Identification of Potential Roles of Cathepsin B-like in the Response to Alkali Treatment in Macrobrachium nipponense
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequence Analysis
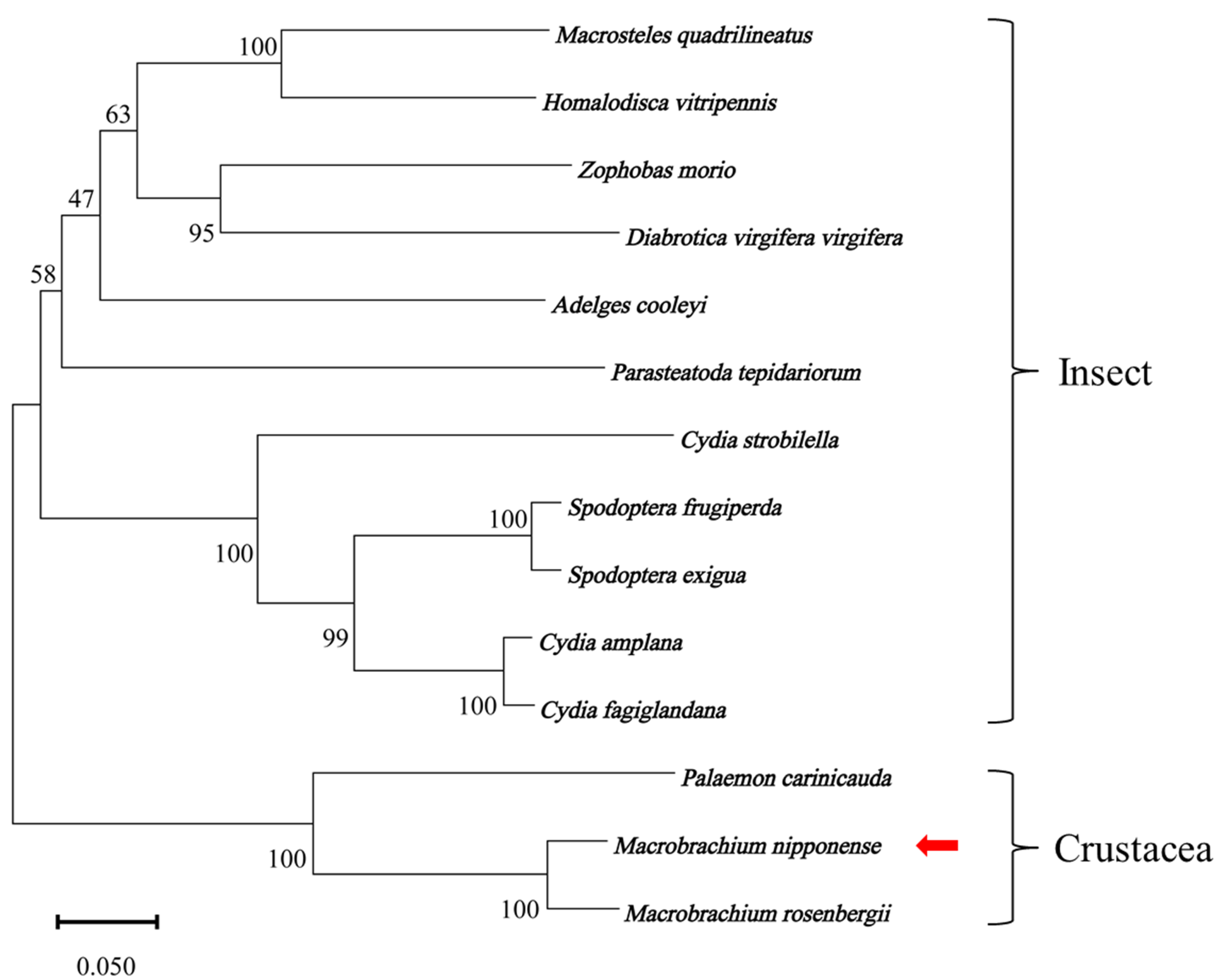
2.2. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
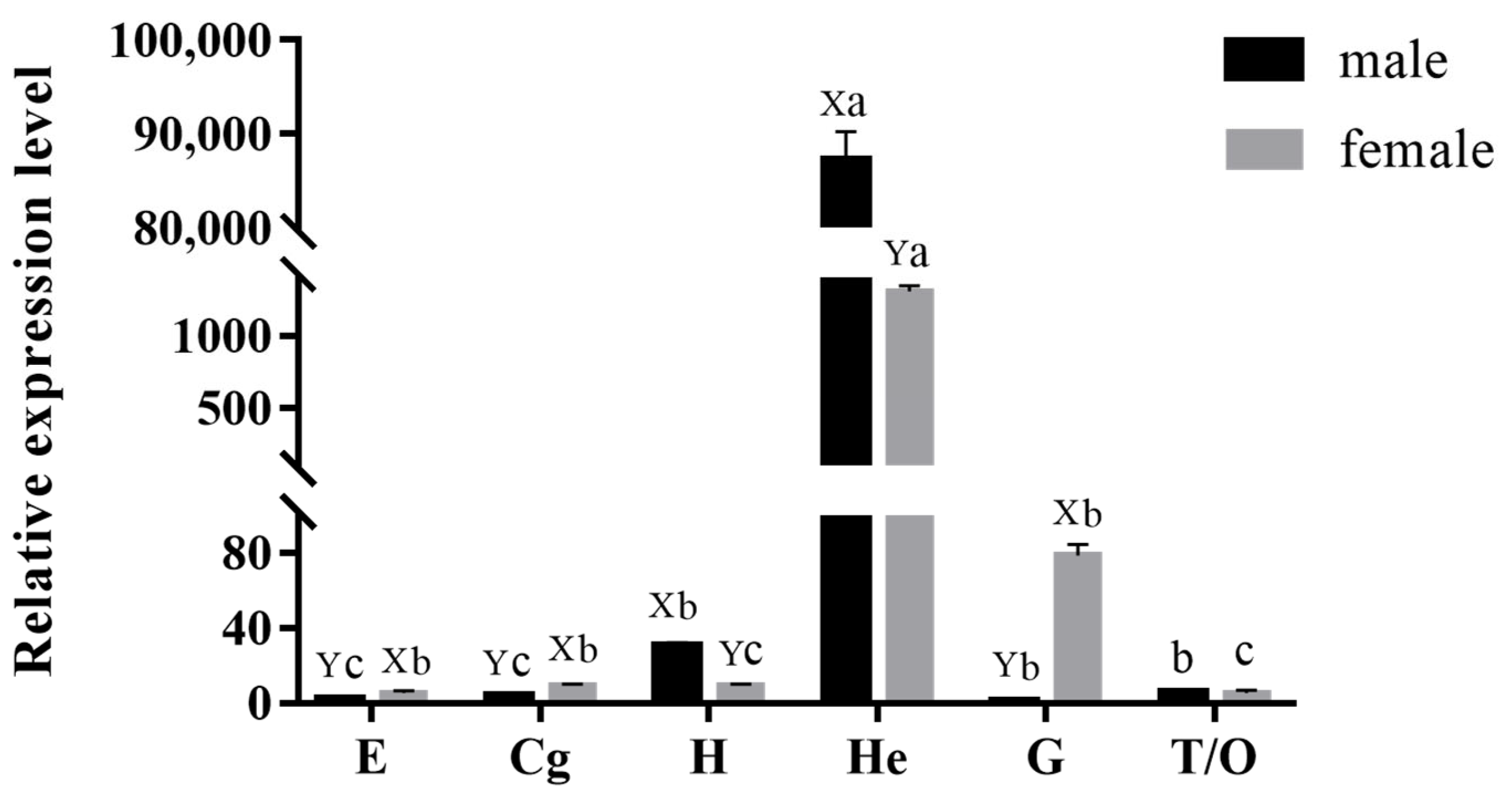
2.3. Expression Pattern of MnCTSB-l in Tissues of M. nipponense
2.4. Expression Analysis of MnCTSB-l in Hepatopancreas and Gills of M. nipponense Under Alkali Stress Conditions
2.5. Localization of MnCTSB-l in the Hepatopancreases and Gills
2.6. RNAi
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
4.2. Total RNA Extraction and Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE) of MnCTSB-l Gene
4.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.4. qPCR Analysis
4.5. In Situ Hybridization (ISH)
4.6. RNAi Analysis
4.7. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, H.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y. Current Status and Prospects of Farming the Giant River Prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) and the Oriental River Prawn (Macrobrachium Nipponense) in China. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 993–998. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Fisheries Administration. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2023; ISBN 978-7-109-30778-0.
- Ren, S.S.; Sun, B.; Luo, L.; Zhang, L.M.; Chang, Y.M.; Liang, L.Q. Tolerance of Freshwater Shrimp (Macrobrachium nipponense) to Alkalinity and Low Temperature in Northeast China. Chin. J. Fish. 2020, 33, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Xu, M.; Gao, X.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, H.; Wu, Y.; Fu, H. Effects of Alkalinity Exposure on Antioxidant Status, Metabolic Function, and Immune Response in the Hepatopancreas of Macrobrachium nipponense. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Zhou, R.; Gao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qiao, H.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Fu, H. Identification of the Effects of Alkalinity Exposure on the Gills of Oriental River Prawns, Macrobrachium nipponense. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saftig, P.; Klumperman, J. Lysosome Biogenesis and Lysosomal Membrane Proteins: Trafficking Meets Function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, A.; Bonifacino, J.S. Lysosomes as Dynamic Regulators of Cell and Organismal Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, A.M.; Zoncu, R. Emerging Roles for the Lysosome in Lipid Metabolism. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 833–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.M.; Zoncu, R. The Lysosome as a Regulatory Hub. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 32, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.E.; Zoncu, R. The Lysosome as a Cellular Centre for Signalling, Metabolism and Quality Control. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Gilberg, E.; Löser, R.; Bajorath, J.; Bartz, U.; Gütschow, M. Cathepsin B: Active Site Mapping with Peptidic Substrates and Inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Sloane, B.F. Cathepsin B: Multiple Roles in Cancer. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 427–437. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.; Lan, F.; Xu, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Li, X. Extralysosomal Cathepsin B in Central Nervous System: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Brain Pathol. 2022, 32, e13071. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yan, C.; Kong, W.; Lan, F.; Narengaowa; Zhao, S.; Yang, Q.; Bai, Z.; Qing, H.; et al. Cathepsin B in Programmed Cell Death Machinery: Mechanisms of Execution and Regulatory Pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khaket, T.P.; Kwon, T.K.; Kang, S.C. Cathepsins: Potent Regulators in Carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 198, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Takio, K.; Towatari, T.; Katunuma, N.; Teller, D.C.; Titani, K. Homology of Amino Acid Sequences of Rat Liver Cathepsins B and H with That of Papain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Ge, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Li, J. Comparative Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis of Exopalaemon carinicauda in Response to Alkalinity Stress. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 759923. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, R.E.; Elshopakey, G.E.; Aly, M.Y.M.; Abdelwarith, A.A.; Younis, E.M.; Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Khamis, T.; Osman, A.; Metwally, M.M.M.; Davies, S.J.; et al. Camel Whey Protein Hydrolysate Diet Mitigates Alkaline Stress–Induced Biochemical Disorders and Restores the Target of Rapamycin, MAPK Pathway, and Autophagy-Related Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia. Aquacult Int. 2024, 32, 9911–9932. [Google Scholar]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Chandler, G.T.; Greig, T.W.; Quattro, J.M. Cathepsin B and Glutathione Peroxidase Show Differing Transcriptional Responses in the Grass Shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio Following Exposure to Three Xenobiotics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3640–3645. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Xian, J.A.; Li, B.; Ye, C.X.; Wang, A.L.; Miao, Y.T.; Liao, S.A. Gene Expression of Apoptosis-Related Genes, Stress Protein and Antioxidant Enzymes in Hemocytes of White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei under Nitrite Stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 157, 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Song, L.; Tan, F.; Su, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Peatman, E. Identification and Mucosal Expression Analysis of Cathepsin B in Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Following Bacterial Challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 751–757. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, L.; Han, L.; Qian, L.; Tian, K.; Yuan, H.; Lou, H. Targeting the Lysosome by an Aminomethylated Riccardin D Triggers DNA Damage through Cathepsin B-Mediated Degradation of BRCA1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1798–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.R.; He, H.S.; Zhang, C.W.; Xu, X.M.; Zeng, Z.P.; Yuan, J.P.; Hong, Y.H.; Wang, J.H. Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of Cathepsin B from Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onming, S.; Thongda, W.; Li, C.; Sawatdichaikul, O.; McMillan, N.; Klinbunga, S.; Peatman, E.; Poompuang, S. Bioinformatics Characterization of a Cathepsin B Transcript from the Giant River Prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii: Homology Modeling and Expression Analysis after Aeromonas hydrophila Infection. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 221–222, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecaille, F.; Kaleta, J.; Brömme, D. Human and Parasitic Papain-Like Cysteine Proteases: Their Role in Physiology and Pathology and Recent Developments in Inhibitor Design. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4459–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Evolutionary Families of Peptidases. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, L. Cathepsin B of Cynoglossus semilaevis: Identification, Expression, and Activity Analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 161, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, D.F.; Gnad, F.; Schropp, K.; Wiśniewski, J.R.; Mann, M. Mapping N-Glycosylation Sites across Seven Evolutionarily Distant Species Reveals a Divergent Substrate Proteome Despite a Common Core Machinery. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Hu, X.; Hu, B.; Wen, C.; Li, Z. Identification and Expression of Cathepsin B from the Freshwater Mussel Cristaria plicata. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 225, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoo, K. Development of Cathepsin Inhibitors and Structure-Based Design of Cathepsin B-Specific Inhibitor. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Hu, Y.; Fu, H.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, W.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Y. Potential Functions of Gem-Associated Protein 2-Like Isoform X1 in the Oriental River Prawn Macrobrachium nipponense: Cloning, qPCR, In Situ Hybridization, and RNAi Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Hu, Y.; Fu, H.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, W.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Y. Identification and Characterization of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase E1 Gene in the Oriental River Prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 752501. [Google Scholar]
- Brix, K.; Dunkhorst, A.; Mayer, K.; Jordans, S. Cysteine Cathepsins: Cellular Roadmap to Different Functions. Biochimie 2008, 90, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Meng, X.; Kong, J.; Luo, K.; Luan, S.; Cao, B.; Liu, N.; Pang, J.; Shi, X. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Cathepsin B Gene from the Chinese Shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.S.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Zhu, B.J.; Liu, C.L. Characterization and Function of a Cathepsin B in Red Crayfish (Procambarus Clarkii) Following Lipopolysaccharide Challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, D.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qiao, H.; Fu, H. Molecular Characterization of a Novel Cathepsin L in Macrobrachium nipponense and Its Function in Ovary Maturation. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 816813. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, S.H.; Liu, L.; Abbas, M.N.; Li, Y.Y.; Kausar, S.; Qian, X.Y.; Ye, Z.Z.; Yu, X.M.; Li, X.K.; Liu, M.; et al. Peroxiredoxin 6 Modulates Toll Signaling Pathway and Protects DNA Damage against Oxidative Stress in Red Swamp Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Rathinam, R.B.; Acharya, A.; Robina, A.J.; Banu, H.; Tripathi, G. The Immune System of Marine Invertebrates: Earliest Adaptation of Animals. Comp. Immunol. Rep. 2024, 7, 200163. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Kong, J.; Luan, S.; Dai, P.; Meng, X.; Cao, B.; Luo, K. Transcriptome Analysis of the Hepatopancreas in the Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) under Acute Ammonia Stress. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Tao, S.; Wang, F.; Shi, Y.; Guan, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z. Alkali Exposure Induces Autophagy through Activation of the MAPK pathway by ROS and Inhibition of mTOR in Eriocheir sinensis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 258, 106481. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.N.; Zhou, J.; Wang, P.; Tian, T.T.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mai, W.; Wang, A.L. Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage and Antioxidant Enzyme Gene Expression in the Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei When Exposed to Acute pH Stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 150, 428–435. [Google Scholar]
- Conus, S. Cathepsins and Their Involvement in Immune Responses. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2010, 140, w13042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, M.; Li, S.; Wei, X.; Ding, L.; Han, S.; Wang, P.; Lv, B.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y. Integrated Application of Multi-Omics Approach and Biochemical Assays Provides Insights into Physiological Responses to Saline-Alkaline Stress in the Gills of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Feng, W.; Kamunga, E.M.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y. Physiological and Molecular Responses of Juvenile Silver Crucian Carp (Carassius gibelio) to Long-Term High Alkaline Stress: Growth Performance, Histopathology, and Transcriptomic Analysis. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 39, 102393. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Fei, F.; Liu, B.; Li, J. The Effect of Astaxanthin on the Alkalinity Stress Resistance of Exopalaemon carinicauda. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170415. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Wu, Y.; Fu, H.; Yang, M.; Ge, X.; Zhu, J.; Xuan, F.; Wu, X. Evaluating Expression of Autophagy-Related Genes in Oriental River Prawn Macrobrachium nipponense as Potential Biomarkers for Hypoxia Exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, H.; Niu, Y.; Qiao, H.; Fu, H. NPC Intracellular Cholesterol Transporter 1 Regulates Ovarian Maturation and Molting in Female Macrobrachium nipponense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Fu, H.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, W.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Y. RNA Interference Analysis Reveals the Positive Regulatory Role of Ferritin in Testis Development in the Oriental River Prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 805861. [Google Scholar]
- SC/T 9406-2012; Water Quality for Aquaculture in Saline-Alkaline Land, Ministry of Agriculture. China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Qiao, H.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, H.; Jiang, S.; Sun, S.; Bai, H.; Jin, S.; Gong, Y. Characterization, Expression, and Function Analysis of Gonad-Inhibiting Hormone in Oriental River Prawn, Macrobrachium nipponense and Its Induced Expression by Temperature. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 185, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Fu, H.; Qiao, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, W.; Jin, S.; Jiang, S.; Gong, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, Y. Validation and Evaluation of Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-Time PCR in Macrobrachium nipponense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P.; Jiang, S.; Qiao, H.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Fu, H. Identification of Potential Functions of Polo-like Kinase 1 in Male Reproductive Development of the Oriental River Prawn (Macrobrachium nipponense) by RNA Interference Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1084802. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Fu, H.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, S.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, W.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Y. Molecular Cloning, Expression, and In Situ Hybridization Analysis of Forkhead Box Protein L2 during Development in Macrobrachium nipponense. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2018, 49, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Z.Q.; Long, S.R.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Ren, H.J.; Cui, J. DsRNA-Mediated Silencing of Nudix Hydrolase in Trichinella spiralis Inhibits the Larval Invasion and Survival in Mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 162, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| MnCTSB-l 3GSP1 | GATATCATGACTAATGGCCCCGT | 3′ RACE |
| MnCTSB-l 3GSP2 | GGCGCCGAAGTCTATAGTTTCTA | 3′ RACE |
| MnCTSB-l 5GSP1 | ACTTCAGCAATGGTTGGACAATG | 5′ RACE |
| MnCTSB-l 5GSP2 | CTGTGGATACAAGCTCTGTCACT | 5′ RACE |
| MnCTSB-l F1 | TAGCAGCGTCACCATTAGGTATC | ORF |
| MnCTSB-l R1 | ACTTCAGCAATGGTTGGACAATG | ORF |
| MnCTSB-l F2 | CATTGTCCAACCATTGCTGAAGT | ORF |
| MnCTSB-l R2 | TCATACTGCATTTCCTCCTCCTG | ORF |
| MnCTSB-l F3 | GGCGCCGAAGTCTATAGTTTCTA | ORF |
| MnCTSB-l R3 | TTCACCACCAGTTAAGCTGGAAT | ORF |
| MnCTSB-l F | ATTCTCTTACTGGGAAAGGTCCG | qPCR |
| MnCTSB-l R | GCTGGTATTCGTCTATGCAGACT | qPCR |
| EIF-F | CATGGATGTACCTGTGGTGAAAC | qPCR |
| EIF-R | CTGTCAGCAGAAGGTCCTCATTA | qPCR |
| MnCTSB-l dsF | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGTGGATCTTGTTGGGCTGTT | RNAi |
| MnCTSB-l dsR | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCTATGCAGACTTCCGTGCAA | RNAi |
| GFP dsF | GATCACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTCCTGGTCGAGCTGGACGG | RNAi |
| GFP dsR | GATCACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGCTTCTCGTTGGGGTCTTTG | RNAi |
| MnCTSB-l antisense-probe | TTCCAGGGGTGTGTCCTCTGCGAAGTTA | ISH |
| MnCTSB-l sense-probe | TAACTTCGCAGAGGACACACCCCTGGAA | ISH |
| Species | Accession Number |
|---|---|
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | XP_066980952.1 |
| Palaemon carinicauda | XP_068219370.1 |
| Adelges cooleyi | XP_050425328.1 |
| Macrosteles quadrilineatus | XP_054283697.1 |
| Spodoptera frugiperda | XP_035432705.1 |
| Cydia strobilella | XP_063548970.1 |
| Cydia amplana | XP_063361903.1 |
| Zophobas morio | XP_063919707.1 |
| Diabrotica virgifera virgifera | CAE47498.1 |
| Parasteatoda tepidariorum | XP_042911940.1 |
| Spodoptera exigua | ABK90823.1 |
| Cydia fagiglandana | XP_063380485.1 |
| Homalodisca vitripennis | XP_046685171.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Fu, H.; Qiao, H.; Jiang, S.; Jin, S. Identification of Potential Roles of Cathepsin B-like in the Response to Alkali Treatment in Macrobrachium nipponense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073361
Xu M, Zhang W, Xiong Y, Fu H, Qiao H, Jiang S, Jin S. Identification of Potential Roles of Cathepsin B-like in the Response to Alkali Treatment in Macrobrachium nipponense. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073361
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Mingjia, Wenyi Zhang, Yiwei Xiong, Hongtuo Fu, Hui Qiao, Sufei Jiang, and Shubo Jin. 2025. "Identification of Potential Roles of Cathepsin B-like in the Response to Alkali Treatment in Macrobrachium nipponense" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073361
APA StyleXu, M., Zhang, W., Xiong, Y., Fu, H., Qiao, H., Jiang, S., & Jin, S. (2025). Identification of Potential Roles of Cathepsin B-like in the Response to Alkali Treatment in Macrobrachium nipponense. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073361








