Designing Efficient Low-Cost Paper-Based Sensing Plasmonic Nanoplatforms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Colloidal GNRs Synthesis
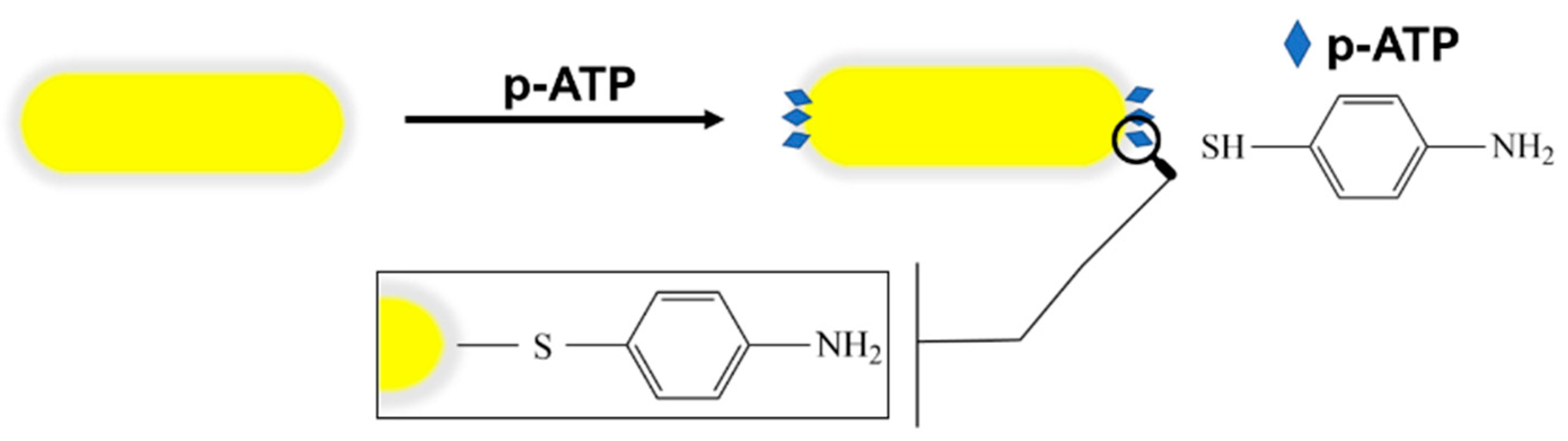
2.3. Raman Labelling Protocol
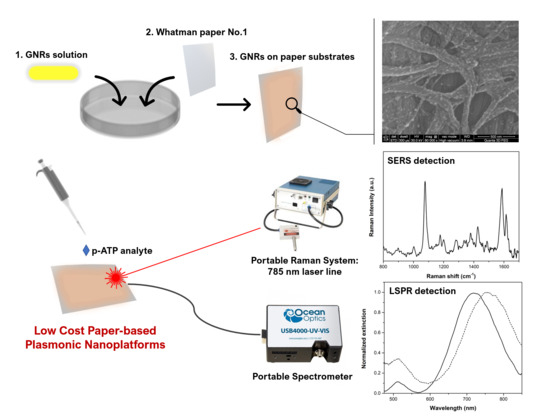
2.4. Fabrication of Paper-Based Plasmonic Nanoplatforms
2.5. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
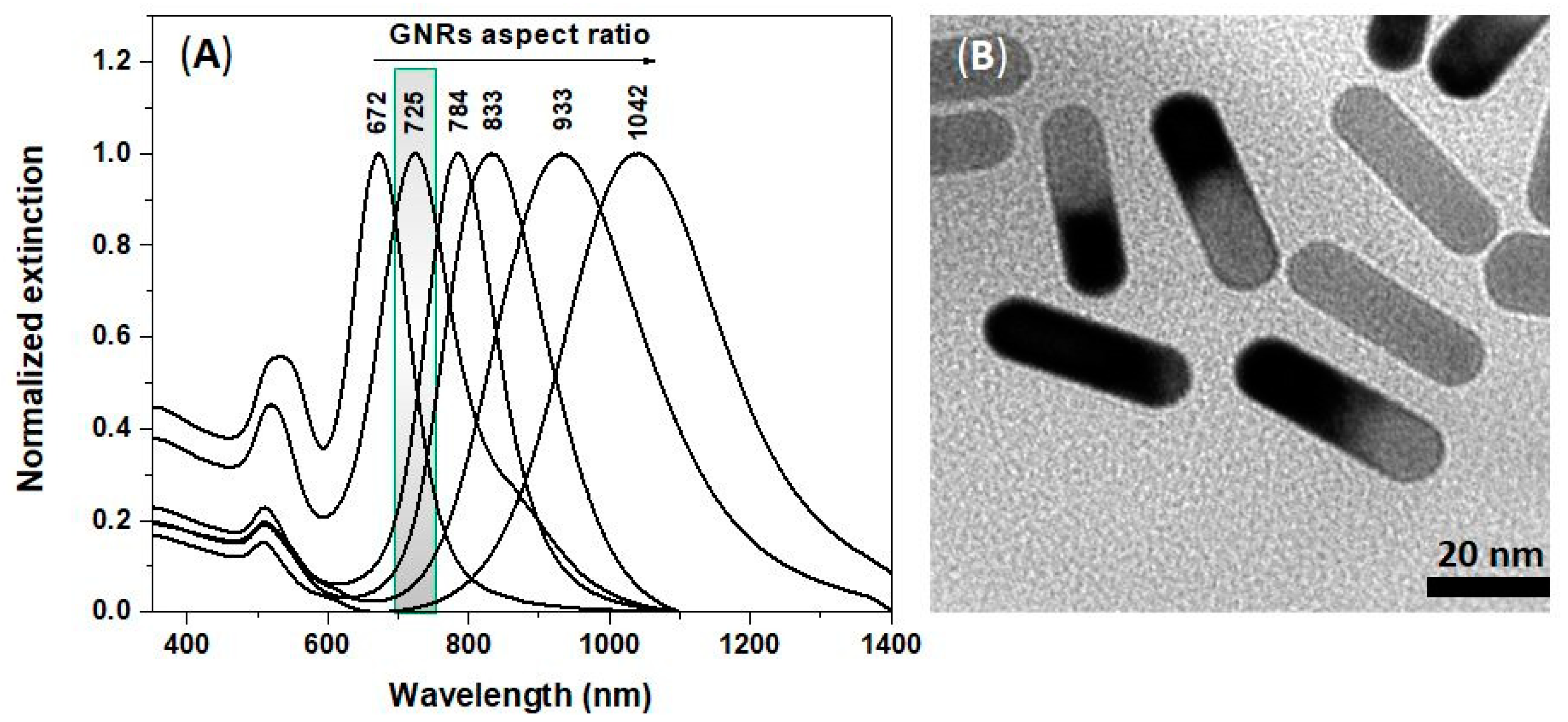
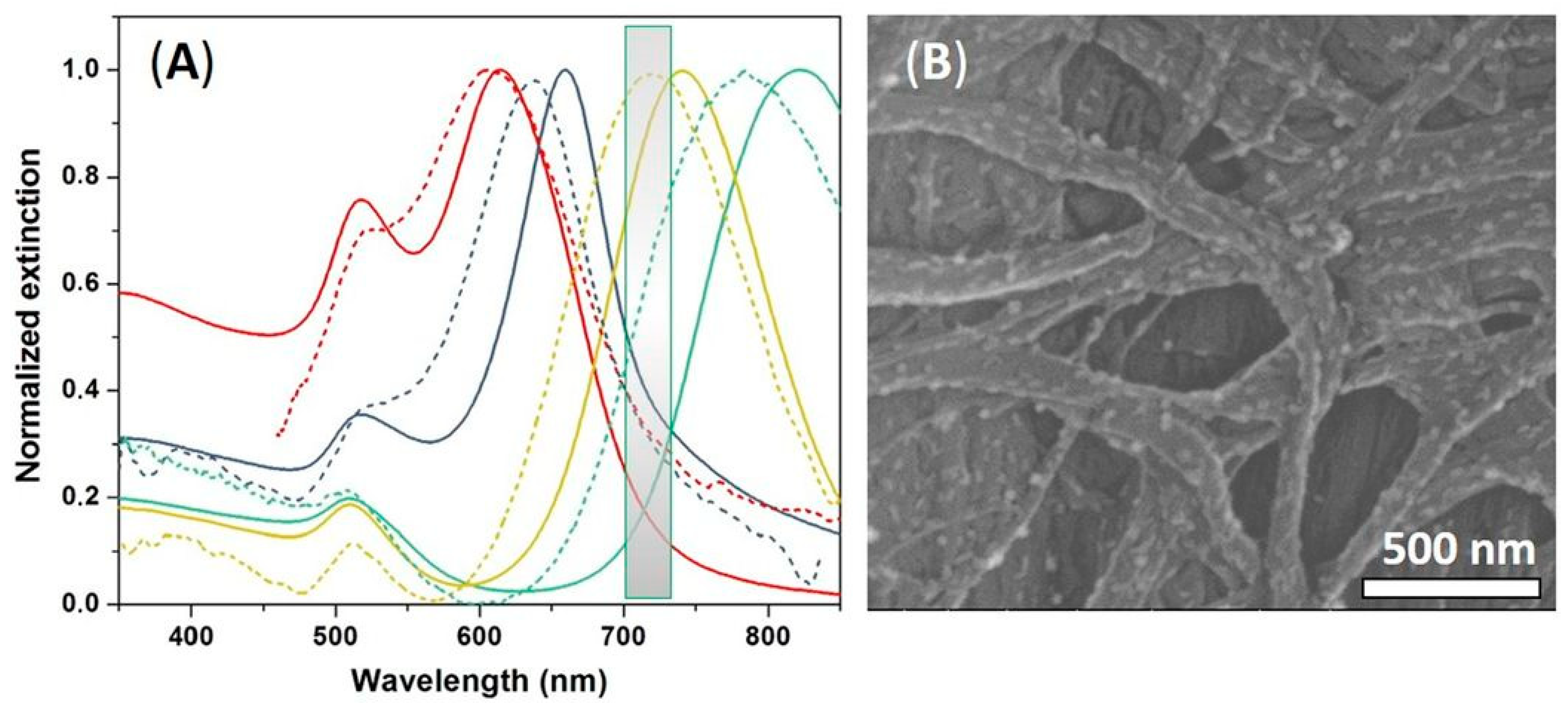
3.1. Optical and Morphological Characterizations of Colloidal GNRs
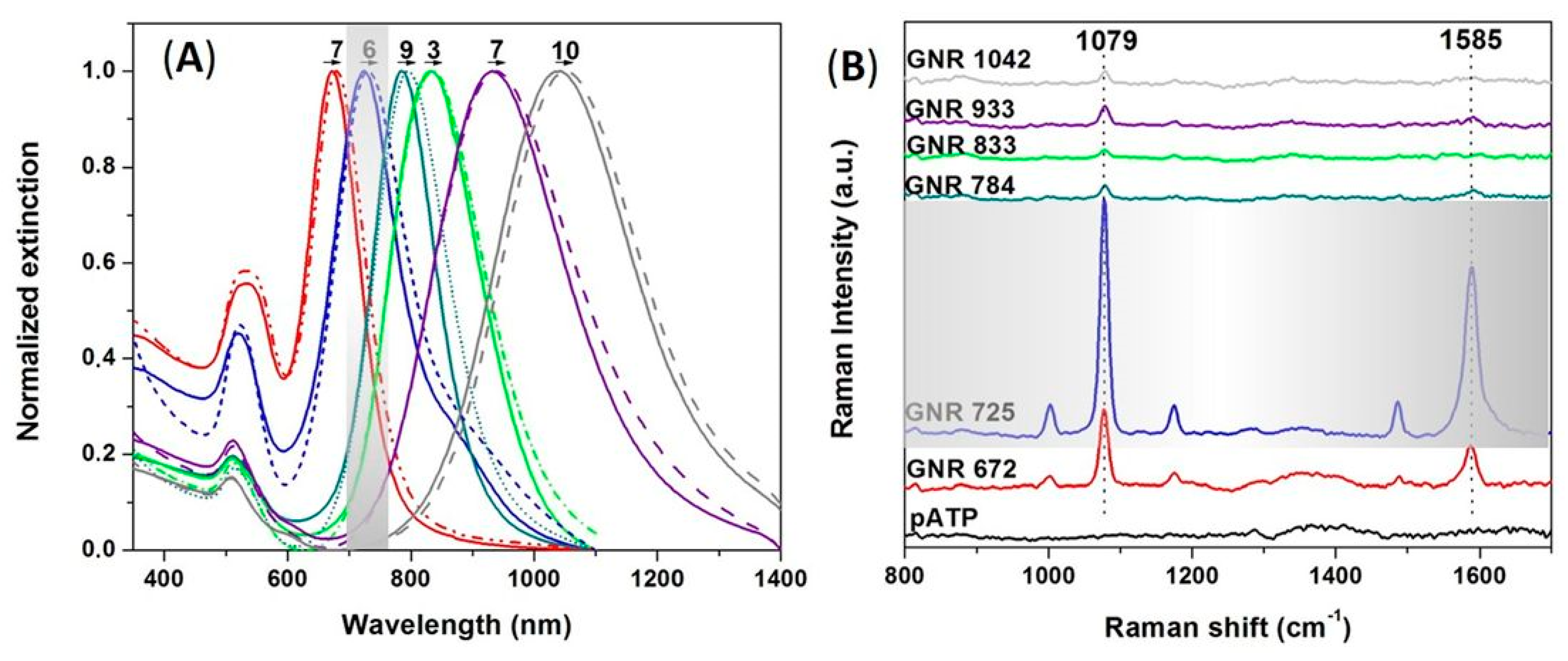
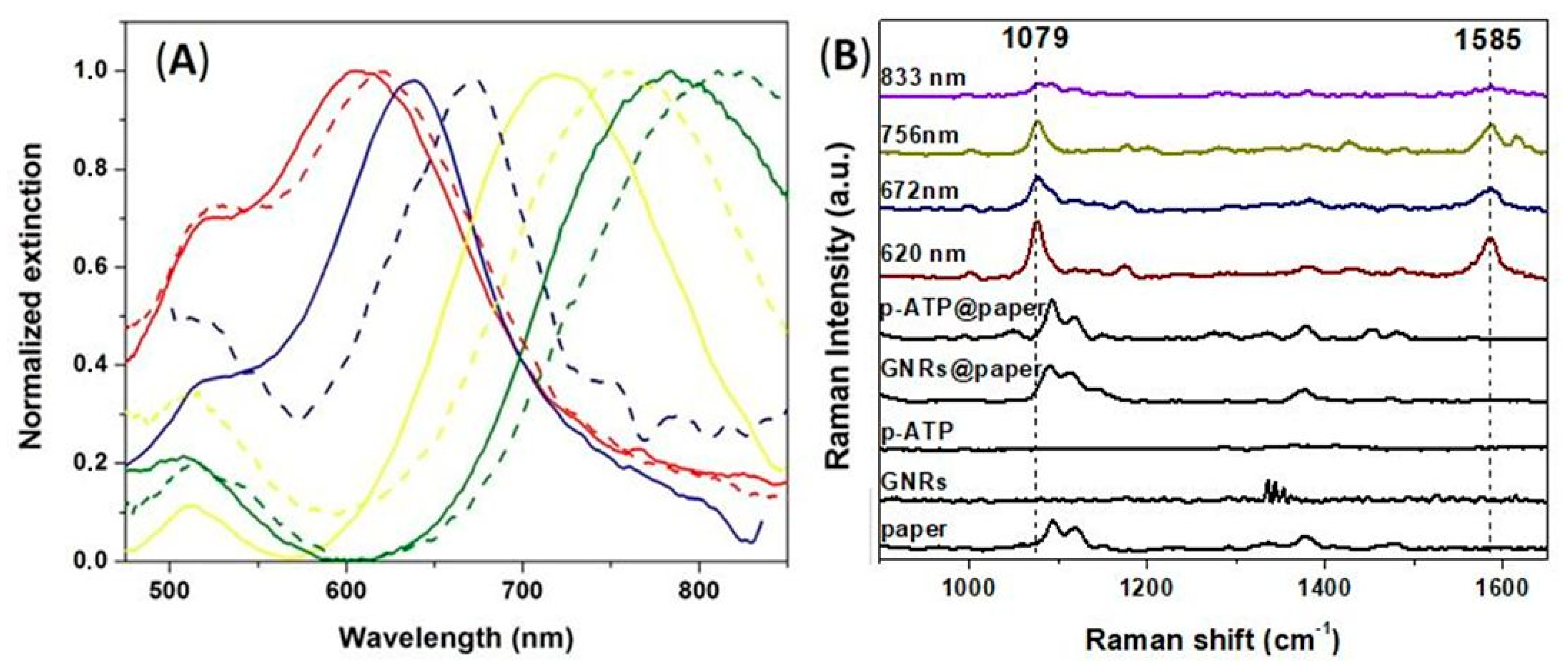
3.2. LSPR-SERS Detection of p-ATP Analyte in Solution
3.3. Fabrication of Tunable Paper-Based Plasmonic Nanoplatforms
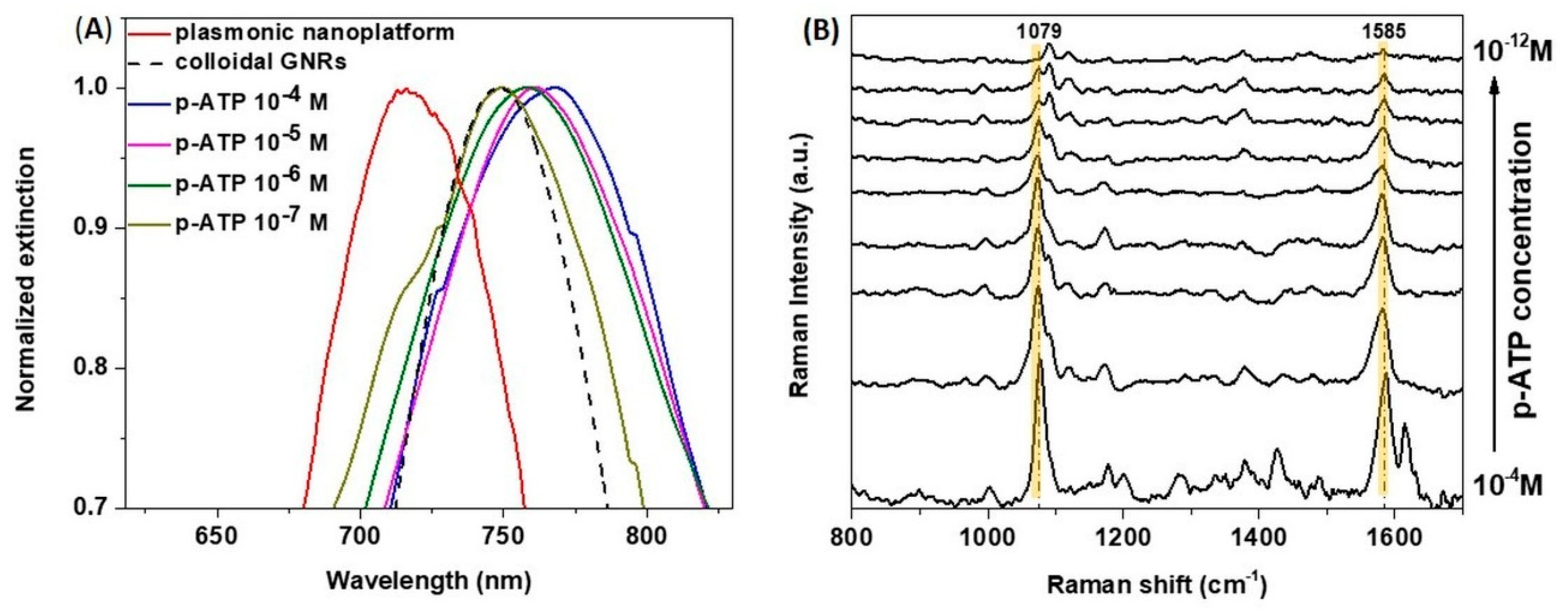
3.4. Evaluating the Tunable Paper-Based Nanoplatforms as Efficient Nanosensors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M.M.; Aguirre, S.D.; Xu, Y.; Filipe, C.D.; Pelton, R.; Li, Y. Detection of DNA using bioactive paper strips. Chem. Commun. Camb. Eng. 2009, 6640–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parolo, C.; Merkoçi, A. Paper-based nanobiosensors for diagnostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yager, P.; Edwards, T.; Fu, E.; Helton, K.; Nelson, K.; Tam, M.R.; Weigl, B.H. Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature 2006, 442, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liana, D.D.; Raguse, B.; Gooding, J.J.; Chow, E. Recent advances in paper-based sensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 11505–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, K.A.; Othman, A.; Andreescu, S. Nanomaterial-Functionalized Cellulose: Design, Characterization and Analytical Applications. Anal. Sci. Int. J. Jpn. Soc. Anal. Chem. 2018, 34, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourreza, N.; Golmohammadi, H.; Naghdi, T.; Yousefi, H. Green in-situ synthesized silver nanoparticles embedded in bacterial cellulose nanopaper as a bionanocomposite plasmonic sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Qin, Y.; He, Y.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C.; Chen, H.-Y. Functional nanoprobes for ultrasensitive detection of biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4234–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The Optical Properties of Metal Nanoparticles: The Influence of Size, Shape, and Dielectric Environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A. Surface plasmons in metallic nanoparticles: Fundamentals and applications. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 283001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baia, M.; Astilean, S.; Iliescu, T. Raman and SERS Investigations of Pharmaceuticals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-78282-7. [Google Scholar]
- Stiles, P.L.; Dieringer, J.A.; Shah, N.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface-Enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. Palo Alto Calif. 2008, 1, 601–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Bui, M.-P.N.; Abbas, A. Paper-based chemical and biological sensors: Engineering aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Vidal, F.J.; Pendry, J.B. Collective Theory for Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focsan, M.; Craciun, A.M.; Potara, M.; Leordean, C.; Vulpoi, A.; Maniu, D.; Astilean, S. Flexible and Tunable 3D Gold Nanocups Platform as Plasmonic Biosensor for Specific Dual LSPR-SERS Immuno-Detection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campu, A.; Lerouge, F.; Chateau, D.; Chaput, F.; Baldeck, P.; Parola, S.; Maniu, D.; Craciun, A.M.; Vulpoi, A.; Astilean, S.; et al. Gold NanoBipyramids Performing as Highly Sensitive Dual-Modal Optical Immunosensors. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8567–8575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmucker, A.L.; Tadepalli, S.; Liu, K.-K.; Sullivan, C.J.; Singamaneni, S.; Naik, R.R. Plasmonic paper: A porous and flexible substrate enabling nanoparticle-based combinatorial chemistry. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 4136–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kang, B.-H.; Jeong, K.-H. Paper-Based Biochip Assays and Recent Developments: A Review. BioChip J. 2018, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankus, M.E.; Tian, L.; Pellegrino, P.M.; Singamaneni, S. Plasmonic paper as a highly efficient SERS substrate. In Proceedings of the SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, Baltimore, MD, USA, 23–27 April 2012; Volume 8358, p. 835815. [Google Scholar]
- Ashley, M.J.; Bourgeois, M.R.; Murthy, R.R.; Laramy, C.R.; Ross, M.B.; Naik, R.R.; Schatz, G.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Shape and size control of substrate-grown gold nanoparticles for surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy detection of chemical analytes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zheng, P.; Kasani, S.; Wu, S.; Yang, F.; Lewis, S.; Nayeem, S.; Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B.; Wigginton, J.G.; Simpkins, J.W.; et al. Paper-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Lateral Flow Strip for Detection of Neuron-Specific Enolase in Blood Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10104–10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Shao, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Gold nanorods and their plasmonic properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2679–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.J.; Thompson, L.B.; Chernak, D.J.; Yang, J.A.; Sivapalan, S.T.; Boulos, S.P.; Huang, J.; Alkilany, A.M.; Sisco, P.N. Gold nanorod crystal growth: From seed-mediated synthesis to nanoscale sculpting. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Hankus, M.E.; Tian, L.; Pellegrino, P.M.; Singamaneni, S. Highly sensitive surface enhanced raman scattering substrates based on filter paper loaded with plasmonic nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8953–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Tian, L.; Singamaneni, S. Paper-based SERS swab for rapid trace detection on real-world surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3429–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Tadepalli, S.; Farrell, M.E.; Liu, K.-K.; Gandra, N.; Pellegrino, P.M.; Singamaneni, S. Multiplexed charge-selective surface enhanced Raman scattering based on plasmonic calligraphy. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Tadepalli, S.; Hyun Park, S.; Liu, K.-K.; Morrissey, J.J.; Kharasch, E.D.; Naik, R.R.; Singamaneni, S. Bioplasmonic calligraphy for multiplexed label-free biodetection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabudean, A.M.; Biro, D.; Astilean, S. Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) studies of 4-aminothiophenol adsorption on gold nanorods. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 993, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.N.; Veigas, B.; Jacob, J.M.; Santos, D.S.; Gomes, J.; Baptista, P.V.; Martins, R.; Inácio, J.; Fortunato, E. A low cost, safe, disposable, rapid and self-sustainable paper-based platform for diagnostic testing: Lab-on-paper. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 094006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.-J.; Roy, P.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. An ink-jet printed, surface enhanced Raman scattering paper for food screening. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40487–40493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoobakht, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Preparation and Growth Mechanism of Gold Nanorods (NRs) Using Seed-Mediated Growth Method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigderman, L.; Zubarev, E.R. High-Yield Synthesis of Gold Nanorods with Longitudinal SPR Peak Greater than 1200 nm Using Hydroquinone as a Reducing Agent. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, K.K.; Wilson, J.N.; Bunz, U.H.; Murphy, C.J. Preferential End-to-End Assembly of Gold Nanorods by Biotin−Streptavidin Connectors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13914–13915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S. Probing Single Molecules and Single Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Science 1997, 275, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-H.; Ossig, R.; Hubenthal, F.; Kronfeldt, H.-D. Influence of surface plasmon resonance wavelength on SERS activity of naturally grown silver nanoparticle ensemble. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baia, M.; Toderas, F.; Baia, L.; Popp, J.; Astilean, S. Probing the enhancement mechanisms of SERS with p-aminothiophenol molecules adsorbed on self-assembled gold colloidal nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 422, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.R.; Liu, M.Y.; Kulkarni, S.; Fang, Y. Study of adsorption behavior of aminothiophenols on gold nanorods using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Nanophotonics 2011, 5, 053513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Fales, A.M.; Vo-Dinh, T. TAT peptide-functionalized gold nanostars: Enhanced intracellular delivery and efficient NIR photothermal therapy using ultra-low irradiance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11358–11361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi Samir, M.A.; Alloin, F.; Dufresne, A. Review of recent research into cellulosic whiskers, their properties and their application in nanocomposite field. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Huo, D.; Hou, C.; Fa, H.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L. Colorimetric measurement of Fe3+ using a functional paper-based sensor based on catalytic oxidation of gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jackman, J.A.; Yang, H.-H.; Chen, P.; Cho, N.-J.; Kim, D.-H. Strategies for enhancing the sensitivity of plasmonic nanosensors. Nano Today 2015, 10, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kim, D.-H. Dark-field microscopy studies of polarization-dependent plasmonic resonance of single gold nanorods: Rainbow nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3228–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unser, S.; Bruzas, I.; He, J.; Sagle, L. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing: Current Challenges and Approaches. Sensors 2015, 15, 15684–15716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumerical. Available online: https://www.lumerical.com (accessed on 11 September 2018).
- Lide, D.R. Optical Properties of Metals and Semiconductors. In CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physic, 74th ed.; CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Susu, L.; Campu, A.; Craciun, A.M.; Vulpoi, A.; Astilean, S.; Focsan, M. Designing Efficient Low-Cost Paper-Based Sensing Plasmonic Nanoplatforms. Sensors 2018, 18, 3035. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093035
Susu L, Campu A, Craciun AM, Vulpoi A, Astilean S, Focsan M. Designing Efficient Low-Cost Paper-Based Sensing Plasmonic Nanoplatforms. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):3035. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSusu, Laurentiu, Andreea Campu, Ana Maria Craciun, Adriana Vulpoi, Simion Astilean, and Monica Focsan. 2018. "Designing Efficient Low-Cost Paper-Based Sensing Plasmonic Nanoplatforms" Sensors 18, no. 9: 3035. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093035
APA StyleSusu, L., Campu, A., Craciun, A. M., Vulpoi, A., Astilean, S., & Focsan, M. (2018). Designing Efficient Low-Cost Paper-Based Sensing Plasmonic Nanoplatforms. Sensors, 18(9), 3035. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093035