Lipophilic Toxins in Chile: History, Producers and Impacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Historical Overview
3. Monitoring of Lipophilic Shellfish Toxins in Chile
4. Lipophilic Shellfish Toxin Producers in Chile: Distribution and Toxic Events
4.1. Dinophysis and Its Lipophilic Toxins
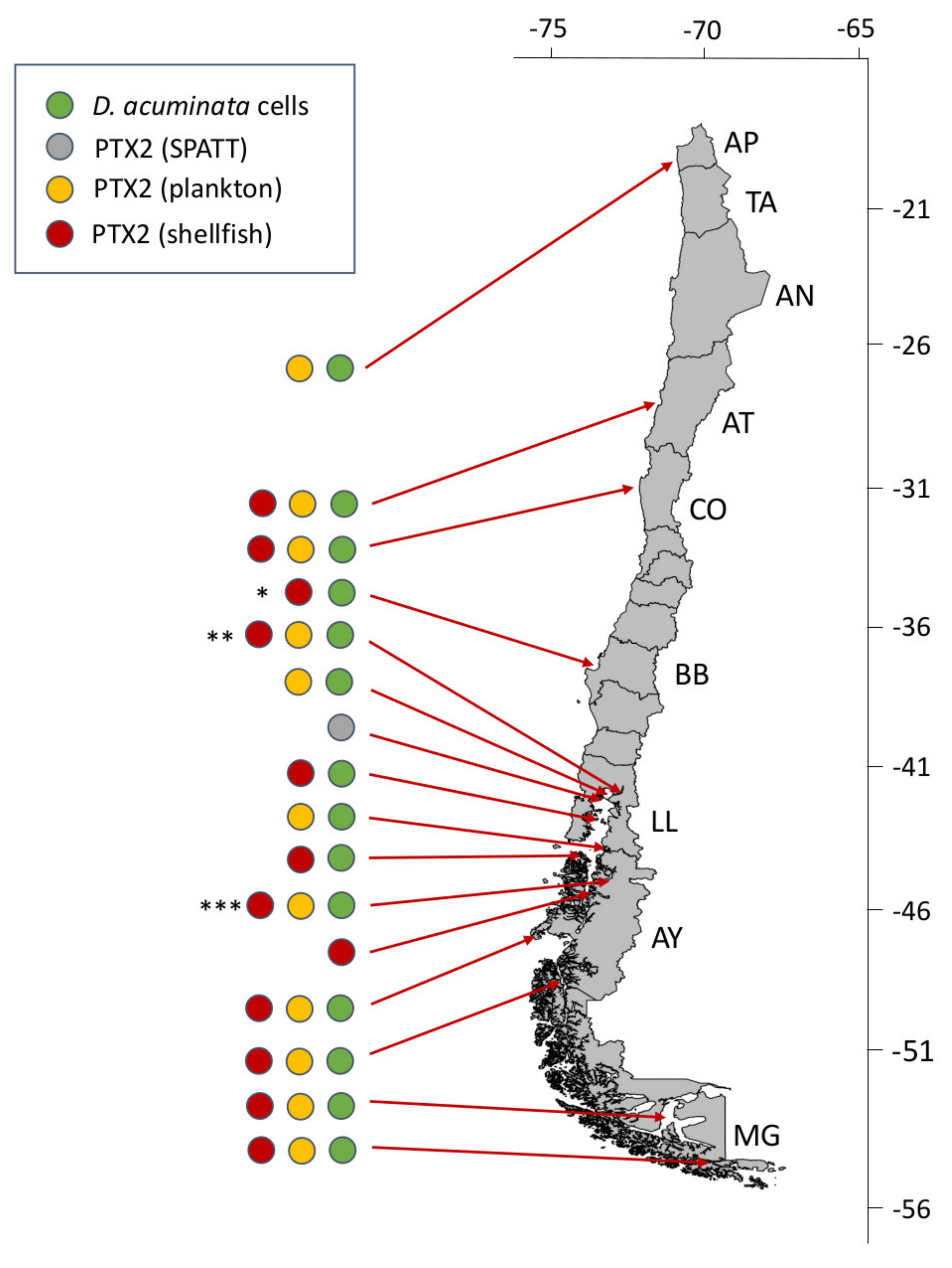
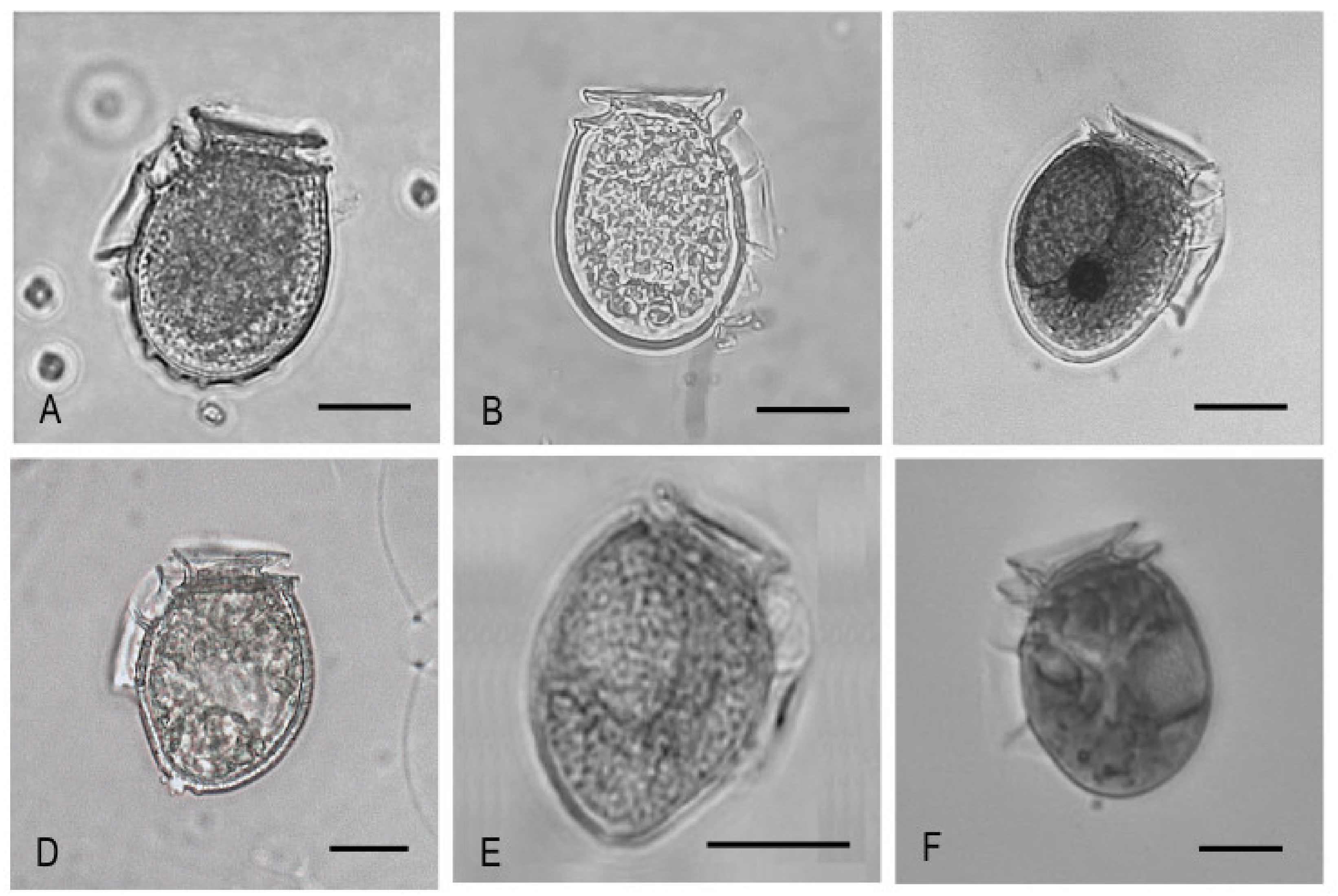
4.1.1. The Dinophysis acuminata Complex
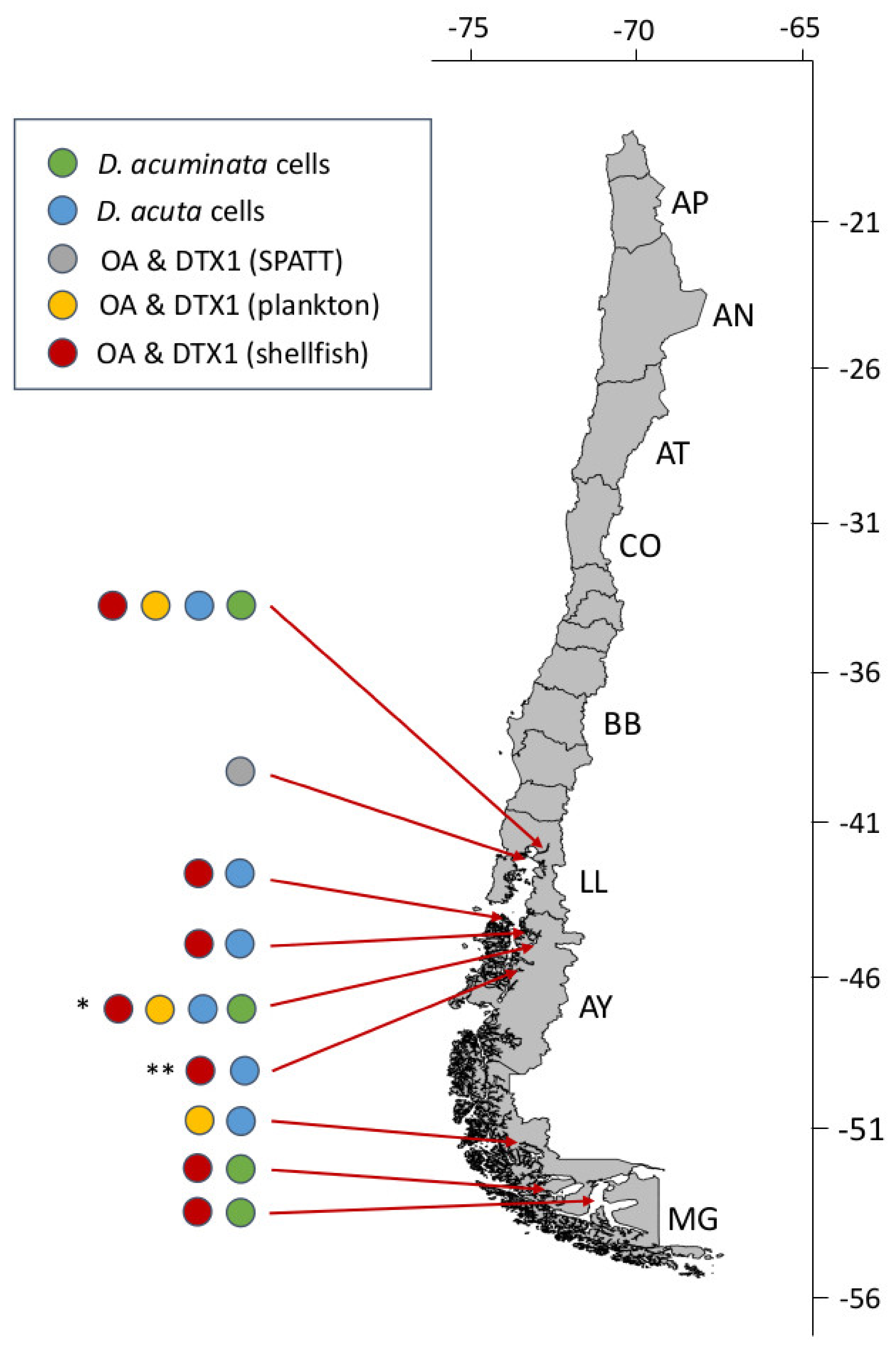
4.1.2. Dinophysis acuta
4.1.3. Other Dinophysis spp.
4.2. Protoceratium reticulatum and Other Yessotoxin Producers
4.2.1. Protoceratium reticulatum
4.2.2. Other YTX Producers
4.3. Azadinium, Amphidoma and Azaspiracids
4.4. Emerging Lipophilic Toxins and Their Producers
4.5. Benthic Primary Sources of LST: Epibenthic Prorocentrum Species
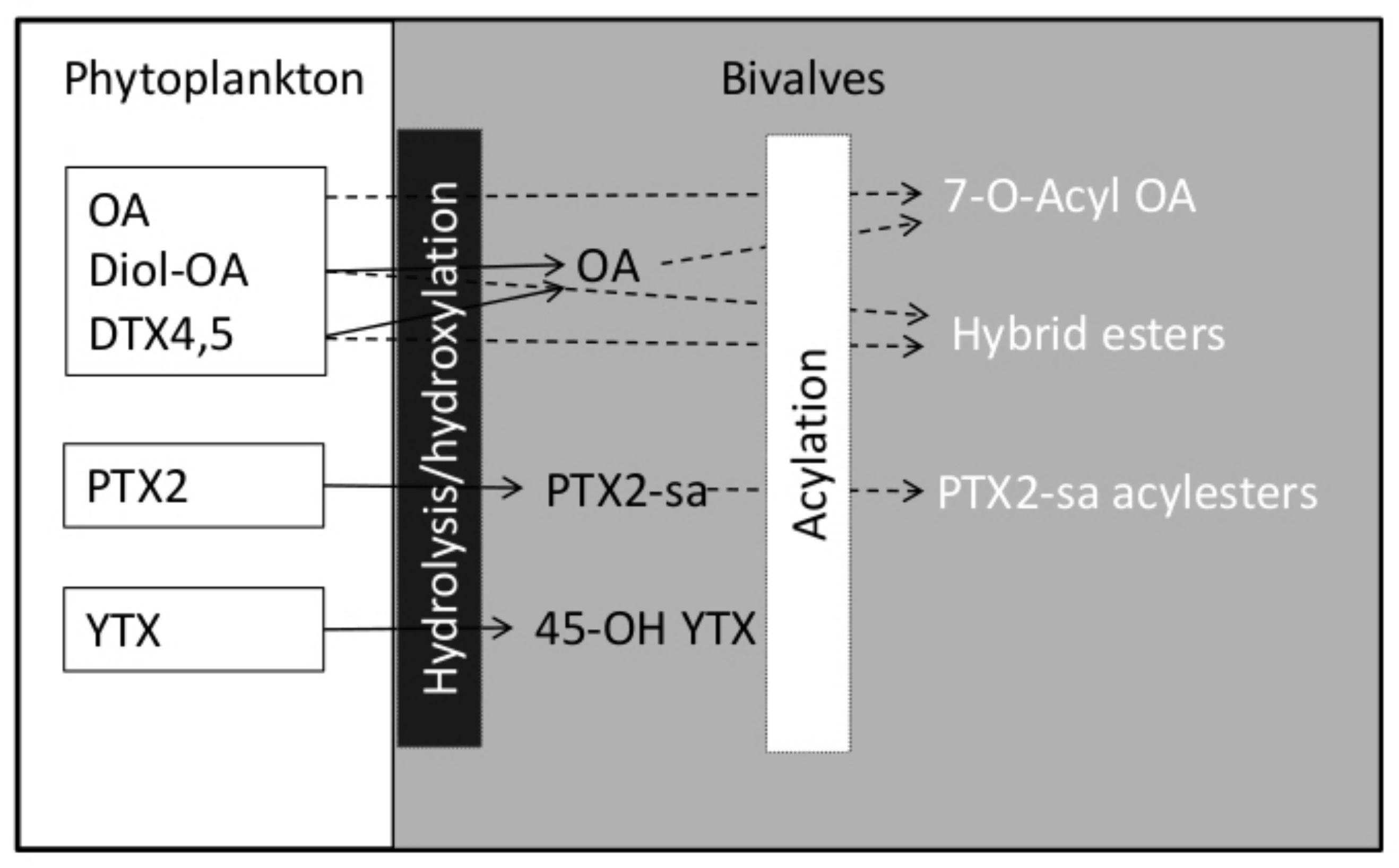
5. Lipophilic Shellfish Toxins and Their Accumulation and Biotransformation by Bivalve Molluscs in Chile
6. New European Regulations for Lipophilic Toxins: Impacts on the Chilean Shellfish Industry, Artisanal Fisheries and Other Coastal Commodities
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grattan, L.M.; Holobaugh, S.; Morris, J.G. Harmful algal blooms and public health. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilarino, N.; Louzao, M.C.; Abal, P.; Cagide, E.; Carrera, C.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Human poisoning from marine toxins: Unknowns for optimal consumer protection. Toxins 2018, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Gil, S.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Velo-Suárez, L.; Reguera, B. Considerations on the toxigenic nature and prey sources of Phalacroma rotundatum. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 64, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; MacKenzie, L.; Yasumoto, T. Identification of Protoceratium reticulatum as the biogenetic origin of yessotoxin. Nat. Tox. 1997, 5, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubaro, A.; Sidari, L.; Della-Loggia, R.; Yasumoto, T. Occurrence of yessotoxin-like toxins in phytoplankton and mussels from Northern Adriatic Sea. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1998; pp. 470–472. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, L.; McNabb, P.; de Salas, M.; Briggs, L.; Beuzenberg, V.; Gladstone, M. Yessotoxin production by Gonyaulax spinifera. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E.; Regueiro, J.; Blanco, J.; Fraga, S. Gonyaulax taylorii, a new yessotoxins-producer dinoflagellate species from Chilean waters. Harmful Algae 2016, 58, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Tebben, J.; Trefault, N.; Gu, H. Two novel azaspiracids from Azadinium poporum, and a comprehensive compilation of azaspiracids produced by Amphidomataceae, (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2019, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paz, B.; Danaras, A.H.; Norte, M.; Riobó, P.; Franco, J.M.; Fernández, J.J. Yessotoxins, a group of marine polyether toxins: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 73–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molgó, J.; Marchot, P.; Aráoz, R.; Benoit, E.; Iorga, B.I.; Zakarian, A.; Taylor, P.; Bourne, Y.; Servent, D. Cyclic imine toxins from dinoflagellates: A growing family of potent antagonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguera, B.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Díaz, P.A.; Pizarro, G.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M.; Blanco, J. Dinophysis toxins: Causative organisms, distribution and fate in shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 394–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Correa, J.; Muñíz, S.; Mariño, C.; Martín, H.; Arévalo, F. Evaluación del impacto de los métodos y niveles utilizados para el control de toxinas en el mejillón. Rev. Galega Recur. Mar. 2013, 3, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.A.; Álvarez, A.; Varela, D.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Díaz, M.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M.; Aguilera-Belmonte, A.; Guzmán, L.; Uribe, E.; et al. Impacts of harmful algal blooms on the aquaculture industry: Chile as a case study. Perspect. Phycol. 2019, 6, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Valencia, I.; Hernández-Castro, J.E.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Turner, A.D.; O’Neill, A.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; López-Cortés, D.J.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.J.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E. Lipophilic toxins in wild bivalves from the Southern Gulf of California, Mexico. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APROMAR. Aquaculture in Spain 2020; Asociación Empresarial de Productores de Cultivos Marinos de España (APROMAR): Madrid, Spain, 2020; p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, L.; Espinoza-González, O.; Carbonell, P.; Martínez, R.; Piarro, G.; Salgado, P.; Mardones, J.; Fuenzalida, G.; Besoain, V.; Cascales, E.; et al. Programa de Manejo y Monitoreo de las Mareas Rojas en el Sistema de Fiordos y Canales de Chile, XIII Etapa Año 2019–2020; Subsecretaria de Economía y EMT—Instituto de Fomento Pesquero: Valparaíso, Chile, 2020; p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón, C.; Toro, C.; Pacheco, H.; Pizarro, G.; Daza, E. Evento Mortandad de Erizos en el Sector de Malaespina, Canal Trinidad. Región de Magallanes y Antártica Chilena. Reporte Interno; Instituto de Fomento Pesquero: Punta Arenas, Chile, 2017; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Frangopulos, M.; Iriarte, J.I.; González, H.; Pacheco, H.; Menschel, E.; Pinto, M.; Alarcón, C.; Toro, C. Distribution and abundance of toxic HABs and oceanographic conditions during summer 2017 in sub antarctic waters of Southern Chile. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018; p. 296. [Google Scholar]
- Toro, C.; Alarcón, C.; Pacheco, H.; Salgado, P.; Frangopulos, M.; Rodríguez, F.; Fuenzalida, G.; Raimapo, R.; Pizarro, G.; Guzmán, L. Harmful Algal bloom species associated with massive Atlantic salmon mortalities while transported through the Gulf of Penas, southern Chile. In Harmful Algae 2018—From Ecosystems to Socioecosystems. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018; Hess, P., Ed.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae: Nantes, France, 2020; pp. 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, F.; Cortez, H.; Uribe, C.; Peña, P.; Cassis, D. Mortality of Chilean farmed salmon in wellboats in transit through a Karenia bloom. Harmful Algae News 2017, 57, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/1709 of 23 September 2021 amending Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/627 as regards uniform practical arrangements for the performance of official controls on products of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union Legis. 2021, 339, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Avaria, S. Red tides off the coast of Chile. In Toxic Dinoflagellate Blooms; Taylor, L.T., Seliger, H.H., Eds.; Elsevier/North-Holland: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Avaria, S.; Muñoz, P. Composición y biomasa del fitoplancton del norte de Chile en mayo de 1981 (Operación Oceanografica MARCHILE XII-ERFEN III). Cienc. Tecnol. Mar. 1983, 7, 109–140. [Google Scholar]
- Avaria, S.; Muñoz, P.; Uribe, E. Composición y biomasa del fitoplancton marino del norte de Chile en diciembre de 1980 (Operación oceanográfica MARCHILE XI-ERFEN II). Cienc. Tecnol. Mar. 1982, 6, 5–36. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Mareas rojas en el plancton del Pacífico oriental: Informe del Segundo Taller del Programa de Plancton del Pacífico Oriental, Instituto del Mar: Callao, Perú 19–20 de Noviembre de 1981. Inf. UNESCO Cienc. Mar. 1982, 19, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.; Palma, S. Progress in the Oceanographic Knowledge of Chilean Interior Water from Puerto Montt to Cape Horn; Comité Oceanográfico Nacional—Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso: Valparaíso, Chile, 2006; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, M.; Blanco, J.L.; Osses, J. Investigación Monitoreo de Marea Roja en la XII Región. Informe a la Subsecretaría de Pesca; Instituto de Fomento Pesquero: Punta Arenas, Chile, 1993; p. 181. [Google Scholar]
- Uribe, J.C.; Guzmán, L.; Jara, S. Monitoreo Nensual de la Marea Roja en la XI y XII Regiones; Fondo de Investigación Pesquera: Valparaíso, Chile, 1995; p. 282. [Google Scholar]
- Lembeye, G.; Marcos, N.; Sfeir, A.; Molinet, C.; Jara, F. Seguimiento de la Toxicidad en Recursos Pesqueros de Importancia Comercial en la X y XI Región; Informe Final Proyecto FIP 97/49; Universidad Austral de Chile: Puerto Montt, Chile, 1998; p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, L.; Campodónico, I. Marea roja en la Región de Magallanes; Publicaciones del Instituto de la Patagonia, Series Monopgráficas, 9; Instituto de la Patagonia: Punta Arenas, Chile, 1975; pp. 3–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lembeye, G.; Yasumoto, T.; Zhao, J.; Fernández, R. DSP outbreak in Chilean fjords. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea; Smayda, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 525–529. [Google Scholar]
- Lembeye, G.; Campodonico, I.; Guzmán, L.; Kiguel, C. Intoxicaciones por consumo de mariscos del Estero de Reloncavi (X Región), Chile (1970–1980). In Proceedings of the Jornadas de Ciencias del Mar, Montemar, Chile, 12–14 August 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Lembeye, G.; Cenci, G.; Wall, B.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin-1 in mussels from Chile, Italy and Ireland. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea; Smayda, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Campodonico, I.; Guzmán, L. Marea roja producida por Amphidoma sp. en el Estrecho de Magallanes. An. Inst. Patagon. 1974, 5, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Takizawa, A. Fluorometric measurement of yesstoxins in shellfish by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E.; Díaz, R.; Braun, M.; Mariño, C.; Blanco, J. Bloom of the yessotoxin producing dinoflagellate Protoceratium reticulatum (Dinophyceae) in northern Chile. J. Sea Res. 2011, 65, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Salud. Programa Nacional de Vigilancia y Control de las Intoxicaciones por Fenómenos Algales Nocivos “Marea roja”; Subsecretaría de Salud Pública: Santiago, Chile, 2018; p. 32.
- Sernapesca. Manual de Inocuidad y Certificación; Servicio Nacional de Pesca y Acuicultura: Valparaíso, Chile, 2018; Available online: http://www.sernapesca.cl/manuales-publicaciones/manual-de-inocuidad-y-certificacion (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- EURLMB. EU Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC-MS/MS; Version 5; European Union Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins: Vigo, Spain, 2015; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- EURLMB. Standard Operating Procedure for Detection of Okadaic Acid, Dinophysistoxins and Pectenotoxins by Mouse Bioassay Version 4.0 (April 2007); European Union Reference Laboratory for Marine Biotoxins: Vigo, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Murata, M.; Oshima, T.; Matsumoto, C.; Clardy, J. Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. In Seafood Toxins; Ragelis, E.P., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; pp. 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, G.; Arévalo, F.; Moroño, A.; Riobó, P.; Franco, J.; Zamora, C.; Guzmán, L. Emergent lipophiclic toxins in the Magellan region (47–55 °S), Chile. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Wellington, New Zealand, 27 October–1 November 2014; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, G.; Zamora, C.; Toro, J.; Raimapo, R.; Alarcón, C.; Pacheco, H. Análisis de Toxinas Lipofílicas Mediante LC-MS/MS en Muestras de Fitoplancton y Moluscos Recolectadas Durante la Floración Estival 2013 de Dinophysis spp. en Magallanes; Instituto de Fomento Pesquero—Subsecretaría de Economía: Punta Arenas, Chile, 2014; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, G.; Díaz, P.A.; Godoy, M.; Araya, M.; Ganuza, I.; Pino, R.; Álvarez, F.; Rengel, J.; Hernández, C.; Uribe, E.; et al. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Mesodesma donacium during an exceptional bloom of Alexandrium catenella associated to an intense mass mortality. Toxins 2019, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armijo, J.; Oerder, V.; Auger, P.; Bravo, A.; Molina, E. The 2016 red tide crisis in southern Chile: Possible in uence of the mass oceanic dumping of dead salmons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza-González, O.; Guzmán, L.; Salgado, P.; Carbonell, P.; Norambuena, L.; Cascales, E.; Mardones, J.; Paredes, J.; Fuenzalida, G.; Tardón, H.; et al. Programa de Manejo y Monitoreo de las Floraciones Algales Nocivas y Toxinas Marinas en el Océano Pacífico del Centro Sur de Chile (36–44° S), Etapa III, 2020–2021; Informe Final (Tomo I y II); Subsecretaría de Economía y EMT, Instituto de Fomento Pesquero: Punta Arenas, Chile, 2021; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Isla, B.A.; Barrera, F.; Carrasco, D.; Cigarra, L.; López-Rivera, A.M.; Rubilar, I.; Alcayaga, C.; Contreras, V.; Seguel, M. Comprehensive study of the occurrence and distribution of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish from production areas in Chile. In Harmful Algae 2018—From Ecosystems to Socioecosystems, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018; Hess, P., Ed.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae: Nantes, France, 2020; pp. 163–166. ISBN 978-87-990827-7-3. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo, F.; Pazos, Y.; Correa, J.; Salgado, C.; Moroño, A.; Paz, B.; Franco, J.M. First reported case of yessotoxins in mussels in the Galician rias during a bloom of Lingulodinium polyedrum Stein (dodge). In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Molluscan Shellfish Safety, Galway, Ireland, 14–18 June 2004; pp. 184–189. [Google Scholar]
- Sernapesca. Anuario Estadistico de Pesca; Servicio Nacional de Pesca: Valparaíso, Chile, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.; Molinet, C.; Cáceres, M.; Valle-Levinson, A. Seasonal and intratidal distribution of Dinophysis spp. in a Chilean fjord. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.A.; Álvarez, G.; Seguel, M.; Marín, A.; Krock, B. First detection of pectenotoxin-2 in shellfish associated with an intense spring bloom of Dinophysis acuminata on the central Chilean coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves de Souza, C.; Varela, D.; Contreras, C.; de la Iglesia, P.; Fernández, P.; Hipp, B.; Hernández, C.; Riobó, P.; Reguera, B.; Franco, J.M.; et al. Seasonal variability of Dinophysis spp. and Protoceratium reticulatum associated to lipophilic shellfish toxins in a strongly stratified Chilean fjord. Deep Sea Res. II 2014, 101, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrich, A.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Álvarez, G.; Reguera, B.; Fernández-Pena, C.; Rodríguez-Villegas, C.; Araya, M.; Álvarez, F.; Barrera, F.; Karasiewicz, S.; et al. Niche differentiation of Dinophysis acuta and D. acuminata in a stratified fjord. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.; Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E. Identification of pectenotoxins in plankton, filter feeders, and isolated cells of a Dinophysis acuminata with an atypical toxin profile, from Chile. Toxicon 2007, 49, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krock, B.; Seguel, C.; Valderrama, K.; Tillmann, U. Pectenotoxins and yessotoxin from Arica Bay, North Chile as determined by tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2009, 54, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Álvarez, G.; Rengel, J.; Diaz, R.; Marino, C.; Martin, H.; Uribe, E. Accumulation and biotransformation of Dinophysis toxins by the surf clam Mesodesma donacium. Toxins 2018, 10, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alves de Souza, C.; Iriarte, J.L.; Mardones, J.I. Interannual variability of Dinophysis acuminata and Protoceratium reticulatum in a Chilean fjord: Insights from the realized niche analysis. Toxins 2019, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fux, E.; Smith, J.L.; Tong, M.; Guzmán, L.; Anderson, D.M. Toxin profles of five geographical isolates of Dinophysis spp. from North and South America. Toxicon 2011, 57, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uribe, J.C.; García, C.; Rivas, M.; Lagos, N. First report of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in Magellanic fjord, Southern Chile. J. Shellfish Res. 2001, 20, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes-Mella, J.; Mardones, J.; Norambuena, L.; Fuenzalida, G.; Nagai, S. First culture of Dinophysis acuminata from southern Chile: Ecophysiology, toxin production and phylogeny. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Harmful Algae, La Paz, Mexico, 10–15 October 2021; p. 161. [Google Scholar]
- Baldrich, A.M.; Molinet, C.; Reguera, B.; Espinoza-González, O.; Pizarro, G.; Rodríguez-Villegas, C.; Opazo, D.; Mejías, P.; Díaz, P.A. Interannual variability in mesoscale distribution of Dinophysis acuminata and D. acuta in Northwestern Patagonian fjords. Harmful Algae 2022. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.A.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Álvarez, G.; Garreaud, R.; Pinilla, E.; Díaz, M.; Sandoval, A.; Araya, M.; Álvarez, F.; Rengel, J.; et al. Multiscale physical background to an exceptional harmful algal bloom of Dinophysis acuta in a fjord system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, G.; Alarcón, C.; Pacheco, H.; Toro, C.; Salgado, P.; Guzmán, L. Decadal and bi-decadal distribution of harmful species in the Magellan. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.A.; Fernández-Pena, C.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Baldrich, A.; Díaz, M.; Rodríguez, F. Dinophysis Ehrenberg (Dinophyceae) in Southern Chile harbours red cryptophyte plastids from Rhodomonas/Storeatula clade. Harmful Algae 2020, 99, 101907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, P.; Avaria, S.; Sievers, H.; Prado, R. Presencia de dinoflagelados toxicos del genero Dinophysis en el seno Aysén, Chile. Rev. Biol. Mar. 1992, 27, 187–212. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, L. Marea roja en el norte de Chile. Not. Mens. Mus. Nac. His. Nat. 1976, 243–244, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Avaria, S.; Muñoz, P. Efectos del fenómeno “El Niño” sobre el fitoplancton marino del norte de Chile en diciembre de 1982. Cienc. Tecnol. Mar. 1985, 9, 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Santander, E.; Herrera, L.; Merino, C. Fluctuación diaria del fitoplancton en la capa superficial del océano durante la primavera de 1997 en el norte de Chile (20°18′ S): II. Composición específica y abundancia celular. Rev. Biol. Mar. Ocenog. 2003, 38, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Orellana, E. Sistemática (Dinoflagellatae) y Distribución del Fitoplancton Marino en un Area del Pacífico Sudoriental (Operación Oceanográfica “MARCHILE VII” Marzo 1968). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Católica del Valparaíso, Valparaíso, Chile, 1971; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.A.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Álvarez, G.; Araya, M.; Álvarez, F.; Reguera, B. Cell cycle, division rate, and feeding of the heterotroph Phalacroma rotundatum in a Chilean Fjord. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seguel, M.; Sfeir, A.; Albornoz, V.; Gangas, M.; Molinet, C.; Díaz, P. Distribucion de los quistes de Alexandrium catenella y Protoceratium reticulatum (Dinophyceae) en la Region Sur-Austral de Chile. Cienc. Tecnol. Mar. 2010, 33, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Seguel, M.; Sfeir, A.; González, J.; Díaz, P.; Molinet, C.; Labra, G. Quistes de dinoflagelados en sedimentos marinos del sur de Chile con énfasis en Alexandrium catenella y Protoceratium reticulatum. Cienc. Tecnol. Mar. 2011, 34, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.A.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M.; Díaz, M.; Labra, G.; Figueroa, R. Coupling planktonic and benthic shifts during a bloom of Alexandrium catenella in southern Chile: Implications for bloom dynamics and recurrence. Harmful Algae 2014, 40, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.A.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M.; Díaz, M.; Labra, G.; Figueroa, R.I. Species diversity and abundance of dinoflagellate resting cysts seven months after a bloom of Alexandrium catenella in two contrasting coastal systems of the Chilean Inland Sea. Eur. J. Phycol. 2018, 53, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Villegas, C.; Lee, M.; Salgado, P.; Figueroa, R.I.; Baldrich, A.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Tomasetti, S.J.; Niklitschek, E.; Díaz, M.; Álvarez, G.; et al. Drivers of dinoflagellate benthic cyst assemblages in the NW Patagonian Fjords System and its adjacent oceanic shelf, with a focus on harmful species. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 47378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, V.; Escribano, R.; Herrera, L. High frequency responses of nano-plankton and microplankton to wind-driven upwelling off northern Chile. J. Marine Syst. 2009, 78, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Fiorillo, I. Biochemical features of a Protoceratium reticulatum red tide in Chipana Bay (Northern Chile) in summer conditions. Sci. Mar. 2010, 74, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz, P.A.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Baldrich, A.; Álvarez, G.; Rodríguez, F.; Montero, P.; Igor, G.; Daneri, G.; Seguel, M.; Guzmán, L.; et al. An exceptional summer bloom of Dinophysis acuta in a Chilean fjord. In Harmful Algae 2018—From Ecosystems to Socioecosystems, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018; Hess, P., Ed.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae: Nantes, France, 2020; pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-87-990827-7-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, G.; Garrido, C.; Zamora, C.; Alarcón, C.; Raimapo, R.; Salgado, P.; Pacheco, H.; Guzmán, L.; Paz, B.; Álvarez-Chaver, P.; et al. Distribución de Alexandrium catenella y de toxina paralizante en el fitoplancton y mariscos entre el estrecho de Magallanes y Tierra del Fuego (primavera 2010). Cienc. Tecnol. Mar. 2015, 36, 35–68. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, P. Revisión taxonómica de los dinoflagelados de Chile. Rev. Biol. Mar. 1985, 21, 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tillmann, U.; Trefault, N.; Krock, B.; Parada-Pozo, G.; De la Iglesia, R.; Vásquez, M. Identification of Azadinium poporum (Dinophyceae) in the Southeast Pacific: Morphology, molecular phylogeny, and azaspiracid profile characterization. J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 350–367. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E.; Ávalos, P.; Mariño, C.; Blanco, J. First identification of azaspiracid and spirolides in Mesodesma donacium and Mulinia edulis from Northern Chile. Toxicon 2010, 55, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rivera, A.; O’Callaghan, K.; Moriarty, M.; O’Driscoll, D.; Hamilton, B.; Lehane, M.; James, K.J.J.; Furey, A.; O’Callaghan, K.; Moriarty, M.; et al. First evidence of azaspiracids (AZAs): A family of lipophilic polyether marine toxins in scallops (Argopecten purpuratus) and mussels (Mytilus chilensis) collected in two regions of Chile. Toxicon 2010, 55, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, P.; Díaz, L.; Pesse, N.; Vivanco, X.; Guzmán, L. Monitoreo de Alexandrium catenella en Zona no Declarada de la Región de Atacama y Coquimbo; Informe Final Convenio—Asesoria Integral para la Toma de Decisiones en Pesca y Acuicultura; Instituto de Fomento Pesquero: Punta Arenas, Chile, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, P.; Pizarro, G.; Guzmán, L. Distribución de Alexandrium ostenfeldii y Alexandrium sp. (Dinophyceae) en Chile. In Proceedings of the XXXII Congreso de Ciencias del Mar, Punta Arenas, Chile, 22–26 October 2012; Sociedad Chilena de Ciencias del Mar: Punta Arenas, Chile, 2012; p. 267. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, P.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Bravo, I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon 2015, 103, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, M.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, M.G. Revisiting the taxonomy of the “Dinophysis acuminata complex” (Dinophyta). Harmful Algae 2019, 88, 101657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolny, J.L.; Egerton, T.A.; Handy, S.M.; Stutts, W.L.; Smith, J.L.; Whereat, E.B.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Henrichs, D.W.; Campbell, L.; Deeds, J.R. Characterization of Dinophysis spp. (Dinophyceae, Dinophysiales) from the mid-Atlantic region of the United States. J. Phycol. 2020, 56, 404–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, P.A.; Ruiz-Villareal, M.; Mouriño-Carballido, B.; Fernández-Pena, C.; Riobó, P.; Reguera, B. Fine scale physical-biological interactions during a shift from relaxation to upwelling with a focus on Dinophysis acuminata and its potential ciliate prey. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 175, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalera, L.; Pazos, Y.; Doval, M.D.; Reguera, B. A comparison of integrated and discrete depth sampling for monitoring toxic species of Dinophysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcántara-Rubira, A.; Bárcena-Martínez, V.; Reyes-Paulino, M.; Medina-Acaro, K.; Valiente-Terrones, L.; Rodríguez-Velásquez, A.; Estrada-Jiménez, R.; Omar Flores-Salmón, O. First report of okadaic acid and pectenotoxins in individual cells of Dinophysis and in scallops Argopecten purpuratus from Perú. Toxins 2018, 10, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Krock, B.; Hansen, P.J. Production and excretion of okadaic acid, pectenotoxin-2 and a novel dinophysistoxin from the DSP-causing marine dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta—Effects of light, food availability and growth phase. Harmful Algae 2013, 23, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, K.; Andersen, P. Relation between the concentration of Dinophysis acuminata and diarrheic shellfish poisoning toxins in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) during a toxic episode in the Limfjord (Denmark), 2006. J. Shellfish Res. 2007, 26, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Samdal, I.A.; Sandvik, M.; Petersen, D.; Quilliam, M.A.; Naustvoll, L.J.; Rundberget, T.; Torgersen, T.; Hovgaard, P.; et al. A novel pectenotoxin, PTX-12, in Dinophysis spp. and shellfish from Norway. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, L. Marea roja en la bahía de San Jorge—Antofagasta, Chile. Not. Mens. Mus. Nac. His. Nat. 1978, 266, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Marasigan, A.M.; Sato, S.; Fukuyo, Y.; Kodama, M. Accumulation of a high level of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in the green mussel Perna viridis during a bloom of Dinophysis caudata and Dinophysis miles in Sapian Bay, Panay Island, the Philippines. Fish. Res. 2001, 67, 994–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, G.; Moroño, A.; Paz, P.; Franco, J.M.; Pazos, Y.; Reguera, B. Evaluation of passive samplers as a monitoring tool for early warning of Dinophysis toxins in shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3823–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reguera, B.; Gonzáles-Gil, S.; Delgado, M. Dinophysis diegensis is a life history stage of Dinophysis caudata (Dinophyceae, Dinophysiales). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balech, E. Los Dinoflagelados del Atlántico Sudoccidental; Publicaciones Especiales del Instituto Español de Oceanografía: Madrid, Spain, 1988; Volume 1, p. 310. [Google Scholar]
- Grindley, J.R.; Nel, E.A. Red water and mussel poisoning at Elands Bay, December 1966. Fish. Bull. S. Afr. 1970, 6, 36–55. [Google Scholar]
- Horstman, D.A. Reported red-water outbreaks and their effects on fauna of the west and south coasts of South Africa, 1959–1980. Fish. Bull. S. Afr. 1981, 15, 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, L. Observaciones sobre fitoplancton y temperatura superficial en la bahía San Jorge, Antofagasta, Chile. Rev. Biol. Mar. 1987, 23, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, G.; Rengel, J.; Álvarez, F.; Pino, R.; Muñoz, P.; Rosales, S.; Hevia, V.; Araya, M.; Díaz, P.A.; Rivera, A.; et al. Mass mortality of marine invertebrates associated by the presence of yessotoxins in northern Chile. Harmful Algae News 2020, 64, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, P.; Rogers-Bennett, L.; Kudela, R.M.; Palumbi, S.R. Forensic genomics as a novel tool for identifying the causes of mass mortality events. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers-Bennett, L.; Kudela, R.; Nielsen, K.; Paquin, A.; O’Kelly, C.; Langlois, G.W.; Crane, D.B.; Moore, J. Dinoflagellate bloom coincides with marine invertebrate mortalities in northern California. Harmful Algae News 2012, 46, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher, G.C.; Foord, C.J.; Macey, B.M.; Mansfield, L.; Mouton, A.; Smith, M.E.; Osmond, S.J.; van der Molen, L. Devastating farmed abalone mortalities attributed to yessotoxin-producing dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2019, 81, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rivera, A.; Pinto, M.; Insinilla, A.; Suarez-Isla, B.A.; Uribe, E.; Álvarez, G.; Lehane, M.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. The occurrence of domoic acid linked to a toxic diatom bloom in a new potential vector: The tunicate Pyura chilensis (piure). Toxicon 2009, 54, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverté, L.; Solino, L.; Carnicer, O.; Diogène, J.; Campàs, M. Alternative methods for the detection of emerging marine toxins: Biosensors, biochemical assays and cell-based assays. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5719–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trefault, N.; Krock, B.; Delherbe, N.; Cembella, A.; Vásquez, M. Latitudinal transects in the southeastern Pacific Ocean reveal a diverse but patchy distribution of phycotoxins. Toxicon 2011, 58, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Miguens, N.; Rodriguez, I.; Botana, L.M. LC-MS/MS analysis of the emerging toxin Pinnatoxin-G and high levels of esterified OA group toxins in Galician commercial mussels. Toxins 2019, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kremp, A.; Tahvanainen, P.; Litaker, W.; Krock, B.; Suikkanen, S.; Leaw, C.P.; Tomas, C. Phylogenetic relationships, morphological variation, and toxin patterns in the Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) complex: Implications for species boundaries and identities. J. Parasitol. 2014, 50, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almandoz, G.O.; Montoya, N.G.; Hernando, M.P.; Benavides, H.R.; Carignan, M.O.; Ferrario, M.E. Toxic strains of the Alexandrium ostenfeldii complex in southern South America (Beagle Channel, Argentina). Harmful Algae 2014, 37, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.; Norambuena, L.; Paredes-Mella, J.; Fuenzalida, G.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Lee Chang, K.L.; Guzmán, L.; Krock, B.; Hallegraeff, G. Unraveling the Karenia selliformis complex with the description of a non-gymnodimine producing Patagonian phylotype. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, E.; Álvarez, G.; Rengel, J.; Blanco, J. Prorocentrum lima, a new diarrhetic shellfish toxins producer in northern Chile. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Harmful Algae—From Ecosystems to Socioecosystems, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018; p. 612. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, G.; Rengel, J.; Uribe, E.; Araya, M.; Díaz, P.A.; Hevia, V.; Muñoz, P.; Sellanes, J.; Blanco, J. First detection of the toxic dinoflagellates Prorocentrum rhathymum and Prorocentrum cf consutum in Rapa Nui (Easter Island). In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Harmful Algae, La Paz, Mexico, 10–15 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, P.; Pizarro, G.; Franco, J.; Riobó, P.; Bravo, I. Perfil de toxinas de Prorocentrum lima (Dinophyceae) aislado desde la costa de Magallanes, sur de Chile. In Proceedings of the XXXII Congreso de Ciencias del Mar, Punta Arenas, Chile, 22–25 October 2012; p. 228. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, S.; Marambio, J.; Ojeda, J.; Rodríguez, J.P.; González-Wevar, C.; Gerard, K.; Contador, T.; Pizarro, G.; Mansilla, A. Trophic ecology of two co-existing Sub-Antarctic limpets of the genus Nacella: Spatio-temporal variation in food availability and diet composition of Nacella magellanica and N. deaurata. ZooKeys 2018, 738, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, C.; Rodriguez-Unda, N.; Contreras, C.; Barriga, A.; Lagos, N. Lipophilic toxin profiles detected in farmed and benthic mussels populations from the most relevant production zones in Southern Chile. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mansilla, C. Distribución, Metabolismo y Composición de las Toxinas Lipofílicas en Especies de Bivalvos y Gasterópodos Endémicos del sur Austral de Chile; Universidad Pablo de Olive: Sevilla, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- García, C.; Oyaneder-Terrazas, J.; Contreras, C.; del Campo, M.; Torres, R.; Contreras, H.R. Determination of the toxic variability of lipophilic biotoxins in marine bivalve and gastropod tissues treated with an industrial canning process. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 1711–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, P.; Vale, C.; Boente-Juncal, A.; Costas, C.; Louzao, M.C.; Botana, L.M. Detection of cyclic imine toxins in dietary supplements of green lipped mussels (Perna canaliculus) and in shellfish Mytilus chilensis. Toxins 2020, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyaneder-Terrazas, J.; Polanco, C.; Figueroa, D.; Barriga, A.; Garcia, C. In vitro biotransformation of OA-group and PTX-group toxins in visceral and non-visceral tissues of Mytilus chilensis and Ameghinomya antiqua. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2020, 37, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Mackenzie, L.; Stirling, D.; Adamson, J. Pectenotoxin-2 seco acid: A toxin converted from pectenotoxin-2 by the New Zealand Greenshell mussel, Perna canaliculus. Toxicon 2001, 39, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Mackenzie, L.; Stirling, D.; Adamson, J. Conversion of pectenotoxin-2 to pectenotoxin-2 seco acid in the New Zealand scallop, Pecten novaezelandiae. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, R.; Dines, M.H.; Hawkes, A.D.; Briggs, L.R.; Sandvik, M.; Jensen, D.J.; Cooney, J.M.; Holland, P.T.; et al. Isolation of pectenotoxin-2 from Dinophysis acuta and its conversion to pectenotoxin-2 seco acid, and preliminary assessment of their acute toxicities. Toxicon 2004, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P. Differential dynamics of dinophysistoxins and pectenotoxins between blue mussel and common cockle: A phenomenon originating from the complex toxin profile of Dinophysis acuta. Toxicon 2004, 44, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M. Pectenotoxin-2 seco acid, 7-epi-pectenotoxin-2 seco acid and pectenotoxin-2 in shellfish and plankton from Portugal. Toxicon 2002, 40, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli, A.; Fernández, D.; Regueiro, J.; Mariño, C.; Blanco, J. Esterification of okadaic acid in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicon 2011, 57, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Arévalo, F.; Correa, J.; Moroño, Á. Lipophilic toxins in Galicia (NW Spain) between 2014 and 2017: Incidence on the main molluscan species and analysis of the monitoring efficiency. Toxins 2019, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, T.; Curtis, J.M.; Walter, J.A.; McLachlan, J.L.; Wright, J.L.C. Two new water-soluble DSP toxin derivatives from the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum maculosum: Possible storage and excretion products. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 9273–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, L.; Selwood, A.I.; Marshall, C.; Baba, T. Isolation and characterization of an enzyme from the GreenshellTM mussel Perna canaliculus that hydrolyses pectenotoxins and esters of okadaic acid. Toxicon 2012, 60, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgensen, T.; Miles, C.O.; Rundberget, T.; Wilkins, A.L. New esters of okadaic acid in seawater and blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9628–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindegarth, S.; Torgersen, T.; Lundve, B.; Sandvik, M. Differential retention of okadaic acid (OA) group toxins and pectenotoxins (PTX) in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.), and european flat oyster, Ostrea edulis (L.). J. Shellfish Res. 2009, 28, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, M.J.; Vale, C.; Joaquim, S.; Costa, S.T.; Soares, F.; Roque, C.; Matias, D. Combined effect of temperature and nutritional regime on the elimination of the lipophilic toxin okadaic acid in the naturally contaminated wedge shell Donax trunculus. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.; Fernández, M.L.; Míguez, A.; Moroño, A. Okadaic acid depuration in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis: One- and two- comportment models and the effect of environmental conditions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 176, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroño, A.; Areválo, F.; Fernández, M.L.; Maneiro, J.; Pazos, Y.; Salgado, C.; Blanco, J. Accumulation and transformation of DSP toxins in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis during a toxic episode caused by Dinophysis acuminata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, J.S.; Munday, R.; Hawkes, A.D.; Jensen, D.J.; Cooney, J.M.; Beuzenberg, V. Production of 7-Epi-Pectenotoxin-2 seco acid and assessment of its acute toxicity to mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, D.T.; Kiermeier, A.; McLeod, C.; Nicolas, J.; Finch, S. Risk assessment of pectenotoxins in New Zealand bivalve molluscan shellfish, 2009–2019. Toxins 2020, 12, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Decision—Establishing Special Health Checks for the Harvesting and Processing of Certain Bivalve Molluscs with a Level of Amnesic Shellfish Poison (ASP) Exceeding the Limit Laid Down by Council Directive 91/492/EEC; European Commission: Luxembourg. Off. J. Eur. Union 2002, 75, 65–66. [Google Scholar]
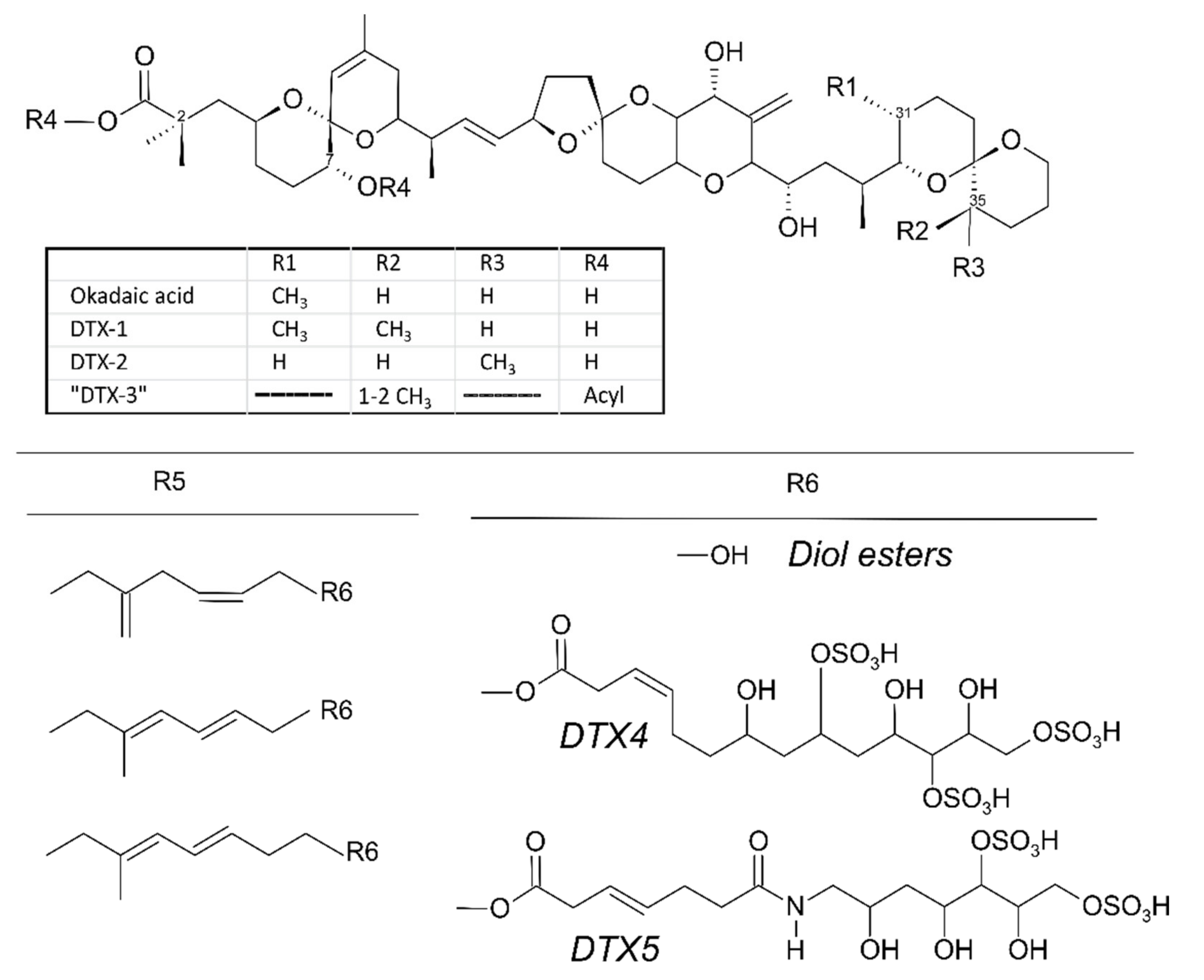
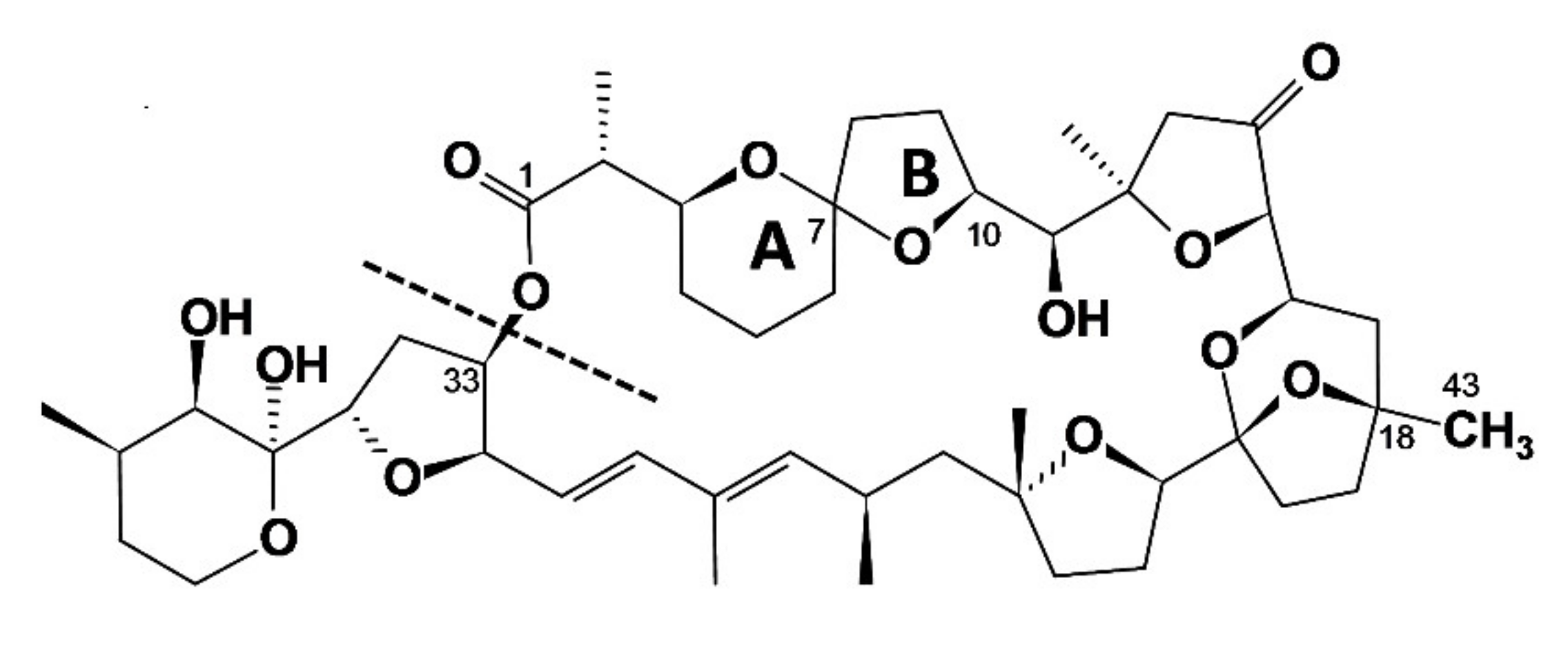
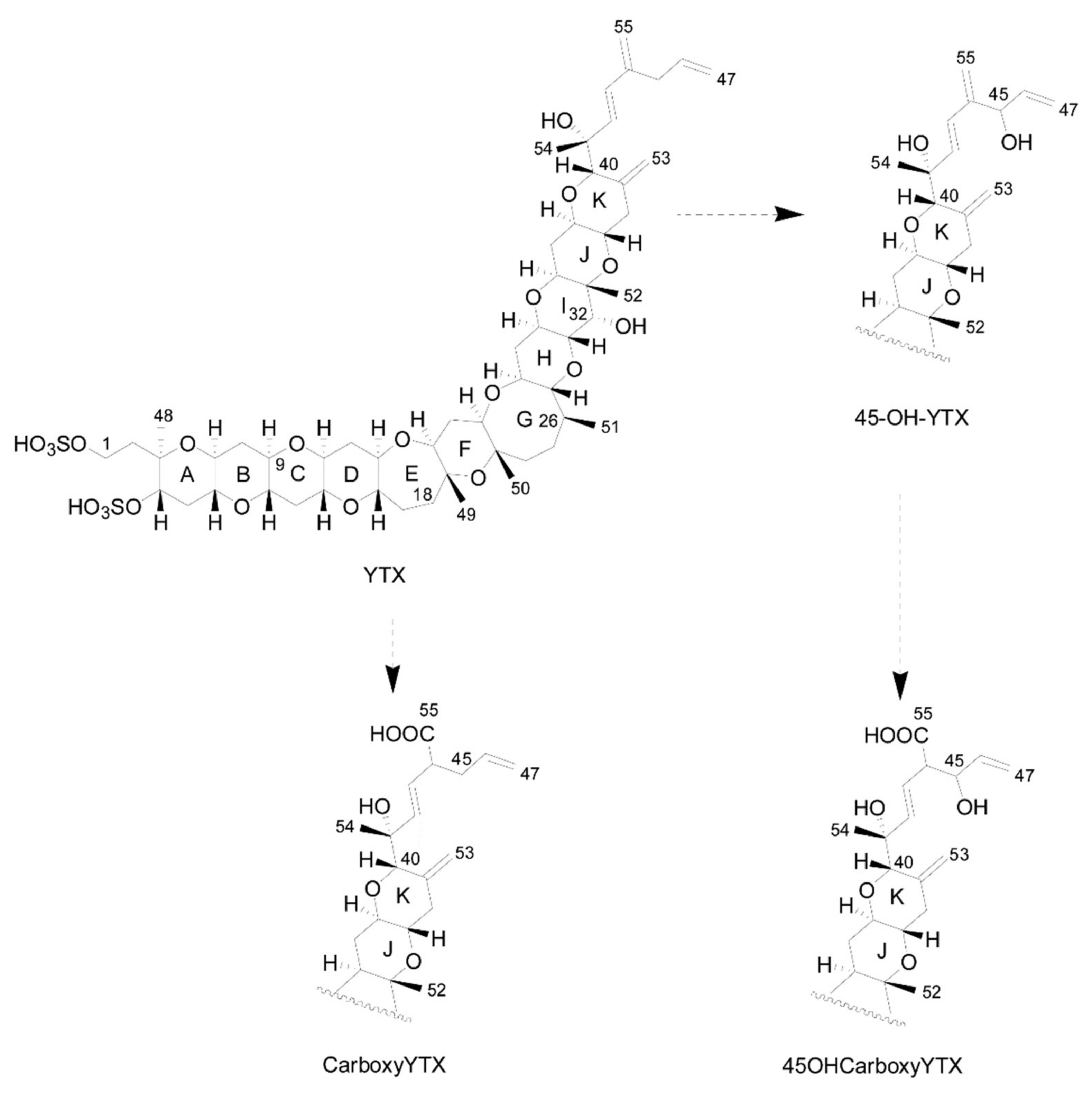
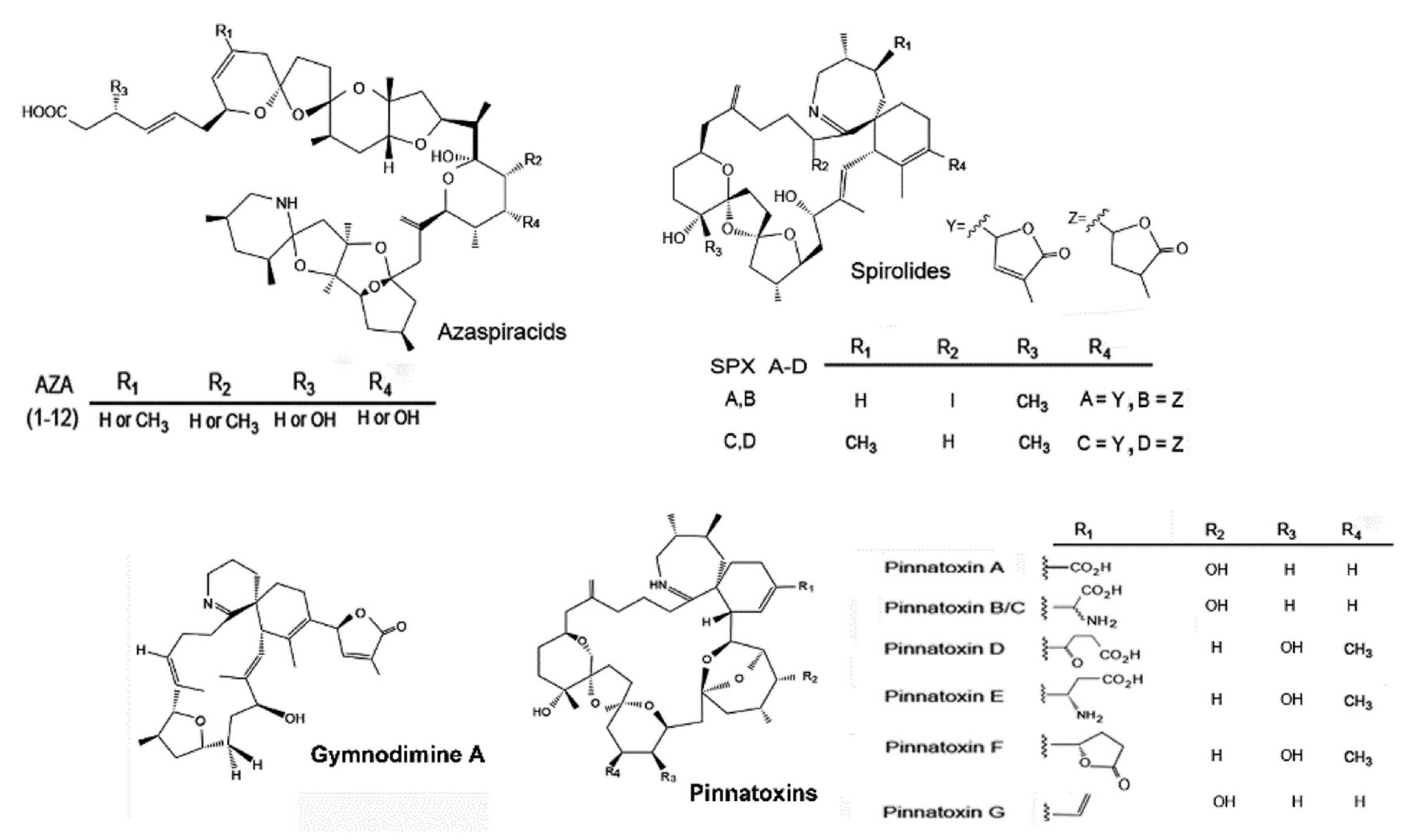



| Scientific Names | Common Names (English) | Common Chilean Names (Spanish) | Price ($US kg−1) | Administrative Regions | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | BB | LL | AY | MG | OR | |||||
| Mytilus chilensis | Blue mussel | Chorito | 1.0 | 7 | 400,230 | 4 | 28 | 35 | 400,304 | |
| Ameghinomya antiqua | Clam | Almeja | 0.8 | 1 | 92 | 10,993 | 57 | 12 | 133 | 11,288 |
| Aulacomya atra | Ribbed mussel | Cholga | 0.6 | 109 | 6037 | 32 | 55 | 81 | 6314 | |
| Argopecten purpuratus | Scallop | Ostion del Norte | 14,5 | 3987 | 380 | 4367 | ||||
| Tagelus dombeii | Hard razor clam | Navajuela | 0.7 | 2700 | 221 | 249 | 3170 | |||
| Choromytilus chorus | Giant mussel | Choro | 0.5 | 41 | 2172 | 99 | 281 | 2593 | ||
| Tawera gayi | Baby clam | Juliana | 0.2 | 2504 | 0 | 2504 | ||||
| Mulinia edulis | Clam | Taquilla | 0.1 | 1191 | 0 | 1191 | ||||
| Ensis macha | Sea asparagus | Huepo | 1.3 | 832 | 328 | 0 | 1160 | |||
| Mesodesma donacium | Surf clam | Macha | 5 | 780 | 71 | 4 | 855 | |||
| Chlamys vitrea | Scallop | Ostion del Sur | 0.8 | 1 | 446 | 0 | 447 | |||
| Ostrea chilensis | Chilean oyster | Ostra Chilena | 0.9 | 401 | 0 | 401 | ||||
| Gari solida | Clam | Culengue | 1.0 | 17 | 282 | 47 | 0 | 346 | ||
| Semele solida | Clam | Tumbao | 0.6 | 159 | 0 | 159 | ||||
| Magallana gigas | Pacific oyster | Ostra del Pacifico | 6.2 | 67 | 2 | 23 | 2 | 94 | ||
| Prothotaca taca | Clam | Taca | 1.4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||||
| Total | 4853 | 4882 | 412,428 | 183 | 529 | 1032 | 423,907 | |||
| Species | Administrative Regions | References | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | TA | AN | AT | CO | VA | OH | MA | BB | AR | LR | LL | AY | MG | |||
| DSP/PTX | Dinophysis acuminata | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [13,24,42,47,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] |
| toxins | D. acuta | + | + | + | [31,32,53,61,62,63,64,65] | |||||||||||
| D. caudata | + | + | + | + | + | + | [23,64,66,67] | |||||||||
| D. forti | + | + | + | + | [23,24,51,67] | |||||||||||
| D. norvegica | + | [59] | ||||||||||||||
| D. ovum | + | + | + | + | + | [24,68] | ||||||||||
| D. saculus | + | + | + | + | [24,69] | |||||||||||
| D. tripos | + | + | [64,68] | |||||||||||||
| Phalacroma rotundatum | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [55,70] | |
| D. exigua | + | + | + | [24] | ||||||||||||
| Potential | D. hastata | + | + | [23,24,67] | ||||||||||||
| DSP/PTX | D. schuettii | + | + | [23,24,67] | ||||||||||||
| D. subcircularis | + | + | [52,64] | |||||||||||||
| Phalacroma rapa | + | + | + | [24] | ||||||||||||
| YTX | Protoceratium reticulatum | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | [36,47,52,55,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79] |
| Gonyaulax spinifera | + | + | + | + | + | + | [80] | |||||||||
| G. taylorii | + | + | + | + | [7] | |||||||||||
| AZP | Azadinium poporum | + | + | + | [8,17,18,19,81,82,83] | |||||||||||
| Amphidoma spp. | + | [17,18,19,34] | ||||||||||||||
| SPX | Alexandrium ostenfeldii | + | + | + | + | [84,85,86] | ||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz, P.A.; Álvarez, G.; Pizarro, G.; Blanco, J.; Reguera, B. Lipophilic Toxins in Chile: History, Producers and Impacts. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020122
Díaz PA, Álvarez G, Pizarro G, Blanco J, Reguera B. Lipophilic Toxins in Chile: History, Producers and Impacts. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(2):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020122
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz, Patricio A., Gonzalo Álvarez, Gemita Pizarro, Juan Blanco, and Beatriz Reguera. 2022. "Lipophilic Toxins in Chile: History, Producers and Impacts" Marine Drugs 20, no. 2: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020122
APA StyleDíaz, P. A., Álvarez, G., Pizarro, G., Blanco, J., & Reguera, B. (2022). Lipophilic Toxins in Chile: History, Producers and Impacts. Marine Drugs, 20(2), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020122









