Abstract
Assessing fish species richness at the scale of an entire watershed or multiple watersheds is important when designing conservation areas and maintaining aquatic biodiversity. Estimating biodiversity at this scale requires considering the effects of habitat heterogeneity within and across drainages on the species-area relationship (SAR). I examined the SAR using unusually complete data to assess fish species richness in minimally disturbed watersheds on large public lands in the Sand Hills ecoregion, southeastern United States of America (USA). My objectives were to compare (1) true richness with estimates produced by different species richness estimators and sampling designs and (2) species richness among reservations. Accurate estimates were obtained for five contiguous watersheds (780 km2 total) by using Chao 2 or first-order jackknife estimators, coupled with (1) a stratified design that apportioned sampling effort over 25 sample sites based on major spatial correlates of assemblage composition, including stream size and drainage basin identity and (2) sufficient sampling effort to collect enough individuals to include rare species. The greatest species richness was in streams within a large land holding characterized by greater instream habitat diversity, less disturbed land coverage, more forested land, and closer proximity to source pools than other reservations. Species richness in these streams was within the range observed in high diversity Neotropical and Indomalayan realms.
1. Introduction
Diversity at the species level is often expressed as species richness—the number of different species in a community, ecosystem, or region. Although other aspects of species-level biodiversity, such as composition and evenness, are also important, number of species is of special interest because of its relevance to conservation biology. It is currently estimated that dozens of species are extirpated each day with the possibility of losing 30–50% of all species by the middle of this century [Center for Biological Diversity, http://www.biologicaldiversity.org/programs/biodiversity/elements_of_biodiversity/extinction_crisis/]. This crisis affects nearly all taxonomic groups, and it is especially severe for freshwater fishes that inhabit lotic ecosystems. Many of these fishes are imperiled because of habitat degradation and fragmentation, flow modifications, translocation of species, over-exploitation, and pollution [,]. North America enjoys the greatest level of temperate freshwater biodiversity in the world, but about 700 species (nearly 40%) of freshwater or diadromous fish in North America are imperiled [].
It is important to accurately estimate the species richness of fish as a baseline for assessing the effectiveness of conservation and management programs. Because the number of species is invariably underestimated by sampling, a variety of techniques are used to estimate true species richness, including occupancy models and depletion methods (e.g., [,]). However, the most commonly used techniques are based on the species-area relationship (SAR), which describes the increase in number of species that occurs as sample area increases. The SAR is attributable largely to passive sampling effects and habitat heterogeneity. Passive sampling effects, which predominate at small spatial scales, occur because sampling larger areas yields more individuals, which increases the likelihood of encountering more species [,]. Habitat heterogeneity is important because more habitats are encountered as the sample area grows, and different habitats often support different species.
The SAR is graphically depicted as a species-area curve (SAC). There are several types of SACs depending on whether sample units are nested, contiguous, noncontiguous, or island; successively larger areas are constructed by retaining the spatial arrangement of sample units; or, the curve is constructed with means or single values []. Most SACs are constructed by plotting means computed from different numbers of sample units; i.e., by averaging the number of species in all possible pairs, triplets, etc. of sample units, each of comparable area []. SACs are scale-dependent, scale referring primarily to grain (the minimum scale sampled, usually the size of the individual sample unit) and extent (the distance between individual sample units) [,,]. Palmer and White [] concluded that there is a scale-dependent suite of SACs for a given region, which underscores the danger of assuming SACs developed for one scale are appropriate for others. The SAR also has a temporal analogue, the species-time relationship, which describes the increase in richness that typically occurs with an increase in the number of sampling events or sampling duration []. Like the SAR, the species-time relationship is attributable to passive sampling (more individuals collected with more time) and ecological processes that occur over time, such as species turnovers from habitat changes and/or dispersals [].
The SAR is influenced by sampling effectiveness because it affects the probability of species detection, which is an underlying component of the “sampling effects” explanation for SARs []. The likelihood of detecting a species is a function of the probability that the species is in the sample area and the probability of detecting the species [], the latter of which is a function of sampling effort and efficiency. Probability of detection is dealt with implicitly in SARs by the application of standardized effort and methodology.
The SAR tells us that richness in a sample will almost always underestimate actual richness, leading to the use of richness estimators that approximate the total richness in an area sampled with smaller sample units. Nonparametric estimators like the first and second order jackknife estimators, Chao family of estimators, bootstrap estimator, and incidence-based coverage estimator use information on the distribution of species in an assemblage []. Asymptotic estimators, such as the Michaelis-Menton formula, extrapolate the SAC to its asymptote and depend on the shape of the SAC [,]. Colwell and Coddington [] found that the Michaelis-Menton equation produced reasonable estimates of true richness from limited numbers of samples, although some nonparametric estimators (Chao 2 and second order jackknife) performed better. Others have found that the jackknife and other nonparametric techniques tend to underestimate richness at low sampling effort and overestimate it at high effort [,]. Estimators can be tested on benchmark data by computing the SAC and then calculating estimates for cumulative levels of sample pooling to determine the number of samples that are needed to produce stable estimates of true richness [,]. Richness estimators are usually used over small spatial scales where sampling effects are the predominant factor driving increases in species number, but can estimate richness over larger areas in which habitat heterogeneity is important. For example, Rosenzweig et al. [] accurately estimated the number of butterfly species in North America using a data set of species number in 110 ecoregions and asymptotic estimators based on the shape of the SAC.
Several studies have investigated methods for assessing fish species richness at the stream reach scale, usually defined as a stream segment (often 100–200 m) sufficient to include a range of mesohabitats (i.e., pools, riffles, and runs) that can be sampled within a relatively short period by electrofishing, seining, fish traps, or other methods [,,,,]. There has been less effort to assess the species richness of stream fish at larger scales, like an entire drainage or multiple drainages; e.g., within a park or conservation area, although this has been done for Great Lakes and Alabama watersheds [,]. Watershed-scale assessments are needed because the maintenance of biodiversity requires the conservation of whole watersheds rather than fragments []. Sampling protocols for the estimation of biodiversity at the scale of multiple, adjacent watersheds require the consideration of the habitat heterogeneity that occurs within and across drainages.
I examined the SAR for stream fish assemblages within watersheds located on large government land holdings—termed “reservations”, herein, although many were not established for conservation purposes—by combining data from numerous sampling programs. The resulting unusually complete data made it possible to empirically assess true species richness with substantial accuracy for individual watersheds and entire reservations. I used this data to address two objectives:
- (1)
- Identify an efficient sampling protocol for accurately estimating species richness at the drainage basin scale by comparing true species richness with species richness estimates produced by different estimators and sampling designs that were derived from sample subsets. I hypothesized that the efficiency of species richness estimation (as indicated by sampling effort required to produce accurate estimates) would be maximized by using a suitable estimator combined with a sampling design that accounted for key spatial factors that influenced species richness within and among drainage basins.
- (2)
- Using methods that were developed under objective 1, compare stream fish species richness among reservations that differed in the degree of disturbance, land use, and other factors. I hypothesized that stream fish species richness would be inversely correlated with anthropogenic development/disturbance within the reservations.
All study areas were in the Sand Hills ecoregion of the upper coastal plain of the southeastern United States, a region that was subject to extensive historical and ongoing anthropogenic modifications and traversed by blackwater streams recommended as a “highest priority focus” for conservation [].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
This study was conducted in the Sand Hills (Level IV) Ecoregion consisting of the inland portion of the southeastern United States of America (USA) coastal plain extending from west central GA to south central NC []. The Sand Hills have deep, sandy soils and are demarcated by the fall line from the higher elevation and geologically distinct Piedmont ecoregion. They have been anthropogenically modified since pre-settlement times, and they now consist of a mosaic of agricultural lands, urban areas, public natural areas, and military training facilities []. Sand Hill streams are generally low gradient and relatively shallow with predominantly sand substrates and relatively poorly defined pool-riffle-run mesohabitats. Instream structure consists primarily of snags, leaves, and other woody debris, followed by root masses, overhanging shoreline vegetation, and undercut banks. Aquatic plants are found in larger streams with sufficient insolation.
The study sites included first through fourth order streams in lightly populated and largely forested public lands or protected private holdings with less anthropogenic disturbance than found in the surrounding land [] (Figure 1). Most study sites represented “least-disturbed” conditions within the region, although a lesser number represented disturbed areas. The sites were in the Chattahoochee, Savannah, Pee Dee, and Cape Fear river basins.
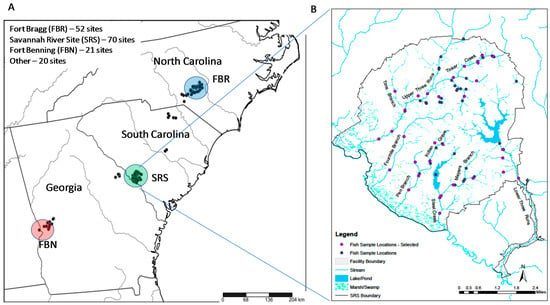
Figure 1.
Electrofishing sample sites in the Sand Hills ecoregion (A) including sample sites located on the Savannah River Site (B). “Selected” sites in (B) are used in the stratified design described in the text. Site in the center of the reservoir in (B) in was sampled before the reservoir was constructed.
The first objective of the study—develop an efficient approach to estimating drainage-wide species richness—was addressed with data from the Savannah River Site (SRS), a 780 km2 reservation that was originally created by the Department of Energy to produce nuclear materials. The SRS consists of relatively small, isolated industrial and administrative areas within a largely forested landscape that is composed mostly of pines in uplands and hardwoods in lowlands. It includes five major stream drainages ranging from 55–545 km2, although large portions of the two largest drainages (460 and 545 km2) are located outside of the SRS. Seventy sites were sampled in these drainages, some on multiple occasions, between 1990 and 2011 for a total of 138 samples. The sites were distributed throughout all five drainages to provide a strong basis for estimating SRS-wide species richness above the Savannah River floodplain (in Figure 1, indicated as “Marsh/Swamp” near the Savannah River). Thirteen additional sites in drainages near but outside the SRS were sampled once during 1992.
The second objective of the study—comparing reservations—was addressed with data collected from three military (i.e., Department of Defense) installations (Fort Bragg, NC; Fort Benning, GA; Fort Gordon, GA) and five state, federal, and private reservations (The Nature Conservancy, GA; Manchester State Forest, SC; Sand Hills State Forest, SC; Carolina Sand Hills National Wildlife Refuge, SC; and, Sand Hills Gamelands, NC) (Figure 1). The two largest military reservations, Fort Bragg (FBR) and Fort Benning (FBN), were sample extensively. Fifty-two sites were sampled at FBR: 55 samples from 32 sites during 2002 and 2008 by C. Bryan, Fort Bragg Endangered Species Branch, and 20 samples from 20 sites during 2009–2011 by Paller et al. []. Twenty-one sites were sampled at FBN: 15 during 2009–2011 by Paller et al. [] and six during 1990–2000 by W. Birkhead, Columbus State University. Twenty samples were collected from the state, federal, and private reservations during 2009–2011 by Paller et al. [] (“other” in Figure 1). Inclusion of the state, federal, and private reservations, which experienced different land uses than the military reservations and SRS, expanded the basis for assessing species richness within the Sand Hills.
2.2. Fish Sampling
All of the sample sites were sampled by direct current electrofishing, which effectively collected fish from the brush, root masses, snags, and other complex structure in Sand Hills streams. The protocol used in SRS streams during 1990, 1992, and 1994/1995 employed five to seven successive passes made while moving upstream through 100–400 m stream segments (mean = 265 m, SD = 70, average 54 channel widths) with the objective of reducing catch rates to near zero by the last pass. Preliminary assessments indicated that these reach lengths provided adequate data for assessing site-level species richness when multiple electrofishing passes were employed. Backpack electrofishing was used in small streams (under 5 m wide). Larger and more powerful gear (barge or boat) was used in larger streams to maintain sampling efficiency. Prior to sampling each site, electrofishing settings (primarily voltage) were adjusted to achieve the maximum catch rate that did not cause fish mortality. Block nets were deployed at the ends of the sample sites. All fish were counted, identified to species, and released.
A less intensive protocol was used to electrofish SRS streams in 1997, 2000, 2003, and 2007, consisting of one electrofishing pass that was made while moving upstream and sampling all microhabitats to collect as many fish as possible in a 150–200 m stream reach (average 42 channel widths). One backpack electrofisher and a two or three-person crew was used in small streams. Two back pack electrofishers and two crews, with a crew covering each bank, were used in larger streams (>5 m). A boat with a generator and electrofisher was used to sample the largest streams (13–17 m). Block nets were not used because they did not improve catch rates, were difficult to keep in place, and field observations indicated little movement of fish from sites while sampling.
Samples that were collected during 2009–2011 (20 from the SRS, 20 from FBR, 15 from FBN and 20 from the state, federal, and private reservations) were collected by direct current backpack electrofishing from 150 m to 285 m stream reaches, with most sites being 200 m long. Longer reaches were sampled in larger streams to better represent all habitats and species. One or two backpack electrofishers and a team of 2–6 personnel was used for electrofishing, with more equipment and personnel being used in larger streams. Two passes were made at each site. All fish were counted, identified, and released. A similar protocol was used to collect samples from FBR and FBN prior to 2009.
2.3. Environmental Data
Environmental data, referred to as “basic” were collected from all sample sites on all sample dates. Basic data included stream identity, year sampled, stream order, sample reach length, number of electrofishing passes, and mean stream width. Additional environmental data, referred to as “comprehensive”, were collected at all sites that were sampled during 2009–2011. Data derived from HUC-12 watershed maps that were generated from LIDAR and National Land Cover data included the amount and type of disturbed land for each watershed (low-, medium-, and high-intensity development plus cultivated, pasture, and bare lands), watershed area, watershed perimeter, drainage density, watershed length and elevation, basin relief and relief ratio, stream gradient, drainage direction, sinuosity, cumulative stream length, stream magnitude, length of mainstem tributaries, and Strahler stream order.
Additional comprehensive environmental data were collected in the field from the sites that were sampled during 2009–2011. Epifaunal substrate quality, pool substrate quality, pool variability, sediment deposition, channel flow status, channel alteration, channel sinuosity, bank stability, vegetative protection, and riparian vegetation were each rated on a scale of one (poor) to 20 (optimal) for each sample site and were summed to provide a summary measure of instream habitat quality []. In addition, 19 instream habitat attributes were either measured or estimated along 14–21 transects perpendicular to the direction of water flow at each sample site. Measured variables included maximum depth and stream width and left and right bank heights. Estimated variables included left and right bank angles; bank vegetative cover; undercut banks (percentage of the total wetted stream width under a bank); percent areal stream bottom coverage of clay, silt/muck, sand, gravel, and rocks; stream bank and riparian zone vegetation coverage; bank erosion; artificial channel modification; and, percent areal coverage of the stream bottom by macrophytes, overhanging vegetation, root mats, coarse woody debris, and small woody debris.
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Estimating Drainage-Wide Species Richness
Samples collected from the SRS were used to produce SACs for each stream drainage and a cumulative SAC for all SRS drainages together. The curves were constructed by plotting species number means computed from 100 random selections of different numbers of samples; i.e., by averaging 100 randomly selected groups of two samples, three samples, etc. Samples were selected without replacement, and the order in which they were collected was ignored. Unconditional variance estimates and 95% confidence intervals for the curves were computed, as shown in Colwell et al. [].
Sample-based SACs, as described above, reflect species density because they are based on the number of species accumulated in progressively larger sample areas, rather than on the accumulation of individuals []. In this paper, the term species richness generally refers to species density rather than to true species richness. However, sample-based SACs have been rescaled by individuals to represent true species richness [], in some cases, to make certain points more clearly.
The SAC for all SRS watersheds produced a benchmark for SRS-wide richness to compare with estimated species richness computed from sample subsets with the goal of selecting suitable richness estimator(s) and developing a parsimonious sampling design. I defined a parsimonious design as one that produced an accurate estimate of species richness with minimal redundant sampling effort expressed as the number of sites sampled and effort expended at each site (defined as number of electrofishing passes). The subset of samples that was included in such a design must include enough sample sites in the right locations to encompass all habitats that may support unique species, thus necessitating an understanding of the relationships between species composition and habitat. I used Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA), which is a constrained ordination technique, to investigate this relationship. The abundance by species data matrix used for CCA was centered and log (X + 1) transformed to deemphasize the influence of highly abundant taxa, and species appearing only once were eliminated because they did not contribute much information. The CCA was conducted with an automated forward selection procedure.
The samples that were used to develop a parsimonious sampling design were multiple (4–7) pass samples, which provided a more complete assessment of the numbers of species at each sample site than single-pass samples []. To examine the effects of sampling effort on the ability to detect true species richness, I estimated species richness for (1) the first pass and (2) the first two passes and compared these estimates to estimates produced with five- seven passes. To determine whether the final design was better than random sample selection, I compared it with null designs that included samples selected randomly with a random number generator from the complete SRS data set.
The species richness estimators evaluated were Chao 1, Chao 2, first-order jackknife, second-order jackknife, ACE, and Michaelis-Menten. The first five are nonparametric and the last is a curve-extrapolation estimator; formulas for each can be found in [] and []. I tested the estimators by estimating species richness for different levels of sample pooling and comparing the estimates to the SRS-wide benchmark to assess the number of samples needed for stable estimates of true richness []. I tested the estimators with the complete SRS data set, as well as the more parsimonious design based on a subset of the SRS samples.
2.4.2. Comparing Species Richness Among Reservations
I computed reservation-wide SACs and total species richness estimates for FBR and FBN and compared them with the SRS. I extrapolated the SAC for FBR and FBN to twice the number of samples that were collected to facilitate comparisons with the more extensively sampled SRS following []. The number of samples sites in the other reservations (state parks, etc.) was insufficient to compute SACs or species richness estimates, so I computed the average number of species per sample sites for them (i.e., alpha diversity) to compare with the average number per site at the SRS, FBR, and FBN using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) with alpha diversity as the dependent variable, stream width as the continuous variable, and reservation (SRS, FBR, or FBN, and smaller reservations combined) as the categorical variable. Stream width was used as a covariable because of its influence on species richness, as explained later. The average sample site length for all the locations in this comparison was generally comparable, as needed for valid comparisons of species richness among samples. I also restricted the comparison to sites with two electrofishing passes (or only included the first two passes at sites with more than two passes) to ensure comparable sampling effort, as was also needed for valid comparisons. The assumptions of normality and homoscedasticity required for ANCOVA were met by the data.
I used additive diversity partitioning [] to identify species richness components associated with individual sample sites, sample sites within a stream drainage, stream drainages within a reservation, and reservations within the Sand Hills to understand how spatial scale contributed to diversity within the reservations with sufficient data (SRS, FBR, and FBN). Diversity components were α1 (average sample site diversity within a drainage), β1 (diversity among sites from the same drainage), α2 (average drainage diversity within a reservation), β2 (diversity among drainages within reservations), α3 (average diversity within a reservation), β3 (diversity among reservations), and γ (total diversity across the entire study area). β1 was estimated as α2 − α1; i.e., the average amount of diversity among sites within a drainage not found within a single sample. β2 was estimated as α3 − α2; i.e., the average amount of diversity among drainages within a reservation not found within a single drainage. β3 was estimated as γ − α3; i.e., the average amount of diversity among reservations that was not found within a single reservation.
To identify reasons for differences in species richness among reservations, I analyzed the comprehensive habitat data collected from the SRS, FBR, and FBN using principal components analysis (PCA). By analyzing the correlation matrix, differently scaled variables were normalized to avoid dominance by those with greater variance. The significance of each PCA axis was assessed by comparing observed eigenvalues with eigenvalues that were generated by null models []. Because the total number of habitat variables was large relative to the number of sample sites (which can lead to indeterminate results), they were divided into three groups for separate analyses: instream habitat variables, watershed morphometry (i.e., size and shape), and watershed land cover.
All species richness estimates, SACs, and SAC extrapolations were computed with EstimateS (9.1.0) software []. Multivariate statistical analyses were conducted with PC-ORD [] and Canoco [], and ANCOVA was conducted with SYSTAT 12 [].
3. Results
3.1. Estimating Drainage-Wide Species Richness
Samples collected from SRS streams yielded 67 species (Table 1). Additional sampling (13 sites) in streams near the SRS yielded no additional species. Only one species (Cyprinus carpio) was non-native. The SAC for the SRS, when extrapolated to twice the number of samples collected, suggested the possible presence of three more undocumented species (70 in total, Figure 2). The presence of additional, undiscovered species was also suggested by some of the species richness estimators (Table 2). The Chao 1 and ACE estimators followed the SAC closely, indicating little predictive power (Figure 3). However, the jackknife and Chao 2 estimators approached the benchmark of 70 more quickly than the SAC, suggesting their potential usefulness in biodiversity surveys (Figure 3). Only the Michaelis-Menton estimator produced an estimate (65) that was lower than the number of species that were collected from the SRS. Excluding the latter, average estimated richness for the SRS was 70.

Table 1.
Fish species collected from first and second order (1–2) streams and third and fourth order (3–4) streams on the Savannah River Site.
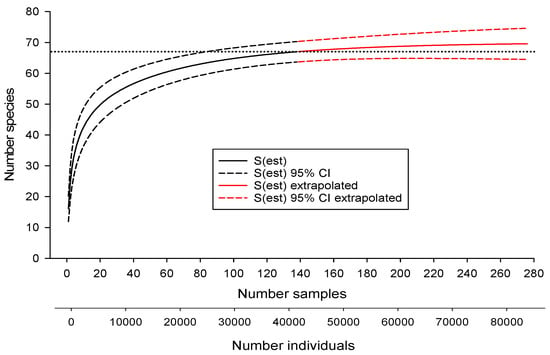
Figure 2.
Relationship between estimated number of fish species [S(est)], confidence intervals (CI), and number of samples and individuals collected from the Savannah River Site plus the extrapolated number if additional samples had been collected. Horizontal dotted line represents actual number of species collected by extensive sampling.

Table 2.
Number of fish species in Savannah River Site streams estimated by species richness estimators based on data from all sample sites or subsets of sample sites. Also shown are the minimum number of samples needed to estimate 67 species, the number actually collected.
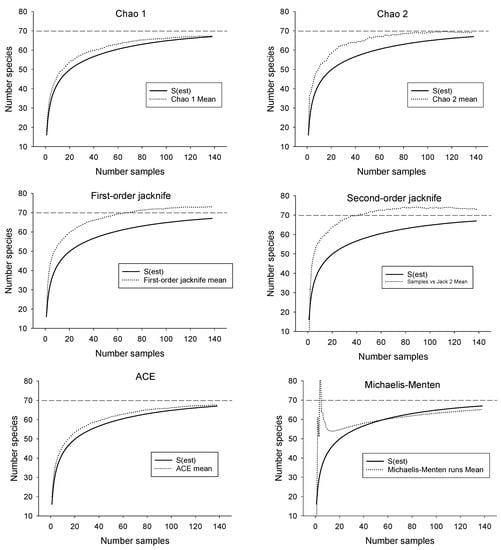
Figure 3.
Performance of six species richness estimators compared with the species accumulation curve for fish from streams on the Savannah River Site (138 samples). Dashed lines represent best estimate of total species richness.
The data used to produce the SRS SAC contained redundant information, including sites that were sampled repeatedly and closely adjacent sites, suggesting that an accurate estimate of species richness might be produced with fewer samples and a more efficient design that accounted for the major factors that affected species distributions. CCA of the basic environmental data (i.e., stream drainage, year sampled, stream order, sample reach length, number of electrofishing passes, and mean stream width) showed that stream width and Strahler stream order had the most influence on fish assemblage structure, as indicated by lambda values for marginal effects (Table 3). Marginal effects rank environmental variables in order of the variance that they explain individually, but do not account for shared covariance. Conditional effects, which showed the effect of each environmental variable independently of shared variance, indicated the importance of stream width (p = 0.002), but deemphasized order because of the latter’s correlation (r = 0.81) with stream width. The importance of stream width/order reflected the changes in species composition as stream size increased (Table 1). Other variables with lesser, but significant (p < 0.05), conditional effects included stream drainage and sample year.

Table 3.
Permutation test results for a canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) of the effects of environmental variables on fish species composition in Savannah River Site (SRS) streams.
Additive diversity partitioning provided a scale-related perspective on species richness that agreed with the CCA (Table 4). The percentage of species diversity that is associated with individual sites (α1) and sites within SRS streams (β1) was 20 and 42, respectively, as compared with 38 (β2) for differences among drainages, again reflecting the relative importance of the species composition changes that occurred among sites and stream orders within the same drainage (Table 4).

Table 4.
Additive diversity partitioning of fish species richness in Sand Hill streams showing diversity components associated with progressively larger spatial scales.
The preceding analyses indicated that an efficient design for accurately assessing species richness should include sample sites representing different stream orders in different basins. One such approach is to make the number of sites in each stream order and basin proportional to the stream length of this order/basin combination, divided by the total length of all streams in all basins (Table 5). I largely restricted this design to 38 SRS sites that were sampled during 1990–1995 with 4–7 electrofishing passes because multiple passes collected more fish but included four sites that were sampled during 2009 with two passes to represent areas that were not sampled during 1990–1995. When a site was sampled more than once, or when two or more samples were closely spaced, all but one was randomly excluded resulting in a final design with 32 sites representing 60 species (86% of the estimated 70 total), hereafter referred to as the stratified design. With this design, Chao 2 and first-order jackknife estimators produced estimates of about 71 species, near the 70 estimated from the full data set (Table 2). The Chao 2 estimator was more stable at this level than the jackknife estimators, which continued to rise, suggesting the potential for overestimation (Figure 4, Table 2).

Table 5.
Stratified design for estimating species richness. Sites were apportioned based on stream length in each stream order and drainage basin (see text).
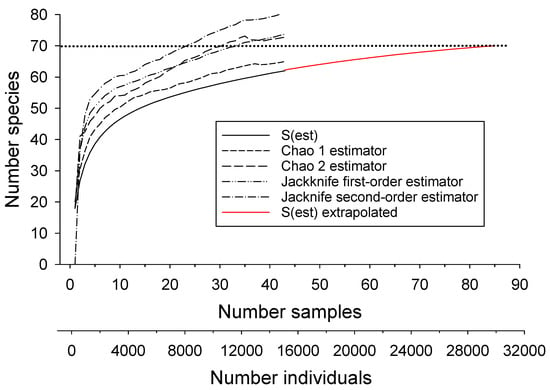
Figure 4.
Performance of species richness estimators compared with the species accumulation curve [S(est)] for fish from collected from 32 sites selected based on a stratified sampling design. Also shown are the extrapolated number expected if additional samples had been collected. Dotted line represents best estimate of total species richness.
Both CCA and additive diversity partitioning indicated that changes in species composition among stream orders contributed to SRS-wide species richness. Although such changes can result from the addition or replacement of species, additions, rather than replacements, were largely responsible for the increased richness in larger SRS streams (Table 1). This suggested that small streams could be excluded when estimating richness over a drainage-wide or larger scale because they did not support novel species. Eliminating the six headwater sites among the 32 sites in the stratified design had almost no effect on the accuracy of the species richness estimates (Table 2).
When using only the first two passes of the data used in the stratified design, all of the estimators except the second order Jack-knife underestimated richness (Table 2). Although spatial coverage was the same as with the original stratified design, the number of individuals that were collected was fewer (4211 as compared with 12,390), thus reducing the probability of collecting all species.
The average number of species collected in 20 sets of 32 samples that were randomly chosen from the full data set was 53.3 (SD = 3.1) as compared with 60 for the stratified design. The average Chao 2 and first order jackknife estimates of SRS-wide richness using the random data were 60.6 and 62.6, respectively. Both of the values differed significantly (p < 0.001) from the empirically determined richness of 67 (t-test for a difference between a parametric mean and sample means []), indicating the superiority of the stratified design.
3.2. Comparing Species Richness Among Reservations
Species density curves showed that richness was greater at the SRS than FBR and FBN (Figure 5). Extrapolated richness at FBN was slightly greater than at FBR, although broad confidence intervals for FBN because of the limited sampling negated firm conclusions. There were insufficient data from the other reservations to compute SACs. The Chao 2 estimator also indicated higher richness at the SRS (69.1, SD = 2.5) than FBR (43.3, SD = 4.1) or FBN (46.4, SD = 9.2). This was not the result of collecting more fish at the SRS (i.e., a passive sampling effect). The average number of fish per site (based on sites with two electrofishing passes) was 110 for the SRS, 114 for FBR, and 164 for FBN. Furthermore, a plot of species versus the number of individuals showed a slightly greater difference between the SRS and the other reservations than the species density curve, again indicating greater diversity in SRS streams. Greater richness at the SRS was also suggested by alpha diversity (average number species per sample site based on two electrofishing passes), which was 14 at the SRS, as compared with 8, 9, and 8, respectively, for FBN, FBR, and the combined smaller reservations. ANCOVA showed that stream size and reservation identity had statistically significant effects on species richness (p < 0.001 for both); however, the interaction between these variables was not significant; i.e., species richness increased with stream size and was greater in SRS streams than elsewhere, regardless of stream size.
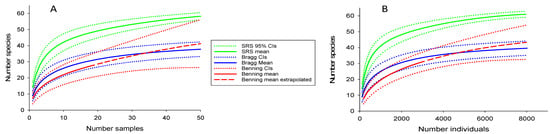
Figure 5.
Species accumulation curves for the Savannah River Site (SRS), Fort Bragg, and Fort Benning. Curve (A) shows relationship between number of species and samples (species density), and (B) shows relationship between number of species and individuals captured (species richness).
Additive diversity partitioning showed that species richness at the SRS was greater than at the other reservation at all scales, including individual sites, among sites within a drainage, and among drainages (Table 4). Individual SRS drainages varied in estimated species richness (Chao 2) from 57 to 71; however, each supported more species than the collective drainages of FBR and FBN. The most diverse and largest drainage on the SRS, Upper Three Runs, supported an estimated 71 species, comparable to the entire number of species that is found on the SRS.
The three PCAs identified habitat differences that may have contributed to species richness differences among reservations. The first two axes of all three PCAs were significant at p < 0.001. The first axis of the PCA of basin size and shape data showed that SRS drainage basins were about the same size as basins in the other reservations (Figure 6A, Table 6). Thus, greater richness in SRS streams was not due simply to sampling larger basins with more diverse fish assemblages. This PCA also showed that SRS drainage elevations and stream gradients were somewhat lower than at the other reservations (average 47 m versus >65 m and average 0. 2 vs. 0.3 cmm−1, respectively). The first axis of the PCA of the instream habitat data represented a mesohabitat and substrate gradient, extending from runs with sand bottoms to riffles with more varied substrates, including gravel, silt, and woody debris, with many of the SRS sites exhibiting the latter characteristics (Figure 6B, Table 6). The second axis represented a gradient of erosion, bank height (indicator of channel incision), and channel modification, with higher scores indicating greater prevalence of these features. There was little separation of the reservations along this axis. The first axis of the PCA of the landcover data largely represented a disturbance gradient extending from developed land and land with more scrub/shrub and deciduous forest cover to land with more pine forest (Figure 6C, Table 6). Almost all SRS sites clustered towards the latter end of this gradient, indicating less developed and more forested land. The second axis represented a gradient of increasing grassland, cultivated land, and road mileage. Most SRS and some FBR sites exhibited less of this cover than the other reservations.
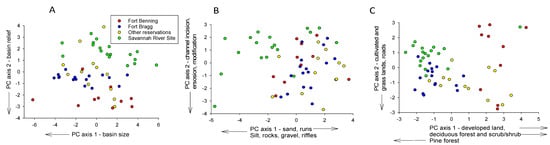
Figure 6.
Principal Components Analyses of sample sites based on variables representing (A) basin size, shape, and relief, (B) instream habitat variables, and (C) land cover variables. Also shown are variables with the strongest effect on each axis plus their direction of increase.

Table 6.
Variable loadings (Pearson r) on axes 1 and 2 of three Principal Components Analyses of sample sites based on (1) variables representing, basin size, shape, and relief, (2) instream habitat variables, and (3) land cover variables. Only variables with Pearson r values > 0.4 are shown.
Although biodiverse compared with the other reservations, the SRS did not support all species in the study area. Total estimated species richness for the entire study area (i.e., all reservations combined) was 94 using the Chao 2 estimator and 95 using the first-order jackknife estimator as compared with 70 for the SRS. Diversity partitioning showed that substantial diversity within the entire study area (on an average basis) was associated with differences among reservations (Table 5). Twenty-five, 5, 5, and 1 unique species were collected from the SRS, FBR, FBN, and the smaller reservations, respectively, with the larger SRS number partly the result of greater sampling effort. While most of these unique species were rare, some were major components of the local ichthyofauna; e.g., the sandhills chub Semotilus lumbee in FBR, the broadstripe shiner Pteronotropis euryzonus and dixie chub Semotilus thoreauianus in FBN, and the yellowfin shiner Notropis lutipinnis, bluehead chub Nocomis leptocephalus, and creek chub Semotilus atromaculatus in the SRS. These differences reflect important changes in species composition across the larger scale of the Sand Hills ecoregion.
4. Discussion
4.1. Estimating Drainage-Wide Species Richness
Most efforts to estimate fish species richness emphasize the “stream reach” scale, typically a stream segment of several hundred meters or less, for the purposes of studying community structure, assessing the effects of environmental perturbations, identifying cost-effective sampling strategies, and ensuring data quality. Other studies address fish species richness at regional, continental, or global scales in order to identify large-scale biodiversity patterns and processes that create them [,]. Although species lists have been compiled for many drainage basins (e.g., []), relatively few studies [,,] have explicitly addressed the problem of estimating fish species richness at the scale of the entire watershed, and no studies have addressed this issue at the scale of multiple contiguous basins, despite its potential importance. The drainage basin or watershed is a highly appropriate unit for conservation because of the physical connectivity of lotic ecosystems combined with the vagility of fish and other aquatic organisms. Accurately and efficiently estimating species richness over multiple, contiguous watersheds is important when designing conservation areas, assessing the large-scale benefits of conservation programs, and identifying potential diversity “hotspots”. From a theoretical standpoint, metacommunity theory emphasizes the need to characterize biological communities at multiple scales to understand how the dispersal of interacting species influences local and regional biodiversity [].
Assessing fish species richness at a drainage basin or larger scale necessitates the effective sampling of numerous individual belonging to differently behaving species that are distributed among different habitats. The basic problem in such large-scale surveys is not sampling all individuals within a habitat, hence missing some species by chance, combined with the problem of not sampling all habitats, some of which may support unique species for ecological reasons []. Regarding catchment scale sampling, Smith et al. [] identified practical problems that are related to differences in gear efficiency across diverse habitats, the species selectivity of different gears, and the need to identify an appropriate level of sampling effort. They believed that using a variety of gear types helped to address these problems. Multiple gears types were not used in this study because abundant coarse and fine woody debris made it difficult to deploy nets and because electrofishing was the historical method of choice due to its overall effectiveness and convenience. The effects of gear bias and related sampling issues on the accuracy of the species richness estimates presented herein is impossible to quantify; however, they were probably greater for large streams where greater habitat volume made it harder to catch fish and to adequately sample all habitats.
Unlike stream-reach scale surveys that encompass habitat diversity on spatial scales of pools, riffles, runs, and smaller, drainage basin or multiple drainage basin surveys must consider larger scale habitat heterogeneity. The most important source of this heterogeneity observed herein was stream width (or its correlate stream order), which was associated with changes in species composition that mainly were caused by the addition of species with increasing stream size. The influence of stream size is supported by previous research showing that it and related measures (e.g., drainage basin area) create environmental heterogeneity that strongly affects fish richness and composition [,,]. Secondary to stream size, and accounting for less variance, were differences in species composition among drainage basins. I did not attempt to identify reasons for differences among drainages basins but habitat, stream-size related factors, and proximity to source pools in larger watercourses likely played a role, as explained more later.
The strata in the stratified design were stream order (a convenient representation of stream size) and drainage basin to account for the major factors affecting species composition in the study area. The result was a mix of higher and lower order stream sites that are located on the main stems and tributaries of all five SRS drainages, with sites sampled randomly within each stratum to the extent possible. The stratified design also spaced the sample sites relatively evenly over the stream networks on the SRS, thereby resembling the spatially spread (hyperdispersed) sampling strategy that was used by Rosensweig et al. [] to efficiently estimate the species richness of butterflies over 110 North American ecoregions. They found that estimates were more accurate when sample sites were spread uniformly than when clustered or selected randomly. The samples in the stratified design were drawn from a data set collected over the shortest time possible to minimize the influence of species changes over time (i.e., species-time relationship) on the results. Research in central European streams showed that the number of species was more strongly influenced by spatial scale than by time, although the latter had a significant effect, especially in larger streams with greater connectivity to other watercourses that facilitated colonization [].
The level of effort associated with the stratified design was much less than the total level of effort expended at the Savannah River Site, expressed as the number of sites sampled (32 vs. 70) and the number of individuals collected (12,390 versus 39,087). It was superior to the random selection of 32 sites, which detected fewer species and almost always resulted in the underestimation of species richness. Ideally, the stratified approach would have been evaluated further by generating multiple stratified designs for statistical analysis, but the number of appropriately located sites sampled with sufficient effort was inadequate for this. Despite this limitation, the results suggest that the efficiency of species richness estimation can be maximized by using a sampling design that accounts for key spatial factors that influence species richness, as was originally hypothesized.
I restricted the stratified design to sites that were sampled with multiple (4–7) electrofishing passes because multiple-pass electrofishing usually results in the detection of more species than single pass electrofishing. For example, Meador et al. [] reported that as little as 40% of estimated total species richness was collected on the first pass, and Kimmel and Argent [] reported that a second electrofishing pass usually added at least one species. Paller [], working with multiple-pass data collected from some of the streams in the present study, found that the number of species increased asymptotically with the number of passes. There are two reasons that more passes collect more species. One is a passive sampling effect—more passes collect more individuals, hence are more likely to detect rare species. The other, less well-documented reason, is that some species may be more likely to appear during a second or third electrofishing pass because of their behavior combined with gear and/or observer biases. I observed that some benthic species (e.g., madtoms Noturus spp. and/or darters Etheostoma and Percina spp.) were often missed on the first pass, perhaps because they initially remained on the bottom where they were hard to see. Others have reported that darters and cyprinids [] or cyprinids and centrarchids [] were most often missed on the first pass.
When restricted to the first two passes, species richness estimates that were based on the stratified design fell slightly short of the benchmark 70 species. Although not analyzed, it is probable that one-pass sampling would produce larger underestimates. The reduced efficacy of two-pass sampling was at least partly due to passive sampling effects—4211 individuals were collected by two-pass sampling as compared with 12,390 by multiple-pass sampling. It may be possible to reduce this effect by increasing the time spent shocking during each pass, increasing the number of electrofishers [], or increasing sample site length since all would result in the collection of more individuals.
Reducing the number of electrofishing passes compromised the accurate estimation of SRS-wide species richness. However, first-order stream sites could be eliminated without such compromise, thereby decreasing the total effort. Modifying the stratified design by eliminating six first order stream sites (20% reduction in number of sites) resulted in no change in the number of species collected from the unmodified design (60), a slight reduction in the number of individuals collected (10,411 as compared with 12,390), and no reduction in the accuracy of species number estimates. First-order stream habitats within the study area did not support species absent from higher order sites nor did they usually support large numbers of individuals. Thus, eliminating them did not affect the inclusion of habitats with unique species nor the number of individuals collected—two factors that are largely responsible for the SAR. Similarly, Smith and Jones [] recommended allocating most sampling effort to third order streams when sampling for watershed-level species richness in Great Lakes streams. However, eliminating or reducing the sampling effort in first or second order streams is inappropriate when these streams support species that differ from those in higher order streams.
Of the six species richness estimators that were examined in this study, the two that produced the most accurate estimates of species richness were the nonparametric Chao 2 and first-order jackknife. Both displayed the desirable features of approaching the benchmark more quickly than the species accumulation curve and stabilizing near the benchmark without greatly overshooting it. In contrast, the other estimators followed the species accumulation curve closely (thereby exhibiting little predictive power) and/or underestimated or overestimated species richness. The variance around all species richness estimates was high when using the stratified design. Although it could be decreased by sampling more sites, large variances are typical of species richness estimators that extrapolate beyond the limits of the data [].
Various estimators have been used by researchers to assess richness at the stream reach scale, including the jackknife, bootstrap, Chao, and Michaelis-Menton [,,,]. Glowacki and Penczak [] found that no estimator was consistently accurate, but preferred the homogenous model of Chao and Lee [], followed by the first-order jackknife at the reach scale. Estimators that were used at the watershed scale include the first-order jackknife for watersheds in the Great Lakes region [] and the Chao 2 for a small watershed in Alabama []. In the latter case, the Chao 2 method produced over-estimates at sites with high numbers of uniques and low numbers of duplicates. The Chao and jackknife families of estimators are dependent on the number of species that are found in only one sample (uniques) or two samples (duplicates) [,]. Since these variables depend on relative abundance patterns, sampling efficiency, and number of samples, it is impossible to predict the success of these estimators using other data sets. Furthermore, all of the estimators compensate only for the incomplete sampling of individuals and not for the incomplete sampling of habitats. Thus, when sampling at the drainage basin scale, they must be paired with a sampling design that adequately represents all habitats that may support unique species.
The SRS data showed that samples from as few as 25 sites (stratified design minus first-order streams), which represented about 85% of the total species, could provide a basis for the accurate estimation of total species richness across five contiguous watersheds occupying 780 km2. For comparison, 9–25 sites and 17–49 sites were needed to represent 80% and 90%, respectively, of the species in individual watersheds (24–433 km2) in the Great lakes region [], and a mean of 8.4 and 15.5 sites were needed to represent 80% and 90%, respectively, of the species in the Little Choctawhatchee River watershed (416 km2) in southeastern Alabama []. These results suggest that sampling about 25–30 sites can provide an adequate basis for estimating species number in individual, small watersheds or contiguous, similar small watersheds assuming sufficient reach-scale sampling at each site. Reach scale sampling at the SRS was relatively intensive—4–7 electrofishing passes within a reach averaging 50 channel widths in length—as compared with one electrofishing pass within a reach averaging 30 channel widths in the other studies that are mentioned above. Reach-scale sampling effort will need to vary with conditions but must be sufficient to collect most species present, and reductions in reach-scale effort will likely require the addition of more sites to assess species richness at the watershed-scale. Additional requirements for accurate watershed-scale species richness assessments are an adequate sampling design that represents all habitats, and the analysis of the data with an appropriate species richness estimator. In all cases, a SAC should be constructed, and, if necessary, extrapolated to assess sampling adequacy by determining if a majority of the species have been collected (e.g., Figure 4, see []).
4.2. Comparing Species Richness Among Reservations
An important reason for estimating species richness is to identify high diversity areas of possible conservation interest. All of the measures of species richness indicated that the SRS supported relatively high fish diversity for the Sand Hills ecoregion. Species richness and density curves were substantially steeper for the SRS than for FBN and FBR, and species richness estimates for the SRS were higher than for these reservations. Alpha diversity was significantly higher at the SRS than at all other reservations, including state, federal, and private reservations that were established and managed for conservation related purposes. SRS diversity was exceptional at all spatial scales, including stream reach, drainage, and across drainages. This was not simply a result of the large size of the SRS (780 km2), which was only slightly greater than the other reservations (650 and 737 km2, respectively, for FBR and FBN). Greater instream habitat diversity, less disturbed land coverage, and higher proportions of forested land coverage were likely contributing factors. These features are associated with fish assemblages that exhibit high biotic integrity and support many species, including those that are sensitive to disturbance.
The assemblage of fish communities is the result of local abiotic and biotic factors that select or exclude potential colonists based on their adaptive traits and regional factors that affect the ability of colonists to reach local habitats []. Habitat features, such as those described previously, are important locally; the size of regional source pools and the distance from them are important regionally. The immediate source pools for the tributaries under study were the major sixth or seventh order rivers that they were connected to: Savannah River for SRS streams, Apalachicola/Chattahoochee River for FBN streams, and Cape Fear and by Pee Dee Rivers for FBR streams. Diversity differences among these large rivers could create diversity differences among their tributaries; however, the total number of species in the Savannah (149) and Apalachicola/Chattahoochee (153) River systems is almost identical []. The 119 species in the Cape Fear River system [] is about 20% lower, which seems unlikely to fully explain why species richness in FBR drainages was 38% lower than in SRS drainages. However, distance from the source pool (connectivity) can also affect colonization rates. Connectivity can increase richness for catostomids, cyprinids, and darters due to immigration from larger streams [,], and such proximity-related effects can occur up to 20 km from the confluence with mainstem rivers []. The average straight-line distance of the SRS sample sites from the Savannah River was 13.6 km, as compared with 25.9 km and 25.4 km for FBN and FBR, respectively, suggesting that this factor could have contributed to the greater diversity of SRS tributaries.
Estimated species richness for individual SRS drainages ranged from 57–71. This can be compared with other North American drainages, despite differences in sampling methods (especially number of sites and individuals sampled, see []) that weaken the comparison. Species richness was 19 in the Virgin River, a tributary of the Colorado River, (123 collections from 76 sites []), and 23 in the Canadian River basin, Texas (eight collections from eight sites []). Many species at both locations were non-native, and both locations were in the western United States where fish communities are relatively depauperate due to biogeographic factors and habitat instability. Forty species were collected from the Pine River drainage in Michigan (48 samples from 12 sites []) and 45 species were collected from the Broad River in Georgia (49 samples from 45 sites) []. The preceding numbers represent species observed, rather than estimated total species richness. Watershed-level species richness estimates derived from Chao 2 or first-order jackknife estimators were 23–58 in nine Great Lakes drainages [] and 43–59 (depending upon season) in the Little Chocktawhatchee River in Alabama []. Estimated species richness (second-order jackknife) at a single site ranged from 24–47 in Illinois streams that are located in the relatively species rich Mississippi River basin []. SRS streams compare favorably to these estimates but are less than the 117 species estimated for the Ivinhema River basin in the Mato Grosso do Sul State of Brazil [] and about the same or slightly greater than estimated for headwater streams of the Paraguay and Parana basins in the Pantanal region of Brazil (50–53 species) [] or the Meghna river estuary in Bangladesh (53 species, []). Thus, biodiversity in SRS streams appears relatively high—greater than in other streams within the Sand Hills ecoregion, higher than in many North American streams, and within the range observed in high diversity Neotropical and Indomalayan biogeographical realms. Upper Three Runs, the SRS stream that supported the greatest fish species richness (71) is also known for its exceptional diversity of aquatic insects, over 550 species, which is one of the highest values worldwide []. These data suggest that SRS streams, especially Upper Three Runs, represent potential “biodiversity hotspots”, at least for the Sand Hills ecoregion, and show how drainage-wide diversity assessments can identify streams of conservation interest.
5. Conclusions
Estimation of species richness at the scale of the drainage basin and/or contiguous, ecologically similar basins is needed to identify streams of high biodiversity for protection, and because the conservation of lotic aquatic resources is most effective at a watershed scale. The species richness of stream fish at this scale is strongly influenced by differences in species composition that are associated with stream reaches of different size, although differences in species composition among basins can also be significant. Thus, assessing species richness at the drainage basin or larger scale requires a sampling design that apportions sample sites among stream reaches of different size within each basin of interest to ensure the inclusion of all habitats that may support unique species. Exceptions may include small headwater streams that do not support unique species. This approach, which tends to disperse sampling effort uniformly through the study area, must be combined with sufficient sampling effort at each site to avoid missing appreciable numbers of species by chance. An appropriate design combined with sufficient sampling effort can be used in conjunction with species number estimators, such as the first order jackknife or Chao 2, to accurately estimate species richness at the drainage basin or larger scale with less sampling than if sites were selected randomly. Application of this approach within the Sand Hills ecoregion of the southeastern USA identified differences in species richness among several public and private land holdings. The most species-rich holding was characterized by large size, relatively little anthropogenic development, and proximity to a large river that could act as a source pool for fishes.
Funding
This research was funded by the Savannah River National Laboratory, operated by Savannah River Nuclear Solutions LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract DE-AC09-798861048. Funding was also provided by the U.S. Department of Defense, Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP), grant number RC-1694.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank DoD natural resource managers in Fort Benning, Fort Bragg, and Fort Gordon, with special thanks to Hugh Westbury, Charles Bryan, and Robert Drumm. Appreciation is extended to Blair Prusha, Colby Farrow, and Matthew Brimm for assisting with field sampling and Susan Blas for mapping sample sites. I thank three anonymous reviewers for suggestions that improved this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.L.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfman, G.S. Fish Conservation: A Guide to Understanding and Restoring Global Aquatic Biodiversity and Fishery Resources; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jelks, H.L.; Walsh, S.J.; Burkhead, N.M.; Contreras-Balderas, S.; Diaz-Pardo, E.; Hendrickson, D.A.; Lyons, J.; Mandrak, N.E.; McCormick, F.; Nelson, J.S.; et al. Conservation status of imperiled North American freshwater and diadromous fishes. Fisheries 2008, 33, 372–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.D.; Conroy, M.J. Estimation of species richness. In Measuring and Monitoring Biodiversity—Standard Methods for Mammals; Wilson, D.E., Cole, J.D., Rudran, R., Foster, M., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Holtrop, A.M.; Cao, Y.; Dolan, C.R. Estimating sampling effort required for characterizing species richness and site-to-site similarity in fish assemblage surveys of wadeable Illinois streams. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2010, 139, 1421–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, E.F.; McCoy, E.D. The statistics and biology of the species-area relationship. Am. Nat. 1979, 113, 791–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.W.; White, P.S. Scale dependence and the species-area relationship. Am. Nat. 1994, 144, 717–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiner, S.M. Six types of species-area curves. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotelli, N.; Colwell, R.K. Quantifying biodiversity: Procedures and pitfalls in the measurement and comparison of species richness. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, M.L. Preston’s ergodic conjecture: The accumulation of species in space and time. In Biodiversity Dynamics: Turnover of Populations, Taxa and Communities; McKinney, M.L., Drake, J., Eds.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 311–348. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, S.; Ostling, A.; Harte, J.; del Moral, R. Impact of curve construction and community dynamics on the species-time relationship. Ecology 2007, 88, 2145–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cam, E.; Nichols, J.D.; Hines, J.E.; Sauer, J.R.; Alpizar-Jara, R.; Flather, C.H. Disentangling sampling and ecological explanations underlying species-area relationships. Ecology 2002, 83, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Colwell, R.K.; Coddington, J.A. Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1994, 345, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdridge, L.R.; Grenke, W.C.; Hatheway, W.H.; Liang, T.; Tosi, J.A. Forest Environments in Tropical Life Zones; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Raaijmakers, J.G.W. Statistical analysis of the Michaelis-Menten equation. Biometrics 1987, 43, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, S.A. A critique of the use of jackknife and related non-parametric techniques to estimate species richness. Community Ecol. 2004, 5, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, R.B. Species richness estimators: How many species can dance on the head of a pin? J. Anim. Ecol. 2005, 74, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotelli, N.; Colwell, R.K. Estimating species richness. In Frontiers in Measuring Biodiversity; Magurran, A.A., McGill, B.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig, M.L.; Turner, W.R.; Cox, J.G.; Ricketts, T.H. Estimating diversity in unsampled habitats of a biogeographical province. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angermeier, P.L.; Smogor, R.A. Estimating number of species and relative abundances in stream-fish communities: Effects of sampling effort and discontinuous spatial distributions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, M.H. Relationships among number of fish species sampled, reach length surveyed, and sampling effort in South Carolina coastal plain streams. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1995, 15, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennard, M.J.; Pusey, B.J.; Harch, B.D.; Dore, E.; Arthington, A.H. Estimating local stream fish assemblage attributes: Sampling effort and efficiency at two spatial scales. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2006, 57, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M.; Wells, S.P.; Mather, M.E.; Muth, R.M. Fish biodiversity sampling in stream ecosystems: A process for evaluating the appropriate types and amount of gear. Aquat. Conserv. 2014, 24, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Jones, M.L. Watershed-level sampling effort requirements for determining riverine species composition. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, J.M.; Stewart, P.M.; Miller, J.M. Species richness estimation and rarefaction of fish assemblages in a small watershed. Southeast. Nat. 2014, 13, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.S.; Benfield, E.F.; Bolstad, P.V.; Helfman, G.S.; Jones, E.B.D., III. Stream biodiversity: The ghost of land use past. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14843–14847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HydroGeoLogic. Prepared for the Legacy Resource Management Program, Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program, and Environmental Security Technology Certification Program. In Proceedings of the Southeast Region Threatened, Endangered, and At-Risk Species Workshop, Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 27 February–1 March 2007; HydroGeoLogic, Inc.: Reston, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, G.E.; Omernik, J.M.; Comstock, J.A.; Lawrence, S.; Martin, G.; Goddard, A.; Hulcher, V.J.; Foster, T. Ecoregions of Alabama and Georgia, (Color Poster with Map, Descriptive Text, Summary Tables, and Photographs); Map Scale 1:1,700,000; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2001.
- Loehle, C.; Wigley, T.B.; Schilling, E.; Tatum, V.; Beebe, J.; Vance, E.; van Deusen, P.; Weatherford, P. Achieving conservation goals in managed forests of the Southeastern Coastal Plain. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paller, M.H.; Feminella, J.; Kosnicki, E.; Sefick, S.; Miller, J.; Tuberville, T.; Fletcher, D.; Grosse, A.; Harris, B.; Sterrett, S.; et al. Factors Influencing Stream Fish Species Composition and Functional Properties at Multiple Spatial Scales in the Sand Hills of the Southeastern United States. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2016, 145, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, M.H.; Feminella, J.; Kosnicki, E.; Sefick, S.; Miller, J.; Tuberville, T.; Fletcher, D.; Grosse, A.; Harris, B.; Sterrett, S.; et al. Development of Ecological Reference Models and an Assessment Framework for Streams on the Atlantic Coastal Plain; Final Report SERDP Project RC-1694; SRNL-STI-2014-00050; Savannah River National Laboratory: Aiken, SC, USA, 2014.
- SCDHEC (South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control). Standard Operating and Quality Control Procedures for Macroinvertebrate Sampling; Technical Report No. 004-98; Bureau of Water, Division of Water Monitoring, Assessment and Protection, Aquatic Biology Section: Columbia, SC, USA, 1998.
- Colwell, R.K.; Mao, C.X.; Chang, J. Interpolating, Extrapolating, and Comparing Incidence-Based Species Accumulation Curves. Ecology 2004, 85, 2717–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazdon, R.L.; Colwell, R.K.; Denslow, J.S.; Guariguata, M.R. Statistical methods for estimating species richness of woody regeneration in primary and secondary rain forests of Northeastern Costa Rica. In Forest Biodiversity Research, Monitoring and Modeling: Conceptual Background and Old World Case Studies; Dallmeier, F., Comiskey, J.A., Eds.; Parthenon Publishing: Paris, France, 1998; pp. 285–309. [Google Scholar]
- Colwell, R.K.; Chao, A.; Gotelli, N.J.; Lin, S.; Mao, C.X.; Chazdon, R.L.; Longino, J.T. Models and estimators linking individual-based and sample-based rarefaction, extrapolation and comparison of assemblages. J. Plant Ecol. 2012, 5, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lande, R. Statistics and partitioning of species diversity and similarity among multiple communities. Oikos 1996, 76, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, B.; Grace, J.B. Analysis of Ecological Communities; MjM Software Design: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Colwell, R.K. EstimateS: Statistical Estimation of Species Richness and Shared Species from Samples, version 9; User’s Guide and Application. 2013. Available online: http://viceroy.eeb.uconn.edu/estimates/EstimateSPages/EstSUsersGuide/EstimateSUsersGuide.htm (accessed on 29 January 2018).
- McCune, B.; Mefford, M.J. PC-ORD. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data, version 6; MjM Software: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5); Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- SYSTAT Software, Inc. SYSTAT 12; SYSTAT Software, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry the Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Oberdorff, T.; Guégan, J.-F.; Hugueny, B. Global scale patterns of fish species richness in rivers. Ecography 1995, 18, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D. Connectivity and vagility determine spatial gradients and diversification of freshwater fish in North America and Europe. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 116, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, P.A.; Beauchard, O.; Bigorne, R.; Blanchet, S.; Buisson, L.; Conti, L.; Cornu, J.-F.; Dias, M.S.; Grenouillet, G.; Hugueny, B.; et al. A global database on freshwater fish species occurrence in drainage basins. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.L.; Swan, C.M.; Auerbach, D.A.; Campbell Grant, E.H.; Hitt, N.P.; Maloney, K.O.; Patrick, C. Metacommunity theory as a multispecies, multiscale framework for studying the influence of river network structure on riverine communities and ecosystems. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2011, 30, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, A.L. Species diversity and longitudinal succession in stream fishes. Ecology 1968, 49, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, M.H. Relationship between fish assemblage structure and stream order in South Carolina coastal plain streams. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1994, 123, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Súarez, Y.R.; Valério, S.B.; Tondado, K.K.; Florentino, A.C.; Felipe, T.R.A.; Ximenes, L.Q.L.; Lourenço, L.S. Fish species diversity in headwaters streams of Paraguay and Paraná Basins. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2007, 50, 1678–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erős, T.; Schmera, D. Spatio-temporal scaling of biodiversity and the species-time relationship in a stream fish assemblage. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, M.R.; McIntyre, J.P.; Pollock, K.H. Assessing the efficacy of single-pass backpack electrofishing to characterize fish community structure. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, W.G.; Argent, D.G. Efficacy of two-pass electrofishing employing multiple units to assess stream fish species richness. Fish. Res. 2006, 82, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos, M.B.; Zuanon, J. Sampling effort and species richness in small terra firme forest streams of central Amazonia, Brazil. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2007, 5, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, B.C.; Thiem, J.D.; Gilligan, D.M.; Lintermans, M.; Wooden, I.J.; Linke, S. Estimating species richness and catch per unit effort from boat electro-fishing in a lowland river in temperate Australia. Austral Ecol. 2008, 33, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Súarez, Y.R.; de Souza, M.M.; Ferreira, F.S.; Pereira, M.J.; da Silva, E.A.; Ximenes, L.Q.L.; de Azevedo, L.G.; Martins, O.C.; Lima Júnior, S.E. Patterns of species richness and composition of fish assemblages in streams of the Ivinhema River basin, Upper Paraná River. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2011, 23, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacki, L.; Penczak, T. Species richness estimators applied to fish in a small tropical river sampled by conventional methods and rotenone. Aquat. Living Resour. 2005, 18, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Lee, S.M. Estimating the number of classes via sample coverage. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1992, 87, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonn, W.M.; Magnuson, J.J.; Rask, M.; Toivonen, J. Intercontinental comparison of small-lake fish assemblages: The balance between local and regional processes. Am. Nat. 1990, 136, 345–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, L.L.; Wiley, M.J. Influence of tributary spatial position on the structure of warmwater fish communities. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, L.L.; Kohler, S.L.; Bailey, P.B.; Day, D.M.; Bertrand, W.A.; Wiley, M.J.; Sauer, R. Influence of stream location in a drainage network on the index of biotic integrity. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1992, 121, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornbrugh, D.J.; Gido, K.B. Influence of spatial positioning within stream networks on fish assemblage structure in the Kansas River basin, USA. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 67, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.N. Distribution of fish in the Virgin River, a tributary of the lower Colorado River. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1985, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.; Parker, M.; Linam, G.; Robertson, C.; Grubb, A. River Studies Report No. 26, Canadian River Bioassessment; Inland Division, Texas Parks and Wildlife: Austin, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.A.; Hayes, D.B. A comparison of fish community composition of headwater and adventitious streams in a coldwater river system. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2006, 21, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinger, J.; Crane, J.; Bulak, J. Piedmont Stream Survey; Completion Report, 28 February; South Carolina Department of Natural Resources: Columbia, SC, USA, 2006.
- Hossain, M.S.; Das, N.G.; Sarker, S.; Rahaman, M.Z. Fish diversity and habitat relationship with environmental variables at Meghna river estuary, Bangladesh. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelz, N.J.; McArthur, J.V. An exploration of factors influencing lotic insect species richness. Biodivers. Conserv. 2000, 9, 1543–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).