Abstract
With ketamine gaining attention as a therapeutic drug, oral administration offers an effective alternative to traditional parenteral routes. However, a significant gap remains in understanding its use via voluntary ingestion. This preliminary study aimed to explore the feasibility of oral ketamine self-administration in mice (Mus musculus), while investigating the effects of low concentrations on the brain, liver, and kidney. Adult mice were divided into three groups and received ketamine in their drinking water for 16 days at 0 (control), 5 (K5), or 10 mg/L (K10). A transient decrease in water consumption was observed in both sexes in the K10 group; however, only females in this group showed differences in ketamine intake between groups on some days. Oxidative stress markers measured in the brain, liver, and kidney only revealed higher catalase activity in the brains of females. No significant alterations were observed in liver and kidney function in either sex, nor in inflammation, apoptosis, or DNA damage in kidney tissues. Overall, these findings support the viability of voluntary oral ketamine administration and accentuate the need to refine the proposed model, not only to prevent water consumption inhibition but also to extend the exposure period, explore potential sex-related differences in ketamine intake, and further confirm the safety of oral ketamine administration.
1. Introduction
Ketamine is a commonly used anaesthetic with a very complex pharmacology, since it acts as a non-competitive antagonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, but it can also exhibit effects through glutamate-independent mechanisms [1]. As a result, ketamine is associated with a range of adverse effects, which limit its use to few specific situations [2,3]. Nevertheless, interest in ketamine as a therapeutic drug has grown significantly over the years as multiple studies have reported ketamine’s analgesic and antidepressant properties at lower doses [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. The antidepressant effects of these lower doses are typically documented in the two hours after the drug’s administration and remain effective for up to a week [17,18]. Similarly, lower doses of ketamine have proved to be effective in acute, chronic, and neuropathic pain management, with its analgesic effects lasting for at least 24 h with minimal adverse effects [19]. These findings indicate that ketamine exerts both rapid and persistent responses and suggests that its metabolites may also play a part in the duration of effects [20,21,22]. Due to its robust response, an urgent need to expand the knowledge on less invasive methods for administering ketamine, such as the oral route, has also emerged [15,16].
Despite its attractive properties, long-term administration of ketamine is often associated with an increased oxidative stress environment, especially in organs that are particularly susceptible to oxidative damage, such as the brain, liver, and kidney, with evidence revealing increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, lipid peroxidation, and altered antioxidant enzyme activity [23,24,25,26,27]. The kidney has an increased potential for drug-induced damage due to its direct role in filtering and excreting chemical agents, which can translate into more severe consequences [28,29]. Notably, these effects are primarily described in association with high doses of ketamine administered through intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, or intravenous routes [23,30,31]. On the other hand, the effects of lower ketamine doses administered orally remains poorly understood. In animal studies, oral ketamine is typically administered via oral gavage, a method that allows for precise dosing but can cause physical stress and confounding physiological effects, such as increased blood pressure, heart rate, and plasma corticosterone levels, which might affect the animal’s welfare and interfere with experimental results [9,31,32,33,34]. To address these limitations, voluntary oral administration of target drugs has been explored as a less stressful alternative [34,35]. However, studies on oral low doses tend to focus on ketamine’s therapeutic or acute adverse effects, leaving a significant gap concerning their long-term impact [15,16].
While rodent models for gavage and parenteral administration of ketamine and its effects are well documented, voluntary oral self-administration remains largely unexplored, delaying the implementation of less invasive drug delivery models in different settings. Thus, the objective of this study was to establish a preliminary murine model of oral ketamine self-administration and investigate the potential adverse effects of low concentrations on the brain, liver, and kidney.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Housing and Maintenance
Thirty-eight FVB/n mice (Mus musculus), bred in the animal facility of University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro (UTAD), were paired in polycarbonate 1284L Eurostandard Type II L cages (Tecniplast, Milan, Italy) based on age (5–9 months) and sex (20 females and 18 males). The mice (27.4 g ± 4.6 g) were housed in a room in the same facility with a controlled 12:12 h light–dark cycle, temperature (23 °C ± 2), and humidity (50% ± 10) [36]. The animals were provided with 30 mL of tap water, a standard diet (4RF1; Mucedola, Milan, Italy) ad libitum, and a standard corncob litter (Corncob ultra 12, Ultragene, Viseu, Portugal) as bedding material along with cotton for nesting. The animals were acclimatized to these conditions for two weeks.
2.2. Experimental Design
The mice were randomly divided into three groups: the control, receiving 0 mg/mL (n = 4/sex), and two treatment groups receiving 5 (K5; n = 8/sex) or 10 mg/mL (K10; n = 6 males, 8 females) of ketamine (100 mg/mL; Nimatek; Dechra, Lisbon, Portugal) diluted daily in their drinking water for a period of 16 days [11,14,37]. Ketamine was introduced into the water at 20% of the final concentration (K5: 1 mg/mL; K10: 2 mg/mL) to allow the mice to acclimate to the solution and reduce the possibility of aversion associated with the altered water (Figure 1). Over the first five days, concentration gradually increased until the final concentrations of 5 (K5) and 10 (K10) mg/mL were reached. At the end of the study, the mice were euthanized by overdose, using an intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital (145 mg/kg; Euthasol® 400 mg/mL, Esteve, Barcelona, Spain). Post-euthanasia, blood samples were collected into lithium-heparin tubes and centrifuged for 15 min at 4 °C and 1400× g. The resulting plasma was transferred to clean tubes and stored at −80 °C alongside the brain, liver, and right kidney from each mouse. All sample processing and analysis were performed blind to each mouse treatment group.
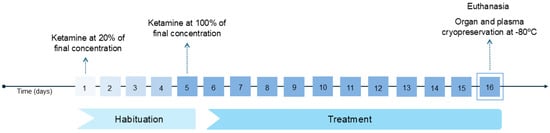
Figure 1.
A timeline of the procedure from the first ketamine administration to the organ collection and cryopreservation. Ketamine’s concentration gradually increased during the habituation period from 20% (day 1) of its final concentration to 100% (day 5). During the treatment period (days 5–16), the administered ketamine concentration (K5: 5 mg/mL; K10: 10 mg/mL) was not altered.
2.3. Water Consumption and Ketamine Intake
The consumption of water (mL), in which ketamine was diluted, was measured daily by recording the volume consumed from each cage’s water tube. This measure was registered daily to monitor ketamine intake and ensure that ketamine administration did not impact on the animals’ normal activities. The amount of ketamine daily ingested per cage was then calculated using the daily concentration administered in the water (mg/mL), water intake (mL), and average weight (kg) of the female or male mice in each cage following Equation (1). The average ketamine doses ingested per group were also calculated.
2.4. Oxidative Stress Quantification in Brain, Liver, and Kidney Samples: Sample Preparation and PROTEIN Quantification
The whole brain and a random piece of liver (0.6 g) and kidney (0.05 g) were placed in separate microcentrifuge tubes and prepared for the analysis of different oxidative stress parameters [38]. ROS levels were quantified using dichlorofluorescein (DCF) standards (0–1 mM), malondialdehyde (MDA) levels using MDA standards (0–100 mM), and protein carbonyl (PC) levels assuming the absorption coefficient of 22.0 mM/cm [38,39,40]. Superoxide dismutase (SOD; 0–150 U/mL), catalase (CAT; liver: 0–480 U/mL; brain and kidney: 0–60 U/mL), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione s-transferase (GST) levels were quantified using their respective standards following established protocols [41,42,43,44].
For the reduced (GSH) and oxidized (GSSG) glutathione tests, the samples were prepared following a different method, and the results were quantified using GSH (0–1000 mM) and GSSG (0–1000 mM) standards [45,46,47].
The total amount of protein in each sample was quantified at 280 nm, using a power wave XS2 microplate scanning spectrophotometer (Bio-Tek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA).
2.5. Analysis of Serum Biomarkers to Evaluate Liver and Kidney Function: Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST,) and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Levels as Indicators of Liver Function, and Creatinine and Serum Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Levels as Indicators of Kidney Function
ALT (ref. number: 41282), AST (ref. number: 41272), ALP (ref. number: 41242), creatinine (ref. number: 1001111), and BUN (ref. number: 1001333) levels were estimated according to the protocol described in the kit by Spinreact (Girona, Spain).
2.6. Evaluation of Additional Parameters in Kidney Samples
Given the kidney’s increased susceptibility to drug-induced damage [29], additional assessments were conducted to evaluate apoptosis (caspase 3 and caspase 9), inflammation (nitric oxide [NO]), and nucleic acid damage (DNA double-strand breaks estimation).
2.6.1. Caspase 3 and 9 Levels as Apoptosis INDUCTION Markers
The activity of both caspase 3, the primary effector of apoptosis, and caspase 9, activated through the intrinsic pathway, served as apoptosis markers in the kidney [48,49]. Samples were incubated with a caspase buffer, and their respective substrates, following a standard protocol [50]. The results were quantified using p-nitroaniline (pNA) standards (0–500 mM) [50].
2.6.2. NO as an Inflammation Marker
Nitric oxide (NO) levels were estimated using Griess reagent and 0.1% N-(1-Naphthyl) ethylenediamine dihydrochloride in a 1:1 proportion and quantified using sodium nitrate (NaNO2) standards (0–0.1 mM) [51].
2.6.3. DNA Double-Strand Break Estimation as a DNA Damage Marker
Double-strand breaks were estimated using 2% SDS buffer followed by 0.12 M potassium chloride (KCl) and incubation at 60 °C [52]. Samples were centrifuged, and the supernatant was incubated with Hoechst 33258 dye diluted in buffer [52]. The results were quantified using DNA standards diluted in TAE 1× [52].
2.7. Data Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 for Windows (Version 9.5.0; La Jolla, CA, USA). The normal distribution and homogeneity of the data were evaluated by the Shapiro–Wilk and Brown–Forsythe tests, respectively. Water and ketamine intake were analyzed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Šidák’s multiple comparison test, with results presented as the mean and standard deviation (SD). For the remaining parameters, normally distributed data was analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tuckey’s pairwise comparison test and the results are presented as the mean and SD. The data that did not follow a normal distribution was evaluated using the Kruskal–Wallis non-parametric test followed by Dunn’s pairwise comparison test, and the results are presented as the median and interquartile range (IQR). For all analyses, a significance level of 5% (p < 0.05) was established. Each analysis was conducted with at least 3 replicas from each group.
3. Results
3.1. Water and Ketamine Intake
Female water intake (mL) varied significantly over time (F (3.689, 25.82) = 14.50, p < 0.0001), with a significant reduction observed in the K10 group compared to the control group on days 11 (95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.993, 9.757, p = 0.0147) and 13 (95% CI = 3.923, 10.83, p = 0.0061), and compared to the K5 group on day 13 (95% CI = 1.824, 9.676, p = 0.01) (Figure 2A, Table S1).
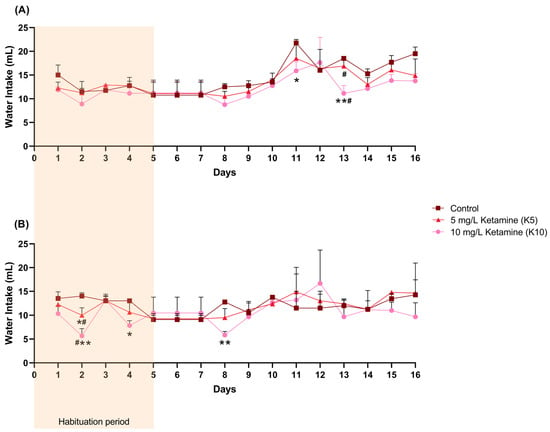
Figure 2.
The female (A) and male (B) daily water intake (mL) per cage (control: 2 cages; K5: 4 cages; K10: 4 cages), including the initial habituation period of 5 days during which ketamine concentration was gradually increased. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA followed by Šidák’s multiple comparison test for each day, and the results are presented as mean and SD. * indicates significant differences from the control group (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01), and # indicates significant differences between the K5 and K10 groups (# p < 0.05).
In male mice, water intake (mL) in the K10 group was only significantly lower than in the control group on days 2 (95% CI = 3.994,12.67, p = 0.0087), 4 (95% CI = 1.627, 8.707, p = 0.0241), and 8 (95% CI = 4.747, 9.086, p= 0.0021), and lower than the K5 group on day 2 (95% CI = 0.3391, 8.328, p = 0.0379) (Figure 2B, Table S2). In addition, the K5 group also revealed a lower consumption when compared to the control group on day 2 (95% CI = 0.6557, 7.344, p = 0.0282).
Female ketamine intake (mg/kg) varied significantly over time (F (3.252, 19.51) = 8.9946, p = 0.0005) and with the administered dose (F (1, 6) = 287.6, p < 0.0001), with a significant interaction between time and dose (F (15, 90) = 1.859, p = 0.038), indicating that intake patterns differed between treatment groups throughout the study. Female mice from the K10 group revealed a significantly higher ketamine intake on days 1 (95% CI = −238.0, −23.68, p = 0.022), 4 (95% CI = −157.7, −52.42, p = 0.0013), 5 (95% CI: −239.0, −18.77, p = 0.0251), 6 (95% CI: −233.9, −18.77, p = 0.0251), 7 (95% CI: −233.9, −18.77, p = 0.0251), and 15 (95% CI: −207.8, −50.89, p = 0.0047) (Figure 3A, Table S3).
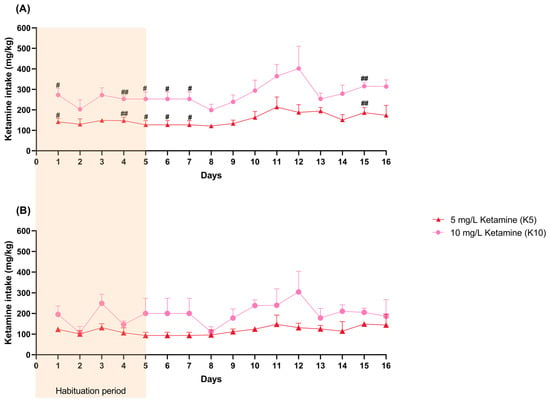
Figure 3.
The female (A) and male (B) daily ketamine intake (mg/kg) per cage (control: 2 cages; K5: 4 cages; K10: 4 cages) calculated based on daily water consumption (mL) and the average weight (kg) of the mice. The habituation period is visually represented in the figure (days 1–5). Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA followed by Šidák’s multiple comparison test for each day, and the results are presented as mean and SD. # indicates significant differences between the K5 and K10 groups (# p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01).
Male ketamine intake yielded similar results as it varied significantly over time (F (2.156, 10.78) = 4.051, p = 0.0465) and with the administered dose (F (1, 5) = 74.22, p = 0.0003,), with a significant interaction between the two (F (15, 75) = 1.971, p = 0.0289). Nevertheless, no differences between groups were observed on specific days (Figure 3B, Table S4).
Although the precise ketamine intake for each mouse could not be determined, an average estimation per group was calculated. Female mice in the K5 group ingested an average of 154.2 ± 12.5 mg/kg, while the K10 group consumed an average of 275.9 ± 7.1 mg/kg. Male mice from the K5 group had an average ketamine intake of 117.9 ± 12.5 mg/kg, while the K10 group consumed an average of 196.9 ± 11.2 mg/kg. Despite receiving the same concentrations, females and males differed significantly in average ketamine intake within both K5 (p = 0.0062) and K10 (p < 0.0001).
3.2. Oxidative Stress Evaluation
CAT levels were significantly higher than the control in the brains of female K5 (p = 0.0156) and K10 (p = 0.032) group mice (Table 1), but no significant changes were observed in the brains of male mice. The oxidative stress parameters were not significantly altered in the liver (Table 2) and kidney (Table 3) of the female or male mice.

Table 1.
Evaluation of oxidative stress parameters on the brain after exposure to 5 (K5) or 10 (K10) mg/L of ketamine. The experimental groups have at least four samples (n = 4) each 1.

Table 2.
Evaluation of oxidative stress parameters on the liver after exposure to 5 (K5) or 10 (K10) mg/L of ketamine. The experimental groups have at least four samples (n = 4) each 1.

Table 3.
Evaluation of oxidative stress parameters on the kidney after exposure to 5 (K5) or 10 (K10) mg/L of ketamine. The experimental groups have at least four samples (n = 4) each 1.
3.3. Liver and Kidney Function Assessment
Ketamine demonstrated no significant effect on the liver of the treated mice, as indicated by the results for AST, ALT and ALP activity. Similar results for kidney function were observed, as ketamine was revealed to cause no significant changes in creatinine and BUN levels (Table 4).

Table 4.
Evaluation of liver and kidney function after exposure to 5 (K5) or 10 (K10) mg/L of ketamine. The experimental groups have at least three samples (n = 3) each 1.
3.4. Apoptosis, Inflammation, and DNA Damage in Kidney Tissues
The apoptosis, inflammation, and DNA damage results showed no significant damage in the kidney tissues or serum of the tested mice (Table 5).

Table 5.
Evaluation of apoptosis, inflammation, and DNA damage parameters in the kidney after exposure to 5 (K5) or 10 (K10) mg/L of ketamine. The experimental groups have at least three samples (n = 3) each 1.
4. Discussion
Ketamine has recently become a valuable pharmacological research target due to its exceptional properties, especially when administered in lower doses through less invasive methods, such as the oral route [5,53]. However, as most animal research focuses on higher doses of ketamine and different administration routes, there is limited knowledge on the effects of oral self-administration at lower doses [30]. This study is the first to address this gap by establishing a murine model of oral ketamine self-administration, while assessing the effects of lower and potential therapeutic concentrations on the brain, liver, and kidney. The increase in ketamine concentration transiently decreases water consumption in both sexes; however, the amount of ketamine ingested is only different between groups in female mice. Moreover, despite altering CAT activity in the brains of female mice, ketamine did not affect other oxidative stress parameters in the brains of males, or in the kidney and liver of either male or female mice, suggesting that the oxidant environment might not have been altered. Accordingly, these concentrations did not impact liver or kidney function, nor did they influence apoptosis, inflammation, or DNA damage in kidney tissues.
When administrated orally, ketamine undergoes a significant first-pass metabolism and is converted into norketamine, a major metabolite thought to contribute to ketamine’s therapeutic effects [19,22,54,55]. This metabolic process shortens the drug’s half-life during the elimination phase, promoting rapid elimination and reducing exposure to ketamine, which might help minimize adverse effects [19,54,55]. Despite its low bioavailability when administered orally (16–30%), several studies have documented its rapid therapeutic efficacy [18,19,20,31]. In this study, ketamine was diluted in the drinking water provided ad libitum, allowing mice to consume it freely. To ensure their welfare, mice were housed in pairs, which introduced a limitation to the study as water and ketamine intake could not be accurately controlled and individual variability could be present. Nevertheless, based on the average water consumption per cage, intake remained within the normal range for the species, with only occasional differences between treatment and control groups that might indicate that ketamine had a slight impact on overall water consumption [56]. In addition, mice in the highest concentration group reported the lowest water intake, which may be related to changes in water taste due to the higher drug levels, as ketamine is known to have a bitter taste [57]. Interestingly, daily ketamine intake only differed between groups on some days in female mice, evidencing a different intake profile between sexes and suggesting gender-related sensitivity. This observation aligns with the existing literature but could be further explored when it comes to oral ketamine [58,59,60,61]. The distributed consumption of ketamine throughout the day, combined with its pharmacokinetic characteristics after oral administration, possibly facilitated its gradual elimination, further minimizing the duration of drug exposure and explaining the reduced adverse effects observed in the brain, liver, and kidney [62,63].
Organs like the brain, liver, and kidneys, are particularly susceptible to oxidative damage and related diseases [64,65,66]. This vulnerability arises from the brain’s high oxygen demand, the liver’s intense metabolic activity, and the kidney’s role in filtering and excreting toxins and chemical agents [65,67,68,69]. The primary cause of oxidative damage is ROS, which are naturally present in the body at low concentrations [70,71]. Antioxidant systems, including antioxidant enzymes and non-enzymatic mechanisms, regulate ROS to prevent toxicity [72,73,74]. However, excessive ROS levels can overwhelm these defense systems, leading to oxidation of lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids with the potential to trigger other biological processes such as apoptosis, necrosis, and inflammation [74]. In this study, while the brain revealed significant changes in an isolated oxidative marker, the liver and kidney reported no alterations, which might suggest that the overall antioxidant capacity may not have been affected. Conversely, the toxicological effects of ketamine administered via conventional routes are well documented in rodents, with several reports revealing increased oxidative stress in the tested organs [24,26,53,75,76]. Still, contradictory findings also exist, as some studies have reported that ketamine administrated subcutaneously in rats or per gavage in mice does not induce oxidative damage in the liver [14,77], while others demonstrate antioxidant effects in rats with traumatic brain injury or acute spinal cord injuries [78,79]. These inconsistencies accentuate the intricacy of ketamine’s pharmacology, which can have a varying impact on different organs, reinforcing the need to fully understand its oxidative impact.
The kidney has an increased potential for drug-induced damage and, as such, a more thorough investigation of the effects of ketamine on this organ was conducted [29]. The kidney is responsible for filtering waste products, including drugs and their metabolites, from the blood and excreting them through urine [29,69,80]. Thus, when kidney function is compromised, this filtration process becomes less efficient, resulting in increased residues in the serum [80,81]. Creatinine and urea, nitrogenous end products of metabolism, are largely eliminated in urine and thus extensively used as biomarkers for assessing kidney function [81]. The results demonstrated no significant alterations in creatinine and BUN levels, which indicates that kidney function may not have been affected by ketamine or its metabolites. Furthermore, the average creatinine and BUN levels were within the range observed in identical strains, further confirming the absence of renal complications [82,83]. A previous study demonstrated renal complications at 300 mg/kg administered daily by oral gavage [31], a cumulative dose similar to the ones reached in this study through gradual self-ingestion over multiple days, yet without evident complications. Nevertheless, another study in rats receiving 15 mg/kg of ketamine by oral gavage for 28 days [84] revealed no signs of toxicity, indicating that this route can still be viable if much lower doses are used. Collectively, the findings available on oral administration reinforce the complexity of ketamine’s action, suggesting that both the dose and method of administration may influence its toxicity profile. In alignment with findings on oxidative stress in the kidney, no significant alterations in the additional parameters were observed, which suggests that ketamine might have a specific range of therapeutic doses that do not significantly impact kidney function, oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, or DNA integrity. In addition, these findings accentuate the discrepancies between the effects observed with higher doses administered through conventional methods and the lower doses administered orally, which warrants further investigation. Nevertheless, the number of studies reporting the consequences of oral ketamine administration—particularly via voluntary administration—is still limited, which leaves a significant gap in the field that the present study begins to fill.
Despite the lessons learned, this study faces some limitations that should be addressed in future research. A primary limitation is the inability to precisely monitor individual water consumption, as water was available ad libitum and measured per cage. This makes it difficult to determine each mouse’s exact ketamine intake and represents a major vulnerability of this method compared to conventional routes where precise dosing is possible. However, the advantages associated with voluntary oral administration are still significant. As a less invasive method, this approach aligns closely with animal welfare principles due to minimal handling procedures and associated stress, which consequently reduces confounding variables. In this light, this study yielded interesting results that could serve as a foundation for future studies aiming to refine the oral ketamine self-administration model, potentially combining a flavoring agent to mask ketamine’s taste and extending the exposure period to fully understand how its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion shape its biological impact. Moreover, including pharmacokinetic analyses that verify whether therapeutic plasma levels are reached, as well as expanded testing of other relevant parameters, would also be a valuable addition to complement these results. Finally, the differences in ketamine intake profiles between sexes warrant further investigation to better understand sex-specific responses and ultimately confirm the safety of oral ketamine administration.
5. Conclusions
Ketamine at lower doses is emerging as a promising treatment for depression and pain conditions, with several studies documenting the rapid improvement of these symptoms following oral administration. While some limitations were addressed, this preliminary approach demonstrates the feasibility of voluntary oral ketamine intake in mice by revealing that mice consume ketamine-dosed water. In addition, these findings demonstrate the potential of sex-based differences in intake that may have an influence on the observed outcomes—an aspect warranting further investigation. The results presented could provide a solid basis for future studies aimed at improving this murine model of voluntary oral ketamine self-administration, specifically by including new strategies that enhance the accuracy of dose monitoring and palatability, as well as exploring extended exposure periods and different test parameters. Refining this non-invasive approach could lead the way for broader research into the therapeutic potential of oral ketamine that ultimately confirms the safety and efficacy of this administration route.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cimb47080592/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A. and C.V.; Data Curation, C.A.R. and L.S.; Formal Analysis, C.A.R., L.S., and L.M.F.; Funding Acquisition, S.M.M., L.A., and C.V.; Investigation, C.A.R., L.S., and L.M.F.; Methodology, L.M.F.; Project Administration, L.M.F., S.M.M., L.A., and C.V.; Resources, L.M.F., S.M.M., L.A., and C.V.; Supervision, L.M.F., S.M.M., L.A., and C.V.; Validation, C.A.R., L.S., and L.M.F.; Visualization, C.A.R. and L.S.; Writing—Original Draft, C.A.R.; Writing—Review and Editing, C.A.R., L.M.F., S.M.M., L.A., and C.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Funds from FCT—Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology—under the projects UIDB/04033/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/04033/2020), LA/P/0126/2020 (https://doi.org/10.54499/LA/P/0126/2020), and 2021.00458.CEECIND (https://doi.org/10.54499/2021.00458.CEECIND/CP1690/CT0001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This project was approved by an Ethics Review Body (Órgão Responsável pelo Bem-Estar Animal da UTAD) on 15 June 2021, under the reference 0421/000/000/2021, and by the General Directorate for Food and Veterinary (Direção Geral de Alimentação e Veterinária) on 28 September 2021, under the acceptance number 013159, in agreement with the European Directive on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes (2010/63/EU).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings described in this article will be provided by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| UTAD | University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro |
| K5 | 5 mg/L of ketamine |
| K10 | 10 mg/L of ketamine |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| PC | Protein carbonyls |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| GSSG | Oxidized glutathione |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GR | Glutathione reductase |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| BUN | Serum urea nitrogen |
| ANOVA | Two-way analysis of variance |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
References
- Félix, L.; Antunes, L.; Campos, S.; Venâncio, C.; Coimbra, A.M. Recreational Use of Ketamine and Its Interaction with NMDA Receptors. In Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 672–680. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Anand, K.J. Developmental neurotoxicity of ketamine in pediatric clinical use. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 220, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, D.; Mercier, M.S. Ketamine and phencyclidine: The good, the bad and the unexpected. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4254–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, R.H. Ketamine as an Analgesic. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2002, 16, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Schoevers, R.A.; Chaves, T.V.; Balukova, S.M.; Rot, M.; Kortekaas, R. Oral ketamine for the treatment of pain and treatment-resistant depressiond. Br. J. Psychiatry 2016, 208, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasburger, S.E.; Bhimani, P.M.; Kaabe, J.H.; Krysiak, J.T.; Nanchanatt, D.L.; Nguyen, T.N.; Pough, K.A.; Prince, T.A.; Ramsey, N.S.; Savsani, K.H.; et al. What is the mechanism of Ketamine’s rapid-onset antidepressant effect? A concise overview of the surprisingly large number of possibilities. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzwiser, D.; Tawfic, Q.A. Expanding Role of NMDA Receptor Antagonists in the Management of Pain. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 347–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, K.; Pu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Wang, S.M.; Xiong, Z.; Ren, Q.; Dong, C.; Fujita, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Comparison of antidepressant and side effects in mice after intranasal administration of (R,S)-ketamine, (R)-ketamine, and (S)-ketamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 181, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoyama, M.; Shimoyama, N.; Gorman, L.; Elliott, K.; Inturrisi, C.E. Oral ketamine is antinociceptive in the rat formalin test: Role of the metabolite, norketamine. Pain 1999, 81, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdinc, M.; Uyar, E.; Kelle, I.; Akkoc, H. Anti-nociceptive effects of low dose ketamine in mice may be mediated by the serotonergic systems. Psychiat Clin. Psychy 2019, 29, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Cao, Y.; Han, J. Repeated administration of low dose ketamine for the treatment of monoarthritic pain in the rat. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Vale, E.M.; Xavier, C.C.; Nogueira, B.G.; Campos, B.C.; de Aquino, P.E.; da Costa, R.O.; Leal, L.K.; de Vasconcelos, S.M.; Neves, K.R.; de Barros Viana, G.S. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ketamine and the Relationship to Its Antidepressant Action and GSK3 Inhibition. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 119, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lee, B.; Liu, R.-J.; Banasr, M.; Dwyer, J.M.; Iwata, M.; Li, X.; Aghajanian, G.; Duman, R.S. mTOR-Dependent Synapse Formation Underlies the Rapid Antidepressant Effects of NMDA Antagonists. Science 2010, 329, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venancio, C.; Antunes, L.; Felix, L.; Rodrigues, P.; Summavielle, T.; Peixoto, F. Chronic ketamine administration impairs mitochondrial complex I in the rat liver. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgibbon, E.J.; Hall, P.; Schroder, C.; Seely, J.; Viola, R. Low dose ketamine as an analgesic adjuvant in difficult pain syndromes: A strategy for conversion from parenteral to oral ketamine. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2002, 23, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.T.; Hermens, D.F.; Dutton, M.; Gallay, C.C.; Jensen, E.; Jones, M.; Scherman, J.; Beaudequin, D.A.; Yang, C.; Schwenn, P.E.; et al. Low dose oral ketamine treatment in chronic suicidality: An open-label pilot study. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, R.S.; Li, N.; Liu, R.J.; Duric, V.; Aghajanian, G. Signaling pathways underlying the rapid antidepressant actions of ketamine. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriger, A.; Pickering, G. Ketamine and depression: A narrative review. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2019, 13, 3051–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonk, M.I.; Koder, B.G.; van den Bemt, P.M.; Huygen, F.J. Use of oral ketamine in chronic pain management: A review. Eur. J. Pain 2010, 14, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. Ketamine for Depression, 4: In What Dose, at What Rate, by What Route, for How Long, and at What Frequency? J. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 78, e852–e857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aan Het Rot, M.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Charney, D.S.; Mathew, S.J. Ketamine for depression: Where do we go from here? Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtman, J.R., Jr.; Crooks, P.A.; Johnson-Hardy, J.K.; Hojomat, M.; Kleven, M.; Wala, E.P. Effects of norketamine enantiomers in rodent models of persistent pain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasikara, H.; Sungu, N.; Arslan, M.; Kucuk, A.; Ozturk, L.; Afandiyeva, N.; Kavutcu, M. Repeated Doses of Ketamine Affect the Infant Rat Urogenital System. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2021, 15, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.; Spiazzi, C.M.; Bortolin, T.; Canever, L.; Petronilho, F.; Mina, F.G.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Quevedo, J.; Zugno, A.I. Different sub-anesthetic doses of ketamine increase oxidative stress in the brain of rats. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Ganguly, S.; Srivastava, M.; Palit, G. Effect of ‘chronic’ versus ‘acute’ ketamine administration and its ‘withdrawal’ effect on behavioural alterations in mice: Implications for experimental psychosis. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 216, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedir, Z.; Erdem, K.T.O.; Ates, I.; Karakurt, T.C.O.; Gursul, C.; Onk, D.; Kurt, N.; Suleyman, Z.; Suleyman, H. Effects of ketamine, thiopental and their combination on the rat liver: A biochemical evaluation. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 31, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venâncio, C.; Félix, L.; Almeida, V.; Coutinho, J.; Antunes, L.; Peixoto, F.; Summavielle, T. Acute Ketamine Impairs Mitochondrial Function and Promotes Superoxide Dismutase Activity in the Rat Brain. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 120, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Gobe, G. Identification and quantification of apoptosis in the kidney using morphology, biochemical and molecular markers. Nephrol. Carlton 2007, 12, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelias, K.; Grapsa, E. Drug abuse and kidney. Hippokratia 2001, 15, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nebendahl, K.; Hauff, P. Drug Administration. In Small Animal Imaging; Kiessling, F., Pichler, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rajandram, R.; Yap, N.; Ong, T.; Mun, K.; Wali, H.; Hasan, M.; Razack, A.; Mohd, M. Oral ketamine induced pathological changes of the urinary tract in a rat model. Malays. J. Pathol. 2017, 39, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Arantes-Rodrigues, R.; Henriques, A.; Pinto-Leite, R.; Faustino-Rocha, A.; Pinho-Oliveira, J.; Teixeira-Guedes, C.; Seixas, F.; Gama, A.; Colaço, B.; Colaço, A.; et al. The effects of repeated oral gavage on the health of male CD-1 mice. Lab. Anim. 2012, 41, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, O.J.; Ademakinwa, O.Q.; Olalekan, T.O.; Onaolapo, A.Y. Ketamine-induced behavioural and brain oxidative changes in mice: An assessment of possible beneficial effects of zinc as mono- or adjunct therapy. Psychopharmacol. Berl 2017, 234, 2707–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.K.; Boberg, J.R.; Walsh, M.T.; Wolf, V.; Trujillo, A.; Duke, M.S.; Palme, R.; Felton, L.A. A less stressful alternative to oral gavage for pharmacological and toxicological studies in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 260, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.A.; Boctor, S.Y. Use of food wafers for multiple daily oral treatments in young rats. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2009, 48, 292–295. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, T.; Silva, J.; Peixoto, F.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.C.; Gama, A.; Seixas, F.; Finimundy, T.C.; Barros, L.; Matos, M.; Oliveira, P.A.; et al. The role of natural compounds in rat mammary cancer: The beneficial effects of Santolina chamaecyparissus L. aqueous extract. Vet. Stanica 2023, 55, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, W.; Pan, J.; Huang, K.; Chen, R.; Pan, T.; Liao, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, D.; et al. Environmental enrichment and abstinence attenuate ketamine-induced cardiac and renal toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, C.; Yu, K.; Shi, X.; Yeung, L.W.; Lam, P.K.; Wu, R.S.; Zhou, B. Hexabromocyclododecane-induced developmental toxicity and apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 93, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, C.S.; Oliveira, R.; Bento, F.; Geraldo, D.; Rodrigues, J.V.; Marcos, J.C. Simplified 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine spectrophotometric assay for quantification of carbonyls in oxidized proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 458, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, B.; Rosengren, B.; Shertzer, H.G.; Camejo, G. Lipoprotein oxidation and measurement of thiobarbituric acid reacting substances formation in a single microtiter plate: Its use for evaluation of antioxidants. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 208, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, I.; Yurtarslanl, Z.; Canbolat, O.; Akyol, O. A methodological approach to superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity assay based on inhibition of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction. Clin. Chim. Acta 1993, 214, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claiborne, A. Catalase activity. In CRC Handbook of Methods for Oxygen Radical Research; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 283–284. [Google Scholar]
- Massarsky, A.; Kozal, J.S.; Di Giulio, R.T. Glutathione and zebrafish: Old assays to address a current issue. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habig, W.H.; Jakoby, W.B. Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzym. 1981, 77, 398–405. [Google Scholar]
- Alisik, M.; Neselioglu, S.; Erel, O. A colorimetric method to measure oxidized, reduced and total glutathione levels in erythrocytes. J. Lab. Med. 2019, 43, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreani, M.; Petrone, M.; Debetto, P.; Palatini, P. A comparison between different methods for the determination of reduced and oxidized glutathione in mammalian tissues. Free Radic. Res 1997, 26, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Gera, R.; Purohit, M.P.; Patnaik, S.; Ghosh, D. Fluorometric Estimation of Glutathione in Cultured Microglial Cell Lysate. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentnall, M.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; Ladron De Guevara, R.; Cepero, E.; Boise, L.H. Caspase-9, caspase-3 and caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuida, K. Caspase-9. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 32, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincberg, M.; Gopas, J.; Tal, J. Minute virus of mice (MVMp) infection and NS1 expression induce p53 independent apoptosis in transformed rat fibroblast cells. Virology 2011, 412, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, M.; Kang, S.C. Vitexin inhibits acrylamide-induced neuroinflammation and improves behavioral changes in zebrafish larvae. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2019, 74, 106811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, P.L. DNA precipitation assay: A rapid and simple method for detecting DNA damage in mammalian cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1998, 11, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Ayeni, O.J.; Ogundeji, M.O.; Ajao, A.; Onaolapo, O.J.; Owolabi, A.R. Subchronic ketamine alters behaviour, metabolic indices and brain morphology in adolescent rats: Involvement of oxidative stress, glutamate toxicity and caspase-3-mediated apoptosis. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2019, 96, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Panetta, J.C.; Roberts, J.K.; Schuetz, E.G. Ketamine Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Are Altered by P-Glycoprotein and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Efflux Transporters in Mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Metabolism and metabolomics of ketamine: A toxicological approach. Forensic Sci. Res. 2017, 2, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmanov, A.A.; Reed, D.R.; Beauchamp, G.K.; Tordoff, M.G. Food intake, water intake, and drinking spout side preference of 28 mouse strains. Behav. Genet. 2002, 32, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domany, Y.; Bleich-Cohen, M.; Tarrasch, R.; Meidan, R.; Litvak-Lazar, O.; Stoppleman, N.; Schreiber, S.; Bloch, M.; Hendler, T.; Sharon, H. Repeated oral ketamine for out-patient treatment of resistant depression: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept study. Br. J. Psychiatry 2019, 214, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponton, E.; Turecki, G.; Nagy, C. Sex Differences in the Behavioral, Molecular, and Structural Effects of Ketamine Treatment in Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 25, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wei, M.; Nie, Z.; Raza, F. Gender Differences in Adverse Events of Ketamine Drugs: A Real-World Study Based on FAERS. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2024, 2024, 4898082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, N.; Kabbaj, M. Sex differences in the antidepressant-like effects of ketamine. Neuropharmacology 2013, 70, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.J.; Perry, E.B.; Cho, H.S.; Krystal, J.H.; D’Souza, D.C. Greater vulnerability to the amnestic effects of ketamine in males. Psychopharmacology 2006, 187, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.A.; Nimmo, W.S.; Grant, I.S. Bioavailability, Pharmacokinetics, and Analgesic Activity of Ketamine in Humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannes, B.; Micheletti, G.; Warter, J.M.; Kempf, E.; Di Scala, G. Behavioural, pharmacological, and biological effect of acute and chronic administration of ketamine in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1991, 128, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daenen, K.; Andries, A.; Mekahli, D.; Van Schepdael, A.; Jouret, F.; Bammens, B. Oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichoz-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S. Oxidative Stress and the Central Nervous System. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 360, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbek, E. Induction of oxidative stress in kidney. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 465897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.E.; Youness, E.R.; Mohammed, N.A.; Omara, E.A.; Sleem, A.A. Effect of ketamine on oxidative stress following lipopolysaccharide administration. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breshears, M.A.; Confer, A.W. The Urinary System. In Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease; Zachary, J.F., Ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2017; pp. 617–681. [Google Scholar]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. World Allergy Organ. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modaresi, A.; Nafar, M.; Sahraei, Z. Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 9, 165–179. [Google Scholar]
- Adwas, A.A.; Elsayed, A.S.I.; Azab, A.E.; Quwaydir, F.A. Oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms in human body. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 6, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2019, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Ahsan, H.; Zia, M.K.; Siddiqui, T.; Khan, F.H. Understanding oxidants and antioxidants: Classical team with new players. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.C.C.; Cito, M.C.O.; Silva, M.I.G.; Moura, B.A.; Neto, M.R.A.; Feitosa, M.L.; Chaves, R.C.; Macedo, D.S.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M.; Fonteles, M.M.F.; et al. Behavioral alterations and pro-oxidant effect of a single ketamine administration to mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 83, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.M.; Chuang, S.M.; Long, C.Y.; Lee, Y.L.; Wang, C.C.; Lu, M.C.; Lin, R.J.; Lu, J.H.; Jang, M.Y.; Wu, W.J.; et al. Ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis and bladder apoptosis involve oxidative stress mediated by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2015, 309, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofael, H.Z. Effect of ketamine pretreatment on cocaine-mediated hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 152, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wu, S.; Xie, W.; He, H. Ketamine ameliorates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in experimental traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2 pathway. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2018, 12, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.H.; Yu, J.G.; Li, J.J.; Sun, J.Y. Neuroprotective effect of ketamine on acute spinal cord injury in rats. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 3551–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finco, D.R. Kidney Function. In Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Kaneko, J.J., Harvey, J.W., Bruss, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 441–484. [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, S.; Bellomo, R.; Goldsmith, D. The meaning of the blood urea nitrogen/creatinine ratio in acute kidney injury. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.D.; Burdeshaw, J.A.; Crosby, R.G.; Cusic, A.M.; Denine, E.P. Hematology and Clinical Chemistry Reference Values for C57BL/6 x DBA/2 F1 Mice. Cancer Res. 1978, 38, 2636–2639. [Google Scholar]
- Serfilippi, L.M.; Pallman, D.R.; Russell, B. Serum Clinical Chemistry and Hematology Reference Values in Outbred Stocks of Albino Mice from Three Commonly Used Vendors and Two Inbred Strains of Albino Mice. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2003, 42, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, P.F.; Simon, K.A.; Hueza, I.M. Toxic and Immunotoxic Evaluation of Ketamine and/or Ethanol in Rats during 28 Days. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).