Abstract
The PII signaling protein is a key protein for controlling nitrogen assimilatory reactions in most organisms, but little information is reported on PII proteins of green microalga Haematococcus pluvialis. Since H. pluvialis cells can produce a large amount of astaxanthin upon nitrogen starvation, its PII protein may represent an important factor on elevated production of Haematococcus astaxanthin. This study identified and isolated the coding gene (HpGLB1) from this microalga. The full-length of HpGLB1 was 1222 bp, including 621 bp coding sequence (CDS), 103 bp 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR), and 498 bp 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR). The CDS could encode a protein with 206 amino acids (HpPII). Its calculated molecular weight (Mw) was 22.4 kDa and the theoretical isoelectric point was 9.53. When H. pluvialis cells were exposed to nitrogen starvation, the HpGLB1 expression was increased 2.46 times in 48 h, concomitant with the raise of astaxanthin content. This study also used phylogenetic analysis to prove that HpPII was homogeneous to the PII proteins of other green microalgae. The results formed a fundamental basis for the future study on HpPII, for its potential physiological function in Haematococcus astaxanthin biosysthesis.
1. Introduction
Inorganic nitrogen acts as an important nutrient in autotrophic microalgae cultivation. It is a limiting factor for cell growth. While under a nitrogen-depleted condition, microalgae will transfer the energy from cell division/growth to produce more secondary metabolites like carotenoids [1,2] and lipids [3], which have widespread commercial value. Therefore, nitrogen regulation is an important approach for microalgae cultivation.
It is believed that nitrogen metabolism is regulated by multiple signal regulators and linked to carbon flux [4]. In most organisms, PII proteins act as the central signal-integrating molecules for controlling nitrogen and/or carbon metabolism, along with some effector molecules (e.g., ATP and 2-oxoglutarate) [5,6,7]. These molecules bind to the intercommunicating sites of the trimeric PII proteins, forming different PII conformations to control a variety of enzymes, transcription factors, and membrane transport proteins [8,9,10]. Although PII proteins have highly conserved structures, they interact with various target metabolisms in different organisms. In cyanobacteria and plants, for example, PII proteins can control the activity of N-acetyl-l-glutamate kinase (NAGK), and then regulate the metabolism of glutamate towards arginine and polyamines [5,11]. In plant chloroplast and bacteria, acetyl-CoA carboxylases, catalysing the committed and rate-limiting step in fatty acid biosynthesis, are regulated by PII proteins [12,13]. It is believed that PII proteins may also play some uncharacterized roles in plant cells [5,14].
Compared to the study on plants and bacteria, research of PII proteins in microalgae is still in the primary stage. To date, the PII proteins have only been reported in two green microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [15] and Chlorella variabilis [14]. It has been reported that PII proteins originate from cyanobacteria and conserve in the evolution of higher plants [5]. Since green algae are in the phylogenetic lineage between cyanobacterial ancestor and higher plants [14], phylogenetic analysis seems to be an efficient approach to verify the newly identified PII protein of the target microalgae, aligned with some reported PII proteins in plants and cyanobacteria. Given the importance of nitrogen metabolism in microalgae, it is essential to characterize more PII proteins and also verify relevant metabolic functions.
The green microalga Haematococcus pluvialis is well known due to its extreme capability of producing a large amount of powerful antioxidant-astaxanthin [16,17,18]. Driven by their nutrition condition, H. pluvialis cells have two different physiological traits: (1) in favorable conditions they are in a green motile stage; (2) under stress conditions (especially nitrogen depletion) the green cells will transform into a reddish non-motile resting stage, coupled with astaxanthin accumulation [19,20,21]. Several key genes related to astaxanthin biosynthesis and stress responding have been cloned and characterized, such as pds [22], CYP97C [23], MnSOD [24], and TR1 [25]. Despite many reports on astaxanthin accumulation of H. pluvialis upon nitrogen depletion [26,27,28], there is no information of its PII protein and associated genetic transcription information on this unicellular microalga.
In this study, we cloned the full length of the PII signaling protein gene on H. pluvialis, analyzed the phylogenetic relationship and structure of this protein, and also investigated its time course-dependent transcriptional regulation. It is anticipated that the results will provide fundamental knowledge on the PII protein of H. pluvialis, and also highlight the importance of its potential regulation/interactions for astaxanthin biosynthesis.
2. Results
2.1. Cloning and Characterization of HpGLB1
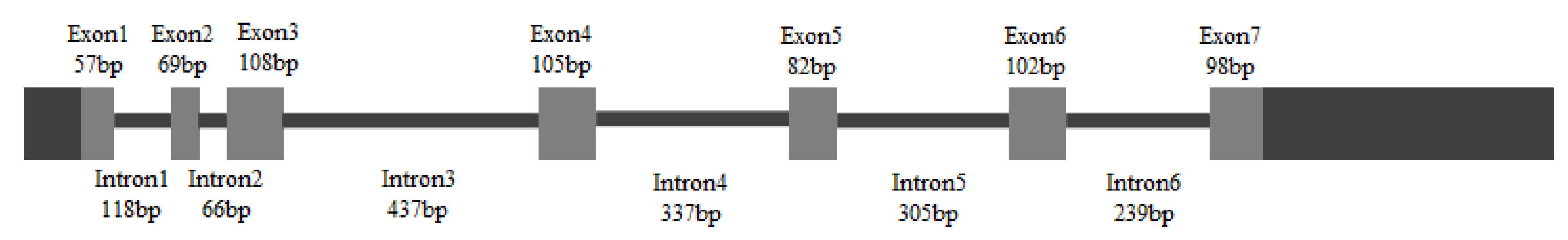
A 148 bp cDNA fragment of HpGLB1 was obtained from H. pluvialis cells by RT-PCR in this study. This fragment was homologous to the GLB1 of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Chlorella variabilis. The results showed that 5′-RACE PCR generated a 568 bp fragment, and 3′-RACE PCR generated a 702 bp fragment. Alignment assay indicated that the complete cDNA sequence of HpGLB1 was 1222 bp, including 621 bp coding sequence (CDS), 103 bp 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR), and 498 bp 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR). The length of the open reading frame of HpGLB1 in genomic DNA was 2123 bp, containing 7 exons and 6 introns (Figure 1). The length of introns varied from 66 bp to 437 bp. The sequence of HpGLB1 has been submitted to NCBI GenBank (Accession number: KT696441).
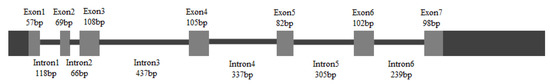
Figure 1.
The gene structure of HpGLB1. Grey boxes and black solid lines represent exons and introns, respectively. Black boxes represent 5′ and 3′ UTRs.
2.2. Characterization of HpPII Protein
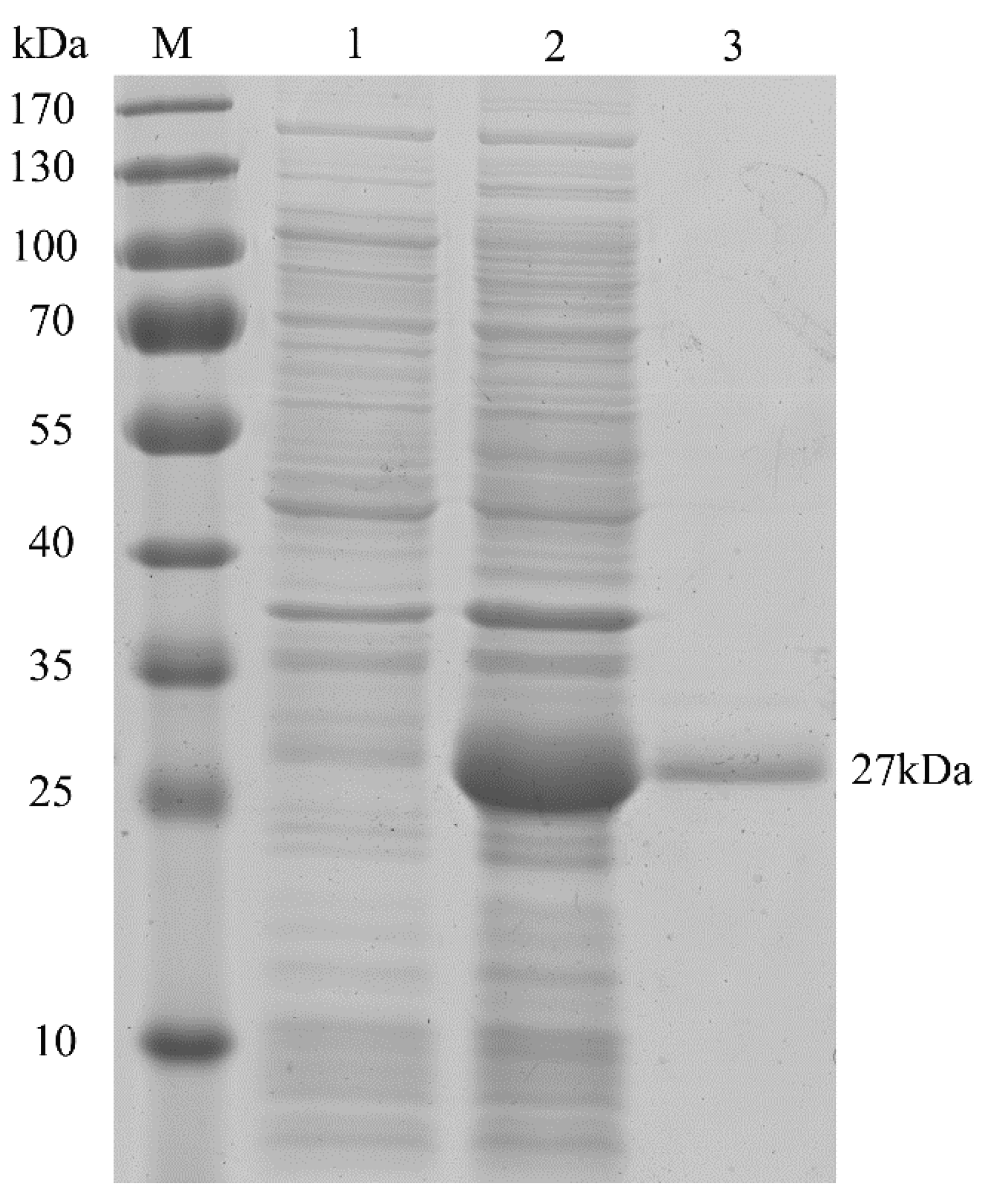
Encoded by HpGLB1 cDNA, the deduced full-length HpPII protein consisted of 206 amino acid residues (Figure 2). According to the Computer pI/Mw Tool, the calculated values of pI and Mw were 9.53 and 22.4 kDa, respectively. However, the molecular mass was approximately 27 kDa after HpPII was expressed and purified in E. coli BL21 (DE3) (Figure 3). This was the sum of the calculated Mw of HpPII (22.4 kDa) and N-terminal tag (4 kDa), and the latter was from the plasmid pET28a used for purification.

Figure 2.
Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of HpGLB1. The asterisk represents the stop codon.
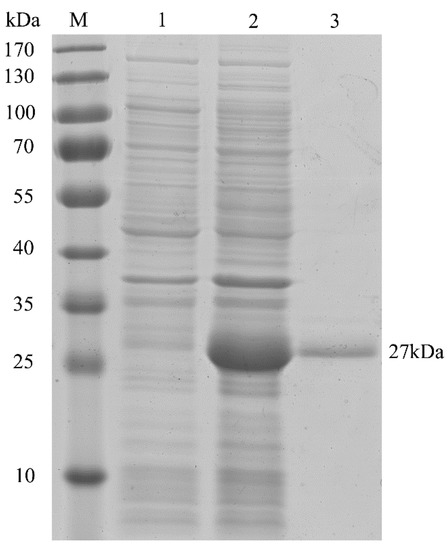
Figure 3.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis of HpPII in E. coli BL21 (DE3). M: protein marker; lane 1: total proteins extracted from uninduced pET28a-HpGLB1 (no HpPII expression, control); lane 2: total proteins extracted from induced pET28a-HpGLB1 (with HpPII expression); lane 3: purified HpPII protein.
2.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Structural Prediction
The derived HpPII protein was aligned with the sequences of representative PII protein from green algae, plants, cyanobacteria, and bacteria (Figure 4). Like the PII proteins of C. reinhardtii and C. variabilis, HpPII had N- and C-terminal extensions, which did not exist in prokaryotes. Furthermore, the sequence from residue 74 to 186 encompassed homology to the entire 112 residues of prokaryotic PII proteins. Within the homology region, the identities of HpPII were aligned up to 78% and 63% with microalgae C. reinhardtii and C. variabilis, respectively. HpPII also had a high similarity with the PII proteins of plants, cyanobacterial, bacterial and red algal, such as: Arabidopsis thaliana (55%), Oryza sativa (52%), Solanum lycopersicum (54%), Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (50%), Synechococcus sp. (47%), Prochlorococcus marinus (47%), Escherichia coli (45%), Porphyra umbilicalis (43%), and Pyropia yezoensis (41%).

Figure 4.
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of PII proteins among different organisms: Haematococcus pluvialis (Hp; AOO85416), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr; EDO96407.1), Chlorella variabilis (Cv; AHW46897.1), Arabidopsis thaliana (At; AAC78333.1), Oryza sativa (Os; NP_001054562.1), Solanum lycopersicum (Sl; NP_001234506.1), Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 (Sc; WP_010873156.1), Synechococcus sp. (Sy; AAA27312.1), Prochlorococcus marinus (Pm; WP_036930683.1), Escherichia coli (Ec; CDZ21367.1), Porphyra umbilicalis (Pu; AFC39923.1), Pyropia yezoensis (Py; YP_536935.1). Residues in black represent >60% identity of aligned PII proteins. Amino acids shaded with grey display similar residues. Box I and box II are PII signature patterns I and II. The white arrow indicates the residue of the corresponding uridylylated threonyl-residue in proteobacteria. The black arrow indicates the residue of corresponding phosphorylated serine-residue in cyanobacteria. Black dots, squares, and triangles show the ATP-, NAGK-, and 2KG-binding residues, respectively.
Two signature patterns (I and II) of extremely high similarity have been proposed at the PROSITE (PS00496 and PS00638) (Figure 4). Escherichia coli of proteobacteria has tyrosyl-residue (Tyr-51) in signature pattern I, which is posttranslational modified by uridylylation. However, in HpPII and PII proteins of green algae C. reinhardtii, C. variabilis, and higher plants, the Tyr-51 residue is substituted by phenylalanyl-residue (Figure 4). Although PII proteins of Synechococcus comprise Tyr-51 residue, they are not uridylylated, due to being modified by phosphorylation at seryl-residue (Ser-49) [29]. Nevertheless, the corresponding Ser-49 residue is replaced by threoninyl-residue in HpPII and PII proteins of green algae C. reinhardtii and C. variabilis (Figure 4). Similar to the other PII proteins, HpPII has T loop, B loop, and C loop (Figure 4). In addition, HpPII also has a consensus sequence of Q loop (R/K, M, Q, G) structure in C-terminal extension (Figure 4), which is comparable to the PII proteins of C. reinhardtii, C. variabilis, and higher plants. They are known to constitute binding sites of metabolite effectors [8]. These binding residues are highlighted in Figure 4.
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
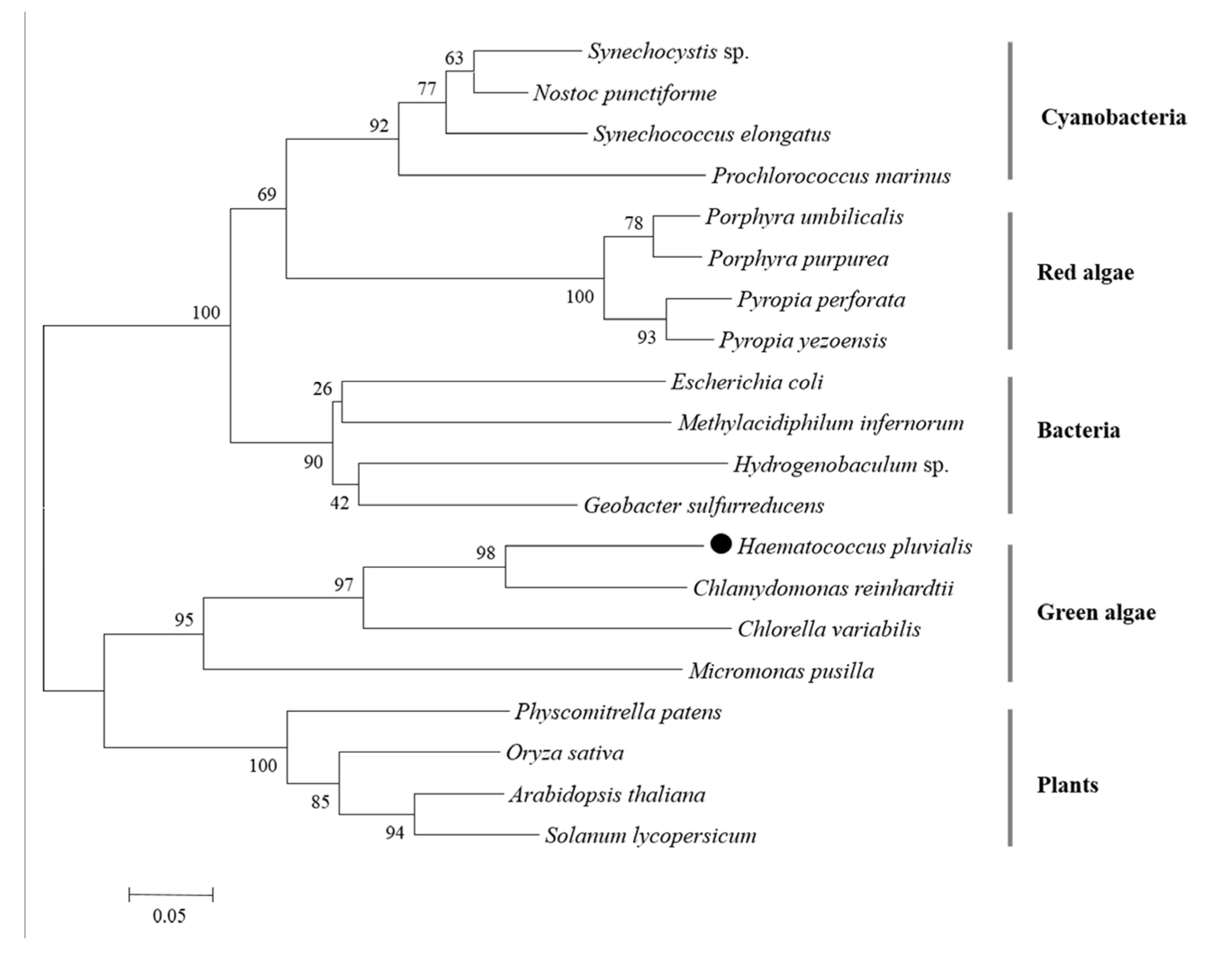
A Neighbor-Joining tree was generated by PII proteins of microalgae, plants, and bacteria via MEGA 6.06 software. There were five clusters: cyanobacteria, red algae, bacteria, green algae, and plants (Figure 5). HpPII protein was grouped with the PII proteins of Chlorophyta algae (C. reinhardtii, C. variabilis, Micromonas pusilla).
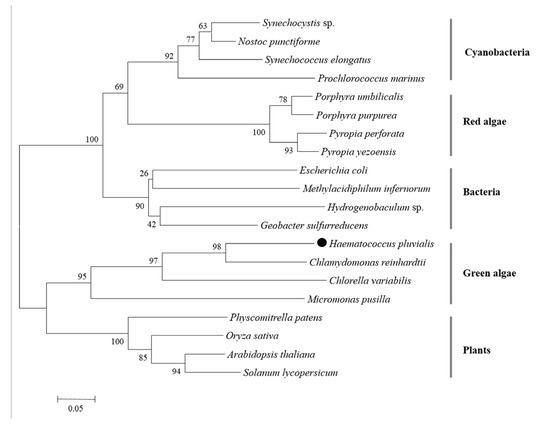
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic tree of PII proteins in different organisms (the black dot represents the derived HpPII in this study). The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the Neighbor-joining method, and the numbers above the nodes represent the bootstrap values.
2.5. Transcription Analysis of HpGLB1 under Nitrogen Deprivation Condition
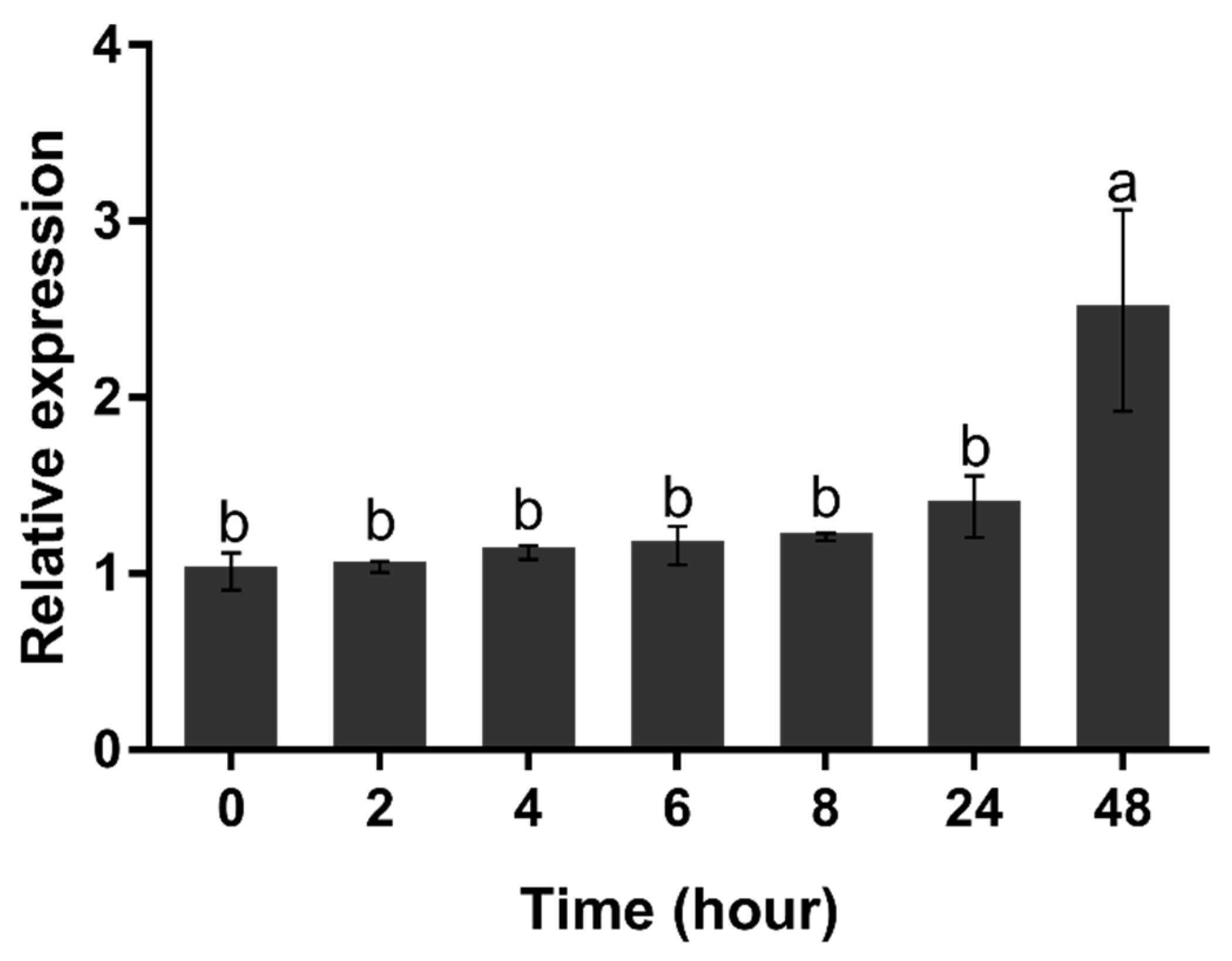
When H. pluvialis cells were exposed to nitrogen starvation, the expression level of HpGLB1 mRNA hardly changed from 0 to 24 h (p > 0.05) (Figure 6). However, its transcription level increased significantly at 48 h (p < 0.05).
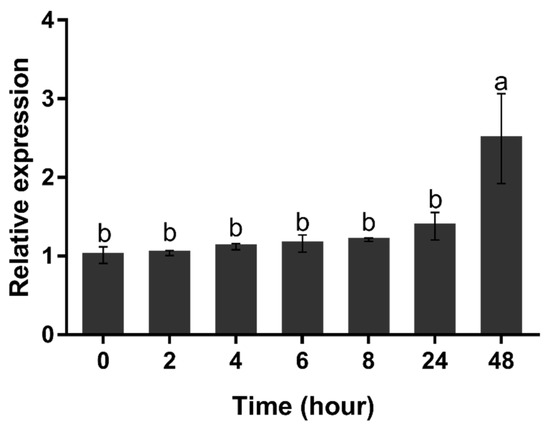
Figure 6.
Transcription level of HpGLB1 under nitrogen deprivation condition. Data in this figure are the mean values of biological triplicates, and the error bar indicates their standard error (SE). Statistical significance differences are represented by different letters at p < 0.05. The H. pluvialis cells (of 5 × 105 cells mL−1) were resuspended in BBM-N medium at 0 h (control). The transcription level of HpGLB1 were measured at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, 48 h by qRT-PCR. The 18S ribosomal RNA gene was used as the reference gene, and the values were normalized to the transcription level of the control.
2.6. Astaxanthin Accumulation Pattern under Nitrogen Deprivation Condition
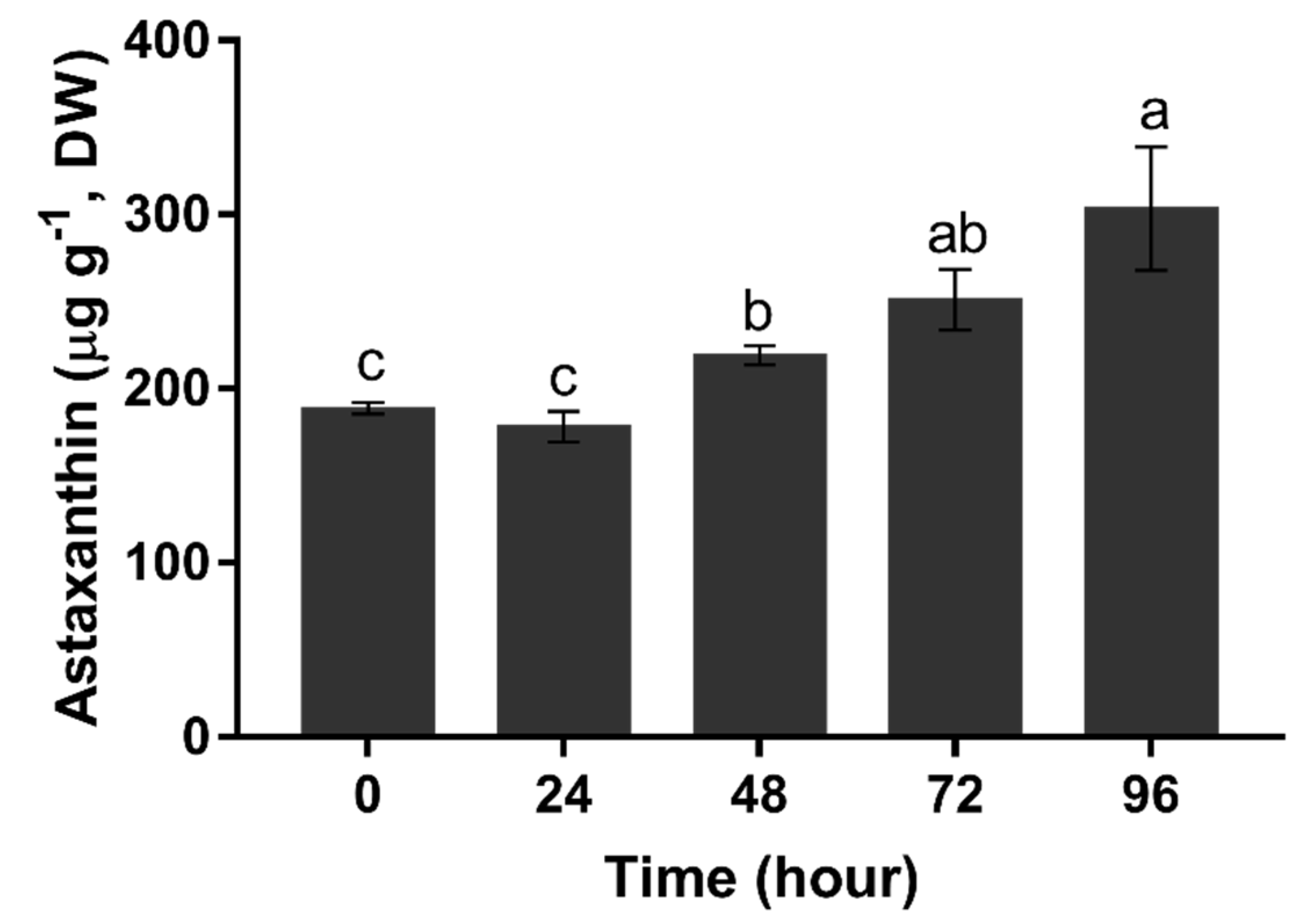
The content of astaxanthin was maintained below 200 μg g−1 in the first 24 h (p > 0.05). It started to increase at 48 h, and then continuously accelerated from 48 h (219.02 μg g−1) to 96 h (303.25 μg g−1) (Figure 7).
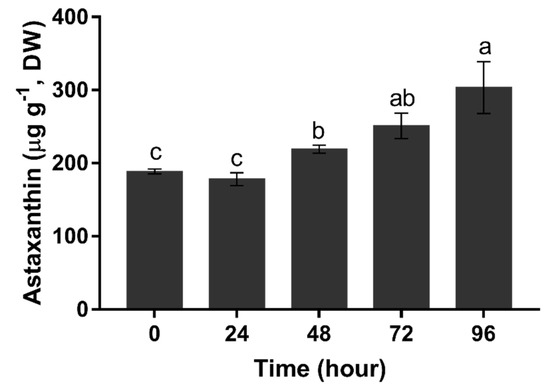
Figure 7.
Total astaxanthin content of H. pluvialis upon nitrogen starvation. Data in this figure are the mean values of biological triplicates, and the error bar indicates their standard error (SE). Statistical significance differences are represented by different letters at p < 0.05.
3. Discussion
This study is the first to isolate and identify a novel gene of PII protein (HpGLB1) on green algae H. pluvialis. The complete cDNA sequence of HpGLB1 was 1222 bp, including 621 bp of CDS, 103 bp 5′UTR, and 498 bp 3′UTR (Figure 1). The open reading frame of HpGLB1 in genomic DNA contained 7 exons and 6 introns, which is the same as for green microalga C. variabilis [14]. It is reported that PII proteins are chloroplast genome-encoded in red algae [6] but in green microalgae they are encoded by nuclear genome [14]. Since H. pluvialis is a green alga and has the same exons and introns distribution of GLB1 as that of C. variabilis, the HpPII is deemed nuclear-encoded in H. pluvialis as well.
The coding sequence (CDS) of HpGLB1 gene encoded a protein of 207 amino acids with 22.4 kDa of calculated weight (Figure 2). When HpPII was expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3), the purified protein Mw was about 27 kDa (Figure 3). Since there was 4 kDa of N-terminal tag, the remaining Mw of protein was similar to the calculated weight of HpPII. In this study, the length of HpGLB1 CDS and the Mw of HpPII were similar to the PII proteins of green microalgae C. reinhardtii (615 bp, 22 kDa) [15] and C. variabilis (630 bp, 22 kDa) [14]. These results indicate that these PII proteins are conserved in green microalgae.
HpPII had a high similarity in the segment of 75 and 185 amino acids to the eukaryotic PII proteins (Figure 4). This was consistent with the phylogenetic analysis of HpPII being in the same cluster with three other green algal PII proteins from C. reinhardtii, C. varLiabilis, and M. pusilla. Since the specific Tyr-51 (uridylylated site) was substituted with phenylalanyl-residue in the signature pattern I region of HpPII (Figure 4), it is indicated that HpPII is not modified by uridylylation. The absence of modification by uridylylation is similar to the literature reports on green algae C. reinhardtii and C. variabilis [14,15]. The Ser-49 was replaced by a threonyl residue in PII protein (Figure 4). This result is the same as PII protein of C. reinhardtii, which has been verified not being modified by phosphorylation [15]. Therefore, it is deduced that HpPII is also not be regulated by phosphorylation.
Different from prokaryotic PII proteins, HpPII had extra N- and C-terminal extensions. As highlighted in green algae and plants, they would represent some additional functions [15,30]. A consensus sequence of Q loop (R/K, M, Q, G) was found in the C-terminal extension of HpPII (Figure 4). Q loop was also observed in PII proteins of green microalgae C. reinhardtii and C. variabilis [14,15]. As reported in C. reinhardtii, Q loop was deemed to play a role in nitrogen assimilation, binding glutamine molecule and forming glutamine-dependent complex with N-acetyl-l-glutamate kinase (NAGK) [5]. Furthermore, the NAGK binding sites of HpPII were conserved with C. reinhardtii and C. variabilis (Figure 4). Hence, HpPII likely behaves as a glutamine sensor through the C-terminal Q loop extension to control the activity of NAGK, and further to regulate nitrogen metabolism. The residues involved in ATP and 2KG binding sites were conserved as well. These results demonstrate that HpPII possibly acts as a signaling protein in nitrogen metabolism. However, a future study is needed to further investigate the contribution of HpPII in nitrogen regulation, targeting the astaxanthin biosynthesis.
The expression of the PII-coding gene was species-specific between different phylogenetic clusters. For example, in cyanobacteria, the expression of PII-coding glnB was increased by nitrogen-poor conditions [31]. However, in the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana, GLB1 expression was not significantly affected by nitrogen [32]. It is worth noting that within the same phylogenetic cluster the GLB1 expression to nitrogen depletion seems species-specific. The expression of GLB1 in H. pluvialis (HpGLB1) was enhanced under a nitrogen starvation condition. A similar result was also reported on the GLB1 expression of green microalga C. reinhardtii [15]. The result in this study showed that HpGLB1 expression was stable in the first 24 h of nitrogen starvation, but increased dramatically at 48 h under nitrogen starvation condition. C. reinhardtii GLB1 was induced from 0.5 h to 4 h upon nitrogen starvation [15]. In contrast, C. variabilis’ GLB1 expression was independent of nitrogen availability [14]. As these microalgae can produce different secondary metabolic bioproducts upon nitrogen depletion, it is deduced that the GLB1 expression is associated with different metabolic activities in microalgae.
In this study, the astaxanthin content is correlated to the HpGLB1 expression. Similar to the HpGLB1 expression, the astaxanthin content was maintained at a low level within the first 24 h. The similar delayed astaxanthin increment was also observed previously in other H. pluvialis strains when exposed to stress condition [20]. In terms of the stable HpGLB1 expression, this may be associated with the initial physiological condition of cells, as these cells reaching exponential stage likely were exposed to N deficient condition prior to the N starvation test in this study. However, both of HpGLB1 expression and astaxanthin content started to increase at 48 h. Then, the astaxanthin content continuously increased after 48 h, even though it was under low light intensity (20 μmol m−2 s−1). It seems that the upregulation of HpGLB1 expression is likely regulated at a posttranslational level. Also, this is elucidated that there may be some physiological connection/interaction between nitrogen metabolism regulation and astaxanthin synthesis on H. pluvialis cells. A number of previous literatures have already confirmed that nitrogen condition plays an important role in H. pluvialis cells’ transformation, growth, and lipid and astaxanthin sythesis; the derived sequence of HpGLB1 and the characterization of HpPII in this study will facilitate further understanding on these metabolic pathways at the molecular level. More importantly, our results provide solid and credible bases for HpPII protein study. These will also provide new insight into the HpPII protein and its potential functions on the nitrogen-driven metabolic mechanism for astaxanthin production on H. pluvialis.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microalga Strain and Culture Conditions
A strain of microalga H. pluvialis HPH was obtained from the Algae Collection at the College of Ocean and Earth Sciences in Xiamen University, China. The algal cells were cultivated in a 1-L glass vessel (15.5 cm in length and 9.5 cm in diameter) with Bold’s Basal Medium (BBM) [33] at 25 °C. The culture was continuously exposed to 20 μmol m−2 s−1 of light radiation, and 2.5% CO2 of aeration at a flow rate of 0.2 vvm [34]. When reaching the late exponential growth phase (approx. 5 × 105 cells mL−1), the H. pluvialis cells were centrifuge-collected at 8000× g for 5 min. The cells were rinsed twice with nitrogen-free medium (BBM-N) and resuspended in BBM-N at a density of 5 × 105 cells mL−1. The culture was continued for the trial (with triplicates), under the same cultivation condition. The culture was sampled with 50 mL (n = 3) at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, and 48 h, respectively. The sampled H. pluvialis cells (3 × 7) were collected via centrifugation and used for the subsequent RNA isolation, cDNA synthesis, and transcription analysis.
4.2. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
The collected cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline buffer (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4), re-centrifuged, and immediately frozen in the liquid nitrogen. The frozen biomass was ground into a fine powder using mortar and pestle, which was cold-maintained by adding more liquid nitrogen. 50 mg of algal powder was used for total RNA extraction, which was achieved by a TaKaRa MiniBEST Universal RNA Extraction Kit (Takara Bio Inc., Kusatsu, Japan). The cDNA first-strand synthesis was carried out using High Capacity cDNA Transcription Kits (Applied Biosystems, Foster, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
4.3. Gene Cloning and Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
Partial cDNA of the PII protein coding gene of H. pluvialis (HpGLB1) was amplified by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) using degenerate primers GLB1-de-F and GLB1-de-R (Table 1). The PCR conditions for amplification were set as a 5 min polymerase activation step at 94 °C followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 56 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 1 min, and a final 10 min of extension at 72 °C. The PCR product was purified with an E.Z.N.A® Gel Extraction Kit (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, USA), cloned into a pMDTM19-T Vector (Takara Bio Inc., Kusatsu, Japan), and then sequenced at the Invitrogen Corporation (Waltham, MA, USA).

Table 1.
Primer sequences used in this study.
In order to generate the full length cDNA of the HpGLB1, this study used the SMART™ RACE cDNA Amplification Kit (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA) to perform 3′ and 5′ rapid amplification of the cDNA ends (RACE). Based on the obtained PCR results, the primers GSP1 and GSP2 (Table 1) were designed for the 5′ RACE and 3′ RACE. Subsequently, genomic DNA of H. pluvialis was isolated using the cetyltrimethylammounium bromide (CTAB) method [35]. Primers GLB1-F and GLB1-R were used to amplify genomic DNA of HpGLB1. As presented, all the PCR products were purified, cloned, and sequenced.
4.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
The open reading frame (ORF) was determined by BioEdit software. The deduced amino acid sequence was analyzed with Primer Premier 5. The homology searches for nucleotide and amino acid sequence similarities were conducted with Clustal W and Blast (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The phylogenetic tree was constructed according to the amino acid sequences of the PII signaling protein by MEGA 6.06 software. Theoretical isoelectric point (pI) and molecular weight (Mw) were calculated with Compute pI/Mw tool (http://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/).
4.5. Plasmid Construction
Based on the nucleotide sequences of start and stop codons of the HpGLB1 gene, the gene specific primers GLB1-B-F and GLB1-B-R were used to amplify the full length of the coding region. The PCR performance was programmed as 94 °C for 5 min followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 65 °C for 30 s, extension at 72 °C for 1 min, and a final 10 min extension at 72 °C. The 5′ and 3′ ends of amplified HpGLB1 coding region contain a BamHI and an EcoRI restriction site, respectively. The amplified coding region was digested with BamHI and EcoRI restriction endonucleases and inserted into the corresponding sites of pET28a for generating the recombinant plasmid pET28a-HpGLB1, and then introduced into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) for expression.
4.6. Expression and Purification of HpPII
HpPII protein expression and purification were performed according to the previous method [36], with some modifications. Briefly, the E. coli BL21 (DE3) harboring pET28a-HpGLB1 was cultured in 10 mL of Luria-Bertani (LB) broth with 50 μg mL−1 of kanamycin (sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) at 37 °C and retained on a shaker (200 rpm) overnight. Then, 0.5 mL of the resulting culture was inoculated to 50 mL of LB broth supplemented with 50 μg mL−1 kanamycin and incubated under the same condition. When the bacterial concentration reached 0.6 of OD600 value, the culture was added with 0.1 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) and incubated for another 6 h. The cells were then harvested by centrifugation (4 °C, 5000× g, 10 min) and washed twice with sodium phosphate buffer (200 mM Na3PO4, 300 mM NaCl, pH 7.4). The pellets were suspended in the sodium phosphate buffer and lysed by sonication (100 W, 60 cycles of 5 s sonication), followed by 5 s incubation on ice. Finally, the soluble lysate was centrifuged (4 °C, 10,000× g, 10 min) for collection. The HpPII protein was purified with Ni-NTA His•Bind Resin. The molecular mass and purity, plus the total proteins, were checked by 12% SDS-PAGE.
4.7. Expression Analysis of HpGLB1 by qRT-PCR
A total of 21 cDNA samples derived from the control and nitrogen depleted treatments (triplicates sampling at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, and 48 h) were used to determine mRNA expressions by real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR). The initial samples (0 h) were treated as the control. qRT-PCR was performed on an ABI-7000 System (Applied Biosystems, Foster, CA, USA) using iTaqTM Universal SYBR® Green Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Primers GLB1-Q-F and GLB1-Q-R were designed to amplify the 120 bp sequence of HpPII for qRT-PCR. The 18S ribosomal RNA gene expression was used as the internal control. Each 20 μL PCR reaction consisted of 10 μL iTaqTM Universal SYBR® Green Supermix, 1 μL of forward and reverse primers (10 μM) each, and 8 μL of cDNA. The thermal cycles were set as stage 1: 95 °C for 10 min; stage 2: 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, and 60 °C for 1 min; and stage 3: 1 cycle of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 1 min, and 95 °C for 15 s. The qRT-PCR data were analyzed by 2−ΔΔCT method based on the cycle threshold (Ct) values.
4.8. Astaxanthin Extraction and Quantification
The freeze-dried cells (10 mg, taken at 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h with triplicated) were mixed with 0.5 g glass beads and vortexed for 2 min. Then 5 mL dichloromethane/methanol (1:1, v/v) was added and vortexed for 1 min. The mixture was centrifuged at 3000× g at 4 °C for 3 min, and the supernatant was collected. The pellet was extracted repeatedly with 3 ml dichloromethane/methanol (1:1, v/v) until it became colorless. The combined supernatant was dried in nitrogen gas, reconstituted with 1 mL of 0.025 M NaOH, and then saponified at 4 °C for 4 h. The pigment extract was diluted with 1 mL of the mix of methanol and acetonitrile/methanol (3:1), and used for astaxanthin quantification.
Separation and identification of astaxanthin was carried out on an Acquity UHPLC system (Waters) equipped with photodiode array (PDA) detector. Samples (5.0 μL) were quantitatively injected into an Acquity UPLC Shield C18 BEH column (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm particle size; Waters, Milford, WI, USA). The eluents were (A) 50% (v/v) acetonitrile in demineralized water; (B) acetonitrile; and (C) ethyl acetate, which all contained 0.10% (v/v) formic acid. The flow rate was maintained at 300 μL min−1. The program was initiated from 25% A/75% B and then as follows: 0–10 min—linear gradient to 100% B, 10–15 min—isocratic at 100% B, 15–20 min—linear gradient to 87.5% B/12.5% C, 20–21 min—linear gradient to 70% B/30% C, 21–28 min—linear gradient to 100% C, and 28–29 min—isocratic at 100% C. After 29 min, the eluent composition reverted to its initial composition in 1 min followed by an equilibration phase of 12 min. Detection wavelength for UV–vis was adjusted to 460 nm. Since astaxanthin esters were saponified, the free astaxanthin peak represented total astaxanthin. The astaxanthin peak was identified by comparing retention time and spectra with astaxanthin standard (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The quantification of astaxanthin was determined by a calibration curve obtained with astaxanthin standard.
4.9. Statistical Analysis
The experiment was conducted with biological triplicates, and the data measurement was performed in triplicates. The data in the figure were showed as mean ± SE in this study. The statistical differences of transcription level between sampling times were detected by one-way ANOVA analysis using IBM SPSS Statistics 24, with nitrogen starvation time as variance and relative transcription level as dependent variables, followed by Duncan’s test with a significant level of 0.05.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31071488), the National Marine Commonweal Research Program, China (No. 201205020-2), and the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21336009).
Author Contributions
Ruijuan Ma and Yinghua Lu conceived and designed the experiments; Ruijuan Ma performed the experiments; Ruijuan Ma, Yan Li, and Yinghua Lu analyzed the data; Yinghua Lu contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Ruijuan Ma and Yan Li wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mulders, K.J.M.; Weesepoel, Y.; Bodenes, P.; Lamers, P.P.; Vincken, J.P.; Martens, D.E.; Gruppen, H.; Wijffels, R.H. Nitrogen-depleted Chlorella zofingiensis produces astaxanthin, ketolutein and their fatty acid esters: A carotenoid metabolism study. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.P.; Park, J.K.; Lee, C.G. Proteomics analysis of proteins in green alga Haematococcus lacustris (chlorophyceae) expressed under combined stress of nitrogen starvation and high irradiance. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2009, 45, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longworth, J.; Wu, D.Y.; Huete-Ortega, M.; Wright, P.C.; Vaidyanathan, S. Proteome response of Phaeodactylum tricornutum, during lipid accumulation induced by nitrogen depletion. Algal Res. 2016, 18, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commichau, F.M.; Forchhammer, K.; Stulke, J. Regulatory links between carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellamuthu, V.R.; Ermilova, E.; Lapina, T.; Luddecke, J.; Minaeva, E.; Herrmann, C.; Hartmann, M.D.; Forchhammer, K. A widespread glutamine-sensing mechanism in the plant kingdom. Cell 2014, 159, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhrig, R.G.; Ng, K.K.S.; Moorhead, G.B.G. PII in higher plants: A modern role for an ancient protein. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninfa, A.J.; Jiang, P. PII signal transduction proteins: Sensors of alpha-ketoglutarate that regulate nitrogen metabolism. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huergo, L.F.; Chandra, G.; Merrick, M. PII signal transduction proteins: Nitrogen regulation and beyond. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 251–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfmann, S.; Lu, W.; Litz, C.; Andrade, S.L.A. Cooperative binding of MgATP and MgADP in the trimeric PII protein GlnK2 from Archaeoglobus fulgidus. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 402, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, E.C.; Araujo, L.M.; Ribeiro, R.R.; Chubatsu, L.S.; Scarduelli, M.; Rodrigues, T.E.; Monteiro, R.A.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Souza, E.M.; Huergo, L.F. Influence of the ADP/ATP ratio, 2-oxoglutarate and divalent ions on Azospirillum brasilense PII protein signalling. Microbiology 2012, 158, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burillo, S.; Luque, I.; Fuentes, I.; Contreras, A. Interactions between the nitrogen signal transduction protein PII and N-acetyl glutamate kinase in organisms that perform oxygenic photosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 3346–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourrellier, A.B.F.; Valot, B.; Guillot, A.; Ambard-Bretteville, F.; Vidal, J.; Hodges, M. Chloroplast acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity is 2-oxoglutarate-regulated by interaction of PII with the biotin carboxyl carrier subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, E.C.M.; Rodrigues, T.E.; Muller-Santos, M.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Souza, E.M.; Forchhammer, K.; Huergo, L.F. The bacterial signal transduction protein GlnB regulates the committed step in fatty acid biosynthesis by acting as a dissociable regulatory subunit of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 95, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minaeva, E.; Ermilova, E. Sequencing and expression analysis of the gene encoding PII signal protein in Chlorella variabilis NC64A. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermilova, E.; Lapina, T.; Zalutskaya, Z.; Minaeva, E.; Fokina, O.; Forchhammer, K. PII signal transduction protein in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Localization and expression pattern. Protist 2013, 164, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwak, Y.; Hwang, Y.S.; Wang, B.B.; Kim, M.; Jeong, J.; Lee, C.G.; Hu, Q.; Han, D.X.; Jin, E. Comparative analyses of lipidomes and transcriptomes reveal a concerted action of multiple defensive systems against photooxidative stress in Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4317–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, R.T.; Cysewski, G.R. Commercial potential for Haematococcus microalgae as a natural source of astaxanthin. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, P.; Bastias, J.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, V.; Caballero-Casero, N.; Caballo, C.; Sicilia, D.; Fuentes, A.; Maire, M.; Crepin, M.; Letourneur, D.; et al. Astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis prevents oxidative stress on human endothelial cells without toxicity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2857–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.E.; Hwang, S.K.; Chang, W.S.; Kim, B.W.; Lee, J.; Sim, S.J. Enhanced autotrophic astaxanthin production from Haematococcus pluvialis under high temperature via heat stress-driven Haber-Weiss reaction. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5203–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.Q.; Meng, C.X.; Chen, Y.C.; Ahmed, F.; Mangott, A.; Schenk, P.M.; Li, Y. Comparison of astaxanthin accumulation and biosynthesis gene expression of three Haematococcus pluvialis strains upon salinity stress. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scibilia, L.; Girolomoni, L.; Berteotti, S.; Alboresi, A.; Ballottari, M. Photosynthetic response to nitrogen starvation and high light in Haematococcus pluvialis. Algal Res. 2015, 12, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.W.; Zhao, F.Q.; Meng, C.X.; Tan, C.P.; Qin, S. Molecular cloning, characterization and evolutionary analysis of phytoene desaturase (pds) gene from Haematococcus pluvialis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.L.; Yu, X.N.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.L.; Li, X.Q.; Liu, Z.P.; Qin, S. Gene cloning and expression profile of a novel carotenoid hydroxylase (CYP97C) from the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Sommerfeld, M.; Hu, Q. Cloning and expression of isoenzymes of superoxide dismutase in Haematococcus pluvialis (chlorophyceae) under oxidative stress. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.H.; Tao, M.; Li, Z.; Hu, Z.L. Cloning and characterization of selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase gene in Haematococcus pluvialis. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recht, L.; Topfer, N.; Batushansky, A.; Sikron, N.; Gibon, Y.; Fait, A.; Nikoloski, Z.; Boussiba, S.; Zarka, A. Metabolite profiling and integrative modeling reveal metabolic constraints for carbon partitioning under nitrogen starvation in the green algae Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 30387–30403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregas, J.; Dominguez, A.; Alvarez, D.G.; Lamela, T.; Otero, A. Induction of astaxanthin accumulation by nitrogen and magnesium deficiencies in Haematococcus pluvialis. Biotechnol. Lett. 1998, 20, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussiba, S.; Bing, W.; Yuan, J.P.; Zarka, A.; Chen, F. Changes in pigments profile in the green alga Haeamtococcus pluvialis exposed to environmental stresses. Biotechnol. Lett. 1999, 21, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchhammer, K.; Tandeau de Marsac, N. The PII protein in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 is modified by serine phosphorylation and signals the cellular N-status. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, Y.; Moorhead, G.B.G.; Ng, K.K.S. Structural basis for the regulation of N-acetylglutamate kinase by PII in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35733–35740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forchhammer, K. Global carbon/nitrogen control by PII signal transduction in cyanobacteria: From signals to targets. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario-Mery, S.; Bouvet, M.; Leleu, O.; Savino, G.; Hodges, M.; Meyer, C. Physiological characterisation of Arabidopsis mutants affected in the expression of the putative regulatory protein PII. Planta 2005, 223, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olguin, E.J.; Dorantes, E.; Castillo, O.S.; Hernandez-Landa, V.J. Anaerobic digestates from vinasse promote growth and lipid enrichment in Neochloris oleoabundans cultures. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.P.; Ho, S.H.; Chen, C.N.N.; Chen, C.Y.; Ng, I.S.; Jing, K.J.; Chang, J.S.; Lu, Y.H. Phototrophic cultivation of a thermo-tolerant Desmodesmus sp. for lutein production: Effects of nitrate concentration, light intensity and fed-batch operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela-Alvarez, E.; Andreakis, N.; Lago-Leston, A.; Pearson, G.A.; Serrao, E.A.; Procaccini, G.; Duarte, C.M.; Marba, N. Genomic DNA isolation from green and brown algae (Caulerpales and Fucales) for microsatellite library construction. J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, I.S.; Chi, X.Q.; Wu, X.M.; Bao, Z.W.; Lu, Y.H.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, X.P. Cloning and expression of Cel8A from Klebsiella pneumoniae in Escherichia coli and comparison to cel gene of Cellulomonas uda. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 78, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).