Abstract
The ability to accurately quantify biodiversity is fundamental to understanding ecological trends, identifying drivers of declines, and selecting effective conservation options. Scientists and resource managers have grappled with what metrics best show relevant biodiversity patterns and are still practical enough to aid on-the-ground resource conservation. Our purpose is to construct empirically derived, functional habitat guilds for prairie stream fish, then recommend future directions for constructing and using diversity metrics that aid field-based conservation. Working in the Upper Neosho River, KS, USA, we used univariate methods, cluster analysis, non-metric multi-dimensional scaling, and an analysis of similarity to functionally group stream fish taxa. The 11 most abundant fish species grouped into seven ecological guilds: riffle specialist, pool specialist, riffle generalist, pool generalist, riffle–run generalist, pool–run generalist, and generalist. Combining the habitat type and strength of association added ecological accuracy to our species groups. Employing multiple statistical methods increased confidence and generality in our grouping results. Moving forward will require a coordinated, coalition-driven, conservation-related strategy on which researchers and practitioners collaborate to synthesize diverse empirical results, organize general principles of structure and function, and balance accuracy with practicality.
1. Introduction
Functional ecology can provide an ecologically meaningful approach to assessing organismal diversity and biological change at the larger spatial and temporal scales needed for conservation and management. Two key goals for resource managers are to take appropriate science-based actions to minimize environmental degradation, and to conserve natural communities in the face of adverse anthropogenic effects (e.g., stream fragmentation, land-use change, and climate change). These tasks are daunting given the increasing number of human-related disturbances, natural variation, and inherent complexity of natural systems across broad geographic scales (state, regional, and national). Functional ecology has the potential to provide a better understanding of population, community, and ecosystem patterns and processes than studies using taxonomic relationships alone [1]. For this reason, the functional ecology approach is increasing across ecological disciplines [2,3,4]. Our purpose here is to construct empirically derived, functional habitat guilds, then make recommendations for future directions that link organismal groupings, biodiversity metrics, and field-based conservation actions.
Scientists and resource managers have grappled with what unit of organismal organization shows relevant natural biodiversity patterns and is still practical enough to aid in on-the ground conservation. At one extreme, individual species have unique features that can be important for conservation (e.g., the Endangered Species Act [5]). However, looking only at a few individual species can miss larger trends, and looking at all individual species in detail can be overwhelming. At the other extreme, community ecology metrics (e.g., richness, evenness, and diversity) are simple ways to quantify the community but can omit important ecological information about groups of organisms [6]. Alternatively, grouping species systematically can make working with large, multi-species datasets easier and has the potential to identify general relationships that can facilitate across-system comparisons [7]. It is important to note that each of these approaches are context-dependent on the research questions being addressed and can provide useful information. Species grouping approaches, concepts, and terminology vary. As two examples, the “guild concept” groups species with overlapping niches without regard to taxonomic classification [8,9,10,11], whereas the “functional group” concept examines organisms in a way that addresses process-oriented ecological questions [7,12,13]. We do not dwell on differences among grouping definitions, but instead focus on how to develop ecologically meaningful groupings for stream fish that can be practical for conservation.
Here we focus on functional habitat guilds because habitat is an important component of fish ecology and life history that is often measured in research and conservation. As examples, the interaction among the stream channel geomorphology, hydrological flows, and connectivity shape distinct stream and river habitat units (e.g., pool, riffle, and run [14,15,16]). Habitat can also be quantified as a mosaic of patches which are delineated by variations of flow velocity, substrate, and depth [17,18]. Previous studies have found strong associations among groups of fish and stream habitat types [19,20,21].
We had two specific objectives. First, we developed mesohabitat groupings for 11 common stream fish species using strength and type of association. Second, we compared these functional guild associations across multiple analytical approaches (univariate, cluster analysis, NMDS, and SIMPER). For both objectives, we discuss the generality of our groupings with the existing literature. The unique findings of our empirical functional habitat guild analysis are that (1) using both mesohabitat type and strength of association adds utility and (2) using multiple statistical methods adds generality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Sites
The study was conducted within the Upper Neosho River watershed along the Neosho and Cottonwood Rivers in Morris, Lyon, and Chase County, KS, USA (Figure 1). The drainage area upstream of the John Redmond Reservoir is approximately 7700 km2 (Figure 1). The Neosho and Cottonwood Rivers are 5th order streams that lie upon Permian age limestone and shale bedrock [22]. The surrounding land use is predominately row crop agriculture of corn, wheat, and soybean [23]. The study area contains approximately 55 native fish species [24] that are well suited to longitudinally-connected, predictably-variable flow and temperature regimes [25].
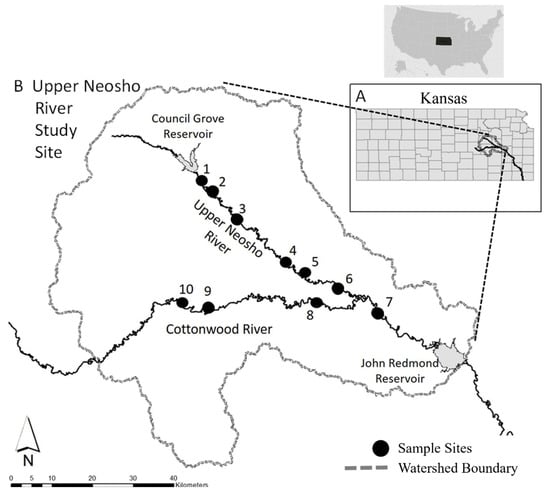
Figure 1.
Map of the study area including (A) the Neosho River within the state of Kansas, and (B) ten 3 km sampling sites (1–10) within the Upper Neosho River watershed along the Neosho and Cottonwood Rivers, KS. The study areas were in Morris, Lyon, and Chase County, KS, USA.
To measure fish biodiversity and habitat, we selected ten sites (Figure 1). At each site, we sampled along 3 km, spatially-continuous, longitudinal mosaics of stream habitats. This design was intermediate between local-site and watershed-regional scales. Great Plains streams have a highly variable hydrologic regime with regular periods of flooding and droughts [25]. The mean annual discharges of the watersheds were 8.72 m3/s (SE ± 0.94, USGS gage 07179730, 1963–2013) along the Neosho River and 24.55 m3/s (SE ± 2.19, USGS gage 07182250, 1963–2013) along the Cottonwood River.
2.2. Fish Sampling
Sampling occurred from April to November 2013. Two observers were used to visually identify stream mesohabitats (pool, riffle, and run) using an objective series of stream flow, channel morphology, and substrate parameters [26,27]. A Garmin GPSmap76Cx (Garmin International, Olathe, KS, USA) was used to delineate each mesohabitat using trackplots at 5 s intervals. These mesohabitats have been shown to be discrete habitat patches based upon stream width, depth, and flow velocity [28]. Fish were collected using a two-person mini-Missouri trawl pulled through individual mesohabitats from upstream to downstream. Using identical sampling protocols in all mesohabitats reduced the bias that could occur from fish movement within and across mesohabitats. We chose to use the mini-Missouri trawl over other gears because the mini-Missouri trawl allowed us to sample in deeper habitats not accessible using backpack electrofishing or seining methods. Prior to the study, we conducted a gear experiment which determined the mini-Missouri trawl performed as well or better than other common gear types (backpack electrofishing, seine, hoop nets) for collecting fish in our study area [29]. Collected fish were placed in an aerated live well, identified to the species level, enumerated, and then released.
2.3. Fish Guild Classification
For our first objective, we used the following steps to identify empirical fish-habitat guilds. For step 1, bar plots of the mesohabitat-specific relative proportion and abundance (±1 SE) were constructed for the 11 most common fish species (captured at >85% of sampling sites; Table 1). For these bar plots, mesohabitat-specific relative proportion was calculated by dividing the number of individuals of a species collected within a particular mesohabitat type by all individuals collected for that species across all mesohabitats. Abundance was calculated as the total number of individuals sampled within a habitat patch. For step 2, differences in species abundance across mesohabitats were assessed using Kruskal–Wallis tests (α = 0.05) followed by post hoc multiple comparisons (kruskalmc function, pgirmess package [30]). As a third step, using the relative abundance patterns in each mesohabitat, the following four criteria (A–D) were used to assign individual fish taxa to functional habitat guilds. For criterion A, if the proportion of total abundance was >0.75 in a single mesohabitat, the species was classified as a single mesohabitat specialist (e.g., riffle specialist or pool specialist). For criterion B, if the proportion of total abundance of a species was 0.75 < x < 0.50 in one mesohabitat, but the proportion did not collectively exceed 0.90 with the addition of a second mesohabitat, the fish species was classified as a single mesohabitat generalist (e.g., riffle generalist or pool generalist). For criterion C, the proportion of the total abundance of a species was >0.33 in any two mesohabitats that together exceeded 0.90, the fish species was classified as a dual mesohabitat generalist (i.e., riffle–run generalist). For criterion D, if none of these conditions were met, the fish species was classified as a generalist.

Table 1.
Guilds of the 11 most commonly collected species within ~250 habitat units at 10 sample sites along the Neosho and Cottonwood Rivers, KS, based upon abundance for each species (N), the percentage of total abundance, and the occurrence (calculated as the percentage of habitat units for which the species was present). The proportion of abundance is reported for each mesohabitat type and used in the analysis to classify species into functional habitat guilds.
For our second objective, we compared the above-described univariate guild classifications across four multivariate analytical tools. First, to quantitatively test how well these criteria identified guild classifications, we used a hierarchical agglomerative cluster analysis (average linkage, Euclidean distance matrix, proportions of common species within mesohabitats; agnes function; cluster package [31]) and bootstrap distributions of Jaccard coefficients (values > 0.75 = valid, stable clusters; function = clusterboot; package = fpc [32]). Second, we conducted a one-way analysis of similarity (ANOSIM) to test for differences in fish assemblage structure among mesohabitats and non-metric multi-dimensional scaling (NMDS) to visualize patterns [33]. Ellipses representing 90% confidence intervals for each of the three mesohabitats (pool, riffle, and run) were calculated from environmental data for habitat width, stream depth, and flow velocity within each mesohabitat. Third, a similarity of percentages (SIMPER) analysis was used to determine the fish species driving differences in assemblage structure among mesohabitats [33,34]. The SIMPER analysis was conducted for both total abundance and presence/absence data due to high variability in species abundances (because of a highly abundant species, Red Shiner, Cyprinella lutrensis). We focused on species that contributed ≥5% of the cumulative sum of the variance (package = vegan [35]).
3. Results
A total of 7791 fish were collected representing 35 species among seven families along ten sampling sites in the Upper Neosho River watershed (Table 1; note that only the 11 most common species had enough collections to be able to run the analyses). Based on the four criteria outlined above (A–D), fish were grouped into seven functional habitat guilds: riffle specialist, pool specialist, riffle generalist, pool generalist, riffle–run generalist, pool–run generalist, and generalist (Table 1). One example of each is described below. The Suckermouth Minnow (Phenacobius mirabilis) was classified as a riffle specialist because its mean abundance was highest in the riffle habitat (χ2 = 20.06, p < 0.001; riffle > run = pool; p < 0.05; Figure 2A) and its proportion of abundance was much higher in the riffle habitat compared to the other mesohabitats (mean proportion in riffle = 0.85; Table 1, refer to criterion A in methods). The Orangespotted Sunfish (Lepomis humilis) was classified as a pool specialist because more individuals of this species occurred in the pool habitat (χ2 = 20.06, p < 0.001; pool > riffle = run, p < 0.05; Figure 2B) where its proportion of abundance was very high compared to other mesohabitats (mean proportion in pool = 0.79; Table 1; refer to criterion A in methods). The Bluntnose Minnow was classified as a riffle generalist because this species was found most often in the riffle habitat (χ2 = 9.74, p < 0.005; riffle > run > pool, p < 0.05) but their abundance in riffles was less than riffle specialists (mean proportion in riffle = 0.56; Table 1; Figure 2C; refer to criterion B in methods). Using the same criterion, the Longear Sunfish (Lepomis megalotis) was classified as a pool generalist (χ2 = 10.83, p < 0.005; pool > run > riffle, p < 0.05; Figure 2D). The Red Shiner (Cyprinella lutrensis) was classified as a riffle–run generalist because this taxon was more abundant in riffle and run habitats than pools (χ2 = 53.93, p < 0.001; riffle = run > pool, p < 0.05; Figure 2E), but was less abundant in these riffle run habitats than single mesohabitat specialists or generalists (proportion in riffle and run: 0.56, 0.34; Table 1; refer to classification criterion C in methods). Based on similar classification criteria, the Sand Shiner (Notropis stramineus) was classified as a pool–run generalist (χ2 = 9.52, p < 0.01; run = pool > riffle, p < 0.05; Figure 2F; proportion in pool and run: 0.32, 0.58; Table 1). The Bullhead Minnow (Pimephales vigilax) was classified as a true generalist because they were found in equal abundance and proportion across all three mesohabitats (χ2 = 3.38, p = 0.19; riffle = run = pool, p > 0.05; Figure 2G; Table 1; refer to criterion D in the methods). Other common fish were similarly classified (Table 1) based on our four quantitative criteria: the Central Stoneroller (Campostoma anomalum)—riffle specialist; the Bluntface Shiner (Cyprinella camura)—riffle generalist; the Mimic Shiner (Notropis volucellus)—pool–run generalist); and the Slenderhead Darter (Percina phoxocephala)—generalist.
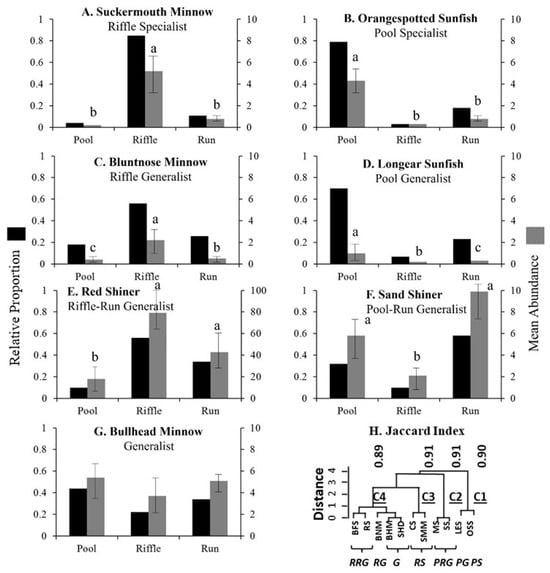
Figure 2.
Bar plots showing relative proportion (primary y-axis—black bar) and mean abundance (secondary y-axis—gray bar) within each mesohabitat (pool, riffle, and run). Functional habitat guilds are shown for each species. Data are mean ± SE. Fish examples include (A) Suckermouth Minnow (SMM), (B) Orangespotted Sunfish (OSS), (C) Bluntnose Minnow (BNM), (D) Longear Sunfish (LES), (E) Red Shiner (RS), (F) Sand Shiner (SS), and (G) Bullhead Minnow (BHM) [Note: plots for the Bluntface Shiner (BFS), Slenderhead Darter (SHD), Central Stoneroller (CS), and Mimic Shiner (MS) were not included in the figure). Additional details on the abundance, occurrence, and proportion of all species are provided in Table 1. Results from the cluster analysis (H) were used to validate the assignment of fish into functional habitat guilds [riffle–run generalist (RRG), riffle generalist (RG), generalist (G), riffle specialist (RS), pool–run generalist (PRG), pool generalist (PG), pool specialist (PS)].
Cluster analysis grouped common fish species into terminal clusters that corresponded to the seven functional guilds identified above (Figure 2H) based on both mesohabitat type and the strength of association. In addition, these seven terminal clusters formed four larger, stable clusters (Jaccard bootstrap mean value > 0.84; Figure 2H). Cluster one identified species and guilds that were more abundant in the slow, deep pool habitat [pool specialist functional guild (PS): Orangespotted Sunfish (OSS) and pool generalist functional guild (PG): Longear Sunfish (LES)]. Cluster two included species that favored slower, deeper mesohabitats but were not limited to pools [pool-run generalist functional guild (PRG): Mimic Shiner (MS) and Sand Shiner (SS)]. Cluster three included species found predominately in the shallow, fast, riffle habitat [riffle specialist functional guild (RS): Central Stoneroller (CS) and Suckermouth Minnow (SMM)]. Cluster four was the largest cluster and included guilds that had weak to moderate associations with the shallow, fast, riffle habitat [riffle–run generalist functional guild (RRG): Bluntface Shiner (BFS) and Red Shiner (RS); riffle generalist functional guild (RG): Bluntnose Minnow (BNM); and generalist functional guild (G): Bullhead Minnow (BHM)]. Although the cluster analysis took a different approach than the guild classification to grouping species, both approaches reached similar conclusions.
NMDS confirmed insights from the previous two analyses but emphasized differences in habitat type (Figure 3). The ANOSIM revealed a distinct separation (R = 0.224; p < 0.01) of pool-, riffle-, and run-related functional guilds. The riffle specialist (RS) and riffle generalist (RG) functional guilds were strongly associated with the riffle habitat (green ellipse; Figure 3). The pool specialist (PS) and pool generalist (PG) functional guilds were strongly associated with the pool habitat (blue ellipse; Figure 3). The riffle–run generalist (RRG) and pool–run generalist (PRG) functional guilds were found between riffle–run and pool–run habitats, respectively (red ellipse; Figure 3). The generalist functional guild was not strongly associated with any mesohabitat (Figure 3).
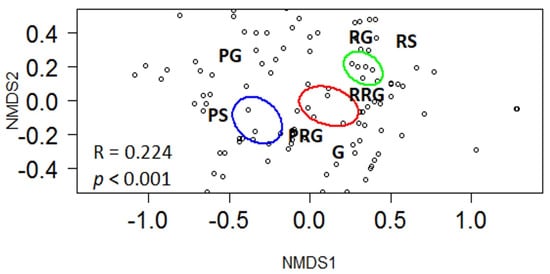
Figure 3.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling biplot for habitat guilds. Points indicate individual sample patches and ellipses indicate 95% confidence intervals. These data formed the basis of the ANOSIM and SIMPER analyses. Green ellipse is the riffle habitat. Pool habitat is the blue ellipse. Red ellipse is the run habitat. The guild acronyms are described in the text.
For abundance data, the SIMPER analysis showed that the Red Shiner (59.6% of total fish captured across 94% of all habitats sampled) contributed substantially to dissimilarities between pool–riffle, pool–run, and riffle–run habitats (0.55, 0.46, 0.54; Table 2A; Figure 4C). For presence/absence data, individual species did not affect groupings as dramatically. The Suckermouth Minnow and Central Stoneroller had the largest effect on dissimilarity across groups, but they still made only small contributions to the dissimilarities between the pool and riffle and riffle and run habitats, respectively (DC% = 0.10 for each fish for each comparison; Table 2B; Figure 4F). Likewise, Sand Shiner, a pool-run generalist, made the greatest contribution to differences between pool and run habitats of any species but their impact was relatively small (0.10; Table 2B; Figure 4I).

Table 2.
SIMPER analysis results for fish based on (A) abundance and (B) presence/absence data contributing the most to dissimilarities among habitats. DC% = percent contribution to dissimilarities.
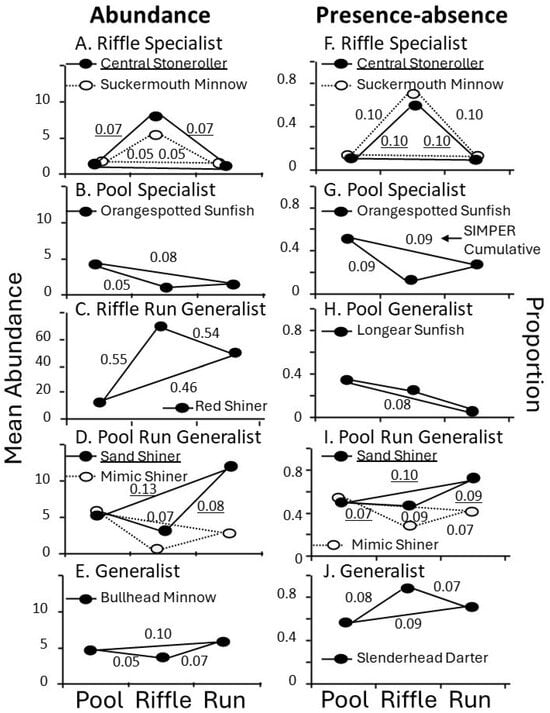
Figure 4.
Plot of SIMPER results for influential fish species from fish–mesohabitat guilds based on (A–E) mean abundance (y-axis) for the abundance dataset and (F–J) proportion (y-axis) for the presence/absence dataset. Data are means. Guilds include (A,F) riffle specialist, (B,G) pool specialist, (C) riffle–run generalist, (D,I) pool–run generalist, (E,J) generalist, and (H) pool generalist. Numbers indicate the cumulative sum explained by the SIMPER analysis per fish species between each set of habitats.
4. Discussion
Our functional habitat guild analysis for native prairie stream fish identified several take-home messages that can assist both researchers and conservation practitioners. First, we review how our seven empirically derived groups of stream fish species can improve ecological understanding and conservation effectiveness of native freshwater ecosystem biodiversity. Second, we illustrate why using both mesohabitat type and the strength of association adds understanding and utility. Third, we establish how using multiple statistical methods adds generality to our groupings. Fourth, we explain why and how insights from our species groupings are relevant and useful regardless of which conceptual framework and methodology is used. Finally, we emphasize the inescapable difficulty but unarguable importance of creating species groups that are ecologically meaningful, accurate, and practical for conservation.
We identified an approach for quantifying species–habitat relationships using functional habitat guilds that can improve ecological understanding, conservation, and management of native freshwater ecosystems’ biodiversity. We classified stream fish into seven functional habitat guilds (1. riffle specialist, 2. pool specialist, 3. riffle generalist, 4. pool generalist, 5. riffle–run generalist, 6. pool–run generalist, and 7. generalist). A clear advantage of our groupings is that they are empirically derived, based upon field sampling within the region, and do not rely on indirect information taken from keys or resources from other regions or states (e.g., [36]). The ‘habitat guild’ concept has been previously applied to stream fish community dynamics [37,38,39]. Our results have features that are both similar and different from other species groupings. Other investigators also concluded, as we did, that (1) the Orangespotted and Longear Sunfish are associated with pool habitats [40,41], (2) the Mimic Shiner is associated with pool and run habitats [42], and (3) the Central Stoneroller is a riffle specialist in the Great Plains and Midwest [40,43,44]. Although empirical species groupings have the advantage of scientific accuracy, individual, site-specific habitat groupings can differ across regions. Our result that the Bluntnose Minnow has a general affinity for riffle habitats is confirmed by other Midwest studies [40], but elsewhere others have associated this species with pools [42,45] or multiple habitats [46]. Our analyses classified the Red Shiner as a riffle–run generalist, but others have found that this common fish uses pools [42] or many different habitats [41]. Finally, we classified the Slenderhead Darter as a mesohabitat generalist species, whereas in other studies this taxon shows affinity for slow riffles [40] or riffle and run habitats [41]. In our study, the Slenderhead Darter showed a non-statistical affinity for the riffle habitat (barely missing the cut off to be classified as a riffle generalist), but in the Neosho watershed it can move into deeper water after spawning [44,47].
Understanding patterns and drivers of similar and different habitat associations across geographic locations and sources of variation are at the heart of science-based stream fish conservation. Identifying both areas of agreement and testable aspects of ambiguous patterns are important future directions for data-driven conservation. Some of the disparity among groupings, as described above, is due to addressable factors (e.g., the use of different gear types for fish collection [45] or how habitats were defined and delineated for a particular study). As such, there is a need to consider implementing ecoregion-wide standardization in definitions and methods. In the future, when empirical data on habitat associations are comparable, the ecological and conservation communities can start to tease apart the degree to which similarly constructed fish–habitat associations naturally differ among different geographical areas or disturbance regimes. Analyzing these broader trends can greatly advance the ecological understanding of natural systems and effective options for biodiversity monitoring.
Using the functional guild approach, we were able to examine mesohabitat specialization (generalists vs. specialists) among our fish–habitat associations. This is critically important as freshwater ecosystems and freshwater fish are facing unprecedented habitat loss, ecological degradation, and stream fragmentation [48,49]. The impacts of habitat changes on fish species distribution and overall diversity requires an understanding of the type and strength of fish–habitat associations. Nine of the eleven most common fish species and 60% of all individuals in our research showed strong affinity for a specific mesohabitat. For example, habitat specialists exhibited a strong, almost exclusive preference for a single habitat. Single-habitat generalists were distinctly associated with specific mesohabitats but spent more time in multiple mesohabitats than specialists. Dual-habitat generalists exhibited a weaker, but still distinct affinity for multiple mesohabitats here and elsewhere. Only two of our eleven common species (~10% of the total numbers) were true generalists with no specific mesohabitat associations [44,50]. The addition of the strength of association to habitat types in present and future species groupings has several advantages. First, as we seek to standardize and compare habitat associations across sites and studies, the addition of the strength of association to habitat type can reduce variation in site-specific fish–habitat associations. Second, identifying specialists has conservation applications. The coexistence of specialist species and generalist species showcases the intricate ecological responses to anthropogenic disturbances [51]. However, habitat specialists can be more susceptible to extinction [52] and more affected by habitat availability [53]. Because the amount of habitat differentially affects habitat specialists [54,55], increasing levels of habitat loss and fragmentation are an especial concern for scientists and managers [56]. Due to the dramatic declines in freshwater biodiversity, it is critical to protect systems, avoid further habitat destruction, and increase recovery efforts [57].
We advocate that environmental professionals define and test functional guilds using multiple statistical analyses. Here, we used univariate (proportion and Kruskal–Wallis) and multivariate (cluster analysis, NMDS, and SIMPER) analyses. Not only were we able to quantify single species–habitat relationships, but cluster analysis and NMDS allowed us to validate our functional habitat groupings from the univariate analyses. Furthermore, different analyses emphasize various aspects of community patterns. One insight was that the cluster analysis illustrated both strength and type of habitat use, whereas the NMDS highlighted habitat-type associations. In the presence/absence analysis, the dominance of a single species was small, but the SIMPER analysis identified that the Red Shiner contributed substantially to the variation seen between pool–riffle, pool–run, and riffle–run habitats. As a numerically dominant species in Midwestern streams [58] that can be found in a variety of habitats [44], the influence of the Red Shiner (and other dominant and abundant species) on species groupings is vital information.
Insights from our groupings apply regardless of the conceptual framework, criteria, or methodology used to group organisms. Researchers and managers use different criteria to group species, which can affect outcomes and the ability to compare trends across sites. In a community ecology approach to grouping organisms, interactions between topically determined species (e.g., predator–prey, competitors, facilitators, keystone species) are priorities [59,60,61]. However, selecting which species to include or exclude can differ with the question and system, and no subgroup of species addresses all issues of interest. Community metrics (e.g., species richness and diversity) and statistical approaches to grouping species (e.g., NMDS and PCA) are useful ways to reduce multi-species complexity and measure biodiversity [62,63]. However, these simplified metrics alone also miss valuable information. Taxonomic groupings can be a useful way of grouping species to simplify communities (e.g., [64,65,66]), but taxonomic groupings alone can have limited relevance to ecological roles. Guilds (defined as a group of species that exploit the same class of environmental resources in a similar way [8] (p. 335) have been widely used in fish research for diet [67,68,69], ecosystem function [4], reproductive strategies [9,10,11], or multiple functions [4]. A developing interest in functional diversity [70] has stimulated much research on functional traits, functional groups, and functional guilds in a variety of taxa including fish [71,72,73,74]. Functional traits are characteristics (morphological, biochemical, physiological, structural, phenological, or behavioral) that are “relevant to the response of such organisms to the environment and/or their effects on ecosystem properties” [75] (p. 2959). We used functional habitat guilds to define our groupings for consistency and to align with others who have combined the subtle differences of guilds and functional ecology (e.g., [11]). However, we do not focus on resolving differences in definitions or expressing a preference for one or another of these approaches. Our functional groupings are useful because they allow for generalizations of species–habitat relationships that can be compared across studies and regions regardless of the grouping definition used.
Our results suggest several future directions that can advance ecology and help conservation. First, quantifying fish community structure and understanding ecological function are both important priorities that can be addressed together. Developing a structure of fish groupings that can be applied immediately by managers across a broad scale is practical, but without evidence of demonstrated function these groupings will not be scientifically robust or generalizable. Considering function (e.g., [76]) through trait-based analyses [36,77] can provide mechanistic understanding of ecosystems [78,79]. However, at present, as a profession, we do not fully understand how natural systems function or the role of most species within those systems. Thus, research on function must be incorporated into analyses of the structure of species groups, and the need to understand function is valuable to both researchers and managers. Second, professionals need to thread the needle between scientific accuracy and simplicity. Effective species groups need to be accurate, but also practical enough to be applied in surveys. The only way to make sure that species groupings match reality is to collect empirical data, create groupings, then assess the generality of those groupings. If guilds or functional groups do not reflect natural patterns, a problem exists for research and conservation. If the groupings require too much data or are too complicated to apply, they will not be used in on-the-ground management surveys. No quick and easy answer exists to this important but complex challenge. Nevertheless, devising creative ways to bridge accuracy and practicality is also a priority for researcher–manager teams. Third, quantifying variation in species groupings across locations is an ever-present challenge. This complication requires teasing apart controllable sources of variation (methods) and true differences in the way that the same species behaves across sites. Further, conservation professionals need to be able to distinguish when taxa trends are generalizable versus when site-specific anomalies exist.
All three of the above-described directions will require a coordinated team effort across researchers and practitioners to work in a specific system (here, Great Plains stream fish). Developing species groupings is a very difficult challenge for which no single approach is adequate alone. As a profession, we need to work together to develop, analyze, and integrate an accurate and practical framework for a coalition-driven and conservation-related master plan. Scientists and managers can benefit from recognizing the power that exists in linking results and approaches together to build an inclusive and coordinated network and strategic plan.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.H., M.E.M. and J.M.S.; data curation, S.M.H. and J.M.S.; formal analysis, S.M.H., M.E.M. and J.M.S.; funding acquisition, M.E.M.; investigation, S.M.H., M.E.M. and J.M.S.; methodology, S.M.H., M.E.M. and J.M.S.; project administration, M.E.M.; resources, M.E.M.; software, S.M.H.; supervision, M.E.M.; validation, S.M.H., M.E.M. and J.M.S.; visualization, S.M.H., M.E.M. and J.M.S.; writing—original draft, S.M.H., M.E.M. and J.M.S.; and writing—review and editing, S.M.H., M.E.M. and J.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The project was funded by a State Wildlife Grant from the United States Fish and Wildlife Service and the Kansas Department of Wildlife, and Parks.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was conducted under the auspices of Kansas State University IACUC Protocol #3170.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset is available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
This project was coordinated through the Kansas Cooperative Fish and Wildlife Research Unit, which is a cooperation among Kansas State University, the United States Geological Survey, the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, the Kansas Department of Wildlife and Parks, and the Wildlife Management Institute. The project was funded by a State Wildlife Grant from the United States Fish and Wildlife Service and the Kansas Department of Wildlife and Parks Ecological Services Section. We are grateful to numerous private landowners for granting access to the Neosho and Cottonwood Rivers. Colleagues including Eric Johnson, Jason Luginbill, Melinda Daniels, and Walter Dodds provided helpful feedback throughout the conceptualization and implementation of this project. Bob Hrabik’s help with fish classification and sampling was invaluable. Sarmistha Chatterjee, Casey Pennock, Jake Danner, Kelsey McCullough, and Casie Lee provided field assistance. Jon Spurgeon and three anonymous reviewers provided thoughtful feedback. Any use of trade, product, or firm names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. government. This research was conducted under the auspices of Kansas State University IACUC Protocol #3170. Scientific and common names of the fish taxa and collection locations were taken from a recent peer-reviewed key and as such have been vetted by experts on this topic [Kansas Fishes Committee. (2014). Kansas Fishes. University Press of Kansas.] No Federally recognized Tribes or geologic names are referenced.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Malaterre, C.; Dussault, A.C.; Mermans, E.; Barker, G.; Beisner, B.E.; Bouchard, F.; Desjardins, E.; Handa, I.T.; Kembel, S.W.; Lajoie, G.; et al. Functional Diversity: An Epistemic Roadmap. BioScience 2019, 69, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeinghaus, D.J.; Winemiller, K.O.; Birnbaum, J.S. Local and Regional Determinants of Stream Fish Assemblage Structure: Inferences Based on Taxonomic vs. Functional Groups. J. Biogeogr. 2007, 34, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, M.; Dias, A.T.C.; De Bello, F.; Altermatt, F.; Chown, S.L.; Azcárate, F.M.; Bell, J.R.; Fournier, B.; Hedde, M.; Hortal, J.; et al. Handbook of Protocols for Standardized Measurement of Terrestrial Invertebrate Functional Traits. Funct. Ecol. 2017, 31, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villéger, S.; Brosse, S.; Mouchet, M.; Mouillot, D.; Vanni, M.J. Functional Ecology of Fish: Current Approaches and Future Challenges. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcclure, M.M.; Alexander, M.; Borggaard, D.; Boughton, D.; Crozier, L.; Griffis, R.; Jorgensen, J.C.; Lindley, S.T.; Nye, J.; Rowland, M.J.; et al. Incorporating Climate Science in Applications of the US Endangered Species Act for Aquatic Species. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarucci, A.; Bacaro, G.; Scheiner, S.M. Old and New Challenges in Using Species Diversity for Assessing Biodiversity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 2426–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, D.M.; Jackson, D.A.; Chu, C. Partitioning Fish Communities into guilds for Ecological Analyses: An Overview of Current Approaches and Future Directions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 78, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, R.B. The Niche Exploitation Pattern of the Blue-Gray Gnatcatcher. Ecol. Monogr. 1967, 37, 317–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balon, E.K. Ecological guilds of Fishes: A Short Summary of the Concept and Its Application: With 2 Tables in the Text and 2 Figures in the Discussion. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. Verh. 1975, 19, 2430–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winemiller, K.O.; Rose, K.A. Patterns of Life-History Diversification in North American Fishes: Implications for Population Regulation. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 2196–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.A.A.; Cowx, I.G.; Goffaux, D.; Kestemont, P. Assessing the Health of European Rivers Using Functional Ecological guilds of Fish Communities: Standardising Species Classification and Approaches to Metric Selection. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2007, 14, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, K.W. Structure and Function of Stream Ecosystems. BioScience 1974, 24, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, J. Guilds or Functional Groups: Does It Matter? Oikos 2003, 100, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frissell, C.A.; Liss, W.J.; Warren, C.E.; Hurley, M.D. A Hierarchical Framework for Stream Habitat Classification: Viewing Streams in a Watershed Context. Environ. Manag. 1986, 10, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, J.A. Riverine Landscapes: Taking Landscape Ecology into the Water. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisson, P.A.; Montgomery, D.R.; Buffington, J.M. Valley Segments, Stream Reaches, and Channel Units. In Methods in Stream Ecology; Hauer, F.R., Lamberti, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 21–47. [Google Scholar]
- Angermeier, P.L.; Schlosser, I.J. Species-Area Relationship for Stream Fishes. Ecology 1989, 70, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchman, S.M.; Mather, M.E.; Smith, J.M. Does Type, Quantity, and Location of Habitat Matter for Fish Diversity in a Great Plains Riverscape? Fisheries 2021, 46, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C. Abundance and Distribution Within a Guild of Benthic Stream Fishes: Local Processes and Regional Patterns. Freshw. Biol. 1996, 36, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, M.-P.; Petts, G.E.; Maddock, I.P. Mesohabitat Use by Bullhead (Cottus gobio). Hydrobiologia 2010, 652, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorney, R.M.; Williams, M.G.; Ferris, D.R.; Williams, L.R. The Influence of Channelization on Fish Communities in an Agricultural Coldwater Stream System. Am. Midl. Nat. 2012, 168, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juracek, K.E.; Perry, C.A. Gravel Sources in the Neosho River in Kansas, 2004; No. 2005–5282; U.S. Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tiemann, J.S.; Gillette, D.P.; Wildhaber, M.L.; Edds, D.R. Correlations Among Densities of Stream Fishes in the Upper Neosho River, with Focus on the Federally Threatened Neosho Madtom Noturus placidus. Trans. Kans. Acad. Sci. 2004, 107, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, F.B. Handbook of Fishes of Kansas; University Kansas. Nat. Hist. Misc. Publ.: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1967; Volume 45, pp. 1–357. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.K.; Gido, K.; Whiles, M.R.; Fritz, K.M.; Matthews, W.J. Life on the Edge: The Ecology of Great Plains Prairie Streams. BioScience 2004, 54, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCain, M.E. Stream Habitat Classification and Inventory Procedures for Northern California; FHR Currents, no. 1; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Region: Vallejo, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, G.L.; Clifford, N.J. Microscale Hydrodynamics and Coherent Flow Structures in Rivers: Implications for the Characterization of Physical Habitat. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchman, S.M.; Mather, M.E.; Smith, J.M.; Fencl, J.S. Identifying Keystone Habitats with a Mosaic Approach Can Improve Biodiversity Conservation in Disturbed Ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fencl, J.S. How Big of an Effect Do Small Dams Have?: Using Ecology and Geomorphology to Quantify Impacts of Low-Head Dams on Fish Biodiversity. Doctoral Dissertation, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Giraudoux, P. pgirmess: Data Analysis in Ecology. R Package Version 1.6.8. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pgirmess/pgirmess.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Maechler, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Struyf, A.; Hubert, M.; Hornik, K.; cluster: Cluster Analysis Basics and Extensions. R Package Version 2.1.6. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=cluster (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Hennig, C. fpc: Flexible Procedures for Clustering; R Package Version 2.2-13. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=fpc (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Science BV.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; 853p. [Google Scholar]
- Bonato, K.O.; Delariva, R.L.; Silva, J.C.D. Diet and Trophic guilds of Fish Assemblages in Two Streams with Different Anthropic Impacts in the Northwest of Paraná, Brazil. Zoologica (Curitiba) 2012, 29, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5-2. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Frimpong, E.A.; Angermeier, P.L. Comparative Utility of Selected Frameworks for Regionalizing Fish-Based Bioassessments Across the United States. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2010, 139, 1872–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, I.J. Fish Community Structure and Function Along Two Habitat Gradients in a Headwater Stream. Ecol. Monogr. 1982, 52, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, H.L. Fish Habitat Association in an Ozark Stream. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1989, 24, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelwick, F.P.; Matthews, W.J. Temporal and Spatial Patterns in Littoral-Zone Fish Assemblages of a Reservoir (Lake Texoma, Oklahoma-Texas, USA). Environ. Biol. Fishes 1990, 27, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadland, L.P. Stream Habitat Types: Their Fish Assemblages and Relationship to Flow. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1993, 13, 790–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, L.M.; Burr, B.M. A Field Guide to Freshwater Fishes: North America North of Mexico; Houghton Mifflin Harcourt: Boston, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, L.; Phelan, J.; Goudreau, C.; Dykes, R. Flow-Biology Relationships Based on Fish Habitat guilds in North Carolina. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, F.B.; Collins, J.T. Fishes in Kansas; Natural History Museum, University of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kansas Fishes Committee. Kansas Fishes; University Press of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vadas, R.L.; Vadas, R.L.; Orth, D.J. Habitat Use of Fish Communities in a Virginia Stream System. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2000, 59, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etnier, D.A.; Starnes, W.C. The Fishes of Tennessee; University of Tennessee Press: Knoxville, TN, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gillette, D.P.; Tiemann, J.S.; Edds, D.R.; Wildhaber, M.L. Habitat Use by a Midwestern USA Riverine Fish Assemblage: Effects of Season, Water Temperature and River Discharge. J. Fish Biol. 2006, 68, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L.; Dudgeon, D. Freshwater Biodiversity Conservation: Recent Progress and Future Challenges. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging Threats and Persistent Conservation Challenges for Freshwater Biodiversity. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, M.E.; Gelwick, F.P. Spatial Variation of Headwater Fish Assemblages Explained by Hydrologic Variability and Upstream Effects of Impoundment. Copeia 2003, 2003, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wang, L.; Heino, J.; Qin, B. Unveiling the Influence of Specialists and Generalists on Macroinvertebrate Assemblage Heterogeneity in Lake Taihu. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, M.L. Extinction Vulnerability and Selectivity: Combining Ecological and Paleontological Views. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1997, 28, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.S. Habitat Selection as an Evolutionary Game. Evolution 1990, 44, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, D.P.; Simberloff, D. Ecological Specialization and Susceptibility to Disturbance: Conjectures and Refutations. Am. Nat. 2002, 159, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L. Habitat Loss, Resource Specialization, and Extinction on Coral Reefs. Glob. Change Biol. 2004, 10, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. Competition and Biodiversity in Spatially Structured Habitats. Ecology 1994, 75, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tickner, D.; Opperman, J.J.; Abell, R.; Acreman, M.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Cooke, S.J.; Dalton, J.; Darwall, W.; Edwards, G.; et al. Bending the Curve of Global Freshwater Biodiversity Loss: An Emergency Recovery Plan. Bioscience 2020, 70, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh-Matthews, E.; Matthews, W.J. Spatial Variation in Relative Abundance of a Widespread, Numerically Dominant Fish Species and Its Effect on Fish Assemblage Structure. Oecologia 2000, 125, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestre, L.; Narimanov, N.; Menzel, F.; Entling, M.H. Non-consumptive Effects Between Predators Depend on the Foraging Mode of Intraguild Prey. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monterroso, P.; Díaz-Ruiz, F.; Lukacs, P.M.; Alves, P.C.; Ferreras, P. Ecological Traits and the Spatial Structure of Competitive Coexistence Among Carnivores. Ecology 2020, 101, e03059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergholz, K.; Sittel, L.-P.; Ristow, M.; Jeltsch, F.; Weiss, L. Pollinator guilds Respond Contrastingly at Different Scales to Landscape Parameters of Land-Use Intensity. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M.; Mather, M.E. Using Assemblage Data in Ecological Indicators: A Comparison and Evaluation of Commonly Available Statistical Tools. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 13, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, C.; De Marco, G.; Labar, S.; Hasnaoui, M.; Grieco, G.; Caserta, L.; Inglese, S.; Vangone, R.; Madonna, A.; Alwany, M.; et al. Biodiversity Studies for Sustainable Lagoon: Thermophilic and Tropical Fish Species vs. Endemic Commercial Species at Mellah Lagoon (Mediterranean, Algeria). Water 2022, 14, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonn, W.M.; Magnuson, J.J. Patterns in the Species Composition and Richness of Fish Assemblages in Northern Wisconsin Lakes. Ecology 1982, 63, 1149–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.; Philipp, D.P. (Eds.) Centrarchid Fishes: Diversity, Biology and Conservation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 264–292. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin, S.J.; Pyron, M. A Century of Morphological Variation in Cyprinidae Fishes. BMC Ecol. 2016, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, L.; Perrow, M.R.; Sayer, C.D.; Tomlinson, M.L.; Davidson, T.A. Relationships Between Fish Feeding guild and Trophic Structure in English Lowland Shallow Lakes Subject to Anthropogenic Influence: Implications for Lake Restoration. Aquat. Ecol. 2006, 40, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, G.A.; Buckley, T.W.; Danielson, S.L. Diet Compositions and Trophic guild Structure of the Eastern Chukchi Sea Demersal Fish Community. Deep Sea Res. II 2017, 135, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tang, J.P.; Su, L.H.; Fan, J.J.; Chang, H.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, L.; Lin, H.J.; Yang, Y. Fish Feeding Groups, Food Selectivity, and Diet Shifts Associated with Environmental Factors and Prey Availability Along a Large Subtropical River, China. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Mukherjee, I.; Tribedi, P. Functional Diversity: An Important Measure of Ecosystem Functioning. Adv. Microbiol. 2017, 07, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.C.; Dias, R.M.; Ruaro, R.; Benedito, E. Functional Diversity: A Review on Freshwater Fish Research. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2023, 21, e230022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milardi, M.; Green, A.J.; Mancini, M.; Trotti, P.; Kiljunen, M.; Torniainen, J.; Castaldelli, G. Invasive Catfish in Northern Italy and Their Impacts on Waterbirds. NeoBiota 2022, 72, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglieri, G.; Baillie, C.; Mariani, S.; Cattano, C.; Calò, A.; Turco, G.; Spatafora, D.; Di Franco, A.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Guidetti, P.; et al. Environmental DNA Effectively Captures Functional Diversity of Coastal Fish Communities. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, S.J.; Saunders, B.J.; Rastoin-Laplane, E.; Salinas-de-León, P.; Harvey, E.S. Functional Diversity of Reef Fish Assemblages in the Galapagos Archipelago. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2022, 549, 151695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Purvis, A.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Mace, G.M.; Donoghue, M.J.; Ewers, R.M.; Jordano, P.; Pearse, W.D. Functional Traits, the Phylogeny of Function, and Ecosystem Service Vulnerability. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 2958–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamothe, K.A.; Alofs, K.M.; Jackson, D.A.; Somers, K.M. Functional Diversity and Redundancy of Freshwater Fish Communities Across Biogeographic and Environmental Gradients. Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 1612–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, B.J.; Enquist, B.J.; Weiher, E.; Westoby, M. Rebuilding Community Ecology from Functional Traits. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violle, C.; Navas, M.-L.; Vile, D.; Kazakou, E.; Fortunel, C.; Hummel, I.; Garnier, E. Let the Concept of Trait Be Functional! Oikos 2007, 116, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, C.T.; Williams, A.K.; Finiguerra, M.; Fong, A.A.; Kellerman, A.; Paver, S.F.; Tolar, B.B.; Toscano, B.J. Realizing the Potential of Trait-Based Aquatic Ecology: New Tools and Collaborative Approaches. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).