3D Printing of Mini Tablets for Pediatric Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Uniformity of Dosage Units According to Ph. Eur. 2.9.40
2.2. Optical Appearance
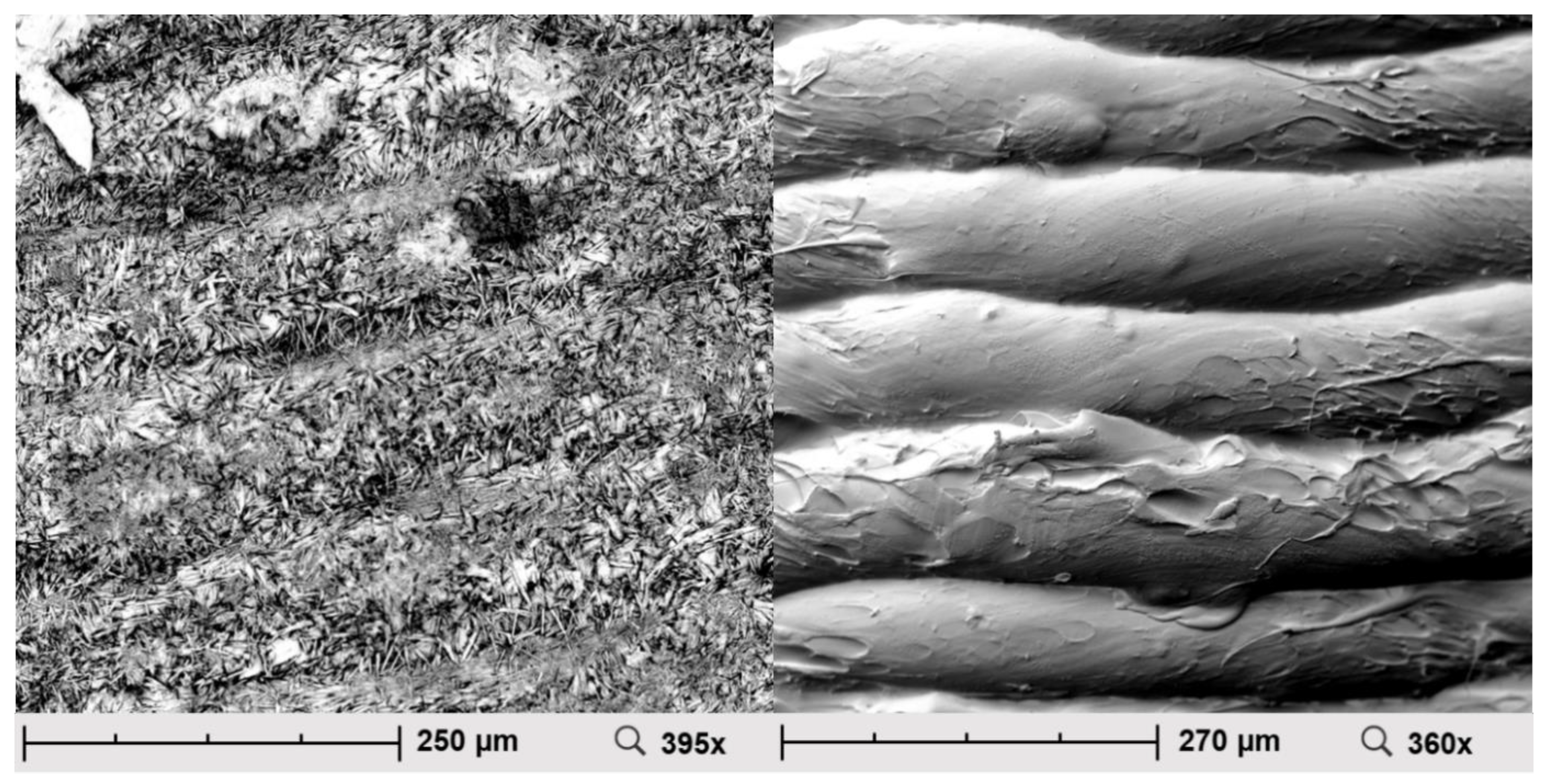
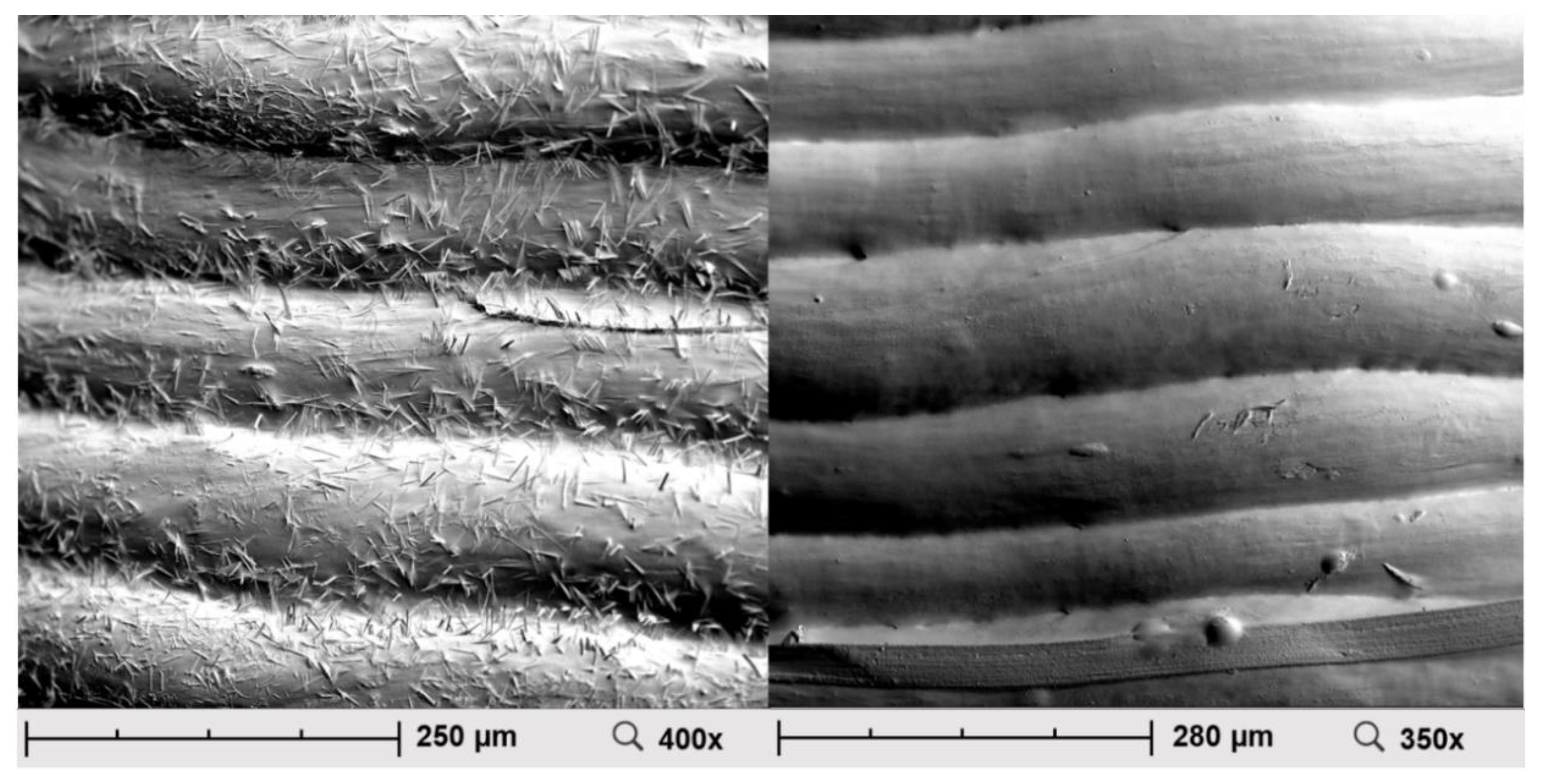
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
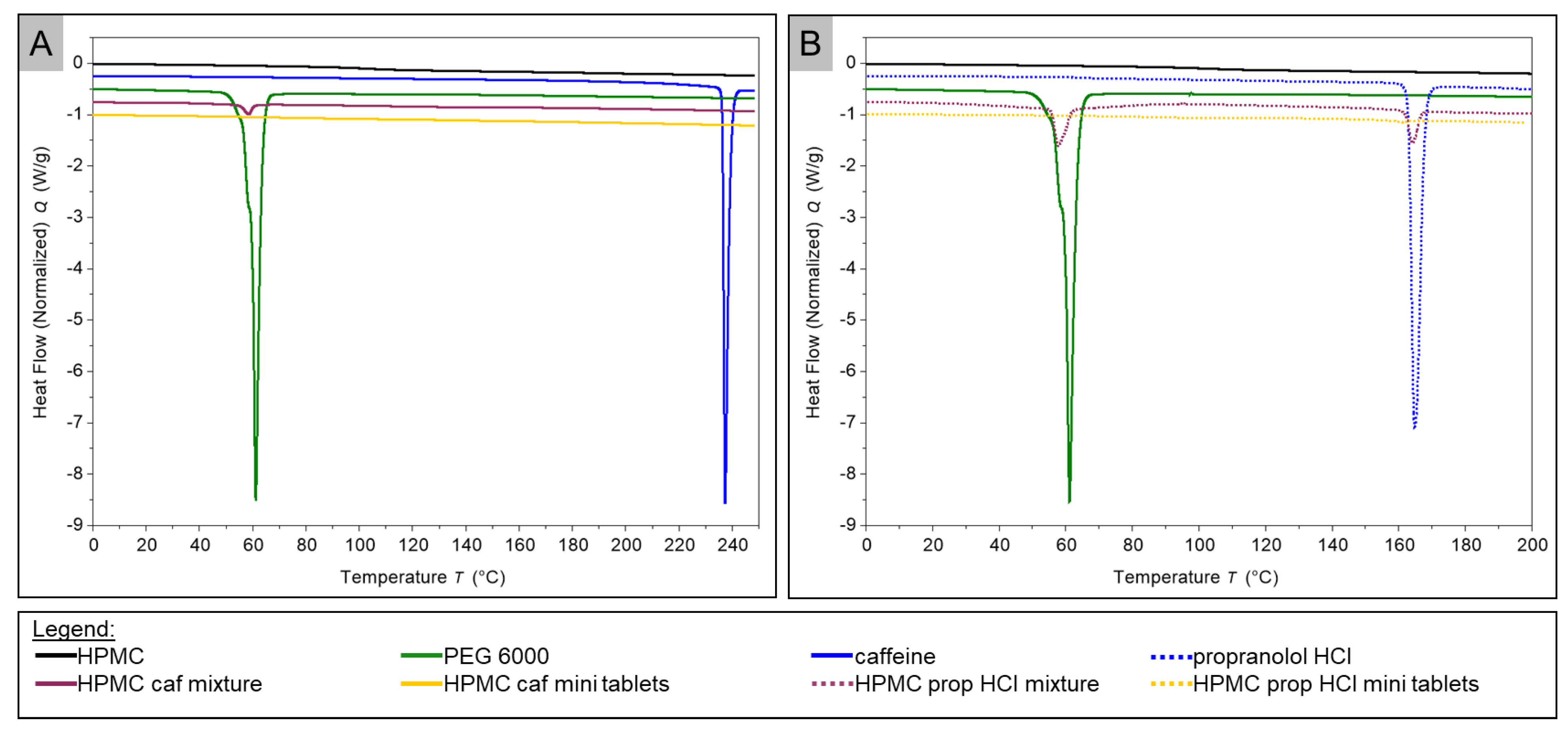
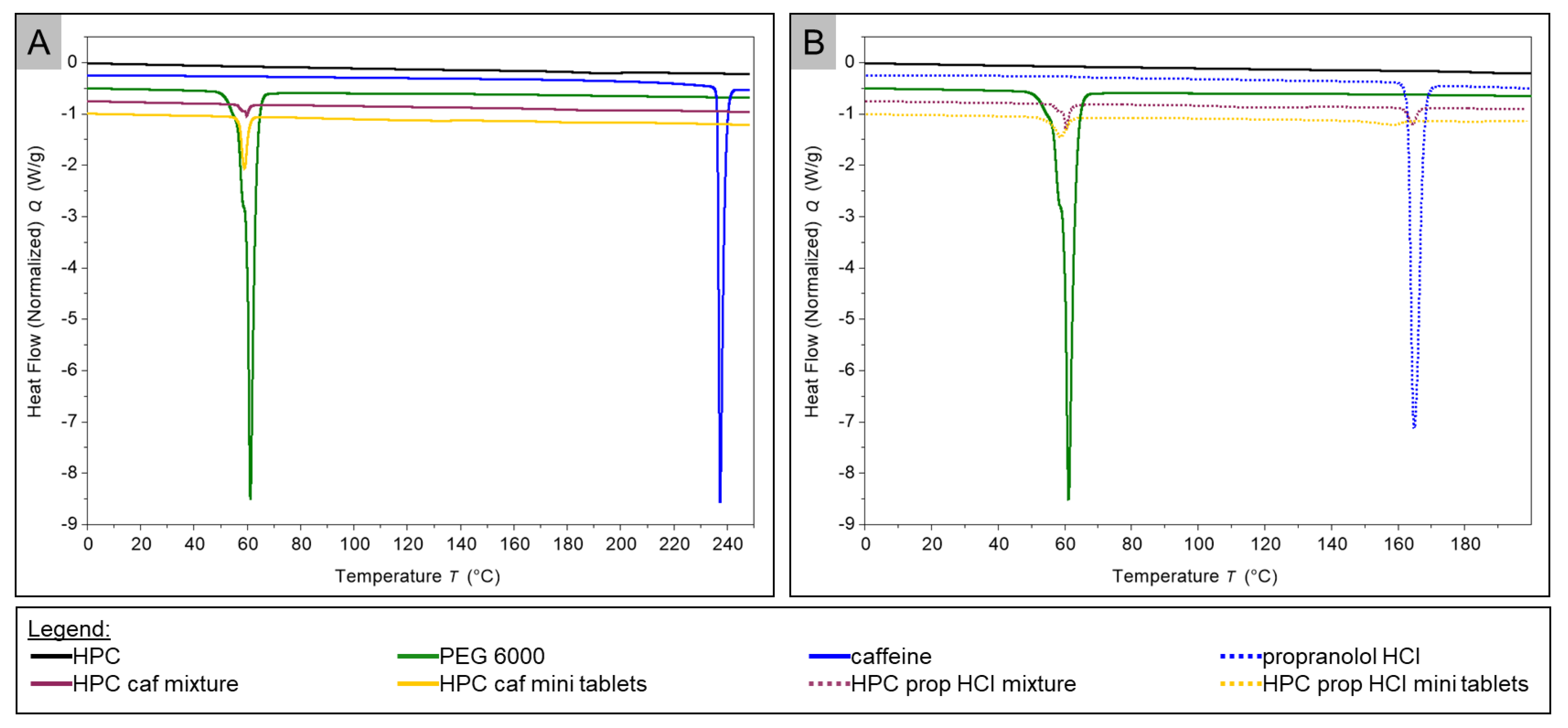
2.4. Thermal Analysis
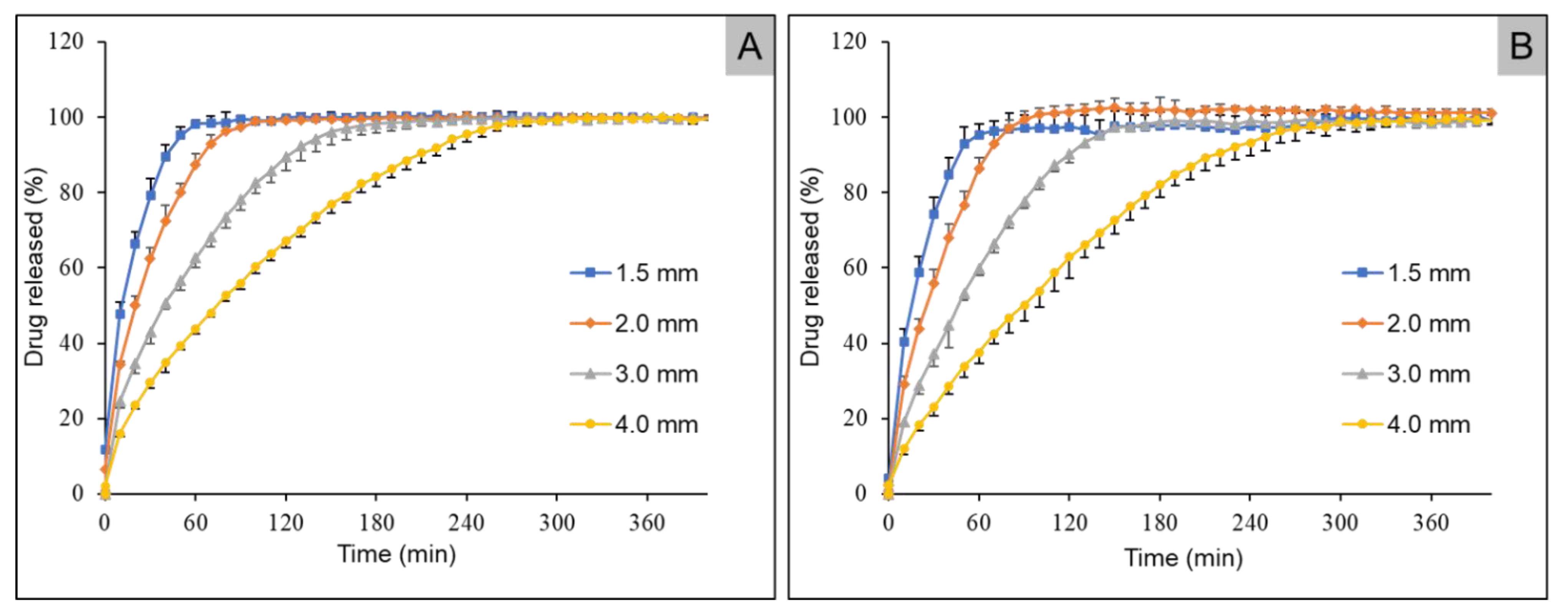
2.5. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
3. Discussion
3.1. Uniformity of Dosage Units According to Ph. Eur. 2.9.40
3.2. Optical Appearance
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.4. DSC
3.5. Dissolution Studies
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of Filaments Using Hot Melt Extrusion
4.2.2. 3D Printing of Mini Tablets
4.2.3. Characterization of Mini Tablets
4.2.4. Uniformity of Dosage Units According to Ph. Eur. 2.9.40
4.2.5. Optical Appearance
4.2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.2.7. Thermal Analysis
4.2.8. In Vitro Drug Release Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alhnan, M.A.; Okwuosa, T.C.; Sadia, M.; Wan, K.-W.; Ahmed, W.; Arafat, B. Emergence of 3D printed dosage forms: Opportunities and challenges. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenfield, S.J.; Awad, A.; Madla, C.M.; Hatton, G.B.; Firth, J.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Shaping the future: Recent advances of 3D printing in drug delivery and healthcare. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.; Akhtar, A.; Ahsan, I.; Shafiq-Un-Nabi, S. Pharmaceutical product development exploiting 3D printing technology: Conventional to novel drug delivery system. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 24, 5029–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öblom, H.; Sjöholm, E.; Rautamo, M.; Sandler, N. Towards printed pediatric medicines in hospital pharmacies: Comparison of 2D and 3D-printed orodispersible warfarin films with conventional oral powders in unit dose sachets. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zema, L.; Melocchi, A.; Maroni, A.; Gazzaniga, A. Three-dimensional printing of medicinal products and the challenge of personalized therapy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyanes, A.; Chang, H.; Sedough, D.; Hatton, G.B.; Wang, J.; Buanz, A.B.M.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Fabrication of controlled-release budesonide tablets via desktop (FDM) 3D printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyanes, A.; Scarpa, M.; Kamlow, M.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W.; Orlu, M. Patient acceptability of 3D printed medicines. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 530, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyanes, A.; Martinez, P.R.; Buanz, A.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Effect of geometry on drug release from 3D printed tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, C.; Katstra, W.; Palazzolo, R.; Giritlioglu, B.; Teung, P.; Cima, M. Multimechanism oral dosage forms fabricated by three dimensional printing™. J. Control. Release 2000, 66, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Martínez-Pacheco, R.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Fused-filament 3D printing of drug products: Microstructure analysis and drug release characteristics of PVA-based caplets. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 514, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Soh, S. Printing tablets with fully customizable release profiles for personalized medicine. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7847–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyanes, A.; Buanz, A.B.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Fused-filament 3D printing (3DP) for fabrication of tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, N.; Määttänen, A.; Ihalainen, P.; Kronberg, L.; Meierjohann, A.; Viitala, T.; Peltonen, J. Inkjet printing of drug substances and use of porous substrates-towards individualized dosing. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 3386–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickley, R.G.; Iwata, Q.; Wu, S.; Dahl, T.C. Pediatric drugs—A review of commercially available oral formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1731–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The selection and use of essential medicines. Report of the WHO Expert Committee, 2007 (including the 12th Model list of essential medicines). World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2007, 950, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, U.; Burau, D.; Spielmann, S.; Whitaker, M.J.; Ross, R.J.; Kloft, C.; Blankenstein, O. Quality of compounded hydrocortisone capsules used in the treatment of children. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Development of Paediatric Medicines: Points to Consider in Formulation; Technical Report Series 2012; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 197–225. [Google Scholar]
- Douroumis, D. Hot-Melt Extrusion: Pharmaceutical Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Publication: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780470711187. [Google Scholar]
- Caffeine Anhydrous Taste Masking by Hot Melt Extrusion. Available online: https://www.roquette.com/media-center/resources/pharma-poster-caffeine-anhydrous-taste-masking-by-hot-melt-extrusion (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Juluri, A.; Popescu, C.; Zhou, L.; Murthy, R.N.; Gowda, V.K.; Kumar, C.; Pimparade, M.B.; Repka, M.A.; Murthy, S.N. Taste masking of griseofulvin and caffeine anhydrous using kleptose linecaps DE17 by hot melt extrusion. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 17, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Tiwari, R.V.; Repka, M.A. Hot-melt extrusion: From theory to application in pharmaceutical formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.C.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Hanff, L.M.; Frijlink, H.W. Personalized medicine in pediatrics: The clinical potential of orodispersible films. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 18, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoutaris, N.; Ross, S.A.; Douroumis, D. 3D printed “starmix” drug loaded dosage forms for paediatric applications. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rycerz, K.; Stepien, K.A.; Czapiewska, M.; Arafat, B.T.; Habashy, R.; Isreb, A.; Peak, M.; Alhnan, M.A. Embedded 3D printing of novel bespoke soft dosage form concept for pediatrics. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, S.A.; Tuleu, C.; Wong, I.C.K.; Keady, S.; Pitt, K.G.; Sutcliffe, A.G. Minitablets: New modality to deliver medicines to preschool-aged children. Pediatrics 2009, 123, e235–e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksovski, A.; Dreu, R.; Gašperlin, M.; Planinšek, O. Mini-tablets: A contemporary system for oral drug delivery in targeted patient groups. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Say, K.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; Abdelbary, M.F.; Ali, B.E.; Aljaeid, B.M.; Zidan, A.S. Risperidone oral disintegrating mini-tablets: A robust-product for pediatrics. Acta Pharm. 2015, 65, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madathilethu, J.; Roberts, M.; Peak, M.; Blair, J.; Prescott, R.; Ford, J.L. Content uniformity of quartered hydrocortisone tablets in comparison with mini-tablets for paediatric dosing. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2018, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingmann, V.; Spomer, N.; Lerch, C.; Stoltenberg, I.; Frömke, C.; Bosse, H.M.; Breitkreutz, J.; Meissner, T. Favorable acceptance of mini-tablets compared with syrup: A randomized controlled trial in infants and preschool children. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1728–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spomer, N.; Klingmann, V.; Stoltenberg, I.; Lerch, C.; Meissner, T.; Breitkreutz, J. Acceptance of uncoated mini-tablets in young children: Results from a prospective exploratory cross-over study. Arch. Dis. Child. 2012, 97, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipping, T.; Rein, H. A new method for the continuous production of single dosed controlled release matrix systems based on hot-melt extruded starch: Analysis of relevant process parameters and implementation of an in-process control. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierickx, L.; Saerens, L.; Almeida, A.; De Beer, T.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Co-extrusion as manufacturing technique for fixed-dose combination mini-matrices. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, S.A.; Alexander, M.R.; Wildman, R.D.; Wallace, M.J.; Sharpe, S.; Yoo, J.; Roberts, C.J. 3D extrusion printing of high drug loading immediate release paracetamol tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, G.; Samaro, A.; Grymonpré, W.; Vanhoorne, V.; Van Snick, B.; Boone, M.N.; Hellemans, T.; Van Hoorebeke, L.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. 3D printing of high drug loaded dosage forms using thermoplastic polyurethanes. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanović, A.; Milošević, M.; Mladenović, G.; Likozar, B.; Čolić, K.; Mitrović, N. Experimental Dimensional Accuracy Analysis of Reformer Prototype Model Produced by FDM and SLA 3D Printing Technology BT—Experimental and Numerical Investigations in Materials Science and Engineering; Mitrovic, N., Milosevic, M., Mladenovic, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- Rebong, R.E.; Stewart, K.T.; Utreja, A.; Ghoneima, A.A. Accuracy of three-dimensional dental resin models created by fused deposition modeling, stereolithography, and Polyjet prototype technologies: A comparative study. Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khizer, Z.; Akram, M.R.; Sarfraz, R.M.; Nirwan, J.S.; Farhaj, S.; Yousaf, M.; Hussain, T.; Lou, S.; Timmins, P.; Conway, B.R.; et al. Plasticiser-free 3D printed hydrophilic matrices: Pharmacokinetic studies. Polymers 2019, 11, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadry, H.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Keshavarz, A.; Alam, F.; Xu, C.; Joy, A.; Ahsan, F. Multi-purposable filaments of HPMC for 3D printing of medications with tailored drug release and timed-absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 544, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, E.; Islam, M.T.; Goodwin, D.J.; Megarry, A.J.; Halbert, G.W.; Florence, A.J.; Robertson, J. Development of a hot-melt extrusion (HME) process to produce drug loaded Affinisol™ 15LV filaments for fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printing. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 29, 100776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNunzio, J.C.; Brough, C.; Hughey, J.R.; Miller, D.A.; Iii, R.O.W.; McGINITY, J.W. Fusion production of solid dispersions containing a heat-sensitive active ingredient by hot melt extrusion and Kinetisol® dispersing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okwuosa, T.C.; Stefaniak, D.; Arafat, B.; Isreb, A.; Wan, K.-W.; Alhnan, M.A. A lower temperature FDM 3D printing for the manufacture of patient-specific immediate release tablets. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xu, X.-Y.; Li, R.; Zang, G.-A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.-R.; Xiong, M.-F.; Xu, J.-R.; Wang, T.; Fu, H.; et al. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of FDM 3D-printed ellipsoid-shaped gastric floating tablets with low infill percentages. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozini, B.; Cervini, P.; Cavalheiro, É.T.G. Thermal behavior of the β-blocker propranolol. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 123, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelpoel, H.; Welink, J.; Amidon, G.L.; Junginger, H.E.; Midha, K.K.; Möller, H.; Olling, M.; Shah, V.P.; Barends, D.M. Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms based on biopharmaceutics classification system (BCS) literature data: Verapamil hydrochloride, propranolol hydrochloride, and atenolol. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-J.; Balakrishnan, P.; Lin, H.; Choi, M.-K.; Kim, D.-D. Application of biopharmaceutics classification system (BCS) in drug transport studies across human respiratory epithelial cell monolayers. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 42, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
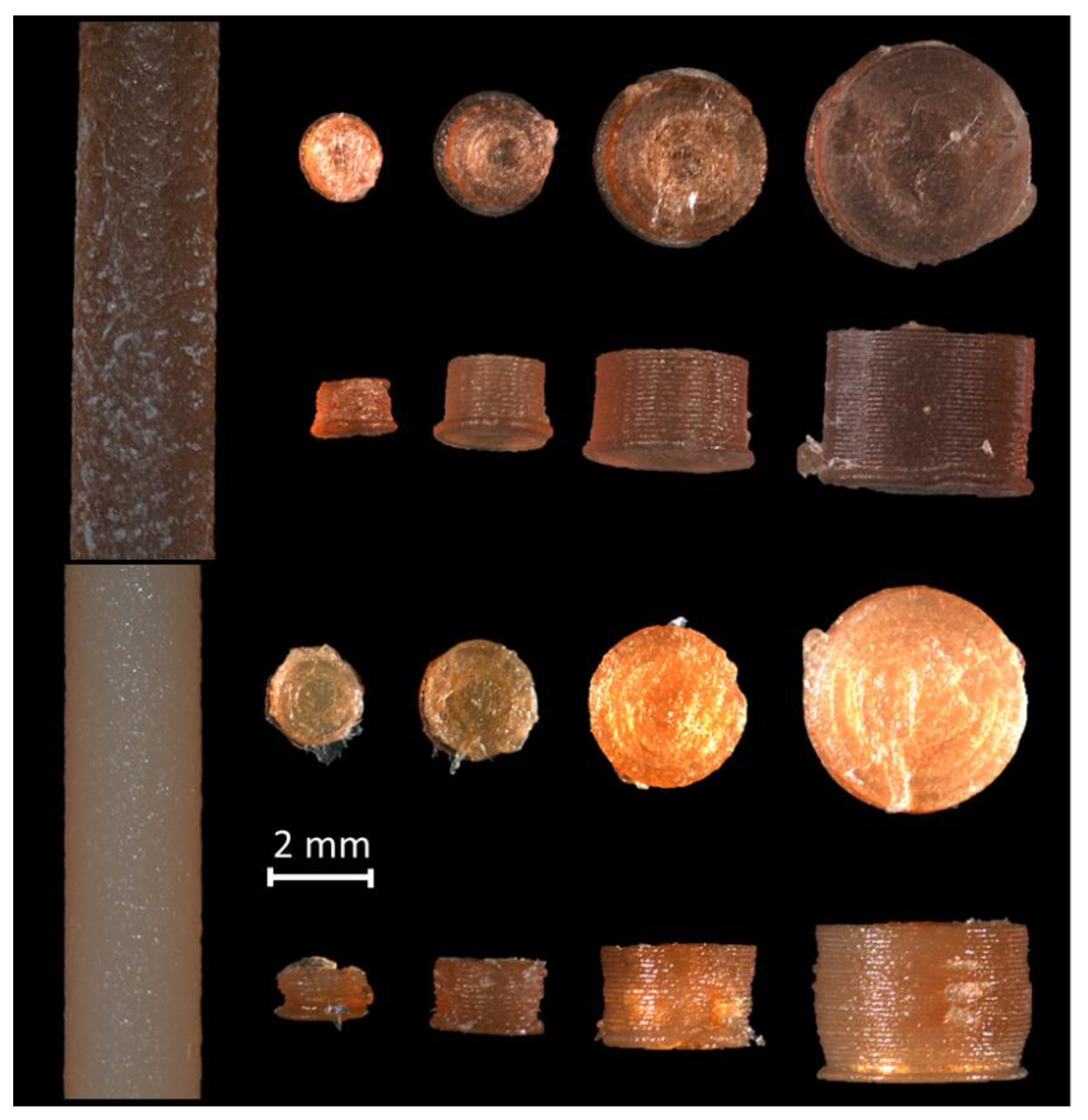
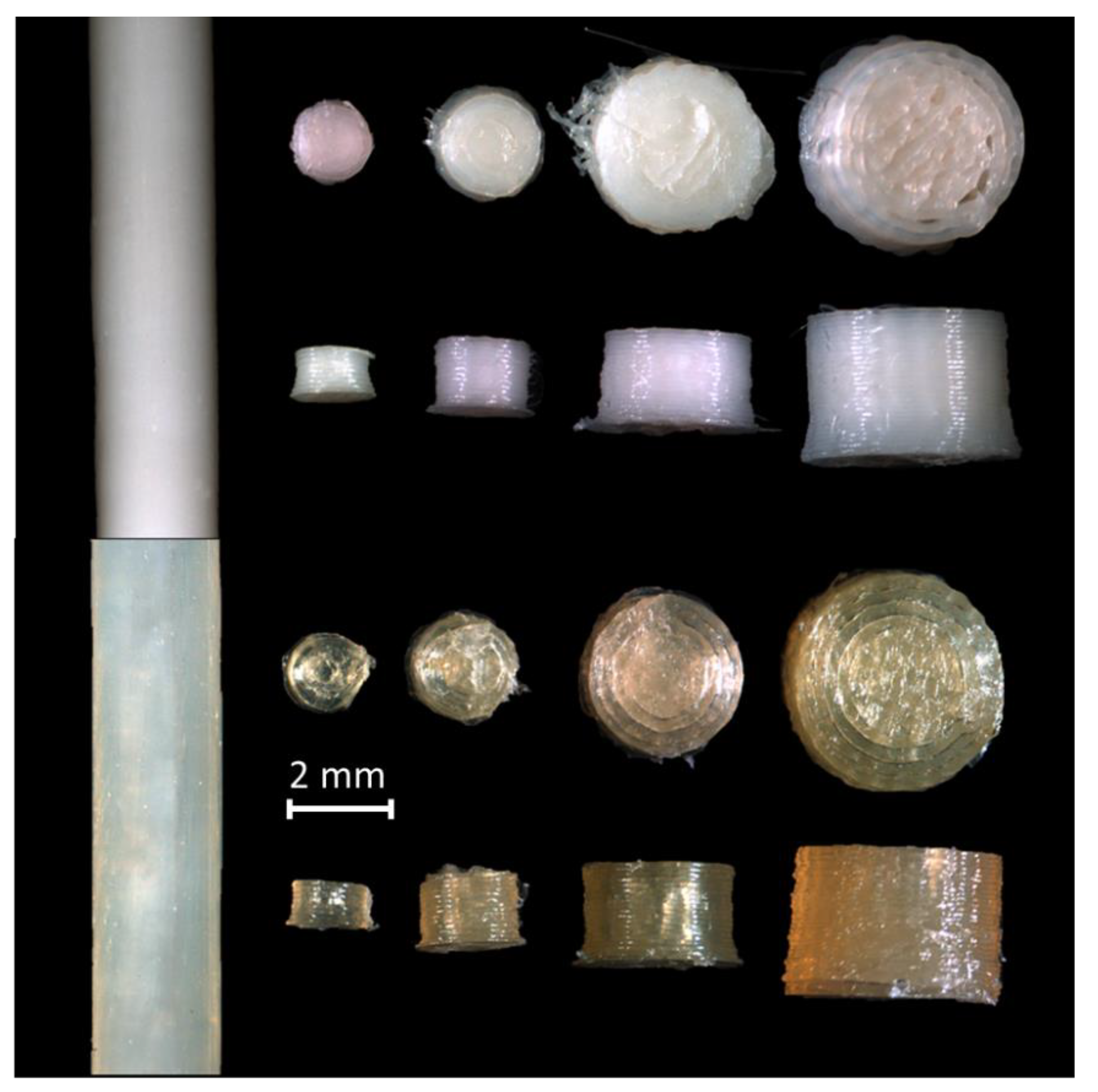



| Tablet Diameter (mm) | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| Measured diameter (mm) | 3.96 | 2.81 | 1.87 | 1.30 |
| Standard deviation of measured diameter (mm) | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
| Measured tablet height (mm) | 3.01 | 1.91 | 1.49 | 0.93 |
| Standard deviation of Measured tablet height (mm) | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| Mean of mass (mg) | 41.70 | 17.49 | 5.63 | 2.47 |
| Standard deviation of mass (mg) | 1.98 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 0.34 |
| Mean of individual content, (%) | 90.55 | 84.87 | 89.26 | 88.84 |
| Reference value, M (%) | 98.5 | 98.5 | 98.5 | 98.5 |
| Sample standard deviation, s | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.19 |
| Sample size, n | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Acceptability constant, k | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Acceptance value, AV | 8.06 | 14.10 | 9.38 | 10.13 |
| Ingredients | Batch Name | |
|---|---|---|
| HPMC-Caffeine | HPMC-Propranolol HCl | |
| Caffeine | 10 | - |
| Propranolol HCl | - | 10 |
| Hypromellose | 79.5 | 79.5 |
| PEG 6000 | 10 | 10 |
| Fumed Silica | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Ingredients | Batch Name | |
|---|---|---|
| HPC-Caffeine | HPC-Propranolol HCl | |
| Caffeine | 10 | - |
| Propranolol HCl | - | 10 |
| Hyprolose | 79.5 | 79.5 |
| PEG 6000 | 10 | 10 |
| Fumed Silica | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Batch | HPMC-Caffeine HPMC-Propranolol HCl | HPC-Caffeine HPC-Propranolol HCl | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Zone 1 (°C) | 120 | 90 |
| Zone 2–4 (°C) | 170 | 140 | |
| Screw speed (rpm) | 25 | 10 | |
| Dimension | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (mm) | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| Height (mm) | 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 1.0 |
| Setting | HPMC-Caffeine HPMC-Propranolol HCl | HPC-Caffeine HPC-Propranolol HCl |
|---|---|---|
| Printing temperature (°C) | 200 | 170 |
| Build plate temperature (°C) | 60 | 60 |
| Printing speed (mm/s) | 30 | 30 |
| Travel speed (mm/s) | 30 | 30 |
| Layer height (mm) | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| First layer height (mm) | 0.17 | 0.17 |
| Infill (%) | 100 | 100 |
| Print cooling fan | Enabled | Enabled |
| Filament retraction | Disabled | Disabled |
| Build plate adhesion | Skirt | Skirt |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krause, J.; Müller, L.; Sarwinska, D.; Seidlitz, A.; Sznitowska, M.; Weitschies, W. 3D Printing of Mini Tablets for Pediatric Use. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020143
Krause J, Müller L, Sarwinska D, Seidlitz A, Sznitowska M, Weitschies W. 3D Printing of Mini Tablets for Pediatric Use. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(2):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020143
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrause, Julius, Laura Müller, Dorota Sarwinska, Anne Seidlitz, Malgorzata Sznitowska, and Werner Weitschies. 2021. "3D Printing of Mini Tablets for Pediatric Use" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 2: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020143
APA StyleKrause, J., Müller, L., Sarwinska, D., Seidlitz, A., Sznitowska, M., & Weitschies, W. (2021). 3D Printing of Mini Tablets for Pediatric Use. Pharmaceuticals, 14(2), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020143