Highlights
What are the main findings?
- n-Octanol blends improve combustion and cut NOx, CO, HC, and smoke emissions.
- Higher blend ratios boost efficiency but slightly raise fuel consumption.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- Optimized blends lower emissions, supporting sustainability and air quality.
- Slight fuel use increase shows these blends are a viable diesel alternative.
Abstract
This study evaluates the viability of n-octanol as an alternative fuel in a direct-injection diesel engine, aiming to enhance sustainability and efficiency. Experiments fueled by different blends of n-octanol with pure diesel were conducted to analyze their impacts on engine performance and emissions. The methodology involved testing each blend in a single-cylinder engine, measuring engine performance parameters such as brake torque and brake power under full-load conditions across a range of engine speeds. Comparative assessments of performance and emission characteristics at a constant engine speed were also conducted with varying loads. The results indicated that while n-octanol blends consistently improved brake thermal efficiency, they also increased brake-specific fuel consumption due to the lower energy content of n-octanol. Consequently, while all n-octanol blends reduced nitrogen oxide emissions compared to pure diesel, they also significantly decreased carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and smoke opacity, presenting a comprehensive reduction in harmful emissions. However, the benefits came with complex trade-offs: notably, higher concentrations of n-octanol led to a relative increase in nitrogen oxide emissions as the n-octanol ratio increased. The study concludes that n-octanol significantly improves engine efficiency and reduces diesel dependence, but optimizing the blend ratio is crucial to balance performance improvements with comprehensive emission reductions.
1. Introduction
Diesel engines are fundamental to global transportation, powering industries from agriculture to logistics and substantially contributing to economic growth. However, they pose considerable environmental challenges, emitting particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and carbon dioxide (CO2), significantly contributing to local air pollution and global climate change. These emissions are linked to severe health implications, including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases [1,2]. The reliance on fossil fuels exacerbates these issues, as oil and gas extraction and refining processes cause substantial ecological damage, including air and water pollution and soil contamination [3].
In response to these challenges, the European Union has been enforcing increasingly stringent emission standards to reduce the harmful gases emitted from vehicles. The evolution of Euro standards represents a clear trend toward stricter emission limits and broader pollutant coverage, as shown in Table 1 for heavy-duty diesel engines. The gradual strengthening of these standards demonstrates the EU’s commitment to reducing vehicle emissions and mitigating their environmental impact. Future regulations are expected to lower allowable emission levels and may include additional pollutants or parameters to address emerging environmental and health concerns.

Table 1.
EU emission standards for heavy-duty CI (diesel) engines [4,5].
This regulatory pressure has accelerated the development of cleaner and more efficient diesel engine technologies [6,7] and also the exploration of alternative fuels to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate environmental impacts. Advances in hybrid technologies, including high compression ratios and two-stage turbochargers with intercoolers, have significantly enhanced fuel efficiency [8]. Additionally, after-treatment systems such as diesel particulate filters (DPFs), diesel oxidation catalysts, and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) have been rigorously studied to decrease atmospheric pollutants [9,10,11]. Innovations in thermal management techniques, such as insulation methods to reduce heat loss, electrically heated catalysts to improve component light-off times, and phase-change materials to stabilize temperature fluctuations, have been crucial in enhancing the efficiency of these technologies [12].
Recent advances in exhaust gas after-treatment technology have demonstrated that injecting water, alcohol, or hydrogen into the exhaust pipe can effectively burn residual exhaust gases and reduce harmful emissions. For instance, injecting water into the exhaust pipe can reduce NOx emissions by lowering combustion temperatures and promoting the conversion of NOx to nitrogen and water vapor. Additionally, water injection helps reduce PM emissions by enhancing the breakdown of soot particles [13].
Moreover, ethanol–water mixtures have proven effective in reducing NOx emissions, even at low temperatures when conventional SCR systems are less efficient [14]. Similarly, butanol significantly boosts NOx reduction when used in HC-SCR, acting as a reductant and promoter. Its high reactivity, polarity, and diffusivity improve catalytic performance, especially at low and medium temperatures [15]. In addition, hydrogen, when used with an Ag/Al2O3 catalyst, markedly enhances NOx removal by promoting the partial oxidation of hydrocarbons to form surface intermediates that facilitate SCR. However, the effectiveness of hydrogen varies with the type of catalyst used, showing no positive effect with Pt-based catalysts [16].
Ongoing research into alternative fuel sources for diesel engines continues to be driven by the need to meet stringent environmental standards. One notable effort involves using biodiesel from natural oils and fats, which provides a renewable and less polluting alternative to conventional diesel [17,18]. In addition, synthetic fuels such as dimethyl ether are gaining attention for their potential utility in diesel engines due to their high cetane numbers and oxygen content, which facilitate cleaner combustion processes and considerably lower emissions of soot and NOx [19]. Moreover, these synthetic fuels are often derived from renewable energy sources like wind power, solar energy, and hydropower, highlighting their role in promoting energy independence and providing sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels [20]. Incorporating hydrogen as a fuel supplement in diesel engines also shows the potential to significantly reduce emissions when it is adequately blended with diesel [21,22]. These innovative fuel options emphasize the varied approaches being explored to achieve cleaner combustion and a reduced environmental footprint in diesel engine operations.
Similarly, research into using alcohol fuels and hydrogen in gasoline engines reveals significant potential for reducing emissions and improving efficiency. When added to gasoline, ethanol reduces carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbon (HC) emissions due to its high oxygen content, which enhances combustion. Ethanol/gasoline blends promote complete and efficient combustion, particularly under specific operational conditions, effectively reducing exhaust emissions in spark-ignition engines, especially during the cold-start phase and across various engine loads and speeds [23].
Lower-alcohol fuels, such as methanol and ethanol, are promising alternative fuels for internal combustion engines due to their high-octane ratings, which enhance engine performance and efficiency [24]. Ethanol can be blended with gasoline in various proportions without significant engine modifications, offering flexibility. However, the challenges associated with their use include lower energy densities compared to gasoline, their hygroscopic nature leading to water absorption and potential phase separation, and the risk of corrosion in fuel systems [25,26]. Moreover, methanol’s toxicity requires careful handling [27,28]. Despite these obstacles, the potential environmental benefits drive ongoing research and development, emphasizing the role of these technologies in reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and strengthening energy autonomy [29].
Research also indicates that incorporating even small amounts of hydrogen into gasoline engines can enhance combustion efficiency, increase engine torque, and lower emissions [30]. Hydrogen’s high diffusivity and flame speed improve combustion, leading to more efficient fuel usage and lower emissions. Furthermore, combining exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) with hydrogen supplementation has been shown to enhance performance by increasing EGR rates, effectively reducing NOx emissions without compromising engine efficiency [31]. These initiatives highlight the varied strategies for achieving cleaner combustion and reducing the environmental impact of engine operations, underscoring the need for solutions tailored to specific engine types.
As part of the broader quest for sustainability, the historical development of alcohol fuels like methanol and ethanol has been a crucial aspect of the journey toward sustainable energy solutions. These fuels were first explored seriously during the oil crises of the 1970s, when the need to reduce dependence on finite petroleum reserves became apparent. Methanol and ethanol, derived from biomass and fermentable crops, emerged as viable alternatives due to their renewable nature and potential for cleaner combustion [32,33]. The late 20th century saw accelerated research into these biofuels, spurred by advancements in production technologies that enhanced both their economic viability and environmental benefits [34,35].
In this context, it is also essential to acknowledge the historical use of alcohol fuels in multi-fuel military vehicles. Previous studies have shown that using methanol fuel in a rotary stratified charge engine allows for smooth operation, despite prolonged fuel injection periods due to nozzle sizing requirements for conventional fuel [36]. Additionally, the use of ethanol fuel in two-stroke outboard engines has demonstrated high torque characteristics at high speeds and faster combustion than other fuels [37]. These examples show the versatility of alcohol fuels in military applications, improving operational flexibility and reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels.
Building upon foundational research into methanol and ethanol, researchers now focus on higher alcohols like n-butanol, n-pentanol, and n-octanol as more effective alternatives. Recent studies highlight n-butanol’s potential in diesel blends, which enhance fuel efficiency and significantly reduce emissions such as soot, although they present challenges like increased NOx emissions [38]. These blends also lower polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon emissions, improving environmental compatibility [39]. Adding alcohols such as butanol and pentanol in high concentrations can lower the cold filter plugging point of the fuel, thereby enhancing performance in cold environments and reducing fuel gelation and filter clogging [40]. Higher alcohols offer greater energy content and cetane numbers, enhancing compatibility with diesel engines and improving performance. Moreover, they address issues like phase separation and volatility, thanks to their increased molecular weights and reduced volatility [41,42,43].
Moreover, n-octanol blends notably decrease PM and NOx emissions, enhancing brake thermal efficiency (BTE) and reducing fuel consumption [44,45]. The oxygen content of these alcohols promotes more complete combustion, which is crucial for minimizing smoke and particulate emissions. Additionally, their seamless blending with diesel offers a practical transition strategy toward more sustainable fuel systems, requiring minimal modifications to existing engine designs or fuel distribution infrastructures [46,47].
However, integrating higher alcohols into diesel fuel presents several challenges despite their benefits. Previous studies underscore the need for further research to optimize combustion processes and address concerns related to the production costs and availability of raw materials [48,49]. While higher alcohols can mitigate emissions like PM and NOx, their use may increase other emissions, notably of aldehydes such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde. This increase largely depends on the type of higher alcohol employed and the specific combustion conditions, including temperature and engine operational parameters [50,51].
The use of various alcohols in diesel engines also presents issues due to their lower cetane numbers compared to conventional diesel fuel. This can lead to increased NOx emissions while reducing PM emissions when methanol or ethanol is added to the fuel. Addressing these issues requires the implementation of variable engine systems, such as adjustable compression ratios, precise fuel injection technology, and variable valve timing (VVT). Changing the compression ratio can significantly impact engine performance and exhaust emissions, especially when using fuels with different cetane numbers. Additionally, applying VVT and variable valve actuation systems optimizes the air–fuel mixture, improving combustion efficiency and effectively balancing PM emission reduction and NOx emission control [52]. Furthermore, the tribological optimization of engine parts can reduce mechanical losses, thereby lowering fuel consumption and decreasing exhaust gas emissions. This approach enhances the durability and efficiency of engine components, contributing to overall emission reduction [53].
Similarly, the addition of n-octanol to diesel fuel affects the combustion characteristics, particularly the peak in-cylinder pressure, which can lead to increased engine noise and vibration. Studies show that n-octanol/diesel blends result in higher peak pressures and heat release rates compared to pure diesel, due to longer ignition delays and enhanced premixed combustion, which is facilitated by n-octanol’s lower cetane number and higher oxygen content [54,55]. For instance, a 30% n-octanol blend in diesel produced higher in-cylinder pressure peaks and heat release rates, especially at advanced injection timings. This suggests that n-octanol can increase combustion intensity and, potentially, noise and vibration. However, the increased oxygen content and improved combustion efficiency of n-octanol blends can contribute to more complete combustion and smoother engine operation, potentially offsetting some of the increased noise and vibration.
To address these complexities comprehensively, a thorough evaluation of alternative fuels through various experimental cases is required, due to the diversity of diesel engine designs and operating conditions. By systematically studying the effects of n-octanol addition across various engine loads and speeds, this research provides valuable insights into the practical implications of using higher alcohols in real-world scenarios. Furthermore, this study contributes to the body of knowledge by offering a comparative analysis of n-octanol’s effects on diesel engines, filling the gaps left by previous research. It highlights the potential of n-octanol as a sustainable alternative fuel that is capable of significantly reducing harmful emissions while maintaining or enhancing engine performance. It aligns with global efforts to reduce GHG emissions and improve air quality. The findings of this research could inform future fuel formulation and engine design, aiding in the transition toward more environmentally friendly and efficient transportation solutions. The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 describes the experimental setup and methodology used in this study. Section 3 presents the results and discusses the effects of n-octanol/diesel blends on engine performance and emission characteristics. Section 4 concludes the paper by summarizing the key findings and suggesting directions for future research.
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Research Engine and Equipment
This study conducted a series of combustion experiments using an MT502E single-cylinder engine test bed (ESSOM, Bangkok, Thailand) to explore the impact of various fuel blends on engine performance and exhaust gas characteristics. The diesel engine was naturally aspirated air-cooled, with a swept volume of 298.6 cm3. The engine was connected to an air-cooled eddy current dynamometer to apply load, with exhaust gas temperature, brake torque, and air and fuel flow rate sensors linked to an instrument panel. The throttle valve opening and the load level were controlled via a computer connected to this panel. Fuel was directly injected into the combustion chamber using a mechanical injector equipped with a hole-type nozzle, and the engine operated at a compression ratio of 21:1. Detailed specifications of the test engine are presented in Table 2, while Figure 1 illustrates the schematic of the experimental setup.

Table 2.
Specifications of the test engine.
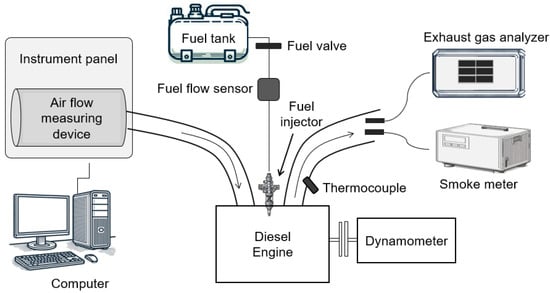
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the experimental apparatus.
The MT502E software can display real-time experimental data both graphically and numerically on the screen. Its user-friendly interface allows for easy control, data collection, and the presentation of test results. The experimental data are collected and recorded in tables, which can also be represented in graph format. Both axes (i.e., x and y) are adjustable, facilitating clear and precise data interpretation. Based on the collected data, performance and combustion characteristics such as brake power, BTE, and brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC) were calculated.
For measuring the major post-combustion exhaust gases, a QRO-402 gas analyzer (QroTech, Bucheon, Republic of Korea) was utilized. The QRO-402 employs a non-dispersive infrared method for measuring CO and HC, along with an electrochemical cell for measuring NOx. The analyzer operates with a resolution of 0.01% for CO and 1 ppm for HC and NOx. The sample flow rate is maintained at between 4 and 6 L/min to ensure accurate measurements.
The smoke opacity was measured using an OPA-102 smoke meter (QroTech, Bucheon, Republic of Korea) based on the light extinction method, providing smoke opacity as a percentage. The machine’s resolution is 0.1%, and the response time is 0.5 s. A warm-up period of 3 to 6 min is required before measurement. The OPA-102 provides real-time data and is designed to handle exhaust temperatures up to 300 °C. However, it does not provide detailed information on PM emissions and filtered smoke number. Table 3 details the exhaust gas components’ concentration measurement range, accuracy, and resolution.

Table 3.
Technical specifications of the gas analyzer and smoke meter.
2.2. Unit Conversion for Exhaust Gases
To ensure consistent and standardized comparative analysis of exhaust gas concentrations, the units of all measured concentrations were converted to g/kWh, according to Equations (1)–(3) for heavy-duty vehicles [56].
The measured smoke opacity was converted to smoke mass fraction using Equation (4) [57], and was then converted to g/kWh using the exhaust gas mass flow rate and brake power:
where Y, Sp, and w″ denote the smoke mass fraction, a specific optical cross-section of smoke, and the mass of filtered gas per unit of filter area, respectively. The terms B and C are empirical constants, as specified by Equation (5).
2.3. Tested Fuels
To analyze and compare the combustion and emission characteristics of n-octanol/diesel blends, commercial diesel was mixed with n-octanol in volume ratios of 10%, 30%, and 50%, respectively, named D90O10, D70O30, and D50O50, with pure diesel designated as D100. The n-octanol used in the experiments was supplied by the Daejung Chemicals & Metals Co., Ltd. (Siheung-si, Republic of Korea), and had a purity of 99–100%. Phase separation was not observed, even 48 h after mixing, and pre-mixing was performed before each experiment to ensure the homogeneity of the fuel blends. According to prior studies [42,43], the phase separation commonly observed in blends with lower alcohols is not expected to impact the experimental outcomes significantly. Table 4 presents the physicochemical properties of the diesel and n-octanol used in the experiments, highlighting differences in the lower heating value, oxygen content, and cetane number.

Table 4.
Fuel properties.
2.4. Test Conditions and Procedure
Performance comparisons of the different fuel blends were conducted under full-load conditions using variable speed tests; the emission characteristics were assessed at a constant engine speed of 1700 rpm with varying brake torques of 6, 8, 10, and 12 Nm. The full-load experiments were carried out from 1400 to 2500 rpm in increments of 100 rpm. Before the experiments, the engine was idling for at least 15 min using D100 to ensure it reached normal operating temperature. Before changing fuels, all remaining fuel was drained from the tank, which was then refilled with D100, and the engine was operated for about three minutes to purge any residual mixed fuel from the fuel system. Engine load and speed were gradually adjusted to stabilize the engine under the new conditions, after which the experimental data were collected. Each experimental condition was repeated three times to establish average values for comparative analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Variable-Speed Tests at Full Load
3.1.1. Brake Torque
The measured brake torque values across various engine speeds for different fuel blends clearly show an increasing trend in torque with engine speed, as depicted in Figure 2. For pure diesel (D100), the torque values rise from 12.02 Nm at 1409 rpm to 14.04 Nm at 2508 rpm. This upward trend is consistent across all fuel blends, although the rates of torque increase vary slightly. D90O10 starts at 12.08 Nm at 1406 rpm and reaches 14.00 Nm by 2503 rpm. D70O30 begins at 11.95 Nm at 1401 rpm and achieves 13.98 Nm by 2509 rpm. Meanwhile, D50O50 starts from 11.75 Nm at 1404 rpm and climbs to 13.90 Nm by 2504 rpm. The rise in torque with increasing engine speed suggests enhanced engine performance, which is likely due to more efficient fuel combustion as the engine speed escalates.
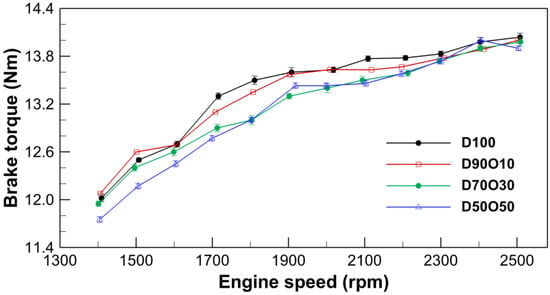
Figure 2.
Comparison of brake torque with engine speed for the test fuels.
Analyzing the relationship between the n-octanol blend ratio and brake torque reveals a pattern whereby an increase in the n-octanol ratio generally correlates with a slight decrease in brake torque. D100 exhibits the highest torque across all engine speeds, with a gradual decline in maximum torque as the n-octanol ratio increases from 10% in D90O10 to 50% in D50O50. This reduction in brake torque with increased n-octanol content can be attributed to several factors inherent to the properties of n-octanol as a fuel component. N-octanol has a lower energy density than diesel, which may result in a lower calorific value per unit of fuel volume. Additionally, the combustion characteristics of n-octanol, including its ignition quality and flame speed, might differ from those of diesel. Notably, n-octanol’s higher viscosity than diesel could be disadvantageous during atomization, evaporation, and the process of mixing with air, potentially affecting combustion and energy conversion efficiency.
3.1.2. Brake Power
Figure 3 indicates a clear trend that brake power increases with engine speed across all the fuel blends tested. For D100, brake power progresses from 1.77 kW at 1409 rpm to 3.69 kW at 2508 rpm. This increasing trend is consistent, albeit with variations in the rate of increase across different blends. D90O10 starts with a power of 1.78 kW at 1406 rpm and peaks at 3.68 kW at 2503 rpm. Similarly, D70O30 begins with 1.76 kW at 1401 rpm, rising to 3.67 kW at 2509 rpm, and D50O50 starts from 1.72 kW at 1404 rpm, increasing to 3.63 kW at 2504 rpm.
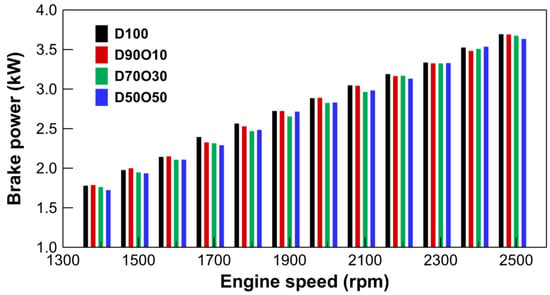
Figure 3.
Comparison of brake power with engine speed for test fuels.
Incorporating n-octanol into diesel has a nuanced impact on brake power output. As the n-octanol content in the fuel blend increases, there is a noticeable but slight variation in power output. Initially, fuel blends with lower n-octanol content, such as D90O10, exhibit brake power outputs that closely match or slightly exceed that of D100. However, the higher n-octanol ratios in D70O30 and D50O50 result in marginally lower power outputs at engine speeds equivalent to D100 and D90O10. This suggests that while n-octanol can be blended with diesel to maintain or slightly enhance power output at lower concentrations, higher concentrations may not proportionally improve or even slightly reduce the engine’s power output. The peak power output for D50O50 is slightly less than that of pure diesel and the lower n-octanol blends, suggesting diminishing returns at higher n-octanol concentrations. Despite this, n-octanol/diesel blends, even those with up to 50% n-octanol, still provide competitive performance for diesel engines. This is particularly significant from an environmental and sustainability perspective, as n-octanol can be derived from renewable sources, offering a pathway to reduce reliance on fossil diesel.
3.1.3. Brake Thermal Efficiency
Figure 4 illustrates a general trend of increasing BTE with engine speed across all fuel blends. For D100, BTE starts at 16.76% at 1409 rpm and peaks at 19.07% at 2207 rpm, before slightly dropping to 18.04% at 2508 rpm. This pattern of increase followed by a slight decrease is consistent across the blends, indicating optimal efficiency at mid-range speeds. The data reveal a nuanced interaction between n-octanol blend ratios and BTE. As the proportion of n-octanol in the fuel blend increases, there is a noticeable improvement in BTE, particularly at mid to high engine speeds.
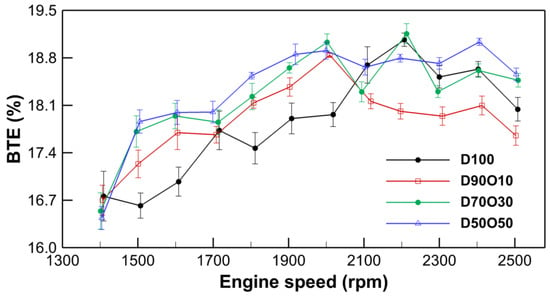
Figure 4.
Comparison of brake thermal efficiency with engine speed for the test fuels.
This improvement could be attributed to the oxygenated nature of n-octanol, which enhances combustion quality and improves thermal efficiency. The highest BTE values observed in D50O50 support the potential for significant efficiency gains with higher n-octanol content, aligning with the environmental goals of reducing fossil fuel usage and emissions. However, the slight decrease in BTE at the highest engine speeds across all blends indicates practical limits to efficiency gains, possibly due to fuel combustion dynamics and engine design constraints. This observation highlights the importance of optimizing engine and fuel blend configurations to maximize efficiency and performance.
3.1.4. Brake Specific Fuel Consumption
Across all fuel blends, BSFC exhibits a declining trend with increasing engine speed up to a certain point, beyond which the values either stabilize or slightly increase, as shown in Figure 5. For example, the BSFC for D100 decreases from 500.52 g/kWh at 1409 rpm to a minimum of 436.90 g/kWh at 2109 rpm, before increasing again to 462.19 g/kWh at 2508 rpm. This pattern suggests an optimal range of engine speeds for fuel efficiency that is consistent across the different fuel blends.
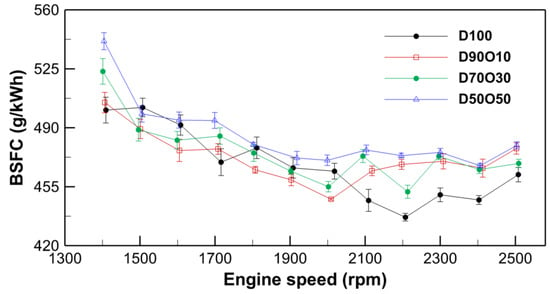
Figure 5.
Comparison of brake-specific fuel consumption with engine speed for the test fuels.
Adding n-octanol to diesel fuel generally results in a slight increase in BSFC, especially with higher n-octanol contents. For instance, D50O50 shows higher BSFC values across most engine speeds than other blends. Specifically, the BSFC for D50O50 starts at 541.44 g/kWh at 1404 rpm and varies across engine speeds, peaking at 479.57 g/kWh at 2504 rpm. The increase in BSFC with higher n-octanol content can be attributed to the lower energy content per unit mass of n-octanol compared to diesel, thus requiring more fuel to produce the same amount of power.
However, the minimal BSFC values for all blends indicate that there is an optimal engine speed range at which the efficiency differences between the blends are less pronounced. This suggests that while n-octanol blends may initially appear less efficient, they can achieve comparable levels of fuel efficiency to pure diesel under optimal operating conditions. The slight increase in BSFC at the highest engine speeds for all blends reflects a common characteristic of diesel engines, whereby fuel efficiency decreases as the engine operates further from its optimal speed range.
3.2. Fixed-Speed Tests at Part Load
3.2.1. Brake Thermal Efficiency
Figure 6 shows a clear trend of increasing BTE, with increasing brake mean effective pressure (BMEP) across all fuel blends. Specifically, for the pure diesel fuel (D100), BTE improves from 14.01% at 0.247 MPa to 17.73% at 0.485 MPa. This trend is consistent with the established understanding that higher engine loads (as indicated by higher BMEP) lead to more efficient fuel consumption and energy conversion within diesel engines, due to improved combustion efficiency and heat utilization.
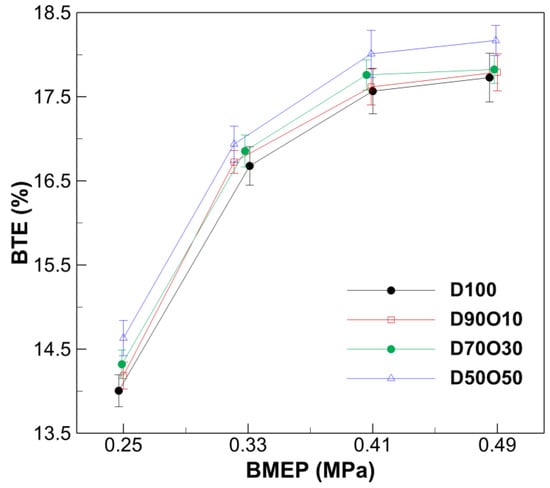
Figure 6.
Comparison of brake thermal efficiency with brake mean effective pressure at 1700 rpm.
The relationship between the n-octanol mixing ratio in the fuel and BTE reveals a clear pattern: as the proportion of n-octanol increases, there is a general trend of improved BTE across all levels of BMEP. Specifically, at the highest BMEP condition (approximately 0.49 MPa), the BTE values increase from 17.728% for D100 to 18.169% for D50O50. This trend suggests that fuel mixtures with higher n-octanol content are more thermally efficient under the tested engine-load conditions.
The observed improvement in BTE with increasing n-octanol content could be attributed to the physicochemical properties, which enhance combustion. N-octanol’s lower self-ignition temperature improves fuel ignition quality and efficiency. Its higher oxygen content also promotes more complete combustion, thus boosting thermal efficiency. As indicated in Table 5, a lower AFR reduces heat losses to the surrounding air, further enhancing combustion.

Table 5.
Air–fuel ratios at 1700 rpm for test fuels.
3.2.2. Brake-Specific Fuel Consumption
The evaluation of BSFC across different BMEP levels for various fuel mixtures provides crucial insights into the fuel efficiency of a diesel engine under part-load conditions. Figure 7 demonstrates a general trend of decreasing BSFC with increasing BMEP for all fuel mixtures. For D100, BSFC decreases from 594.53 g/kWh at a BMEP of 0.247 MPa to 469.68 g/kWh at a BMEP of 0.485 MPa. This decreasing trend in BSFC with higher BMEP levels indicates improved fuel efficiency as the engine operates under higher load conditions. The reduction in BSFC is attributed to the more effective conversion of fuel energy into work, a characteristic efficiency behavior of diesel engines as they move toward their optimal operating range.
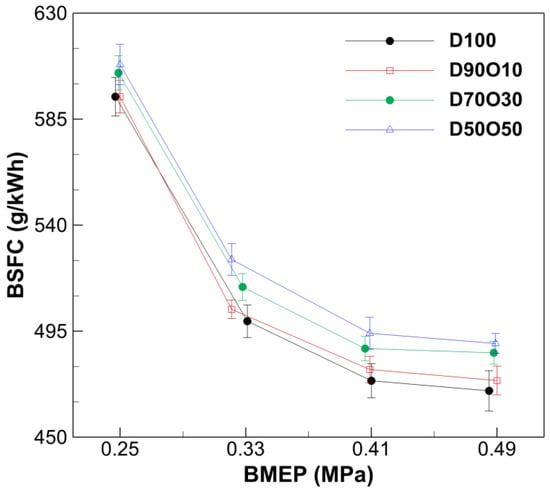
Figure 7.
Comparison of brake-specific fuel consumption with brake mean effective pressure at 1700 rpm.
Analyzing the relationship between the n-octanol mixing ratio in the fuel and BSFC reveals a nuanced interaction. At similar BMEP levels, introducing n-octanol initially results in a slight increase in BSFC for D90O10 compared to D100, indicating a marginal decrease in fuel efficiency. However, as the n-octanol content increases to 30% and 50% (D70O30 and D50O50), the BSFC values rise more significantly, reaching 485.84 g/kWh and 489.81 g/kWh at the highest BMEP level, respectively. This increase in BSFC with higher n-octanol content can be interpreted in the context of the physicochemical properties of n-octanol. While n-octanol may improve combustion efficiency through its oxygenation effects, these benefits appear to be offset by the lower energy content per unit volume of n-octanol compared to diesel. Consequently, higher n-octanol blends require more fuel (by mass) to produce the same energy output, leading to increased BSFC values.
The observed trends suggest that while n-octanol/diesel blends can enhance combustion efficiency and thermal performance, they do so at the cost of increased fuel consumption per unit of energy produced, particularly at higher n-octanol concentrations. This trade-off highlights the importance of optimizing the n-octanol/diesel ratio to balance the benefits of improved combustion and emissions characteristics with maintaining fuel efficiency.
3.2.3. NOx Emissions
Figure 8 illustrates a clear trend in which the concentration of NOx generally increases with rising BMEP across all fuel types, peaking before decreasing at the highest BMEP values tested. For example, in D100, NOx levels rise from 2.00 g/kWh at a BMEP of 0.247 MPa to a peak of 3.20 g/kWh at 0.410 MPa, then decrease slightly to 2.61 g/kWh at 0.485 MPa. This pattern aligns with the typical behavior of diesel engines, whereby increased combustion temperatures at higher engine loads lead to more thermal NOx formation. More energy is available to overcome the activation energy needed to break nitrogen and oxygen bonds.
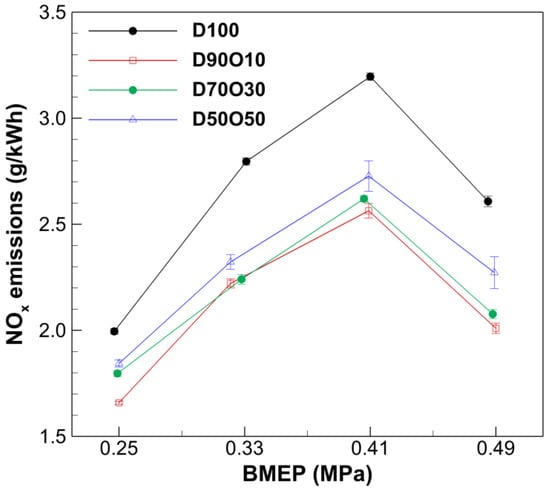
Figure 8.
Comparison of NOx emissions with brake mean effective pressure at 1700 rpm.
Introducing n-octanol into diesel significantly impacts NOx emissions, with a general trend of increasing NOx concentrations as the percentage of n-octanol increases. NOx emissions in diesel engines are primarily of thermal NOx, predominantly influenced by combustion temperature and oxygen concentration. The higher latent heat of vaporization of n-octanol compared to diesel fuel may reduce NOx emissions, owing to its cooling effect. However, oxygen in n-octanol can accelerate combustion, increasing in-cylinder temperatures and, consequently, NOx concentrations. Despite this, n-octanol/diesel blended fuels produce significantly lower NOx emissions than D100 across all experimental conditions, indicating that while n-octanol’s cooling effect is substantial, it is partially offset by NOx formation in post-flame gases. This finding is consistent with the results of several other researchers showing that NOx emissions are reduced even though thermal efficiency is improved by mixing n-octanol [55,58].
Additionally, at a BMEP of 0.41 MPa or less, the AFR exceeds the stoichiometric values of 14.8/14.4/13.9 for D90O10/D70O30/D50O50, creating a lean mixture that reduces local hot spots during combustion. Conversely, at a BMEP of 0.49 MPa, when the AFRs of 13.7/13.6/13.8 are below stoichiometric levels, NOx emissions decrease owing to the incomplete combustion caused by oxygen deficiency, resulting in lower NOx concentrations in the exhaust gas.
3.2.4. CO Emission
Figure 9 illustrates that CO concentration progressively increases with rising BMEP across all the tested fuel blends. This upward trend aligns with typical diesel engine behavior, whereby higher engine loads often facilitate richer combustion environments. Consequently, these conditions lead to more incomplete fuel combustion, substantially increasing CO emissions. For instance, with D100, the CO concentration escalates sharply from 1.80 g/kWh at a BMEP of 0.247 MPa to 40.60 g/kWh at 0.485 MPa, demonstrating a significant escalation as the engine load intensifies.
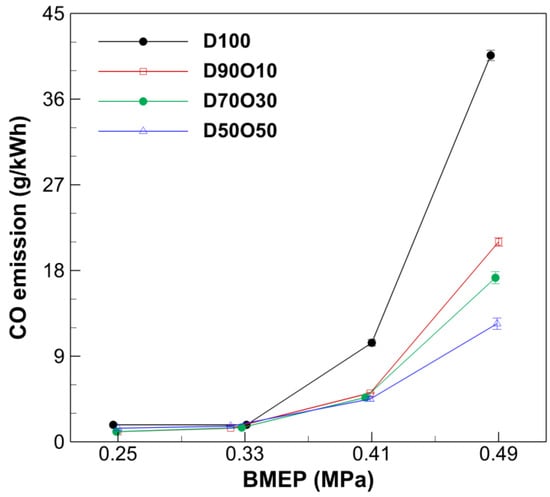
Figure 9.
Comparison of CO emissions with brake mean effective pressure at 1700 rpm.
The integration of n-octanol into diesel fuel markedly influences CO concentrations, predominantly exhibiting a reduction in CO levels as the percentage of n-octanol in the blend increases. For example, while CO emissions for D100 at the highest BMEP tested (0.485 MPa) reach 40.60 g/kWh, D50O50 at a slightly higher BMEP (0.489 MPa) demonstrates considerably lower emissions, measuring only 12.41 g/kWh. This reduction highlights n-octanol’s effectiveness in enhancing the combustion process. The genesis of CO emission is typically linked to the suppression of the fuel’s oxidation reaction due to a deficit in available air and the presence of low combustion temperatures, which are both indicative of incomplete combustion within diesel engines. In areas where the fuel mixture is vibrant, incomplete combustion is more prevalent, exacerbated by the local formation of rich mixtures. Additionally, the enhanced viscosity of n-octanol, relative to D100, could further complicate the fuel atomization and mixing processes, potentially expanding the presence of rich zones that contribute to incomplete combustion and subsequent CO emissions. This relationship underscores the complex interplay between fuel composition, engine operating conditions, and emission characteristics, demonstrating the potential of n-octanol to improve emission outcomes in modern diesel engines.
This finding aligns with the results from other studies, which have shown that increasing the n-octanol content in diesel blends results in lower CO emission due to enhanced combustion efficiency, which is facilitated by the higher oxygen content in n-octanol [54,55]. These consistent findings imply that n-octanol is a promising alternative fuel for reducing the environmental impact of diesel combustion.
3.2.5. HC Emissions
Various factors, including fuel properties, AFR, and the characteristics of air–fuel mixing, influence HC emissions. Additionally, flame quenching in the combustion chamber walls, particularly with high-pressure fuel injection systems, is a notable source of HC emissions. Figure 10 demonstrates an apparent increase in HC concentrations as the BMEP rises, which is consistent across all fuel blends. This indicates that higher engine loads create conditions that favor incomplete combustion, thus escalating HC emissions. For example, in D100, the HC levels surge from 0.0060 g/kWh at a BMEP of 0.247 MPa to 0.080 g/kWh at 0.485 MPa. This significant rise reflects the difficulties in achieving complete combustion at higher engine loads, a challenge that is prevalent in diesel engines owing to the necessity of having a rich fuel mixture under these conditions.
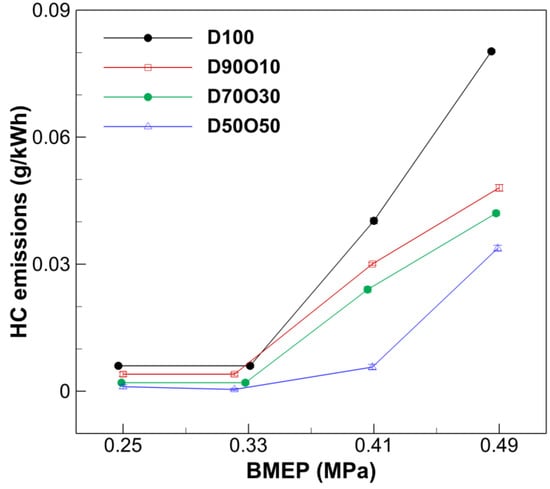
Figure 10.
Comparison of HC emissions with brake mean effective pressure at 1700 rpm.
Introducing n-octanol into diesel fuel notably impacts HC emissions, demonstrating an apparent mitigation effect. As the n-octanol content increases, a substantial decrease in HC emissions is observed. For instance, at a BMEP of 0.489 MPa, the HC emissions in D50O50 are markedly lower at 0.034 g/kWh, compared to 0.080 g/kWh in D100 at 0.485 MPa. This decrease is mainly due to the oxygenated nature of n-octanol, which significantly improves the combustion process. The inherent oxygen in the n-octanol molecule facilitates the more thorough combustion of hydrocarbons, thereby diminishing the emission of unburned or partially burned fuel particles. This effect underscores the role of fuel composition in enhancing combustion efficiency and reducing harmful emissions in diesel engines.
This finding aligns with the results from other studies, which have shown that increasing the n-octanol content in diesel blends results in lower HC emissions due to improved combustion efficiency, which is facilitated by the higher oxygen content in n-octanol [45]. Additionally, a higher n-octanol content leads to longer combustion duration, allowing for more complete fuel conversion [58]. These consistent results across different studies reinforce the conclusion that n-octanol is effective at reducing HC emissions in diesel engines.
3.2.6. Smoke Emissions
Smoke is a complex mixture of tiny solid particles, liquid droplets, and gases that is primarily produced from incomplete fuel combustion. The specific composition of smoke can vary with changes in the combustion environment, including fuel type, temperature, and the quality of air–fuel mixing. Figure 11 illustrates a distinct trend in which smoke emissions escalate with increasing BMEP values across all fuel blends, showing that higher engine loads often lead to richer combustion conditions and enhanced smoke production. For instance, in the case of D100, the smoke emissions rise markedly from 0.181 g/kWh at a BMEP of 0.247 MPa to 64.519 g/kWh at 0.485 MPa. This demonstrates the challenges of achieving efficient combustion at elevated loads due to incomplete fuel burning.
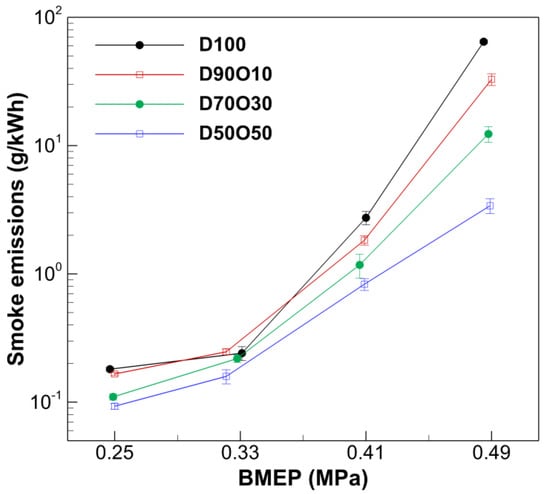
Figure 11.
Comparison of smoke emissions with brake mean effective pressure at 1700 rpm.
Adding n-octanol to diesel fuel significantly influences smoke emissions, showing a clear trend of decreased smoke emissions as the percentage of n-octanol increases. For instance, while D100 displays 64.519 g/kWh at the highest BMEP tested, D50O50 shows a markedly lowered value of 3.399 g/kWh at a similar BMEP of 0.489 MPa. The reduction in smoke emissions with n-octanol can be directly attributed to its oxygenated nature, which promotes the more complete combustion of hydrocarbons. This thorough burning effectively reduces the emission of unburned carbon particles, which are significant contributors to visible smoke. Furthermore, the oxygen in the n-octanol-enhanced fuel ensures that a more significant proportion of the carbon in the fuel is oxidized to CO2, thus significantly diminishing smoke formation.
In addition to optimizing the fuel mixture, incorporating an advanced after-treatment system such as a DPF can further reduce smoke emissions. Studies have shown that retrofitting diesel engines with DPFs can reduce the particle number (PN) by more than 95% [9]. This means that when the oxygenation properties of n-octanol are combined with the high efficiency of a DPF, smoke emissions can be reduced even further. This combination of fuel composition and after-treatment technology can substantially improve emissions control and enhance the overall environmental performance of diesel engines.
3.2.7. PM-NOx Trade-Off
In this study, direct PM measurements were not available. However, considering the strong correlation between soot and smoke opacity, as demonstrated in a previous study [59], smoke opacity can be used to indirectly assess PM emissions. As previously analyzed, adding n-octanol can reduce PM emissions, but it also affects NOx emissions. The PM-NOx trade-off is a well-known phenomenon in diesel engine research. Strategies to reduce PM emissions often lead to increased NOx emissions, due to higher combustion temperatures. Our findings show that n-octanol helps lower PM emissions, although it may also increase NOx emissions, depending on combustion conditions and engine operating parameters. Nevertheless, NOx emissions were significantly suppressed compared to pure diesel in all experimental conditions.
Several studies support our findings that n-octanol/diesel blends can reduce both PM and NOx emissions. For example, a 30% n-octanol blend under naturally aspirated conditions significantly reduces NOx and smoke opacity, due to n-octanol’s high oxygen content, which enhances combustion efficiency and reduces soot formation, even under EGR conditions [45,55]. Additionally, n-octanol’s higher latent heat of vaporization contributes to lower combustion temperatures, further reducing NOx emissions. This behavior, combined with a reduction in PN, demonstrates n-octanol’s capability to lower PM emissions.
Further studies using the response surface methodology have confirmed that optimizing blend composition, EGR, and injection timing can achieve simultaneous reductions in NOx and smoke emissions, while maintaining engine performance [60]. These findings indicate that the PM-NOx trade-off with n-octanol can be effectively managed through optimized fuel injection strategies and advanced after-treatment technologies. By leveraging the high oxygen content and favorable combustion properties of n-octanol, it is possible to enhance emissions performance, making n-octanol a viable and sustainable alternative fuel for diesel engines. Future research should explore these optimization techniques to fully realize the environmental benefits of n-octanol.
3.3. Economic and Environmental Evaluation
3.3.1. Economic Considerations
While the technical feasibility and environmental benefits of n-octanol/diesel blends have been demonstrated, it is equally important to consider the economic viability of n-octanol as an alternative fuel. The production costs of n-octanol, which are influenced by raw material availability, production processes, and scalability, are critical factors that determine its market price and competitiveness with existing fuels. Table 6 shows the price of n-octanol as USD 111.4 per gallon, which is significantly higher than for conventional fuels such as gasoline (USD 3.65 per gallon), diesel (USD 4.07 per gallon), and biodiesel (B20) (USD 3.94 per gallon). This substantial price difference highlights the economic challenges that n-octanol faces in terms of being a practical alternative fuel. However, it is essential to consider the potential long-term savings made from reduced emissions and improved engine efficiency, which can lower maintenance and operational costs over time.

Table 6.
National average retail fuel prices in April 2024 in the US [61,62].
3.3.2. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The production of conventional diesel involves the extraction, refining, and transportation of crude oil, processes that are energy-intensive and generate significant GHG emissions. In contrast, n-octanol can be produced from renewable sources such as lignocellulosic biomass. This bio-based production pathway not only reduces dependency on fossil fuels but also mitigates the carbon footprint associated with fuel production [63]. The production of n-octanol from biomass using advanced catalytic systems can achieve high yields with lower energy inputs, further enhancing its sustainability profile [64,65].
During combustion, n-octanol exhibits several advantages over conventional diesel. The high oxygen content in n-octanol promotes more complete combustion, resulting in lower emissions of PM and CO [66]. Additionally, n-octanol’s higher latent heat of vaporization helps to reduce peak combustion temperatures, thereby decreasing NOx emissions. Comparative studies have demonstrated that n-octanol/diesel blends can significantly reduce both PM and NOx emissions compared to pure diesel [58].
When considering the entire lifecycle, n-octanol offers a reduced environmental impact compared to conventional diesel. The use of renewable feedstocks for n-octanol production helps sequester CO2 during the growth phase of the biomass, contributing to a lower net carbon footprint. Furthermore, the potential for using waste biomass and agricultural residues as feedstocks for n-octanol production supports a circular economy and reduces waste. Several studies support these findings, highlighting n-octanol’s potential to enhance combustion efficiency and reduce emissions. For instance, n-octanol/diesel blends significantly reduce NOx and smoke emissions, due to their high oxygen content and cooling effect from the higher latent heat of vaporization [45]. Similarly, n-octanol blends improve combustion efficiency and lower both NOx and PM emissions, making it a promising sustainable alternative to conventional diesel [58].
4. Conclusions
This study has thoroughly evaluated the effects of n-octanol/diesel fuel blends on a compression ignition engine’s performance and emission characteristics. The findings reveal significant emission reductions and efficiency improvements, underscoring the potential of n-octanol as a sustainable alternative fuel despite some challenges in emission behaviors, particularly regarding NOx emissions.
Across various engine loads and speeds, the experiments consistently exhibited reductions in CO, HC, and smoke with the addition of n-octanol, along with enhancements in BTE. It was found that increases in the n-octanol ratio in the fuel blend led to higher NOx emissions relative to lower n-octanol concentrations; however, these levels remained substantially below those emitted by pure diesel. The properties of n-octanol, such as its oxygen content and the cooling effects from its higher latent heat of vaporization, contribute positively, albeit complicatedly, to emission control.
The results suggest that a 30% blend of n-octanol (D70O30) offers a balanced improvement in both performance and emissions. This blend maintains competitive brake torque and power while significantly enhancing BTE and reducing harmful emissions, presenting an optimal compromise between performance benefits and environmental impact.
The significance of these results is underscored by global carbon neutrality goals. N-octanol, when potentially derived from renewable sources, reduces critical pollutants and boosts engine efficiency, aligning closely with efforts to decrease fossil fuel reliance and lessen transport’s environmental impact. Positioned as a promising candidate for more sustainable and environmentally friendly internal combustion engine technologies, n-octanol shows significant potential. Future research should focus on expanding its scope to include multi-cylinder engines and a wider range of engine speeds and loads. This broader investigation will provide a more comprehensive understanding of n-octanol’s effects under varied operating conditions. Additionally, refining higher-octanol blends to balance performance benefits and minimize potential increases in NOx emissions remains crucial. Innovations in fuel formulation and engine design are expected to address these challenges, enhancing the viability of high-octanol blends for widespread use. By incorporating these elements, future studies will further solidify n-octanol’s role in advancing sustainable transportation solutions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K.; methodology, J.A. and J.K.; software, K.J. and B.K.; formal analysis, J.A. and J.K.; investigation, K.J., J.Y. and B.K.; resources, B.K. and JY; data curation, J.A. and K.J.; writing—original draft preparation, J.A. and K.J.; writing—review and editing, J.Y. and J.K.; visualization, J.A. and K.J.; supervision, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Silverman, D.T.; Samanic, C.M.; Lubin, J.H.; Blair, A.E.; Stewart, P.A.; Vermeulen, R.; Coble, J.B.; Rothman, N.; Schleiff, P.L.; Travis, W.D.; et al. The diesel exhaust in miners study: A nested case–control study of lung cancer and diesel exhaust. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 2012, 104, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grahame, T.J.; Schlesinger, R.B. Cardiovascular health and particulate vehicular emissions: A critical evaluation of the evidence. Air. Qual. Atmos. Health 2010, 3, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, L.; Al-Thukair, A.A. Environmental Assessments in the Oil and Gas Industry. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2009, 9, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU: Heavy-Duty Truck and Bus Engines. Available online: https://dieselnet.com/standards/eu/hd.php (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Regulation (EU) 2024/1257 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 April 2024 on Type-Approval of Motor Vehicles and Engines and of Systems, Components and Separate Technical Units Intended for Such Vehicles, with Respect to Their Emissions and Battery Durability (Euro 7), Amending Regulation (EU) 2018/858 and Repealing Regulations (EC) No 715/2007 and (EC) No 595/2009, Commission Regulation (EU) No 582/2011, Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1151, Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/2400 and Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/1362. Official Journal of the European Union. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=OJ:L_202401257 (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Singh, A.P.; Agarwal, A.K. Low-temperature combustion: An advanced technology for internal combustion engines. In Advances in Internal Combustion Engine Research; Srivastava, D.K., Agarwal, A.K., Datta, A., Maurya, R.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 9–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ayodhya, A.S.; Narayanappa, K.G. An overview of after-treatment systems for diesel engines. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35034–35047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Yao, M. Thermal Efficiency Enhancement of a Turbocharged Diesel Engine Dedicated for Hybrid Commercial Vehicle Application; SAE Technical Paper, No. 2022-01-7053; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ge, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, C.; Yan, X.; Hao, L.; Tan, J. Effects of different diesel particulate filter on emission characteristics of in-use diesel vehicles. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 2989–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Cheung, C.S.; Chan, T.L.; Yao, C.D. Emission reduction from diesel engine using fumigation methanol and diesel oxidation catalyst. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4497–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Jo, S.; Kwon, S.; Lee, J.T.; Park, S. NOX emission analysis according to after-treatment devices (SCR, LNT+ SCR, SDPF), and control strategies in Euro-6 light-duty diesel vehicles. Fuel 2022, 310, 122297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Feng, G.; Li, Y.; Ling, T.; Peng, X.; Su, Z.; Zhao, X. A Review of Thermal Energy Management of Diesel Exhaust after-Treatment Systems Technology and Efficiency Enhancement Approaches. Energies 2024, 17, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.; Kosaka, H.; Bady, M.; Abdel-Rahman, A.K. Effects of intake and exhaust manifold water injection on combustion and emission characteristics of a DI diesel engine. J. Therm. Sci. Tech.-Jpn. 2017, 12, JTST0014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Cheikh Mohamad Ahmad, M.; Keskin, A.; Özarslan, H.; Keskin, Z. Properties of ethyl alcohol-water mixtures as a reductant in a SCR system at low exhaust gas temperatures. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 42, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros, J.M.; George, P.; Umar, M.; Tsolakis, A. Enhancing selective catalytic reduction of NOx with alternative reactants/promoters. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.O.; Kim, K.T.; Song, Y.H.; Kim, E.; Han, H.S. Hydrogen in plasma-assisted hydrocarbon selective catalytic reduction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 3225–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Grift, T.E.; Hansen, A.C. Effect of biodiesel on engine performances and emissions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, W.N.M.W.; Mamat, R.; Masjuki, H.H.; Najafi, G. Effects of biodiesel from different feedstocks on engine performance and emissions: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, C.S. Applicability of dimethyl ether (DME) in a compression ignition engine as an alternative fuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 86, 848–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänggi, S.; Elbert, P.; Bütler, T.; Cabalzar, U.; Teske, S.; Bach, C.; Onder, C. A review of synthetic fuels for passenger vehicles. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Suman, A.; Das, L.M.; Kaushik, S.C.; Tyagi, S.K. A renewable pathway towards increased utilization of hydrogen in diesel engines. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 5577–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, Y.; Sandalcı, T.; Yüksek, L.; Dalkılıç, A.S.; Wongwises, S. Effect of hydrogen–diesel dual-fuel usage on performance, emissions and diesel combustion in diesel engines. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1687814016664458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, P.; Cardone, M. Ethanol/gasoline blends as alternative fuel in last generation spark-ignition engines: A review on CO and HC engine out emissions. Energies 2021, 14, 4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speth, R.L.; Chow, E.W.; Malina, R.; Barrett, S.R.; Heywood, J.B.; Green, W.H. Economic and environmental benefits of higher-octane gasoline. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6561–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.; Malone, P. Phase equilibria of ethanol fuel blends. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2005, 228, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, M.; Awad, E.N.; Ibrahim, V.; Barakat, Y. Effect of ethyl acetate addition on phase stability, octane number and volatility criteria of ethanol-gasoline blends. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tephly, T.R. The toxicity of methanol. Life Sci. 1991, 48, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, K. Handbook for Handling, Storing, and Dispensing E85 and Other Ethanol-Gasoline Blends; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jamrozik, A.; Tutak, W.; Grab-Rogaliński, K. Combustion stability, performance and emission characteristics of a CI engine fueled with diesel/n-butanol blends. Energies 2021, 14, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’andrea, T.; Henshaw, P.F.; Ting, D.K. The addition of hydrogen to a gasoline-fuelled SI engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2004, 29, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, L.; Li, R.; Zuo, X.; Sun, Y. Effect of addition of hydrogen and exhaust gas recirculation on characteristics of hydrogen gasoline engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 8288–8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsul, N.S.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Rahman, N.A.; Kofli, N.T. An overview on the production of bio-methanol as potential renewable energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielenz, J.R. Ethanol production from biomass: Technology and commercialization status. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Saka, S. Chemical conversion of cellulose as treated in supercritical methanol. Cellulose 2001, 8, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güllü, D.; Demirbaş, A. Biomass to methanol via pyrolysis process. Energy Convers. Manag. 2001, 42, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C. Advanced Development of Rotary Stratified Charge 750 and 1500 HP Military Multi-Fuel Engines at Curtiss-Wright; SAE Technical Paper, No. 840460; SAE International: Warrendale, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; McChesney, R. Development of Multi-Fuel Spark Ignition Engine; SAE Technical Paper, No. 2004-32-0038; SAE International: Warrendale, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, N.; Vigil, F.M.; Atmanli, A.; Donaldson, B. Detailed analysis of PAH formation, toxicity and regulated pollutants in a diesel engine running on diesel blends with n-propanol, n-butanol and n-pentanol. Energies 2022, 15, 6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, C.E. Biomass ethanol: Technical progress, opportunities, and commercial challenges. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 1999, 24, 189–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; García-Contreras, R.; Campos-Fernández, J.; Dorado, M.P. Stability, lubricity, viscosity, and cold-flow properties of alcohol− diesel blends. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4497–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.; Ileri, E.; Atmanli, A. Performance of biodiesel/higher alcohols blends in a diesel engine. Int. J. Energy Res. 2016, 40, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algayyim, S.J.M.; Wandel, A.P.; Yusaf, T.; Hamawand, I. The impact of n-butanol and iso-butanol as components of butanol-acetone (BA) mixture-diesel blend on spray, combustion characteristics, engine performance and emission in direct injection diesel engine. Energy 2017, 140, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heufer, K.A.; Sarathy, S.M.; Curran, H.J.; Davis, A.C.; Westbrook, C.K.; Pitz, W.J. Detailed kinetic modeling study of n-pentanol oxidation. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6678–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarajan, Y.; Munuswamy, D.B.; Nagappan, B.; Pandian, A.K. Performance, combustion and emission analysis of mustard oil biodiesel and octanol blends in diesel engine. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 54, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.; Saravanan, S.; Rana, D.; Anish, V.; Nagendran, A. Effect of a sustainable biofuel–n-octanol–on the combustion, performance and emissions of a DI diesel engine under naturally aspirated and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) modes. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 118, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Combustion and emissions of compression ignition in a direct injection diesel engine fueled with pentanol. Energy 2015, 80, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidharth; Kumar, N. Performance and emission studies of ternary fuel blends of diesel, biodiesel and octanol. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 42, 2277–2296. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, M.; Martin, D.W. Combustion characteristics of higher-alcohol/gasoline blends. Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs. Part A 2000, 214, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilyurt, M.K. A detailed investigation on the performance, combustion, and exhaust emission characteristics of a diesel engine running on the blend of diesel fuel, biodiesel and 1-heptanol (C7 alcohol) as a next-generation higher alcohol. Fuel 2020, 275, 117893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Martin, D.W.; Carder, D. Emissions characteristics of higher alcohol/gasoline blends. Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs. Part A 2000, 214, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.; Saravanan, S. Use of higher alcohol biofuels in diesel engines: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 84–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojević, S.; Savić, S.; Marić, D.; Stopka, O.; Krstić, B.; Stojanović, B. Correlation between emission and combustion characteristics with the compression ratio and fuel injection timing in tribologically optimized diesel engine. Teh. Vjesn. 2022, 29, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Milojević, S.; Glišović, J.; Savić, S.; Bošković, G.; Bukvić, M.; Stojanović, B. Particulate Matter Emission and Air Pollution Reduction by Applying Variable Systems in Tribologically Optimized Diesel Engines for Vehicles in Road Traffic. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, R. Blending n-octanol with biodiesel for more efficient and cleaner combustion in diesel engines: A modeling study. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 403, 136877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Poures, M.V.; AP, S.; Rana, D.; Babu, R.K.; Subramani, S.; Sethuramasamyraja, B. Using renewable n-octanol in a non-road diesel engine with some modifications. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilusa, T.J.; Mollagee, M.M.; Muzenda, E. Reduction of vehicle exhaust emissions from diesel engines using the whale concept filter. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, H.S. Conversion Factors among Smoke Measurements; SAE transactions; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1985; pp. 533–547. [Google Scholar]
- Nour, M.; Attia, A.M.; Nada, S.A. Combustion, performance and emission analysis of diesel engine fuelled by higher alcohols (butanol, octanol and heptanol)/diesel blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 185, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yao, A.; Yao, C.; Wang, B.; Lu, H.; Feng, J.; Feng, L. Study of the characteristics of PM and the correlation of soot and smoke opacity on the diesel methanol dual fuel engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 148, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, K.; Sathiyagnanam, A.P.; Kumar, B.R.; Saravanan, S.; Rana, D.; Sethuramasamyraja, B. Prediction of emissions and performance of a diesel engine fueled with n-octanol/diesel blends using response surface methodology. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clean Cities and Communities. Alternative Fuel Price Report April 2024; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA. Available online: https://afdc.energy.gov/fuels/prices.html (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Avantor. Available online: https://us.vwr.com/store/catalog/product.jsp?product_id=39031710 (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Vo, D.V.N. Recent advances and sustainable development of biofuels production from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Jiang, J.; Hse, C.Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K.; Ye, J.; Xu, J. Selective catalytic conversion of waste lignocellulosic biomass for renewable value-added chemicals via directional microwave-assisted liquefaction. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julis, J.; Leitner, W. Synthesis of 1-octanol and 1, 1-dioctyl ether from biomass-derived platform chemicals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8615–8619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, L.Y.; Mustaffa, A.A.; Hashim, H.; Mat, R.; Manan, Z.A.; Yunus, N.A. Performance and emission characteristics of green diesel blends containing diethyl-succinate and 1-octanol. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).