Abstract
Background: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have emerged as anti-hyperglycemic agents that improve glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients, either as monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic drugs. Methods: A novel series of dihydropyrimidine phthalimide hybrids was synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro and in vivo DPP-4 inhibition activity and selectivity using alogliptin as reference. Oral glucose tolerance test was assessed in type 2 diabetic rats after chronic treatment with the synthesized hybrids ± metformin. Cytotoxicity and antioxidant assays were performed. Additionally, molecular docking study with DPP-4 and structure activity relationship of the novel hybrids were also studied. Results: Among the synthesized hybrids, 10g, 10i, 10e, 10d and 10b had stronger in vitro DPP-4 inhibitory activity than alogliptin. Moreover, an in vivo DPP-4 inhibition assay revealed that 10g and 10i have the strongest and the most extended blood DPP-4 inhibitory activity compared to alogliptin. In type 2 diabetic rats, hybrids 10g, 10i and 10e exhibited better glycemic control than alogliptin, an effect that further supported by metformin combination. Finally, 10j, 10e, 10h and 10d had the highest radical scavenging activity in DPPH assay. Conclusions: Hybrids 10g, 10i and 10e are potent DPP-4 inhibitors which may be beneficial for T2DM treatment.
1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is a rapidly growing chronic disease that threatens human health worldwide. T2DM is characterized by insulin resistance and impaired glucose homeostasis, resulting in hyperglycemia [1]. Currently, there are a number of antidiabetic drugs including sulfonylureas, meglitinides, thiazolidinediones, biguanides, α-glucosidase inhibitors aimed at suppressing hepatic glucose output, stimulating insulin release, mitigating glucose absorption, and increasing peripheral glucose utilization [2,3]. Unfortunately, the use of these drugs is associated with various side effects including weight gain and hypoglycaemia which deteriorate the optimum glycemic control over a longer time [4,5]. Therefore, many newer approaches with novel mechanism of action have been emerged for better T2DM management. Among these newer approaches, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors that gained extensive interest in T2DM treatment with proved long term efficacy and better glycemic control. Additionally, DPP-4 inhibitors play an important role in regeneration and differentiation of pancreatic β-cells and also proved to be well tolerated as well as decreasing the risk of hypoglycemia and cardiovascular side effects [6].
DPP-4 is widely expressed in most tissues and body fluids including the biliary tract, kidney, gastrointestinal tract, uterus and liver [7]. It is the key regulatory enzyme and a signaling factor of incretin hormones (insulin-stimulating hormones, glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1), and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)) [8]. These hormones play a crucial role in promoting β-cell proliferation, increasing insulin biosynthesis, reducing β-cell apoptosis [9,10]. As a consequence of rapid degradation by DPP-4, both GLP-1 and GIP have very short half-life which is 1–2 minutes for the former and 7 minutes for the latter [11,12]. Currently, there are several structurally diverse DPP-4 inhibitors some of them have been approved on the market such as sitagliptin, alogliptin, linagliptin, gemigliptin, anagliptin and teneligliptin [13,14].
On the other hand, pyrimidines represented one of the most important versatile scaffolds in medicinal chemistry [15] that possess many activities including antidiabetic [16], anti-inflammatory [17], anticancer [18], antibacterial [19], antihypertensive [20], antifungal [21] and antitubercular [22]. Moreover, some of the synthesized N-methylated and N-benzylated pyrimidinediones have shown in vitro DPP-4 inhibitory activity in significant range [23]. In addition, excellent IC50 values were recorded for novel pyrimidinedione derivatives when evaluated for their DPP-4 inhibitory activity and in vivo anti-hyperglycemic efficacy [24].
On the other hand, phthalimide-containing compounds are precious synthetic scaffolds that showed different biological activities such as: antihyperglycemic [25], anti-inflammatory [26], antimicrobial [27], antihyperlipidimic [28], anticonvulsant [29], antiviral [30] and anticancer effects [31]. Additionally, a novel series of potent DPP-4 inhibitors bearing an N-phenylphthalimide skeleton has been synthesized and displayed higher potency compared to a well-known DPP-4 specific inhibitor [32,33]. Recently, some non-competitive DPP-4 inhibitors have been synthesized from a series of benzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine phthalimide derivatives and have shown better activity compared to DPP-4 inhibitors synthesized from amine precursors [34].
Based on the aforementioned information, we aimed at combining pyrimidine and phthalimide moieties into a single candidate template for the purpose of synergistic activity (Figure 1). To better elucidate their DPP-4 inhibitory activity, our synthesized hybrids were subjected to in vitro DPP inhibition assay utilizing human recombinant DPP-4, DPP-8 and DPP-9; alogliptin used as a reference standard. Moreover, the effect of our compounds on in vivo DPP-4 activity was assessed in SD rats, where DPP-4 activity was evaluated in the blood over 2 days using alogliptin as a reference standard. Additionally, to gain better understanding of the role of our compounds on T2DM, we studied the effect of chronic treatment of the synthesized hybrids 10a–j in presence and absence of metformin (MET) on HFD-induced T2DM in rats. Also, the target hybrids were tested for any possible antioxidant activity using DPPH method. Finally, the effect of synthesized hybrids 10a–j on cell viability was examined on normal hepatic LO2 cells using MTT assay, to check for any cytotoxic effect. Furthermore, structure activity relationship and molecular docking analysis of the titled hybrids were performed to get a distinct insight about the binding mode and interactions of the compounds with DPP-4 active site.
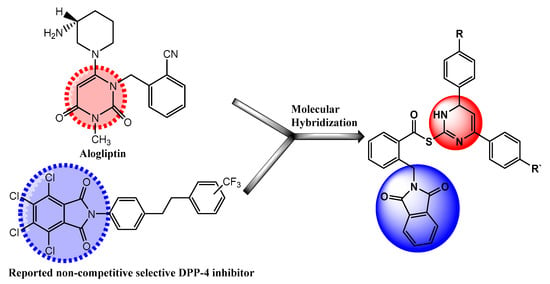
Figure 1.
Diagram represents design of novel DPP-4 inhibitors.
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
The synthetic protocols applied to synthesize the target compounds 10a–j are illustrated in Scheme 1. Substituted acetophenone 1 reacted with various aromatic aldehydes 2 in 10% sodium hydroxide solution following Claisen-Schmidt condensation conditions to afford exclusively the E-chalcone isomers 3a–j in high yields [35]. These chalcones 3a–j were further reacted with thiourea (4) in the presence of sodium hydroxide in abs. ethanol to give 4,6-diaryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones 5a–j. The structures of compounds 5e, g, i and j were confirmed on the basis of their spectral data (FT-IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, MS) and elemental analyses (see Section 4).
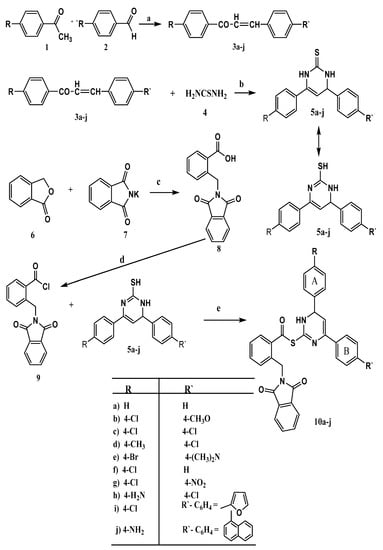
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of the target compounds 10a–j. Reagents and conditions: (a) NaOH, dil. EtOH, rt; (b) NaOH, abs. EtOH; (c) DMF, reflux; (d) SOCl2, reflux, dry benzene, distillation; (e) abs. dichloromethane, TEA, rt.
Reduction of phthalimide gave phthalide (6) which on refluxing with potassium phthalimide in DMF afforded α-phthalimido-o-toluic acid (8). Reaction of 8 with thionyl chloride brought about α-phthalimido-o-toluyl chloride (9) [36]. Treatment of 4,6-diaryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones 5a–j with 9 in dichloromethane, and in the presence of triethyl amine (TEA) as a base brought about the target compounds (4,6-diaryl-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)-2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl) benzothioates 10a–j. Notably, the S-substituted product was isolated as nucleophilicity of sulphur is greater than nitrogen and no N-substituted product was isolated. The structure of 10a–j hybrids were elucidated on the bases of both spectral data (IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, MS) and elemental analyses.
In the IR spectra the following peaks were observed: 3476–3384 cm−1 (NH), 3071–2918 cm−1 (Ar-CH), 1774–1770 cm−1, 1725–1714 cm−1 (CO), 1677–1603 cm−1 (C=N), 1595–1502 cm−1, 1491–1467 cm−1 (C=C). Beside the δ values of OCH3, CH3, Nme2, NH2 side chains in the 1H-NMR spectra of the hybrids 10b, 10d, 10e, 10h and 10j which appear at 3.76, 2.34, 2.52, 6.19 and 6.17, respectively, the δ values of the other functional groups fall in the following ranges: NH:11.52–11.19 ppm; Ar-H: 8.51–6.75 ppm; HC=CH-Ar: 6.68–6.35 ppm; CH-Ar: 5.29–5.27 ppm; CH2: 5.08–5.01 ppm. Also, the 13C-NMR spectra of some selected compounds were resolved in appropriate regions confirming the assigned structures. Both mass spectra and elemental analyses of 10a–j hybrids are a further support of their structures by giving correct molecular formula and molecular ion peaks.
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. In Vitro DPP Inhibition Assay
All the target hybrids listed in Table 1 were evaluated for the inhibition of human recombinant DPP-4 and alogliptin was chosen as a reference compound. Additionally, all the synthesized hybrids were tested for the inhibition of DPP-8 and DPP-9 which is closely related to DPP-4 and whose inhibition is associated with great toxicity.

Table 1.
DPP-4, DPP-8 and DPP-9 inhibitory activities of hybrids 10a–j and alogliptin.
Interstingly, hybrids 10g and 10i identified as the most potent DPP-4 inhibitors with picomolar potency, exhibiting IC50 values of 0.51 and 0.66 nM, respectively; which represented 11.2, 8.6 fold superior activity than alogliptin. The potent DPP-4 inhibitory activity of these compounds may be attributed to electronic behavior of the nitro group in ring B of hybrid 10g and the small size of the furanyl group in ring B of hybrid 10i, which facilitated the formation of hydrogen bond with DPP-4 active site.
Of considerable interest, the mesomeric effect raised from 4-Me2N group in ring B as well as 4-bromo substitutions in ring A of hybrid 10e markedly boosted DPP-4 inhibition resulted in low nanomolar potency activity (1.42 nM, 4 fold increased activity than that of alogliptin). Moreover, introducing an electron donating groups (methyl group in ring A and methoxy group in ring B) retained the potent DPP-4 inhibitory activity of hybrids 10b and 10d, whose activities were 1.5 fold and 2.6 fold the activity of alogliptin with IC50 values of 3.78, 2.19 nM, respectively. According to the basis of electron donating properties, hybrid 10j expected to be the most potent DPP-4 inhibitor but on the contrary, the DPP-4 inhibitory potency is eroded (IC50 = 7.35 nM). The probable reason could be the worse fit of the naphthyl group in ring B with more steric inhibition into the receptor pocket compared to the phenyl ring in the other synthesized compounds. On the other hand, the enzyme inhibition activity was dramatically decreased in the unsubstituted phenyl group and upon introducing the electron withdrawing chlorine atom in 10h, 10c and hybrids 10f which was confirmed by their high IC50 values compared to alogliptin. Out of these, it might be concluded that the substituent electronic character and the steric volume of the phenyl ring considerably influenced the DPP-4 inhibition activity.
On the other hand, all the synthesized hybrids targeted DPP-8 and DPP-9 at IC50 exceeding 100 µM which indicates that our compounds have superior selectivity for DPP-4 and neglected affinity toward DPP-8 and DPP-9.
2.2.2. Effects of Synthesized Hybrids (10a–j) on Cell Viability
The cytotoxic effect of the synthesized hybrids 10a–j was examined on normal hepatic LO2 cells using MTT assay. The test was done using 3 different concentrations (10 µM, 30 µM and 50 µM) for each compound. As shown in (Figure 2a), hybrid 10c had the most cytotoxic effect with 72.57% and 72.50% cell viability at 30 µM and 50 µM concentration, respectively. However, hybrid 10i came in the second place with cell viability percent of 74.60 at 10 µM concentration, followed by hybrid 10h with cell viability percent of 77.47 at 50 µM concentration, as presented in (Figure 2b). While, the cell viability percent for other synthesized hybrids ranged from 80.13 to 101.2. In conclusion, our compounds showed weak cytotoxic effect against hepatic LO2 cells.
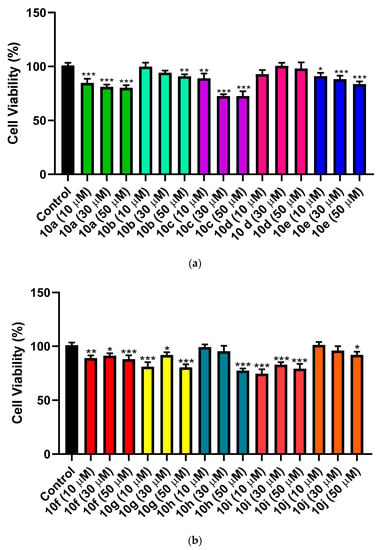
Figure 2.
(a) Effect of hybrids 10a–e on viability of normal hepatic LO2 cells. (n = 5). (b) Effect of hybrids 10f–j on viability of normal hepatic LO2 cells (n = 5). *** Significant from control group at p < 0.001, ** Significant from control group at p < 0.01, * Significant from control group at p < 0.05.
2.2.3. Effect of Synthesized Hybrids (10a–j) on In Vivo DPP-4 Activity
The effect of the synthesized hybrids 10a–j on blood DPP-4 activity was investigated in SD rats, as shown in (Figure 3a,b). The hybrids were administrated in a single oral dose of 10 mg/kg and in vivo DPP-4 activity was evaluated over 2 days, using alogliptin as reference compound. Notably, among all tested hybrids and aloglipin, hybrid 10g has both the strongest and longest DPP-4 inhibitory action, with 18.45% and 47% DPP-4 blood activity at 12 h and 24 h, respectively, followed by hybrid 10i with DPP-4 blood activity of 18.8% and 49.9% at 12 h and 24 h, respectively. While, alogliptin achieved DPP-4 blood activity of 20.95% and 56.1% at 12 h and 24 h, respectively. Importantly, hybrids 10g and 10i also showed extended DPP-4 inhibitory activity at 48 h with blood DPP-4 activity of 73.3% and 76%, respectively, while, alogliptin DPP-4 blood activity was 97.05%. Worthily, hybrids 10g, 10i and 10e had the strongest in vitro and in vivo DPP-4 inhibiting activity.
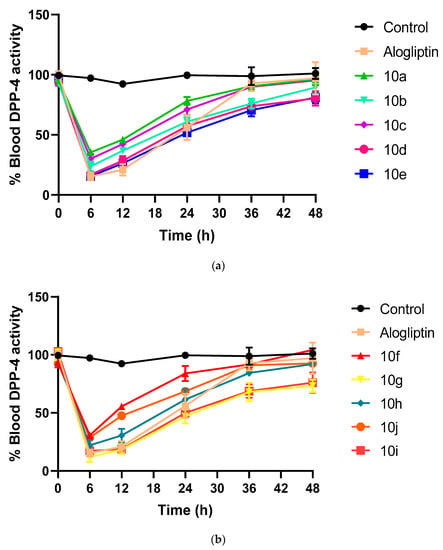
Figure 3.
(a). The in vivo DPP-4 activity of 10a–e hybrids and alogliptin within 48 h. (n = 3). (b) The in vivo DPP-4 activity of 10f–j hybrids and alogliptin within 48 h. (n = 3).
2.2.4. Effect of Chronic Treatment of Compounds 10a–j with or without MET on HFD-Induced Type 2 Diabetic rats
HFD significantly induced insulin resistance in SD rats as evident by extremely significant increase in the AUC of OGTT in non-treated diabetic group compared to control group, as shown in (Figure 4a,b). We studied the chronic effect of oral administration of hybrids 10a–j at a dose of 10 mg/kg/day in absence and presence of MET, on insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic rats. In absence of MET, hybrids 10g, 10i and 10e significantly improved glucose tolerance above alogliptin, as evident by the reduction in the AUC of OGTT when compared to non-treated diabetic group, (Figure 5a,b). Moreover, oral administration of MET (150 mg/kg/day) together with hybrids 10a–j, further enhanced insulin sensitivity with a profound reductions in AUC of OGTT almost in all treated groups. Interestingly, MET addition to 10g, 10i and 10e-treated groups reduced AUC of OGTT by 22.93%, 21.7% and 22.82%, respectively. Accordingly, glucose tolerance in 10g/MET treated group reached a normal level with AUC equals 13787 ± 201 mg.min/dL compared to 14305 ± 318 mg.min/dL for normal control group. Similarly, addition of MET to alogliptin treated group reduced AUC of OGTT from 20835 ± 146 mg.min/dL in alogliptin treated group to 15451 ± 110 mg.min/dL in MET/alogliptin treated group.
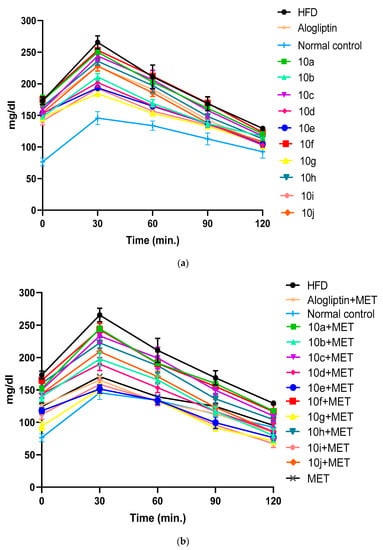
Figure 4.
(a) Chronic effect of hybrids 10a–j and alogliptin administration on blood glucose levels during an OGTT in type 2 diabetic rats. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 7). (b) Chronic effect of combined administration of 10a–j/MET, alogliptin/MET on blood glucose levels during an OGTT in type 2 diabetic rats. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 7).
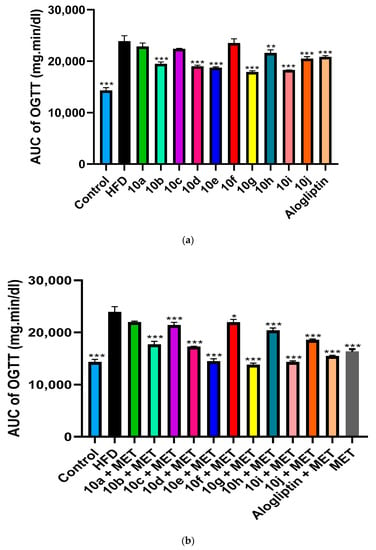
Figure 5.
(a) Chronic effect of hybrids 10a–j and alogliptin administration on area under the curve (AUC) of OGTT in type 2 diabetic rats. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 7). *** Significant from diabetic control group at p < 0.001, ** Significant from diabetic control group at p < 0.01. (b) Chronic effect of combined administration of 10a–j/MET, alogliptin/MET on area under the curve (AUC) of OGTT in type 2 diabetic rats. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 7). *** Significant from diabetic control group at p < 0.001, * Significant from diabetic control group at p < 0.05.
2.2.5. Antioxidant Activity
The in vitro antioxidant activity of the synthesized hybrids 10a–j was tested depending on DPPH method using ascorbic acid as standard. The results in Table 2 revealed that all the synthesized compounds showed good antioxidant activity, wherein hybrids 10j, 10e, 10h and 10d have the highest radical scavenging activity in DPPH assay at 100 µM concentration.

Table 2.
Antioxidant activity of hybrids 10a–j using the DPPH method.
2.2.6. Molecular Docking Study: Docking at the DPP-4 active site
To verify the protein-ligand binding properties and the key structural features required for the inhibitory activity of the novel synthesized hybrids 10a–j with the protein DPP-4, a molecular docking study was performed using the molecular docking program MOE. The results of energy binding scores and binding interactions were depicted in Table 3 and Figure 6. The 3D crystal structure of DPP-4 was obtained from the Protein Data Bank [PDB code 3G0B, resolution 2.25 Å (www.rcsb.org, accessed on 10 February 2021)] and alogliptin was used as a reference DPP-4 inhibitor. DPP-4 active site is formed of two main binding pockets Figures S1 and S2 in addition to Figure S2 extensive subsite pocket. Figure S1 pocket is formed of highly hydrophobic residues Ser 630, Tyr 631, Tyr 547, Val 656, Trp 659, Tyr 662, Tyr 666, Asn 710, Val 711 and His 740), Figure S2 pocket (formed by Glu 205 and Glu 206 dyad and Arg 125) [37]. The Figure S2 pocket is surrounded by residues of Val 207, Ser 209, Arg 358, Phe 357, Lys 544, Trp 627, Trp 629 and Asp 708 which constitute the Figure S2 extensive subsite [38].

Table 3.
Types of binding interactions and energy scores (kcal/mol) for hybrids 10a–j and alogliptin at the DPP-4 active site.
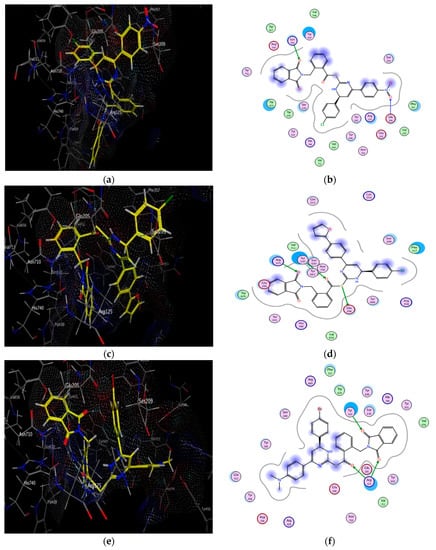
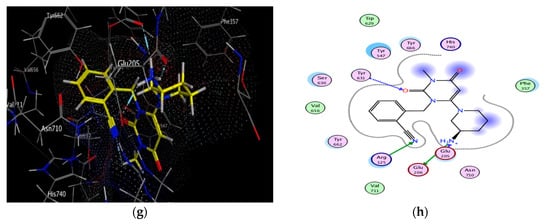
Figure 6.
Docking and binding pattern of compounds 10g (a,b), 10i (c,d), 10e (e,f) and alogliptin (g,h) showing interactions with different amino acid residues found in the active site of DPP-4 (PDB code: 3G0B).
The SiteMap analysis highlighted the importance of the Tyr 547, Lys 554, and Trp 629 residues as a top-ranked binding pocket of DPP-4 in the formation of the enzyme–inhibitor complex [39]. Moreover, the hydroxyl group of Tyr 547 plays an oxyanion-stabilizing role in the DPP-4 catalytic mechanism as well as Trp 629 residue forms catalytic Figure S2 pocket in this protease [40]. The DPP-4 inhibitory activity is markedly increased when the inhibitor can interact to Figures S1 and S2 pockets. Interestingly, studies suggested that only few inhibitors can bind into Figure S2 extensive subsite and enhancing the bioactivity of DPP-4 inhibitors through the interactions with Lys 554 so it is the target of DPP-4 inhibitor selectivity [41].
It was obvious from the results depicted in Table 3 that nearly all of the novel hybrids achieved energy binding scores higher than that of alogliptin. Additionally, hybrids 10b, 10d, 10e, 10g, 10i bind efficiently with the key amino acids located in the receptor pockets which explained the potent DPP-4 inhibitory activity of these hybrids. Of considerable interest, hybrid 10g recorded the highest energy binding score and the lowest in vitro DPP-4 IC50 inhibitory activity among the other synthesized hybrids via binding mainly to the Figure S2 pocket and Figure S2 extensive subsite through formation of two strong hydrogen bonds between both oxygen of the free nitro group and phthalimido carbonyl group with Glu 206 and Lys 554 which have a vital role in the enhancement of DPP-4 affinity. However, the binding mode showed that the phthalimido carbonyl oxygen and S atom of hybrid 10i participated in a hydrogen-bonding network with Arg 125 and Glu 206 residues in Figure S2 pocket together with another strong hydrogen bond formed with Tyr 547 in Figure S1 pocket. Similarly, compound 10d was buried in Figures S1 and S2 pockets via formation of four hydrogen bonds as well as π-H bond with Arg 125 and Tyr 547.
Notably, one hydrogen bond is formed between one of the phthalimido carbonyl oxygen of compound 10e and free OH group of Tyr 547 residue in Figure S1 pocket together with another three hydrogen bonds between the another carbonyl oxygen and the free NH2 of Arg 125 in Figure S2 pocket. However, hybrid 10b stacked with the side chain of Lys 554 and Trp 629 in Figure S2 extensive subsite via weak π-cation and π-hydrogen interactions which explained its higher IC50 value comparable to the previously mentioned hybrids but its DPP-4 inhibitory activity still higher than that of alogliptin. On the other hand, in Figure S2 pocket, the nitrogen of the free amino group of hybrid 10j is responsible for binding with Glu 205 and Glu 206 residues through two hydrogen bonds together with another hydrogen bond formed with Tyr 631 in Figure S1 pocket. Moreover, the phenyl ring of that compound provided additional binding affinity with Figure S2 extensive subsite via H-π interaction with Trp 629 residue while the naphthyl ring forms another π-H stacking with Tyr 456 side chain.
However, the electron withdrawing effect of chlorine atom in hybrid 10c negatively affects its binding with the receptor site and hence its DPP-4 inhibitory activity. In addition hybrid 10a binds weakly with the receptor site via only one hydrogen bonding with Arg 125. Meanwhile, 10f and 10h exhibited weak DPP-4 inhibitory activity as they could not be able to bind to the crucial amino acids responsible for the activity. Finally, it can be concluded that most of the titled synthesized hybrids interact with DPP-4 protein in distinct manner and thus are able to inhibit its activity efficiently.
3. Structure Activity Relationship
Based on the aforementioned results, it becomes clear that the electronic nature of the substituents and the steric factor greatly affect the biological activity of the synthesized hybrids, so the present SAR study focused on the effect of substituents on position 4 in the aryl groups that located in positions 2 and 4 of dihydropyrimidine as in hybrids 10a–h, as well as the furanyl and 1-naphthyl groups in hybrids 10i and 10j. It is worth noting that positions 2 and 4 in dihydropyrimidine are equivalent due to the migration of hydrogens and electron transition which is cleared in (Figure 7).
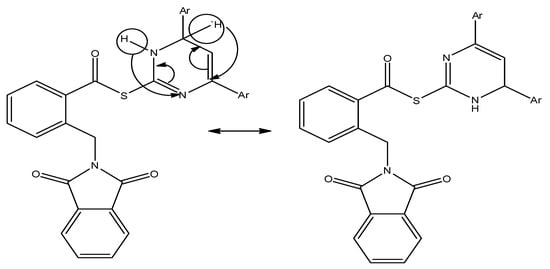
Figure 7.
Equivalence of positions 2 and 4 in dihydropyrimidine.
Moreover, the structures of most of the title compounds 10a–j contain a 4-chlorophenyl group. Consequently, the compounds under investigation are related structurally to the substituents attached to the other phenyl group. On the basis of the electron donating effect of both the 1-naphthyl and 4-aminophenyl groups and the lipophilic character of the latter, hybrid 10j should be the top ranked electron donor and consequently expected to be the most potent DPP-4 inhibitor via formation of more strong H-bonds with the receptor binding sites but on the contrary, the steric factor of the 1-naphthyl and 4-aminophenyl groups hinder the efficient binding with the receptor binding site, indicating that the steric factor is more effective, but it is still potent enough for inhibiting the enzyme activity as its IC50 was slightly less than that of alogliptin. Interestingly, hybrid 10g achieved the most potent DPP-4 inhibitory activity owing to the electron donating properties and the unique electronic ionic behavior of the nitro group leading to higher ability to form strong H-bond with Figure S2 extensive subsite as evidenced by its higher energy binding score.
Additionally, the DPP-4 inhibitory activity is markedly increased thanks to the lipophilic character and the small size of the furanyl group in hybrid 10i which enhance its fit to the receptor site, and accordingly its ability to form strong H- bond with the receptor site as evidenced by its molecular docking results. On the other hand, the lipophilic electron donating character of the methyl group, via hyperconjugative effect, in hybrid 10d resulted in an increase of its ability to form more H-bonds which, in turn, reflected on the marked difference in DPP-4 inhibitory IC50 values compared to that of the corresponding electron-withdrawing chlorine-atom in hybrid 10c. Moreover, the mesomeric effect raised from 4-Me2N group as well as 4-bromo atom in 10e hybrid seemed to be the most effective factor than hyperconjugative effect of 4-methyl and mesomeric effect of 4-chloro in hybrid 10d, that led to stabilization of H-bonding and consequently better DPP-4 inhibiting activity. Meanwhile, the lipophilic electron donating methoxy group of hybrid 10b experienced much higher DPP-4 inhibiting activity than the hydrophilic electron-withdrawing chlorine-atom hybrid 10f which exhibited much weaker binding interaction with the key amino acid residue in the receptor site as evidenced by its high IC50 value. Finally, it is concluded from the aforementioned SAR results that the electronic nature, the steric factor and lipophilicity of the substituents greatly affected the biological activity of the system incorporated.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
Male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (6–7 weeks old and 100–120g body weight) were purchased from Abu-rawash Animal House (Giza, Egypt). Rats were allowed to acclimatize for one week with free access to food and water and kept under controlled laboratory conditions of humidity and 12 h light-dark cycle. All experimental protocols were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Port-said University (R 20.5.1527).
4.2. Experimental Design
After acclimatization period, rats were randomly divided into 25 groups, each of seven rats. The first group was normal control group which maintained on normal rat chow for the entire experiment period (16 weeks). The second group served as diabetic control group in which T2DM was induced by HFD that consisted of casein (30%), raw beef fat (Suet, 40%), wheat flour (7%), glucose (10%), salt mixture (6%), vitamin mixture (3%), and bran (4%), for 16 weeks. The remaining groups consumed HFD for 16 weeks, however, in the last four weeks, HFD was administrated together with each compound from our synthesized hybrids 10a–j at a dose of 10 mg/kg/day, orally, or with alogliptin (Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Deerfield, IL, USA) at a dose of 20 mg/kg/day, orally, with and without MET (Alfa Aesar, ThermoFisher Inc., Haverhill, MA, USA) at a dose of 150 mg/kg/day, orally.
4.3. In Vitro DPP-4, DPP-8 and DPP-9 Inhibition Assay
DPP-4 inhibition was assessed, as previously described [42,43], based on a continuous fluorometric assay method in which the substrate Gly-Pro-AMC (Gly-Pro-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin hydrobromide) was split by DPP-4 to release fluorescent aminomethyl coumarin (AMC). The liberated AMC was continuously monitored using an excitation wavelength of 360 nm and an emission wavelength of 460 nm using an EnVision microplate reader (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The reaction mixture consisted of different concentrations of the synthesized hybrids 10a–j, 20 µU/µL of recombinant human DPP-4 (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), 10 µM Gly-Pro-AMC (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and assay buffer (150 mM NaCl, 25 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), 0.12 mg/ml bovine serum albumin (BSA)) and pH of 7.5. The assay was carried out in quadruplicate. IC50 was calculated using GraphPad Prism 8 software (San Diego, CA, USA). Similar to the DPP-4 assay, DPP-8 and DPP-9 inhibition assay was performed and the pH of the assay buffer was 8.
4.4. Cytotoxicity Test
We assessed any possible cytotoxic effect of our synthesized hybrids 10a–j on hepatic LO2 cells using MTT assay. The cells, in DMEM (Gibco, Invitrogen), were seeded in 96 well plates at density of 1 × 104/well. The synthesized compounds were added to the cells and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Then, MTT reagent was added and the cells were re-incubated for further 4 h. After discarding the supernatants, the formed formazan crystals were dissolved in DMSO. The intensity of color was assessed using microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) at 490 nm wavelength.
4.5. In Vivo DPP-4 Inhibition Assay
The assay was performed using male SD rats (n = 3 per group), as previously described [44]. The synthesized hybrids 10a–j were suspended in 0.5 carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and administrated orally at a single dose of 10 mg/kg.
Blood samples were collected at time points 0, 6, 12, 24, 36 and 48 h. Plasma samples were extracted and kept at −20 °C until analysis time. Similar to the in vitro DPP-4 assay principle, plasma samples were mixed with equal volumes of Gly-Pro-AMC in assay buffer (100 mM HEPES, 0.1 mg/ml BSA) and pH of 7.5. The liberated AMC was continuously monitored using an excitation wavelength of 360 nm and an emission wavelength of 460 nm using EnVision microplate reader (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The data were expressed as% blood DPP-4 activity.
4.6. In Vivo Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) in SD Rats
At the end of treatment regimen that lasted for four weeks; using our synthesized hybrids 10a–j with and without MET, rats were fasted overnight (12 h) with free access to water. Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed as previously described [45]. Briefly, blood samples were collected from retro-orbital sinuses veins using glass capillaries at 0 time, 30, 60, 90 and 120 min after oral glucose loading (2 g/kg) and glucose concentration was determined with an automatic blood glucose meter (Accu-Chek; Roche Diagnostics, Rotkreuz, Switzerland).
4.7. Antioxidant Activity (DPPH Method)
DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) free radical is stable at rt and has a purple colour with a maximum absorption at 517 nm. This free radical is reduced by antioxidant molecules into 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazine with resultant discolouration of free radical; this discolouration is stoichiometric with regard to the captured electrons. Accordingly, the fluctuation in the absorbance is an indicator for the antioxidant activity. Our synthesized hybrids 10a–j (100 µM) were mixed with DPPH (100 µM) and left for 20 min at rt, the absorbance was measured at 517 nm.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Results were expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) and were analyzed for statistically significant differences using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). P values less than 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001 were considered significant. GraphPad Prism® 8 was used for statistical calculations (GraphPad Software, St. Louis, MO, USA).
4.9. Molecular Docking
Molecular docking studies of the synthesized hybrids 10a–j and alogliptin were performed using MOE software. Ligands were built into the builder interface of the MOE program and their energies were minimized until a root mean square deviation (RMSD) gradient of 0.01 kcal/mol and root mean square (RMS) distance of 0.1 Å with MMFF94× (Merck molecular force field 94×) force-field and the partial charges were automatically calculated. The X-ray crystallographic structure of DPP-4 (PDB code: 3G0B) was downloaded from protein data bank (www.rcsb.org, accessed on 10 February 2021). The enzymes were prepared, the hydrogens were added then the atoms connection and type were checked with automatic correction. The obtained poses were studied and the poses showed best ligand-enzyme interactions were selected and stored for energy calculations.
4.10. Chemistry
Melting points were determined by open tube capillary on a Mel-Temp hot stage apparatus (Stuart, Staffordshire, UK) on the Celsius scale and are uncorrected. Reactions were monitored by thin-layer chromatography on silica gel PF254 plates (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) using dichloromethane/ethyl acetate (9:1) as mobile phase, and spots were detected with UV analyses lamp at 254 and 366 nm. IR spectra were recorded as KBr disks on a Fourier Transform (FT-IR) spectrophotometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recordedout on a Bruker NMR spectrometer operating at 400 MHz and 100 MHz, respectively, using TMS as internal reference. Chemical shifts (δ values) are given in parts per million (ppm) using CDCl3 (7.26) or DMSO-d6 (2.49) as solvents and coupling constants (J) in Hz. Splitting patterns are designated as follows: s, singlet; bs, broad singlet; d, doublet; t, triplet; m, multiplet. GCMS: Mass spectra was recorded on a LCMS-QQQ instrument (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Elemental analyses were performed on a 2400 CHN elemental analyzer (Perkin–Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA) and were within ± 0.4% of theoretical values unless otherwise specified.
4.11. Materials
Chemicals and solvents are of commercial grade, and purchased from Alfa Aesar (Haverhill, MA, USA), Cambrian Chemicals (Ontario, CA), Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), Acros Organics (Haverhill, MA, USA), Fluka (Gillingham, Dorset, UK), Merck (Ontario, CA), and El-Nasr Pharmaceutical Chemical Company (Cairo, Egypt). Chemicals were used without purification. Solvents were purified following the reported methods.
Substituted 1,3-diaryl-2-propene-1-ones 3 were prepared according to a procedure described elsewhere in the literature [46,47,48,49,50,51]. α-Phthalimido-o-toluic acid (8) and α-phthalimido-o-toluyl chloride (9) were prepared according to the literature [36]. 4,6-Diaryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones: 5a, 5b, 5c, 5f and 5h were synthesized following the reported procedure in the literatures [52,53,54,55].
4.12. Synthesis
4.12.1. General Procedure for Synthesis of 4,6-diaryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones 5d–g, i, j [53]
A mixture of 1,3-diaryl-2-propen-1-one derivatives 3 (2.404 mmol), prepared by Claisen-Schmidt condensation between substituted acetophenones 1, benzaldehydes 2, and thiourea 4 (2.404 mmol) and NaOH (2.404 mmol) in absolute ethanol (25 mL) was heated under reflux for 4–6 h. The reaction progress was monitored by TLC using dichloromethane/ethyl acetate (9:1). The reaction mixture was cooled to rt and poured onto crushed ice. The solid product was filtered off, washed with water and crystallized from ethanol to yield the following pure titled compounds.
4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-6-(p-tolyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (5d)
Yield: 0.574 g, 76% (pale yellow solid); m.p. 138–9 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3183, 2967 (Ar-CH), 1672 (C=N), 1551, 1462 (C=C), 1178 (C=S). 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 10.12 (s, 1H, 1NH), 9.54 (s, 1H, 1NH), 7.39 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 7.31 (d, 4H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 7.21(d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 6.38 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H5), 5.17 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H4), 2.39 (s, 3H, OCH3). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz): δ 175.5 (CS), 141.5, 140.0, 134.5, 133.7, 129,128.0, 127.7, 125.7, 124.9 (ArC), 99.3 (NH—C=C), 55.5 (CHAr), 21.2 (CH3). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 314 (M.+, 100), 297 (13), 281 (34), 268 (26), 241 (54), 239 (43), 223 (63), 203 (30), 160 (19), 113 (19),100 (11). Anal. Calcd. for C17H15ClN2S (314.83); C, 64.85; H, 4.80; N, 8.90; S, 10.18. Found: C, 64.77; H, 5.01; N, 8.72; S, 10.33.
6-(4-Bromophenyl)-4-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (5e)
Yield: 0.633 g, 68% (orange solid); m.p.112–3 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3195 (NH), 3084, 2925 (Ar-CH), 1679 (C=N), 1523, 1482 (C=C), 1174 (C=S). 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 10.52 (s, 1H, 1NH), 9.76 (s, 1H, 1NH), 7.63 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 7.57 (d, 2H, J = 8,1 Hz, ArH), 7.32 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 7.22 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 6.34 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H5), 5.08 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H4), 2.98 (s, 6H, NMe2). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 388 (M.+, 100), 372 (21), 355 (60), 332 (17), 301 (16), 268 (65), 232 (31), 186 (21), 157 (23), 120 (17). Anal. Calcd. for C18H18BrN3S (388.32); C, 55.67; H, 4.67; N, 10.32; S, 8.26. Found: C, 55.93; H, 4.72; N, 10.11; S, 8.25.
6-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-phenyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (5f)
Yield: 0.384 g, 66% (white solid); m.p. 162–3 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3188 (NH), 3028, 2979 (Ar-CH), 1671 (C=N), 1569,1486 (C=C), 1190 (C=S). 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 10.00 (s, 1H, 1NH), 9.67 (s, 1H, 1NH), 7.70–7.27 (m, 17H, ArH), 6.72 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H5), 5.24 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H4). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 300 (M.+, 67), 285 (40), 254 (48), 225 (100), 219 (55), 189 (32), 161 (49), 137 (31), 103 (14). Anal. Calcd. for C16H13ClN2S (300.81); C, 63.88; H, 4.36; N, 9.31; 10.66. Found: C, 64.06; H, 4.22; N, 10.41; S, 8.14.
6-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (5g)
Yield: 0.589 g, 71% (grey solid); m.p. 210–12 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3155 (NH), 3070 (Ar-CH), 1678 (C=N), 1552,1493 (C=C), 1177 (C=S). 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 10.28 (s, 1H, 1NH), 9.72 (s, 1H, 1NH), 8.30 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 8.10 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 7.59 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 7.42 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 6.43 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H5), 5.26 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H4). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz): δ 176.6 (CS), 144.5, 140.0, 135.0, 132.4, 1312.0, 130.0, 128.4, 126.2, 123.8 (ArC), 101.9 (NH-C=C), 52.0 (CHAr). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 345 (M.+, 100), 312 (50), 310 (6), 270 (26), 255 (9), 223 (16), 190 (9), 176 (16), 134 (16), 122 (28). Anal. Calcd. for C16H12ClN3O2S (345.80); C, 55.57; H, 3.50; N, 12.15; S, 9.27. Found: C, 55.33; H, 3.62; N, 12.23; S, 9.15.
6-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-(furan-2-yl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (5i)
Yield: 0.509 g, 73% (yellow solid); m.p. 165–7 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3187 (NH), 3104, 2984 (Ar-CH), 1676 (C=N), 1571,1477 (C=C), 1186 (C=S). 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ: 10.08 (s, 1H, 1NH), 9.86 (s, 1H, 1NH), 7.69–7.39 (m, 7H, 4 ArH & 3 furyl-H), 6.23 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H5), 5.35 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H4). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 290 (M.+, 100), 257 (32), 235 (15), 215 (32), 190 (16), 179 (42), 159 (23), 131 (13), 115 (5). Anal. Calcd. for C14H11ClN2OS (290.77); C, 57.83; H, 3.81; N, 9.63; S, 11.03. Found: C, 58.14; H, 3.69; N, 9.48; S, 10.83.
6-(4-Aminophenyl)-4-(naphthalen-1-yl)-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (5j)
Yield: 0.555 g, 73% (pale yellow solid); m.p. 155–6 °C; IR(KBr, cm−1) υ: 3217 (NH), 3051,2924 (Ar-CH), 1669 (C=N), 1559,1464 (C=C), 1177 (C=S). 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 9.28 (s, 1H, 1NH), 9.23 (s, 1H, 1NH), 8.16 (d, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 7.88–7.53 (m, 6H, ArH), 7.43 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 6.75 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz, ArH), 6.68 (bs, 2H, NH2), 6.30 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H5), 5.30 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, H4). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 331 (M.+, 100), 298 (50), 274 (43), 256 (23), 239 (15), 204 (23), 160 (17), 136 (16), 119 (8), 112 (10). Anal. Calcd. for C20H17N3S (331.43); C, 72.48; H, 5.17; N, 12.68; S, 9.67. Found: C, 72.22; H, 4.93; N, 12.53; S, 9.9.82.
4.12.2. General Procedure for Synthesis of (4,6-diaryl-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)-2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioates 10a–j
A solution of equimolar amounts of α-phthlimido-o-toluyl chloride (9, 0.668 mmol) and an appropriate 4,6-diaryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thione 5a–j (0.668 mmol) in 10 mL absolute dichloromethane was stirred at rt for 4–6 h. The progress of the reaction was monitored periodically by TLC using dichloromethane/ethyl acetate (9:1) as mobile phase. The reaction mixture was then treated with brine, extracted with ethyl acetate, treated with dil. hydrochloric acid, sod. bicarbonate and finally washed with water. The organic solvent was dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate and evaporated under vacuum. The solid product was purified by crystallization from the appropriate solvent to give the title hybrids 10a–j.
S-(4,6-Diphenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10a)
Yield: 0.233 g, 66% (white solid, ethanol); m.p. 147–8 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3399 (NH), 3071,3011 (Ar-CH), 1772,1716 (CO), 1603 (C=N), 1547,1491 (C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.46 (s, 1H, NH), 7.90–721 (m, 18 H, ArH), 6.42 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 5.12 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CHAr), 5.06 (s, 2H, CH2). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 100 MHz): δ 189.7 (CO), 168.3 (2CO), 156.4, 144.0, 140.5, 136.0, 136.7, 135.5, 135.0, 132.0, 132.6, 131.4, 129.3, 128.4, 127.6, 127.0, 126.7, 126.3, 124.6, 124.0 (ArC), 107.8 (C=CH-Ar), 55.1 (CHAr). (GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 529 (M.+, 36), 452 (29), 392 (43), 338 (20), 280 (100), 265 (60), 236 (20), 223 (10), 173 (35), 146 (28). Anal. Calcd for C32H23N3O3S (529.61); C, 72.57; H, 4.38; N, 7.93; S, 6.05. Found: C, 72.34; H, 4.30; N, 8.07; S, 6.23.
S-(4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10b)
Yield: 0.278 g, 70% (pale yellow solid, ethanol); m.p. 142–3 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3450 (NH), 3064,2918 (Ar-CH), 1772, 1725 (CO), 1676 (C=N), 1594,1489 (C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.49 (s, 1H, NH), 7.99–6.92 (m, 16 H, ArH), 6.28 (d, 1H, J= 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 5.20 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CHAr), 5.08 (s, 2H, CH2), 3.76 (s, 3H, OCH3). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 100 MHz): δ 188.5 (CO), 168.3 (2CO), 159.4, 145.0, 138.3, 137.8, 136.1, 135.6, 135.9, 134.3, 133.7, 132.8, 132.2, 131.5, 129.3, 129.0, 128.5, 128.3, 127.3, 124.5, 120.6, 114.9 (ArC), 111.4 (C=CH-CHAr), 55.5 (CHAr). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 593 (M.+, 100), 562 (50), 462 (34), 382 (43), 355 (61), 329 (23), 264 (32), 186 (26), 160 (35), 132 (20). Anal. Calcd. for C33H24ClN3O4S (594.08); C, 66.72; H, 4.07; N, 7.07; S, 5.40. Found: C, 66.39; H, 4.22; N, 8.11; S, 5.91.
S-(4,6-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10c)
Yield: 0.258 g, 65% (pale yellow solid, ethanol/chloroform); m.p. 118–19 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3432 (NH), 3064, 2964 (Ar-CH), 1772,1616 (CO), 1672 (C=N), 1592, 1489 (C=C). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.43 (s, 1H, NH), 7.92–7.19 (m, 16H, ArH), 6.42 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 5.19 (d,1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CHAr), 5.06 (s, 2H, CH2). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 598 (M.+, 100), 487 (86), 466 (20), 568 (37)521 (17), 398 (28), 358 (18), 302 (42), 266 (59), 275 (27), 190 (19), 160 (30), 147 (46), 132 (23). Anal. Calcd. for C32H21Cl2N3O3S (598.50); C, 64.22; H, 3.54; N, 7.02; S, 5.36. Found: C, 64.00; H, 3.3.78; N, 7.21; S, 5.30.
S-(6-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-(p-tolyl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10d)
Yield: 0.282 g, 73% (yellow solid, ethanol); m.p. 144–6 °C; IR(KBr, cm−1) υ: 3413 (NH), 3061,3041, 2922 (Ar-CH), 1771,1715 (CO), 1677 (C=N), 1545, 1490 (C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.45 (s, 1H, 1NH), 7.89–7.18 (m, 16H, ArH), 6.34 (d,1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 5.20 (d,1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH-Ar), 5.08 (s, 2H, CH2), 2.34 (s, 3H, CH3). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 577.5 (M.+, 31), 487 (70), 466 (100), 457 (20), 385 (30), 375 (21), 314 (39), 297 (81), 264 (57), 217 (10), 160 (26), 146 (22), 132 (16). Anal. Calcd. for C33H24ClN3O3S (578.08); C, 68.56; H, 4.18; N, 7.27; S, 5.55. Found: C, 68.84; H, 4.01; N, 7.37; S, 5.23.
S-(4-(4-Bromophenyl)-6-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl) 2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10e)
Yield: 0.304 g, 70% (brown solid, ethanol/chloroform); m.p. 135–6 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3476 (NH), 2920 (Ar-CH), 1770,1715 (CO), 1674 (C=N), 1578,1485(C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.45 (s, 1H, NH), 8.08–6.75 (m, 16H, ArH), 6.34 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 5.18 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CHAr), 5.05 (s,2H, CH2), 2.52 (s, 6H, NMe2). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 651 (M.+, 41), 569 (19), 546 (100), 531 (13), 519 (18), 415 (21), 362 (49), 302 (36), 264 (30), 236 (18), 202 (12), 146 (16), 132 (24). Anal. Calcd. for C34H27BrN4O3S (651.57); C, 62.67; H, 4.18; N, 8.60; S, 4.92. Found: C, 62.93; H, 4.28; N, 8.44; S, 4.88.
S-(4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-6-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10f)
Yield: 0.282 g, 75% (pale yellow solid, ethanol); m.p. 143–4 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3464 (NH), 3061, 2970 (Ar-CH), 1772,1716 (CO), 1677 (C=N), 1557,1490 (C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.42 {s, 1H, NH), 8.18–7.15 (m, 17H, ArH), 6.45 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 5.16 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH-Ar), 5.01 (s,2H, CH2). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance); 563.5 (M.+, 100), 543 (48), 443 (43), 414 (38), 389 (18), 375 (36), 300 (28), 265 (31), 227 (24), 161 (36), 146 (27), 132 (17). Anal. Calcd. for C32H22ClN3O3S (564.05); C, 68.14; H, 3.93; N, 7.45; S, 5.68. Found: C, 67.83; H, 4.17; N, 7.27; S, 5.55.
S-(4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-6-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10g)
Yield: 0.280 g, 69% (brown solid, ethanol/chloroform); m.p.161–3 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3418 (NH), 3030,2926 (Ar-CH), 1774,1715 (CO), 1623 (C=N), 1521 (C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.52 (s, 1H, NH), 8.51–7.15 (m, 16H, ArH), 6.39 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 5.21 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CHAr), 5.02 (s, 2H, CH2). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 100 MHz): δ 188.4 (CO), 168.3 (2CO), 157.5, 148.0, 146.1, 142.0, 137.9, 137.7, 135.3, 135.0, 133.7, 132.5, 131.8, 129.8, 129.0, 128.1, 127.4, 126.1, 125.1, 124.6, 124.5 (ArC), 112.0 (C=CH—CHAr), 45.2 (CHAr). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 608.5 (M.+, 50), 551 (17), 532 (25), 504 (55), 446 (31), 373 (100), 346 (22), 311 (25), 306 (9), 264 (39), 232 (21), 188 (31), 163 (16). Anal. Calcd. for C32H21ClN4O5S (609.05); C, 63.11; H, 3.48; N, 9.20; S, 5.26. Found: C, 62.88; H, 3.59; N, 9.18; S, 5.17.
S-(4-(4-Aminophenyl)-6-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10h)
Yield: 0.285 g, 74% (orange solid, ethanol/chloroform); m.p. 185–7 °C; IR(KBr, cm−1) υ: 3430 (NH), 3060,2942 (Ar-CH), 1772,1716 (CO), 1677 (C=N), 1545,1490 (C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.48 (s, 1H, NH), 8.10–6.98 (m, 16H, ArH), 6.68 (d,1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 6.19 (bs, 2H, NH2), 5.23 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CHAr), 5.03 (s, 2H, CH2). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 578.5 (M.+, 47), 514 (9), 432 (22), 394 (11), 342 (100), 312 (49), 282 (46), 264 (34), 238 (27), 196 (17), 140 (14), 132 (11). Anal. Calcd. for C32H23ClN4O4S (579.07); C, 66.37; H, 4.00; N, 9.68; S, 5.54. Found: C, 66.20; H, 3.83; N, 9.83; S, 5.50.
S-(4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-6-(furan-2-yl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10i)
Yield: 0.274 g, 74% (grey solid, ethanol); m.p. 146–8 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3464 (NH), 3064,2928 (Ar-CH), 1770,1716 (CO), 1666 (C=N), 1502 (C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.19 (s,1H, NH), 7.92–7.09 (m, 12 ArH and 3 furanyl-H), 6.25 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 5.21 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CHAr), 5.02 (s, 2H, CH2). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 553.5 (M.+, 100), 511 (11), 449 (41), 393 (20), 315 (44), 287 (18), 254 (23), 238 (26), 264 (20), 160 (21), 132 (16). Anal. Calcd. for C30H20ClN3O4S (554.02); C, 65.04; H, 3.64; N, 7.58; S, 5.79. Found: C, 65.33; H, 3.78; N, 7.42; S, 5.51.
S-(4-(4-Aminophenyl)-6-(naphthalen-1-yl)-1,6-dihydropyrimidin-2-yl)2-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)benzothioate (10j)
Yield: 0.287 g, 74% (orange solid, ethanol); m.p. 176–8 °C; IR (KBr, cm−1) υ: 3384 (NH), 3062,2975 (Ar-CH), 1771,1714 (CO), 1667 (C=N), 1598,1467 (C=C). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.52 (s, 1H, NH), 8.50–7.12 (m, 18H, ArH), 6.58 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CH=C-Ar), 6.17 (bs, 2H, NH2), 5.23 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, CHAr), 5.05 (s, 2H, CH2). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6, 100 MHz): δ 188.1 (CO), 167.5 (2CO), 157.5, 145.3, 143.1, 137, 136.6, 135.8, 135.5, 135.3, 134.3, 134.0, 133.5, 132.5,132.3, 130.8, 129.7, 129.1, 128.9, 128.6, 127.8, 126.0, 125.5, 125.0, 124.0, 123.5 (ArC),113.3 (C=CH-Ar), 55.0 (CHAr). GCMS m/z (rel. abundance): 594 (M.+, 42), 475 (28), 434 (16), 358 (100), 330 (29), 317 (10), 264 (28), 232 (11), 127 (15), 133 (27), 104 (9). Anal. Calcd. for C36H26N4O3S (594.68); C, 72.71; H, 4.41; N, 9.42; S, 5.39. Found: C, 72.63; H, 4.62; N, 9.65; S, 5.23.
5. Conclusions
A novel series of dihydropyrimidine phthalimide hybrids was synthesized, characterized and evaluated for their DPP-4 inhibitory activity, as well as, antioxidant activity. Hybrids 10g, 10i, 10e, 10d and 10b showed superior DPP-4 inhibitory activity compared to alogliptin, in the in vitro DPP-4 inhibition assay. Additionally, hybrids 10g and 10i have the most potent and longest DPP-4 inhibitory activity among the synthesized hybrids and alogliptin, in the in vivo study that carried on SD rats. Furthermore, investigation of antihyperglycemic effect of our synthesized hybrids in HFD-induced type 2 diabetic rats, revealed that hybrids 10g, 10i and 10e exhibited better glycemic control than alogliptin; this effect was further potentiated by addition of MET. Notably, glucose tolerance reached a normal level in 10g/MET treated group. Finally, hybrids 10j, 10e, 10h and 10d showed potent radical scavenging activity in DPPH assay.
Supplementary Materials
IR spectroscopy, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and mass spectroscopy of all the synthesized compounds are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/14/2/144/s1, Figure S1: IR spectrum of compound 5a, Figure S2: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5b, Figure S3: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5c, Figure S4: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5d, Figure S5: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5e, Figure S6: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5f, Figure S7: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5g, Figure S8: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5h, Figure S9: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5i, Figure S10: IR Spectroscopy of compound 5j, Figure S11: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10a, Figure S12: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10b, Figure S13: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10c, Figure S14: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10d, Figure S15: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10e, Figure S16: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10f, Figure S17: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10g, Figure S18: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10h, Figure S19: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10i, Figure S20: IR Spectroscopy of compound 10j, Figure S21: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5b, Figure S22: 1H-NMR spectrum of compound 5c, Figure S23: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5d, Figure S24: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5e, Figure S25: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5f, Figure S26: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5g, Figure S27: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5h, Figure S28: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5i, Figure S29: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5j, Figure S30: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10a, Figure S31: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10b, Figure S32: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10c, Figure S33: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10d, Figure S34: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10e, Figure S35: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10f, Figure S36: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10g, Figure S37: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10h, Figure S38: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10i, Figure S39: 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10j, Figure S40: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5a, Figure S41: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5d, Figure S42: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5g, Figure S43: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 5h, Figure S44: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10a, Figure S45: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10b, Figure S46: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10d, Figure S47: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10g, Figure S48: 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Compound 10j, Figure S49: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5b, Figure S50: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5c, Figure S51: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5d, Figure S52: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5e, Figure S53: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5f, Figure S54: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5g, Figure S55: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5h, Figure S56: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5i, Figure S57: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 5j, Figure S58: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10a, Figure S59: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10b, Figure S60: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10c, Figure S61: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10d, Figure S62: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10e, Figure S63: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10f, Figure S64: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10g, Figure S65: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10h, Figure S66: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10i, Figure S67: Mass Spectroscopy of Compound 10j.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.E.M. and M.A.E.M.; methodology, A.A.E.M.; software, A.A.E.M. and S.S. validation, A.E.K., S.S. and A.A.E.M.; resources, A.A.E.M.; M.A.E.M.; S.S. and A.E.K.; writing—review and editing, A.M., A.E.K. and M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All the in vivo protocols were approved by animal research ethics committee, faculty of pharmacy, Port-Said University, Egypt.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available at doi.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Reimann, M.; Bonifaci, E.; Solimena, M.; Schwarz, P.E.; Ludwig, B.; Hanefeld, M.; Bornstein, S.R. An update on preventive and regenerative therapies in diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 121, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabchi, A.E.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Miles, J.M.; Fisher, J.N. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.X.; Zhou, Z.W.; Yang, Y.X.; Yang, T.X.; Pan, S.Y.; Qiu, J.X.; Zhou, S.F. A perspective overview of clinically approved oral antidiabetic agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 42, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahrani, A.A.; Bailey, C.J.; Prato, S.D.; Barnett, A.H. Management of type 2 diabetes: New and future developments in treatment. Lancet 2011, 378, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, D.E. New drug targets for type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Nature 2001, 414, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. Therapeutic potential of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Expet. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2003, 12, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Gong, J.; Goud, J.; Srinivasamahraj, A.; Rajagopalan, S. Recent Advances in Dipeptidyl-Peptidase-4 Inhibition Therapy: Lessons from the Bench and Clinical Trials. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulinger, B.A.; Bedorf, A.G.; Kutscherauer, H.J.; De, J.J.; Holst, G.; Göke, B.; Schirra, J. Defining the role of GLP-1 in the enteroinsulinar axis in type 2 diabetes using DPP-4 inhibition and GLP-1 receptor blockade. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Drucker, D.J. Pharmacology, Physiology, and Mechanisms of Action of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 992–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.F. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A comparative review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J. Efficacy and safety of incretin based therapies: Clinical trial data. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2009, 49, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulifa, D.L.; Adnyana, I.K.; Levita, J.; Sukrasno, S. 4-Hydroxyderricin Isolated from the Sap of Angelica keiskei Koidzumi: Evaluation of Its Inhibitory Activity towards Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV. Sci. Pharm. 2019, 87, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Wang, L.; Beconi, M.; Eiermann, G.J.; Fisher, M.H.; He, H.; Hickey, G.J.; Kowalchick, J.E.; Leiting, B.; Lyons, K.; et al. (2R)-4-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: A potent, orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, T.A.; Chikhalia, K.H. Studies on Synthesis of Pyrimidine Derivatives and their Pharmacological Evaluation. E-J. Chem. 2007, 4, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosle, M.R.; Deshmukh, A.R.; Pal, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Mane, R.A. Synthesis of new thiazolylmethoxyphenyl pyrimidines and antihyperglycemic evaluation of the pyrimidines, analogues isoxazolines and pyrazolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2442–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keche, A.P.; Hatnapure, G.D.; Tale, R.H.; Rodge, A.H.; Birajdar, S.S.; Kamble, V.M. A novel pyrimidine derivatives with aryl urea, thiourea and sulfonamide moieties: Synthesis, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3445–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanage1, S.G.; Raju, S.A.; Mohite, P.B.; Pandhare, R.B. Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Some New Pyrimidine Derivatives Containing 1,2,4-Triazole. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 2, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, L.; Kumar, P.S.V.; Poornachandra, Y.; Kumar, C.G.; Chandramouli, G.V.P. Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel pyrazolo-pyrimido[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives as potent antibacterial and biofilm inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, O.; Khan, S.A.; Siddiqui, N.; Ahsan, W.; Verma, S.P.; Gilani, S.J. Antihypertensive activity of newer 1,4-dihydro-5-pyrimidine carboxamides: Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5113–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, J.-F.; Bai, Y.-B.; Wang, P.; Wang, T.; Gao, J.-M.; Zhang, Z.-T. Synthesis of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives and their antifungal activities against phytopathogenic fungi in vitro. Mol. Divers. 2016, 20, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitre, T.S.; Kathiravan, M.K.; Chothe, A.S.; Rakholiya, V.K.; Asgaonkar, K.D.; Shital, M. Synthesis and Antitubercular activity of some substituted pyrimidine derivatives. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 4, 1882–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, V.; Bhadoriya, K.S. Synthesis, pharmacological evaluation and molecular docking studies of pyrimidinedione based DPP-4 inhibitors as antidiabetic agents. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1158, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, N.; Wanga, L.-J.; Jianga, B.; Guoa, S.-J.; Lia, X.-Q.; Chene, X.-C.; Luoa, J.; Lia, C.; Wange, Y.; Shia, D.-Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pyrimidinedione derivatives as DPP-4 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2131–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, N.; Kaushik, D. Recent Advances and Future Prospects of Phthalimide Derivatives. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.M.; Castro, P.; Machado, A.L.; Fraga, C.A.; Lugnier, C.; de Moraes, V.L.; Barreiro, E.J. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of phthalimide derivatives designed as new thalidomide analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 3067–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.U.M.; Jayakar, B.; Srinivasan, R. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of a N-phthalimido and acetimido derivatives from amino acids and anhydrides. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2010, 1, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sena, V.L.M.; Srivastava, R.M.; Silva, R.O.; Lima, V.L.M. Synthesis and hypolipidemic activity of N-substituted phthalimides. Part V. Farmaco 2003, 58, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, V.; Pathak, D.P. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of some N-substitutedphthalimide analogues. Pharm. Innov. 2012, 1, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, U.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, N.; Singh, B. Recent advances in the chemistry of phthalimide analogues and their therapeutic potential. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 678–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, S.H.; Gambari, R.; Chui, C.H.; Yuen, M.C.; Lin, E.R.S.; Wong, F.Y.; Lau, G.Y.; Cheng, W.S.; Lam, S.H.; Chan, K.H.; et al. Synthesis and anticancer activity of benzothiazole containing phthalimide on human carcinoma cell lines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 3626–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimazawa, R.; Takayama, H.; Kato, F.; Kato, M.; Hashimote, Y. Nonpeptide small-molecular inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV:N-phenylphthalimide analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoshima, K.; Sugita, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Non- competitive and selective dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors with phenethylphenylphthalimide skeleton derived from thalidomide-related a-glucosidase inhibitors and liver X receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 3041–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomovic, K.; Ilic, B.S.; Miljkovic, M.; Dimov, S.; Yancheva, D.; Mavrova, M.K.T.; Kocic, G. Benzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine phthalimide derivative, one of the rare noncompetitive inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase-4. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life. Sci. 2020, 353, 1900238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducki, S. Antimitotic chalcones and related compounds as inhibitors of tubulin assembly. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, J.; Bedell, S.F.; Drummond, P.E.; Kosloski, C.L. The synthesis of α-amino-o-tolualdehyde diethylacetal and its attempted conversion to pseudoisoindole. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1955, 78, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeno, M.; Akahoshi, F.; Kishida, H. A comparative study of the binding modes of recently launched dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors in the active site. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Kyono, K. The crystal structure of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) complex with diprotin A. Bio. Chem. 2004, 385, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Oi, S.; Asakawa, T.O.; Kataoka, K.; Takeuchi, N.; Suzuki, K.I.; Kosaka, T.; Tsubotani, S.; et al. Identification of 3-aminomethyl-1,2-dihydro-4-phenyl-1-isoquinolones: A new class of potent, selective, and orally active non-peptide dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors that form a unique interaction with Lys554. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4953–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Montes, M.J.; Gimeno, A.; Tomas-Hernández, S.; Cereto-Massagué, A.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Valls, C.; Mulero, M.; Pujadas, G.; Garcia-Vallvé, S. Activity and selectivity cliffs for DPP-IV inhibitors: Lessons we can learn from SAR studies and their application to virtual screening. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1874–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezaki, H.; Tawada, M.; Yamashita, B.T.; Miyamoto, Y.Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ikedo, K.; Kosaka, T.; Tsubotani, S.A.; Tani, T.; Asakawa, N.; et al. Design of potent dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) inhibitors by employing a strategy to form a salt bridge with Lys554. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3565–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, H.; Cui, S.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Su, M.; Gong, Y.; Qiu, S.; Jiao, Q.; Qin, C.; et al. Discovery and rational design of natural-product-derived 2-Phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[f]chromen-3-amine analogs as novel and potent dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6772–6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Su, M.; Wang, J.; Deng, G.; Deng, S.; Li, Z.; Tang, C.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of hetero-aromatic moieties substituted pyrrole-2-carbonitrile derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 75, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Qin, C.; Cui, S.; Xu, H.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Su, M.; Fang, X.; Li, D.; Jiao, Q. Discovery of a naturalproduct-derived preclinical candidate for once-weekly treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2348–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Wanibuchi, H.; Hamaguchi, A.; Miura, K.; Yamanaka, S.; Iwao, H. Angiotensin blockade improves cardiac and renal complications of type II diabetic rats. Hypertension 1997, 30, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, W.; Zhu, H. (E)-1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one. Acta Cryst. 2006, E62, 1627–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, W.; Zhang, D. 1,3-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one. Acta Cryst. E 2005, 61, 2820–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, A.M.; Karabacak, M.; Sakthivel, S.; Al-youbi, A.O.; Muthu, S.; Hamed, S.A.; Renuga, S.; Alagesan, T. Synthesis, molecular structure, spectral investigation on (E)-1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(4-(dimethylamino) phenyl) prop-2-en-1-one. J. Mol. Str. 2016, 1103, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamuna, T.S.; Yathirajan, H.S.; Jasinski, J.P.; Keeley, A.C.; Narayana, B.; Sarojini, B.K. (2E)-1- (4-Chlorophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one. Acta Cryst. E 2013, 69, 790–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, P.S.; Teh, J.B.; Fun, H.K.; Abdul Razak, I.; Dharmaprakash, S.M. 3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-nitrophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one. Acta Cryst. E 2006, 62, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichou, D.; Watanabe, T.; Takeda, T.; Miyata, S.; Goto, y.; Nakayama, M. Influence of the ring substitution on the second harmonic generation of chalcone derivatives. Jap. J. App. Phys. 1988, 27, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei-Ghomi, J.; Ghasemzadeh, M.A. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of dihydropyrimidine-2-thiones. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2011, 76, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajjar, F.H.; Al-Farkh, Y.A.; Hammoud, H.S. Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of the pyrimidine-2(1H)-thione derivatives. Can. J. Chem. 1979, 57, 2734–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, J.; Ghasemzadeh, M.A. Preparation of 4,6-diaryl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thiones in an ionic liquid. Org. Prep. Proc. Int. 2012, 44, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.C.; Pandya, D.D.; Satodiya, H.M.; Rajpara, K.M.; Joshi, V.V.; Vaghani, H.V. An efficient, solvent free microwave-assisted synthesis and antimicrobial screening of 1,6-dihydropyrimidine analogues. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 4412–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).