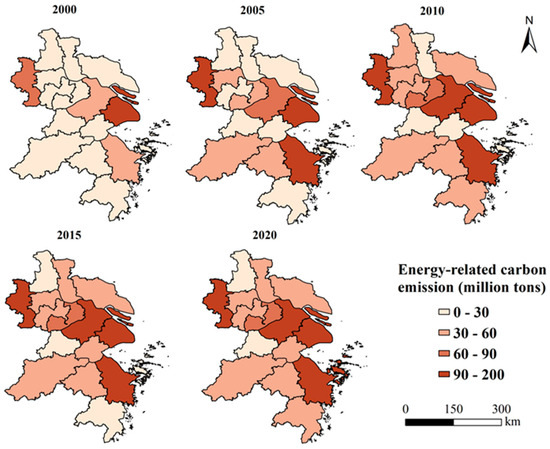
Figure 2.
Spatial pattern of ERCEs in the 16 cities from 2000 to 2020.
As shown in Figure 2, the 16 cities were divided into four types based on their ERCEs: low level (0–30 million tons), relatively low level (30–60 million tons), relatively high level (60–90 million tons), and high level (>90 million tons). Economically developed coastal cities had relatively higher ERCEs than those internal cities in the study period (Figure 2). Shanghai, Suzhou, Nanjing, and Ningbo had higher levels of economic growth, and they also generated a larger amount of ERCEs. On the contrary, Taizhou (in Zhejiang), Huzhou, and Taizhou (in Jiangsu), with relatively low levels of economic growth, had relatively low ERCEs. Shanghai always had high levels of ERCEs from 2000 to 2020, while Huzhou always had low levels (Figure 2). It is worth mentioning that Hangzhou, as the capital of Zhejiang Province, was never listed as a city with high-level ERCEs during the study period.
3.2. Dynamics of Energy Structure in Different Cities
In 2000, 16 cities in the YRD consumed a total of 238.46 billion kg of coal, 174.31 billion kg of oil, and 0.62 billion kg of natural gas (Figure 3). From 2000 to 2020, with economic development, the consumption of all three energy types continued to increase. In 2020, the consumption of coal increased to 674.15 billion kg, oil increased to 516.27 billion kg, and natural gas increased to 74.44 billion kg. In terms of proportion, from 2000 to 2020, coal’s share decreased from 57.68% to 53.26%, oil’s share declined from 42.17% to 40.78%, while natural gas’s proportion increased significantly, from 0.15% to 5.96%. Among the 16 cities, Shanghai, Suzhou, and Nanjing consumed the most coal in 2000, while in 2020, the top three cities of coal consumption changed to Suzhou, Nanjing, and Ningbo. As for oil consumption, Shanghai, Nanjing, and Ningbo were always the top three cities. Shanghai consumed the highest amount of natural gas in the YRD, with its consumption being 15.88 times higher than the second-ranked city in 2000 and 1.60 times higher in 2020.
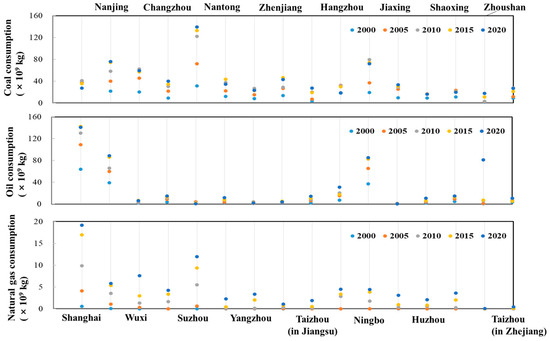
Figure 3.
Dynamics of energy intensity in 16 cities from 2000 to 2020.
Figure 4 shows the dynamics of energy structure in different cities in the YRD. From 2000 to 2020, coal was the dominant carbon source in 11 of the 16 cities. Specifically, coal consumption resulted in over 80% of the carbon emissions in Suzhou, Jiaxing, Wuxi, Yangzhou, and Zhenjiang. In Huzhou and Shaoxing, the carbon emissions caused by coal occupied a proportion of over 70% during 2000–2005 and then decreased to about 50% in 2020, while the carbon emissions caused by oil and natural gas increased during 2000–2020. The carbon emissions from coal in four cities, including Changzhou, Nantong, Taizhou (in Zhejiang), and Taizhou (in Jiangsu), have always accounted for over 50% of their total ERCEs, with a small change from 2000 to 2020.
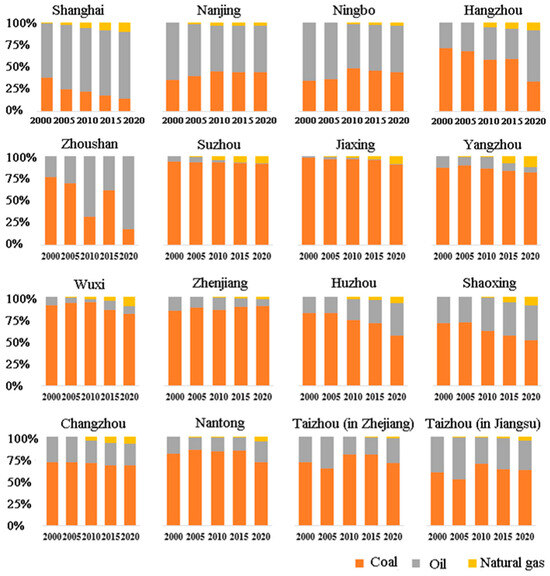
Figure 4.
Dynamics of energy structure in 16 cities from 2000 to 2020.
From 2000 to 2020, oil was the leading source of carbon emissions in Shanghai, Nanjing, and Ningbo (Figure 4). Specifically, in Shanghai, the proportion of carbon emissions from oil gradually increased from 61.20% to 75.08%, while that from coal gradually decreased from 38.27% to 14.70% and that from natural gas increased from 0.53% to 10.22%. In Nanjing, the carbon emissions from oil decreased from 64.18% to 52.02% during 2000–2020, while the carbon emissions from coal and natural gas gradually increased. Ningbo’s carbon emissions from oil consumption decreased from 65.55% to 52.82% from 2000 to 2020, with those from coal and natural gas slightly increasing from 34.45% to 44.43% and from 0% to 2.75%, respectively. In Hangzhou, the main carbon source from 2000 to 2015 was coal, while in 2020, oil became the dominant carbon source. As for Zhoushan, the main carbon source constantly changed in coal and oil products from 2000 to 2020. Overall, during 2000–2020, coal and oil remained the primary energy sources in most cities, though there was a gradual increase in the use of natural gas.
3.3. Decoupling between Economic Growth and ERCEs
The status of economic growth decoupling from ERCEs in 16 cities is shown in Figure 5. From 2000 to 2020, only the economic growth in Zhoushan showed an expansive negative decoupling with ERCEs, while that in the other 15 cities showed a weak decoupling trend. During 2000–2005, the economic growth of cities was closely linked to ERCEs. Six cities including Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Taizhou (in Jiangsu), Huzhou, and Shaoxing showed expansive coupling, Jiaxing presented a state of expansive negative decoupling, while the other nine cities showed weak decoupling. From 2005 to 2010, the coupling was gradually weakened between ERCEs and economic growth. Only Taizhou (in Jiangsu) remained in a state of expansive coupling, while 14 cities showed a state of weak decoupling. During 2010–2015, the economic growth in Yangzhou, Hangzhou, Ningbo, and Taizhou (in Zhejiang) showed a strong decoupling relationship with ERCEs, but the four cities showed weak decoupling during 2015–2020, which indicated that the impact of economic growth on ERCEs gradually reduced. Shanghai, Nantong and Zhenjiang achieved strong decoupling from 2005 to 2020, indicating that they struck a balance, achieving a win–win scenario where economic growth was accompanied by a reduction in ERCEs. However, since 2005, the state between ERCEs and economic growth has turned from weak decoupling to expansive negative decoupling in Zhoushan.
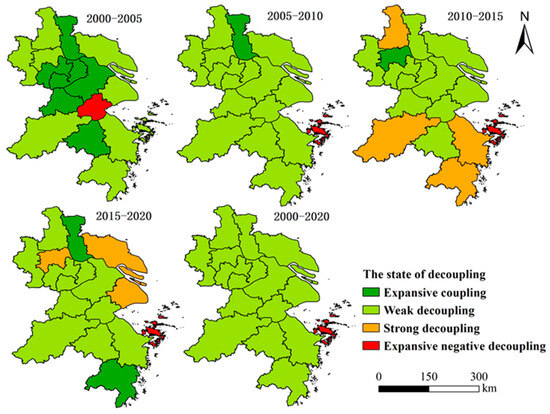
Figure 5.
Spatial pattern of the decoupling elasticity index during 2000–2020.
In terms of the changes in the decoupling elastic coefficient, it decreased obviously from 2000 to 2020 in all of the cities, except Zhoushan and Taizhou (in Jiangsu), showing that the link between economic growth and ERCEs weakened. Among them, the decoupling elastic coefficients of Shanghai, Nanjing, Suzhou, and Nantong continued to decline during 2000–2020, and the coupling between economic growth and ERCEs gradually weakened. The decoupling elastic coefficients of nine cities, including Wuxi, Changzhou, Yangzhou, Taizhou (in Jiangsu), Hangzhou, Ningbo, Jiaxing, Huzhou, and Shaoxing, showed a trend of declining first and then increasing. The decoupling elastic coefficients of Zhenjiang and Taizhou (in Zhejiang) continued to fluctuate, while the decoupling elastic coefficient of Zhoushan continued to rise, showing that economic growth gradually coupled with ERCEs in Zhoushan.
3.4. Influencing Factors of ERCEs
Figure 6 shows that economic growth was the leading positive driver of ERCEs for the entire study area from 2000 to 2020. Its contribution rate showed an upward trend, peaking at 493.27% between 2010 and 2015. Population size also contributed positively to the rise in ERCEs, but its contribution rate was only 10–20% of that of economic growth. As for energy intensity, it was a negative driver of ERCEs. Its negative impact gradually increased from 2000 to 2015, and its maximum contribution rate appeared during 2010–2015 at −449.13%. Comparatively speaking, energy structure had the weakest effect on ERCEs. It mainly played a negative driving role from 2000 to 2020, but from 2005 to 2020, the energy structure showed a positive contribution of 2.03%.
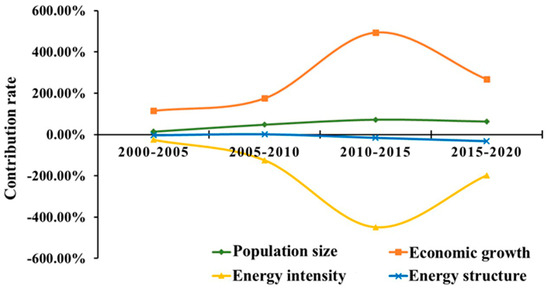
Figure 6.
Dynamics of the contribution rates of ERCE drivers from 2000 to 2020.
Comparing the driving factors of ERCEs in each city, economic growth was a leading one (Figure 7). The ERCEs in Nanjing and Shanghai were most severely affected by economic growth, with increases of over 200 million tons of ERCEs. And its impact in Huzhou, Jiaxing, Yangzhou, Taizhou (in Zhejiang), Shaoxing, and Taizhou (in Jiangsu) was relatively weak, resulting in an increase in ERCEs of less than 40%. Population size played weak negative roles in Taizhou (in Jiangsu) and Yangzhou, reducing ERCEs by 1.07 million tons and 0.10 million tons, respectively, but it had a positive impact in the other 14 cities. The largest contribution rates of population size were in Shanghai and Suzhou, increasing ERCEs by 61.83 million tons and 49.15 million tons, respectively. Energy intensity resulted in 42.41 million tons of ERCEs in Zhoushan, with a contribution rate of 43.90%; however, it had a negative effect on the other 15 cities. Shanghai and Nanjing were mostly influenced by energy intensity, which helped reduce 198.33 million tons and 173.56 million tons of ERCEs, respectively. As for energy structure, it was a positive driver in Nantong, Taizhou (in Jiangsu), Nanjing, and Ningbo, while it had a negative effect on the other 12 cities. Among them, the energy structure of Shanghai had the largest negative impact on ERCEs, reducing carbon emissions by 15.22 million tons. The positive effect on Ningbo was the greatest, with ERCEs increasing by 5.74 million tons. Overall, economic growth and population size mainly played a positive role, whereas energy intensity and structure mainly helped to reduce the ERCEs in the YRD.
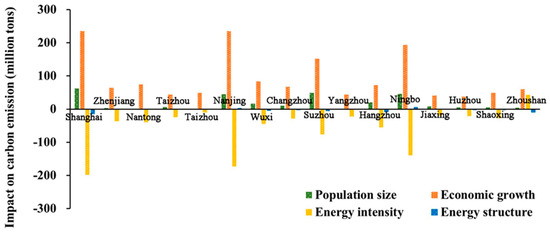
Figure 7.
Decomposition of drivers of ERCEs from 2000 to 2020.
4. Discussion
4.1. A Win–Win Situation between ERCE Reduction and Economic Growth
Cities in the YRD have achieved remarkable economic growth, which has also positioned the region as a major carbon emission hotspot in China. The decoupling analysis conducted in this study reveals that economic growth has decoupled from ERCEs in most cities, except Zhoushan and Taizhou (in Jiangsu). Notably, Shanghai, Nantong, and Zhenjiang achieved strong decoupling in 2020, suggesting that their ERCEs are no longer directly tied to economic growth. It is worth mentioning that during the time period, COVID-19 impacted the entire world in 2019 and lasted a few years, which may have influenced our results in 2020. On the one hand, COVID-19 may have reduced the amount of energy-related carbon emissions in 2020, as it influenced transportation for residents and production in factories [50]. On the other hand, COVID-19 may have affected economic growth, thus influencing the decoupling status between ERCEs and economic growth. However, during 2000–2020, a status from coupling to decoupling occurred in many cities; thus, a win–win scenario has been achieved between economic growth and ERCE reduction in the YRD.
The proportion changes of different energy sources also proved this win–win situation. Cities in the YRD are pursuing a low-carbon economy through energy transition [31]. This paper emphasizes that during the period from 2000 to 2020, coal and oil were the primary energy sources utilized in the study area, exhibiting a trend of gradual decline in their proportions, while most cities saw increasing consumption of natural gas. Notably, natural gas reduces greenhouse gas emissions by approximately one-third compared to oil and more than half compared to coal; thus, its increasing consumption aids in reducing ERCEs. The analysis of influencing factors further revealed that both energy intensity and structure help reduce ERCEs in the YRD, and their contribution rates increased during 2000–2020. In particular, the contribution rate of energy intensity reached −449.13% during 2010–2015, nearly matching the contribution rate of economic growth (493.27%). While the consumption of sustainable clean energy was not included due to data limitations, the energy transition process, encompassing reductions in energy intensity and optimizations in energy structure, contributed to the achievement of a win–win situation in the YRD.
4.2. Policy Implications for Carbon Reduction
Mitigating global warming necessitates an urgent reduction in carbon emissions. The cities in the YRD have exhibited notable disparities in their decoupling status and drivers of their ERCEs across various time periods. In light of this comprehensive analysis, tailored proposals have been formulated to facilitate carbon emission reduction efforts in diverse cities across the YRD.
Regarding economic growth in the YRD, while it has gradually decoupled from ERCEs, it remains a dominant driver in the region. To further promote a low-carbon economy in YRD cities, especially Zhoushan and Taizhou (Jiangsu), industrial upgrading and structural optimization are crucial. On the one hand, there should be a focus on fostering high-tech industries and service sectors, such as the IT industry and ecotourism. On the other hand, local governments must expedite industrial innovation and optimize the geographical layout of regional pillar industries and strategic sectors to foster a greener and more sustainable economic development model.
As for energy intensity and structure, they functioned as negative factors in the majority of cities in the YRD. Despite the fact that coal remained the primary carbon source in most YRD cities, there was a gradual increase in the rate of natural gas utilization in some areas. Shanghai’s government, for instance, has introduced measures to control energy consumption in terms of both quantity and intensity, with a focus on enhancing energy structure and emission reductions in key sectors like electricity, steel, and chemicals [51]. Other cities have also formulated strategies to promote energy structural improvements and reduce consumption [52]. Moving forward, Zhoushan specifically should address the reduction of energy intensity, as it is the only city where energy intensity currently has a positive effect. Conversely, cities like Nantong, Taizhou (Jiangsu), Nanjing, and Ningbo, where energy structure currently contributes positively, should continue to formulate policies aimed at optimizing their energy mix. Across the board, all cities in the YRD should prioritize policies that encourage the adoption of clean energy sources, thereby strengthening their energy transition efforts.
Population size was found to contribute to an increase in ERCEs in most cities, except Yangzhou and Taizhou (in Jiangsu). The YRD, boasting a high-level economy and numerous job opportunities, has attracted a significant influx of migrants in recent years. Shanghai, for instance, has set a long-term target of maintaining its permanent population below 25 million to control population growth. However, in other YRD cities, policies aimed at accelerating economic growth have often entailed attracting outsiders, particularly high-quality talent [53]. This approach could potentially exacerbate carbon emissions and lead to various environmental issues. Therefore, it is crucial for YRD cities to scientifically manage population size and migration flows to ensure sustainable development.
Moreover, since the implementation of the national strategy of integrated development of the YRD, local governments have indeed put forth significant efforts to promote integration across various aspects, including transportation and trade [54,55]. The recent implementation of the Implementation Plan for Carbon Peaking in the YRD Eco-Green Integrated Development Demonstration Zone further underscores the importance of cooperation and collaboration between cities in the region. This plan aims to achieve carbon-peaking goals through the joint efforts of all cities in the YRD. In this context, cities need to work closely with each other, formulate targeted carbon emission reduction policies, and develop an integrated approach to achieving the “Double Carbon” goal through win–win cooperation.
4.3. Limitations and Prospects
Due to limitations in data availability, earlier investigations predominantly concentrated on analyzing ERCEs at the national level [13] and provincial levels [14,15], thereby lacking guidance for policymaking in smaller-scale regions. In our study, we delved into the spatio-temporal dynamics of ERCEs and their decoupling from economic growth across 16 cities in the YRD. Our result was consistent with that of Shan et al. [23], which can help in shaping strategies for a win–win situation at the city level. Nonetheless, while Shan et al. [23] merely focused on ERCE evaluation, our study extended further to explore its underlying drivers. Moreover, in previous explorations of influencing factors, most studies overlook the quantitative analysis of their respective contribution rates. This oversight poses challenges in developing effective policy recommendations. Our study addresses this gap, and our insights provide scientific support for carbon reduction initiatives in the YRD.
However, several limitations need to be acknowledged. Firstly, owing to data availability constraints, only a select few commonly used energy sources were considered for ERCE estimation, potentially leading to an underestimation of the overall emissions. Future studies should consider a wider range of energy types to provide a more comprehensive reflection of ERCE dynamics. Secondly, the factors influencing ERCEs were broadly categorized into four aspects, and their contribution rates were calculated accordingly. However, the underlying mechanisms driving ERCEs are intricate and require a more systematic examination, especially from the perspectives of specific industries like manufacturing and transportation [52,56]. Econometric methods can be further applied to reveal the influencing mechanism of carbon emissions quantitatively. Meanwhile, we solely explored the influencing factors of ERCEs, neglecting the potential reasons for the different levels of relationships between the dynamics of ERCEs and the rates of economic growth. In future studies, they should be explored to help low-carbon economy development. Lastly, apart from carbon emissions, exploring carbon sinks is also crucial to achieving the “Dual Carbon” goal through a balanced carbon budget perspective. This area represents a promising direction for future research.
5. Conclusions
Carbon emission reduction along with economic growth has become a great challenge for Chinese cities against the background of China’s “Double Carbon” goal. Exploring their decoupling status and influencing factors is of great significance in guiding policies for carbon reduction. In this study, including 16 cities in the YRD as the study area, we evaluated ERCEs and their decoupling with economic growth using the Tapio method and explored the contribution rate of four drivers by using the LMDI method.
Our result showed that during 2000–2020, the total ERCEs increased more than three times, from 413.40 million tons to 1265.86 million tons in the YRD. Spatially, coastal economically developed cities owned significantly higher carbon emissions than those internal cities. The energy structure was continuously improved in the YRD, with the consumption of natural gas gradually increasing from 0.15% to 5.96% from 2000 to 2020. Except for Zhoushan and Taizhou (in Jiangsu), the other 14 cities showed a decoupling relationship between ERCEs and economic growth from 2000 to 2020. The change in energy consumption and decoupling status in most cities both indicated a win–win situation between economic growth and ERCE reduction. As for influencing factors, economic growth was always the key positive factor for ERCEs, while energy structure and intensity played negative roles. Finally, we put forward carbon reduction proposals for achieving the “Double Carbon” goal in the YRD.
Our city-level study addresses a crucial gap, examining ERCE dynamics in 16 YRD cities and quantifying the contribution rate of drivers. This nuanced understanding reveals specific emission drivers and regional differences, informing tailored carbon reduction strategies. Our research bridges the gap between large-scale analyses and policy implementation, contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.H. and X.L.; methodology, Y.H. and X.L.; software, X.L.; validation, J.G., Z.Z., Q.Z. and X.N.; formal analysis, J.G., Z.Z., Q.Z. and X.N.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.H. and X.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. and X.L.; visualization, X.L., J.G. and X.N.; supervision, Y.H.; funding acquisition, Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42201102).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study are available from the following resources in the public domain: energy consumption and socio-economic data were obtained from the Statistical Yearbook of Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Shanghai, China Energy Statistical Yearbook; population data and GDP data were obtained from the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center https://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 1 September 2023); and administrative boundary data were obtained from the National Geographic Information Public Service Platform https://www.tianditu.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 September 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change; Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Peng, Y. Energy-related carbon emissions and structural emissions reduction of China’s construction industry: The perspective of input–output analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39515–39527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, J.; Davis, S.J.; Narloch, U.; Hallegatte, S. Climate constraints on the carbon intensity of economic growth. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, Z.; Dehbidi, N.K.; Tarazkar, M.H. Energy intensity, economic growth and environmental quality in populous Middle East countries. Energy 2022, 239, 122164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Da, Y. The decomposition of energy-related carbon emission and its decoupling with economic growth in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, M. A comparative study on decoupling relationship and influence factors between China’s regional economic development and industrial energy–related carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, R.; Sarwar, S.; Chen, W. The survey of economic growth, energy consumption and carbon emission. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, S.; Hessen, D.O.; Tian, H.; Obersteiner, M.; Chen, D. Drivers of change in China’s energy-related CO2 emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IEA. CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion; IEA: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, M.; Long, X.; Dauda, L.; Mensah, C.N. The impact of institutional quality on economic growth and carbon emissions: Evidence from Indonesia, South Korea and Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, T. Comparative and relational trajectory of economic growth and greenhouse gas emission: Coupled or decoupled? Energies 2020, 13, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireille, C.A.; Mouez, F.; Yassine, K. Carbon curse in developed countries. Energy Econ. 2020, 90, 104829. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, R.; Jiang, X.-T. Exploring the role of nuclear energy in the energy transition: A comparative perspective of the effects of coal, oil, natural gas, renewable energy, and nuclear power on economic growth and carbon emissions. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wu, H. Do carbon emissions and economic growth decouple in China? An empirical analysis based on provincial panel data. Energies 2019, 12, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Graus, W.; Worrell, E.; Huang, B. Estimating CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions at urban scales by DMSP/OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imagery: Methodological challenges and a case study for China. Energy 2014, 71, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazzino, C. Economic growth, CO2 emissions and energy use in Israel. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2015, 22, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen, M.; Schaeffer, R.; Karstensen, J.; Peters, G.P. Drivers of change in Brazil’s carbon dioxide emissions. Clim. Chang. 2013, 121, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Mo, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S. Achieving China’s energy and climate policy targets in 2030 under multiple uncertainties. Energy Econ. 2018, 70, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkley, C. Decoupled: Successful planning policies in countries that have reduced per capita greenhouse gas emissions with continued economic growth. Environ. Plan. C-Gov. Policy 2014, 32, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H. Examining the driving factors of energy related carbon emissions using the extended STIRPAT model based on IPAT identity in Xinjiang. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachan, N.; Foxon, T.; Fujino, J. Policy implications from the Low-Carbon Society (LCS) modelling project. Clim. Policy 2008, 8, S17–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Shan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Hubacek, K. Assessment to China’s recent emission pattern shifts. Earth’s Future 2021, 9, e2021EF002241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Hang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Guan, D.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Hubacek, K. City-level emission peak and drivers in China. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wu, Y.; Lou, Y.; Zeng, D.; Shuai, C.; Song, X. What drives the carbon emission in the Chinese cities?—A case of pilot low carbon city of Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Tian, L. How to advance China’s carbon emission peak? A comparative analysis of energy transition in China and the USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 71487–71501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, W. China’s energy transition pathway in a carbon neutral vision. Engineering 2022, 14, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xing, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ji, Y. Factors influencing carbon emissions from China’s electricity industry: Analysis using the combination of LMDI and K-means clustering. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 93, 106724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Shen, L.; Jiao, L.; Wu, Y.; Tan, Y. Identifying key impact factors on carbon emission: Evidences from panel and time-series data of 125 countries from 1990 to 2011. Appl. Energy 2017, 187, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.X.; Chen, X.Z.; Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, N.; Kuang, Y. China’s 19-year city-level carbon emissions of energy consumptions, driving forces and regionalized mitigation guidelines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzigeorgiou, E.; Polatidis, H.; Haralambopoulos, D. CO2 emissions, GDP and energy intensity: A multivariate cointegration and causality analysis for Greece, 1977–2007. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cai, W.; Ma, M.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Li, L.; Chen, X. Driving forces of China’s CO2 emissions from energy consumption based on Kaya-LMDI methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kong, Q. Analysis on the influencing factors of carbon emissions from energy consumption in China based on LMDI method. Nat. Hazards 2017, 88, 1691–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Guo, X.; Wu, K.; Wang, G. Driving effect analysis of energy-consumption carbon emissions in the Yangtze River Delta region. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Li, M.; Tan, T. How urban agglomeration improve the emission efficiency? A spatial econometric analysis of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, T.; Xie, X.; Huang, Z. Regional low carbon development pathways for the Yangtze River Delta region in China. Energy Policy 2021, 151, 112172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resource and Environment Science and Data Center. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- National Geographic Information Public Service Platform. Available online: https://www.tianditu.gov.cn (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- IPCC. IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. 2006. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/index.html (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Lai, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, Q. Decomposition analysis of PM2.5 emissions based on LMDI and Tapio decoupling model: Study of Hunan and Guangdong. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43443–43458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Wei, K.; Liu, J. Decoupling relationship between carbon emissions and economic development and prediction of carbon emissions in Henan Province: Based on Tapio method and STIRPAT model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 52679–52691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, M. Study on the decoupling relationship between CO2 emissions and economic development based on two-dimensional decoupling theory: A case between China and the United States. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Su, M. The effects of urbanization and industrialization on decoupling economic growth from carbon emission—A case study of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 51, 101758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Su, B. Using a new two-dimensional decoupling model to evaluate the decoupling state of global energy footprint. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, P. Towards a theory of decoupling: Degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, L.; Wang, Q. The impact of energy efficiency on carbon emissions: Evidence from the transportation sector in Chinese 30 provinces. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: A practical guide. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Jiang, T.; Li, S.; Nie, J. China’s carbon emissions structure and reduction potential on the supply-side and demand-side of energy: Under the background of four influencing factors. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, M.Y.; Lin, B. Decoupling and mitigation potential analysis of CO2 emissions from Pakistan’s transport sector. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Deng, K.; Dong, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y. Comprehensive assessment of land use carbon emissions of a coal resource-based city, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdell, C.A. Economic, social and political issues raised by the COVID-19 pandemic. Econ. Anal. Policy 2020, 68, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, G.; Cao, X.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, F. The strategy of energy-related carbon emission reduction in Shanghai. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Yang, Y. Energy carbon emission structure and reduction potential focused on the supply-side and demand-side. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Chang, M.; Xie, C. Macroeconomic determinants of high-tech migration in China: The case of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Cities 2020, 107, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Cai, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yang, J.; Qiao, L.; Yao, L.; Li, W. Application of mobile monitoring to study characteristics of air pollution in typical areas of the Yangtze River Delta Eco-Green Integration Demonstration Zone, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Sun, W. Study on the evolution, driving factors, and regional comparison of innovation patterns in the Yangtze River Delta. Land 2022, 11, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirikkaleli, D.; Oyebanji, M.O. Consumption-based carbon emissions, trade, and globalization: An empirical study of Bolivia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).