Abstract
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is one of the most common metabolic complications during pregnancy, affecting up to 14% of pregnancies globally. GDM is characterized by glucose intolerance that arises or is first identified during pregnancy and is linked to significant short- and long-term adverse outcomes for both mothers and their offspring. The pathophysiology of GDM involves more than maternal insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. It is influenced by complex interactions among placental hormones, adipokines, inflammatory mediators, and oxidative stress pathways. Additionally, placental-derived exosomes and metabolomic signatures have emerged as promising biomarkers for early prediction and monitoring of the disease. Despite advancements in clinical diagnosis and management, including lifestyle interventions and pharmacological treatments, current strategies are still inadequate to prevent complications for both mothers and newborns entirely. Recent molecular insights into GDM development have been explored, along with emerging biomarkers and potential therapies. This synthesis also considers prospects for precision medicine strategies that could significantly improve GDM management. The urgent need for improved prevention and treatment of GDM is evident. A deeper understanding of the molecular foundations of GDM is essential and urgent, as it may enhance clinical outcomes and provide opportunities for early prevention of intergenerational metabolic disease risk.
1. Introduction
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as any degree of glucose intolerance first diagnosed during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester, when prior overt diabetes has been ruled out [,,]. Diagnostic standards vary, but the widely accepted International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) and World Health Organization criteria recommend a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with thresholds of fasting ≥ 5.1 mmol/L, 1 h ≥ 10.0 mmol/L, and 2 h ≥ 8.5 mmol/L plasma glucose [,,]. In some regions, a two-step strategy (screening followed by OGTT) is still used for pragmatic reasons []. Globally, the prevalence of GDM is rising, with current estimates around 14% of pregnancies, depending on diagnostic criteria and population [,,,].
Key risk factors for GDM include maternal obesity, advanced maternal age (>35 years), family history of type 2 diabetes, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), previous macrosomic infant or previous GDM, and specific ethnic backgrounds (e.g., South Asian, African, Hispanic, Pacific Islander) [,,]. Genetic predisposition also plays a role: polymorphisms in genes such as transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2), melatonin receptor 1B protein (MTNR1B), insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1), potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1 (KCNQ1), among others, have been associated with impaired β-cell function, insulin secretion, and predisposition to GDM [,,]. Lifestyle and environmental factors such as sedentary behavior, unhealthy diet, and obesity exacerbate insulin resistance during pregnancy [,,,].
Pregnancy naturally induces a state of progressive insulin resistance, especially in the second and third trimesters, mediated by placental hormones (human placental lactogen (hPL)), prolactin, progesterone, cortisol, estradiol, cytokines, and adipokines (e.g., tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), leptin, resistin) [,]. In healthy pregnancies, pancreatic β-cells expand and increase insulin output to maintain euglycemia. In GDM, β-cell compensation fails—often due to genetic defects, weight gain of the mother, and hormonal disorders, leading to maternal hyperglycemia [,,]. Figure 1 illustrates the main molecular mechanisms involved in GDM.
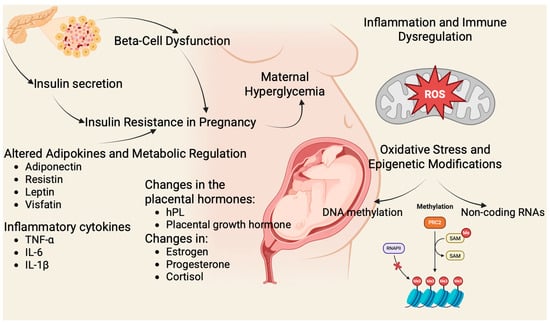
Figure 1.
Molecular Mechanisms in GDM. (Figure created in BioRender. Assani, M. (2025) https://BioRender.com/0xnbu0m). Pregnancy-induced insulin resistance is driven by placental hormones (human placental lactogen (hPL), placental growth hormone, estrogen, progesterone, cortisol) and inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor α (TNF α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), interleukin 1β (IL-1β)) [,]. Inadequate β-cell adaptation due to mitochondrial dysfunction, and impaired incretin signaling leads to hyperglycemia. Dysregulated adipokines (↓ adiponectin, ↑ leptin, resistin, visfatin), oxidative stress, and epigenetic modifications (deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation, non-coding ribonucleic acids (RNAs)) further exacerbate disease and contribute to adverse maternal and fetal outcomes [,].
These maladaptations link deeply to molecular mechanisms: oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in β-cells and placenta; aberrant hepatocyte growth factor/c-mesenchymal–epithelial transition factor (HGF/c-MET) signaling affecting β-cell proliferation; inflammatory activation involving macrophages and cytokines; and impaired insulin signaling pathways [,,,]. Epigenetic changes, including deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation, histone modification, and non-coding ribonucleic acids (RNAs) such as microRNAs, modify gene expression in maternal tissues and the placenta, influencing both maternal metabolism and fetal programming [,,].
The maternal and fetal complications of GDM are considerable: mothers face higher rates of preeclampsia, hypertension, cesarean delivery, and birth trauma; infants face macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia, respiratory distress, and increased neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) admissions [,]. Untreated or poorly controlled GDM further elevates these risks, including stillbirth and birth injuries [,]. It has recently been demonstrated that severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) severe infection during pregnancy is associated with higher odds of developing GDM [].
Crucially, GDM has long-term sequelae: women with GDM presented higher chances to develop type 2 diabetes postpartum, especially if they required insulin or had obesity [,]. Offspring born to GDM mothers have higher lifetime risks for childhood obesity, impaired glucose tolerance, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease—often attributable to fetal metabolic programming through epigenetic and microbiome alterations [,,].
2. Pathophysiology and Molecular Mechanisms
2.1. β-Cell Dysfunction, Inflammation and Immune Regulation, Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
In healthy pregnancies, β-cells expand and increase insulin secretion to compensate for pregnancy-induced insulin resistance. In GDM, this compensation fails due to molecular stressors such as oxidative stress, glucolipotoxicity, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) damages β-cells, impairing insulin gene transcription and secretion, and promoting apoptosis [,]. Additionally, failure of translational control and autophagy pathways further compromises β-cell survival and function [,]. Heterogeneity analyses show women with combined insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, compared to single defects, experience more severe GDM phenotypes and worse perinatal outcomes [].
Systemic inflammation is central in promoting insulin resistance. Elevated TNF-α and IL-6 levels contribute to metabolic dysregulation. This inflammation radiates from adipose tissue into the liver, skeletal muscle, and placenta, aggravating insulin resistance across multiple tissues [,,].
Recent studies in GDM placental and metabolic tissues demonstrate that mitochondrial dysfunction impairs adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation and elevates ROS, which drives serine phosphorylation of IRS1, impairing insulin signaling across skeletal muscle, adipose and trophoblast cells. This reinforces a vicious cycle of oxidative damage, inflammation, and persistent insulin resistance [,,]. Further mechanistic parallels are observed in type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance (IR) models, reinforcing the centrality of dysfunctional oxidative metabolism in promoting insulin resistance [,].
2.2. Insulin Resistance During Pregnancy, Adipokines and Metabolic Regulation
During pregnancy, rising levels of placental hormones, including hPL, leptin, TNF-α, interleukin 6 (IL-6), and cortisol, disrupt insulin signaling. hPL promotes lipolysis and increases free fatty acids, which activate protein kinase C (PKC) and induce serine phosphorylation of IRS-1/2 rather than activation-promoting tyrosine phosphorylation. This impairs phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling and glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4)-mediated glucose uptake in maternal tissues [,,,]. Leptin, often elevated in GDM, inhibits insulin receptor expression through janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathways, while hypoadiponectinemia reduces adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity, further impairing GLUT4 activation and insulin sensitivity [,,]. Chronic low-grade inflammation—driven by TNF-α and IL-6 from adipose tissue macrophages—activates stress kinases Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) and I-kappa-B Kinase (IKK), promoting IRS1 serine phosphorylation and exacerbating systemic insulin resistance []. Leptin, an adipokine mainly secreted by adipose tissue and the placenta, is critical in regulating energy balance, insulin sensitivity, and metabolic adaptation during pregnancy. In women with GDM, circulating leptin levels are often elevated compared to healthy pregnancies, reflecting increased adiposity, placental overproduction, and a state of leptin resistance. This dysregulation is thought to contribute to the development of insulin resistance, impaired β-cell compensation, and adverse metabolic outcomes. Clinical studies have confirmed that higher maternal leptin concentrations, particularly in early pregnancy, are associated with an increased risk of developing GDM later in gestation [,].
Adiponectin, an adipokine secreted mainly by adipose tissue, exerts insulin-sensitizing, anti-inflammatory, and anti-atherogenic effects. Unlike leptin and visfatin, circulating adiponectin levels are typically reduced in women with GDM compared to healthy pregnancies. Low adiponectin concentrations, especially in early pregnancy, have been consistently identified as a predictor of subsequent GDM development, reflecting impaired insulin sensitivity and β-cell dysfunction. Furthermore, hypoadiponectinemia in GDM has been associated with greater maternal insulin resistance and increased risk of adverse metabolic outcomes in offspring. These findings suggest that adiponectin plays a protective role in pregnancy metabolism, and its deficiency contributes to the pathophysiology of GDM [,,]. Cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, in GDM, lower adiponectin levels, disrupting adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1) and adiponectin receptor 2 (AdipoR2) signaling, and reducing AMPK activation. This disruption impairs fatty acid oxidation and glucose uptake, worsening insulin resistance [].
Resistin, another adipokine elevated in obesity, has also been implicated in insulin resistance and inflammatory responses, although its exact role in human GDM remains under investigation [,]. In the context of GDM, several studies report that maternal circulating resistin levels are dysregulated, often showing higher concentrations compared to normoglycemic pregnancies. This imbalance may contribute to the pro-inflammatory state and impaired insulin sensitivity characteristic of GDM. Moreover, resistin has been detected in placental tissue, where its expression may further influence maternal glucose metabolism and fetal nutrient supply. Overall, current evidence suggests that resistin plays a role in the pathophysiology of GDM by linking inflammation, adipose tissue dysfunction, and insulin resistance [,].
Visfatin is an adipokine with insulin-mimetic effects that is secreted by visceral adipose tissue and the placenta, and it participates in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Several original studies have reported that maternal circulating visfatin levels are altered in pregnancies complicated by GDM, commonly showing elevated concentrations in early and mid-gestation among women who develop GDM [,,]. However, some investigations, particularly in later pregnancy, have found lower visfatin levels in women with GDM compared to normoglycemic controls, and visfatin levels have been inversely correlated with insulin resistance markers such as homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in healthy pregnancies but not consistently in GDM. Overall, while the direction varies by timing and population, visfatin appears to be dysregulated in GDM and to have a potential role in insulin resistance and metabolic adaptation during pregnancy [].
2.3. Epigenetic and Genetic Factors: MicroRNAs
Genetic variants in key genes, such as TCF7L2, IRS1, solute carrier family 30 member 8 (SLC30A8), cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulatory subunit associated protein 1-like 1 (CDKAL1), MTNR1B, and glucokinase (GCK), have been linked to susceptibility to GDM through effects on β-cell function and insulin action. Epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation in metabolic gene promoters, histone modifications, and dysregulated microRNAs, modulate gene expression relevant to insulin signaling and glucose metabolism. These epigenetic marks may reflect in utero environment or maternal metabolic state and contribute to both GDM and fetal programming [,,,].
Specific microRNAs, such as miR-375, are highly enriched in pancreatic β-cells and play crucial roles in regulating insulin secretion and β-cell mass maintenance. Although predominantly examined within the context of type 2 diabetes mellitus, emerging evidence suggests that miR-375 may also be integral to β-cell adaptation processes during pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Additionally, other microRNAs, including miR-21 and miR-23a, have been identified through recent biomarker studies in GDM, implicating them in underlying mechanistic pathways of the disease [,,,,]. miRNAs such as miR-21, miR-23a, miR-130a, miR-193a are consistently dysregulated in circulation and placental tissues from women who develop GDM, even in early pregnancy [,,]. These exosomal miRNAs, derived from placental or maternal tissues, serve as both mechanistic mediators and early predictors, with candidate panels under active investigation [].
GDM arises from a multifactorial network of molecular insults: placental and adipose-derived hormones triggering insulin resistance, failing β-cell compensation under oxidative and inflammatory stress, dysregulation of adipokines, and contributions from genetic susceptibility coupled with epigenetic modulation. These pathways converge on disrupted IRS-PI3K-Akt-GLUT4 signaling, mitochondrial impairment, stress-kinase activation, and defective insulin secretion [,,].
Table 1 summarizes all the above pathophysiological processes and molecular mechanisms.

Table 1.
Brief description of pathophysiology and molecular mechanisms underlying GDM [,,,,,,,,].
3. Biomarkers of GDM
Current screening approaches, mainly based on fasting plasma glucose (FPG), OGTT, and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), often detect GDM after pathological processes have already been established. This delayed diagnosis limits opportunities for early intervention, increasing the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. Therefore, the identification of biomarkers capable of predicting GDM in the first trimester or even preconceptionally has become a central research focus [].
Biomarkers serve not only as diagnostic and predictive tools but also as windows into the molecular mechanisms underlying GDM. Advances in molecular biology and omics technologies—such as genomics, metabolomics, and proteomics—have revealed novel classes of biomarkers including circulating microRNAs, placental-derived exosomes, and metabolic signatures that reflect impaired insulin action, β-cell stress, inflammation, and oxidative imbalance. These emerging candidates carry dual potential: they may allow early detection and risk stratification while also identifying new therapeutic targets [,,]. For a better overview, refer to Table 2.

Table 2.
Biomarkers in GDM [,,].
Importantly, biomarker research in GDM is not limited to glucose metabolism alone. Increasingly, focus has shifted toward integrative biomarker panels that combine clinical characteristics (e.g., maternal age, BMI, family history) with molecular indicators of immunometabolism, adipokine signaling, and placental function. Such multi-parameter models are demonstrating superior predictive performance compared to single markers. However, challenges remain in standardization, reproducibility, and cost-effectiveness, which currently prevent large-scale clinical implementation [,,].
3.1. Classical Glycemic Markers
- FPG: Widely used; FPG in the first trimester shows moderate predictive power with area under the curve (AUC) between ~0.630 and 0.738 (sensitivity 64–79%, specificity 56–59%) when thresholds range from 81 to 88.5 mg/dL [,,,];
- HbA1c: First-trimester cut-offs (5.33–5.45%) deliver an AUC of 0.809–0.84; in second-trimester, levels (5.45–5.7%) maintain good predictive performance, with an AUC of 0.826–0.848 [];
- Insulin-derived indices: Calculated biomarkers such as secretory capacity of pancreatic β-cells (SPINA-GBeta) (a computational estimate of maximal β-cell insulin output) outperform homeostatic model assessment of β-cells function (HOMA-Beta) in estimating beta-cell function and may provide additional insight into early GDM pathophysiology [].
3.2. Emerging Molecular Biomarkers
3.2.1. Placental-Derived Exosomes and Proteomic and Metabolomic Markers
- Exosome proteomics and transcriptomics analyses reveal distinct signatures in pregnant women who develop GDM compared to controls. Proteins isolated from plasma- and placenta-derived exosomes show differential abundance in pathways related to insulin signaling, inflammation, and mitochondrial function [,,];
- Advances in exosome isolation and platform sensitivity are making these vesicular biomarkers more practical for early detection [].
- Metabolomic profiling, particularly using targeted acylcarnitines (e.g., C5 isovalerylcarnitine and C5:1 tiglylcarnitine), enabled a predictive model with an AUC of 0.934 for GDM detection before 18 weeks of gestation [];
- Combined proteomic/metabolomic fingerprinting studies identify networks of proteins and metabolites that correlate with GDM pathogenesis and postpartum metabolic risk [,].
3.2.2. Immune and Cytokine Biomarkers
- A recent first-trimester panel including total immunoglobulin G (IgG), total IgM, IL-7, anti-phosphatidylserine IgG immune complexes, and IL-15 achieved AUC of 0.906 (sensitivity 75%, specificity ~95%) in In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) pregnancies. These immune markers reflect early immunometabolic dysregulation and may add predictive power beyond classical glycemic indices [].
3.2.3. Potential Risks and Roles of Chemerin in GDM
Chemerin, an adipokine, has a complex and important role in the development of GDM, affecting the mother and baby by impacting metabolic, inflammatory, and genetic processes. Elevated circulating chemerin levels serve as a key marker for GDM in mothers, a finding supported by a meta-analysis that demonstrated significantly higher concentrations in GDM cases compared to normoglycemic controls. This link is especially significant among women under 30 and Asian populations. The pathogenic mechanism involves chemerin acting as a pro-inflammatory cytokine, which promotes insulin resistance, a key feature of GDM, by disrupting glucose uptake, influencing pancreatic beta-cell function, and correlating with other inflammatory markers associated with GDM [].
Besides its systemic effects, chemerin also directly influences placental health by increasing lipid buildup when levels are excessive, disrupting the differentiation and growth of essential trophoblast cells, and impairing overall placental development []. Genetic predisposition also influences risk, with specific single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the chemerin gene (rs4721) interacting with other variants potentially heightening GDM risk. This may occur through abnormal chemerin secretion and disrupted glucose-lipid metabolism [,]. These maternal dysfunctions directly pose risks to the newborn. Higher maternal chemerin levels are associated with increased fetal growth, greater birth weight, and a higher likelihood of large-for-gestational-age infants, which is a common complication of GDM []. This effect occurs via the placenta, where chemerin’s control of fatty acid oxidation is essential for the healthy development of trophoblast cells that support the fetus []. While changed fetal growth is the main risk, animal studies indicate other possible effects, such as chemerin accumulation potentially leading to fetal cognitive issues or, alternatively, aiding in neutralizing placental oxidative stress. This suggests a complex role that warrants further research [,].
3.3. Clinical Applicability and Limitations
- Timing is crucial, as many molecular markers can be detected in the first trimester, providing an early opportunity for risk assessment and preventive measures, unlike OGTT, which is performed later [,];
- Multivariable models combining conventional risk factors with panels of cardiometabolic biomarkers show improved discrimination for GDM. For example, full prediction models yielded an AUC of 0.842 and a proportion of cases followed (PCF) of 0.695, in early pregnancy, 10 to 14 gestational weeks, compared to an AUC of 0.720 and PCF of 0.491 for the model using only conventional risk factors [];
- Key barriers include: deciding on a selective or universal screening, assay standardization (especially for miRNA and exosome quantification), cost, and the need for prospective validation in diverse populations. Clinical uptake will depend on reproducible thresholds, ease of sampling, and cost-effectiveness compared to current universal OGTT screening [,,].
In Table 3, we have summarized the main implications described previously of practical biomarkers in GDM to provide a holistic overview.

Table 3.
Summarization of practical biomarkers in GDM [,,,,,,,,].
4. Clinical Management
Effective clinical management of GDM requires an integration of timely diagnosis, lifestyle modification, pharmacologic therapy when indicated, and innovative molecularly informed strategies. As GDM is both a metabolic and molecularly heterogeneous condition, management strategies increasingly aim to move beyond glycemic control to also address underlying pathways such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and microbiome dysbiosis [,,].
4.1. Diagnostic Approaches and Lifestyle Interventions
The diagnosis of GDM remains grounded in OGTT, with the IADPSG criteria widely adopted: fasting plasma glucose ≥ 92 mg/dL, 1-h ≥ 180 mg/dL, or 2-h ≥ 153 mg/dL following a 75 g glucose load. While these thresholds are highly sensitive, their specificity varies across populations, and controversies persist regarding overdiagnosis in certain ethnic groups and the lack of early-pregnancy markers []. Furthermore, conventional OGTT does not capture molecular heterogeneity of GDM subtypes, including those dominated by β-cell dysfunction versus those driven primarily by insulin resistance [,].
Nutritional therapy is the cornerstone of management. Controlled carbohydrate intake, low glycemic index foods, and adequate protein and fiber reduce postprandial glycemic excursions and modulate insulin secretion. Molecularly, nutrition and dietary supplements might attenuate activation of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, lower circulating TNF-α, and improve adiponectin secretion, thereby reducing systemic inflammation [,,].
Exercise improves maternal insulin sensitivity by enhancing GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle and activating AMPK, which promotes fatty acid oxidation and decreases hepatic gluconeogenesis. Regular moderate activity also reduces oxidative stress by upregulating superoxide dismutase and catalase in placental tissue. Combined lifestyle interventions have consistently shown a reduction in the need for pharmacological therapy, highlighting their molecular and clinical efficacy [,,].
4.2. Pharmacological Therapies
Insulin remains the gold standard therapy when lifestyle interventions fail. Due to its large molecular size, it does not cross the placenta, minimizing direct fetal exposure. Insulin therapy primarily corrects maternal hyperglycemia without directly modulating inflammatory or oxidative stress pathways. However, its need for injections, risk of hypoglycemia, and maternal weight gain remain barriers [,,,].
Metformin is now widely used as a first-line or adjunct therapy in GDM []. Mechanistically, metformin activates AMPK, reduces hepatic gluconeogenesis, enhances insulin receptor phosphorylation, and suppresses ROS generation [,]. It has also been shown to reduce maternal weight gain and the incidence of large-for-gestational-age neonates []. Despite these benefits, metformin readily crosses the placenta, and emerging animal data suggest potential long-term effects on offspring brain development, and it may cause fetal programming, harming metabolic health in later life [].
Glyburide (Glibenclamide) stimulates maternal pancreatic β-cell insulin secretion via ATP-sensitive potassium channel inhibition. However, it crosses the placenta more readily than metformin, exposing the fetus to pharmacologic activity. Clinical studies have reported higher rates of neonatal hypoglycemia and macrosomia compared to insulin or metformin, limiting its widespread adoption [,,].
Consensus favors insulin as the safest pharmacologic choice, with metformin an effective alternative when patient preference or cost are considered. Glyburide remains a less favored option due to fetal safety concerns [].
4.3. Emerging and Molecularly Targeted Therapies
Given the central role of oxidative stress and systemic inflammation in GDM pathophysiology, several nutraceuticals and supplements have been tested. Magnesium–zinc–calcium–vitamin D co-supplementation reduced circulating high-sensitivity C reactive protein (hsCRP), TNF-α, and malondialdehyde, while improving antioxidant enzyme activity [,,]. Polyphenolic compounds such as curcumin, punicalagin, and naringenin inhibit NF-κB signaling and enhance mitochondrial biogenesis in placental and adipose tissues, offering mechanistic promise [,,,].
Gut dysbiosis in GDM is characterized by depletion of short chain fatty acid (SCFA)–producing bacteria and expansion of pro-inflammatory Gram-negative species. This promotes insulin resistance via lipopolysaccharide–Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathways []. Probiotic and synbiotic interventions have demonstrated improvements in fasting glucose, HOMA-IR, and inflammatory cytokines, though results vary depending on the bacterial strains used and the dosage administered [,,,].
New anti-inflammatory compounds, such as NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome inhibitors–1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-one derivative 5 (INF200), have shown notable improvements in glucose tolerance and systemic inflammation in preclinical models of diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Although not yet examined in GDM, these agents underscore the potential of targeted molecular therapies [,,].
Artificial intelligence (AI)–driven closed-loop insulin delivery systems are being explored in type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and their adaptation to pregnancy could provide more precise glycemic control. Reinforcement learning–based insulin titration has shown promising results in simulation models. Translating such systems to GDM may improve maternal and fetal outcomes while reducing the burden of frequent monitoring [,,,].
5. Maternal and Fetal Outcomes
GDM conveys substantial short- and long-term risks for mothers and offspring. Understanding the molecular underpinnings helps inform how these complications emerge and persist [,,].
5.1. Short-Term Outcomes
Hyperglycemia in pregnancy leads to fetal hyperinsulinemia and excessive growth, resulting in macrosomia (birth weight ≥ 4000 g), which occurs 2–3 times more often in GDM compared to normoglycemic pregnancies [,]. Macrosomia increases risks for shoulder dystocia, Erb’s palsy, neonatal hypoglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia, and admission to neonatal intensive care [,,].
After delivery, infants of diabetic mothers may develop neonatal hypoglycemia due to lingering hyperinsulinemia, along with polycythemia and electrolyte disturbances (hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia) and increased risk of respiratory distress from delayed lung maturation [,].
Women with GDM face a heightened risk of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. Placental dysfunction driven by oxidative stress, inflammation (elevated TNF-α, leptin, resistin), and endothelial disturbances contribute to increased vascular resistance and hypertensive complications [,,].
5.2. Long-Term Outcomes
A history of GDM is one of the strongest predictors of later type 2 diabetes. A meta-analysis of over 675,000 women showed more than a seven-fold increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in time for the women who developed GDM, compared to women with a normoglycemic status in pregnancy [,]. Beyond diabetes, women with prior GDM exhibit increased rates of metabolic syndrome, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular events at younger ages. Prospective cohorts and pooled analyses report up to two-fold or greater elevated risk of cardiovascular disease in this population [,,]. The American Heart Association recognizes prior GDM as a female-specific risk factor for future cardiovascular disease [,].
Emerging epidemiological studies link a history of GDM to increased risk of microalbuminuria and chronic kidney disease later in life, even controlling for progression to diabetes [,,].
Intrauterine exposure to hyperglycemia and altered nutrient milieu programs the fetus toward enhanced adiposity, insulin resistance, and risk for childhood and adult obesity and type 2 diabetes, a phenomenon coined metabolic imprinting and consistent with the developmental origins of health and disease hypothesis (DOHaD) [,,]. Longitudinal and mechanistic studies show that maternal GDM and overnutrition increase the risk of metabolic disorders in offspring later in life [,].
A recent extensive pooled analysis, around 56 million pregnancies, found that maternal diabetes, including GDM, was associated with a higher risk of neurodevelopmental disorders (1:28 risk ratio), including autism (1:25 risk ratio), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (1:30 risk ratio), and intellectual disabilities (1:32 risk ratio). While causality is still under investigation, experts emphasize the need for glycemic control to mitigate these risks [].
5.3. Epigenetic and Transgenerational Effects: Integration of Molecular Insights into Outcomes
Molecular evidence suggests that prenatal hyperglycemia triggers epigenetic modifications in key metabolic genes, such as DNA methylation changes and altered microRNA expression. These changes may persist after birth, influencing long-term gene expression and metabolic phenotype in offspring [,,]. Genetic factors potentially influencing GDM risk include SNPs in genes such as TCF7L2 and succinate receptor 1 (SUCNR1), which are linked to changes in insulin secretion and placental endothelial function. These inherited variants operate independently of epigenetic modifications, another regulatory layer important in disease development susceptibility [,,]. Recent studies have begun to link specific molecular biomarkers with clinical endpoints. Elevated placental succinate and SUCNR1 expression are associated with endothelial proliferation and may underlie placental dysfunction and fetal overgrowth in GDM []. Circulating microRNAs and exosomal markers measured during pregnancy are being evaluated for predictive power for GDM onset and the likelihood of macrosomia or future metabolic disease [,].
Figure 2 illustrates the clinical consequences and long-term outcomes of GDM.
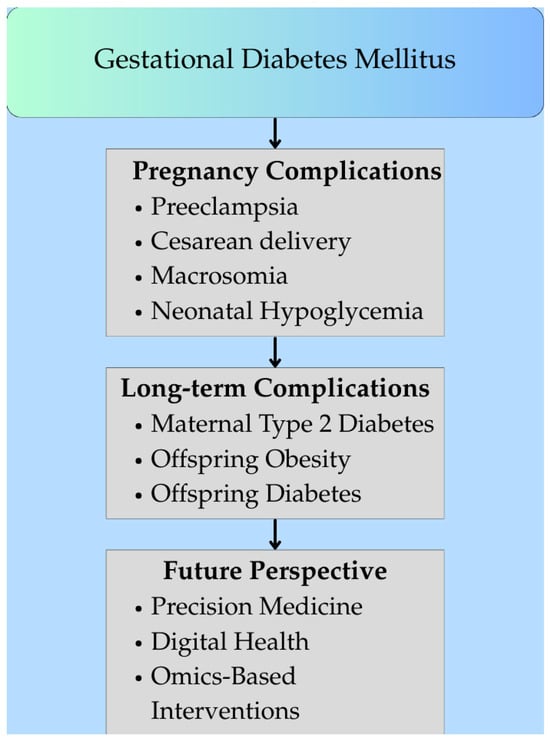
Figure 2.
Clinical consequences and long-term outcomes of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). (Figure created in Canva, https://www.canva.com). The figure outlines GDM complications. During a pregnancy with GDM, complications such as preeclampsia, cesarean delivery, and neonatal issues (e.g., hypoglycemia) may occur. Long-term, women are more prone to type 2 diabetes, while offspring face obesity and diabetes. Future approaches focus on using precision medicine, omics, and digital health for early detection, risk assessment, and prevention.
6. Future Perspective
Research into GDM is rapidly expanding, driven by advances in omics technologies, computational modeling, and precision medicine initiatives. Bridging molecular insights with clinical care represents the next frontier in reducing both immediate and long-term complications of GDM [,].
6.1. Advances in Omics Technologies
High-throughput omics platforms have transformed the ability to characterize GDM at the genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic, and epigenomic levels. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified SNPs in genes such as TCF7L2, MTNR1B, and KCNQ1, which are linked to impaired insulin secretion and elevated GDM risk [,].
Metabolomics has provided new candidate biomarkers—such as altered amino acid, lipid, and bile acid profiles—that show predictive potential for GDM before clinical diagnosis. Integrating multi-omics datasets may allow for precise molecular subtyping of GDM, distinguishing women with predominant insulin resistance versus β-cell dysfunction [,].
6.2. Precision Medicine, Risk Stratification, and Novel Therapeutic Targets
One of the most promising directions is the translation of molecular findings into precision medicine approaches. Predictive models that integrate clinical risk factors with genetic and epigenetic markers have shown improved accuracy in forecasting GDM development and adverse outcomes. Personalized interventions such as tailoring dietary, lifestyle, and pharmacologic therapies according to molecular subtypes could improve glycemic control and treatment strategies [,].
MicroRNA and exosomal profiling are particularly attractive for early screening, as they can be measured in maternal plasma in the first trimester and may predict not only GDM onset but also downstream outcomes such as macrosomia or preeclampsia [,,].
Beyond conventional therapies (insulin, metformin, glyburide), molecular research highlights new avenues for intervention [,,]:
- Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant therapies: Given the role of cytokine-driven inflammation and oxidative stress in GDM pathophysiology, agents targeting NF-κB signaling, ROS scavenging, or mitochondrial protection are under investigation;
- Gut microbiome modulation: Dysbiosis in GDM pregnancies suggests potential benefit of probiotics, prebiotics, and dietary interventions to restore microbial diversity and improve metabolic outcomes;
- Epigenetic therapeutics: While still experimental, strategies that target DNA methylation or histone modification pathways could theoretically modulate fetal programming effects of maternal hyperglycemia.
6.3. Digital Health, Predictive Analytics, and Ongoing Challenges
Digital health technologies are increasingly integrated into GDM management. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and wearable sensors provide real-time metabolic profiling, which can be combined with machine-learning models for individualized prediction of glycemic excursions. Mobile health platforms are also enhancing adherence to diet and exercise regimens, with early trials suggesting improved outcomes in glucose control and maternal satisfaction [,].
Despite progress, several challenges limit the clinical translation of molecular insights. GDM arises from diverse mechanisms (insulin resistance, β-cell dysfunction, inflammation), complicating biomarker validation. Cost, scalability, and ethical considerations (e.g., genetic testing during pregnancy) remain major obstacles to adopting omics-based diagnostics in clinical practice [,,,,].
6.4. Toward Integrated Care
Future research must bridge molecular and clinical domains through large, prospective, multi-ethnic cohorts that integrate omics profiling, digital health data, and clinical endpoints. Such efforts could enable the development of clinically actionable molecular signatures and lay the foundation for integrated care models, where early prediction, personalized intervention, and long-term follow-up are standard practice [].
The future of GDM research lies in leveraging omics technologies, precision medicine, and digital health tools to predict, prevent, and personalize care. Advances in biomarkers, therapeutic targeting of inflammation, oxidative stress, and microbiome modulation, along with machine-learning powered predictive models, hold promise. Yet, successful translation will require rigorous validation, equitable research across populations, and integration of molecular data into accessible clinical workflows [].
7. Conclusions
GDM represents a unique metabolic disorder that emerges in pregnancy but carries lasting implications for maternal and offspring health. Over the past decade, significant progress has been made in unraveling the molecular mechanisms underlying GDM, including the interplay of insulin resistance, β-cell dysfunction, inflammation, oxidative stress, and epigenetic programming. These molecular insights have enriched our understanding of why some women develop GDM and why its effects extend far beyond pregnancy. Figure 3 illustrates a comprehensive overview of GDM.
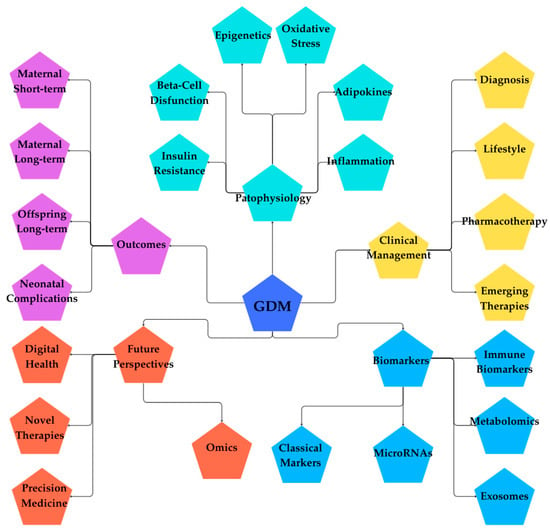
Figure 3.
Mind map of GDM. (Figure created in Canva, https://www.canva.com). The mind map provides a holistic overview of GDM, centered on five major domains: Clinical Management, Biomarkers, Pathophysiology, Outcomes, and Future Perspectives. Clinical Management covers diagnosis, lifestyle interventions, pharmacotherapy, and emerging therapies. Biomarkers include metabolomics, exosomes, microRNAs, classical markers, and immune biomarkers. Pathophysiology explores the mechanisms behind GDM, such as epigenetics, oxidative stress, adipokines, inflammation, beta-cell dysfunction, and insulin resistance. Outcomes highlight maternal short- and long-term risks, neonatal complications, and offspring’s long-term health impacts. Finally, Future Perspectives point toward omics, precision medicine, novel therapies, and digital health innovations. This overview demonstrates the complexity of GDM by combining clinical practice, biological mechanisms, patient outcomes, and future research directions into a unified, comprehensive model.
GDM remains a significant health challenge. While oral glucose tests are standard, they have limitations, emphasizing the need for earlier, less invasive biomarkers. Advances in genomics and metabolomics suggest circulating microRNAs, placental exosomes, and metabolites as promising options. Incorporating these could enable early detection, risk assessment, and personalized treatments. GDM management mainly involves lifestyle, insulin, and oral drugs such as metformin and glyburide. Recognition of inflammation, oxidative stress, and gut microbiota’s roles introduces new therapies beyond glucose control, potentially improving outcomes and reducing long-term risks for mothers and offspring. GDM has significant consequences. Mothers face risks such as preeclampsia and other maternal complications; newborns are vulnerable to macrosomia, hypoglycemia, and respiratory distress. Long-term, mothers face higher risks of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and kidney issues, while children are prone to obesity, diabetes, and neurodevelopmental disorders. Epigenetic mechanisms play a key role in transmitting these risks across generations, emphasizing the importance of early intervention.
The future of GDM research and care hinges on integrating molecular discoveries with clinical management. Precision medicine, driven by omics and digital health, can shift from a generic approach to personalized strategies based on each woman’s unique molecular and clinical profile. Challenges include disease heterogeneity, the need for diverse cohorts, and barriers to cost-effective real-world implementation. GDM should be seen not just as a transient pregnancy complication but as a window into future health for mother and child. Combining molecular insights with innovative clinical strategies can reduce the burden of GDM. Progress requires collaboration among scientists, clinicians, public health experts, and policymakers. Integrating science with translational and clinical research is vital for prevention, better maternal–fetal outcomes, and breaking the cycle of intergenerational disease risk.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.-Z.A. and L.B.; methodology, A.-D.A. and M.-M.M.; software, M.-M.M.; validation, C.-C.V., L.B. and I.S.; resources, C.-C.V., M.-Z.A. and M.V.B.; data curation, M.-M.M. and M.V.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-Z.A., A.L.D. and L.B.; writing—review and editing, L.B., I.S. and M.-M.M.; visualization, A.-D.A., M.-M.M. and M.V.B.; supervision, M.-Z.A. and A.L.D.; project administration, A.L.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Article Processing Charges were funded by the University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova, Romania.
Acknowledgments
Lidia Boldeanu and Mohamed-Zakaria Assani share equal contributions and status as main/first authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Iman, A.E.H.; Huniadi, A.; Sandor, M.; Zaha, I.A.; Rotar, I.; Iuhas, C. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Romania: Maternal and Fetal Outcomes. Medicina 2025, 61, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Torres, J.; Monroy-Muñoz, I.E.; Perez-Duran, J.; Solis-Paredes, J.M.; Camacho-Martinez, Z.A.; Baca, D.; Espino-y-Sosa, S.; Martinez-Portilla, R.; Rojas-Zepeda, L.; Borboa-Olivares, H.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Kapur, A.; Divakar, H.; Hod, M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus—Innovative Approach to Prediction, Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Future NCD—Mother and Offspring. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 614533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, B.E.; Gabbe, S.G.; Persson, B.; Lowe, L.P.; Dyer, A.R.; Oats, J.J.N.; Buchanan, T.A. International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Recommendations on the Diagnosis and Classification of Hyperglycemia in Pregnancy: Response to Weinert. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO Consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Tong, L.; Xu, A.; He, Y.; Huang, H.; Qiu, D.; Guo, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: New Thinking on Diagnostic Criteria. Life 2024, 14, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeting, A.; Wong, J.; Murphy, H.R.; Ross, G.P. A Clinical Update on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 763–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bekai, E.; Beaini, C.E.; Kalout, K.; Safieddine, O.; Semaan, S.; Sahyoun, F.; Ghadieh, H.E.; Azar, S.; Kanaan, A.; Harb, F. The Hidden Impact of Gestational Diabetes: Unveiling Offspring Complications and Long-Term Effects. Life 2025, 15, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, M.; Mousavi, S.H.; Rafiee, M.; Heidari, R.; Shahrokhi, S.Z. Biochemical and molecular biomarkers: Unraveling their role in gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Prasad, K.; Lemos, J.R.N.; Arevalo, G.; Hirani, K. Unveiling Gestational Diabetes: An Overview of Pathophysiology and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, N.; Chivese, T.; Werfalli, M.; Sun, H.; Yuen, L.; Hoegfeldt, C.A.; Elise Powe, C.; Immanuel, J.; Karuranga, S.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Estimation of Global and Regional Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prevalence for 2021 by International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group’s Criteria. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsad, A.; Kushwah, A.S.; Singh, R.; Banerjee, M. Pharmaco-epi-genetic and patho-physiology of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM): An overview. Health Sci. Rev. 2023, 7, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Chavarro, J.; Olsen, S.; Lin, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Bao, W.; Rawal, S.; Grunnet, L.G.; Thuesen, A.C.B.; Mills, J.L.; et al. Genetic variants of gestational diabetes mellitus: A study of 112 SNPs among 8722 women in two independent populations. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, S.V.; Raizada, N. Genetics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus—The Indian Perspective. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 26, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cui, L.; Tam, W.H.; Ma, R.C.W.; Wang, C.C. Genetic variants associated with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and subgroup analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalha, M.; Iskander, R.; Hassan, H.; Spiegel, E.; Erez, O.; Nachum, Z. Gestational diabetes mellitus—More than the eye can see—A warning sign for future maternal health with transgenerational impact. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2025, 6, 1527076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dłuski, D.F.; Wolińska, E.; Skrzypczak, M. Epigenetic Changes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, T.O.; Chhetri, G.; Yeh, H.; Dong, H.H. Beta-cell compensation and gestational diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyce, B.L.; Dolinsky, V.W. Maternal β-Cell Adaptations in Pregnancy and Placental Signalling: Implications for Gestational Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Badri, M.R.; Zantout, M.S.; Azar, S.T. The role of adipokines in gestational diabetes mellitus. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 6, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo, R.; Ortega-Camarillo, C.; Ferreira-Hermosillo, A.; Díaz-Velázquez, M.F.; Meixueiro-Calderón, C.; Valencia-Ortega, J. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Perez, J.C.; Ernst, S.; Demirci, C.; Casinelli, G.P.; Mellado-Gil, J.M.; Rausell-Palamos, F.; Vasavada, R.C.; Garcia-Ocaña, A. Hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling is required for β-cell regeneration. Diabetes 2014, 63, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, C.; Ernst, S.; Alvarez-Perez, J.C.; Rosa, T.; Valle, S.; Shridhar, V.; Casinelli, G.P.; Alonso, L.C.; Vasavada, R.C.; García-Ocana, A. Loss of HGF/c-Met Signaling in Pancreatic β-Cells Leads to Incomplete Maternal β-Cell Adaptation and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrevia, L.; Valero, P.; Grismaldo, A.; Villalobos-Labra, R.; Pardo, F.; Subiabre, M.; Armstrong, G.; Toledo, F.; Vega, S.; Cornejo, M.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the fetoplacental unit in gestational diabetes mellitus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedika, R.; Sharma, P.; Reddy, A. Signature precursor and mature microRNAs in cervical ripening during gestational diabetes mellitus lead to pre-term labor and other impediments in future. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2023, 22, 945–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicklow, B.; Retnakaran, R. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Implications across the Life Span. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, A.-M.; Popa, R.-F.; Vaduva, C.; Georgescu, C.V.; Adam, G.; Melinte-Popescu, A.-S.; Popa, C.; Socolov, D.; Nechita, A.; Vasilache, I.-A.; et al. Pregnancy Outcomes, Immunophenotyping and Immunohistochemical Findings in a Cohort of Pregnant Patients with COVID-19—A Prospective Study. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennison, R.A.; Chen, E.S.; Green, M.E.; Legard, C.; Kotecha, D.; Farmer, G.; Sharp, S.J.; Ward, R.J.; Usher-Smith, J.A.; Griffin, S.J. The absolute and relative risk of type 2 diabetes after gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 129 studies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 171, 108625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, I.P.; Song, Y.; Jagasia, S.M. Disparities in postpartum follow-up in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin. Diabetes 2014, 32, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.H.; Jang, H.C. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-P.; Lin, S.; Xie, B.-Y.; Zhao, H.-F. Recent progress in metabolic reprogramming in gestational diabetes mellitus: A review. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1284160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, W.; Meng, X.; Zhao, W.; Pan, J.; Tang, J.; Huang, Y.; Tao, M.; Liu, F. Heterogeneity of insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction in gestational diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort study of perinatal outcomes. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElwain, C.J.; McCarthy, F.P.; McCarthy, C.M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Maternal Immune Dysregulation: What We Know So Far. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sugiyama, T.; Murabayashi, N.; Umekawa, T.; Ma, N.; Kamimoto, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Sagawa, N. The inflammatory changes of adipose tissue in late pregnant mice. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Bai, Y.; Li, L.; Shao, Y.; Wu, N. Insulin resistance-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and pyroptosis in trophoblasts: Protective role of metformin. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Fang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, S.; Du, Y.; Su, R.; Guo, L.; et al. The Role of Placental MFF-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2025, 18, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; DeFronzo, R.A. Mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2008, 8, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, D.; Naumovski, N.; Heilbronn, L.K.; Abeywardena, M.; O’Callaghan, N.; Lionetti, L.; Luscombe-Marsh, N. Mitochondrial (Dys)function and Insulin Resistance: From Pathophysiological Molecular Mechanisms to the Impact of Diet. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, G.W.; Zeng, Q.; Kusi, P.; Zhang, H.; Shao, T.; Yang, T.; Wei, Y.; Li, M.; Che, X.; Guo, R. Genetic and inflammatory factors underlying gestational diabetes mellitus: A review. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1399694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngo, C.; Jayabalan, N.; Salomon, C.; Lappas, M. Molecular pathways disrupted by gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2019, 63, R51–R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Guadix, P.; Dueñas, J.L.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Leptin and Nutrition in Gestational Diabetes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, M.; Choubey, M.; Tirumalasetty, M.B.; Arbee, S.; Mohib, M.M.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Mamun, M.A.; Uddin, M.B.; Mohiuddin, M.S. Adiponectin: A Promising Target for the Treatment of Diabetes and Its Complications. Life 2023, 13, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.Q.; He, J.R.; Shen, S.Y.; Lu, J.H.; Kuang, Y.S.; Wei, X.L.; Qiu, X. Maternal circulating leptin profile during pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 161, 108041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Su, S.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xie, S.; Yue, W.; Liu, R.; Yin, C. The effect of circulating adiponectin levels on incident gestational diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2224046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horosz, E.; Bomba-Opon, D.A.; Szymanska, M.; Wielgos, M. Third trimester plasma adiponectin and leptin in gestational diabetes and normal pregnancies. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberger, E.; Larsson, A.; Kunovac Kallak, T.; Sundström Poromaa, I.; Wikström, A.-K.; Österroos, A.; Ahlsson, F. Maternal early mid-pregnancy adiponectin in relation to infant birth weight and the likelihood of being born large-for-gestational-age. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.M.; Chen, M.S.; Tan, H.Z. Maternal serum level of resistin is associated with risk for gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Teague, A.M.; Tryggestad, J.B.; Lyons, T.J.; Chernausek, S.D. Fetal circulating human resistin increases in diabetes during pregnancy and impairs placental mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawah, A.T.; Seini, M.M.; Abaka-Yawason, A.; Alidu, H.; Nanga, S. Leptin, resistin and visfatin as useful predictors of gestational diabetes mellitus. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.K.; Deng, H.Y.; Qiao, Z.Y.; Gong, F.X. Visfatin level and gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 127, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telejko, B.; Kuzmicki, M.; Zonenberg, A.; Szamatowicz, J.; Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek, N.; Nikolajuk, A.; Kretowski, A.; Gorska, M. Visfatin in gestational diabetes: Serum level and mRNA expression in fat and placental tissue. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 84, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akturk, M.; Altinova, A.E.; Mert, I.; Buyukkagnici, U.; Sargin, A.; Arslan, M.; Danisman, N. Visfatin concentration is decreased in women with gestational diabetes mellitus in the third trimester. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2008, 31, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bao, W.; Rong, Y.; Yang, H.; Bowers, K.; Yeung, E.; Kiely, M. Genetic variants and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2013, 19, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami, A.; Javed, A.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Ozsahin, I.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Genetics of diabetes and its complications: A comprehensive review. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 17, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swathi, N.L.; Shakhatreh, Z.; Tahir, A.; Singh, J.; Sulaiman, S.; Athul, H.; Sadhankar, A.; Patel, P.; Patel, R.; Nashwan, A.J. Epigenetic Mechanisms in the Transfer of Metabolic Disorders: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e80418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesen, S.; El-Faitarouni, A.; Frisk, N.L.S.; Sørensen, A.E.; Dalgaard, L.T. Circulating microRNA as Biomarkers for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Rutter, G.A.; Latreille, M. MiRNAs in β-Cell Development, Identity, and Disease. Front. Genet. 2017, 7, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, L. The small RNA miR-375—A pancreatic islet abundant miRNA with multiple roles in endocrine beta cell function. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 456, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPierre, M.P.; Stoffel, M. MicroRNAs as stress regulators in pancreatic beta cells and diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Moon, J. Circulating MicroRNAs for Early Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Metab.—Clin. Exp. 2021, 116, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, T.; Gulati, R.; Uppal, A.; Kumari, S.R.; Tripathy, S.; Ranjan, P.; Janardhanan, R. Prospecting of exosomal-miRNA signatures as prognostic marker for gestational diabetes mellitus and other adverse pregnancy outcomes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1097337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razo-Azamar, M.; Nambo-Venegas, R.; Quevedo, I.R.; Juárez-Luna, G.; Salomon, C.; Guevara-Cruz, M.; Palacios-González, B. Early-Pregnancy Serum Maternal and Placenta-Derived Exosomes miRNAs Vary Based on Pancreatic β-Cell Function in GDM. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 109, 1526–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalpour, S.; Zain, S.M.; Vazifehmand, R.; Mohamed, Z.; Pung, Y.F.; Kamyab, H.; Omar, S.Z. Analysis of serum circulating MicroRNAs level in Malaysian patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20295, Erratum in: Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5121. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-32260-w. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustianowski, Ł.; Udzik, J.; Szostak, J.; Gorący, A.; Ustianowska, K.; Pawlik, A. Genetic and Epigenetic Factors in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Maianu, L.; Zhu, J.H.; Hancock, J.A.; Golichowski, A.M. Multiple defects in the adipocyte glucose transport system cause cellular insulin resistance in gestational diabetes. Heterogeneity in the number and a novel abnormality in subcellular localization of GLUT4 glucose transporters. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iheagwam, F.N.; Joseph, A.J.; Adedoyin, E.D.; Iheagwam, O.T.; Ejoh, S.A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Diabetes: Shedding Light on a Widespread Oversight. Pathophysiology 2025, 32, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsad, A.; Gautam, T.; Singh, R.; Banerjee, M. Genetic and epigenetic alterations associated with gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse neonatal outcomes. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2025, 14, 99231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Hu, C. Molecular biomarkers for gestational diabetes mellitus and postpartum diabetes. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, B.; Thakur, S.S. Proteins and metabolites fingerprints of gestational diabetes mellitus forming protein–metabolite interactomes are its potential biomarkers. Proteomics 2023, 23, 2200257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Van Oostdam, A.S.; Toro-Ortíz, J.C.; López, J.A.; Noyola, D.E.; García-López, D.A.; Durán-Figueroa, N.V.; Martínez-Martínez, E.; Portales-Pérez, D.P.; Salgado-Bustamante, M.; López-Hernández, Y. Placental exosomes isolated from urine of patients with gestational diabetes exhibit a differential profile expression of microRNAs across gestation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Qian, F.; Grewal, J.; Sacks, D.B.; Chen, Z.; Tsai, M.Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C. Early prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus based on systematically selected multi-panel biomarkers and clinical accessibility-a longitudinal study of a multi-racial pregnant cohort. BMC Med. 2025, 23, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansu-Celik, H.; Ozgu-Erdinc, A.S.; Kisa, B.; Findik, R.B.; Yilmaz, C.; Tasci, Y. Prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus in the first trimester: Comparison of maternal fetuin-A, N-terminal proatrial natriuretic peptide, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and fasting glucose levels. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 63, 121–127, Erratum in Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 64, 97. https://doi.org/10.20945/2359-3997000000203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansu-Celik, H.; Ozgu-Erdinc, A.S.; Kisa, B.; Eldem, S.; Hancerliogullari, N.; Engin-Ustun, Y. Maternal serum glycosylated hemoglobin and fasting plasma glucose predicts gestational diabetes at the first trimester in Turkish women with a low-risk pregnancy and its relationship with fetal birth weight; a retrospective cohort study. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 34, 1970–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lin, S.; Li, L.; Cui, J.; Zhou, S.; Fan, J. First-trimester fasting plasma glucose as a predictor of gestational diabetes mellitus and the association with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthavong, S.; Jatavan, P.; Tongsong, T. Predictive Utility of Biochemical Markers for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.W.; Dasgupta, R.; Anoop, S.; Jebasingh, F.; Kurian, M.E.; Inbakumari, M.; Boehm, B.O.; Thomas, N. SPINA Carb: A simple mathematical model supporting fast in-vivo estimation of insulin sensitivity and beta cell function. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razo-Azamar, M.; Nambo-Venegas, R.; Meraz-Cruz, N.; Guevara-Cruz, M.; Ibarra-González, I.; Vela-Amieva, M.; Delgadillo-Velázquez, J.; Santiago, X.C.; Escobar, R.F.; Vadillo-Ortega, F.; et al. An early prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus based on metabolomic biomarkers. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, S.; Hanumanthappa, R.; Bhokare, K.; Datta, N.; Vastrad, N.; David, M.; Maharaj, N.; Anand, K. Exploring the Vertical Transmission of Exosomes in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets for Pregnancy Complications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ren, J.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X. Using metabolomics and proteomics to identify the potential urine biomarkers for prediction and diagnosis of gestational diabetes. EBioMedicine 2024, 101, 105008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Liu, M.; Han, S.; Wu, H.; Qin, R.; Ma, K.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y. Novel first-trimester serum biomarkers for early prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Diabetes 2025, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldharee, H.; Makki, Y.R.; Hamdan, H.Z. The Association Between Chemerin Levels and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.X.; Le, A.W.; Han, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Lei, X.H.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J.V. Chemerin sustains the growth of spongiotrophoblast and sinusoidal trophoblast giant cells through fatty acid oxidation. BMC Biol. 2025, 23, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.T.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, W.T.; Hong, B.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.S.; Wu, S.W.; Wang, Q.; et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in genes involved in folate metabolism or selected other metabolites and risk for gestational diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2025, 16, 103602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-P.; Sun, F.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Wang, L.-K.; Chen, C.-Y. Associations between first-trimester screening biomarkers and maternal characteristics with gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese women. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1383706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestry, C.; Ashavaid, T.F.; Shah, S.A. Key methodological challenges in detecting circulating miRNAs in different biofluids. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2023, 60, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-N.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.-Q.; Yang, M.-M.; Chen, C.; Zhao, B.-H.; Huang, H.-F.; Luo, Q. MiRNAs in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 4632745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragea, C.; Gica, N.; Botezatu, R.; Peltecu, G.; Panaitescu, A.M. Gestational diabetes: Universal or selective screening in pregnancy? Rom. J. Med. Pract. 2022, 17, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, S.I.; Khan, H.A.; Ekhzaimy, A.; Masood, A.; Sakharkar, M.K. Significance of HbA1c Test in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Diabetic Patients. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, N. MicroRNAs and Exosomal microRNAs May Be Possible Targets to Investigate in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchuluun, B.; Al Rijjal, D.; Prentice, K.J.; Eversley, J.A.; Burdett, E.; Mohan, H.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Liu, Y.; Wheeler, M.B. Elevated Medium-Chain Acylcarnitines Are Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Early Progression to Type 2 Diabetes and Induce Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction. Diabetes 2018, 67, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Zhao, D.; Liang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, M.; Tang, X.; Zhuang, H.; Wang, H.; Yin, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Proteomic analysis of plasma total exosomes and placenta-derived exosomes in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus in the first and second trimesters. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545196/ (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Vasile, F.C.; Preda, A.; Ștefan, A.G.; Vladu, M.I.; Forțofoiu, M.-C.; Clenciu, D.; Gheorghe, I.O.; Forțofoiu, M.; Moța, M. An Update of Medical Nutrition Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 5266919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboudi-Gandevani, S.; Amiri, M.; Bidhendi Yarandi, R.; Ramezani Tehrani, F. The impact of diagnostic criteria for gestational diabetes on its prevalence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, O.; Ojo, O.O.; Wang, X.H.; Adegboye, A.R.A. The Effects of a Low GI Diet on Cardiometabolic and Inflammatory Parameters in Patients with Type 2 and Gestational Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipla, K.; Zafeiridis, A.; Mintziori, G.; Boutou, A.K.; Goulis, D.G.; Hackney, A.C. Exercise as a Therapeutic Intervention in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Endocrines 2021, 2, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cao, M.; Liu, K.; Gu, Y. The Impact of Exercise during Pregnancy on Maternal and Offspring Outcomes in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Biocell 2025, 49, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Moreira, C.F.A.; Paulino, D.S.M.; Pereira, B.G.; Rehder, P.M.; Surita, F.G. Metformin versus insulin in glycemic control in pregnancy (MevIP): A randomized clinical trial protocol. Trials 2025, 26, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledano, Y.; Hadar, E.; Hod, M. Pharmacotherapy for hyperglycemia in pregnancy—The new insulins. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 145, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethwani, P.; Saboo, B.; Jethwani, L.; Chawla, R.; Maheshwari, A.; Agarwal, S.; Jaggi, S. Use of insulin glargine during pregnancy: A review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 379–384, Erratum regarding missing Declaration of Competing Interest statements in previously published articles. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2022, 16, 102506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agius, L.; Ford, B.E.; Chachra, S.S. The Metformin Mechanism on Gluconeogenesis and AMPK Activation: The Metabolite Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Kampmann, U.; Dalsgaard Clausen, T.; Laurie, J.; Ma, R.C.W. Gestational Diabetes: An Update 60 Years After O’Sullivan and Mahan. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 110, e19–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, D.T.; Sassin, A.M.; Aagaard, K.M.; Gannon, M. Developmental effects of in utero metformin exposure. Trends Dev. Biol. 2021, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bodier, L.; Le Lous, M.; Isly, H.; Derrien, C.; Vaduva, P. Efficacy and safety of pharmacological treatments for gestational diabetes: A systematic review comparing metformin with glibenclamide and insulin. Diabetes Metab. 2025, 51, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Ma, J.; Tang, J.; Hu, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Metformin, Glyburide, and Insulin in Treating Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 9804708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilian, M.; Mirhosseini, N.; Eslahi, M.; Bahmani, F.; Shokrpour, M.; Chamani, M.; Asemi, Z. The effects of magnesium-zinc-calcium-vitamin D co-supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation, oxidative stress and pregnancy outcomes in gestational diabetes. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motamed, S.; Nikooyeh, B.; Anari, R.; Motamed, S.; Mokhtari, Z.; Neyestani, T. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngo, C.; Willcox, J.C.; Lappas, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic acids punicalagin and curcumin in human placenta and adipose tissue. Placenta 2020, 100, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacka-Aleksić, M.; Pirković, A.; Vilotić, A.; Bojić-Trbojević, Ž.; Jovanović Krivokuća, M.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M.; Dekanski, D. The Role of Dietary Polyphenols in Pregnancy and Pregnancy-Related Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mendonça, E.L.S.S.; Fragoso, M.B.T.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Xavier, J.A.; Goulart, M.O.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: The Crosslink among Inflammation, Nitroxidative Stress, Intestinal Microbiota and Alternative Therapies. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Z.; Yang, H. Interactions between host and gut microbiota in gestational diabetes mellitus and their impacts on offspring. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasain, Z.; Che Roos, N.A.; Rahmat, F.; Mustapa, M.; Raja Ali, R.A.; Mokhtar, N.M. Diet and Pre-Intervention Washout Modifies the Effects of Probiotics on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Hou, H.; Yang, S. The effect of probiotics on gestational diabetes mellitus: An umbrella meta-analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, G. The Effects of Probiotics/Synbiotics on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetinkaya Özdemir, S.; Küçüktürkmen Paşa, B.; Metin, T.; Dinçer, B.; Sert, H. The effect of probiotic and synbiotic use on glycemic control in women with gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 194, 110162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiazza, F.; Couturier-Maillard, A.; Benetti, E.; Mastrocola, R.; Nigro, D.; Cutrin, J.C.; Serpe, L.; Aragno, M.; Fantozzi, R.; Ryffel, B.; et al. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome to Reduce Diet-induced Metabolic Abnormalities in Mice. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldi, S.; Rocca, C.; Gianquinto, E.; Granieri, M.C.; Boscaro, V.; Blua, F.; Rolando, B.; Marini, E.; Gallicchio, M.; De Bartolo, A.; et al. Discovery of a novel 1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-one-based NLRP3 inhibitor as a pharmacological agent to mitigate cardiac and metabolic complications in an experimental model of diet-induced metaflammation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 257, 115542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, D.T.; de Paula Souza, J.; Donath, M.Y. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome-IL-1β pathway in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Diabetologia 2025, 68, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beunen, K.; Van Wilder, N.; Ballaux, D.; Vanhaverbeke, G.; Taes, Y.; Aers, X.P.; Nobels, F.; Marlier, J.; Lee, D.; Cuypers, J.; et al. Closed-loop insulin delivery in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes (CRISTAL): A multicentre randomized controlled trial—Study protocol. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2023, 23, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Si, J.; Li, Y.; Tse, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Ren, J.; Xu, J.; Sun, J.; Yao, X. Effectiveness and safety of AI-driven closed-loop systems in diabetes management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 17, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhalima, K.; Beunen, K.; Van Wilder, N.; Ballaux, D.; Vanhaverbeke, G.; Taes, Y.; Aers, X.-P.; Nobels, F.; Marlier, J.; Lee, D.; et al. Comparing advanced hybrid closed loop therapy and standard insulin therapy in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes (CRISTAL): A parallel-group, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 12, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Ying, Z.; Yang, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yan, H.; Lu, Y.; Gao, Y.; et al. Optimized glycemic control of type 2 diabetes with reinforcement learning: A proof-of-concept trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2633–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.A.; Devi Rajeswari, V. Gestational diabetes mellitus—A metabolic and reproductive disorder. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.-S.; Feng, C.; Yu, D.-Q.; Tian, S.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.-T.; Cai, Y.-T.; Chen, J.; Zhu, M.-M.; Jin, M. Long-term outcomes and potential mechanisms of offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1067282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esakoff, T.F.; Cheng, Y.W.; Sparks, T.N.; Caughey, A.B. The association between birthweight 4000 g or greater and perinatal outcomes in patients with and without gestational diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 200, 672.e671–672.e674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KC, K.; Shakya, S.; Zhang, H. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Macrosomia: A Literature Review. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiq, W.; Hussain, S.; Jan, M.; Najar, B. Clinical and metabolic profile of neonates of diabetic mothers. Int. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2015, 2, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda-Całus, M.; Dąbrowska, K.; Gulczyńska, E. Infant of a diabetic mother: Clinical presentation, diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 30, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova-Parlapanska, K.; Kostadinova-Slavova, D.; Angelova, M.; Sadi, J.A.-D.R.; Georgieva, E.; Goycheva, P.; Karamalakova, Y.; Nikolova, G. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Status in Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Late-Onset Complication of Pre-Eclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 15. Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2024, 48, S306–S320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Qi, L.; He, Y.; Xu, Z.; Tang, J. Influence of gestational diabetes mellitus on the cardiovascular system and its underlying mechanisms. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1474643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, L.; Casas, J.-P.; Hingorani, A.D.; Williams, D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2009, 373, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, C.; Wei, Y.-M.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.-X. Updates in Long-term Maternal and Fetal Adverse Effects of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Matern.-Fetal Med. 2019, 1, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.K.; Campbell, S.; Retnakaran, R. Gestational diabetes and the risk of cardiovascular disease in women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berra, K.; Bezanson, J.L.; Dolor, R.J.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Newby, L.K.; Piña, I.L.; Roger, V.L.; Shaw, L.J.; et al. Effectiveness-Based Guidelines for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Women—2011 Update. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1404–1423, Erratum in J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gunderson, E.P.; Chiang, V.; Pletcher, M.J.; Jacobs, D.R.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Sidney, S.; Lewis, C.E. History of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Future Risk of Atherosclerosis in Mid-life: The Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomback, A.S.; Rekhtman, Y.; Whaley-Connell, A.T.; Kshirsagar, A.V.; Sowers, J.R.; Chen, S.C.; Li, S.; Chinnaiyan, K.M.; Bakris, G.L.; McCullough, P.A. Gestational diabetes mellitus alone in the absence of subsequent diabetes is associated with microalbuminuria: Results from the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP). Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2586–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmer, E.W.; Phadnis, M.A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Lewis, C.E.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Engel, S.M.; Jonsson Funk, M.; Kramer, H.; Kshirsagar, A.V.; Heiss, G. Association Between Gestational Diabetes and Incident Maternal CKD: The Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beharier, O.; Shoham-Vardi, I.; Pariente, G.; Sergienko, R.; Kessous, R.; Baumfeld, Y.; Szaingurten-Solodkin, I.; Sheiner, E. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Is a Significant Risk Factor for Long-Term Maternal Renal Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1412–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.N.; Rajindrajith, S. Fetal programming of obesity and type 2 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2022, 13, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, A.; Ferrara, A.; Windham, G.C.; Greenspan, L.C.; Deardorff, J.; Hiatt, R.A.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Laurent, C.; Mirabedi, A.S.; Kushi, L.H. Maternal hyperglycemia during pregnancy predicts adiposity of the offspring. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2996–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.H.Y.; Godfrey, K.M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Developmental Programming. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 76 (Suppl. S3), 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Luo, C.; Zhou, J.; Liang, X.; Wen, J.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Association between maternal diabetes and neurodevelopmental outcomes in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 202 observational studies comprising 56·1 million pregnancies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, S.; Guillemin, C.; Ergaz, Z.; Dimov, S.; Suderman, M.; Weinstein-Fudim, L.; Ornoy, A.; Szyf, M. Gestational Diabetes Alters Offspring DNA Methylation Profiles in Human and Rat: Identification of Key Pathways Involved in Endocrine System Disorders, Insulin Signaling, Diabetes Signaling, and ILK Signaling. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 2222–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, P.V.; Klyushina, A.A.; Vasilyeva, L.B.; Tkachuk, A.S.; Vasukova, E.A.; Anopova, A.D.; Pustozerov, E.A.; Gorelova, I.V.; Kravchuk, E.N.; Li, O.; et al. Association of Common Genetic Risk Variants With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Their Role in GDM Prediction. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 628582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah, R.; Gindlhuber, J.; Platzer, W.; Bärnthaler, T.; Tatzl, E.; Toller, W.; Strutz, J.; Rittchen, S.; Luschnig, P.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; et al. SUCNR1 Is Expressed in Human Placenta and Mediates Angiogenesis: Significance in Gestational Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthon, S.; Tangjittipokin, W. Mechanisms and Physiological Roles of Polymorphisms in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, E.; Delli Poggi, C.; Grieco, G.E.; Cenci, V.; Ceccarelli, E.; Crisci, I.; Sebastiani, G.; Dotta, F. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Updates and Perspectives. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 6380463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benham, J.L.; Gingras, V.; McLennan, N.-M.; Most, J.; Yamamoto, J.M.; Aiken, C.E.; Ozanne, S.E.; Reynolds, R.M.; Tobias, D.K.; Merino, J.; et al. Precision gestational diabetes treatment: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biete, M.; Vasudevan, S. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Impacts on fetal neurodevelopment, gut dysbiosis, and the promise of precision medicine. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1420664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Cho, Y.M.; Go, M.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Choi, S.H.; Moon, M.K.; Jung, H.S.; Shin, H.D.; Kang, H.M.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Women. Diabetes 2012, 61, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, T.O.; Salisu, T.; Abdulrahman, Y.B.; Umar, A.K. Update on the genetic and epigenetic etiology of gestational diabetes mellitus: A review. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2020, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, W.; Koo, J.N.; Oh, I.H.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, S.M.; et al. Metabolomic profiling reveals early biomarkers of gestational diabetes mellitus and associated hepatic steatosis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, S.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L.; et al. Genetic architecture and risk prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese pregnancies. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Pineda, T.; Peña-Montero, N.; Fragoso-Bargas, N.; Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Lima-Rubio, F.; Suarez-Arana, M.; Sánchez-Pozo, A.; Tinahones, F.J.; Molina-Vega, M.; Picón-César, M.J.; et al. Epigenetic marks associated with gestational diabetes mellitus across two time points during pregnancy. Clin. Epigenet. 2023, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04198857 (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Gong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Kang, R.; Wang, J.; Wei, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Heterogeneity of Gestational Diabetes and Risk for Adverse Pregnancy Outcome: A Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 110, e2264–e2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, H.; Han, L.; da Silva Costa, F.; Paganoti, C.; Dyer, B.; Kundur, A.; Singh, I.; Holland, O.J. Advancement in predictive biomarkers for gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosis and related outcomes: A scoping review. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e089937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taschereau, A.; Doyon, M.; Arguin, M.; Allard, C.; Desgagné, V.; Cote, A.-M.; Massé, É.; Jacques, P.-É.; Perron, P.; Hivert, M.-F.; et al. Cohort profile: The Genetics of Glucose regulation in Gestation and Growth (Gen3G)—A prospective prebirth cohort of mother–child pairs in Sherbrooke, Canada, 3-year and 5-year follow-up visits. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e093434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).