Abstract
The electric field distortion caused by space charge is an important factor affecting the operation reliability of oil–paper insulation in a converter transformer. To study the accumulation and decay characteristics of the space charge within oil-impregnated pressboard under DC and polarity reversal voltage, and consider the possible operating conditions of the converter transformer, the space charge behavior of oil-impregnated pressboard was measured by the pulsed electro-acoustic (PEA) method in the temperature range from −20 °C to 60 °C. The effect of temperature on the accumulation and decay characteristics of space charge is also analyzed. The space charge accumulated within the pressboard at low temperature is mainly homocharge injected by the electrode, while heterocharge formed by ion dissociation counteracts some of the homocharge at high temperature. Thus, the space charge of pressboard first increases, then decreases, with an increase in temperature. However, slow decay of the space charge causes severe distortion of the electric field distribution in the pressboard during voltage polarity reversal.
1. Introduction
A converter transformer is one of the core pieces of equipment for AC/DC conversion in HVDC transmission projects [1]. The HVDC transmission project has the function of bi-directional power flow, which is achieved through changing the polarity of the DC voltage. In this case, the converter transformer will work under polarity reversal voltage. Oil-paper insulation near the value side of a converter transformer works under AC-DC combined voltage, which allows space charge to accumulate within the sample more easily. Space charge will accelerate the aging of the insulator and distort the electric field, which directly affects the operational reliability of the converter transformer [2,3,4].
Accumulation and decay of space charge in oil–paper insulation is affected by temperature, moisture, aging, electric field, and so on [5,6,7,8]. Tang et al. studied the space charge characteristics of multi-layer oil-impregnated paper at high temperatures, and concluded that space charge distribution and charge mobility were affected by the temperature [9]. Wu et al. studied the space charge characteristics of single-layer and double-layer oil-impregnated paper under different temperature gradients, and concluded that the space charge and electric field, at the low temperature side, increased with the increase in the temperature gradient. A numerical simulation of the space charge distribution in the oil-impregnated paper under temperature gradient was also carried out, based on the bipolar charge transport model [10,11]. Wang et al. studied the effects of the paper-aged state on space charge characteristics in oil-impregnated paper, and concluded that the amount of space charge, and the decay speed of space charge, increased with the increase in the aging of the paper [12]. Huang et al. studied the effects of thermal and electrical stress on the space charge of oil-impregnated paper insulation, and concluded that the space charge accumulated within the pressboard increased with an increase in the stress duration, and the speed of charge accumulation is largest within electro-thermally stressed oil–paper [13,14]. George Chen et al. studied the effects of space charge on electric field distribution in oil-paper insulation under polarity reversal voltage by a numerical calculation method, and concluded that the space charge accumulated inside the pressboard increased the electric field in the oil after the voltage polarity is reversed [15]. Zhou et al. used the pulsed electro-acoustic (PEA) method to study space charge distribution in oil-impregnated pressboard under polarity reversal voltage at room temperature, and concluded that the charge and the electric field at the interface were severely distorted after the voltage polarity was reversed [16,17].
At present, most the research on space charge has concentrated on room temperature or high temperature [18,19,20,21], while the space charge characteristics at low temperature have rarely been reported. In this paper, the space charge distribution under DC and polarity reversal voltage in the temperature range from −20 °C to 60 °C was measured by the PEA method, then the electrical field distribution was analyzed. The effects of temperature on the space charge and electric field of oil-impregnated pressboard under DC and polarity reversal voltage was then also studied.
2. Experimental Method
2.1. Sample Preparation
The thickness of the pressboard used for the test was 1 mm, and its diameter was 6 cm. The pressboard was dried under vacuum for 48 h, then was impregnated by transformer oil (Karamay 45#), also under vacuum. The moisture content of the pretreated oil-impregnated pressboard was measured by the extraction method. Table 1 lists the moisture content, and dielectric parameters, of the oil and pressboard at room temperature.

Table 1.
Moisture content and dielectric parameters of transformer oil and pressboard.
2.2. Test System
The space charge measurement system is shown in Figure 1 [22,23]. The amplitude of the DC power supply was ±30 kV. The pulse electric field generated by the pulse power supply (pulse width 10 ns) acts on the space charge to form a stress wave. The stress wave is converted into a voltage signal by the piezoelectric sensor. In this experiment, a P(VDF-TrFE) copolymer (which can typically work from −60 °C to 100 °C) was used for the piezoelectric sensor. The amplifier was used to linearly amplify the voltage signal. The oscilloscope was used to record the waveforms and upload the data to the PC. The temperature of the upper and lower electrodes was controlled by the oil bath cycle, and the test temperatures were set to −20 °C, 0 °C, 20 °C, 40 °C, and 60 °C. The test voltage of the DC electric field was set to 10 kV and 20 kV, and the measurement time for the voltage-on test and the short-circuit test was 1 h, with the measurement data were recorded every 10 s. The experiment was performed repeatedly, selecting three samples each time, and the data which reflects the average trend was selected for the experimental results.
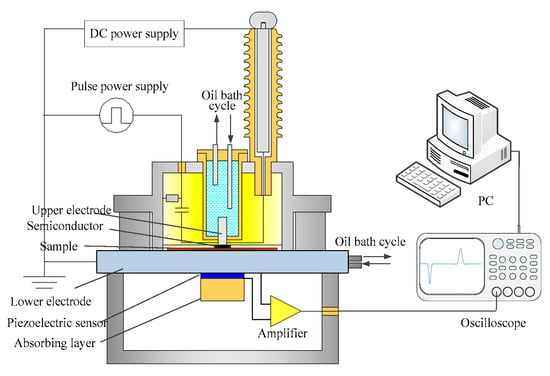
Figure 1.
Space charge measurement system.
Figure 2 shows the process of voltage polarity reversal. Firstly, the positive voltage (+10 kV) was applied to the sample for 1 h. Then the voltage polarity was reversed from positive to negative in 60 s. Finally, the negative voltage (−10 kV) was applied to the sample for 1 h.
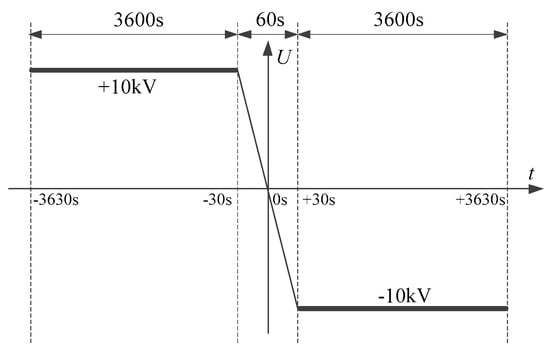
Figure 2.
Process of voltage polarity reversal.
3. Test Results
3.1. Space Charge Distribution under DC Electric Field
The test results needed to be calibrated at a lower electric field to convert the measured voltage signal into charge density. Figure 3 shows the space charge distribution of oil-impregnated pressboard at both a low temperature and room temperature. The two dotted lines in the figure indicate the electrode position. The left line is the lower electrode and the right line is the upper electrode. Homocharge gradually accumulates within the sample, and the interface charge decreases accordingly. When the applied voltage is constant, the space charge increases with the increase in temperature; there is almost no space charge within the sample at −20 °C. The accumulation of space charge increases with the increase in temperature and electric field stress. This indicates that charge mobility increases with the increase in both temperature and electric field stress. Because of the large attenuation of sound waves propagating in the pressboard, the received acoustic signal near the upper electrode had a smaller amplitude and a wider width than that near the lower electrode.
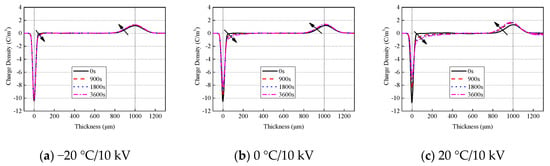
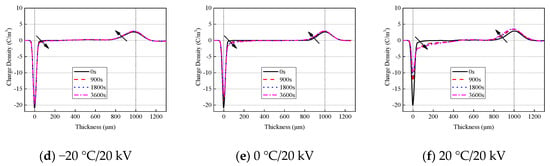
Figure 3.
Space charge distribution of pressboard at low temperature and room temperature.
Figure 4 shows the space charge distribution of oil-impregnated pressboard at high temperatures. Homocharge accumulates within the sample at high temperatures. The charge distribution curves at 900 s and 3600 s are basically coincident at 60 °C, indicating that the space charge ha reached stability. The space charge near the lower electrode shrinks at the high temperature, in other words, the negative charge near the lower electrode is less than the negative charge within the sample. Moreover, the shrinkage amplitude at 60 °C is significantly greater than that at 40 °C. Figure 4c,d show a partial amplification of the space charge distribution near the lower electrode. The negative charge first increases, and then decreases, with time.
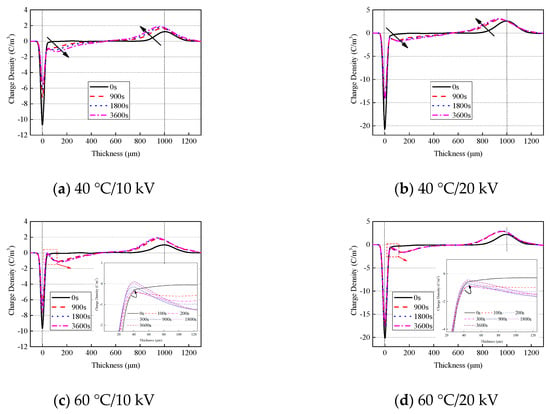
Figure 4.
Space charge distribution of pressboard at high temperatures.
3.2. Space Charge Distribution During Short-Circuit
Figure 5 shows the space charge distribution of oil-impregnated pressboard at different temperatures during a short-circuit. Negative charge is accumulated near the lower electrode, and positive charge is accumulated near the upper electrode. At the beginning of a short-circuit, the space charge of the sample increases with the increase in the pre-applied electric field stress. Space charge then increases, and subsequently decreases, with the increase in temperature (the maximum value appears at 40 °C). Space charge decreases gradually during the short-circuit, with the decay being faster in the initial stage, and slower in the later stage. Moreover, the decay rate of the space charge clearly increases with increasing temperature. At the end of the short-circuit, the space charge within the sample at 60 °C has decayed completely.
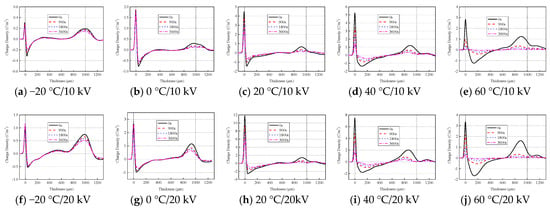
Figure 5.
Space charge of pressboard at different temperatures during a short-circuit.
3.3. Space Charge Distribution under Polarity Reversal Voltage
Figure 6 shows the space charge distribution of oil-impregnated pressboard under polarity reversal voltage. The distribution curves of the space charge within the sample, at −30 s, 0 s, and 30 s, almost coincide, indicating that space charge decays slowly during voltage polarity reversal. After the voltage polarity is reversed, the interface charge at the lower electrode is clearly enhanced, and first increases, then decreases, with the increase in temperature (the maximum value appears at 40 °C). Then, the interface charge at the lower electrode gradually decreases, and the polarity of the space charge near the lower electrode gradually changes from negative to positive. However, the interface charge at the upper electrode is not enhanced after the voltage polarity is reversed, and is less than the interface charge at both +3630 s and −30 s. At high temperature, the space charge distribution at both −30 s and +3630 s is symmetrically distributed with respect to the horizontal axis.
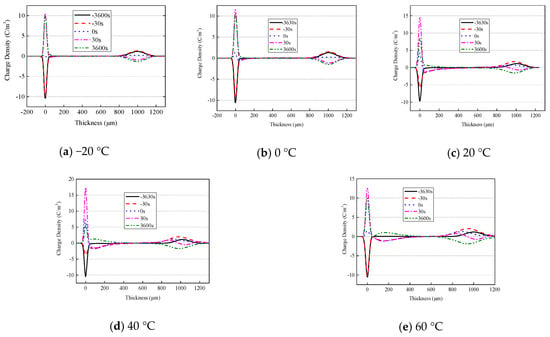
Figure 6.
Space charge distribution under polarity reversal voltage.
3.4. Electric Field Distribution under Polarity Reversal Voltage
According to the measurement results of the space charge, the electric field of oil-impregnated pressboard is calculated as follows:
where E is the electric field stress (kV/mm), ρ(x) is the space charge density (C/m3), ε0 is the vacuum permittivity, and εr is the relative permittivity of the sample.
Figure 7 shows the electric field distribution of oil-impregnated pressboard under polarity reversal voltage. When the applied voltage is positive, the electric field at the interface decreases, and the electric field within the sample increases. After the voltage polarity is reversed, the interface electric field distribution at the lower electrode is clearly enhanced, and it first increases, then decreases, with the increase in temperature (the maximum value appears at 40 °C). Then, the interface electric field gradually decreases, and the electric field within the sample increases. At high temperatures, the electric field distribution at both −30 s and +3630 s is symmetrically distributed with respect to the horizontal axis. Moreover, the electric field distribution-curves at the left side of the sample, at −30 s, 0 s, and +30 s, have a “parallel” relationship, indicating that the effect of charge on the electric field distribution is the same during voltage polarity reversal.
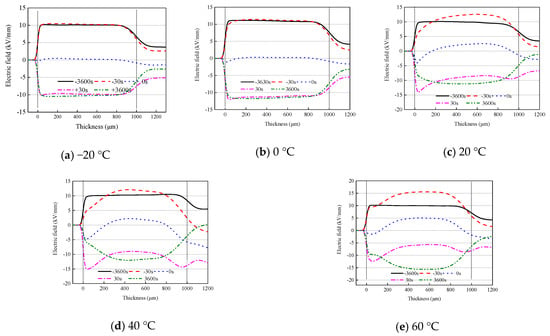
Figure 7.
Electric field distribution under polarity reversal voltage.
4. Analysis and Discussion
The space charge distribution of oil-impregnated pressboard with a thickness of 1 mm at different temperatures was measured. The accumulation and decay characteristics of space charge at room temperature are consistent with the test results in [24]. The mean volume density is used to further analyze the accumulation and decay characteristics of space charge, and its calculation formula is shown as follows:
where Q(t) is the mean volume density of the sample (C/m3), ρ (x,t) is the space charge density (C/m3), and L is the thickness of the sample (mm).
Figure 8 shows the mean volume density of the space charge at different temperatures and voltages. The mean volume density of the space charge increases significantly in the initial stage, and tends to be stable in the later stage. The higher the temperature and electric field stress, the more the mean volume density increases before the 600 s point. At the end of the voltage-on test, the mean volume density of space charge first increases, then decreases, with the increase in temperature (the maximum value appears at 40 °C). The mean volume density changes little at 60 °C in the later stage of the voltage-on test, indicating that the space charge distribution of the sample has reached stability.
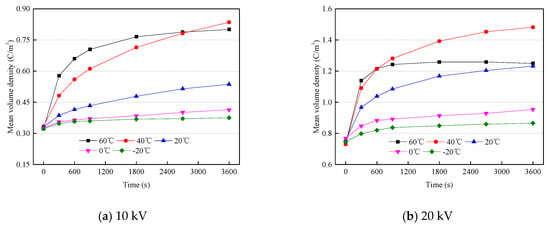
Figure 8.
Mean volume density of space charge at different temperatures and voltages.
The accumulation of space charge within the insulator is affected by the factors such as, generation, migration, recombination, and extraction of space charge. Temperature and electric field stress affect the above physical processes, and this affects the space charge distribution.
4.1. Effect of Temperature on the Generation and Migration of Charge
As the measurement results obtained by the PEA method can only reflect the “net charge” of the corresponding position, even if the measurement results show homocharge, the effect of heterocharge on the measurement result cannot be ignored. The heterocharge is derived from the thermal dissociation of impure molecules within the sample. As the maximum field stress during the test is 20 kV/mm, the homocharge within the sample is mainly injected by the Schottky effect. According to the Schottky effect, the electrode injection current density is expressed as follows:
where j is the electrode injection current density (Am−2), A is the Richardson constant (Am−2·K−2), W is the injection barrier of the charge (eV), kb is the Boltzmann constant (J/K), T is the absolute temperature (K), and e is the electronic charge. Electrode injection current density increases with increasing temperature and electric field stress, and the amount of charge injected into the sample increases accordingly, causing an increase in the trapped space charge. The electric field at the interface decreases with an increase in the homocharge, and the injection current density decreases accordingly. Therefore, space charge within the sample increases slowly during the later stage of the experiment.
Thermal dissociation of impure molecules is affected by temperature, and the generated positive and negative ions will migrate to the interface with the action of the electric field, forming the heterocharge. The dissociation rate of molecules per unit of volume and unit of time is expressed as follows:
where N0 is the concentration of impure molecules (m−3), v0 is the relative thermal vibration frequency between atomic groups in the molecule (Hz), and ∆Udis is the barrier to be overcome when the molecules are dissociated from their stable state (eV). The dissociation rate increases with increasing temperature, and the heterocharge accumulated in the sample increases accordingly.
Thermal dissociation of impure molecules can be regarded as a slow polarization behavior. As relative permittivity is an important parameter reflecting polarization, the dielectric spectrum of the oil-impregnated pressboard at different temperatures was measured in the range from 10−2 Hz to 107 Hz, as shown in Figure 9. The relative permittivity increases with the increase in temperature, and also increases with a decrease in the frequency. The parameters in the DC steady state should be the same as that under low frequency. The relative permittivity at 60 °C increases the most in the range from 100 Hz to 10−2 Hz, followed by 40 °C, while the relative permittivity at low temperature increases little in that range. This indicates that polarization is easier to form at higher temperatures, and the impure molecules are more easily dissociated to form the heterocharge. This is consistent with the analysis results of Equation (3).
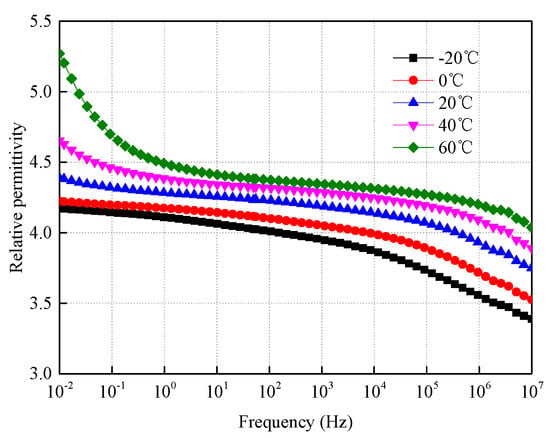
Figure 9.
Dielectric spectra of pressboard at different temperatures.
The space charge distribution is affected by the capacity for charge migration. The oil-impregnated pressboard is composed of transformer oil and cellulose, and the cellulose contains both crystalline phase and amorphous phase. The barrier that hinders charge migration is formed between adjacent crystalline structures. With the increase in temperature, the increase in charge energy makes it easier to cross the barrier, and charge mobility increases accordingly. The migration of charge is fastest within the sample at 60 °C, which makes the process of injection, trapping, detrapping, and recombination, of charge reach equilibrium in a short time. That is, the space charge distribution reaches stability quickly.
In summary, both homocharge and heterocharge exist in the oil-impregnated pressboard at the same time, but the former more so than the latter, so the test results show homocharge at different temperatures. Both homocharge and heterocharge increase with increasing temperature, but the magnitude of the increase of each is different. As the thermal dissociation of impure molecules at −20 °C, 0 °C, and 20 °C, is not obvious, the space charge accumulated within the sample is mainly homocharge. The schematic diagram of space charge distribution at high temperature, and the corresponding PEA measurement results (ignore the waveform of the interface charge), are shown in Figure 10. The heterocharge increases with the increase in temperature, and the heterocharge is mainly distributed near the interface. Therefore, the net charge near the electrode decreases with the increase in the temperature. As the heterocharge, and the charge recombination, increase at 60 °C, the mean volume density of space charge at 60 °C is less than that at 40 °C. During the voltage-on test, the negative charge injected from the lower electrode gradually decreases, while the positive charge formed by thermal dissociation gradually increases. Hence, space charge near the lower electrode first increases, and then decreases, at 60 °C.
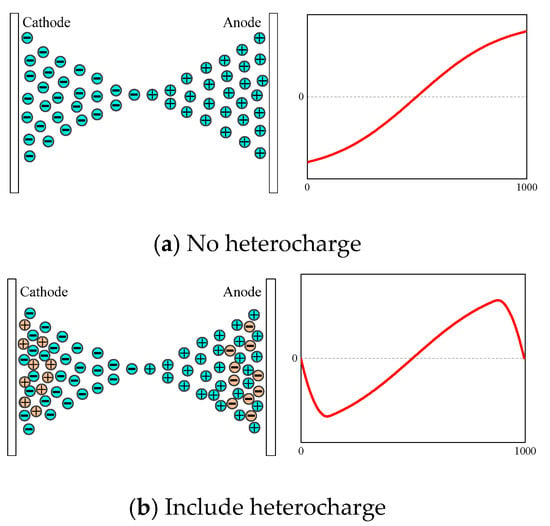
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram of space charge distribution and corresponding pulsed electro-acoustic results at high temperature.
The signal near the upper electrode in the measurement results is different from that in the schematic diagram. This is because the space charge is measured by the PEA method. The sound wave propagating within the sample has both attenuation and dispersion, which causes the amplitude of the measured signal to decrease, and the pulse width to increase. The acoustic attenuation coefficient is obtained from the waveforms at the upper and lower electrodes in the reference signal [25]. The left side waveform in Figure 6e is mirrored as the upper electrode un-attenuated signal, as shown in Figure 11a. The attenuated signal is calculated with the attenuation coefficient and the un-attenuated signal, as shown in Figure 11b.
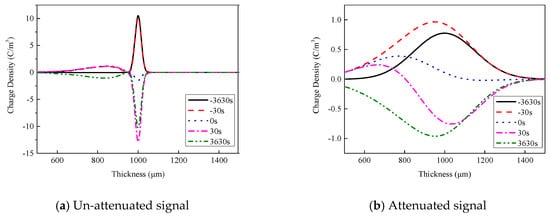
Figure 11.
Simulated results of attenuation on space charge distributions during voltage polarity reversal.
As shown in Figure 11, there is a big difference between the attenuated signal and the un-attenuated signal. The trend of the attenuated signal changing with time in Figure 11b is consistent with the measurement results near the upper electrode at 60 °C, indicating that the trend of space charge change over time, at both the upper and lower electrodes, is basically equivalent. However, the signals of the upper and lower electrodes in the measurement results are different because of the attenuation of the sound waves.
4.2. Effects of Temperature on Space Charge During a Short-Circuit
Figure 12 shows the mean volume density of space charge under different temperatures during a short-circuit. The mean volume density decreases gradually during a short-circuit, decreasing significantly in the initial stage. The rate and amplitude of charge decay increases with the increase in temperature. At the beginning of the decay process, the max mean volume density appears at 40 °C, indicating that the residual charge within the sample is largest at this temperature.
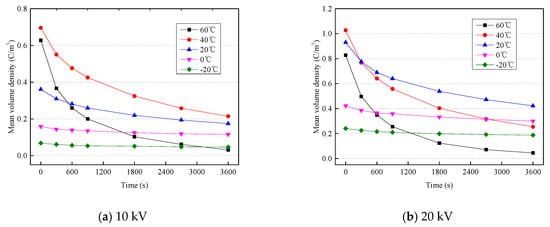
Figure 12.
Mean volume density of space charge during a short-circuit.
Charge detrapping is affected by temperature and trap levels. The charge detrapping rate can be expressed as follows:
where nt is the charge in the trap (C/m3), v is the electronic oscillation frequency (Hz), and Ec and Et are the energy levels of the conduction band and the trap (eV), respectively. The charge detrapping rate increases with both the increase in temperature and trap level. Charge decay accelerates with the increase in temperature, and the detrapping rate of a shallow trap is higher than that of a deep trap. The formation of space charge is mainly related to shallow traps. The charge in a shallow trap is easier to break away from its bond, so the charge decays faster in the initial stage. Moreover, the residual charge will form an electric field within the sample during a short-circuit, which will help the space charge decay. As the space charge gradually decays, the electric field decreases correspondingly, so charge decays slowly in the late stage of a short-circuit.
4.3. Effects of Temperature on Distribution of Space Charge and Electric Field under Polarity Reversal Voltage
The test results show that the charge density, and the electric field, at the lower electrode increase significantly after the voltage polarity is reversed, and the signal at the upper electrode is attenuated. Therefore, analysis was focused on the distribution of space charge and the electric field at the lower electrode. The electric field, and charge density, at the lower electrode during voltage polarity reversal are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Electric field and charge density at the lower electrode during voltage polarity reversal.
Table 2 shows that the electric field at the lower electrode at time −30 s, 0 s and 30 s differ by approximately 10 kV/mm at different temperatures, and the charge density at time −30 s, 0 s and 30 s differs by approximately 10 C/mm3. After the voltage polarity is reversed, the increase in the charge density and the electric field is largest at 40 °C.
The space charge within the sample will form an induced charge at the interface, which will in turn change the charge density and electric field at the interface. As the lower electrode is grounded, the interface charge density and electric field at the lower electrode can be expressed as follows:
where σd is the interface charge density at the lower electrode (C/m2), Ed is the electric field at the lower electrode (kV/mm), ρ(x) is the space charge density (C/m3), and E is the applied electric field stress (kV/mm). E = 0 kV/mm indicates a short-circuit.
Equations (6) and (7) show that the homocharge within the sample will reduce σd and Ed, while the heterocharge will increase σd and Ed. Before the voltage polarity is reversed, the space charge accumulated within the sample is homocharge, making σd and Ed decrease. Relative to the applied voltage, the charge accumulated within the sample is changed from homocharge to heterocharge after the voltage polarity is reversed, making σd and Ed increase correspondingly. Moreover, σd and Ed are affected by the amount and distribution of space charge, and the applied electric field. The space charge near the electrode has a greater effect on σd and Ed. The space charge within the sample is highest at 40 °C, and it is mainly distributed near the electrode, so the increase of σd and Ed are the largest after the voltage polarity is reversed. As shown in Figure 8a, the mean volume density at 60 °C is larger than that at 20 °C, but the space charge within the sample is less distributed near the electrode at 60 °C. Therefore, the increase of σd and Ed are smaller than that at 20 °C, after the voltage polarity is reversed. Moreover, the test results show that space charge remains basically unchanged during voltage polarity reversal. Therefore, the effect of the internal space charge on the interface charge density and electric field during voltage polarity reversal is equivalent according to Equations (6) and (7). The electric field, and charge density, at the interface vary linearly with the applied field stress during voltage polarity reversal.
After the voltage polarity is reversed, the negative charge injected by the lower electrode is changed to a positive charge, and it is known from Equation (3) that the electric field distortion causes the electrode to inject more charge. The positive charge injected will neutralize the residual negative charge, and the space charge within the sample gradually changes from heterocharge to homocharge. Moreover, the amount and mobility of injected charge increases more at high temperatures, making space charge basically stable at +3630 s, hence the space charge distribution at both −30 s and +3630 s is symmetrically distributed.
5. Conclusions
The space charge distribution of oil-impregnated pressboard at different temperatures under DC and polarity reversal voltages was measured, and the effect of space charge on electric field distribution was analyzed. The conclusions are as follows:
- The space charge accumulated inside the oil-impregnated pressboard is not clear at −20 °C; homocharge and heterocharge both increase with an increase in temperature, but heterocharge only accumulates at high temperatures. Therefore, the space charge within the pressboard first increases, then decreases, with the increase in temperature.
- The decay rate of space charge increases with an increase in temperature. Moreover, space charge decays rarely during voltage polarity reversal, leading to a serious distortion of the electric field distribution at the interface.
- The electric field at the interface is affected not only by the charge density but also by the charge distribution. The electric field at the interface at 40 °C is largest after the voltage polarity is reversed, while the electric field inside the sample at 60 °C is largest under DC voltage.
- Compared to thin oil-impregnated paper (thickness less than 500 μm), the space charge inside thick oil-impregnated pressboard takes a long time to reach stability, and it decays slowly during a short-circuit test.
Author Contributions
Q.C. and J.Z. conceived and designed the experiments; P.T. and W.S. performed the experiments; J.Z. and M.C. analyzed the data; J.Z. wrote the paper.
Funding
This project was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFB0902704), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51677046) and the University Nursing Program for Young Scholars with Creative Talents in Heilongjiang Province (No. UNPYSCT-2016159).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Amoiralis, E.I.; Tsili, M.A.; Kladas, A.G. Power transformer economic evaluation in decentralized electricity markets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2329–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chi, M.; Guo, C. Breakdown Characteristics of Oil-Pressboard Insulation under AC-DC Combined Voltage and Its Mathematical Model. Energies 2018, 11, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, G.C. Binging an insulation to failure: E role of space charge. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, G.; Montanari, G.C.; Dissado, L.A. Electrical aging and life models: The role of space charge. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2005, 12, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgaard, L.E.; Hansen, W.; Linhjell, D.; Painter, T.J. Aging of oil-impregnated paper in power transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Zhou, R.; Liao, R.; Yang, L.; Liao, Q. New Method for Shallow and Deep Trap Distribution Analysis in Oil Impregnated Insulation Paper Based on the Space Charge Detrapping. Energies 2018, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Huang, M.; Chen, W.J.; Jin, F.B. Space charge behavior of oil-paper insulation thermally aged under different temperatures and moistures. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2015, 10, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Chen, G.; Liao, R.; Yang, L.; Tang, C. Influence of Moisture on Space Charge Dynamics in Multilayer Oil-Paper Insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Chen, G.; Fu, M.; Liao, R.J. Space Charge Behavior in Multi-layer Oil-paper Insulation under Different DC Voltages and Temperatures. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2010, 17, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, K.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, Z.; Wang, H. Space charge distribution in oil impregnated papers under temperature gradient. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y. Effect of temperature gradient on space charge distribution in oil impregnated papers. High Volt. Eng. 2011, 37, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Mu, H.; Wang, D.; Lei, M.; Suwarno, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Takada, T. Effects of paper-aged state on space charge characteristics in oil-impregnated paper insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, C.; Chen, W.; Lu, L.; Sha, Y. Charge Transport in thermally and Electrically Stressed Oil-impregnated Paper Insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Lu, L.; Jin, F.; Huang, J. Space Charge Behavior Evolution with Thermal Aging of Oil-paper Insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Hao, M.; Hao, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, G. Space charge characteristics in oil and oil-impregnated pressboard and electric field distortion after polarity reversal. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Sha, Y.; Jin, F. Influence of voltage reversal on space charge behavior in oil-paper insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Lu, L.; Jin, F.; Huang, J. Space charge dynamics at the physical interface in oil-paper insulation under DC voltage. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Ho, Y.F. Temperature effect on space charge dynamics in XLPE insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2007, 14, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Dissado, L.A.; Chen, G.; Fothergill, J.C. Space charge formation and its modified electric field under applied voltage reversal and temperature gradient in XLPE cable. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2008, 15, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallot-Lavallée, O.; Teyssèdre, G.; Laurent, C.; Rowe, S. Space charge behaviour in an epoxy resin: The influence of fillers, temperature and electrode material. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, N.; Chen, G. Analysis of space charge formation in LDPE in the presence of crosslinking byproducts. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Sakai, T. Measurement of electric-fields at a dielectric electrode interface using an acoustic transducer technique. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1983, 18, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshuis, P.; Jeroense, M. Space charge measurements on impregnated paper: A review of the PEA method and a discussion of results. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 1997, 13, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, G.; Wilson, G.; Jarman, P. Space charge behaviour in thick oil-impregnated pressboard under HVDC stresses. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Hanawa, K.; Suzuki, K.; Takada, T. Attenuation recovery technique for acoustic wave propagation in PEA method. In Proceedings of the 2001 International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials (ISEIM 2001), Himeji, Japan, 22–22 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).