Abstract
Marchica Lagoon, a Ramsar site on the Mediterranean coast of Morocco, is experiencing the impacts of watershed pollution, which includes pollutants from the domestic, agricultural, industrial, and mining sectors. Restoration actions were undertaken around this lagoon during the last decade in order to protect its ecological value and to develop tourist activity. To conserve the biodiversity in the lagoon, it is important to assess the environmental state of this ecosystem. This study aims to evaluate the ecotoxicological state of sediments through the post restoration characterization of the trace elements Pb, Cu, Zn, Cr, Co, and Ba, as well as their correlation to the major elements, grain size, and total organic carbon, sampled during two campaigns (the wet and dry seasons of 2018) across a sampling network of thirteen stations. Multivariate analysis and ecotoxicological risk assessment of the trace elements using the sediment quality guidelines and five pollution indices (geoaccumulation index (Igeo), enrichment factor (EF), contamination factor (CF), pollution-load index (PLI), and mean effect range median quotient (m-ERM-Q)) revealed contamination of the lagoon by Pb, Zn, and Cu, and minimal pollution by Cr, Co, and Ba. The distribution of the biological-risk index reveals that four zones of the lagoon may present a high probability of toxicity, thus constituting potential risk areas for aquatic organisms: during the wet season, the area in the northwestern sandbar border, the southwest eutrophication zone, and the mouth of the stream valley conveying industrial discharges; and during dry season, the northwestern eutrophication zone. Despite the restoration actions achieved around the lagoon, the lead, zinc, and copper concentrations increased, and their variation was significant between group stations. The biodiversity conservation of Marchica Lagoon requires continuous monitoring and assessment, as well as the implementation of an integrated management plan with restoration actions, not only around the lagoon, but also at its watershed level.
1. Introduction
Coastal lagoons are very important ecosystems, characterized as the most valuable global coastal habitats, providing valuable ecosystem goods and services to humans [1,2,3]. These semi enclosed ecosystems have not only economic value, but also heritage, societal, aesthetic, and scientific importance [4,5,6]. Nevertheless, these vulnerable areas are among the world’s most altered and threatened natural systems [2,7]. Coastal lagoons face significant issues, including pollution, overexploitation, biological invasions, habitat destruction, and biodiversity changes [8,9,10]. They are sensitive to land–sea interactions and can be severely affected by anthropogenic pollutants [11,12,13,14,15].
Trace elements are among the many anthropogenic contaminants reaching coastal lagoons, particularly those located in watersheds containing mines and mining industries. Their cumulative impact on biota can have a harmful effect on the health of marine ecosystems and humans [16,17]. The distribution of trace elements in coastal marine areas is affected by hydrodynamic and biogeochemical processes, thereby modifying trace element bioavailability and associated environmental risks [18,19]. Sediment provides a compartment that records the temporal variation of anthropogenic inputs into the environment since the Industrial Revolution [20], and allows for an ecotoxicological evaluation of trace elements.
The Marchica Lagoon, a unique coastal lagoon on the Mediterranean coast of Morocco, and the second largest in North Africa, is an example of these vulnerable ecosystems. Besides its ecological value as a Ramsar site and socioeconomic services [21,22,23,24], the lagoon and its immediate surroundings have been undergoing major socioeconomic changes (tourism projects, construction of marinas, etc.). The strong urbanization of its shoreline has caused disturbances of various kinds, such as pollution and loss of habitat, which have had repercussions on the ecological values of the ecosystem. The current challenge is to reach a consensus between the conservation issues of its heritage values and the increasing development and amenities that the region is experiencing. The lagoon has qualified as an environmental hotspot on the Mediterranean coast, as it presents a eutrophication problem [25,26]. Restoration actions were undertaken during the last decade by Moroccan authorities to protect the valuable qualities of the Marchica Lagoon, with the main actions related to the construction of a channel between the lagoon and sea, the installation of two wastewater treatment plants around the lagoon, and an operation to remediate lagoon water quality, which includes the collection of solid waste and dredging where wadis (intermittent stream valleys) enter the lagoon [27].
The objectives of this study were to:
- characterize the variation in trace element concentrations of Pb, Cr, Zn, Cu, Co, and Ba and their correlation to major elements Si, Al, Fe, Mn, Ca, Ti, K, and P, grain size, and total organic carbon (TOC) in the surface sediments of the Marchica Lagoon following restoration actions during the wet and dry seasons, in order to establish the main factors controlling the distribution of some toxic metals;
- assess the ecotoxicological risk by comparing the concentration of trace elements with sediment-quality guidelines (SQGs) and assessment indices as good indicators: contamination factor (CF), pollution-load index (PLI), enrichment factor (EF), geoaccumulation index (Igeo), and the mean sediment-quality-guidelines quotient (m-ERM-Q) to examine the potential biological effects of the toxicity of trace elements in surface sediment [28,29,30,31,32,33,34];
- determine the potential sources of trace elements in the sediment;
- identify highly polluted areas by clustering the stations with pollution similarity and comparing the distribution with previous studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
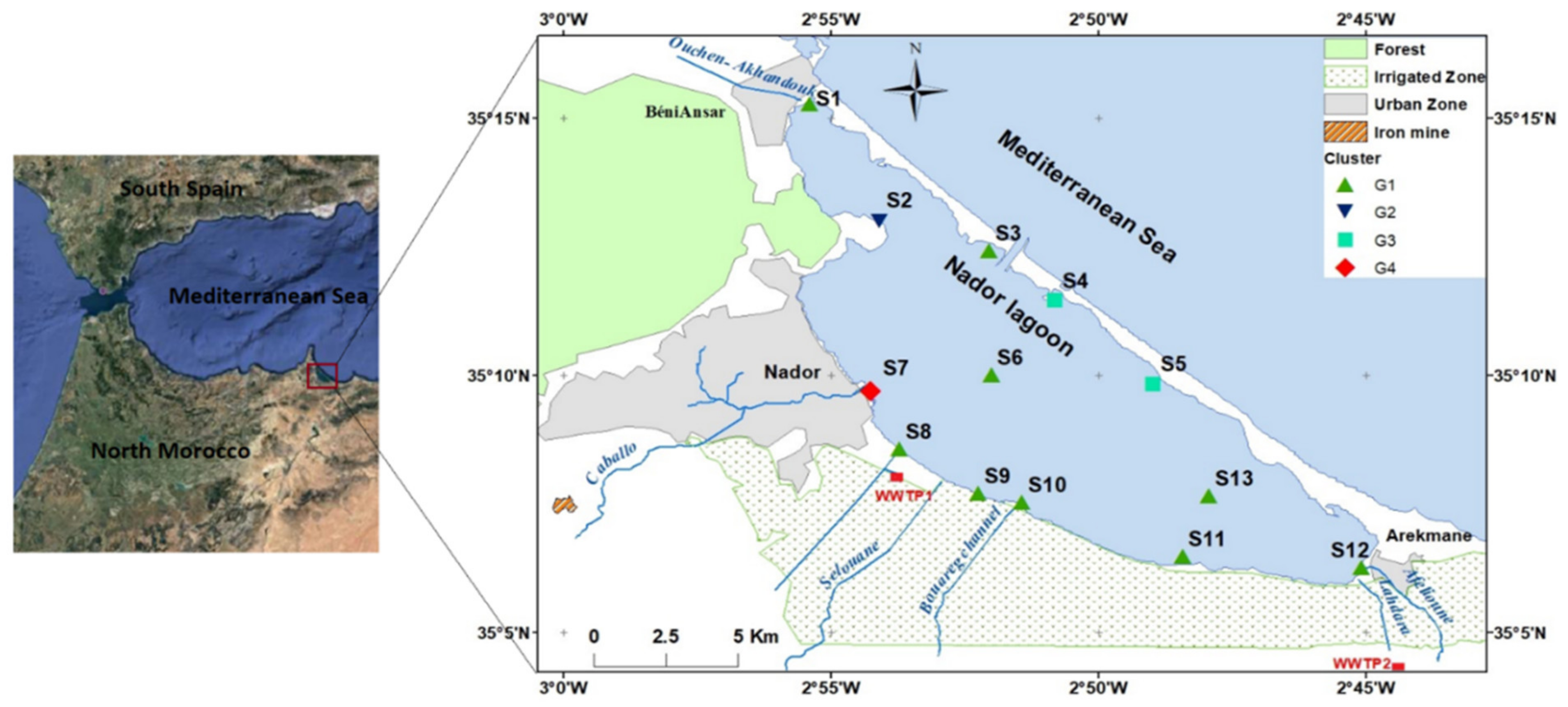
The Marchica Lagoon (02°45′–02°55′ and 35°16′–35°06′), also called Sabkha Bou-Areg or Nador, is the largest lagoon in Morocco, with a surface area of 115 km2 and maximal depth of 8 m. The lagoon and the Mediterranean Sea are separated by a 25 km-long sandbar crossed by an artificial inlet 300 m wide and 6 m deep, which allows for water exchanges between these two ecosystems. The sedimentological study of the deposits of the lagoon permitted identification of five sedimentation media, namely, the internal border of the sandbar under marine influence; the central part of the lagoon, also under marine influence; the continental border under continental influence in the lagoon; two confined zones northwest and southeast of the lagoon; and the mouths of the wadis in the continental environment [35]. The lagoon is limited on its northwestern side by the volcanic Gourougou massif, on its southeast by the Kebdana massif, on its southwest side by the Beni Bou Ifrour massif and the Bouarg plain, and on the northern coastal zone by marine inputs [36]. The main wadis that drain into the lagoon are Akhandouk and Ouchen, crossing the city of Beni Ensar; Selouane, crossing the cities of Al Arouit, Selouane, and Bouarg; Cabaillo, crossing the cities of Iksane, Zeghanghan, Beni Bou Ifrour, Ihaddaden, and Nador; and Afelioun and Lhdara, crossing the city of Arekmane (Figure 1).
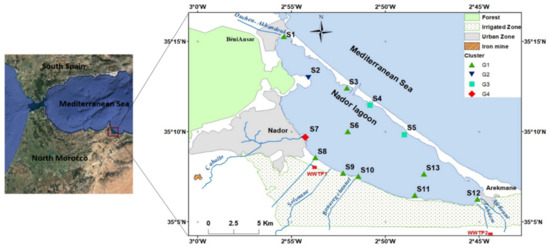
Figure 1.
Map of Marchica Lagoon (S, sample station; G, group station).
The dominant climate around the lagoon is Mediterranean, with hot and dry summers and mild and rainy winters [37]. The wind is the main driver of marine circulation of the waters of the Marchica Lagoon [38,39], which has two dominant directions, east–northeast to east from May to October, and west–southwest to west between November and May. The watershed of the lagoon is characterized by the abandoned iron-mining site at Iksane, the iron and steel industries at Selouane and Al Arouit, irrigated agriculture (including fertilizer and pesticide use) on the Bouarg plain, and fishing industries in Beni Ensar [40].
2.2. Environmental Sampling
The samples were collected during the wet (March) and dry (July) seasons in 2018. Sampling stations were established by considering the sedimentological characteristics, bathymetry, and currentology of the lagoon, ensuring the coverage of all areas and accounting for all potential sources of pollution: 3 stations in the internal border of the sandbar under marine influence; 2 stations in the center of the lagoon, also under marine influence; 2 stations at the confined zones northwest and southeast of the lagoon; 3 stations under continental influence, including the mouths of the wadis (Cabaillo wadi, Selouane wadi, and Bouarg channel); 1 station at the outfall of the great Nador wastewater treatment plant; one marina station; and another between Bouarg and Arekmane. There were 13 sampling stations inside the lagoon for each campaign (Figure 1).
2.3. Analysis Methods
Superficial sediment cores (5 cm) were sampled and conserved at a temperature of about −4 °C in an airtight transparent plastic container. The position and depth of the samples collected were determined using an equipment board of the National Institute of Fisheries Research (INRH) Zodiac with reference FURUNO FCV-627/587 Fish Finder, including a global positioning system (GPS) receiver and depth-probe GPS [41]. For each station, the surface sediment samples were separated into four subsamples, one for particle size analysis, one for the total organic carbon (TOC) analysis, and two others for chemical analysis of the major and trace elements. A WTW Multi-parameter Meter, model 3430, was used in situ to measure the physicochemical parameters (temperature, salinity, pH, and dissolved oxygen) of the water (0.5 m under the surface water of the lagoon for each station).
Sediment granulometry was measured with a laser particle size analyzer (Malvern Mastersizer 2000 ©) after preparing the sediments in a sodium hexametaphosphate solution [42]. The particle-size distribution was calculated using Gradistat © Excel software [43] after each measurement and expressed as relative proportions (%) of sand (2 mm–63 μm), silt (63–2 μm), and clay (< 2 μm). TOC was measured with a LECO © carbon analyzer that estimates the percentages of CO2 after a combustion of oxygen at 1400 °C and a mineral decarbonization with a sulfuric acid solution [44]. Two analyses were used and the precision of the total carbon data is expressed by the range of standard deviations and estimated to 0.001–0.042. Granulometry and TOC were analyzed at LETG-Nantes, France [45].
The major elements were analyzed using a Bruker S1 Turbo SD hand-held X-ray fluorescence (HHXRF) spectrometer (Bruker AXS GmbH) using the certified standard reference material NIST 2702 at the National Center for Energy, Sciences and Nuclear Techniques [46]. The principle of the HHXRF technology is based on the fact that the incident rays eject electrons from the atoms of the elements in the sample, resulting in the emission of X-rays with energies that are characteristic of the elements present in the sample. The emitted X-rays are analyzed using a silicon drift detector. The results are immediately displayed and stored. All the sediment samples were analysed in two replicates. The recovery (%) and the relative standard deviation (RSD%) of the major elements from the Certified Reference Material (CRM) were 100.4–7.77 for Al, 83.8–2.72 for P, 108.2–2.85 for K, 112.5–9.33 for Ca, 99.9–5.61 for Ti, 99.6–3.13 for Mn, and 96.7–3.85 for Fe. Detection limits (ppm) of the analyzed elements were 1058 for Al, 16 for Fe, 10 for Mn, 795 for Si, 87 for P, 51 for K, 50 for Ca, and 23 for Ti.
Trace elements were analyzed using an Agilent 4200 microwave plasma atomic emission spectrometer (MP-AES) according to the NFX 31-147 standard analysis methods at the National Laboratory of Studies and Monitoring of Pollution [47]. Sediments and Certified Reference Material (CRM) were digested in a microwave digestion system with mineralization by attack of 65% nitric acid HN03 (9 mL) and with hydrochloric acid HCL at 37% (2 mL) in a microwave oven of the “ETHOS One” type for digestion of the samples at a temperature of 180 °C for 40 min. A blank was included in each digestion. The CRMs were analyzed every 10 samples. The recovery (%) and RSD (%) of the trace elements from CRM were 110–1.25 for Cu, 100–0.53 for Pb, 105–1.24 for Zn, 95–0.54 for Cr, 105–0.63 for Co, and 110–0.26 for Ba. Detection limits (mg/kg) of the analyzed elements were 0.0003 for Cr, 0.0003 for Cu, 0.0044 for Pb, 0.0028 for Zn, 0.0031 for Co, and 0.0002 for Ba.
2.4. Statistical Methods
To test the season’s effect, significant differences between the mean values of each parameter (major and trace elements, grain size, TOC, and physico-chemical parameters) between the wet and dry seasons were tested using the Kruskal–Wallis test; the normality being not verified overall (Shapiro–Wilk test, p > 0.5). Spearman’s rank coefficient was calculated to test the relationship between the above parameters.
The data matrix by season (parameters values x sampling stations) was fourth-root transformed and the Pearson similarity calculated between the stations. Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted on the environmental variables to explore the main gradients in the study area [48]. To identify the affinity groups of the stations, cluster analysis (CA) based on squared Euclidean distance and Ward’s method as well as the SIMPROF test of similarity profile were used. The significance of the differences between the group stations and between seasons for all the parameters was investigated with permutational multivariate ANOVA (PERMANOVA).
The Shapiro–Wilk and Kruskal–Wallis tests were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics software version 20 while the Spearman test was performed using the R program. PCA and CA were performed with PRIMER v.6 software [49]. All statistical methods were applied with a confidence level of 95% (p < 0.05).
The maps of the lagoon were produced with ESRI software ArcGIS Desktop 10.
2.5. Sediment Contamination and Risk Assessment Indices
Ecological risk was assessed using various indices (Table 1): enrichment factor (EF) [29], contamination factor (CF) [32], pollution-load index (PLI) [33], and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) [34]. For the EF calculation, normalization was used to quantify the anthropogenic metal pollution from the natural variability of trace elements. The major conservative elements commonly used for geochemical normalization are Al [50,51,52] and Fe [53,54,55,56], two of the most abundant elements on earth. In this study, Fe was selected as the reference element for calculation. Local background values (LBV) were elaborated from a previous study for some trace elements [57]. In order to study the ecological risk for the trace elements Pb, Cr, Zn, Cu, Co, and Ba, reference values were taken from Rudnick and Gao (2003) [58]. Sediment concentrations were compared with sediment-quality guidelines (SQGs) for marine ecosystems to evaluate the ecotoxicological risk [28,30,31,59,60]: values below the effect range low (ERL) and threshold effect level (TEL) refer to essentially uncontaminated samples presenting a limited risk of toxicity. Mean sediment-quality guideline quotients (m-ERM-Q) were applied [28,59] to examine the potential biological effects of the toxicity of the trace elements in the surface sediment.

Table 1.
Metal pollution index and descriptions.
3. Results
3.1. Seasonal Distribution of the Geochemical Parameters in Marchica Lagoon Sediment
3.1.1. Physicochemical Lagoon Parameters
The physicochemical parameters of the surface waters in the lagoon during the wet and dry seasons shown in Table 2 revealed seasonal variation in temperature (T °C) (p < 0.05), with values fluctuating from 16.7 to 18.4 during the wet season and from 26 to 28.2 during the dry season. No differences (p > 0.05) for pH were found, with variation from 7.64 to 8.54 during the wet season and from 7.82 to 8.72 during the dry season. Salinity (Sal) varied from 22.1 to 36.9 during the wet season and from 34.5 to 38.5 during the dry season, with seasonal variation (p < 0.05). For dissolved oxygen (O2), significant difference was observed (p < 0.05), with variation from 4.9 to 11.83 during the wet season and 4.91 to 7.33 during the dry season. The depth of the sediment samples varied from 0.5 near the border to 6.7 at the lagoon center.

Table 2.
Physicochemical parameters of the surface waters in the lagoon during the wet and dry seasons.
3.1.2. Granulometry and TOC
The seasonal granulometric distribution and TOC sediment in the lagoon during 2018 are shown in Table 3. The sediment particle grain size analysis indicated seasonal variation (p < 0.05), while the analyzed TOC contents in the surface sediment were not affected seasonally (p > 0.05).

Table 3.
Seasonal and spatial concentrations of the grain size fractions (%), total organic carbon (TOC; %), major elements (%), and trace elements (mg/kg).
Seven sampling stations were classified as muddy sand facies during the wet season and sandy mud during the dry season: near the eutrophication zone of the Beni Ensar lagoon side (S1); near the Beni Ensar sandbar border side (S3); near the marina zone (S2); near the area of the great Nador wastewater treatment plant outfall (S8); near the Selouane wadi (S9); in the area between Bouarg and Arekmane (S11); and center of the Arekmane lagoon side (S13). The area near the Arekmane sandbar border side (S4 and S5) and the area near the Cabaillo wadi (S7) were characterized as sand facies during both seasons. The center of the lagoon (S6) was sand facies during the wet season and sandy mud during the dry season. The eutrophication zone side of Arekmane (S12) was muddy sand facies during the wet season and mud (fine silt) during the dry season. Near the Bouarg channel, characterized by agricultural effluents (S10), sediments were muddy sand facies during the wet season and sand during the dry season.
The TOC results ranged from 0.17% to 6.19% during wet season and from 0.38% to 6.5% during dry season. An elevated TOC value was observed near the sandbar border side of Beni Ensar (S3; depth: 2.85 m) during the wet and dry seasons.
3.1.3. Major and Trace Elements
Seasonal variation of the major and trace sediment elements in the lagoon during 2018 are reported in Table 3. Except for Pb (p < 0.05), no significant differences for these elements among seasons were observed (p > 0.05), while Co was below the detection limit during the wet season.
The mean concentrations of the major elements during the wet and dry seasons were, in descending order, Si (16.29%) > Ca (15.12%) > Fe (4.52%) > Al (4.17%) > K (1.66%) > Ti (0.34%) > P (0.11%) > Mn (0.05%). The mean concentrations of the trace elements were, in descending order, Zn (674.45 mg/kg) > Pb (361.16 mg/kg) > Ba (276.09 mg/kg) > Cr (42.55 mg/kg) > Cu (40.35 mg/kg) > Co (5.12 mg/kg).
The concentration ranges of the major elements Al, Fe, Mn, Si, Ti, Ca, K, and P (%) during the two seasons were, respectively, 0.22–8.43, 1.07–11.70, 0.04–0.10, 9.21–20.45, 0.09–0.52, 4.25–33.30, 0.29–2.68, and 0.05–0.18, with maximal concentrations near the mouth of the Cabaillo wadi and the marina zone (S2 and S7) for Al, Fe, and Mn; near the mouth of Cabaillo wadi (S7) for Si, Ti, and K; and at the sandbar border near the inlet (S4 and S5) for Ca.
The concentration ranges of the trace elements (mg/kg) Zn, Pb, Ba, Cr, Cu, and Co during the two seasons were, respectively, 11.70–4398.70, 127.85–1622.05, 66.08–955.42, 7.43–84.75, 2.41–268.75, and <LD–9.90 (LD, limit of detection), with maximal concentrations at the sandbar border side of Beni Ensar and the eutrophication zone of Arekmane (S3 and S12) for Zn; at the eutrophication zone of Beni Ensar and near the Selouane wadi (S1 and S9) for Pb; at the Cabaillo wadi (S7) for Ba; at the marina zone (S2) for Cr and Cu; and the maximum near the outfall of the wastewater treatment plant (S8), and the minimum at S2 and S7 for Co.
3.2. Spatial Pattern and Correlation of the Geochemical Parameters, Granulometry, and TOC in Marchica Lagoon Sediment
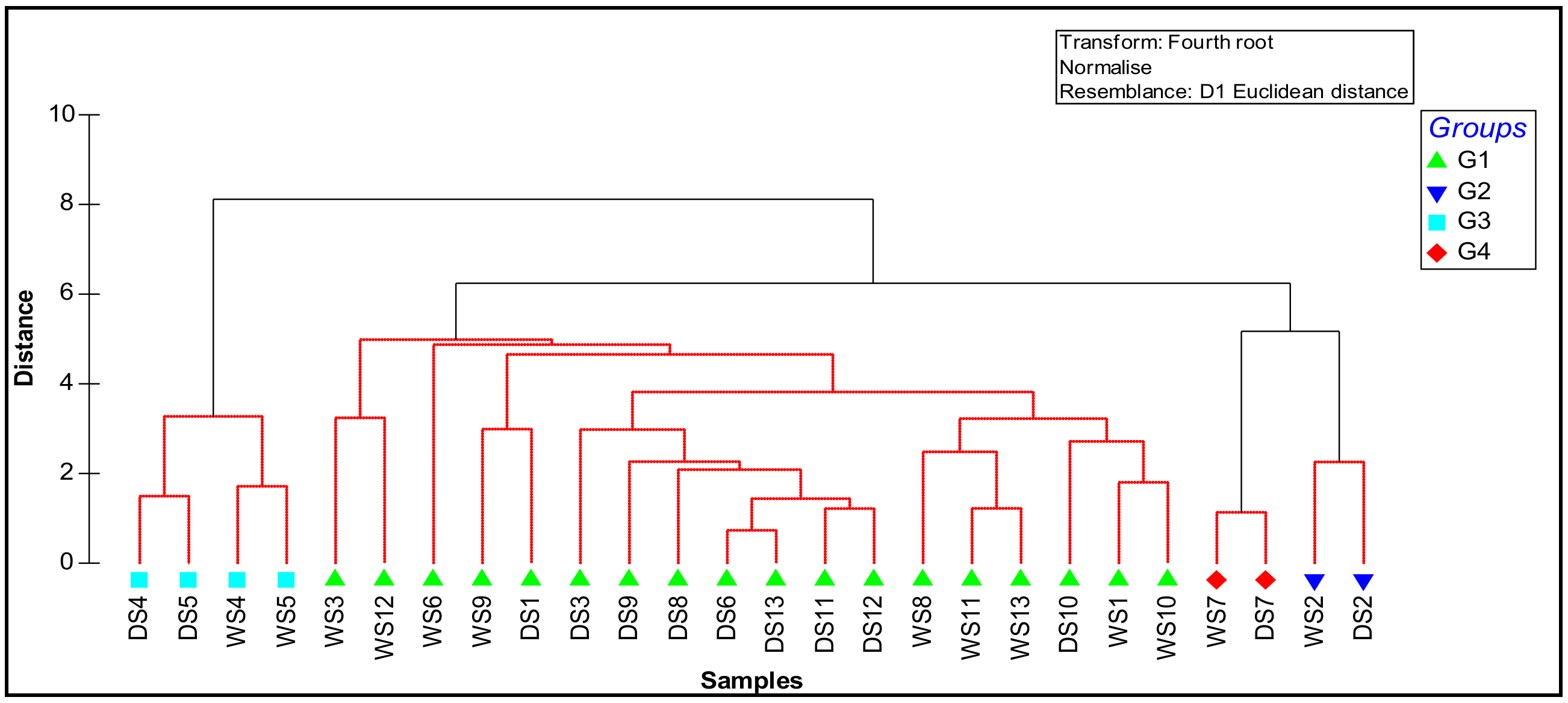
All geochemical parameters were grouped into four significant clusters during the wet and dry seasons (Figure 2). The first group, G1, was the largest, with 9 stations (eutrophication zones northwest and southeast of lagoon, station near the agricultural channel, station near the outfall of the great Nador step, 2 stations in the lagoon center, station at the sandbar border, and 3 stations near the mouths of wadis at Bouarg and Arekmane); this group is exposed to untreated wastewater from agglomerations of Beni Ensar and Arekmane, industrial wastewater from Selouane wadi, agricultural effluents from the Bouarg plain, and wastewater from the great Nador and Arekmane wastewater treatment plants. The second group, G2, represents the wet and dry stations of the marina. Two sampling sites from the sandbar were grouped into G3, which is under marine influence with Ca and P as the dominant elements. G4 represents the wet and dry season station (S7) that lies near the mouth of the Cabaillo wadi and downstream from the iron mine.
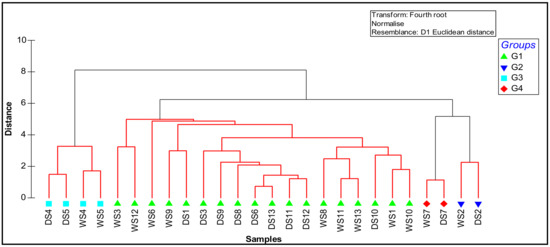
Figure 2.
Dendrogram showing the cluster pattern during wet and dry seasons (WS, wet station and DS, dry station) of the geochemical parameters, granulometry, and TOC, on the basis of similarity.
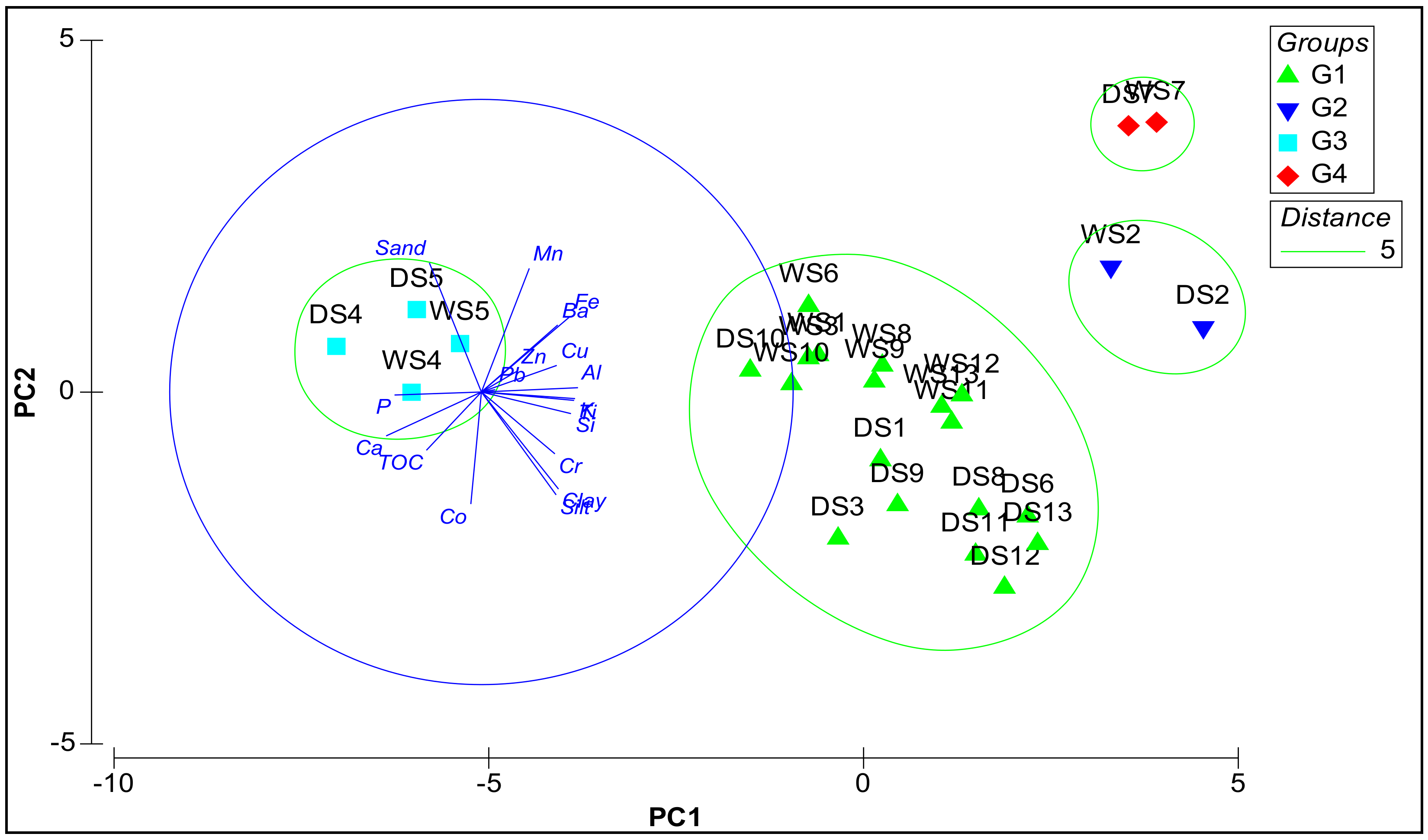
Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to evaluate the geochemical processes in Marchica Lagoon and distinguish the potential sources of trace elements in the sediment (Figure 3). Two axes, PC1 and PC2, explained 68.1% of total variance. The first accounted for 52.7% of total variance, and showed positive loadings on Al, Fe, Mn, Si, Ti, K, silt, clay, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cr, and Ba, and negative loadings on Ca, P, TOC, sand, and Co. The second component accounted for 15.4% of total variance, and showed positive loadings on sand, and negative loadings on TOC and Co. PC1 suggested that the pressure exerted on G1, G2, and G4 could be attributed to Cu, Zn, Pb, Cr, and Ba in correlation with Al, Fe, Mn, Si, Ti, K, silt, and clay, with the maximal concentration at G4 and a decrease at G1. However, the pressure exerted on G3 was attributed to marine influence.
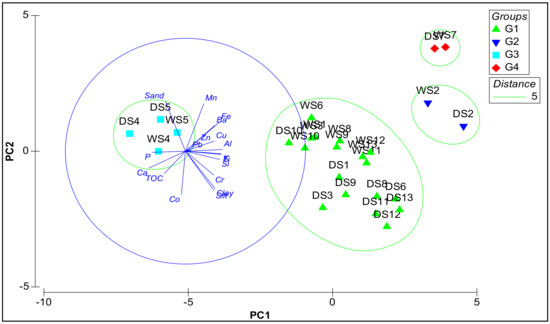
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of the wet and dry seasons (WS, wet station and DS, dry station) for the geochemical parameters, granulometry, and TOC.
The PERMANOVA conducted for all the geochemical parameters, granulometry, and TOC in the lagoon revealed significant differences between group stations, while for seasonality this was not found; also, groups G2 and G4 were similar in the pairwise comparison, making them constitute a single group.
Spearman’s correlation analysis was conducted to explore the relationship between the grain size, TOC, and major and trace elements in sediment and the physicochemical parameters of the surface waters (Table 4). All trace elements except Co showed a positive correlation with Al and Fe. A strong positive correlation was found between Al and Fe (ρ = 0.95, p < 0.01), K (ρ = 0.76, p < 0.01), Si (ρ = 0.56, p < 0.05), Cu (ρ = 0.57, p < 0.05), Pb (ρ = 0.59, p < 0.05), and Cr (ρ = 0.60, p < 0.05). Strongly positive correlation was also found between Fe and Mn (ρ = 0.62, p < 0.05), K (ρ = 0.84, p < 0.01), Si (ρ = 0.60, p < 0.05), and Cu (ρ = 0.60, p < 0.01). Highly positive correlation was found between Cu and Zn (ρ = 0.86, p < 0.01), Cr (ρ = 0.71, p < 0.01), and Ba (ρ = 0.61, p < 0.05); and between Zn and Cr (ρ = 0.74, p < 0.01) and Ba (ρ = 0.60, p < 0.05). Except for TOC with temperature, which shows a significant correlation (ρ = 0.65. p < 0.05), no other significant correlation was observed between the surface waters’ physicochemical parameters (T °C, pH, O2, and Sal) and TOC, granulometry, and the major and trace elements.

Table 4.
Spearman’s correlation coefficients of the major and trace elements, grain size fractions, and TOC in sediment and the physicochemical parameters of the surface waters in Marchica Lagoon.
3.3. Ecological Risk of the Trace Elements in Marchica Lagoon Sediment
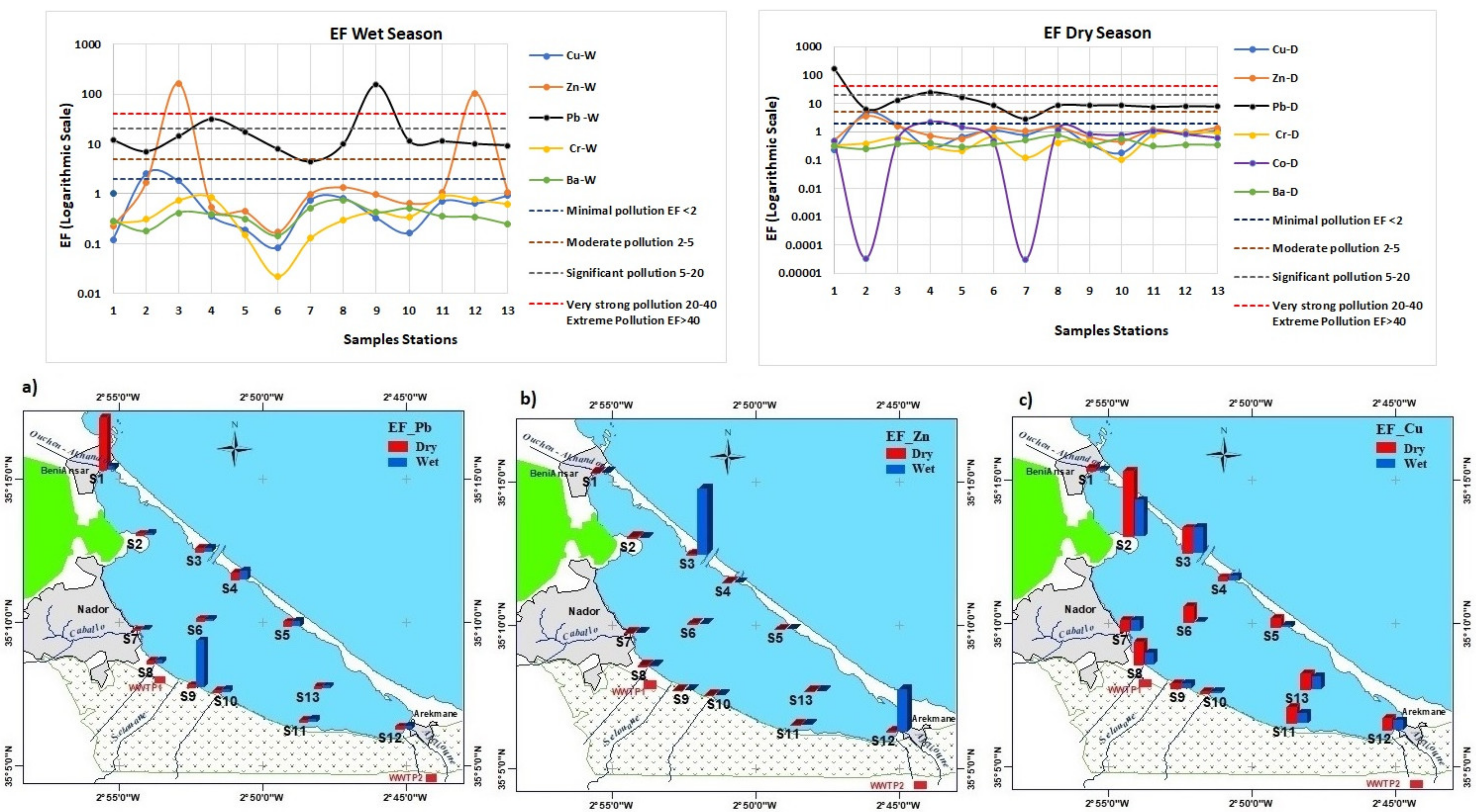
The spatial distribution of the wet and dry enrichment factors (EFs) in the lagoon is reported in Figure 4. According to Sutherland (2000) [29], the Pb results revealed extreme pollution at the eutrophication zone of Beni Ensar during the dry season and at the mouth of the Selouane wadi during the wet season (S1 and S9); very strong pollution was observed at the sandbar border during the wet and dry season (S4); and significant pollution was found in all others stations during the wet and dry seasons, except near the Cabaillo wadi (S7), which was characterized by moderate pollution. The EF values for Zn indicated extreme pollution at the northwest sandbar border and at the eutrophication zone of Arekmane during the wet season (S3 and S12); moderate pollution at the marina zone (S2) during the dry season; and minimal pollution was observed in all other stations during both the wet and dry seasons. Minor enrichment of the trace elements Cr, Co, and Ba was found in the lagoon during both the wet and dry seasons. The EF values for Cu during the wet and dry seasons were under 2 in all stations, except in the marina zone (S2), which showed moderate pollution.
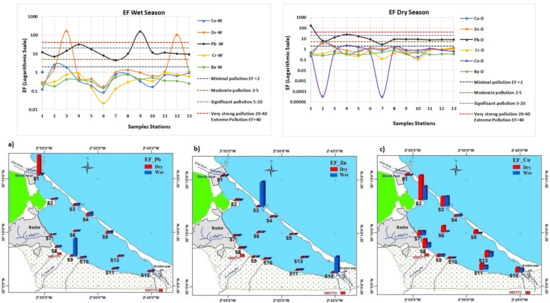
Figure 4.
Wet and dry enrichment factor (EF): (a) EF of Pb; (b) EF of Zn; and (c) EF of Cu.
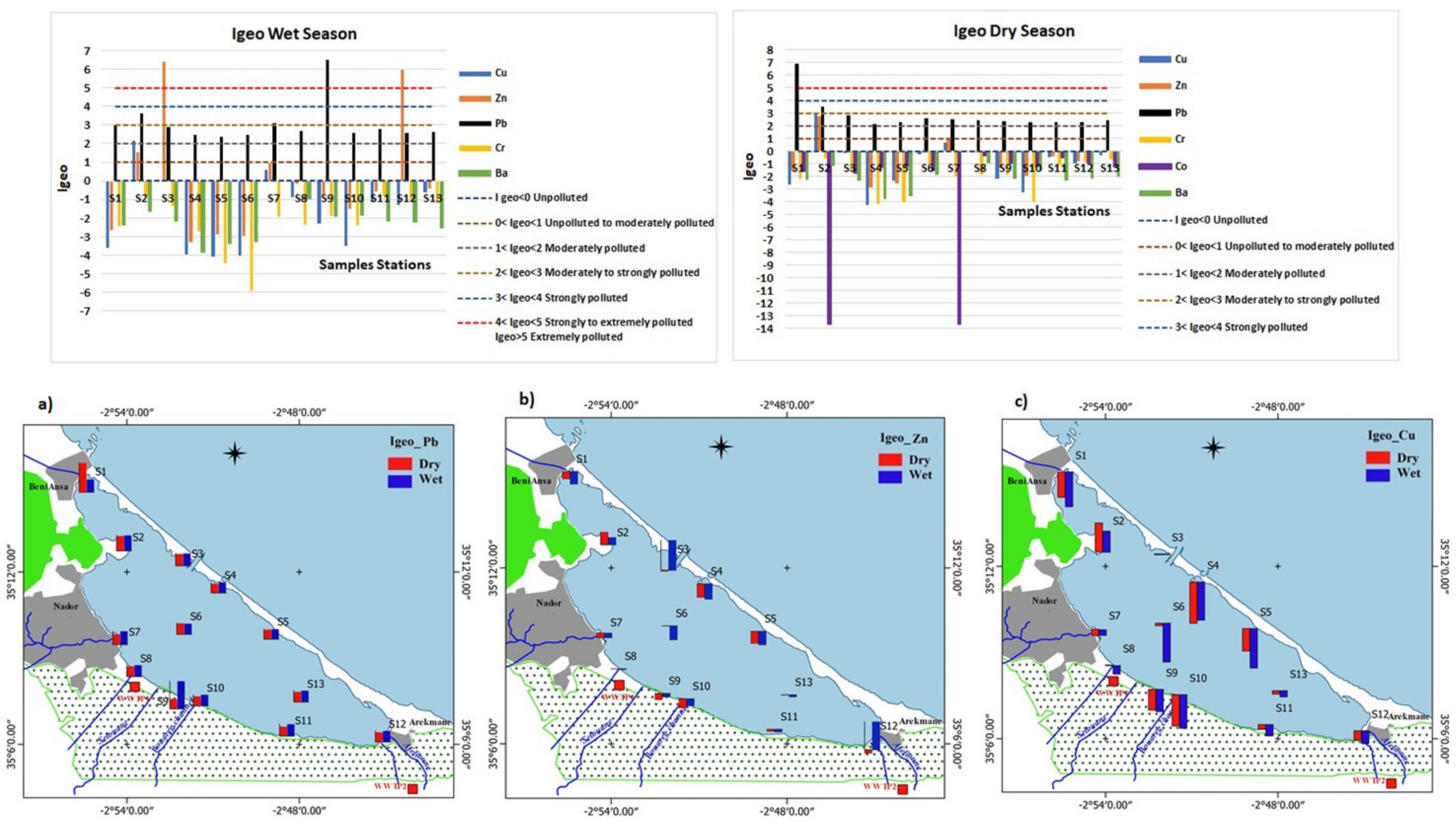
The spatial distribution of geoaccumulation index (Igeo) during wet and dry seasons is reported in Figure 5. According to the scale reported by Müller (1981) [61], Igeo Pb results revealed extreme pollution level at the mouth of Selouane wadi (S9) during wet season and the northwest eutrophication zone (S1) during dry season and all the other stations were between moderately to strongly polluted during wet and dry seasons. Igeo values for Cr, Co, and Ba were found to be at unpolluted levels for all stations in the lagoon during both wet and dry seasons. Igeo values of Cu were found during wet and dry seasons unpolluted except for the marina zone (S2) which were between moderately to strongly polluted and the mouth of Cabaillo wadi (S7) which were unpolluted to moderately polluted. For zinc, Igeo values during wet season were observed to be at extreme pollution level at the sandbar border (S3) and at the eutrophication zone of Arekmane (S12); at a moderate pollution level at the marina zone (S2) and at unpolluted to moderate pollution at the mouth of Cabaillo wadi (S7); during dry season marina zone (S2) was found at moderate to strongly polluted and (S7) was at unpolluted to moderate pollution as during the wet season; the other stations were unpolluted during both wet and dry seasons.
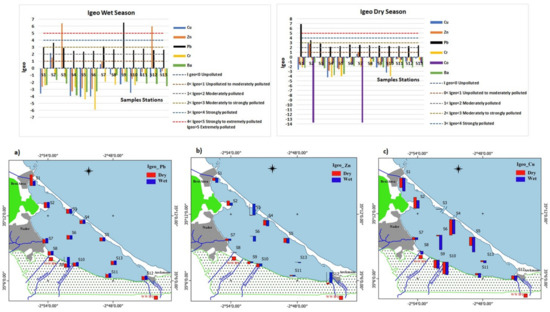
Figure 5.
Wet and dry geoaccumulation index (Igeo): (a) Igeo of Pb; (b) Igeo of Zn; and (c) Igeo of Cu.
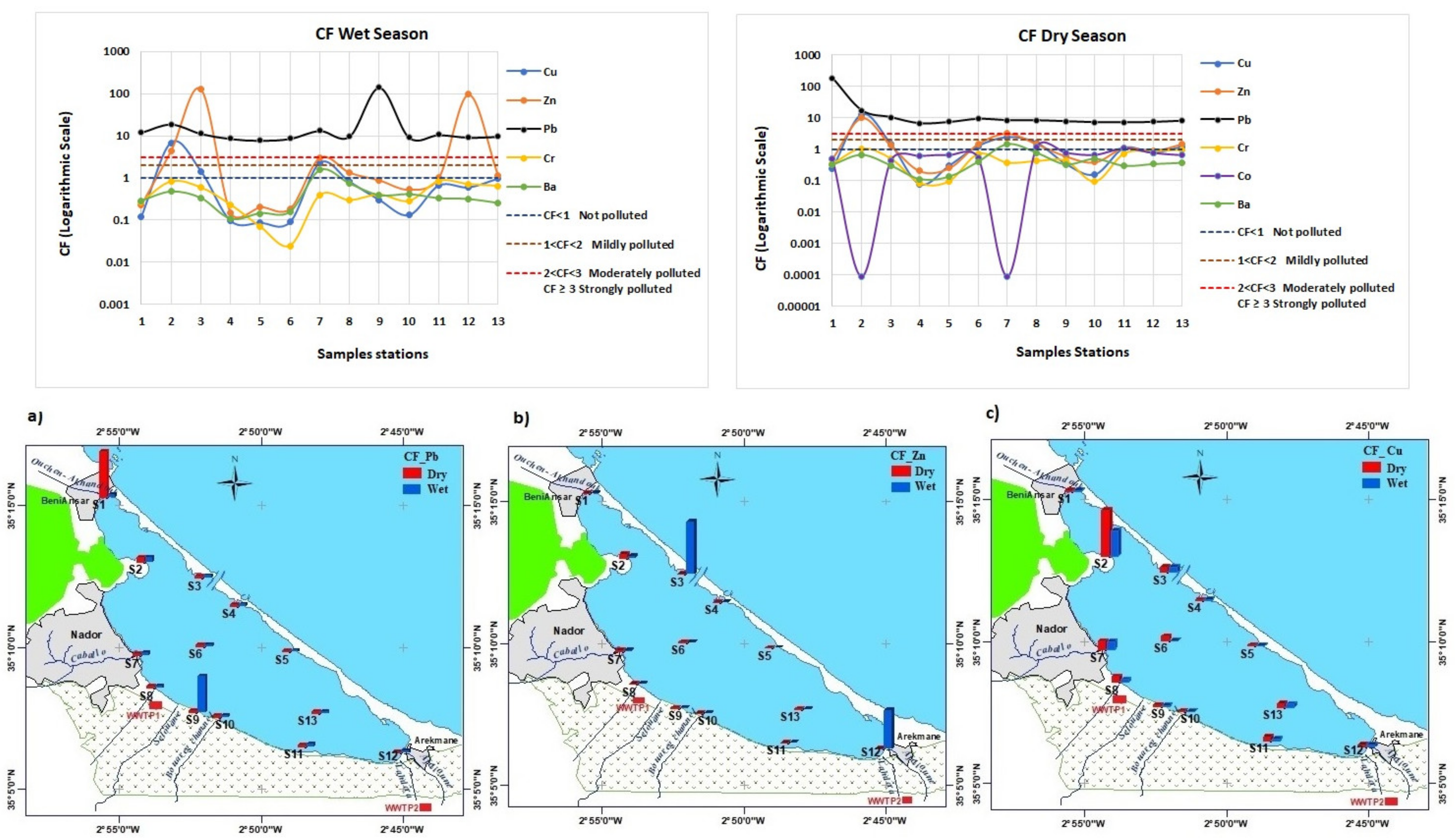
The spatial distribution of the contamination factor (CF) during the wet and dry seasons in the superficial sediment in the lagoon is presented in Figure 6. The results indicated that all CF values of Pb during the wet and dry seasons were greater than 3, suggesting the presence of strong lead pollution in the study areas. For the CF values of zinc, 3 stations during the wet season (S2, S3 and S12) and 2 others (S2 and S7) during the dry season were observed to be strongly polluted, 1 station was found to be moderately polluted during the wet season (S7), 3 stations during the wet and dry seasons (S8, S11 and S13), and 2 others during the dry seasons (S3 and S6) were found mildly polluted—the other stations were not polluted. The CF values of Cu indicated strong pollution at S2 during the wet and dry seasons, moderate pollution at S7 during the wet and dry seasons, mild pollution at S3 during the wet and dry seasons and at S8, S6, and S13 during the dry season, and no pollution in the other study areas. The CF values of Co during the dry season showed that no pollution was found except at 2 stations (S8 and S11), which were mildly polluted. The CF values of Cr were less than 1, suggesting no pollution in the study area except at the Marina zone during the dry season, which was mildly polluted. The CF values of Ba also showed no pollution except for S7 during the wet and dry seasons, where the CF values showed mild pollution.
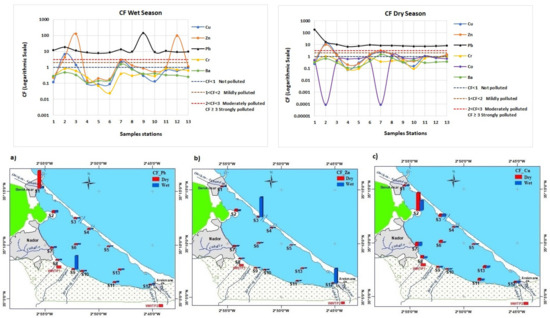
Figure 6.
Wet and dry contamination factor (CF): (a) Cf of Pb; (b) CF of Zn; and (c) CF of Cu.
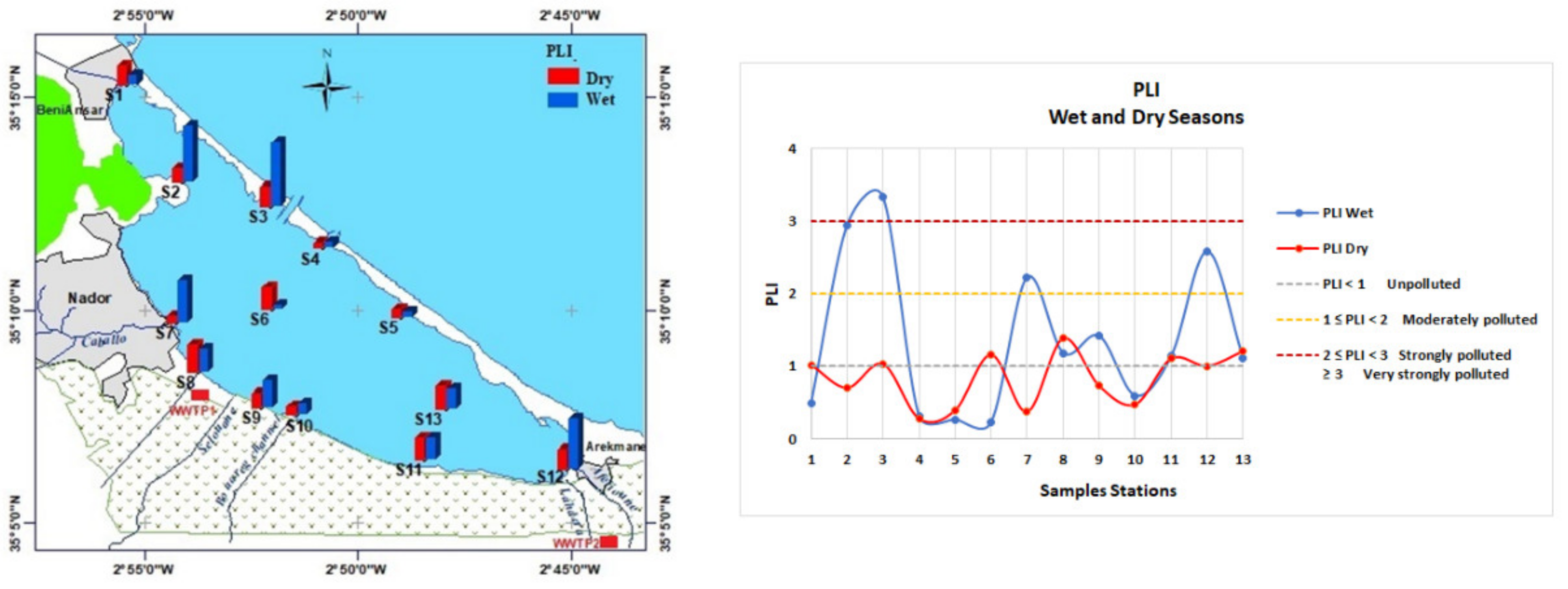
The pollution-load index (PLI) values in the lagoon, reported in Figure 7, ranged from 0.22 to 3.33 during the wet season and from 0.27 to 1.39 during the dry season. The highest PLI value was observed at the station in the sandbar border (S3) during the wet season.
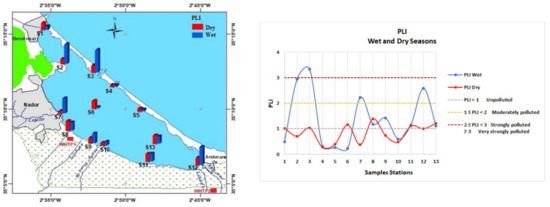
Figure 7.
Wet and dry pollution-load index (PLI).
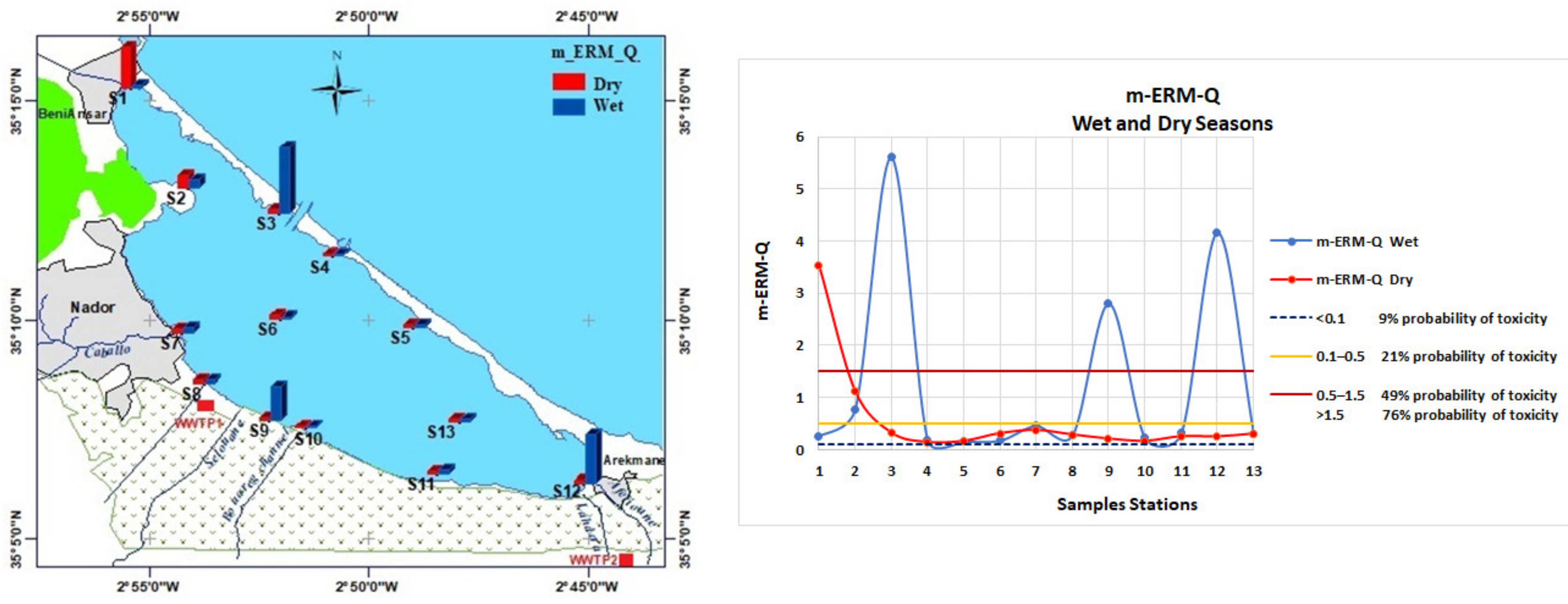
The biological-risk index (m-ERM-Q) for Pb, Zn, Cu, and Cr reported in Figure 8 shows that 4 stations (S1 during dry season, and S12, S3, and S9 during wet season) had values greater than 1.5, while the value of S2 was between 0.5 and 1.5 during both the wet and dry seasons, and all the other stations’ values were between 0.1 and 0.5.
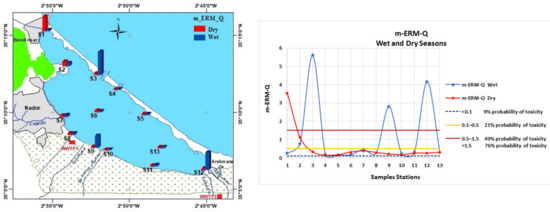
Figure 8.
Wet and dry biological-risk index (m-ERM-Q).
The mean of wet and dry concentrations of Pb, Zn, Cr, and Cu were compared with the SQGs presented by Macdonald et al. (1996) [30] and Long et al. (1995) [31] in Table 5. All stations’ sampling values for Pb were higher than their PEL, and those of S1, S2, and S9 were higher than their ERM. Three areas for Zn, covering S2, S3, and S12, were higher than their PEL and ERM. For Cu, only the marina area was higher than its PEL. Concentrations higher than PEL and ERM indicate risks for the marine biota. Stations that were between its TEL and PEL values were located, for Cr, in the marina zone, the eutrophication zone of Arekmane, and the station of the Arekmane side lagoon center; for Zn, in the area near Cabaillo wadi; and for Cu, in the center of the lagoon, in the eutrophication zone of Arekmane, and at the sandbar border near the inlet, indicating potential pollution at these stations. The other stations’ values were lower than their TEL values for Cu, Zn, and Cr.

Table 5.
Comparison of the trace element concentrations with background values and guidelines.
4. Discussion
Sedimentation in the lagoon is essentially governed by turbulence at the inlet and intra-lagoon currents, which allow for the resuspension of particles and their transport in the lagoon through natural contributions of exogenous origin (erosion, decomposition of plant matter), or anthropogenic contributions (urban and agricultural discharges) and native production that generates microalgae debris [26].
Lagoon granulometry showed that all stations except at the inlet areas were characterized by the highest content of sand during the wet season. The fine content was higher during the dry season, and the highest values were found at the Arekmane side of the lagoon center, the continental border at the marina zone, and the area of the great Nador wastewater treatment plant outfall. The clay content was also higher during the dry season and dominated the center part of the lagoon and the eutrophication zone side of Arekmane, as indicated by Aknaf et al. (2017) [62]. Sediment inputs are relatively important at the outlet of the wadis and on the sandbar border, especially near the inlet, as reported by Lefebvre (1997) [63].
Concerning TOC, elevated values were recorded during the wet and dry season in the northwest sandbar border in the same area as that with the highest TOC value (20%) during the eutrophication period of the lagoon, with a mean value of 5% according to SEEE/INRH (2009) [26]. During the post restoration period, the TOC in the lagoon was reduced to a mean value of 3.9% in 2011, with a maximal value of 10.4% according to Najih et al. (2017) [64]. A significant decrease in TOC was likely due to the restoration actions, as reported by Najih et al. (2017) [64].
Spearman’s correlation coefficient matrix of the concentrations of grain size contents and major and trace elements in the surface sediment showed that the trace elements are associated with smaller grain size particles, which constitute important elements in the distribution of metals in sediments, as reported by El Barjy et al. (2020) [65], Watts et al. (2017) [66], Hu et al. (2013) [67], Whitney (1975) [68], and Horowitz and Elrick (1987) [69].
Ecotoxicological risk assessment of the trace elements during the wet and dry seasons, by comparing the concentrations with sediment-quality guidelines (SQGs) and assessment indices, showed the existence of lead pollution in the lagoon, with peaks in the northwestern eutrophication zone during the dry season and near the Selouane wadi during the wet season. Indeed, during the wet season, a very high concentration of Pb was recorded at the mouth of the Selouane wadi, which contains the majority of the industrial units of the region. During the dry season, the same situation was noted at the eutrophication zone of Beni Ensar, which is under the influence of discharges from certain areas and industrial activities not yet connected to the wastewater treatment plant. Zn pollution was found in two lagoon areas during the wet season, with a maximum at the northwest sandbar border, followed by the southwestern eutrophication zone, which can be explained by the discharges from certain activities without treatment. Cu pollution was also found in two lagoon areas during the wet and dry seasons, with a maximum at the marina zone, followed by the mouth of Cabaillo wadi. On the other hand, for other trace elements Cr, Co, and Ba, no pollution was observed in the lagoon.
PLI values in the lagoon indicated that, during wet season, the northwestern sandbar border zone was very strongly polluted; the Marina zone, the mouth of Cabaillo wadi, and the southwest eutrophication zone were strongly polluted; and, during dry season, these areas were found between moderately polluted to unpolluted. The distribution of the biological-risk index reveals that the four zones of the lagoon may present a 76% probability of toxicity: during wet season, the area in the northwestern sandbar border, southwest eutrophication zone, and the mouth of the Selouane wadi; and during the dry season, the northwestern eutrophication zone; in turn, the marina zone has a 49% probability of toxicity, at a potential risk to aquatic organisms according to Long et al. (2000) [28]. All other areas presented a low probability of toxicity, varying from 9% to 21%.
Generally, the trace element concentrations in the lagoon sediment depend on the hydrological state of the lagoon water and sediment entering the lagoon, which impacts the geochemical processes, as reported by Barik et al. (2020) [70] and Jain et al. (2007) [71]. Principal factors that control the facies and changes in the characteristics of Marchica Lagoon sediment, according to Hamoumi et al. (2011) [35], are related to the climate, the geological context of the watershed, the morphology of the lagoon, the position of the inlet, and anthropogenic activities. According to the study of Maicu et al. (2018) [72], after restoration action concerning the construction of the new inlet between the Marchica Lagoon and Mediterranean Sea, the average water renewal time (WRT) decreased from approximatively 60 to 16 days, with an increasing trend during summer periods. This study showed that the lowest values of WRT are present in a restricted area close to the inlet where tidal flushing is the highest and higher values of WRT were recorded in the northern and southern areas where the residual circulation is negligible, which can explain the maximum lead pollution found in the northwest eutrophication zone during the dry season compared to the wet season.
The Marchica Lagoon watershed hosts one of the largest Moroccan iron mines, which was intensively exploited and abandoned without restoration. The significant quantity of tailings and waste rock around the abundant mining area exposed to air and water during rainy periods provides for the production of acid mine drainage, and the release of Fe and trace elements, according to Cadmus et al. (2018) [73] and Wittmann (1981) [74], into the surrounding wadis of the Marchica Lagoon, as proven by Azzeddine and El Hassan (2020) [75] and Lakrim et al. (2014) [76].
The PCA and Spearman’s correlation coefficient matrix indicated that trace elements except Co are derived from the same content, as reported by Maanan et al. (2015) [57], related to iron oxides or clays of the smectite or chlorite type, as reported by Bloundi et al. (2009) [40]. These findings suggested that, apart from geological sources, Pb, Zn, Cu, and Cr also originated from anthropogenic sources, as agriculture often uses chemical fertilizers and pesticides that contain these elements, so too industrialization, as reported by Alloway (2013) [77] and Nriagu and Pacyna (1988) [78]. According to De Lacerda (1994) [19], the higher lead concentrations recorded in the lagoon may have also originated from marine activities related to fishing boats, as mentioned by Najih et al. (2015) [22].
Previous studies conducted by Maanan et al. (2015) [57], Bloundi et al. (2009) [40], Gonzalez et al. (2007) [79], and Ruiz et al. (2006) [80] (Table 5) confirmed that the surface sediment of the Marchica Lagoon is polluted by lead, zinc, and copper. For Inani (1995) [81], the concentrations exceeding the SQGs in Marchica Lagoon mainly concern zinc and copper. This study confirmed that concentrations of these trace elements have significantly increased despite the restoration actions realized during the last decade, as proved by the Marchica Lagoon water quality assessment study [82].
In order to place the Marchica Lagoon in a regional context of trace-element pollution status, a comparison was made with other Mediterranean lagoons (Table 6). The comparison showed that the maximal concentrations of Pb, Zn, and Cu recorded in the Marchica Lagoon were higher than those in Bizerte Lagoon, as reported by Barhoumi et al. (2016) [83]; Berre Lagoon, as reported by Arienzo et al. (2013) [84]; Izmit Bay, as reported by Tan et al. (2020) [85]; Prokopos Lagoon, as reported by Katsaros et al. (2017) [86]; Málaga Bay, as reported by Castillo et al. (2013) [13]; Santa Gilla Lagoon, as reported by Atzori et al. (2018) [87]; Burullus Lake, as reported by Melegy et al. (2019) [88]; and Gialova Lagoon, as reported by Kanellopoulos et al. (2020) [89].

Table 6.
Comparison of the minimum and maximum trace elements (mg/kg) in sediment of Marchica Lagoon with previous studies and with others lagoons in the Mediterranean Sea.
5. Conclusions
This post restoration characterization of the trace elements Pb, Cu, Zn, Cr, Co, and Ba, and their correlation to the major elements Si, Al, Fe, Ti, Mn, K, P, Ca, grain size, and TOC in the surface sediment of the Marchica Lagoon during the wet and dry seasons, revealed that element abundance is regulated by the sediment grain size characteristics, and trace elements tend to be concentrated in finer sediment particles. Multivariate analysis and ecotoxicological risk assessment of the trace elements using sediment-quality guidelines (SQGs) and the pollution indices EF, Igeo, and CF revealed the contamination of Marchica Lagoon by Pb as the primary pollutant in all study areas, with two peaks in the mouth of the Selouane wadi during the wet season and the northwestern eutrophication zone during the dry season. Zn constituted a secondary pollutant, with two peaks in the northwest sandbar border and southwest eutrophication zone during the wet season and the mouth of the Cabaillo wadi during the dry season. Cu pollution was found in the marina zone and the mouth of the Cabaillo wadi during both the wet and dry seasons. Minimal pollution was found for Cr, Co, and Ba. The pollution-load index in the lagoon indicated that, during the wet season, the northwest sandbar border zone was very strongly polluted, and that the Marina zone, the mouth of the Cabaillo wadi, and the southwest eutrophication zone were strongly polluted; during dry season, these areas were found to be between moderately polluted and unpolluted. The biodiversity conservation of Marchica Lagoon requires an integrated environmental management plan that addresses watershed activities, especially the restoration of the abandoned iron mining site, as well as a continuous monitoring network with control and assessments, including all areas that were identified as polluted.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: B.O., M.L. and N.E.O.; data curation, B.O. and H.B.; formal analysis, R.B. and H.B.; investigation, B.O., M.E.B., M.L., H.O. and N.E.O.; methodology, B.O., M.L. and N.E.O.; resources, M.E.B., M.T., S.B., H.O., M.B. and M.M.; software, H.B.; supervision, N.M. and M.S.; writing—original draft, B.O.; writing—review and editing, M.E.B., M.T., M.L., S.B., H.O., M.B., N.E.O., M.M., H.B., N.M. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks all partners of the Lag-Nad 2016 project that supported this study. We are grateful to the editors and reviewers who contributed to the improvement of the quality of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Pérez-Ruzafa, I.M.; Newton, A.; Marcos, C. Coastal lagoons: Environmental variability, ecosystem complexity, and goods and services uniformity. In Coasts and Estuaries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 253–276. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, A.; Brito, A.C.; Icely, J.D.; Derolez, V.; Clara, I.; Angus, S.; Schernewski, G.; Inácio, M.I.; Lillebø, A.; Sousa, I.A.; et al. Assessing, quantifying and valuing the ecosystem services of coastal lagoons. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 44, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, A.M.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Martínez-Paz, J.M.; Marcos, C. Ecosystem services and main environmental risks in a coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Murcia, SE Spain): The public perception. J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 43, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; Van Der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennish, M.J.; Paerl, H.W. Coastal Lagoons: Critical Habitats of Environmental Change; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, L.A.; Boesch, D.F.; Covich, A.; Dahm, C.; Erséus, C.; Ewel, K.C.; Kneib, R.T.; Moldenke, A.; Palmer, M.A.; Weslawski, J.M.; et al. The function of marine critical transition zones and the importance of sediment biodiversity. Ecosystems 2001, 4, 430–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenreich, S.J.; Bernasconi, C.; Campostrini, P. Climate Change and the European Water Dimension; EU Report No. 21553; Joint Research Centre, European Commission: Ispra, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Watson, R. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Micheli, F.; Kappel, C.V. Evaluating and ranking the vulnerability of global marine ecosystems to anthropogenic threats. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 5, p. 563. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Walker, T.R.; Davis, E.; Ma, G. Ecological risk assessment of metals in small craft harbour sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.; Cristina, S.; Brito, A.; Cardoso, A.C.; Colijn, F.; Riva, S.D.; Gertz, F.; Hansen, J.; Holmer, M.; et al. An overview of ecological status, vulnerability and future perspectives of European large shallow, semi-enclosed coastal systems, lagoons and transitional waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 140, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.A.; Trujillo, I.S.; Alonso, E.V.; de Torres, A.G.; Pavón, J.C. Bioavailability of heavy metals in water and sediments from a typical Mediterranean Bay (Málaga Bay, Region of Andalucía, Southern Spain). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affian, K.; Robin, M.; Maanan, M.; Digbehi, B.; Djagoua, E.V.; Kouamé, F. Heavy metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Ebrié lagoon sediments, Côte d’Ivoire. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 159, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ruzafa, A.; Fernández, A.I.; Marcos, C.; Gilabert, J.; Quispe, J.I.; García-Charton, J.A. Spatial and temporal variations of hydrological conditions, nutrients and chlorophyll a in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Spain). Hydrobiologia 2005, 550, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutahar, L.; Maanan, M.; Bououarour, O.; Richir, J.; Pouzet, P.; Gobert, S.; Bazairi, H. Biomonitoring environmental status in semi-enclosed coastal ecosystems using Zostera noltei meadows. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 776–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Han, L.; Gao, B.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J.; Wan, X. Distribution, bioavailability, and potential risk assessment of the metals in tributary sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir: The impact of water impoundment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Li, K.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, X. Optimizing a coastal monitoring network using a water-quality response grid (WRG)-based sampling design for improved reliability and efficiency. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lacerda, L.D. Biogeochemistry of heavy metals in coastal lagoons; Elsevier Oceanography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 60, pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, J.G. The perturbation of historical pollution records in aquatic sediments. Environ. Geochem. Health 1991, 13, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selfati, M.; El Ouamari, N.; Franco, A.; Lenfant, P.; Lecaillon, G.; Mesfioui, A.; Bazairi, H. Fish assemblages of the Marchica lagoon (Mediterranean, Morocco): Spatial patterns and environmental drivers. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 32, 100896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najih, M.; Berday, N.; Lamrini, A.; Nachite, D.; Zahri, Y. Situation de la pêche aux petits métiers après l’ouverture du nouveau chenal dans la lagune de Nador. Rev. Maroc. Sci. Agron. Vét. 2015, 3, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dakki, M. Diagnostic pour l’aménagement des zones humides du nord-est du Maroc: Sebkha Bou Areg (lagune de Nador); final report, UNEP/Secr. Etat Env./Départ. Eaux & Forêt, Maroc; MedWetCoast project Morocco: Arles, France, 2003; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Malouli, I.M.; Zahri, Y.; Houssa, R.; Abdelaoui, B.; El Ouamari, N. Pêche artisanale dans la lagune de Nador: Exploitation et aspects socio-économiques. Available online: http://webco.faocopemed.org/old_copemed/vldocs/0000762/case_std_nador.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- UNEP; EEA. Priority Issues in the Mediterranean Environment; Report No 4; United Nations Environment Program; European Environment Agency: Nairobi, Kenya; Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- SEEE; I.N.R.H. Eutrophication Study of Nador Lagoon; UNEP Report; (MEDPOL program): Nairobi, Kenya, 2009; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Agency for the Development of the Marchica Lagoon. 2010. Available online: http://www.agencemarchica.gov.ma/ (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Long, E.R.; MacDonald, D.D.; Severn, C.G.; Hong, C.B. Classifying probabilities of acute toxicity in marine sediments with empirically derived sediment quality guidelines. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2000, 19, 2598–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.D.; Carr, R.S.; Calder, F.D.; Long, E.R.; Ingersoll, C.G. Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 1996, 5, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; MacDonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Heavy metals in the sediment of the Rhine-Changes Seity. Umsch. Wiss. Tech. 1979, 79, 778–783. [Google Scholar]
- Hamoumi, N.; Hourimeche, A.; Chafik, M.; Hazim, M.E.; Terhzaz, L.; Kharbaoui, R.; Louaya, A. Contrôle et évolution des Milieux Sédimentaires de la Lagune de Nador (Littoral Méditerranéen Oriental, Maroc). In Proceedings of the Second Coastal and Maritime Mediterranean Conference, Tangier, Morocco, 22–24 November 2011; pp. 177–180. Available online: http://www.paralia.fr (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Karim, B.M. Etude Géochimique de la Lagune de Nador (Maroc Oriental): Impacts des Facteurs Anthropiques. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Mohamed V-Agdal, Rabat, Morocco, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Raji, O.; Dezileau, L.; Tessier, B.; Niazi, S.; Snoussi, M.; Von Grafenstein, U.; Poujol, A. Climate and tectonic-driven sedimentary infill of a lagoon as revealed by high resolution seismic and core data (the Nador lagoon, NE Morocco). Mar. Geol. 2018, 398, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, H.; Ahmed, D.M.; Mohammed, I.; Benyounes, D.A. Circulation marine de la lagune de Nador (Maroc) par modélisation hydrodynamique. Eur. Sci. J. 2015, 11, 418–428. [Google Scholar]
- Guelorget, O.; Perthuisot, J.P.; Frisoni, G.F.; Monti, D. The role of confinement in the biogeological organization of Nador Lagoon (Morocco). Oceanol. Acta 1987, 10, 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Bloundi, M.K.; Duplay, J.; Quaranta, G. Heavy metal contamination of coastal lagoon sediments by anthropogenic activities: The case of Nador (East Morocco). Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Fisheries Research. Morocco. Available online: https://www.inrh.ma (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Gee, G.W.; Or, D. 2.4 Particle-size analysis. Methods Soil Anal. Part 4 Phys. Methods 2002, 5, 255–293. [Google Scholar]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. GRADISTAT: A grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.E.; Samways, G.; Shimmield, G.B. Historical storage budgets of organic carbon, nutrient and contaminant elements in saltmarsh sediments: Biogeochemical context for managed realignment, Humber Estuary, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littoral - Environnement - Télédétection – Géomatique, (LETG), UMR 6554, University of Nantes. Available online: https://letg.cnrs.fr (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- National Center for Energy, Sciences and Nuclear Techniques. Morocco. Available online: https://www.cnesten.org.ma (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- National Laboratory of Studies and Monitoring of Pollution. Morocco. Available online: https://labo.environnement.gov.ma (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Jackson, J.E. A User’s Guide to Principal Components; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 587. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial. PRIMER-E: Plymouth; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK.
- Niencheski, L.F.; Windom, H.L.; Smith, R. Distribution of particulate trace metal in Patos Lagoon Estuary (Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1994, 28, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schropp, S.J.; Lewis, F.G.; Windom, H.L.; Ryan, J.D.; Calder, F.D.; Burney, L.C. Interpretation of metal concentrations in estuarine sediments of Florida using aluminum as a reference element. Estuaries 1990, 13, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruland, K.W.; Bertine, K.; Koide, M.; Goldberg, E.D. History of metal pollution in southern California coastal zone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1974, 8, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, O.S.; Ozmen, M.; Güngördü, A.; Yılmaz, A.; Yakan, S.D.; Karacık, B.; Schramm, K.W. Heavy metal pollution in sediments and mussels: Assessment by using pollution indices and metallothionein levels. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.; Landesman, C.; Maanan, M.; Zourarah, B.; Fattal, P.; Sahabi, M. Evaluation of the anthropogenic influx of metal and metalloid contaminants into the Moulay Bousselham lagoon, Morocco, using chemometric methods coupled to geographical information systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4729–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, S.; Larsson, U.; Borg, H. Heavy metal decrease in the sediments of a Baltic Bay following tertiary sewage treatment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1992, 24, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.D.; Tittlebaum, M.E. Metal distribution and contamination in sediments. J. Environ. Eng. 1985, 111, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S.; Holland, H.D.; Turekian, K.K. Composition of the continental crust. Crust 2003, 3, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Long, E.R.; Field, L.J.; MacDonald, D.D. Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1998, 17, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; MacDonald, D.D. Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 1998, 4, 1019–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. The heavy metal pollution of the sediments of Neckars and its tributary: A stocktaking. Chem. Zeit 1981, 105, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Aknaf, A.; Akodad, M.; Hmeid, H.A.; Layachi, M.; Mesfioui, A.; Andich, K.; Baghour, M. Granulometric Analysis and Environtment of Deposits of Surface Sediments of the Marchica Lagoon (North-East of Morocco). In Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1677–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, A.; Guelorget, O.; Perthuisot, J.P.; Dafir, J.E. Évolution biologique de la lagune de Nador (Maroc) au cours de la période 1982–1993. Ocean. Acta 1997, 20, 371–385. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.; Driss, N.; Nadia, B.; Roberto, P.; Abdeljaouad, L.; Nor-Dine, R. Charactérization of the new status of Nador lagoon (Morocco) after the implementation of the management plan. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Barjy, M.; Maanan, M.; Maanan, M.; Salhi, F.; Tnoumi, A.; Zourarah, B. Contamination and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in marine sediments from Tahaddart estuary (NW of Morocco). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, M.J.; Mitra, S.; Marriott, A.L.; Sarkar, S.K. Source, distribution and ecotoxicological assessment of multielements in superficial sediments of a tropical turbid estuarine environment: A multivariate approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Cui, R.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Zhao, J.; Bai, F.; Ding, X. Occurrence and distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Changhua River Estuary and adjacent shelf (Hainan Island). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, P.R. Relationship of manganese-iron oxides and associated heavy metals to grain size in stream sediments. J. Geochem. Explor. 1975, 4, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.J.; Elrick, K.A. The relation of stream sediment surface area, grain size and composition to trace element chemistry. Appl. Geochem. 1987, 2, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S.S.; Prusty, P.; Singh, R.K.; Tripathy, S.; Farooq, S.H.; Sharma, K. Seasonal and spatial variations in elemental distributions in surface sediments of Chilika Lake in response to change in salinity and grain size distribution. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.K.; Malik, D.S.; Yadav, R. Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of Lake Nainital, Uttaranchal, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maicu, F.; Abdellaoui, B.; Bajo, M.; Hilmi, K.; Umgiesser, G. The use of the SHYFEM numerical model to assess the improvement in the hydrodynamics and in the water renewal of the Nador Lagoon (Morocco) after the construction of a new inlet. In Proceedings of the 20th EGU 2018 General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 4–13 April 2018; p. 12657. [Google Scholar]
- Cadmus, P.; Brinkman, S.F.; May, M.K. Chronic toxicity of ferric iron for North American aquatic organisms: Derivation of a chronic water quality criterion using single species and mesocosm data. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 74, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, G. Toxic metals. In Metal Pollution in The Aquatic Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 3–70. [Google Scholar]
- Azzeddine, K.; El Hassan, T. Assessment of Metallic Contamination of Water Resources in the Area Around the Abandoned Mining Site of Ouixane (North East Morocco). In Proceedings of the 4th Edition of International Conference on Geo-IT and Water Resources 2020, Geo-IT and Water Resources 2020, Al-Hoceima, Morocco, 11–12 March 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lakrim, M.; Mesrar, L.; El Aroussi, O.; Lahrach, A.; Beaabidate, L.; Garouani, A.; Chaouni, A.; Tabyaoui, H.; Jabrane, R. Impact Study of Mining Waste of the Nador Mine on the Environment (North-Eastern of Morocco). Rev. Ljee 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alloway, B.J. Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. In Heavy Metals in Soils; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 11–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nriagu, J.O.; Pacyna, J.M. Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature 1988, 333, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, I.; Águila, E.; Galán, E. Partitioning, bioavailability and origin of heavy metals from the Nador Lagoon sediments (Morocco) as a basis for their management. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Abad, M.; Olías, M.; Galán, E.; González, I.; Aguilá, E.; Cantano, M. The present environmental scenario of the Nador Lagoon (Morocco). Environ. Res. 2006, 102, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inani, I. Dynamique sédimentaire et pollution dans la lagune de Nador. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Mohammed V-Agdal, Rabat, Morocco, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Oujidi, B.; Tahri, M.; Layachi, M.; Abid, A.; Bouchnan, R.; Selfati, M.; Snoussi, M. Effects of the watershed on the seasonal variation of the surface water quality of a post-restoration coastal wetland: The case of the Nador lagoon (Mediterranean sea, Morocco). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, B.; Elbarhoumi, A.; Clérandeau, C.; Al-Rawabdeh, A.M.; Atyaoui, A.; Touil, S.; Cachot, J. Using an integrated approach to assess the sediment quality of an Mediterranean lagoon, the Bizerte lagoon (Tunisia). Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1082–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arienzo, M.; Masuccio, A.A.; Ferrara, L. Evaluation of sediment contamination by heavy metals, organochlorinated pesticides, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Berre coastal lagoon (southeast France). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, İ.; Aslan, E. Metal pollution status and ecological risk assessment in marine sediments of the inner Izmit Bay. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 33, 100850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsaros, D.; Panagiotaras, D.; Kontopoulos, N.; Avramidis, P. Sediments characteristics and heavy metals distribution of a very shallow protected coastal lagoon, Prokopos Lagoon, Mediterranean Sea Western Greece. Feb-Fresenius Environ Bull. 2017, 26, 6093. [Google Scholar]
- Atzori, G.; Aru, V.; Marincola, F.C.; Chiarantini, L.; Medas, D.; Sarais, G.; Cabiddu, S. Sediments distribution of trace metals in a coastal lagoon (Southern Sardinia, Mediterranean Sea): Assessment of contamination and ecological risk. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 34, 727–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melegy, A.A.; El-Bady, M.S.; Metwally, H.I. Monitoring of the changes in potential environmental risk of some heavy metals in water and sediments of Burullus Lake, Egypt. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, T.D.; Eleftheriadi, E.; Karageorgis, A.P.; Kambouri, G.; Papageorgiou, A.; Stavrakaki, I. Sediment grain size and elemental geochemistry in the coastal area of SW Messinia and the Gialova Lagoon. In COASTAL H2020 Programme 2020, The SW Messinia Case Study: Environmental Assessment of the Freshwater and Marine Systems; Karageorgis, A.P., Kanellopoulos, T.D., Eds.; Final Scientific Report; Hellenic Centre for Marine Research: Anavyssos, Greece; pp. 48–54.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).