Abstract
Background: Many studies have identified key factors affecting the rates of engagement in physical activity in older adults with chronic disease. Environmental conditions, such as weather variations, can present challenges for individuals with chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes when engaging in physical activity. However, few studies have investigated the influence of weather on daily steps in people with chronic diseases, especially those with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Objective: This study investigated the association between weather variations and daily self-monitored step counts over two years among individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in Sweden. Methods: The study is a secondary analysis using data from the Sophia Step Study, aimed at promoting physical activity among people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, which recruited participants from two urban primary care centers in Stockholm and one rural primary care center in southern Sweden over eight rounds. This study measured physical activity using step counters (Yamax Digiwalker SW200) and collected self-reported daily steps. Environmental factors such as daily average temperature, precipitation, and hours of sunshine were obtained from the Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute. A robust linear mixed-effects model was applied as the analysis method. Results: There was no association found between weather variations and the number of steps taken on a daily basis. The analysis indicated that only 10% of the variation in daily steps could be explained by the average temperature, precipitation, and sunshine hours after controlling for age, gender, and BMI. Conversely, individual factors explained approximately 38% of the variation in the observations. Conclusion: This study revealed that there was no association between weather conditions and the number of daily steps reported by individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes taking part in a physical activity intervention over two years. Despite the weather conditions, women and younger people reported more steps than their male and older counterparts.
Keywords:
physical activity; precipitation; prediabetes; steps; sunshine; temperature; type 2 diabetes 1. Introduction
Research strongly suggests that physical activity promotes healthy aging [1,2]. According to a 2016 estimation, approximately 28% of the world’s adult population is insufficiently physically active [3]. Individuals with type 2 diabetes are typically less physically active than those without this condition [4,5], and this can negatively affect their health. The evidence indicates that regular physical activity can effectively manage blood glucose levels and delay and even prevent complications in individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes [6]. It is crucial to comprehensively understand the factors affecting these groups’ physical activity levels to develop effective strategies for increasing engagement in physical activity and promoting healthy aging.
The key factors associated with physical activity engagement in older adults are demographics, personal and behavioral characteristics, psychological and social aspects, and physical environmental factors [7,8,9]. Physical environmental factors play an important role in shaping older adults’ physical activity behaviors [10]. Physical environmental factors include built environments like road safety and walking facilities, residential neighborhoods [9,11], as well as natural environmental factors such as weather, terrain, and vegetation [12,13]. The main challenges of promoting physical activity in older adults are posed by uncontrollable environmental conditions such as weather and day length [14,15]. In addition, physical decline and health issues are common during aging, and these phenomena are sensitive to adverse weather conditions, which could negatively affect older adults’ physical activity levels [15,16].
Adverse weather conditions are associated with a higher mortality and morbidity risk rate in individuals with chronic health conditions [17]. This negative correlation has been observed in outcomes related to cardiovascular issues and other health concerns linked to high- or low-temperature weather conditions [18,19]. Therefore, gathering evidence on how weather affects physical activity levels is imperative, particularly for those with chronic health conditions, as the information can help individuals make informed decisions about their outdoor activities and enable healthcare professionals to provide more favorable and affordable prescriptions for outdoor exercise and as it is crucial for individuals with chronic health conditions to reach the recommended level of physical activity [20]. Various studies have investigated the correlation between weather conditions and physical activity behavior. Some studies have utilized self-reports to evaluate physical activity levels [18,21,22], while others have objectively assessed daily physical activity over a short period [23,24,25]. Therefore, the need for long-term, objectively measured physical activity assessments with different weather conditions is paramount to overcome the limitations created by self-reported bias.
Although previous weather-related studies have not specifically focused on populations with chronic diseases, many have examined how weather and seasonal changes impact objectively measured physical activity levels in older adults [21,26,27]. For instance, Klenk et al. found a strong positive association between the daily maximum temperature and global radiation and objectively measured walking among older adults, but found no strong correlation with daylight length [28]. A similar study conducted with individuals aged 65 and over showed that they tend to spend more time outside and walk for longer on warm, sunny days [29]. Although weather data were collected daily and physical activity was measured objectively in these studies, they were short-term studies.
To our knowledge, few studies have investigated the influence of weather conditions on daily steps in people with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. A study by Dasgupta et al. explored the impact of seasonal changes on walking patterns and vascular risk factors in people with type 2 diabetes. The results showed that during the fall and winter months, daily steps decreased. Furthermore, this study found a negative correlation between daily steps and systolic blood pressure but showed no significant seasonal differences concerning Hemoglobin A1c levels [30].
The current study is a secondary analysis of the Sophia Step Study. The primary study revealed no intervention effect on cardiometabolic risk factors, although the intervention maintained moderate to vigorous physical activity over two years. However, there was significant variation in individual activity levels [31].
This study investigates the association of weather variations with daily self-monitored steps over two years among individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in Sweden.
2. Materials and Methods
This study is a secondary analysis using data from the two intervention groups participating in the Sophia Step Study, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) aimed at promoting physical activity among people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Participants were recruited from two urban primary healthcare centers in Stockholm and one rural primary healthcare center in southern Sweden over eight rounds. The first-round participants began the study in February 2013, while the last group started in January 2018. Those interested in participating were given information about the study and were booked for baseline assessment. A total of 385 participants were invited, and a general practitioner assessed each participant’s eligibility. A study protocol providing a detailed description of the Sophia Step Study has been published elsewhere [32].
Inclusion criteria: HbA1c > 39 mmol/mol or fasting blood glucose > 5.6 mmol/L, duration of type 2 diabetes diagnosis > 1 year, age 40–80, and ability to read, write, and express themselves in the Swedish language.
Exclusion criteria: myocardial infarction in the past six months, serum creatinine > 140, diabetic ulcer or risk for ulcers, prescribed insulin in the past six months, additional disease prohibiting physical activity, repeated hypoglycemia or severe hypoglycemia in the last 12 months, classified in the very-high-intensity activity group according to Stanford Brief Activity Survey [33], and no access to the internet.
In total, 203 participants were included as study participants before randomization. After applying the exclusion criteria, the project allocated 188 participants into three arms: 64 were assigned to the multiple-component group, 59 to a single-component group, and 65 to a standard care group. The multi-component group received daily step-monitoring support and individual and group counseling sessions, while the single intervention group only received a daily step-monitoring device. The standard care group did not receive a monitoring device. As a result, the current study only analyzed the daily step data of the two intervention groups, which included 120 participants.
Participants in the intervention groups were given step counters (Yamax Digwalker SW200: manufactured by Yamax Corporation Tokyo, Japan) and asked to monitor their daily steps using a website [34]. The participants were instructed to log their daily steps in a paper diary and then submit their logs weekly to the website for two years. In case any issues were encountered with the step counters or if it was lost, a new one could be obtained from the healthcare center or sent via post.
As the individuals reported their own steps, we found some typographical errors that required correction. As a result, we examined the data for outliers and concluded that any values below 200 or above 40,000 steps per day were unrealistic and treated them as missing data.
Weather data were obtained from the Swedish Metrological and Hydrological Institute. The data included the daily temperature in degrees Celsius (°C), daily precipitation in millimeters (mm), and daily sunshine (in seconds converted to hours). The study focused on two geographical regions, Stockholm and Kalmar, and all metrological stations were within a 20 km radius of the participants’ residences. A questionnaire with items on gender, diet, educational levels, and income collected demographic data at baseline. Weight and height were measured wearing light clothes at baseline.
Given multiple observations within each individual, a linear mixed model is an appropriate analysis, i.e., the data are not independent such as the case is in longitudinal studies [35]. However, due to the presence of several influential observations which may distort the relationships when using an ordinary linear mixed model, the data were modeled using a robust linear mixed model approach. Robust linear models can be used to remove some of the effects in such cases by weighting the data, giving influential cases less importance [36]. We modeled the association between steps (the dependent variable) and daily temperature, precipitation, and hours of daily sunshine (independent variables). The model was further adjusted for sex, age, intervention group, and body mass index (BMI). Due to the fact that the residuals were not normally distributed, a Box–Cox transformation was conducted, which indicated that a square root transformation of the dependent variable was suitable to satisfy the assumption of normally distributed residuals [37]. The p-values from the robust linear mixed model were calculated using the Satterthwaite method [38]. Figures were made using the ggplot2 package in R [39].
3. Results
The daily step data from 120 participants collected over two years were analyzed. Table 1 shows that 58% (n = 70) of the participants were men, the average age was 64.6 (sd. = 7) years, and 82% (n = 98) had type 2 diabetes, with an average disease duration of 8.7 (sd. = 6.3) years at baseline. The participants had a mean BMI of 29 (sd. = 4.3) kg/m2 and a mean waist circumference of 103 (sd. = 13.3) cm at baseline.

Table 1.
Characteristics of participants.
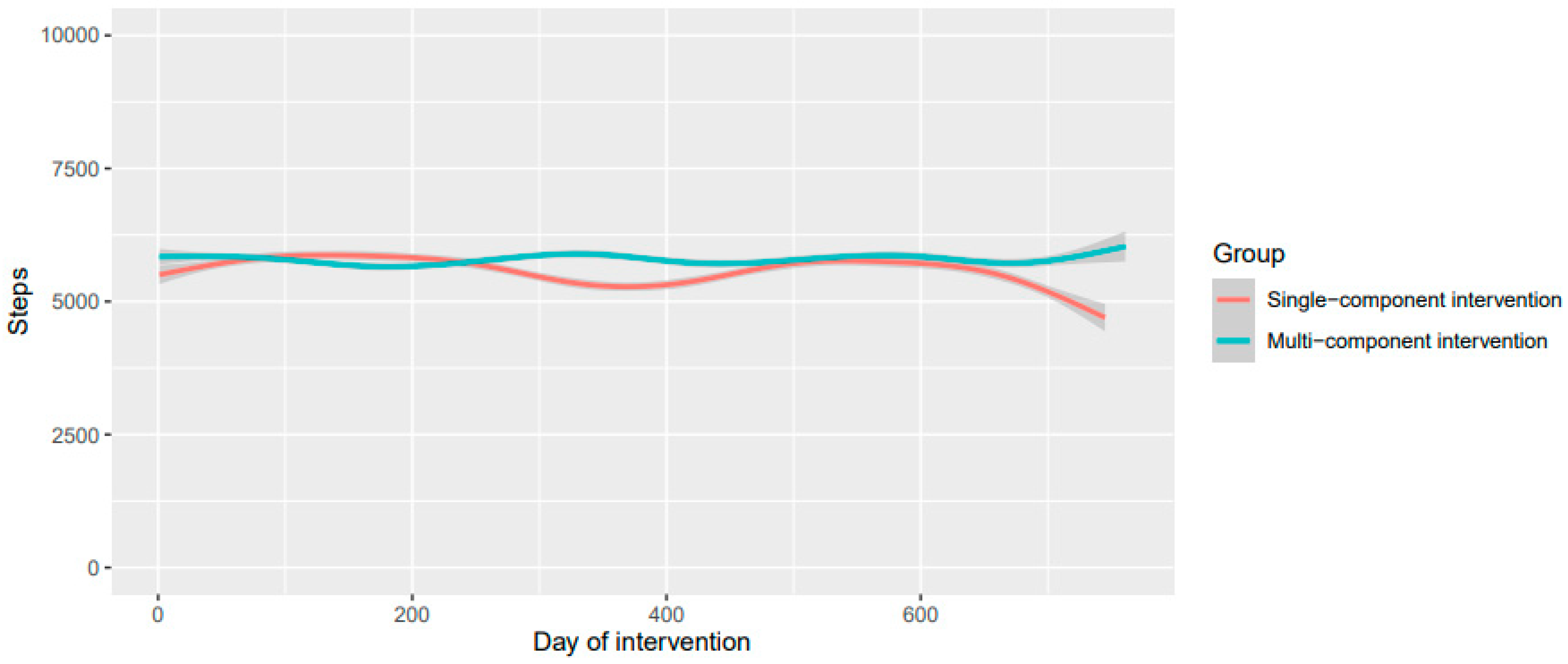
The mean daily step count at baseline was 7441 (sd. = 4157). Figure 1 shows the mean daily steps per intervention group during the Sophia Step Study intervention period. Over the two years, the mean temperature was 8.6 (sd. = 7.2) (°C), the mean precipitation per day was 1.5 (sd. = 3.8) mm, and the average sunshine hours in one day were 5.5 (sd. = 5).
Figure 1.
Mean daily steps per intervention group during the Sophia Step Study intervention period.
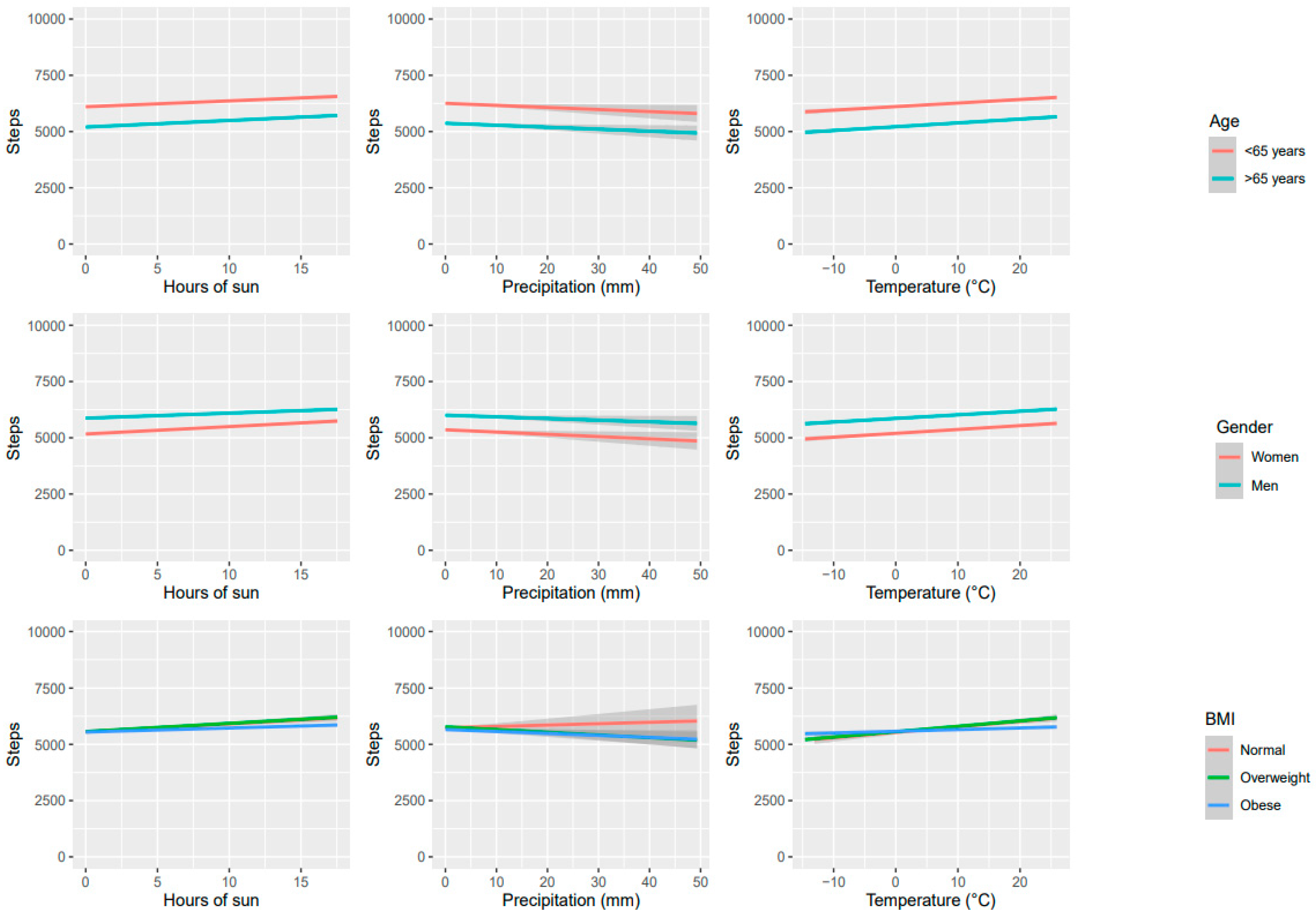
Figure 2 illustrates the association between step counts and weather variables, considering the participants’ age (below or above 65), gender (men or women), and body mass index (BMI) for normal weight, overweight, and obese individuals. Participants under the age of 65 had slightly higher daily step counts than those over 65. Moreover, women had slightly higher step counts as compared to men. These differences were not significant but remained consistent across various weather conditions such as temperature, precipitation, and sunshine duration. Finally, there was no association between weather conditions and step counts across different BMI levels.
Figure 2.
Associations between weather variables and step counts were analyzed by age, sex, and BMI level.
Table 2 presents the results of the robust linear mixed-effect model, showing that the independent variables (temperature, precipitation, and sunshine) accounted for 10% of the variation in daily steps after controlling for age, gender, and BMI. Conversely, individual factors explained approximately 38% of the variations in the daily steps. The analysis revealed no relationship between variations in weather conditions and daily step counts. Additionally, the overall beta estimates of the weather variables remained consistently below ±0.3. The intervention group was non-significant (p = 0.810) when tested in the model and was not included in the final model.

Table 2.
Coefficients of associations of weather variables with daily steps, covariates, and 95% confidence intervals from the robust linear mixed model.
4. Discussion
We examined the influence of different weather conditions on daily steps taken by people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes during a physical activity intervention. The study did not explain the variations in step counts among individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes during the two-year physical activity intervention based on weather conditions. However, the analysis revealed a significant relationship between weather variables and daily steps, mainly due to the high number of observations being analyzed (around 740 observations per individual). Additionally, the study found that higher temperatures, longer sunshine hours, and lower precipitation rates tended to increase daily step counts insignificantly. On the other hand, when weather conditions were unfavorable, there was a decreasing trend in daily steps.
The current study found that participants under the age of 65 tended to record more daily steps than those over 65. Women appeared to have a slightly higher and more consistent step count than men irrespective of weather conditions, but the difference was insignificant. The study also indicated that these differences in step counts remained consistent across various weather conditions, such as temperature, precipitation, and sunlight duration. While previous studies have suggested that men tend to walk more as a leisure activity than women [40,41], this study presents opposing findings that challenge this notion. There was no significant difference in step counts between the intervention groups in our current study, which is consistent with the previous results of the two intervention groups of the same RCT [31]. In addition, we found no association between weather conditions and step counts across different BMI levels and intervention groups in our study population.
A study investigating how weather affected the physical activity levels of older adults found that warmer temperatures and lower rainfall increase walking among seniors [42]. Similarly, another study conducted in Norway used accelerometers and hourly weather data to measure physical activity levels and discovered that increased temperatures have a positive impact on physical activity, while higher precipitation has a negative effect [16]. It should be noted that the previous studies only collected objective physical activity data for short periods, while this current study considered two years of self-reported steps. The discrepancies in physical activity outcomes may be due to differences in measurement methods, data collection types, period lengths, and weather conditions considered.
A two-year phone-based survey on physical activity found that participants were less likely to engage in outdoor physical activity in extreme hot and cold temperatures [19], which contradicts the current study’s findings without considering extreme weather conditions. However, this study also found that severe cold weather did not have an impact on the activity level of individuals with non-communicable diseases (NCDs), including type 2 diabetes, except for those with cardiovascular disease [19]. To understand the health implications for those with chronic illnesses, long-term studies that thoroughly examine the relationship between extreme weather and physical activity may be necessary.
It appears that physical activity levels are influenced by various factors rather than solely by weather variations. The results of the current study indicate that the amount of precipitation during the intervention was not significantly correlated with the number of steps taken. A previous study that analyzed the relationship between physical activity behavior and weather conditions using a wrist-worn Fitbit activity tracker over 13 months discovered that physical activity intensity played a crucial role in engaging in activity in adverse weather conditions. For instance, precipitation affected adults who partook in moderate to vigorous physical activity significantly more than those who partook in light physical activity [43]. This may be because weather conditions such as ice, snow, or severe cold would be more of an impediment for higher-intensity activities like running than for lower-intensity activities like walking. In addition, a study conducted by Aspvik et al. suggested that physically fit individuals may not be as affected by precipitation and other weather conditions as physically unfit individuals [16]. In the present study, we did not take into account exercise intensity or fitness levels but found no correlation between weather conditions and BMI.
A recent study aimed to investigate the possible correlation between weather conditions and outdoor walking in older adults with the activPAL sensor over the course of a week. The study found a strong correlation between longer sunny days and the participants’ inclination to spend more time outdoors and walk for longer periods of time [29]. This is in contrast to the findings of the current study, in which a clear association with sunshine was not observed.
In the current study, the participants were involved in a pedometer intervention program that lasted for over two years. The program involved using a pedometer to set a daily step goal and monitor daily steps. An interview study conducted with a sample of the participants revealed that the pedometer was a motivating factor and that they had adopted problem-solving techniques to achieve their goals [44]. The improved accessibility and accuracy of weather forecasting through digital platforms and public broadcasting services and warnings help individuals make informed decisions about when to be active [24,45], which may have contributed to the lower impact of weather on their physical activity. In addition, Ferguson et al. (2023) suggested that light physical activity is not significantly affected by extreme weather if proper clothing and equipment, such as an umbrella, are used to address the challenge [43]. The factors above highlight some of the significance of having effective adaptation strategies to cope with different weather conditions at the individual level [46]. Similarly, the current study’s participants were individuals with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes who were in relatively good health and had rather high levels of physical activity [31]. It is important to mention that they may have developed coping strategies to manage different weather conditions since they were part of a physical activity intervention.
One of the strengths of the current study is that step counts were measured over two years, which allowed the associations of various weather conditions over an extended time frame to be examined. Secondly, our study used daily weather data on temperature, precipitation, and sunshine to reduce the impact of external factors on seasonal patterns and physical activity. This approach is advantageous, as sudden weather changes are unlikely to occur within a day, minimizing changes in activity decisions.
Some of the limitations of the current study must be addressed. The present study is a secondary analysis of an intervention study which induces some bias to the internal validity. The study utilized step counters to measure the number of steps taken by participants. However, these pedometers were not sensitive enough for individuals with a high BMI, and as a result, some participants’ actual numbers of steps may have been underestimated. Additionally, participants were required to report their daily steps on a website, which could have led to social desirability bias. They were also instructed to convert time spent engaging in activities like swimming or cycling to an equivalent number of steps. It would have been better to keep track of whether the step counts were obtained from indoor, outdoor, or non-ambulant activities. Furthermore, the study did not take into account the impact of surface conditions during cold and icy seasons. Additionally, the pedometers did not measure the intensity, duration, or type of exercise that the participants engaged in [47]. Finally, the study participants were selected from only two geographical regions of Sweden, which limits the geographical diversity of the results. Therefore, it is essential to exercise caution when applying the results of this study to a larger population.
Finally, the current study’s findings reveal that individual factors play a more significant role in influencing self-monitored physical activity than weather conditions. However, it is still important to consider weather conditions while promoting physical activity on a larger scale. By implementing effective interventions and considering alternatives for indoor activities in extreme weather conditions, we can increase physical activity levels and enhance the safety of the participants in different weather conditions. This, in turn, can positively impact people’s well-being and public health.
5. Conclusions
Our study found no significant association between weather conditions (temperature, precipitation, and sunshine) and self-reported step counts among individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes taking part in a physical activity intervention over two years. Despite the weather conditions, women and younger people reported more steps compared to their male and older counterparts.
Author Contributions
J.R., M.H. and U.-B.J. contributed to the design and evaluation of the Sophia Step Study. J.R. collected the data with the help of a nurse specialized in diabetes. Y.W. analyzed the data descriptively and double-checked and cleaned the data files. P.B. analyzed the data, and J.R., Y.W., P.v.R., P.B., M.H. and U.-B.J. assisted in the validation and interpretation of the analysis. Y.W. developed the manuscript in close collaboration with J.R. P.v.R., P.B., M.H. and U.-B.J. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Sophiahemmet Foundation, The Swedish Diabetes Foundation (DIA2015-045), the King Gustav V and Queen Victoria’s Order of Freemason’s research foundation, Forte (Vårdalsstiftelsen) and the Skandia and Sibling Svensson’s Foundation for Medical Research. The funders had no role in the conducting or design of the study; in the collection, management, analysis, or interpretation of the data; or in the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript. Open-access funding was provided by Sophiahemmet University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Stockholm Regional Ethical Review Board approved this study (Dnr. 2012/1570-31/3, and 2015 2075-32), which was registered at ClinicalTrial.gov (NCT02374788). The study was conducted in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed Consent Statement
All participants provided their consent via signed informed consent forms before participating in the research.
Data Availability Statement
To access the data used in this study, one must follow the data legislation of Sweden and the EU since the datasets are not publicly available. Each request for access will be handled on a case-by-case basis and will require a data transfer and use agreement with the recipient to ensure appropriate regulation.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to all the individuals who participated in the Sophia Step Study and the healthcare professionals who provided their valuable contributions to the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Manning, K.M.; Hall, K.S.; Sloane, R.; Magistro, D.; Rabaglietti, E.; Lee, C.C.; Castle, S.; Kopp, T.; Giffuni, J.; Katzel, L.; et al. Longitudinal analysis of physical function in older adults: The effects of physical inactivity and exercise training. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e13987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalopoulou, C.; Stubbs, B.; Kralj, C.; Koukounari, A.; Prince, M.; Prina, A.M. Physical activity and healthy ageing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 38, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Worldwide trends in insufficient physical activity from 2001 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 358 population-based surveys with 1·9 million participants. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e1077–e1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, H. Daily physical activity and type 2 diabetes: A review. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerly, A.-M.; Kirk, A. Physical activity and sedentary behaviour of adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Pract. Diabetes 2018, 35, 86–89g. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Yardley, J.E.; Riddell, M.C.; Dunstan, D.W.; Dempsey, P.C.; Horton, E.S.; Castorino, K.; Tate, D.F. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notthoff, N.; Reisch, P.; Gerstorf, D. Individual Characteristics and Physical Activity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Gerontology 2017, 63, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lounassalo, I.; Salin, K.; Kankaanpää, A.; Hirvensalo, M.; Palomäki, S.; Tolvanen, A.; Yang, X.; Tammelin, T.H. Distinct trajectories of physical activity and related factors during the life course in the general population: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, D.W.; Barnett, A.; Nathan, A.; Van Cauwenberg, J.; Cerin, E.; Council on Environment and Physical Activity (CEPA)—Older Adults Working Group. Built environmental correlates of older adults’ total physical activity and walking: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys.Act. 2017, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.; Van Cauwenberg, J.; Hercky-Linnewiel, R.; Cerin, E.; Deforche, B.; Plaut, P. Understanding the relationships between the physical environment and physical activity in older adults: A systematic review of qualitative studies. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, S.S.; Whitt-Glover, M.C.; Lancaster, K.J.; Odoms-Young, A.M.; Gary, T.L. Built environment and health behaviors among African Americans: A systematic review. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2009, 36, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Bell, M. Off the couch and on the move: Global public health and the medicalisation of nature. Soc. Sci. Med. 2007, 64, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinn, A.P.; Evenson, K.R.; Herring, A.H.; Huston, S.L. The relationship between leisure, walking, and transportation activity with the natural environment. Health Place 2007, 13, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.B.; Ryan, D.A. Assessing the effects of weather conditions on physical activity participation using objective measures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 2639–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Luben, R.; Wareham, N.; Griffin, S.; Jones, A.P. Weather, day length and physical activity in older adults: Cross-sectional results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) Norfolk Cohort. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspvik, N.P.; Viken, H.; Ingebrigtsen, J.E.; Zisko, N.; Mehus, I.; Wisløff, U.; Stensvold, D. Do weather changes influence physical activity level among older adults?—The Generation 100 study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, A.G.; Hajat, S.; Gasparrini, A.; Rocklöv, J. Cold and heat waves in the United States. Environ. Res. 2012, 112, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, S.A.; Whitfield, G.P.; Davis, R.T.; Peterson, E.L.; Fulton, J.E.; Berrigan, D. Associations between Perceptions and Measures of Weather and Walking, United States—2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.Y.; Lam, H.Y.C.; Huang, Z.; Liu, S.; Goggins, W.B.; Mo, P.K.H.; Chan, E.Y.Y. Factors affecting outdoor physical activity in extreme temperatures in a sub-tropical Chinese urban population: An exploratory telephone survey. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.L.; Keusch, F.; Yan, T.; Clarke, P.J. The impact of weather on summer and winter exercise behaviors. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Masoumi, H.; Loureiro, V.; Gomes, M.; Ratinho, F.; Ribeiro, T.; Mehriar, M.; Rakovac, M.; Šentija, D.; Bahr, A.; et al. Seasonality and Objective Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour among Older Adults from Four European Countries. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.A.; Shaw, W.D.; Trousdale, M.A. The effect of weather on walking behavior in older adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2012, 20, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, L.R.; White, M.P.; Sarran, C.; Grellier, J.; Garrett, J.K.; Scoccimarro, E.; Smalley, A.J.; Fleming, L.E. The effects of meteorological conditions and daylight on nature-based recreational physical activity in England. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 42, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrisi, T.B.; Bittel, K.M.; West, A.B.; Hojjatinia, S.; Hojjatinia, S.; Mama, S.K.; Lagoa, C.M.; Conroy, D.E. Seasons, weather, and device-measured movement behaviors: A scoping review from 2006 to 2020. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnardottir, N.Y.; Oskarsdottir, N.D.; Brychta, R.J.; Koster, A.; van Domelen, D.R.; Caserotti, P.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Sverrisdottir, J.E.; Johannsson, E.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Comparison of Summer and Winter Objectively Measured Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Older Adults: Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility Reykjavik Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garriga, A.; Sempere-Rubio, N.; Molina-Prados, M.J.; Faubel, R. Impact of Seasonality on Physical Activity: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkley, S.; Herrmann, S. Seasonal Variation of Physical Activity in Community-Living vs. Residential-Dwelling Older Adults. Californian J. Health Promot. 2017, 15, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenk, J.; Büchele, G.; Rapp, K.; Franke, S.; Peter, R. Walking on sunshine: Effect of weather conditions on physical activity in older people. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2012, 66, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimek, M.; Peter, R.S.; Denkinger, M.; Dallmeier, D.; Rapp, K.; Rothenbacher, D.; Klenk, J. The relationship of weather with daily physical activity and the time spent out of home in older adults from Germany—The ActiFE study. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2022, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, K.; Joseph, L.; Pilote, L.; Strachan, I.; Sigal, R.J.; Chan, C. Daily steps are low year-round and dip lower in fall/winter: Findings from a longitudinal diabetes cohort. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2010, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, J.; Larsson, K.; Hagströmer, M.; Yngve, A.; Brismar, K.; Ainsworth, B.; Åberg, L.; Johansson, U.B. Effects of a three-armed randomised controlled trial using self-monitoring of daily steps with and without counselling in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes-the Sophia Step Study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, J.; Yngve, A.; Hagströmer, M.; Brismar, K.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Iskull, C.; Möller, P.; Johansson, U.-B. Physical activity promotion in the primary care setting in pre- and type 2 diabetes—The Sophia step study, an RCT. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Piliae, R.E.; Norton, L.C.; Haskell, W.L.; Mahbouda, M.H.; Fair, J.M.; Iribarren, C.; Hlatky, M.A.; Go, A.S.; Fortmann, S.P. Validation of a new brief physical activity survey among men and women aged 60–69 years. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://steg.se/en/start.aspx (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Twisk, J.W.R. Applied Longitudinal Data Analysis for Epidemiology. A Practical Guide; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Koller, M. robustlmm: An R Package for Robust Estimation of Linear Mixed-Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 75, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, S.G. Evaluating significance in linear mixed-effects models in R. Behav. Res. 2017, 49, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripley, B.D. (Ed.) Modern Applied Statistics with S; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pollard, T.M.; Wagnild, J.M. Gender differences in walking (for leisure, transport and in total) across adult life: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delclòs-Alió, X.; Marquet, O.; Vich, G.; Schipperijn, J.; Zhang, K.; Maciejewska, M.; Miralles-Guasch, C. Temperature and Rain Moderate the Effect of Neighborhood Walkability on Walking Time for Seniors in Barcelona. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, R.G.; van Lenthe, F.J. The hour-to-hour influence of weather conditions on walking and cycling among Dutch older adults. Age Ageing 2015, 44, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, T.; Curtis, R.; Fraysse, F.; Olds, T.; Dumuid, D.; Brown, W.; Esterman, A.; Maher, C. Weather associations with physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep patterns of Australian adults: A longitudinal study with implications for climate change. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2023, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, J.; Lööf, H.; Yngve, A.; Hagströmer, M.; Brismar, K.; Johansson, U.-B. ‘This is why I’m doing a lot of exercise’—A qualitative study of participant’s experiences of the Sophia Step Study. Int. Diabetes Nurs. 2017, 14, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjatinia, S.; Hojjatinia, S.; Lagoa, C.M.; Brunke-Reese, D.; Conroy, D.E. Person-specific dose-finding for a digital messaging intervention to promote physical activity. Health Psychol. 2021, 40, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, A.; Hitchings, R. Weather and exercise: A comparative review and the role of geographers. Geogr. Compass 2023, 17, e12686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Toth, L.P.; LaMunion, S.R.; Crouter, S.E. Step Counting: A Review of Measurement Considerations and Health-Related Applications. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).