Abstract
Statins, primarily prescribed for their lipid-lowering effects, have garnered significant attention for their potent anti-inflammatory effects. This review explores the underlying molecular pathways and clinical relevance of statins’ anti-inflammatory actions, extending beyond cardiovascular disease management to chronic inflammatory conditions and oncological applications. The lipid-lowering effect of statins stems from their ability to suppress HMG-CoA reductase, a crucial enzyme in cholesterol synthesis; however, their pleiotropic effects include modulation of critical inflammatory pathways such as the inhibition of NF-κB signalling, a reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and enhancement of endothelial function. We delve into the molecular pathways influenced by statins, including their effects on inflammatory mediators like C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukins (IL-6, IL-1β), and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). Clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of statins in managing chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, and osteoarthritis, is critically reviewed. Additionally, we investigate the emerging role of statins in oncology, examining their impact on inflammation-driven carcinogenesis, tumour microenvironment modulation, and cancer progression. Despite their broad therapeutic potential, the safety profile of statins, particularly concerning adverse effects such as myopathy, hepatotoxicity, and potential diabetes risk, is discussed. Controversies surrounding the extent of their anti-inflammatory benefits and the variability in patient responses are also addressed. This review consolidates the current literature, elucidating the biochemical mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory properties of statins and evaluating their clinical applications and associated controversies. Future research directions are identified, including the development of novel statin analogues with enhanced anti-inflammatory effects and the investigation of new therapeutic indications in inflammatory diseases and cancer. By providing an in-depth analysis, this review underscores the expanding therapeutic scope of statins and advocates for their integration into broader clinical strategies for the management of inflammation and cancer.
1. Introduction
Statins, constituting a pharmacological class of competitive inhibitors targeting 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl–coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase—the catalytic arbiter of the rate-limiting step in the mevalonate pathway of endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis—have emerged as a principal therapeutic axis in the prophylaxis and longitudinal management of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. By orchestrating a sustained decrement in circulating low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) concentrations, these agents attenuate lipid-driven endothelial injury, modulate plaque biology, and substantially diminish the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events across both primary- and secondary-prevention cohorts. Key clinical trials, including the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S) [], the Heart Protection Study (HPS) [], the Cholesterol and Recurrent Events (CARE) trial [], the Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischemic Disease (LIPID) trial [], the Pravastatin or Atorvastatin Evaluation and Infection Therapy (PROVE-IT TIMI 22) trial [], the Justification for the Use of Statins in Prevention: an Intervention Trial Evaluating Rosuvastatin (JUPITER) [], and the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study (WOSCOPS) [] have demonstrated these effects, establishing statins as a foundational therapy in cardiovascular disease management. However, beyond their well-established lipid-lowering properties, statins have garnered significant attention for their potent anti-inflammatory effects, which extend their therapeutic potential far beyond the realm of cardiovascular disease. For example, the JUPITER trial demonstrated that rosuvastatin significantly reduced high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels [], a marker of inflammation, while the Controlled Rosuvastatin Multinational Trial in Heart Failure (CORONA) trial observed a reduction in inflammatory biomarkers in heart failure patients treated with rosuvastatin []. Similary in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial–Lipid Lowering Arm (ASCOT-LLA) trial, a reduction in inflammatory biomarkers such as IL-6 and TNF-α in patients treated with atorvastatin was observed, highlighting its anti-inflammatory benefits alongside its lipid-lowering effects [].
The pleiotropic effects of statins (Figure 1)—those unrelated to their capacity to induce sustained reductions in atherogenic lipoprotein concentrations—have been the subject of extensive research. These pharmacodynamic effects encompass the perturbation of pivotal pro-inflammatory signalling cascades, most notably the suppression of nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB)-dependent transcriptional activity [], concomitant with an attenuation of downstream pro-inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis [], along with improved endothelial function []. These effects are of particular interest given the central role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of numerous chronic diseases and malignancies [].
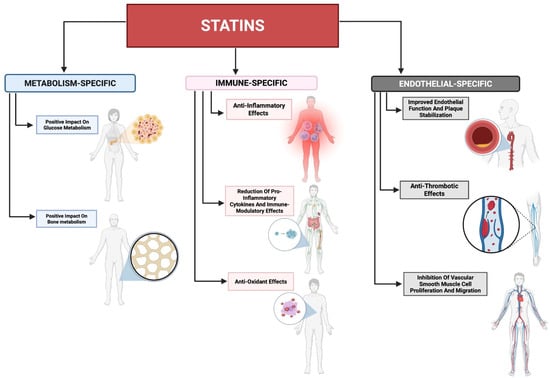
Figure 1.
Pleiotropic effects of statins. A summary of statins’ pleiotropic effects beyond their primary lipid-lowering properties that extend into metabolic processes (metabolism-specific), the immune system (immune-specific), and the lymphovascular system (endothelial-specific). These pleiotropic effects of statins can allow statins to be utilized as a therapeutic regimen in multiple conditions.
Inflammation serves as a crucial biological response to harmful stimuli such as pathogens, cellular damage, and irritants [,,]. This process involves the release of numerous inflammatory mediators, including cytokines and chemokines, which coordinate the activation and migration of immune cells to the affected site. Whereas acute inflammation constitutes a temporally restricted, evolutionarily conserved reparative and immunoprotective response, its chronic persistence engenders a maladaptive immunopathological milieu that underpins the etiopathogenesis of a broad spectrum of morbidities, including—but not limited to—rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteoarthritis (OA), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and diverse malignancies. The latter being a fascinating niche to investigate as chronic inflammation is a well-recognized driver of carcinogenesis, promoting tumour initiation, progression, and metastasis [,,]. Statins, by modulating inflammatory pathways, may advantageously affect the tumour microenvironment (TME) and inhibit cancer progression.
Epidemiological evidence derived from large-scale, population-based cohorts has suggested an inverse association between statin exposure and the incidence of select malignancies, notably breast, prostate, and colorectal carcinomas []. Complementary preclinical investigations have elucidated pleiotropic oncostatic mechanisms attributable to statins, encompassing the attenuation of neoplastic cell proliferation, the induction of programmed cell death, and the suppression of tumour progression across diverse experimental models []. Furthermore, clinical trials are currently in progress to assess the effectiveness of statins as adjuvant therapy in cancer treatment (refer below for details), exploring their potential to enhance the effects of conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Statins are also being explored for their potential benefits in specific diseases where inflammation plays a pivotal role, such as psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Therefore, the anti-inflammatory effects of statins offer a promising potential for therapeutic intervention in these conditions.
Despite the broad therapeutic potential of statins, their safety profile warrants careful consideration. Common adverse effects of statin therapy include myopathy, hepatotoxicity, and an increased risk of diabetes [,]. These side effects, although generally rare, necessitate a thorough risk-benefit analysis when prescribing statins, particularly for long-term use in chronic inflammatory conditions or cancer. Controversies also exist regarding the extent of the anti-inflammatory benefits of statins and the variability in patient responses. Genetic factors, comorbidities, and concurrent medications can influence the efficacy and safety of statin therapy [], underscoring the need for personalized treatment approaches.
This paper reviews the body of evidence surrounding statins’ anti-inflammatory effects, focusing on the biochemical mechanisms at play as well as their practical clinical implications and ongoing controversies. It highlights important avenues for future research, including the investigation of novel therapeutic applications of statins in inflammatory diseases and cancer. By thoroughly analyzing current data, the paper highlights the widening role of statins in medicine and calls for their incorporation into treatment strategies targeting inflammation, especially within oncology.
2. Statins at a Glance
Statins may be dichotomised into hydrophilic and lipophilic subclasses (vide Figure 2), a physicochemical stratification that exerts profound influence upon their pharmacokinetic disposition, tissue penetrance, and attendant adverse-event spectra. The salient agents within each subclass are enumerated in Table 1, which concomitantly catalogues pivotal, large-scale, randomized controlled trials that have served as the evidentiary fulcrum for contemporary lipid-lowering paradigms. These landmark investigations have yielded methodologically rigorous and statistically robust proof-of-concept for the salutary impact of statin therapy upon both primary and secondary prophylaxis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). The aggregate corpus of such trial-derived data constitutes the foundational substrate upon which current American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) clinical practice guidelines are predicated—guidelines that promulgate the initiation of statin pharmacotherapy in individuals manifesting elevated ASCVD risk indices, irrespective of antecedent baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) concentrations, with therapeutic intensity being meticulously titrated in proportion to the calculated global cardiovascular risk burden [,].
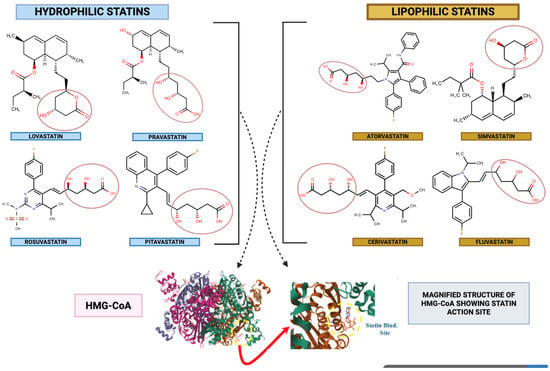
Figure 2.
Classification of statins. An illustration of the commonly utilized statins classified based on hydrophilicity and lipophilicity, along with their molecular structures. The lipophilic nature of statins allows them to easily penetrate various membranes. On the other hand, hydrophilicity allows them ease of transport in the bloodstream, thus affecting not only their therapeutic potential but also contributing to their possible side effect potential. Furthermore, the figure details the functional group of statins (3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid) that is structurally and functionally similar to the active site of HMG-CoA (PDB code 1HW8), allowing for competitive inhibition.

Table 1.
Statin classification with their representative trials.
Hydrophilic statins, exemplified by pravastatin and rosuvastatin, possess a high aqueous solubility profile, resulting in preferential hepatocellular uptake via active, carrier-mediated transport mechanisms, particularly organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs). In contrast, lipophilic congeners—such as atorvastatin, simvastatin, and lovastatin—exhibit pronounced lipid solubility, thereby facilitating passive transmembrane diffusion and enabling a broader intracellular distribution across extrahepatic tissues. The biotransformation of statins is predominantly hepatic, engaging a constellation of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. Among these, CYP3A4 constitutes the principal metabolic axis for atorvastatin, simvastatin, and lovastatin, whereas CYP2C9 predominates in the oxidative metabolism of agents such as fluvastatin and rosuvastatin. This isoform-specific metabolic routing exerts profound influence over their pharmacokinetic disposition, susceptibility to pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic interactions, and the qualitative spectrum of adverse event profiles [,,].
Therapeutically, statins are ubiquitously deployed in the pharmacological management of hyperlipidemia, operating through competitive antagonism at the catalytic domain of HMG-CoA reductase, wherein they displace the natural substrate, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl–coenzyme A. This blockade disrupts the mevalonate biosynthetic cascade (Figure 2), leading to a reduction in endogenous cholesterol synthesis and subsequent upregulation of hepatic LDL receptors, thereby enhancing plasma LDL clearance. The clinical utility of this pharmacodynamic mechanism is underscored by pivotal outcome trials—ASCOT-LLA for atorvastatin [], the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S) for simvastatin [], and JUPITER for rosuvastatin []—each demonstrating substantial reductions in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Cumulatively, these data affirm the dual therapeutic paradigm of statins—potent lipid-lowering efficacy coupled with pleiotropic anti-inflammatory actions—positioning them as indispensable agents within contemporary cardiovascular risk reduction strategies and potentially as modulators of disease processes extending beyond atherosclerosis.
2.1. Cholesterol-Lowering Mechanism of Statins
Statins exert their hypocholesterolemic activity via a complex, multistage pharmacodynamic cascade, the fulcrum of which is the high-affinity, reversible inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl–coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. This microsomal, NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase represents the committed, rate-limiting enzymatic locus within the mevalonate biosynthetic pathway, catalyzing the stereospecific reduction in HMG-CoA to mevalonate—a pivotal early-stage metabolite that governs the flux and overall throughput of endogenous cholesterol synthesis (Figure 3). By occupying the catalytic site in a manner structurally mimetic of the natural substrate, statins arrest this critical step, thereby attenuating intracellular cholesterol pools, triggering compensatory upregulation of hepatic low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor expression, and enhancing receptor-mediated endocytosis of circulating LDL particles. The cholesterol-lowering efficacy of statins thus emerges from a synergistic interplay of primary enzymatic blockade with downstream regulatory adaptations, culminating in a pronounced reduction in plasma LDL concentrations and a concomitant improvement in overall lipid profile.

Figure 3.
Statins inhibit mevalonate pathway and RhoA and Ras activation. This diagram depicts the mevalonate pathway, detailing how the intermediates, GGPP and FPP, are utilized for activation of small G-proteins RhoA and Ras. HMG-CoA (1) is reduced to mevalonate (2), which leads to downstream conversion into non-steroidal isoprenoids (3), GGPP and FPP (4). RhoA and Ras become activated by these small G-proteins (4) via prenylation, specifically geranylgeranylation via GGPP and farnesylation via FPP. (5) These allow these molecules to be anchored to the cell’s inner membrane (6). The subsequent activation of several downstream signalling and outcomes, such as inflammation and cell progression (7), have been implicated in diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and more. Thus, by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA, statins can inhibit the downstream cascade, allowing the attenuation of further signalling.
2.1.1. Inhibition of HMG-CoA Reductase
Owing to their structural congruence with the endogenous substrate HMG-CoA (Figure 3), statins engage in high-affinity, competitive occupancy of the catalytic domain of HMG-CoA reductase. This substrate mimicry sterically hinders enzymatic turnover, thereby abrogating the reductive conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate []. The pharmacological significance of this blockade lies in the fact that mevalonate constitutes an obligatory biosynthetic precursor not only for cholesterol but also for an array of isoprenoid derivatives that are essential to diverse cellular functions []. Suppression of mevalonate biosynthesis thus precipitates a coordinated series of downstream metabolic perturbations, culminating in a sustained diminution of systemic cholesterol levels.
Decreased Cholesterol Synthesis in Hepatocytes
Through the targeted inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, the de novo biosynthetic output of cholesterol within hepatocytes is markedly attenuated. Cholesterol, a pivotal structural constituent of cellular bilayers and an indispensable substrate for the biosynthesis of bile acids, steroid hormones, and vitamin D, thus becomes limited at its primary site of production. The hepatocentric suppression of cholesterol synthesis induced by statins precipitates a pronounced intracellular depletion, which in turn elicits a suite of homeostatic counter-regulatory responses, most notably the transcriptional upregulation of LDL receptors and the concomitant diminution of isoprenoid intermediates.
2.1.2. Upregulation of LDL Receptors
Following the suppression of endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis, hepatocytes initiate a compensatory transcriptional programme characterized by marked upregulation of LDL receptor expression at the plasma membrane. This adaptive shift augments the capacity for receptor-mediated sequestration of circulating LDL particles, the predominant cholesterol transport vehicles within the systemic circulation. Ligand–receptor engagement facilitates clathrin-dependent endocytosis, delivering LDL cargo into endosomal–lysosomal compartments, where hydrolytic degradation liberates free cholesterol for intracellular utilization. This process simultaneously attenuates the extracellular LDL-C burden, and the receptor upregulation-driven acceleration of LDL-C clearance constitutes a pivotal mechanistic axis underpinning the lipid-lowering efficacy of statins.
2.1.3. Reduction in VLDL Secretion
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), a triglyceride- and cholesterol-enriched lipoprotein fraction synthesized within the hepatic parenchyma, undergoes progressive intravascular remodelling to yield LDL as its metabolic endpoint. Statin-mediated inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis, coupled with attenuation of triglyceride availability, constrains the substrate pool required for VLDL assembly within hepatocytes. This restriction in precursor lipid supply translates into a diminished rate of VLDL secretion into the circulation, thereby limiting the downstream intravascular generation of LDL particles and contributing to the overall reduction in atherogenic lipoprotein burden.
2.1.4. Inhibition of Isoprenoid Synthesis
Inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase by statins concomitantly suppresses the biosynthetic generation of critical isoprenoid intermediates, notably farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) (Figure 3). These polyisoprenoid derivatives serve as indispensable lipid moieties for the post-translational prenylation of a diverse repertoire of proteins integral to intracellular cholesterol trafficking and signal transduction. Among these, the covalent attachment of isoprenoid chains to small GTP-binding proteins such as Ras and Rho is essential for their membrane localisation and functional activation, thereby governing key regulatory axes in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Through attenuation of isoprenoid synthesis, statins exert secondary modulatory effects on these signalling cascades, with consequent ramifications for lipid homeostasis and broader aspects of cellular physiology.
2.1.5. Impact on Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Proteins (SREBPs)
The diminution of intracellular cholesterol concentration exerts a regulatory influence on the activity of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs), a family of membrane-bound transcription factors orchestrating the expression of genes implicated in cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthetic pathways []. In the basal state, SREBPs remain sequestered within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane as inactive precursors. A decline in cholesterol availability initiates their proteolytic activation, enabling the release and nuclear translocation of the mature transcriptionally competent forms, which subsequently upregulate the expression of LDL receptor genes and enzymatic mediators of cholesterol synthesis [,]. Under conditions of HMG-CoA reductase inhibition by statins, however, the SREBP-mediated transcriptional response is functionally biassed towards robust enhancement of LDL receptor expression, thereby potentiating plasma LDL-C clearance rather than restoring endogenous cholesterol synthesis [,,].
2.1.6. Reduction in Circulating LDL-C and Other Lipoproteins
The integrated outcome of attenuated cholesterol biosynthesis, augmented LDL receptor upregulation, diminished hepatic VLDL output, and suppression of isoprenoid generation culminates in a pronounced reduction in circulating LDL-C concentrations. In addition, statin therapy is associated with modest decrements in plasma triglyceride levels and slight elevations in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol []. Collectively, these shifts engender a favourable remodelling of the lipid profile, thereby mitigating atherogenic burden and conferring a measurable reduction in the incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular events.
In conclusion, through the comprehensive inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase and the subsequent cascade of metabolic changes, statins effectively lower plasma cholesterol levels, primarily by reducing LDL-C. This mechanism not only involves direct reduction in cholesterol synthesis but also enhances cholesterol clearance from the bloodstream, decreases VLDL secretion, and influences other lipid-related pathways.
2.1.7. Reflection from Clinical Trials
A comprehensive analysis of clinical trials involving statins provides critical insights into their cholesterol-lowering effects and cardiovascular benefits (Table 1). These trials encompass various statins, each with unique pharmacological properties, but collectively, they underscore the importance of LDL-C reduction in managing cardiovascular risk. Below, we detail the findings from key clinical trials for each statin, including their impact on cholesterol levels and cardiovascular outcomes.
Atorvastatin has undergone extensive evaluation within multiple large-scale, randomized, controlled clinical investigations. The Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial—Lipid-Lowering Arm (ASCOT-LLA), enrolling 10,305 hypertensive subjects with normocholesterolemia or cholesterol concentrations below the population mean [], demonstrated that atorvastatin administration yielded an approximate 35% decrement in LDL-C concentrations, concomitantly effecting a 36% relative risk reduction in major cardiovascular events. Notably, this therapeutic benefit was consistently observed across diverse stratified subpopulations, including those with comparatively low baseline cholesterol, thereby indicating that the cardioprotective effects of atorvastatin extend beyond its conventional lipid-lowering indications. Complementing these findings, the Collaborative Atorvastatin Diabetes Study (CARDS) specifically investigated individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus who did not exhibit substantially elevated LDL-C levels []. In this cohort, atorvastatin therapy was associated with a 37% diminution in the incidence of major cardiovascular events, reinforcing the paradigm that statin-mediated risk reduction in diabetic populations is operative irrespective of initial LDL-C status.
Simvastatin has been rigorously interrogated in multiple landmark clinical investigations, among which the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S) remains one of the most seminal []. This randomized trial enrolled 4444 subjects with established coronary heart disease and hypercholesterolemia, demonstrating that simvastatin therapy elicited a ~35% reduction in LDL-C concentrations and a 30% decrease in all-cause mortality—the latter being principally attributable to a 42% diminution in coronary heart disease-related deaths. These data provided compelling, high-grade evidence substantiating the cholesterol-lowering and survival-prolonging properties of statins within the framework of secondary prevention. Building on these foundational results, the Heart Protection Study (HPS) recruited in excess of 20,000 participants identified as being at elevated risk for cardiovascular events, including individuals with diabetes mellitus, peripheral arterial disease, and prior cerebrovascular pathology []. The HPS demonstrated a 24% reduction in major vascular events with simvastatin therapy, irrespective of baseline cholesterol concentrations—a pivotal observation that substantiated the broader clinical utility of statins in high-risk populations, even in the absence of overt LDL-C elevation.
Lovastatin, among the earliest statin agents to be developed and clinically deployed, underwent pivotal evaluation in the Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study (AFCAPS/TexCAPS) []. This landmark randomized, primary prevention trial enrolled 6605 individuals without prior clinical manifestations of cardiovascular disease and demonstrated that lovastatin therapy conferred a 37% relative risk reduction in the incidence of a first major acute coronary event. This outcome was mechanistically associated with an approximate 25% reduction in LDL-C concentrations. The findings from AFCAPS/TexCAPS underscored the prophylactic efficacy of lovastatin in individuals exhibiting normocholesterolemia or only moderate hypercholesterolaemia, thereby establishing that, even in the absence of clinically apparent cardiovascular pathology, statin administration can deliver substantial cardioprotective benefit.
Fluvastatin was subjected to rigorous evaluation within the framework of the Lescol Intervention Prevention Study (LIPS), a multicentre, randomized investigation enrolling patients who had recently been subjected to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) []. In this trial, fluvastatin administration effected a 20–25% decrement in LDL-C concentrations and was associated with a statistically robust 22% relative risk attenuation in major adverse cardiac events (MACE). The clinical relevance of these findings is particularly pronounced in the post-PCI setting, wherein intensive lipid-lowering pharmacotherapy serves as a critical determinant in curtailing the likelihood of recurrent ischaemic episodes in a population with heightened vascular vulnerability. The performance of fluvastatin in this context consolidates its role as a cornerstone of secondary prevention, particularly in individuals undergoing recent coronary revascularisation procedures.
Pravastatin has been rigorously appraised across multiple landmark, randomized, controlled investigations, notably the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study (WOSCOPS) [], the Cholesterol and Recurrent Events (CARE) trial [], and the Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischemic Disease (LIPID) study []. In WOSCOPS, a cohort of 6595 male participants with elevated LDL-C concentrations and no antecedent myocardial infarction exhibited a ~26% decrement in LDL-C accompanied by a 31% relative risk attenuation in incident coronary events under pravastatin therapy. The CARE trial, enrolling patients with prior myocardial infarction and moderate baseline cholesterol levels, recorded a 24% reduction in the recurrence of coronary events with pravastatin intervention. The LIPID study, encompassing 9014 subjects with a history of myocardial infarction or unstable angina, corroborated these outcomes, documenting a 24% relative risk reduction in MACE over a 16-year longitudinal follow-up period. Collectively, these datasets substantiate the efficacy of pravastatin in both primary and secondary prevention paradigms, conferring cardioprotection across a broad continuum of baseline cardiovascular risk profiles.
Rosuvastatin, distinguished by its pronounced potency in reducing LDL-C concentrations, underwent pivotal evaluation in the Justification for the Use of Statins in Prevention: an Intervention Trial Evaluating Rosuvastatin (JUPITER) []. This large-scale, randomized investigation enrolled 17,802 individuals without overt hyperlipidemia but exhibiting elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) concentrations. Rosuvastatin therapy yielded a 50% diminution in LDL-C and a 37% reduction in hs-CRP, accompanied by a 44% relative risk attenuation in major cardiovascular events, encompassing myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, and coronary revascularisation. The JUPITER trial was paradigm-shifting in its implications, as it underscored the utility of statin therapy in a cohort lacking conventional dyslipidemic indications, thereby broadening the conceptual framework of statins to encompass anti-inflammatory as well as cardioprotective mechanisms in primary prevention.
Pitavastatin, a newer statin, has shown promise in several trials, though it has not been as extensively studied as some of the other statins. It has been noted for its strong LDL-C lowering effect with a relatively low risk of increasing blood glucose levels, making it a potential choice for patients at risk of diabetes [,]. The PEARL and JAPAN-ACS trials have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing LDL-C and improving endothelial function, though more extensive trials are needed to fully establish its long-term cardiovascular benefits [,].
Cerivastatin, although exhibiting pronounced potency in lipid-lowering efficacy, was ultimately withdrawn from clinical use following accumulating reports of severe myotoxicity, most notably rhabdomyolysis [,]. The clinical development trajectory and post-marketing pharmacovigilance data revealed substantial LDL-C reductions; however, these benefits were counterbalanced by an unacceptably adverse safety profile. The cerivastatin experience serves as a critical exemplar of the necessity for rigorous safety surveillance in statin pharmacotherapy and underscores the delicate equilibrium between therapeutic efficacy and the potential for serious, treatment-limiting toxicities.
In summation, the aggregated corpus of evidence derived from an array of large-scale, randomized, controlled evaluations encompassing multiple statin pharmacophores substantiates their capacity to effectuate substantive reductions in LDL-C concentrations and concomitantly attenuate the incidence of adverse cardiovascular endpoints. Collectively, these trials delineate the extensive therapeutic latitude of statin pharmacotherapy across heterogeneous patient strata, encompassing individuals with and without antecedent cardiovascular pathology, spanning a continuum of baseline lipid phenotypes, and incorporating diverse comorbid constellations. A unifying observation emergent from these datasets is the reproducible decrement in LDL-C burden and the attendant diminution in cardiovascular event rates, findings that have irrevocably entrenched statins as foundational agents within the armamentarium of preventive cardiology. While inter-statin heterogeneity persists in physicochemical attributes, pharmacokinetic disposition, and safety–tolerability spectra, the overarching net clinical benefit in mitigating cardiovascular morbidity and mortality remains unequivocal. This formidable evidentiary framework continues to underpin the pervasive clinical deployment of statins, informed by nuanced, individualized risk stratification and tailored to patient-specific therapeutic exigencies.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Statins
The multifaceted immunoregulatory attributes of statins have been subjected to exhaustive interrogation, with an extensive corpus of in vitro and in vivo experimentation delineating their modulatory repercussions across disparate pro-inflammatory signalling architectures. These distal sequelae are precipitated via abrogation of flux through the mevalonate biosynthetic conduit, wherein attrition of isoprenoid derivatives engenders perturbation of lipid-anchorage-dependent spatial disposition and the operational competency of low-molecular-weight GTP-binding modulators such as Rho, Rac, and Ras (Figure 3) [,,]. In the interest of curtailing prolixity, Table 2 enumerates exemplar pre-clinical interrogations appraising the anti-inflammatory capacities of statins within both animal and cell-based milieus, whereas Table 3 subsequently encapsulates translational deployments of these anti-inflammatory capacities in controlled clinical scenarios targeting non-cardiovascular morbidities. The purpose of this segment is to expound the subordinate and collateral mechanistic ramifications of HMG-CoA reductase antagonism, thereby furnishing both corroborative and dialectical perspectives regarding the extension of statin pharmacology into domains exceeding its orthodox cardiovascular prophylactic remit.

Table 2.
Statins’ anti-inflammatory effects investigated in pre-clinical trials.

Table 3.
Table of clinical trials investigating activity of inflammatory markers in different disease states.
3.1. Effect on NLRP3 Inflammasome
Figure 4 illustrates the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of statins, particularly focusing on their role in inhibiting the NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome pathway that is crucial for activating pro-inflammatory cytokines. The NLRP3 inflammasome is a multiprotein assembly comprising the pattern-recognition receptor NLRP3, the adaptor molecule ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain), and the effector protease caspase-1. In the context of inflammatory insult, cellular injury provokes the liberation of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which engage and prime the NLRP3 scaffold. Its activation may be instigated by a broad spectrum of upstream triggers, encompassing microbial pathogens, crystalline particulates, perturbations in metabolic homeostasis, and hyperglycemic states. Following activation, the NLRP3 sensor undergoes conformational rearrangements that permit high-affinity engagement with the adaptor ASC. This interaction nucleates the formation of a supramolecular signalling platform, enabling the proximity-induced autocatalytic conversion of pro-caspase-1 into its enzymatically active form [,,].
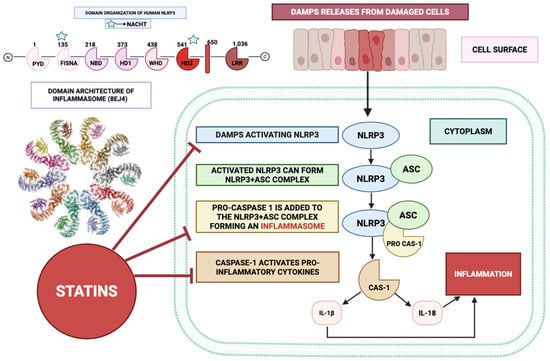
Figure 4.
Statins inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome to attenuate pro-inflammatory cytokine release. This figure highlights the structure of the NLRP3 inflammasome (PDB code 8EJ4), with its associated NACHT domain, which acts as a molecular switch. Stress signals such as DAMPs activate the complex DAMP/NLRP3/CAS-1 axis. Statins inhibit this cascade at multiple points, allowing the attenuation of this pathway towards an anti-inflammatory state.
Subsequently, the catalytically active form of caspase-1 proteolytically cleaves the zymogen precursors of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18), thereby converting them from their latent pro-cytokine states into biologically active, mature forms. These cytokines are potent mediators of inflammation, playing key roles in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory diseases, including atherosclerosis, RA, and metabolic syndrome [,]. In particular, IL-1β is a critical mediator of fever and local inflammation, whereas IL-18 stimulates the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and promotes the differentiation of T-helper cells. Figure 4 shows how the inflammasome complex, upon activation, leads to the release of these cytokines, culminating in an inflammatory response.
Figure 4 illustrates that statins inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome at multiple levels, thus preventing the downstream inflammatory cascade. This inhibition can occur through several mechanisms. By suppressing the mevalonate biosynthetic pathway, statins curtail the generation of isoprenoid derivatives—farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP)—which serve as essential lipid moieties for the post-translational prenylation of small GTP-binding proteins, including members of the Ras, Rho, and Rac families. By reducing the availability of these intermediates, statins effectively disrupt the proper functioning of these GTPase proteins, thereby inhibiting the assembly and activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
The nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signalling axis serves as a pivotal transcriptional regulator in inflammation, orchestrating the expression of genes for pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β and IL-18. Evidence indicates that statins can attenuate NF-κB activity by impeding the nuclear translocation of its heterodimeric complex, thereby limiting downstream pro-inflammatory gene expression [,]. This inhibition reduces the transcription of IL-1β and IL-18, thereby limiting the substrates available for caspase-1 activation [,].
Oxidative stress serves as a strong trigger for NLRP3 activation. Statins possess antioxidant properties that can reduce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). By lowering oxidative stress, statins prevent ROS-mediated stimulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, thereby decreasing the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 [].
3.2. Effect on the NF-κB Pathway
Figure 5 depicts the sequence of molecular events through which damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) initiate NF-κB activation, followed by the anti-inflammatory effects exerted by statins. The process commences when DAMPs, released from injured or stressed cells, are detected by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) expressed by macrophages. The binding of DAMPs to TLRs triggers a signalling cascade involving several key proteins, ultimately resulting in the activation of the NF-κB pathway [,,,]. Following the detection of danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), Toll-like receptors (TLRs) engage the adaptor molecule myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88). This adaptor functions as a central signalling nexus, propagating downstream cascades that culminate in the activation of Tank-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and the IκB kinase (IKK) complex. The IKK complex phosphorylates IκB, an inhibitory protein that binds to NF-κB dimers in the cytoplasm, preventing their translocation to the nucleus. Phosphorylation of IκB leads to its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation, releasing NF-κB [,].
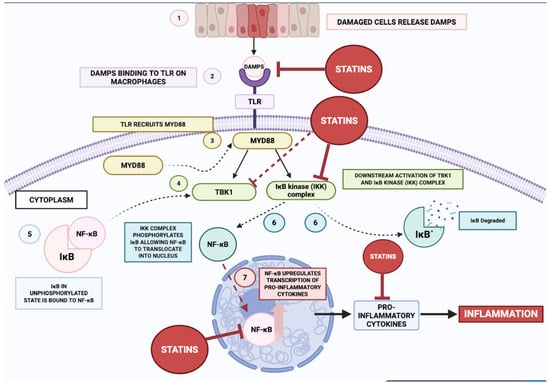
Figure 5.
Statins attenuate DAMP-stimulated NF-κB activation and subsequent inflammation. This figure highlights how DAMPs (1) (released from damaged cells due to pathogens, metabolic stress, and other pathological states) activate the NF-κB signalling cascade (7) by binding to TLRs (2) on macrophages, leading to the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines (3) (4) (5) (6). Statins exert its inhibitory effects at multiple points in this cascade, thus exerting potent multi-target, anti-inflammatory effects that can be leveraged by the clinical community for therapeutic potentials in patients.
Upon liberation from cytoplasmic sequestration, NF-κB translocates to the nuclear compartment, where it engages cognate κB consensus motifs within genomic DNA, thereby instigating transcriptional programmes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. These effector molecules constitute pivotal immunopathological mediators, orchestrating the initiation and propagation of inflammatory cascades implicated in the aetiopathogenesis of diverse disorders, notably cardiovascular disease and atherogenesis. The biosynthesis and extracellular liberation of these cytokines facilitate chemotactic recruitment and activation of additional leucocytic populations, thereby amplifying the inflammatory milieu and exacerbating parenchymal injury and pathological progression.
Statins attenuate such pro-inflammatory signalling through multipoint interference within the NF-κB activation axis. Primarily, they impede the catalytic competency of the IKK complex, forestalling the phosphorylation-induced proteasomal catabolism of IκB [,]. This preservation of the cytoplasmic NF-κB–IκB complex precludes nuclear ingress of NF-κB, thereby abrogating transcriptional induction of pro-inflammatory gene networks. By interdicting this rate-limiting event, statins effectuate a net suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis.
Additionally, statins disrupt MyD88-dependent signal transduction [] via diminution of isoprenoid intermediates—FPP and GGPP—whose availability is requisite for the post-translational prenylation and functional competence of small GTPases operating within this pathway. This biochemical attrition compromises the downstream transductional fidelity of TLR-initiated signalling, resulting in attenuated activation of TBK1 and IKK and, consequently, diminished NF-κB activation.
Beyond these canonical effects, statins mitigate the liberation of DAMPs from structurally compromised cells through enhancement of membrane stability and cytoprotection against cell death. Attenuation of extracellular DAMP release curtails TLR engagement and subsequent pro-inflammatory signalling, thereby diminishing the priming stimuli for innate immune activation.
Cumulatively, these mechanisms culminate in downmodulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules, and ancillary inflammatory mediators, leading to reduced immune cell ingress and activation at inflamed loci. This decrement in immunopathological burden translates to mitigated tissue injury and improved clinical endpoints in pathologies such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Inhibitory modulation of NF-κB signalling by statins thus constitutes a principal molecular axis through which these agents confer anti-inflammatory and vasculoprotective efficacy.
3.3. Comparative Integration of NF-κB and NLRP3 Signalling Under Statin Modulation
The NF-κB pathway and the NLRP3 inflammasome are closely interconnected yet functionally distinct components of the innate inflammatory response. NF-κB plays an upstream role in transcribing the precursor forms of IL-1β and IL-18, while NLRP3 mediates their proteolytic maturation via caspase-1 activation. This two-step inflammatory cascade ensures tight control over the release of potent pro-inflammatory cytokines, preventing excessive tissue damage while maintaining effective immune responses [].
Statins exert inhibitory effects on both pathways through shared upstream mechanisms, including blockade of isoprenoid synthesis and reduced ROS generation. By inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, statins prevent the synthesis of FPP and GGPP, crucial isoprenoids required for the posttranslational modification of small GTPase proteins such as Ras, Rho, and Rac1. These proteins are essential for membrane localization and activation of downstream signalling cascades that regulate both NF-κB activation and NLRP3 inflammasome assembly [].
The depletion of GGPP by statins disrupts Rac1-mediated NADPH oxidase activity, leading to reduced ROS generation. This is particularly significant because ROS serve as both direct activators of NLRP3 through thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) dissociation and indirect promoters of NF-κB activation through IκB degradation. Furthermore, statins activate the pregnane X receptor (PXR), which directly inhibits NF-κB binding to NLRP3 gene promoter regions, providing an additional mechanism for dual pathway suppression [].
However, the relative dominance of NF-κB versus NLRP3 signalling may vary by disease context. In chronic vascular inflammation, such as atherosclerosis, NF-κB appears to be more prominent in driving sustained inflammatory gene expression, including adhesion molecules (VCAM-1, ICAM-1), chemokines, and cytokine precursors. Statins effectively reduce these inflammatory markers through multiple NF-κB inhibitory mechanisms, including stabilization of IκB-α, prevention of p65 nuclear translocation, and activation of anti-inflammatory transcription factors like KLF4 [].
Conversely, NLRP3 plays a greater role in metabolic or acute inflammasome-driven tissue injury, particularly in diabetes mellitus and its complications. In diabetic conditions, hyperglycemia acts as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) that directly activates NLRP3, leading to IL-1β maturation and subsequent insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Studies demonstrate that NLRP3 expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and plasma IL-1β concentrations are significantly elevated in diabetic patients and correlate with carotid intima-media thickness, a marker of atherosclerotic progression [].
Understanding the differential sensitivity of these axes to various statin types and doses remains an area for future translational research. Lipophilic statins (simvastatin, atorvastatin, fluvastatin) demonstrate superior anti-inflammatory effects compared to hydrophilic statins (pravastatin), likely due to enhanced cellular penetration and more effective isoprenoid depletion. High-dose atorvastatin therapy has shown particularly robust effects on both NF-κB and NLRP3 pathways, with significant reductions in IL-6, NLRP3, and STAT3 levels, alongside increased AMPK activation, which promotes autophagy and inflammasome clearance [,].
The dual inhibition of these pathways by statins may therefore explain their broad anti-inflammatory utility across atherosclerosis, diabetes, and certain cancers. In coronary microembolization studies, rosuvastatin demonstrated cardioprotective effects through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition, reducing pyroptotic cell death and preserving mitochondrial function []. Similarly, in diabetic atherosclerosis models, statin therapy reduced intrapancreatic macrophage infiltration and cytokine production, correlating with decreased acinar-to-ductal metaplasia formation, a precursor to pancreatic cancer development [].
The mechanistic convergence of NF-κB and NLRP3 inhibition by statins also provides a molecular rationale for their pleiotropic effects beyond cardiovascular protection, including neuroprotection, cancer prevention, and metabolic disease management. However, the precise balance between these pathways and their relative contributions to different disease states require further investigation to optimize statin selection and dosing strategies for specific inflammatory conditions [,].
3.4. Effect on the MAPK Pathway
Figure 6 schematically delineates the anti-inflammatory modulatory interface of statins as mediated through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling architecture. Analogous to the NF-κB cascade, DAMPs serve as proximal activators of principal MAPK subfamilial modules—ERK1/2, JNK, and p38—within innate immune effector populations. Engagement of these kinase axes precipitates phosphorylation-dependent signal propagation culminating in the activation of downstream transcriptional regulators, thereby driving the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemotactic mediators, including IL-6 [,]. Furthermore, DAMP species of mitochondrial provenance have been implicated in the activation of neutrophils via ligation of the formyl peptide receptor-1 (FPR-1), initiating phosphorylation and catalytic potentiation of p39 and ERK1/2, processes requisite for the stimulus-coupled secretion of IL-8 [].

Figure 6.
Statins modulate DAMP-induced MAPK signalling to attenuate inflammation. This figure illustrates how DAMPs (1), through binding TLRs (2), can also activate key MAPK families (ERK1/2, JNK, p38) (5) in immune cells, leading to upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Statins exert anti-inflammatory effects primarily by inhibiting the mevalonate pathway, which reduces GTPase prenylation (3) and subsequently dampens MAPK activation (4), thereby attenuating all downstream signalling and inflammatory outcomes (6) as shown above.
As delineated previously, statin pharmacodynamics involve suppression of flux through the mevalonate biosynthetic axis, thereby curtailing the generation of isoprenoid intermediates indispensable for the post-translational prenyl conjugation and functional conformational licencing of small GTP-binding proteins. Attenuation of this lipid-modification process constrains downstream mobilization of MAPK subfamilial modules—ERK, JNK, and p38, which constitute pivotal regulatory nodes in the inducible transcriptional programming of pro-inflammatory cytokines and endothelial adhesion determinants within vascular and immunocompetent cell populations. Notwithstanding this canonical suppressive profile, statins under certain experimental or microenvironmental conditions have been observed to potentiate p38 MAPK signalling, a phenomenon capable of priming the NLRP3 inflammasome and augmenting IL-1β secretion from macrophages, thereby exemplifying the context- and lineage-contingent variability of response []. The prevailing anti-inflammatory phenotype is principally ascribed to inhibiting Rho-GTPase-governed MAPK activation cascades, culminating in diminished NF-κB pathway throughput. Through the downmodulation of MAPK signalling competency, statins effectuate a broad repression of inflammatory mediator biosynthesis, concomitantly attenuating leucocyte trafficking and endothelial cell activation [,,].
3.5. Effect on T-Cell Differentiation
Innate immunological reactivity to pro-inflammatory stimuli entails the ontogenetic progression of thymocyte-derived precursors into naïve CD4+ T lymphocytes, which subsequently undergo lineage commitment toward regulatory T cells (T-reg) or T helper 17 cells (Th17) through an intricately orchestrated integration of T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated signalling, cytokine milieu, and a network of cross-modulatory cascades incorporating the MAPK axis, Toll-like receptor (TLR) signalling, and the NF-κB pathway. Within this framework, TCR-initiated signal transduction exerts a pivotal role in dictating T-reg versus Th17 lineage bias, in part through the activity of interleukin-2–inducible T cell kinase (ITK), whose functional predominance favours Th17 specification at the expense of T-reg development []. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) constitutes an obligate cue for both lineages, instigating the activation of SMAD3/4 heterotrimeric transcriptional assemblies to promote T-reg commitment via Foxp3 expression, whereas the concomitant presence of IL-6 or IL-21 engages STAT3, which interacts with SMAD3 in a manner that obstructs SMAD3/4 complex assembly, thereby biassing differentiation toward the Th17 lineage via induction of RORγt expression [,].
Foxp3-expressing T-regs mitigate inflammatory tone by eliciting anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β, upregulating inhibitory co-receptors including CTLA-4, and imposing metabolic restrictions upon effector T lymphocytes [,]. Furthermore, Foxp3 transcriptionally antagonizes pro-inflammatory drivers such as RORγt, thereby directly suppressing Th17 ontogeny and effector functionality. Induction of the T-reg phenotype is accompanied by attenuated MAPK and Rho-GTPase signalling relative to Th17 differentiation, a biochemical configuration that contributes to the acquisition of suppressive competence []. In the context of T-regs, TLR-dependent signalling can fine-tune suppressive activity; however, hyperactivation of the TLR/MyD88/IKK cascade has the potential to destabilize Foxp3 expression and compromise suppressive efficacy. TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) exerts an indirect yet modulatory influence on T-reg biology via its regulatory intersections with NF-κB and IRF-dependent pathways [,].
Conversely, Th17 cells potentiate inflammatory responses through RORγt-directed transcriptional programmes driving IL-17 and IL-22 production [,]. The acquisition of the Th17 phenotype necessitates coordinated input from TCR engagement, TGF-β signalling, and IL-6/IL-21-mediated cues, with STAT3 activation serving as the principal transcriptional driver of RORγt induction and activity []. IL-6/STAT3 signalling additionally impedes SMAD3/4 complex formation, reinforcing the preferential commitment to Th17 over T-reg fate. In this lineage, the MAPK and Rho-GTPase pathways exhibit heightened activation, thereby sustaining effector functionalities and amplifying cytokine output. Furthermore, TLR/MyD88/IKK signalling within antigen-presenting cells augments IL-6 and IL-23 production, providing an extrinsic cytokine milieu that intensifies Th17 polarization [,,].
Through the above mechanisms, and as summarized in Figure 7, statins increase the frequency of Treg expression while suppressing Th17 differentiation through inhibition of the mevalonate pathway [,]. Statins also induce T-reg recruitment to sites of inflammation via CCL1-dependent chemotaxis []. Additionally, inhibition of RORγt expression and IL-17 production involves interference with STAT3 and MAPK signalling. As shown in studies investigating models of autoimmune disease and atherosclerosis, this results in a shift in the Th-17/Treg balance towards immune tolerance and reduced inflammation [,,].
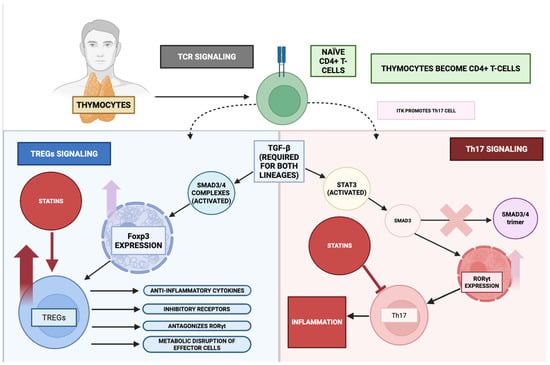
Figure 7.
Statins modulate T-cell plasticity towards an anti-inflammatory phenotype. This figure demonstrates the dynamic balance between Tregs and Th17 cells from naïve CD4+ T cells. Anti-inflammatory Tregs (Foxp3 expression) are upregulated via statins’ anti-inflammatory activity. On the other hand, pro-inflammatory Th17 cells (expressing RORγt) are attenuated by statins, thus shifting this balance towards lower inflammatory levels in the body.
3.6. Effect on Leukocyte Adhesion and Migration
Leucocyte tethering, arrest, and transendothelial migration represent cardinal phases in both immunosurveillance and inflammatory pathophysiology, unfolding through a sequentially orchestrated multistep paradigm. The initial phase involves selectin-mediated capture and rolling interactions, succeeded by chemokine-triggered activation of integrin conformational states, culminating in firm adhesion via αLβ2 (LFA-1) and α4β1 (VLA-4) integrins, and eventual diapedesis across the endothelial barrier. These processes necessitate highly plastic modulation of integrin affinity–avidity parameters, cytoskeletal remodelling driven by small GTPases such as Rho and Rac, and a coordinated endothelial programme incorporating upregulation of adhesion determinants (e.g., ICAM-1, VCAM-1) alongside junctional architecture reorganization to facilitate leucocyte extravasation [,,].
As depicted in Figure 8, pharmacological suppression of the mevalonate biosynthetic cascade by statins perturbs the molecular machinery governing leucocyte adhesive and migratory behaviour. Such intervention compromises integrin activation and cytoskeletal dynamism within leucocytes, thereby attenuating adhesion molecule display and diminishing leucocyte–endothelial engagement [,]. Concomitantly, statins exert a transcriptional downmodulatory effect on endothelial adhesion molecules—including E-selectin, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1—further constraining immune cell ingress into inflamed parenchyma [].

Figure 8.
Statins attenuate leukocyte adhesion, transmigration, and inflammation. This figure illustrates the multi-step cascade of leukocyte activity—from adhesion and transmigration to modulating inflammation—during inflammation. Statins inhibit this cascade at multiple levels, by inhibiting chemokines, inhibiting leukocyte transmigration, and overall inhibiting the inflammation observed in the tissues.
Empirical observations indicate heterogeneity in the magnitude of these effects, with lipophilic statins manifesting a more pronounced immunomodulatory profile relative to their hydrophilic counterparts [,]. Lipophilic congeners more effectively abrogate Rho GTPase prenyl conjugation, resulting in more profound suppression of adhesion molecule expression, more substantial impairment of integrin activation, and greater restriction of leucocyte migratory competence. Beyond these effects on innate immune trafficking, such agents more potently facilitate T-reg expansion and functional competence while concurrently restraining Th17 differentiation and IL-17 synthesis, via interference with MAPK and STAT3 signalling modules downstream of the mevalonate axis. Collectively, statin-mediated disruption of leucocyte adhesion–migration dynamics contributes to the mitigation of both vascular and systemic inflammatory burden by reducing immune cell infiltration and recalibrating adaptive immune responses.
3.7. Effect on Cytokine Production
The principal immunostimulatory mediators central to the inflammatory signalling frameworks described above [], notably the interleukin-1 family member β-isoform, the pleiotropic glycoprotein interleukin-6, and tumour necrosis factor of the α-subclass—arise from the convergent activation of multiple upstream signal transduction architectures. The β-isoform of interleukin-1, acting through canonical NF-κB signal relay, potentiates the inflammatory cascade by inducing pyrogenic responses, enhancing the transcriptional upregulation of endothelial counter-receptors for immune cell arrest, and facilitating the recruitment and translocation of circulating leukocyte subsets [,,,]. This mediator further amplifies the network by driving additional soluble immunoregulatory factors—including the α-subclass tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-6—and by supporting polarization toward the T helper 17 phenotype, thus interlinking innate pattern-recognition responses with antigen-specific adaptive immunity [].
Interleukin-6, whose synthesis is inducible via β-interleukin-1, α-tumour necrosis factor, and integrated NF-κB/MAPK activation, exerts systemic actions that encompass stimulation of hepatocyte-driven acute-phase reactant synthesis, promotion of B-cell terminal differentiation, and reinforcement of Th17 lineage commitment, while concurrently attenuating T-regulatory cell development [,]. It constitutes the predominant molecular trigger for hepatic C-reactive protein biosynthesis through STAT3-mediated transcriptional programming, with β-interleukin-1 and α-tumour necrosis factor providing synergistic potentiation of this effect. This β-interleukin-1/interleukin-6/C-reactive protein triad forms a critical inflammatory amplification loop: the β-isoform of interleukin-1 induces interleukin-6 expression via NF-κB- and C/EBPβ-dependent pathways, which in turn drives direct transcriptional activation of the C-reactive protein gene [,].
The α-subclass tumour necrosis factor, generated by myeloid and T-lineage cells following activation of NF-κB and MAPK modules, engages its cognate receptors to further propagate NF-κB-dependent transcription, initiate programmed cell death, and induce expression of vascular adhesion ligands (including ICAM-1 and VCAM-1), thereby facilitating immune cell tethering, arrest, and transendothelial passage. In addition, it reinforces the inflammatory network by stimulating the synthesis of β-interleukin-1 and interleukin-6, establishing a reciprocally amplifying cytokine circuit. As elaborated in preceding sections and schematically depicted in Figure 9, statins recalibrate these mediator networks via suppression of mevalonate-derived intermediates, dampening pro-inflammatory effector output and enhancing counter-regulatory anti-inflammatory signalling.

Figure 9.
Pro-inflammatory cytokine network and statin-mediated attenuation. This figure illustrates the network of key pro-inflammatory cytokines and other inflammatory molecules, such as CRP, and their consequent effects. These effects are inhibited via statins’ anti-inflammatory activity on cytokines, thus attenuating downstream signalling.
4. Statins in Chronic Inflammatory Conditions
Given the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of statins on a molecular and genetic level, several studies have extensively investigated the use of statins in chronic inflammatory conditions. Through in vitro models, in vivo models, and clinic trials, the following sections integrate the underlying inflammatory pathway with the application of statins in the following chronic inflammatory conditions: diabetes, OA, and cancer. Additional sections also review the use of statins in RA and COPD. It is important to note how several studies highlight the anti-inflammatory role of statins independent of their lipid-lowering mechanisms.
4.1. Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
As delineated previously, statin-mediated pharmacological interference attenuates the biosynthetic availability of isoprenoid derivatives, principally farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP), whose presence is indispensable for the post-translational lipid conjugation–dependent signalling competency of low–molecular-weight GTP-binding proteins, including members of the RhoA, Rac, and Ras subfamilies []. In the context of diabetes, this poses immense clinical relevance, due to its hallmark state of chronic inflammation and metabolic stress [,]. This stress can impair the normal signalling of these small GTPases, thus implicating them in the pro-inflammatory state and insulin resistance in metabolically relevant tissues—vascular endothelium, adipocytes and skeletal muscles. For instance, RhoA is implicated in oxidative stress and increased vascular permeability, contributing to diabetic vascular complications [,]. Moreover, Rho GTPases induce the expression of inflammatory adipokines in adipocytes [], thus further promoting an inflammatory state and insulin resistance in the diabetic patient. In addition, Rac1 dysfunction leads to insulin resistance in skeletal muscles via attenuated GLUT4 transport and glucose uptake []. As such, the administration of statins would allow the aberrant activity of these signalling molecules/pathways to be attenuated via the inhibition of the mevalonate pathway.
Multiple investigative efforts have elucidated the proximate molecular modalities through which statins perturb small GTPase functionality. In this context, Tanaka et al. reported that both atorvastatin and pitavastatin potentiate the transcriptional and/or translational output of small GTP-binding protein GDP dissociation stimulator (SmgGDS), a chaperoning entity that orchestrates proteasome-dependent catabolism of the Rac1 isoform within endothelial nuclei, thereby facilitating its turnover and functional attenuation []. Vecchione et al. demonstrated that atorvastatin mitigates reactive oxygen species (ROS) accrual within human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) by constraining the pathologically dysregulated activation state of Rac1 []. Concordantly, Bruder-Nascimento et al. documented that atorvastatin induces a substantive downmodulation of RhoA abundance in murine models of diabetes mellitus, specifically within the pathophysiological milieu of diabetic nephropathy [].The chronic inflammatory environment in diabetic patients is in part facilitated by the NF-κB cascade [], which is triggered by free fatty acid (FFA)-induced inflammation and glucolipotoxicity (increased glucose and lipid levels) and lead to beta islet cell dysregulation []. NF-κB drives the transcription of the inflammatory molecules TNF-α and IL-6, which facilitates the dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) []. In Type 1 Diabetes (T1D), pro-inflammatory cytokines secreted by immune cells within the islets induce NF-κB activation in β-cells, contributing to their auto-induced damage []. Furthermore, NF-κB pathway stimulation can result in vascular complications in not only the pancreas, but also in the kidney, heart and retina, hence exacerbating the systemic inflammatory damage in diabetic patients []. This inflammatory over-activation translates into severe clinical manifestations such as diabetic nephropathy, cardiomyopathy, and retinopathy.
Statins offer alternative therapeutic avenues that can reduce the incidence of the above adverse outcomes in diabetic patients. One such study by Zhang et al. showed atorvastatin ameliorated nephrotoxicity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice via attenuated NF-κB and TNF-α signalling []. Similarly, simvastatin showed cardio-protective properties by reducing NF-κB translocation and TNF-α activation in the myocardium of diabetic mice, allowing for reduced hypertrophy and improved cardiac function []. Simvastatin’s anti-inflammatory activity is further supported by Lin et al., which showed a downregulation in NF-κB and TNF-α in mice fed a high-fat diet [].
However, while molecular and mechanistic insights are increasingly robust, effective clinical translation remains limited by an incomplete understanding of how these biochemical pathways interact with patient-level inflammatory and metabolic risk. Recent clinical evidence highlights that low-grade inflammation and glycemic dysregulation, frequent in individuals with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) or metabolic syndrome, not only shape the pattern of atherosclerotic damage but also modulate the efficacy of lipid-lowering therapies such as statins, independent of achieved LDL-C levels. For example, the referenced study by Di Giacomo Barbagallo et al. demonstrated that among genetically defined FH patients, those with non-LDL receptor mutations exhibited worse glycemic control, higher fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c, and greater peripheral atherosclerotic plaque burden compared to those with LDL-receptor mutations, even though LDL-C levels were higher in the LDLR mutation group. Notably, glycemic profile and inflammatory state were associated with distinct distributions of atherosclerotic lesions, namely, high glycemic status and insulin resistance correlated with greater peripheral plaque, whereas higher lifelong LDL-C exposure in certain genotypes was linked to more pronounced coronary artery calcification [].
These findings underscore that glycemic abnormalities and chronic low-grade inflammation act as independent drivers of vascular injury, and their interplay can attenuate or modify the vascular benefits of statin therapy beyond simple LDL-C reduction. Evidence indicates that measures such as the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index are emerging as valuable markers connecting dysglycemia [], insulin resistance, and circulating inflammatory mediators to early atherosclerotic changes. Therefore, optimal risk stratification and evaluation of statin efficacy should move beyond traditional lipid endpoints to incorporate assessment of inflammatory biomarkers (e.g., hs-CRP, interleukin-6, TNF-α) and detailed patient-specific metabolic profiling. This approach could identify patients at “residual inflammatory risk” who may benefit from adjunctive or alternative anti-inflammatory therapies and ultimately provide a more tailored prevention strategy for high-risk groups including FH and those with metabolic dysfunction [].
There have been many studies that have highlighted the pleiotropic anti-inflammatory action of statins independent of the drug’s primary lipid-lowering mechanism that can be extended in inflammatory-driven conditions such as OA. For instance, two separate Mendelian randomization studies demonstrate the protective effects of atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin on hip and knee OA [,]. As such, these have given researchers ground for investigating the role statins can play in the management of OA. The chronic inflammatory processes underlying the disease progression in OA are primarily orchestrated by cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 that are produced by activated chondrocytes, synovial fibroblasts, and infiltrating immune cells []. These pro-inflammatory mediators orchestrate the propagation of a catabolic synovial milieu, wherein the augmented transcriptional activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), concomitant attenuation of anabolic extracellular matrix biosynthesis, and sustained synovial inflammatory signalling synergistically exacerbate joint tissue degeneration []. Notably, the catabolic bioactivity of IL-1β encompasses the induction of programmed chondrocytic cell death, the suppression of proteoglycan biosynthetic pathways, and the upregulation of secondary pro-inflammatory mediator cascades, collectively engendering a self-perpetuating degenerative circuit that accelerates articular cartilage attrition [].
Statins’ benefit in directly suppressing these cytokines has been shown in a study using porcine cartilage explant models that were designed to mimic OA []. Treatment with atorvastatin was shown to significantly inhibit the release of TNF-α induced by IL-1β stimulation. Another study investigating the effects of simvastatin in fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), a cell type involved in synovitis associated with RA and OA, demonstrated dose-dependent inhibition of IL-6 and IL-8 production []. This inhibitory effect was maintained even when the FLS were stimulated with IL-1β []. Additionally, the inhibitory effects of simvastatin on IL-6 and IL-8 were reversed by co-incubation with mevalonic acid (specifically GGPP), while the addition of FPP failed to reverse the inhibition. This indicates that simvastatin can counteract the effects of pro-inflammatory signals and mediate anti-cytokine effects through depletion of GGPP, independent of the FPP-dependent branches of the mevalonate pathway. This elucidates a testable mechanism for the pleiotropic anti-inflammatory effects of statins and suggests that the potency of different statins may correlate with their ability to inhibit GGPP synthesis in target joint cells.
Persistent, dysregulated inflammatory signalling constitutes a central oncogenic driver, with diverse neoplastic lineages exhibiting a sustained elevation of immunomodulatory mediators that potentiate malignant progression, metastatic dissemination, and therapeutic refractoriness. In colorectal carcinoma (CRC), pathognomonic amplification of tumour-promoting immunocytokine networks—exemplified by the overabundance of tumour necrosis factor superfamily ligands, IL-1 family members, pleiotropic IL-6–type glycoproteins, and Th17-associated effector cytokines—propels disease evolution. Contemporary pharmacological strategies aimed at curtailing malignancy-associated inflammation have interrogated discrete nodal points within these signalling axes; for instance, antagonism of the IL-1 receptor with monoclonal agents such as canakinumab has demonstrated efficacy in attenuating lung cancer incidence and mortality []. Mechanistic interrogation by Sun et al. revealed that inflammatory mediator–driven repression of tumour-suppressive microRNAs, notably miR-615-5p, derepresses oncogenic transcripts such as STC1, thereby expediting tumour proliferative kinetics []. A prospective cohort by Florescu et al. delineated progressive stage-dependent escalation in circulating concentrations of IL-1–related, IL-6–related, and TNF-associated proteins in CRC, with IL-6 exhibiting the steepest trajectory [], findings corroborated by a meta-analysis identifying IL-6 signalling as a prognostic correlate of augmented tumour burden and diminished survival []. Analogous immunopathological patterns have been documented in breast malignancies, wherein IL-17A orchestrates a pro-tumorigenic cytokine-chemokine cascade—including IL-6, TGF-β, IL-1 isoforms, IL-8, TNF ligands, CXCL1, and CCL2—to reinforce a tumour-supportive stromal niche [,]. Elevated IL-1 family signalling has likewise been associated with advanced disease and therapeutic non-responsiveness in breast carcinoma [,]. In pulmonary neoplasia, hyperactivation of inflammatory mediator production by tumour-associated alveolar macrophages yields marked surges in IL-6– and IL-1–related factors both locally and systemically, correlating with adverse clinical trajectories [,,]. Cumulatively, these oncological datasets converge on the conclusion that dysregulated cytokine networks sculpt a microenvironment conducive to malignancy. In this context, the pleiotropic immunomodulatory properties of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have garnered considerable investigative interest, particularly their capacity to attenuate principal cytokine-driven signalling circuits.
Despite early concerns regarding a potential increase in cancer incidence among statin users, recent research show that statins reduce cancer risk by 20–28%, and also lower the likelihood of recurrence in prostate cancer patients post-radical prostatectomy []. Experimental evidence indicates that simvastatin exerts a pronounced suppressive effect on neoplastic cell–elicited pro-inflammatory immunocytokine release—specifically attenuating IL-1 family β-isoform and type II interferon output—while concomitantly restraining the proliferative kinetics of colorectal carcinoma cells [,]. In vitro experiments further support this, showing that simvastatin reduces IL-6 and IL-8 levels in colorectal cancer cells []. In the context of breast cancer, statins have been extensively researched for their ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines. A comprehensive review conducted by Dang et al. outlines several mechanisms by which statins, especially lovastatin, regulate tumour progression, notably through the suppression of inflammatory cytokine signalling via the LKB1–AMPK–p38–MAPK–p53 pathway []. Supporting this, Liu et al. demonstrated that treatment with simvastatin has been shown to inhibit protein prenylation in breast cancer cells, leading to decreased IL-6 secretion and reduced proliferation of senescent conditioned media on breast cancer cells []. In lung cancer, simvastatin has demonstrated comparable potential. Treatment of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) isolated from lung cancer patients led to a significant reduction in the production of IL-6 and chemokines like CCL2, and CCL3 that play key roles in tumour progression and immune modulation []. Moreover, simvastatin has been shown to inhibit the NF-κB pathway, leading to suppression of IL-8 production, further highlighting its anti-inflammatory potential []. Additionally, a study found that both pitavastatin and pravastatin significantly reduced IL-6 and IL-8 expression in LPS-stimulated bronchial epithelial cells, underscoring their potential to modulate cytokine-driven inflammation within the lung TME []. Together, the evidence across colorectal, breast, and lung cancer models highlights a consistent anti-cytokine effect for statins. By attenuating IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and related chemokines, statins may weaken the inflammatory pathways that sustain tumour growth and immune evasion in cancer and strengthen the efficacy of therapeutic regimens in cancer patients.
To complement the mechanistic discussion and enhance translational clarity, we provide below a concise summary of clinical studies evaluating the effects of various statins on key inflammatory biomarkers and cancer-related outcomes across different patient populations. This synthesis highlights the heterogeneity in statin responses and underscores their emerging adjunctive potential beyond lipid lowering (Table 4).

Table 4.
Clinical evidence regarding statins’ effects on key inflammatory markers and cancer-related outcomes.
Beyond statins, emerging lipid-lowering therapies that also exhibit anti-inflammatory or metabolically neutral profiles are gaining traction, particularly in patient populations with comorbid cardiovascular, metabolic, and neoplastic conditions. One notable example is inclisiran, a small interfering RNA (siRNA) that targets hepatic PCSK9 synthesis. Unlike traditional statins, inclisiran lowers LDL-C by enhancing LDL receptor recycling in hepatocytes, utilizing a unique RNA interference mechanism that allows for infrequent (biannual) dosing and may improve adherence over long-term therapy []. Crucially, recent clinical data highlight that inclisiran not only offers robust LDL-C, lowering efficacy, with reductions consistently around 50%, but also sustains a neutral or potentially favourable profile regarding glycometabolic and inflammatory parameters. Large-scale phase III trials (such as ORION-9, -10, and -11) and real-world studies report an absence of glycemic perturbations or negative impacts on glucose metabolism, a concern that can affect statins in predisposed patients. Similarly, inclisiran does not appear to induce pro-inflammatory changes, and its hepatic specificity minimizes off-target effects that might be problematic in patients with metabolic syndrome, diabetes, or cancer-associated dysmetabolism [].
These characteristics render inclisiran an attractive adjunct or alternative to statin therapy, especially in high-risk subgroups for whom inflammation, metabolic imbalance, and cancer biology are closely intertwined. As ongoing research continues to evaluate the long-term cardiovascular outcomes and immunometabolic effects of inclisiran, there is growing interest in its potential synergy with statins, not only for complementary LDL-C lowering, but also for co-modulation of immunometabolic pathways that underlie complex cardiovascular and oncologic comorbidities. Future studies should further delineate the benefits of combining inclisiran with statins and anti-inflammatory agents to optimize risk reduction in these especially vulnerable patient populations [].
4.2. Modulation of Immune Cell Phenotypes
The dynamic modulation and expression of immune cell phenotypes, particularly the plasticity of T helper cells, Treg, and macrophage subsets, are central to the pathogenesis and treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Aberrant immunophenotypic plasticity, manifested as maladaptive skewing from anti-inflammatory/tolerogenic lineages (e.g., Foxp3+ regulatory T cells, alternatively activated M2 macrophages) toward pro-inflammatory/effector subsets (e.g., IFN-γ–dominant Th1, IL-17–producing Th17, classically activated M1 macrophages), perpetuates a state of unresolved inflammation and collateral tissue injury. Contemporary immunotherapeutic paradigms increasingly focus on recalibrating these lineage-differentiation trajectories to re-establish immunological equilibrium and facilitate resolution of chronic inflammatory pathology.
Another crucial aspect of diabetic pathology is the modulation of immune cell phenotypes. Diabetic patients tend to present with a pro-inflammatory immune cell phenotype, which allows for the perpetual inflammatory-mediated damage and loss of repair in the affected tissues []. One such example is Th1 lymphocytes and their pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IFN-γ []. Consequently, by inhibiting the prenylation and functional activation of G-proteins as discussed before, statins can potentially dampen TCR signalling and lead to a significant reduction in the secretion of these Th1-associated inflammatory mediators, thereby inhibiting the overall Th1 immune response. In T2D, elevated levels of TNF-α and IFN-γ play a major role in causing insulin resistance by disrupting insulin signalling pathways and promoting pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction []. A predominance of Th2-skewed immune polarization may confer a cardiometabolic advantage, as evidenced by the findings of Madhumita et al. [], wherein individuals with diabetes mellitus and concomitant coronary artery pathology exhibited a disproportionately augmented Th1 cytokine milieu concomitant with an attenuated Th2-associated secretome. Coward and Chow [] demonstrated in a cohort of immunologically healthy volunteers that atorvastatin attenuated the prevalence of Th1-effector cytokine–producing lymphocytes, predominantly IFN-γ and IL-2-secreting subsets, while concomitantly skewing the immune axis toward a Th2-biassed cytokine profile, typified by augmented IL-4 and IL-10 production. In an independent clinical evaluation encompassing middle-aged and elderly cohorts with established Type 2 diabetes mellitus and coexistent periodontitis, therapeutic administration of atorvastatin precipitated a marked attenuation in pro-inflammatory cytokine burden, evidenced by substantially diminished IL-6 and TNF-α titers within both gingival crevicular exudates and salivary secretions—findings congruent with a localized downmodulation of inflammatory activity. Complementary in vitro analyses revealed that cerivastatin, simvastatin, lovastatin, and atorvastatin each induced a concentration-dependent repression of Th1 lineage commitment (manifested as reduced IFN-γ output) alongside potentiation of Th2 differentiation (elevated IL-4 production) in murine T lymphocytes, with cerivastatin displaying the most potent immunopolarizing efficacy. Importantly, this Th1→Th2 repolarization was abrogated upon exogenous mevalonate supplementation, implicating canonical blockade of the mevalonate-isoprenoid biosynthetic axis as the mechanistic substrate for these immunomodulatory effects [].
Attenuation of a Th1-skewed immunological milieu has also been documented within the context of Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D). In the TCR-HA/RIP-HA double-transgenic (dTg) murine model of autoimmune diabetes, oral administration of atorvastatin elicited a marked immunophenotypic reorientation: splenic lymphocyte populations in “protected” atorvastatin-treated mice exhibited a pronounced Th2-dominant signature, in contrast to the overt Th1 predominance observed in untreated diabetic counterparts []. Quantitative RT-PCR profiling revealed significant transcriptional upregulation of canonical Th2-associated transcription factors—STAT6, c-MAF, and GATA3—in the atorvastatin-protected cohort. In contrast, diabetic controls displayed elevated expression of Th1-defining regulators STAT4 and T-bet. Complementary findings by Espinosa-Carrasco et al. corroborated the immunomodulatory capacity of statins, demonstrating a reduction in pathogenic CD8+ T-cell infiltration into pancreatic islets []. The evidence delineates a role for statin-driven immunomodulation in attenuating autoreactive effector T-lymphocyte functionality, suppressing the transcriptional and translational programmes underpinning pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis, and consequently forestalling β-cell attrition. By orchestrating a shift in CD4+ T-cell lineage commitment away from a Th1-dominant axis toward a more immunoregulatory Th1/Th2 equilibrium, such pharmacological intervention disrupts the feed-forward inflammatory circuitry that perpetuates the autoimmune milieu in T1D.
When it comes to inflammation, macrophages are among the first immune cells at the site of the inflammatory response to initiate, signal other inflammatory cells, and to regulate the environment according to the body’s requirements. In immunologically quiescent states, monocyte-derived macrophages retain a high degree of phenotypic malleability, transitioning bidirectionally along the polarization continuum between classically activated (M1) pro-inflammatory effector phenotypes and alternatively activated (M2) immunoregulatory phenotypes []. In the context of diabetic pathology, however, this polarization axis becomes skewed toward sustained M1 predominance [], thereby reinforcing and perpetuating a chronic pro-inflammatory milieu through amplification of cytokine-driven feed-forward inflammatory cascades. In a recent in vitro study conducted by Muffova et al., the human macrophages showed that fluvastatin suppresses pro-inflammatory M1 markers and enhances anti-inflammatory M2 markers []. While not necessarily conducted in the disease setting of diabetes, the aspect of M1 polarization phenotype is vital in diabetic pathophysiology.
While discussing the pro-inflammatory phenotype of diabetes, it is important to investigate the anti-inflammatory landscape in diabetes as well, specifically the lack thereof. Due to the overwhelming inflammatory signalling, anti-inflammatory immune cells, such as Treg, are noted to be diminished. In order for successful management of diabetes, it is vital to increase these anti-inflammatory immune cell phenotypes to suppress the pro-inflammatory state and lead to better health outcomes.
Meng et al. reported that simvastatin augments Treg abundance and enhances the intraplaque expression of Foxp3, TGF-β, and IL-10 within atherosclerotic lesions of apolipoprotein E-null (ApoE−/−) murine models []. Concordantly, atorvastatin exposure in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) elevated the frequencies of CD4+CD25high and CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ subsets, while in hyperlipidaemic patients, simvastatin similarly elicited an upsurge in circulating Treg levels []. Downregulation of inflammation in these plaques can lead to reduced endothelial dysfunction and diabetic cardiomyopathy [,]. In previous studies, statin-induced Treg upregulation was observed during non-treatment periods. To address the evidentiary gap concerning the immunomodulatory capacity of statins, Rodrigues-Perea et al. performed an in vivo longitudinal intervention in normocholesterolaemic male volunteers, quantifying CD4+ T-cell transcript abundance for FOXP3, IDO, TGF-β, and IL-10 over a 45-day regimen, with sampling on days 0, 7, 30, and 45. Both statin treatments elicited a significant expansion in Treg frequency concomitant with elevated FOXP3 mRNA expression []. Although the study was conducted in non-diabetic volunteers, it provides robust evidence of statins’ anti-inflammatory activity; thus, further triangulation and experiments must be conducted as well. The findings from these studies, however, can be translated to potential benefits in protection the onset and progression of diabetic microvascular and macrovascular complications.
The chronic inflammatory infiltrate in the synovium of an OA joint is largely populated by macrophages, mostly of M1 phenotype [], with emerging evidence pointing towards the involvement of adaptive immune cells []. Statins’ immunomodulatory effects appear to actively reprogram the functional phenotype of these immune cells towards a more tolerogenic and anti-inflammatory state []. While direct investigations of these effects on OA models are pending, data from other disease models show compelling evidence of statins’ effect on macrophage phenotype imbalance. In an experimental rat model of immune-mediated glomerulonephritis, atorvastatin administration not only attenuated overall macrophage infiltration but also promoted a phenotypic reprogramming, evidenced by a diminution of M1-like macrophage subsets characterized by a pro-inflammatory cytokine/chemokine expression profile, alongside an expansion of M2 macrophage populations exhibiting anti-inflammatory, immunoregulatory, and tissue-reparative functional attributes, including IL-10–producing cells []. A similar reprogramming effect was observed in a co-culture model simulating the inflammatory environment of periodontal disease, where simvastatin suppressed the inflammatory response of macrophages while upregulating markers associated with tissue homeostasis and the M2 phenotype [].
Additionally, statins also exhibit modulatory effects on T-lymphocytes as shown in a study on human PBMCs []. Both simvastatin and lovastatin were effective at inhibiting T-cell proliferation against polyclonal and antigen-specific stimuli by inducing cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase. Additionally, statins’ ability to promote regulatory T-cell action by dually inhibiting IL-6 and promoting antigen-presenting cells to be more “tolerogenic” highlights the drug’s therapeutic potential in mitigating the immunologic landscape associated with OA.
Modulation of immune cell phenotypes within the tumour microenvironment (TME) is a pivotal determinant of cancer progression. In this context, diverse leukocyte populations undergo reprogramming to adopt tumour-supportive roles. These include myeloid lineage cells such as tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs), tumour-associated neutrophils (TANs), and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs); lymphoid subsets such as CD4+ T helper cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs); and antigen-presenting populations such as dendritic cells (DCs). Tumour cells exploit this phenotypic plasticity through alterations in cytokine signalling, thereby fostering an immunosuppressive milieu that subverts anti-tumour immunity and promotes malignant growth [,]. In CRC, MDSCs are among the most prevalent immunosuppressive populations, known to inhibit T- and NK-cell activity while promoting the expansion of Tregs and TAMs and thus contributing to immune evasion and metastasis []. Additionally, CRC-derived CCL5 has been shown to recruit and polarize suppressive immune cells, including Tregs, TAMs, and mast cells, while activating pathways such as CCR5-p65/STAT3 to suppress cytotoxic T-cell activity further aiding in immune escape []. In the context of breast cancer, TAMs are among the most prevalent immune cells within the tumour microenvironment and are linked to more aggressive disease characteristics, such as poor prognosis and resistance to hormone therapies []. Similarly, in lung cancer, immune resistance often arises from multiple factors such as reduced antigen presentation, impaired T-cell responses, and activation of alternative immune checkpoints all of which contribute to reduced tumours less responsiveness to immunotherapy []. As a result, targeting the immune microenvironment has become a central strategy in overcoming tumour progression and therapeutic resistance.
Statins, in particular, have demonstrated immunomodulatory and anti-tumour effects across various cancer types. In colorectal cancer, they have been associated with reduced angiogenesis in early stages and increased Treg infiltration in advanced stages, indicating stage-specific mechanisms that may limit tumour aggressiveness []. Additionally, statins may impair immunosuppressive signalling by lowering cholesterol levels in tumour cells, thereby restoring T cell function. Additionally, statins may impair immunosuppressive signalling by lowering cholesterol levels in tumour cells, thereby restoring T cell function []. In the early stages of lung cancer, statin use has been associated with reduced infiltration of pro-tumorigenic TAMs in premalignant adenocarcinoma lesions, indicating a potential chemopreventive effect []. In the context of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), statin administration has been reported to attenuate PD-L1 surface expression and trigger ferroptotic cell death pathways, thereby potentially constraining tumoural aggressiveness and metastatic competence []. Within experimental breast carcinoma paradigms, lovastatin has been shown to recalibrate tumour-associated macrophage (TAM) polarization toward a classically activated, M1-skewed phenotype, a shift mechanistically linked to suppression of IL-10 and concomitant augmentation of IFN-γ expression within CD45+ leukocyte populations []. Moreover, combinatorial regimens incorporating lovastatin with the microtubule-stabilizing chemotherapeutic paclitaxel have demonstrated synergistic efficacy, characterized by enhanced intratumoural infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes, downmodulation of PD-L1 expression, and superior tumour growth control in both in vitro and in vivo experimental frameworks []. By modulating macrophage polarization, enhancing T cell activity, and suppressing immune checkpoint expression, statins demonstrate potential as adjuncts to immunotherapy. Their consistent effects across colorectal, lung, and breast cancers suggest a common mechanism of immune modulation that merits further clinical investigation.
4.3. Endothelial Protection and Inflammation Reduction
Statins can also significantly improve endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Endothelium health is an important factor to consider in inflammatory conditions such as diabetes, OA, and cancer; besides the release of inflammatory factors and immune cell adhesion, in conditions that are hyper-dependent on endothelium for their pathogenesis, statins’ effect must be investigated to investigate if it can attenuate their progression.
The state of chronic hyperglycemia in diabetes is the underlying mechanism of the disease’s pathogenesis. While in non-diseased individuals, glucose can be taken by metabolic cells via insulin stimulation, the insulin dysfunction in diabetic patients does not allow for such measures, leading to a pathologic state of hyperglycemia. Hyperglycaemia constitutes a critical precipitant of diabetic cardiomyopathy, primarily through endothelial perturbations mediated by non-enzymatic protein glycation and the subsequent accumulation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) []. The initiation and progression of such endothelial dysfunction are governed by a multifactorial interplay involving impaired nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability, elevated oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) burden, and heightened inflammatory mediator activity—each of which is adversely modulated by hyperglycaemia-induced downregulatory effects [,].
NO is a key modulator of endothelial function (anti-inflammatory and vasodilatory effects) []. Hyperglycemia can trigger depletion of NO by impairing eNOS activity, via decreased expression, impairing tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) formation leading to eNOS uncoupling [,]. Furthermore, hyperglycemia can inhibit NO’s activity directly via an increased production of superoxides which can deactivate NO by forming peroxynitrite (ONOO-) []. On the other hand, the role of hyperglycemia and ox-LDL is another major contributor to this on-going inflammatory endothelial damage in diabetes. The hyperglycemic state and increased oxidative stress leads to ox-LDL, which in turn leads to endothelial dysfunction, positive reinforcement of oxidative stress, reduced NO and activation of pro-inflammatory pathways []. To add to this, once inflammatory cells and cytokines are stimulated and recruited to the endothelium, they also add to the eNOS impairment and oxidative stress, creating another debilitating and progressive cycle of endothelial damage in diabetic patients.
Multiple experimental studies have delineated a favourable modulatory influence of statins on the nitric oxide (NO) axis and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) functionality. In male db/db mice, Luo et al. demonstrated that oral administration of simvastatin at 40 mg/kg/day elicited a pronounced induction of endothelial Krüppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) expression within the aortic endothelium, a transcriptional programme that translated into enhanced eNOS catalytic activity and, consequently, greater endothelial resilience via NO-mediated cytoprotection []. Expanding this line of enquiry, Ota et al. examined the actions of atorvastatin, pravastatin, and pitavastatin in endothelial cultures subjected to oxidative insult—a milieu conducive to premature endothelial cellular senescence and thereby to vascular dysfunction and atherogenic remodelling []. The authors reported that all three agents facilitated phosphorylation of Akt at Ser473, which, in turn, augmented eNOS-dependent NO generation in senescent human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). In Sirt1+/– murine models of streptozotocin-induced diabetes, pitavastatin treatment was likewise associated with a discernible upregulation of eNOS expression. Complementary findings by Li et al. revealed that rosuvastatin conferred neurovascular benefits in diabetic neuropathy, acting through neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS)-driven NO signalling to restore endoneurial vascular perfusion, preserve neural NO bioactivity, and improve overall nerve functional integrity []. Mason et al. further provided evidence that atorvastatin ameliorated eNOS uncoupling phenomena, thereby reinstating endothelial homeostasis through the restoration of NO signalling capacity []. Similarly, Tian et al. observed that rosuvastatin administration in db/db mice enhanced NO signalling potential by attenuating reactive oxygen species (ROS) production downstream of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R)-linked NAD(P)H oxidase activation [].
The NF-κB pathway crosslinks with adhesion molecule expression, such as ICAM-1, LFA-1, and MAC-1 on endothelial cells []. These adhesion molecules serve as pivotal mediators in the tethering, firm arrest, and subsequent transmigration of inflammatory leukocytes across the vascular endothelium, thereby sustaining the self-amplifying inflammatory milieu characteristic of diabetic vasculopathy and contributing to progressive endothelial structural and functional compromise [,]. There is also strong evidence to show the inhibitory effects statins have on not only the NF-κB transcription, but also on these vital adhesion molecules. Rezaie-Majd et al. investigated the effects of simvastatin intervention in a group of hypercholesterolemic patients with high diabetes risk and vascular inflammation. Observed by the researchers in both in vivo and vitro settings, simvastatin significantly reduced ICAM-1 and LFA-1 expression on monocytes and endothelial cells, at a genomic (mRNA) and proteomic level []. However, Rezaie-Majid et al. were not the only ones to note these lowering effects; Nomura et al. saw a significant decrease in sE-selectin and sL-selectin levels in hyperlipidemic diabetic patients after 6 months of pitavastatin treatment [].
In the context of T1D, evidence from a randomized, double-blind clinical trial demonstrated that atorvastatin administration augmented both endothelium-dependent vasodilation, as assessed by flow-mediated dilation, and endothelium-independent vasodilation, as determined by glyceryl trinitrate–mediated dilation, within the brachial arteries. These vascular benefits were mechanistically linked to enhanced nitric oxide (NO) bioactivity concomitant with attenuation of oxidative stress []. Complementary in vitro investigations revealed that cerivastatin and fluvastatin upregulated mRNA expression of GTP cyclohydrolase (GTPCH), the rate-limiting enzyme in tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) biosynthesis, and increased endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) abundance in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) []. Similarly, Wenzel et al. also demonstrated how in male Wistar rats, atorvastatin was able to upregulate (GTPCH-I), a key enzyme for de Novo BH4 synthesis. This increased BH4 would allow for augmented eNOS activity and endothelial protection []. In addition, researchers have also investigated the efficiency of statins over other medications. For instance Landmesser et al. found that flow-mediated dilation, superoxide dismutase activity and active endothelial progenitor cells number was markedly improved after simvastatin, as compared to ezetimibe treatment, which showed no improvement []. Lastly, studies showed that this improvement in endothelial function was not just localized to improve NO functionality but also connected to ox-LDL levels. Sallam et al. conducted a randomized control trial showing how the combination of amlodipine with atorvastatin improved the lipid profile []. Moreover, Tsimikas et al. conducted a study with 2341 patients affected by acute coronary syndrome, assessing their ox-LDL content in blood samples at baseline and after treatment with 80 mg per day atorvastatin or placebo. The researchers found a reduction in all ox-LDL carried by apoB-100 particles, suggesting atorvastatin’s potent anti-inflammatory activity. Furthermore, the researchers also noted a small increase in lipoprotein (a), suggesting atorvastatin may upregulate levels of lipoprotein (a) in order to mobilize and clear ox-LDL []. Overall, these studies suggest to the scientific community the clinical relevance of statins in diabetic endothelial management.
The synovial membrane is a highly vascularized tissue, that plays a key role in the development of OA []. Activation of endothelial cells provokes an enhanced transcriptional and translational programme for adhesion molecules, thereby facilitating the tethering, firm adhesion, and subsequent transendothelial migration of circulating leukocytes into the synovial compartment [], a process that sustains and amplifies the local inflammatory milieu. Statins’ modulation of NO production and interference with surface adhesion molecules expression (such as E-selectin and ICAM-1) underlie their vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory properties [,].
The inflamed synovial microenvironment is characterized by significant hypoxia due to a mismatch between the metabolic demands of the hyperplastic synovial tissue and its blood supply [,]. This local hypoxia can itself be a damaging stimulus, triggering activation of the complement system on the surface of endothelial cells, leading to inflammation and cell injury []. Statins have been shown to specifically counteract this hypoxia-induced damage. Under normal oxygen conditions, statins have little effect on the expression of the vital complement-inhibitory protein CD59 on endothelial cells. However, under hypoxic conditions that mimic the rheumatoid joint, atorvastatin induces a potent, dose-dependent upregulation of CD59 expression []. This upregulation, which is dependent on HMG-CoA reductase inhibition and NO production, provides the endothelium with enhanced protection against attack by the complement membrane attack complex (MAC). This finding suggests that the vasculoprotective effects of statins are not generic but are amplified within the specific pathological milieu of an inflamed joint. The effect of statins on angiogenesis itself is more complex and appears to be biphasic; low concentrations can be pro-angiogenic, whereas high concentrations are angiostatic []. This dose-dependent duality is a critical consideration, as the high doses potentially required for anti-inflammatory effects might simultaneously inhibit beneficial repair processes, adding another layer of complexity to their therapeutic use in OA.
In the context of cancer, sustained inflammation within the TME can cause endothelial cell dysfunction, thereby promoting tumour progression and metastasis. These dysfunctional endothelial cells influence cancer progression through several mechanisms, including disrupted cell adhesion, increased vascular permeability, and activation of key pro-inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB and STAT3 signalling []. Cancer prevention and treatment can also occur through statins’ other pleiotropic effects of mediating angiogenesis, apoptosis and cell proliferation []. These effects have been demonstrated to occur in a dose-dependent manner with, lower doses activating Akt and downstream NO production and higher doses inhibiting production of non-sterol derivatives of mevalonate. In CRC, tumour-associated endothelial cells (TECs) have been shown to support epithelial proliferation and contribute to immune remodelling []. Similarly, in breast cancer, endothelial cells can enhance tumour cell survival even under nutrient-deprived conditions, ultimately increasing metastatic potential []. In the context of pulmonary malignancies, particularly non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), circulating concentrations of Cripto-1 (CR-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) have been shown to be markedly elevated relative to those observed in healthy control cohorts. Importantly, CR-1 titres exhibited a pronounced increase in patient subsets presenting with distant metastatic dissemination []. Given this critical role of endothelial dysfunction in cancer, targeting the vascular component has become a key therapeutic strategy. Statins have shown strong anti-angiogenic properties at micromolar concentrations. They inhibit endothelial cell growth and migration while inducing apoptosis in TECs []. In CRC experimental models, co-administration of statins with the anti-angiogenic agent bevacizumab elicited a marked attenuation of endothelial cell viability, invasive capacity, and capillary-like tube morphogenesis, collectively culminating in suppression of tumour expansion and metastatic dissemination []. In breast cancer, statin therapy has also been associated with vascular protection, particularly in patients undergoing radiotherapy, where statins like rosuvastatin and pravastatin were linked to a lower incidence of MACE, reflecting improved endothelial function []. Likewise, in lung cancer, atorvastatin has been reported to attenuate VEGF expression by limiting reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation through inhibition of Rac1-driven NADPH oxidase, while concurrently enhancing antioxidant defences such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This combined effect suppresses pro-inflammatory signalling cascades and preserves endothelial structural and functional integrity []. Collectively, these findings underscore the multifaceted mechanistic roles of statins in oncological contexts, highlighting their capacity to modulate tumour-promoting pathways, remodel the tumour microenvironment, and attenuate pro-angiogenic and pro-inflammatory signalling, thereby contributing to improved therapeutic outcomes. This positions statins as promising adjunct therapies that can improve vascular health and may also boost the effectiveness of current cancer therapies across various tumour types.
4.4. Inhibition of Inflammasome Activation
Inflammasome-driven signalling constitutes a pivotal axis in the pathobiology of chronic inflammatory states, orchestrating maladaptive immune activation across metabolic, neoplastic, and degenerative joint disorders. Among these cytosolic multiprotein platforms, NLRP3 inflammasome represents a principal effector node, whose activation is precipitated by a diverse repertoire of metabolic derangements, redox disequilibria, and sterile danger-associated molecular patterns, thereby amplifying tissue-destructive inflammatory cascades and accelerating disease trajectory. The involvement of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathophysiology of diabetes remains a subject of considerable scientific contention, with experimental and clinical evidence yielding divergent interpretations. Certain studies delineate a context-dependent regulatory role, wherein NLRP3 activation mediates controlled inflammatory resolution through downstream IL-1 family signalling attenuation, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory influences. Conversely, other investigations implicate sustained or dysregulated NLRP3 activation in the perturbation of insulin receptor signalling cascades via chronic IL-1β overproduction, oxidative stress amplification, and crosstalk with stress-activated kinases, ultimately impairing insulin sensitivity and glycaemic control. This apparent dichotomy underscores the necessity for refined mechanistic dissection of inflammasome kinetics, spatial activation patterns, and cell-type-specific contributions within metabolic tissues.
NLRP3 is part of the innate immunity; as such, it is stimulated by DAMPs and activates pro-apoptotic caspases for maturation and release of other pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β and IL-18 []. In diabetes, the body recognizes the abnormal elevated free fatty acids, the sustained hyperglycemic levels and ROS as DAMPs, compelling the trigger of NLRP3 inflammasome activation []. Thus, another inflammatory pathway enters the scene to facilitate the beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance discussed before.
In osteoarthritis (OA), a comparable pattern of inflammasome misregulation is evident; persistent hyperactivation of the NLRP3 inflammasome constitutes a central pathogenic axis driving articular cartilage matrix attrition and synovitis, thereby promoting progressive disease evolution []. NLRP3 inflammasome functions as a sensor to endogenous metabolic stressors such as cholesterol crystals by recruiting and activating caspase-1 [,].
In oncological contexts, an accumulating body of evidence indicates that multiple malignancies are characterized by heightened NLRP3 inflammasome activation. This dysregulated inflammasome signalling contributes to tumour growth and has been linked to poorer clinical outcomes in several malignancies. NLRP3 activation in macrophages promotes invasion and migration of tumour cells by driving epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) []. Similarly, in lung cancer, stimulation of the inflammasome with LPS and ATP enhances proliferation and migration of cells []. Clinically, high NLRP3 expression in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with increased infiltration of immunosuppressive M2 macrophages and poorer survival outcomes []. Additionally, cancer-associated fibroblasts respond to DAMPs by activating the inflammasome and releasing IL-1β, amplifying pro-inflammatory signalling in the tumour stroma [].
In the context of diabetes, Lv et al. demonstrated that simvastatin can inhibit activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in vascular endothelial cells thereby protecting against hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction and improving vascular permeability []. Similarly, Luo et al. successfully showed how rosuvastatin can elevate inflammatory-driven diabetic cardiomyopathy by downregulating NLRP3 inflammasome activity along with MAPK pathway []. Furthermore, evidence indicates that statins can attenuate lysosomal injury–driven activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, thereby mitigating obesity-associated increases in endothelial permeability []. Despite the study being scoped on obesity, these results can be utilized for diabetic patients management as well, since obesity is a major factor in the pathogenesis of diabetes []. Furthermore, statins when taken in combination also demonstrate the same inhibitory activity, as investigated by Wang et al. Two statins—simvastatin and mevastatin—were administered in endothelial cells to see if statins can improve endothelial outcomes. Collectively, the statins show inhibitory activity of inflammasome in the endothelial cell lines. Although not particularly investigated in the context of diabetes, the same pregnane X receptor (PXR)-dependent mechanism is also present in diabetes, hence the translational relevance of the study can be seen [].
Statins administered in combination therapy with other non-statin drugs can increase the potency of targeted action. In a cohort of insulin-resistant Wistar rats, treatment was administered either with dapagliflozin alone or in combination with atorvastatin []. In the monotherapy group, dapagliflozin partially reversed metabolic disruption and reduced kidney injury in these rats; however, the effects were much less compared to the combination group, which demonstrated substantial improvement in inflammasome activation and autophagy dysfunction.
Conversely, some studies have reported how statins exacerbate diabetic pathogenesis by increasing risk of new-onset diabetes. Recently, a study by Henriksbo et al. found atorvastatin activated p38, hence primed p38 to act on NLRP3 inflammasome []. Similarly, a study by Henriksbo et al. demonstrated that fluvastatin dose-dependently enhanced IL-1β secretion from macrophages, indicative of NLRP3 inflammasome activation []. Both sides carry robust evidence, hence warranting further in-depth investigation of statins in NLRP3 inflammasome activity.
In OA as well, statins appear to modulate inflammasome activity. In clinical studies, statin therapy was shown to downregulate the gene expression of NLRP3 in PBMCs from patients with cardiovascular disease [,]. As previously mentioned, this is further substantiated by an in vivo study on vascular endothelial cells, where simvastatin and mevastatin significantly suppressed NLRP3 inflammasome activation []. In rat model investigations, atorvastatin has been found to attenuate NLRP3 inflammasome activation in intracerebral hemorrhage by interfering with TLR4 and MyD88 signalling pathways, and likewise in TNF-α–stimulated nucleus pulposus cells, which display phenotypic similarities to chondrocytes [].
It is important to note statins’ opposing effect on the NLRP3 inflammasome- initiating activation through the upregulation of IL-1β synthesis and enhancement of caspase-1 enzymatic function []. This contradictory action can depend on the lipophilicity of the statin used, the signalling pathways involved, the current metabolic state, and the initial inciting event [,,]. For OA, it implies that a statin could potentially be beneficial by suppressing inflammasome activity in chondrocytes and synoviocytes while having neutral or even detrimental effects elsewhere.
While direct studies in tumour models remain limited, mechanistic findings from related systems suggest that statins may exert anti-inflammatory effects in cancers characterized by high oxidative stress. Evidence indicates that rosuvastatin attenuates ox-LDL–driven upregulation of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP), a pivotal upstream regulator of NLRP3 inflammasome activation, thereby diminishing IL-1β–dependent inflammatory signalling [,]. Although these findings derive from non-cancer models, the specific role of statins in inhibiting inflammasome activation within cancer models remains underexplored. Thus, it is plausible that statins may show comparable anti-inflammasome effects in cancer contexts, particularly in malignancies characterized by high oxidative stress.
In summary, statins modulate NLRP3 inflammasome activity through mechanisms such as NF-κB inhibition, TXNIP suppression, and PXR activation. While anti-inflammatory effects have been observed in models of diabetes, cancer, and osteoarthritis, findings in diabetes and OA remain mixed, suggesting statin responses may be context-dependent, influenced by factors like statin lipophilicity, tissue environment, and disease stage.
4.5. Modulation of Protease-Activated Receptor-2 (PAR-2) Signalling
Protease-activated receptors (PARs 1–4) constitute a subclass of G-protein–coupled receptors engaged in diverse physiological and pathophysiological processes []. These are key mediators of cellular responses in inflammation and disease progression. Although direct studies on statins’ effects on PAR signalling are scarce, emerging evidence, particularly on PAR-2, suggests statins may attenuate this pathway, contributing to their therapeutic effects across diabetes, cancer, and osteoarthritis.
In diabetes specifically, PAR-2 has been shown to stimulate inflammatory pathways and attenuate cellular metabolism, increasing insulin resistance and promoting obesity []. PAR-2, in particular, has been implicated in driving inflammation through activation of NF-κB and induction of TNF-α []. In work conducted by Hayashi et al., the interplay between PAR-2 and factor Xa was examined within the context of inflammation-driven diabetic nephropathy. In this condition, factor Xa levels are elevated, which in turn enhances PAR-2 signalling, with both elements acting synergistically to sustain inflammation through NF-κB and MAPK pathways []. Furthermore, PAR-2 has been observed to promote fibro-proliferate disorders, initiate podocyte injury, tubular epithelial cell inflammation and kidney damage via IgA-induced nephropathy [].
In OA, the inflamed joint, marked by its catabolic environment, is rich in enzymes released from synovial cells and infiltrating leukocytes that can degrade the cartilage matrix. PAR, specifically PAR-2, is a key sensor for these cellular responses by inciting pro-inflammation and catabolism that drives joint destruction [,,,,]. Studies have demonstrated a marked upregulation of PAR-2 in cartilage and chondrocytes derived from OA patients, as compared to those from normal, healthy tissue []. In OA, elevated PAR-2 expression increases the sensitivity of chondrocytes to proteolytic stimuli present in the surrounding matrix, leading to the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases such as MMP-1 and MMP-13, as well as induction of the inflammatory enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) []. This downstream effect is driven by the activation of intracellular signalling pathways involving Erk1/2 and p38 MAPK. Additionally, targeting PAR-2 expression in OA has shown potential therapeutic benefit in a study investigating oleocanthal’s activity in in vitro human chondrocyte models []. Treatment with Oleocanthal led to a significant, dose-dependent reduction in PAR-2 expression, accompanied by decreased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β.
A comparable pattern of dysregulation is evident in oncology, with PAR-2 overexpression documented across diverse tumour types. In prostate and pancreatic cancers, elevated PAR-2 levels have been linked to enhanced proliferative capacity, while in colorectal malignancies, overexpression correlates with more aggressive invasion patterns. Similar associations are seen in hepatic and cutaneous cancers, where heightened PAR-2 expression is tied to accelerated tumour progression and poorer patient prognosis [,]. In CRC particularly, PAR-2 activation reduces doxorubicin-induced cell death by promoting anti-apoptotic signalling []. Research findings indicate that PAR-2 drives breast-cancer cell migration and invasion [] and in lung adenocarcinoma its overexpression is associated with lymphatic spread and poor postoperative survival [].
Statins’ effects on PAR-2 modulation have been investigated in several cell lines, including HUVECs and CRC cell lines [,]. The former study showed how statins prevent the induction of tissue factor by specific PAR-2 activating peptides, proving statins can exert upstream regulatory control []. Although direct studies examining the effects of statins on PAR-2 signalling in specific diseases remain limited, Patnaik et al. demonstrated that both atorvastatin and rosuvastatin selectively suppress PAR-2 expression at the transcript and protein levels in a dose-dependent fashion []. These downstream events resulted in diminished release of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and a mitigation of aberrant calcium signalling. Although conducted in a cancer model, the core mechanism, i.e., attenuation of PAR-2 activity, may be relevant across multiple inflammatory conditions where PAR-2 is implicated to play a pathogenic role.
In our recent investigation, we examined the effects of the lipophilic statin atorvastatin and the hydrophilic statin rosuvastatin on PAR-2 expression in the human CRC cell lines HT-29 and Caco-2. Both agents elicited a marked downregulation of PAR-2 at both the protein (translational) and mRNA (transcriptomic) levels, accompanied by a concomitant suppression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α []. Furthermore, statin treatment favourably modulated intracellular calcium dynamics, an effect with potential implications for PAR-2-dependent signalling cascades, inflammatory amplification, and tumour cell survival []. However, these findings warrant further extension through mechanistic dissection of the downstream signalling networks, assessment of PAR-2 knockdown or knockout models, and evaluation of the potential synergistic effects of statins with conventional chemotherapeutics or targeted agents. Such studies will be essential to fully delineate the therapeutic potential of statin-mediated PAR-2 modulation in CRC and its impact on tumour progression, angiogenesis, and the inflammatory tumour microenvironment. Importantly, the implications of statin-mediated PAR-2 modulation may extend beyond the cancer cell itself to include alterations in the surrounding stromal and adipose compartments, particularly peritumoral adipose tissue (PTAT), which is increasingly recognized as a metabolically active and immunologically dynamic contributor to tumour progression.
PTAT is increasingly recognized as an active participant in tumour progression, functioning not only as a metabolic reservoir but also as a paracrine signalling hub. Recent evidence indicates that PTAT frequently undergoes browning, a phenotypic conversion of white adipocytes into a more thermogenically active, brown or beige-like state. This process is characterized by mitochondrial enrichment, enhanced oxidative metabolism, and upregulation of uncoupling proteins, notably UCP1 []. Such metabolic reprogramming fundamentally alters the inflammatory and angiogenic profile of the TME, with consequences for immune cell recruitment, nutrient availability, and cancer cell survival. The phenomenon has been documented in breast cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and likely other malignancies, highlighting its relevance across multiple tumour types [].
In breast cancer models, tumour-derived adrenomedullin (ADM), a hypoxia-inducible peptide, drives UCP1 expression in adjacent adipocytes through paracrine signalling []. This results in delipidation of cancer-associated adipocytes, with smaller lipid droplets, increased mitochondrial density, and heightened thermogenic capacity. These changes facilitate fatty acid mobilization and modulate cytokine networks, ultimately supporting tumour invasiveness. In renal cell carcinoma, perirenal adipose tissue adjacent to the tumour exhibits markedly higher UCP1 expression compared to normal perirenal fat []. This browning correlates positively with Fuhrman grade and tumour stage, while histological examination reveals smaller adipocyte size, greater cell density, and increased expression of thermogenic markers. Such findings suggest that browning in PTAT is not merely a by-product of systemic cachexia or metabolic disturbance, but rather a locally orchestrated adaptation driven by tumour–stroma interactions.
PARs, particularly PAR-2, have emerged as important mediators of adipose tissue remodelling within the peritumoral niche []. PAR-2 activation in the TME has been linked to enhanced cancer cell survival, reduced chemosensitivity, and the upregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins. In breast cancer models, genetic deficiency of PAR-2 delays tumour progression and reduces angiogenesis, implicating it in the angiogenic switch associated with browning and vascular remodelling []. Mechanistically, PAR-2 may influence adipocyte phenotype through ERK/MAPK and NF-κB signalling, which intersect with transcriptional programmes controlling UCP1 expression and mitochondrial biogenesis.
Statins, by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, modulate isoprenoid-dependent signalling, mitochondrial function, and inflammatory pathways. These pleiotropic effects create a plausible framework for statins to influence adipocyte browning in the peritumoral compartment. A key mechanism involves activation of AMPK, a master regulator of metabolic reprogramming in adipose tissue. Statin-induced AMPK activation can promote mitochondrial biogenesis via PGC-1α and PPARγ coactivation, enhance fatty acid oxidation through acetyl-CoA carboxylase phosphorylation and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 activation, and induce UCP1 expression, driving thermogenic programming in white adipocytes.
However, this relationship is not straightforward. Recent data suggest that statins may paradoxically suppress browning in certain contexts []. In vitro experiments have shown that statin treatment can reduce UCP1 and thermogenic gene expression in human white adipocytes, while short-term statin administration in animal models has diminished brown adipose tissue activity []. This suppressive effect is thought to occur through depletion of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, an essential intermediate for the prenylation of small GTP-binding proteins such as Rho and Rac1, which are necessary for adipocyte differentiation and mitochondrial recruitment. Thus, the influence of statins on browning is likely dose- and context-dependent, with potential differences between short- and long-term exposure, as well as between tissue types.
Regardless of their effects on browning per se, statins consistently demonstrate significant anti-inflammatory activity within adipose tissue depots. They reduce the proportion of pro-inflammatory macrophages, promote M2-like anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization, and attenuate inflammatory cytokine production []. In addition, statin therapy has been associated with reductions in epicardial adipose tissue thickness and improvements in local immune–metabolic profiles []. Within PTAT, these anti-inflammatory actions could indirectly suppress tumour-promoting inflammation, even in scenarios where browning is diminished.
Although direct clinical evidence linking statin therapy to modulation of PTAT browning in cancer patients is currently lacking, converging observations from basic and translational studies support a testable hypothesis. Statins, through AMPK activation and mitochondrial regulation, their modulation of macrophage phenotypes, and potential interference with PAR-2 signalling, could alter the immune–metabolic crosstalk within the peritumoral adipose compartment. These interactions may influence oxidative metabolism, angiogenesis, and inflammatory signalling, thereby impacting tumour progression.
Future research in this domain should focus on integrating advanced imaging modalities with biopsy-based assessments to quantify PTAT browning in cancer patients undergoing statin therapy. In vitro co-culture models incorporating tumour cells, adipocytes, and macrophages will be essential for dissecting the interplay between statin pharmacodynamics, PAR-2 activity, and UCP1 expression. Multi-omics approaches, including transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, could illuminate the metabolic rewiring of PTAT under statin influence, and clinical correlation with tumour aggressiveness, treatment response, and survival outcomes will be crucial to establish translational relevance.
If validated, the capacity of statins to modulate PTAT phenotype, either by directly altering thermogenic programming or indirectly via anti-inflammatory effects, could add a novel dimension to the pleiotropic anti-cancer mechanisms of this drug class. Such insights would not only deepen understanding of tumour–stroma metabolic interactions but also open avenues for targeted therapeutic strategies combining metabolic modulation with conventional or immune-based cancer therapies.
4.6. Antioxidant and ROS Scavenging Activity
The pathological involvement of oxidative–antioxidant imbalance in inflammation-driven disorders such as OA, diabetes, and cancer has been extensively examined, both to delineate the mechanistic underpinnings of disease pathogenesis and to identify prospective avenues for therapeutic intervention. ROS are part of the normal inflammatory signalling and immune protection; however, when levels reach pathogenic levels, it can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, increased inflammation, and further metabolic dysregulation [].
Researchers have documented a pronounced disequilibrium between reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and the endogenous antioxidant defence network in diabetes, a disruption that underpins the persistent oxidative stress characteristic of the condition []. The underlying hyperglycemic state promotes ROS production through multiple pathways that ultimately activate the NADPH oxidase enzyme, a key synthesizer of ROS [,]. Rac1, a key subunit of NADPH, can become dysregulated as highlighted earlier and can further increase NADPH enzyme levels. Furthermore, elevated activation of NADPH can amplify ER stress, which exacerbates the insulin resistance experienced in diabetes []. This results in a positive loop of further protein folding dysfunction and NADPH activation, which worsens the chronic inflammatory state and overall prognosis. This hyperglycemia-stimulated NADPH oxidase activity and downstream cascade has several complications, one of which is in a diabetic retinopathy model []. ROS generated via NADPH oxidase serves as an essential mediator in the signalling cascade that drives hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) synthesis and the subsequent angiogenic response. Similarly, within OA joints, excess ROS production contributes directly to chondrocyte dysfunction, promoting cellular senescence, apoptosis and enzymatic degradation of the extracellular matrix components [,]. This is exacerbated with comorbidities such as hypercholesterolemia, which has been proven to induce profound mitochondrial dysfunction in chondrocytes. Furthermore, multiple studies have shown the crosstalk between NOX activity and ER stress, contributing to the insulin resistance experienced in diabetes [,].
Cancer cells typically exhibit a state of heightened oxidative stress, characterized by persistently elevated intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which act as critical mediators in both the initiation and progression of malignant transformation []. These reactive intermediates engage in deleterious interactions with essential cellular macromolecules, including nucleic acids, proteins, and membrane lipids—thereby inducing cumulative oxidative damage that underpins genomic instability and functional impairment of key regulatory pathways. In CRC, sustained ROS overproduction has been mechanistically linked to the promotion of carcinogenesis, dynamic remodelling of the tumour microenvironment, and the emergence of therapeutic resistance phenotypes [,]. Analogously, in breast cancer, ROS act as potent drivers of both genetic reprogramming and immunomodulatory alterations, fostering an environment conducive to tumour growth, metastatic dissemination, and evasion of therapeutic pressure []. Moreover, estrogen-mediated ROS generation constitutes a pivotal pathogenic axis in breast carcinogenesis, wherein it amplifies the transcriptional upregulation of pro-proliferative and pro-inflammatory cytokine networks, further potentiating neoplastic progression [].
Statins’ antioxidative properties—encompassing direct free radical neutralization, suppression of pro-oxidant enzymes, and curtailment of excessive ROS generation—underscore their potential to attenuate the pathogenesis of diverse inflammatory disorders [,,,,,]. Anjos et al. showed that atorvastatin, when given to T2D patients, inhibited NADPH-oxidase dependent ROS generation []. Similarly, Cheng et al. highlighted the role of pitavastatin in reno-protective features in Dahl salt-sensitive rat model. They found that among other anti-inflammatory activity, it attenuated NADPH oxidase activity and also ameliorated Rac1 expression []. Piconi et al. cultured HUVECs treated with rosuvastatin at different glucose concentration and found that rosuvastatin inhibition of the overexpression of genetic subunits of NADPH oxidase, such as p47-phox, p67-phox, and p22-pho []. Additionally, Bruder-Nascimento et al. elucidate Rac1-sensitive NOX mechanisms whereby atorvastatin protects against ROS-mediated vascular injury in diabetes through inhibition of cytosol-to-membrane translocation of p47(phox), Rac1 and Nox1/2/4 [].
Similarly, another study demonstrated that atorvastatin, pravastatin, and cerivastatin suppress NADPH oxidase function by inhibiting p21 Rac, a critical subunit of the enzyme complex, in rat aortic segments with intact endothelial lining []. Conversely, these suppressive effects are not confined to mitigating the chronic inflammatory milieu of diabetes but also encompass downstream sequelae, with studies demonstrating their influence on complications such as diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy. A study evaluating the impact of rosuvastatin on the glomerular filtration barrier in Zucker obese rats demonstrated that the treatment reduced NADPH oxidase activity and enhanced podocyte membrane integrity []. Another study conducted in Zucker obese rats found that pitavastatin decreased ROS and NADPH levels (even at an mRNA level) in the mice []. Li et al. reported that lovastatin lowered NADPH oxidase 4 expression in retinal capillary endothelial cells (RCECs) as well as in db/db mice receiving lovastatin treatment [].
Moreover, several studies have also shown the alleviation of ER stress via various statins, which contribute to ROS production in many inflammatory diseases. For instance, Xu et al. demonstrated how rosuvastatin can alleviate ER stress in HUVECs through attenuation of ER stress biomarkers []. Another study demonstrated that atorvastatin attenuated activation of the eIF2α–ATF4–CHOP signalling pathway in obese C57BL/6J mice, thereby contributing to the alleviation of endoplasmic reticulum stress []. Furthermore, when 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells were treated with simvastatin, it showed a reduction in ER stress via downregulation of ox-LDL-induced ER stress []. Such studies underscore the importance of statins’ actions on mitigating the inflammatory milieu underlying diabetes.
In the context of OA, an in vitro comparative study that measured the ability of different statins to antagonize the oxidation of a test substrate by both hydroxyl and peroxyl radicals found that all tested statins exhibited antioxidant activity []. Within this class, simvastatin was identified as the most effective scavenger of hydroxyl radicals, while fluvastatin displayed the highest capacity for scavenging peroxyl radicals, indicating differential properties among the various statins. In an animal model where OA was precipitated by a high-cholesterol diet, treatment with atorvastatin was shown to significantly attenuate the progression of cartilage degradation. This protective effect was explicitly associated with the mitigation of chondrocyte mitochondrial dysfunction and the suppression of ROS overproduction. By dually mitigating the imbalance of ROS production, these studies underscore the benefit of treatment with statins in OA patients, especially those with underlying metabolic risk factors.
Due to their role in cancer progression, ROS are increasingly seen as promising therapeutic targets, with statins showing particular potential through their effects mediated by mevalonate pathway inhibition and antioxidant effects []. In mouse models of CRC, simvastatin reduced tumour growth by downregulating ROS levels and triggering caspase-1–dependent pyroptosis []. In breast cancer cells, statins were shown to activate the antioxidant transcription factor NRF1 via ROS signalling, leading to increased expression of tumour-suppressive miR-140-5p []. Together, these findings indicate the central role of ROS in cancer progression and highlight the potential of statins as adjunct therapies with antioxidant and anti-tumour effects.
4.7. Reduction in Acute Phase Proteins
Acute phase proteins (APPs) are systematic markers for inflammation that are widely utilized in clinical practice. For systemic diseases such as OA, diabetes and cancer that often had chronic low-grade inflammation, CRP, fibrinogen and serum amyloid A (SAA) are often elevated []. In addition to its established diagnostic and prognostic roles, CRP directly participates in inflammatory processes by promoting pro-inflammatory cytokine production and triggering activation of the complement cascade [].
These APPs been linked to the development of insulin resistance and the progression of metabolic and vascular complications arising from diabetes [,]. IL-6 released from adipose tissue and immune cells stimulates the production of CRP and SAA, both of which act to intensify the inflammatory cascade []. While their levels are typically elevated to a much lesser extent than in classic systemic inflammatory diseases like RA, they serve as valuable markers for systemic inflammatory burden and disease activity in OA []. Similarly, APP are consistently elevated in various cancers and are associated with poorer outcomes. In CRC, increased plasma levels of CRP and fibrinogen have been associated with significantly elevated risk of disease development [,]. In breast cancer, CRP and SAA concentrations are elevated in patients with advanced disease stages [], and higher levels of these proteins have been associated with lower overall survival rates []. Notably, SAA expression in TAMs and tumour cells has been linked to the occurrence of lymphovascular infiltration and the spread of cancer to regional lymph nodes [].In lung cancer, SAA levels were found to be higher in patient serum and plasma [].
In the PRINCE trial, researchers observed that pravastatin decreased CRP levels, at both 12 and 24 weeks, largely independent of LDL-C reduction []. A recent meta-analysis conducted by Mashaba et al. [] evaluated the impact of statin therapy on C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations and carotid intima–media thickness (CIMT) in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The analysis demonstrated that statin administration led to significant reductions in both CIMT and CRP, with a daily dose of 20 mg atorvastatin emerging as the most efficacious regimen. Similarly, in another meta-analysis by Zhang et al., the researchers investigated various statin types and dosages in reducing CRP []. As previously noted, the JUPITER trial, show that statin therapy lowers serum hs-CRP levels in individuals with dyslipidemia or coronary heart disease, highlighting simvastatin 40 mg/day as a notably effective option, while atorvastatin 80 mg/day demonstrated superior long-term benefits []. Since CRP is part of the initial innate immune system response to inflammatory triggers, reduction in CRP levels could suggest a lower incidence of acute and initial-phase diabetes onset and attenuation of the perpetual inflammatory cycle.
In contrast, evidence regarding the influence of statins on serum amyloid A (SAA) remains inconsistent. Experimental studies employing collagen-induced arthritis in mice reported that statin administration did not produce any notable reduction in systemic SAA levels. However, circulating levels of the oxidatively modified lipoprotein complex (SAA-LDL) were significantly reduced in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Given that ox-LDL has been implicated in activating synovial cells and promoting inflammation in the joint [], the ability of statins to selectively reduce this modified lipoprotein species could be highly relevant to OA pathogenesis. Therefore, further studies investigating molecular mechanisms of statins on these specific biomarkers in OA joints may yield beneficial therapeutic results.
Statins exert pleiotropic effects in cancer by inhibiting tumour cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, impairing angiogenesis, and modulating the tumour microenvironment, partly through reduction in APPs [,,]. Evidence suggests that atorvastatin significantly reduces IL-6 and CRP levels in cancer patients [,], and other research has confirmed statin-mediated CRP reduction across various diseases and cell types []. In breast and colorectal cancer specifically, statins have been shown to downregulate inflammatory signalling pathways and may reduce cancer-related mortality, with evidence suggesting that lipophilic statins may be more effective in this regard [,]. For liver cancer, statins may attenuate inflammation-driven carcinogenesis, as chronic hepatic inflammation is a key driver of hepatocellular carcinoma []. These findings suggest that statins may help mitigate cancer-associated inflammation by downregulating APP levels.
4.8. Statins and Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is an autoimmune chronic inflammatory condition with a multifactorial pathogenesis. It has been hypothesized that targeting the inflammatory pathways in this condition would alleviate its symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. Additionally, RA is closely linked with increased cardiovascular risk due to chronic inflammation, which exacerbates atherosclerosis and vascular dysfunction []. Discontinuation of statins in RA patients is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality []. Therefore, investigating the use of statins to not only modulate the inflammatory pathways involved in RA pathogenesis, but to also alleviate concomitant cardiovascular manifestations, invites exploration into statins as a promising therapeutic option in RA patients.
Studies have demonstrated that atorvastatin effectively exerts its lipid-lowering ability in RA patients []. In terms of their anti-inflammatory effects, a meta-analysis showed that atorvastatin significantly decreased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), CRP, TNF-α and IL-6 levels, markers of inflammation [,]. Additionally, an in vivo study has also shown that specific statins such as simvastatin may confer better efficacy than its more popular counterpart’s atorvastatin and rosuvastatin []. Conversely, a double-blind study with lovastatin treatment showed no effect on disease activity or CRP levels [].
A study by Yokota et al. highlighted earlier demonstrated that simvastatin inhibits IL-6 and IL-8 production, as well as cell proliferation induced by TNF-α in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from RA patients []. These findings build on those by Takemoto et al. [], suggesting that simvastatin mediates this anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing Rho and Ras-like protein activities through depletion of isoprenoid compounds. In an in vitro study using PBMC cultures, atorvastatin decreased the levels of IL-17A, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10, with the magnitude of suppression varying according to the administered concentration. Analysis showed that cytokine reduction was significant in samples of patients with severe RA []. Additionally, research has indicated that atorvastatin improves regulatory T cell activity by inhibiting PI3K-Akt-mTOR and ERK transduction pathways, addressing defects in regulatory T cells implicated in RA [].
The Trial of Atorvastatin in Rheumatoid Arthritis (TARA) demonstrated that atorvastatin therapy led to a significant reduction in the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28), a validated composite index for RA disease activity, with outcomes ranging from moderate to good clinical responses. These improvements were accompanied by marked decreases in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels []. As a follow-up, Mäki-Petäjä et al. demonstrated that simvastatin and ezetimibe resulted in similar decreases in inflammatory markers, supporting the notion that the anti-inflammatory benefits of statins are connected to their cholesterol-lowering effects []. Furthermore, Xing et al. proved that, when compared with the used of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), atorvastatin showed a significant reduction in DAS28 [,]. In contrast, a much larger cohort study conducted by Lodi et al. disproved the findings from the TARA study, highlighting that the anti-inflammatory benefits that statins confer on RA patients do not match those of DMARDs [].
Across these investigations, the predominant pathway by which statins confer anti-inflammatory effects in RA patients involves elevation of HDL levels []. This elevation facilitates cholesterol efflux, thereby diminishing the lipid raft content within immune cell plasma membranes, while concurrently lowering the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and the interleukin-3 receptor β-subunit (IL-3Rβ).
Although existing evidence suggests that statins may offer anti-inflammatory benefits in RA, further randomized clinical trials and large-scale cohort studies are needed to validate these results and fully establish the therapeutic potential of statins in RA management.
4.9. Statins and COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) constitutes a persistent inflammatory disorder of the lower airways, typified by progressive airflow limitation and associated respiratory morbidity. In this context, considerable investigative attention has been directed toward leveraging the pleiotropic anti-inflammatory properties of statins to attenuate acute exacerbations, enhance clinical outcomes, and suppress both inflammatory signalling cascades and the structural remodelling of pulmonary tissue.
In a rat model of COPD, atorvastatin administration attenuated structural alterations of the pulmonary vasculature and dampened inflammatory responses []. Histopathological examination demonstrated a pronounced reduction in the accumulation of inflammatory cells within the perivascular compartment, together with amelioration of endothelial damage in the vascular wall. Mechanistically, these effects are linked to inhibition of acetyl-CoA conversion to cholesterol, leading to decreased guanosine triphosphate–binding protein synthesis and prevention of NF-κB nuclear translocation. This signalling interruption suppresses the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-8 and TNF-α, ultimately constraining pulmonary vascular inflammation and limiting pathological tissue remodelling. Additionally, atorvastatin was found to increase HDAC2 expression via NF-κB acetylation and reduce vascular endothelial growth factor production, thus modulating pulmonary vascular inflammation and remodelling. However, such anti-inflammatory benefits are dose-dependent, as high doses may further exacerbate lung damage []. A pilot-study conducted by Mroz et al. (ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT01748279) confirmed atorvastatin’s anti-inflammatory effects [], with a follow-up clinical trial currently investigating its effect on COPD exacerbations (ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT04789057).
Statins have also been linked to decreased frequency of COPD exacerbations and related hospitalizations. A population-based nested case–control study reported a 30% reduction in the risk of hospitalization among statin users, with more pronounced effects observed in patients within six months of statins use or at higher doses []. The Rotterdam study highlighted the long-term benefits of statin use in reducing mortality in COPD patients, with up to a 39% reduction in all-cause mortality and 64% decrease in pulmonary-associated mortality []. The protective effect was particularly significant in COPD patients with elevated systemic inflammation (indicated by high CRP levels), suggesting that statin’s mechanism of modulating inflammatory processes is crucial for mortality reduction. A systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating data from more than 238,000 individuals with COPD, across 15 studies, identified a statistically significant association between statin therapy and reduced mortality risk, specifically, a 38% decrease in all-cause mortality and a 52% decrease in COPD-specific mortality [].
The concomitant administration of statins with other anti-inflammatory interventions, such as omega-3 fatty acids, which attenuate NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and lycopene, which suppresses IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β production—has demonstrated potential in modulating inflammatory pathways in COPD []. Interestingly, the study displayed rosuvastatin’s pro-inflammatory properties, as evidenced by increased neutrophilic airway inflammation. The increase in neutrophils was primarily associated with changes in LTB4R and ALOX15 gene expressions, known for their role in neutrophil recruitment.
These results highlight the potential of statins as adjunctive therapy in managing COPD. Future studies should aim to optimize dosing strategies and investigate combination therapies to enhance their therapeutic potential in COPD.
5. Limitations
While statins exhibit many beneficial effects, several studied provide an opposing view on their toxic and harmful side effects. The following section discusses the limitations of statins in respect to their effects on organ dysfunction, hormonal axes, epigenetics, and socioeconomic status.
5.1. Organ Dysfunction
Figure 10 demonstrates the toxic side effects of statins on the liver, pancreas, muscle and brain. Statin therapy is frequently accompanied by adverse musculoskeletal sequelae, collectively termed statin-associated myopathies, which represent a subset within the broader clinical spectrum of statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS). The exact mechanism of action is still a point of contention; however, it is postulated that the mechanism of action differs due to genetic polymorphism, as genetic dysregulations of specific genes like Uncoupling protein 3 (UCP3) make individuals more susceptible to SAMS [,]. Furthermore, statin-mediated downregulation of the intermediates in the de novo cholesterol pathway and Co-enzyme Q10 biosynthesis, leads to mitochondrial dysregulation, reduced energy production and muscular atrophy [,]. An observational study by Casula et al. found that 9.6% of the cohort experienced SAMS, with higher rates reported among women and subjects with physical activity []. An estimate of 7–29% SAMS was reported by statin-users in various observational studies; this indicates a potential adverse effect of statin therapy [,,].
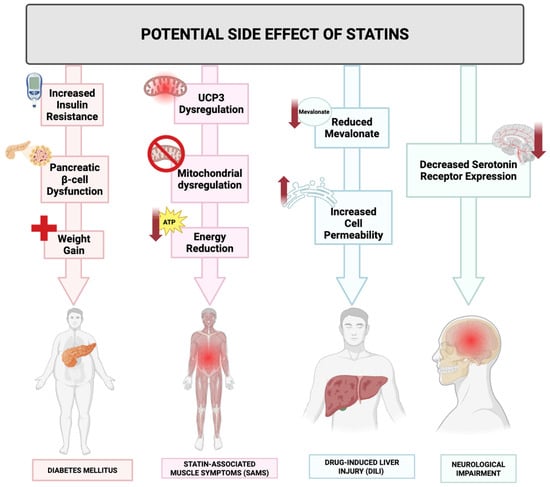
Figure 10.
Potential adverse effects associated with statin therapy. This figure depicts the commonly reported adverse effects of statin administration, most commonly statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMSs) (linked to genetic predisposition and mitochondrial dysfunction), increased risk of T2D, drug-induced liver injury (DILI), and various neurological impairments, all possibly due to altered cholesterol metabolism and subsequent molecular expressions.
Furthermore, a series of meta-analyses undertaken at the University of Glasgow consistently delineated an association between statin therapy and an elevated incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D), with the 2015 meta-analysis specifically reporting an 11% higher relative risk of T2D onset in statin-treated individuals compared to those receiving placebo []. While the precise mechanism remains under investigation, statin-induced diabetes has been linked to pancreatic-beta cell dysfunction from increased intracellular cholesterol, weight gain, and augmented insulin resistance.
Statins’ primary mechanism of reducing cardiovascular risk plays an important role in patient with comorbid liver disease, especially fatty liver disease []. However, studies exploring this use is limited due their capability of causing drug-induced liver injury (DILI). While statins have beneficial pleiotropic effects on the liver, there have been studies that suggest that reduction in mevalonate may cause an increase in liver enzymes. Furthermore, statins may reduce cell permeability, resulting in increased leakage and elevated detection of liver enzymes, contributing to the DILI []. Chen et al. carried out a population based case–control study with 4165 cases and found that statin-induced liver injury was not significant compared to control group; however, when looking at the statin group, a higher dosage of rosuvastatin before DILI occurred showed significant association with liver injury [].
Statin-administration has been associated with a number of neurological impairments, ranging from aggressive behaviour to decreased serotonin expression. An association between decreased cholesterol and decreased serotonin receptor expression has been postulated []. Serotonin is a key neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of mood and behaviour. However, population-based studies have suggested a protective association between statin use and depression [].
While reviewing studies investigating statins, it is important consider studies reporting the drug’s negative or non-significant results. Table 5 and Table 6 list such studies where statins—used alone, in combination with other statins, or alongside different drug classes– yielded such results. Such limitations add a holistic approach to investigating the drug’s potential therapeutic benefits and provides further research avenues.

Table 5.
Statins exhibiting negative or non-significant results in different studies.

Table 6.
Statins exhibiting negative or non-significant results when co-administered with different medications in different studies.
One limitation to the research designs investigating the benefits of statins include the variety of research designs. Observational studies, being purely correlational in nature, contrast with the in vivo animal models. Although they present statistically significant data, the extent to which this data can be applied to human patients is limited in understanding statin-mediated toxicity. Furthermore, often these studies are performed with a limited sample size, which results in reduced statistical power and possible inconclusive data being presented, leading to issues in determining the true effects, extent and clinical application of statins. When extending the results to populations of different gene pools, the results lack predictability. Hence, the cytotoxic effect of statins observed on a specific population and sample might have a different manifestation in a different population, compelling further research into the statin-mediated effects on these conditions.
Among the studies listed, the randomized clinical trials are ones with the highest internal validity, allowing the researchers to establish a reliable cause-and-effect relationship of the statin variable being studied. However, when investigating statins in clinical trials, another factor to weigh in is the compliance rate. Although randomized clinical trials minimize the researcher bias, inconsistent adherence to trial protocols results in data variability. A meta-analysis encompassing data from 20 studies involving a cumulative cohort of 376,162 patients demonstrated suboptimal adherence to statin therapy, with a substantial proportion discontinuing treatment following initiation []. A different retrospective analysis of statin administration was performed, and it was found that there was a decline in statin persistence, with women showing a lower persistence rate than men []. Reasons for non-compliance with statins are varied, including, but not limited to, access to medical care, transitions between multiple healthcare providers, and the cost of medications [].
Beyond issues like medication adherence, another aspect to consider when looking into statins is the difference in concentrations. Statins’ effects on the endothelial cells are dependent on the dosage given, i.e., lower concentrations of statins impose anti-senescence, and antiapoptotic effects, whereas the opposite seems to be true for higher statin dosage [], which highlights the importance of using consistent dosage of statins in research studies to avoid misinterpretations of results due to varying concentrations.
A point to consider when evaluating statin-mediated effects is the model of the statin being evaluated. simvastatin and atorvastatin are lipophilic statins and rosuvastatin is non-lipophilic. This allows simvastatin and atorvastatin to be more readily absorbed by the body, as their ability to freely permeate the cell membrane allows for greater rates of diffusion and drug utilization. On the other hand, rosuvastatin being hydrophilic allows it to be more readily excreted by the renal system. Taking this into account, when determining the ability of statins to present cytotoxicity or other adverse effects, the efficacy, safety profile and interactions are dynamic in different clinical scenarios, e.g., lipophilic stains are postulated to exhibit higher cardiovascular benefits but result in more SAMS [].
However, large-scale meta-analyses and randomized controlled trials have shown no clinically significant difference in the incidence of SAMS between lipophilic and hydrophilic statins at equivalent lipid-lowering doses [,,]. In vitro studies suggest greater cytotoxicity of lipophilic statins in muscle cells, especially in genetically susceptible individuals, but this has not translated into a higher clinical incidence of muscle adverse events in the general population. The American Heart Association and the National Lipid Association both emphasize that all statins can cause SAMS, and the choice of statin should be individualized based on patient comorbidities, drug interaction risk, and prior intolerance.
In addition, when considering the therapeutic effect of statins in conditions like CRC, real-world applications of these statins involve co-therapy with other drugs, necessitating a poly-pharmacodynamic evaluation. Investigating any possible synergistic effect occurring would allow statins to be further evaluated as a possible therapeutic avenue. On the other hand, if there is any drug-induced antagonization of statin, that suggests that statins on their own might have a beneficial effect, but in co-therapy that effect may become harmful, allowing healthcare practitioners to further consider how statins may be initiated in future treatment strategies of conditions like cancer, diabetes, or rheumatological conditions. Similarly, researchers studying the pharmacokinetics interaction of these drugs with statins may be presented with drugs “masking” or reducing the bioavailability of statins, potentially hindering their true therapeutic potential. This was observed in the study listed above by Lee et al., which showed that Sarilumab used to treat rheumatoid arthritis reduce bioavailability of statins (Table 6) [].
Despite the above findings, Rea et al.’s study demonstrated that statin discontinuation was associated with increased risk of hospital admissions []. Similarly, among patients with acute myocardial infarction that survived at least 1 year after the event, researchers found an increased risk of all-cause, CVD and non-CVD mortality with low statin adherence, suggesting an association between low-adherence and increased risk in the following years [].These findings underscore that maintaining high adherence to statin therapy is critical for reducing both cardiovascular events and mortality, and that even moderate lapses in adherence can significantly diminish the protective benefits of statins.
5.2. Hormones
While statins are generally safe and effective for lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), understanding how other hormones affect them is pivotal. In liver cells cholesterol can be excreted in the form of bile or can be stored as esters []. Cholesterol homeostasis within hepatocytes is subject to regulatory control by thyroid hormones, an effect mediated predominantly via thyroid hormone receptor-β (TRβ) signalling pathways []. Under normal conditions TSR-β lowers the level of cholesterol; however, dysregulation in thyroid hormone can have an adverse effect on LDL-C metabolism []. For instance, in hypothyroidism, lower levels of TSR-β will lead to higher levels of cholesterol and consequently patients would require higher statin doses to achieve effective lipid lowering. Conversely a meta-analysis showed that 55–60% of patients with untreated hyperthyroidism exhibited liver dysfunction due to high levels of thyroid hormone [,]. This dysfunction includes direct liver toxicity and hepatocyte anoxia due to the increased levels of thyroid hormone [,]. Since the liver is essential for statin metabolism via CYP450 enzymes, a decrease in the enzyme due to liver dysfunction will significantly reduce statin metabolism potentially increasing the risk of statin-related adverse effects [,].
Apart from thyroid hormones, research suggests that there are several other hormones that affect statin metabolism, one of which is corticosteroids. Corticosteroids, specifically glucocorticoids, have a significant impact on the liver function by causing liver enlargement, steatosis and glycogenesis. Additionally, high levels of intravenous corticosteroids, particularly methylprednisolone, have been associated with acute liver injury leading to acute liver failure. This impaired liver function caused due to corticosteroids can then affect the body’s ability to metabolize statins, leading to increased levels of statin in the bloodstream with further associated side effects [].
While certain hormones can affect statin metabolism, there is substantial research revolving around how statins themselves might influence the function of other hormones. Statins inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis, which may have a negative impact on gonadal steroidogenesis []. A prospective study conducted involved men with pre-existing T2D that were given high dosage of statins. The study revealed that high dosage of statin caused a decrease in androgen levels in the participants []. Subsequent investigations have identified an association between sustained statin administration and a diminution in total circulating testosterone concentrations in males, accompanied by concomitant reductions in sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) levels [,].
In addition to that, statins act on body’s hormonal balance in other different ways. Research shows that simvastatin and high doses of atorvastatin are significantly associated with impaired glucose metabolism leading to a potentially higher risk of developing T2D in patients, especially those with a family history of the disease [,]. In light of the well-documented pathophysiological association between polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance, an independent clinical investigation evaluated the therapeutic impact of concomitant statin and metformin administration in women with PCOS. The findings demonstrated that such combination therapy failed to elicit a meaningful enhancement in insulin sensitivity or a reduction in hyperandrogenic indices in the study cohort [,,]. Furthermore, the impact of statins on patients with existing type 1 diabetes remains a topic of ongoing research; their effectiveness and safety profile for T1D patients require further exploration using in-depth clinical trials.
5.3. Epigenetics
While this review discusses the biological aspect of statin therapy and the potential pleiotropic effects, in order to holistically evaluate statin utilization in patients, the interplay between social and biological mechanisms must also be highlighted. Ochoa-Rosalea et al. conducted 5 cohort studies to look at the epigenetic correlation between stain-usage and risk of T2D, and they found a downregulation of ABCG1 gene expression. ABCG1 plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels, hence its downregulation indicated to the researchers an increased risk of diabetes []. Furthermore, some genetic variants may allow statins to become less effective compared to their counterparts. Cano-Corres et al. observed 6 genetic variants effect on statin’s ability to reduce cholesterol levels in hyperlipidemic patients []. Among the 6 variants, the researcher observed that patients with variant HMGCR c.1564-106A > G showed the least reduction cholesterol with statin therapy, putting these patients at a disadvantage. Furthermore, Niemi et al. found when observing single nucleotide protein rs4149056 mutations, specifically found in a family of organic anion transporter family which encoded for hepatic organic anion transporter P1B1, that statins may induce downregulation, hence increasing the concentration of hydrophilic statins and plasma, and hence increasing the risk of SAMS [].
Another gene that has been the focus of research when investigating the pharmacogenetics of statins is the gene the encodes for the CYP450 family of proteins, as it is one of the main classes of proteins responsible for metabolizing statins. A mutation in CYP class of enzyme can lead to inhibited activity of drug, causing excess buildup of statins in plasma and increasing the risk of statin-induced side effects, like rhabdomyolysis. Preissner et al. identified 2000 mutations in the CYP gene, with single nucleotide protein mutations (SNP) having the most impact. The mutations in Caucasians was observed with other ethnicities to reveal 199 SNP mutations affecting this class of enzymes [], hence suggesting the prevalence of these mutations and their impact in effecting, predicting and allowing personalized treatment to patients under statin care. Mulder et al. found that homozygous carriers of CYP2D6 gene were prone to withdrawing from statin treatment due to rhabdomyolysis [,]. CYP3A5 is another enzyme in the class of CYP enzymes that are involved in the hepatic metabolization of statins. Individuals with an CYP3A5 * 1 allele require higher dosages of lipophilic statins to achieve the same therapeutic outcome compared to other individuals with different alleles for the same enzyme []. Such studies demonstrate how genetic variations play a significant role in understanding statins effect on patients.
5.4. Socioeconomic
There have been a number of studies that investigate the correlation between socioeconomic status (SES), disparity and statin therapy, with many postulating that a lower SES disposes the patient to lower statin adherence, and hence statin benefits. Erickson et al. investigated statin adherence and accessibility to pharmacies in Michigan and found that adherence to statin prescription was lower for patients residing in lower income areas []. A study that investigated the correlation of socioeconomic disparity and statin adherence in preventing premature CVD in Hungary found that individuals from a lower tax bracket were less likely to receive prescriptions for preventive statin therapy against CVD []. Thomsen et al. found that patients in the retired workers group, when compared to the top managers group, showed lower rates of statin utilization []. Socioeconomic background of a patient undertaking statin therapy is significant in determining the success of the therapy. Patients that come from a lower socioeconomic bracket may have difficulty adhering to statin therapy, as seen in these studies, due to multifarious reasons, such as inability to afford medication and other priorities in life interfering in taking the medication. Patients being informed on the significance of undertaking statins or their role in their disease management is another essential factor to ensuring that statin adherence is high and accurate. However, often times, patients from a lower SES background do not have adequate literacy to support their therapy. Furthermore, access to healthcare can also determine the efficacy of statins. Patients from a lower SES background, when compared to their counterparts, have harder times accessing adequate healthcare, which can lead to delays in adjusting statin medications (if needed), regular checkups, and more. Lastly, lifestyle differences in individuals in these varying socioeconomic brackets also affect the efficacy of statins. If an individual is following a relatively healthy lifestyle, compared to a relatively morbid lifestyle, the efficacy of statins will be greater in an individual with a healthy lifestyle. The compliance to a drug being low, administration not meeting the set guidelines, and morbid lifestyle modifications due to socioeconomic disparity is another point for clinical practitioners to consider, as the reduction in statin potential may not be due to the drug itself but due to other systematic factors.
6. Conclusions
The anti-inflammatory pleiotropy of statins, historically viewed as a subordinate corollary to their lipid-lowering action, is now assuming the contours of a distinct therapeutic paradigm. By engaging and modulating cardinal molecular circuits—most notably NF-κB, the NLRP3 inflammasome, MAPK cascades, and T-cell lineage specification—statins orchestrate a concerted suppression of pro-inflammatory signalling that traverses the domains of metabolic dysregulation, vascular pathology, and oncogenesis. Such mechanistic breadth, supported by an ever-expanding corpus of preclinical and clinical evidence, compels a reappraisal of statins as immunomodulatory pharmacophores with a therapeutic ambit that transcends their canonical cardiovascular remit.
In an era increasingly defined by polypharmacy, particularly within the management of multimorbid states such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, statins occupy a uniquely advantageous position. Their molecular promiscuity, when judiciously harnessed, permits the attenuation of inflammatory crosstalk that often underlies treatment resistance or drug–drug antagonism. Indeed, their combinatorial deployment alongside nutraceuticals (e.g., oleocanthal, curcumin), anti-cytokine biologics, or cytotoxic chemotherapeutics offers a tantalizing prospect of synergistic immunomodulation coupled with the potential rational de-escalation of toxic drug burdens. The immunomodulatory potential of statins, manifested through their ability to remodel the TME and recalibrate immune effector cell phenotypes, augments their strategic value as co-adjuvants to immune checkpoint blockade or precision-targeted small-molecule therapeutics, especially in neoplastic settings wherein inflammation-driven oncogenic progression constitutes a major impediment to sustained therapeutic efficacy.
The future trajectory of statin research must therefore be anchored in pharmacogenomic stratification to delineate responder phenotypes, unravel inter-individual variability in pleiotropic efficacy, and inform the construction of precision-based combination regimens. Parallel advances in medicinal chemistry could yield second-generation statin derivatives, explicitly optimized for anti-inflammatory potency and minimal diabetogenic risk. Equally, systems biology approaches integrating transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data will be indispensable in deconvoluting the statin interactome and predicting optimal polypharmacological synergies.
In its broader implications, the evolving narrative of statins underscores a paradigm shift in drug discovery: a recognition that established agents, when interrogated through the lens of network pharmacology, can transcend their original indication to reshape therapeutic landscapes. As chronic inflammation emerges as the cardinal nexus linking cardiometabolic disease, neurodegeneration, and cancer, statins are poised not merely to persist as lipid-centric prophylactics but to assume the mantle of cornerstone modulators within an integrated, multi-targeted therapeutic armamentarium.
7. Future Perspectives
The pleiotropic nature of statins, while mechanistically compelling, still demands rigorous clinical translation. Large-scale, genotype-stratified trials that simultaneously capture lipidomic, metabolomic and single-cell transcriptomic outputs are essential to identify the molecular “responders” who derive maximal anti-inflammatory benefit, and to parse out those at highest risk for diabetogenic or myopathic complications. Deep-phenotyping approaches that integrate Mendelian randomisation with multi-omic read-outs should clarify whether on-target (HMGCR-dependent) or off-target pathways, such as TLR4/MyD88, NLRP3 or PAR-2, drive the clinically relevant immunomodulation seen in disparate diseases.
Network pharmacology increasingly reveals that chronic diseases cluster around shared inflammatory hubs [], repositioning statins within poly-drug regimens that deliberately converge on these hubs could reduce overall pill burden and limit cumulative toxicity. Proof-of-concept studies are already pairing statins with SGLT-2 inhibitors to blunt NLRP3 activity in diabetic kidney disease, and with low-dose colchicine to extinguish residual IL-1β signalling after acute coronary events. The sequence, dose-intensity and relative timing of such combinations will require adaptive platform trials that use early changes in CRP, IL-6 or plaque 18F-FDG (Fluorodeoxyglucose) uptake as gate-keeping biomarkers instead of hard clinical end points.
Second-generation “inflammation-focused” statin analogues are another frontier. Scaffold remodelling aimed at maintaining HMG-CoA reductase affinity while selectively enhancing isoprenoid depletion in macrophages has yielded lead compounds that amplify Treg polarization and M2 macrophage switching without significantly perturbing skeletal muscle prenylation []. Coupling these analogues to hepatotropic or leukocyte-targeted nanoparticles may further increase therapeutic indices and allow inhaled, intra-articular, or tumour-localized delivery for COPD, osteoarthritis, or solid-tumour immunotherapy, respectively.
In oncology, the synergy between statins and immune-checkpoint inhibitors merits urgent exploration. Pre-clinical data show that cholesterol efflux driven by ABCA1 upregulation augments CD8+ T-cell metabolic fitness and enhances anti-PD-1 efficacy. Small basket trials that integrate high-dose rosuvastatin with PD-(L)1 blockade across inflamed tumours, such as microsatellite-instable colorectal, triple-negative breast, and smoking-related lung cancers, could establish whether statins can convert “immune-cold” lesions to “immune-hot” phenotypes and thereby rescue checkpoint resistance.
Beyond therapeutic development, implementation science must tackle the persistent adherence gap. Digital pill dispensers linked to cloud-based inflammatory dashboards, community pharmacist-led titration clinics, and culturally tailored education modules have all reduced statin discontinuation in pilot studies by up to 30%. Embedding such adherence–support systems in future efficacy trials would yield efficacy–effectiveness concordance data that are currently lacking in real-world cohorts.
Finally, the public health impact of statins in low- and middle-income countries remains under-realized. Cost-efficient fixed-dose combinations that marry generic statins to antihypertensives and nutraceutical antioxidants could generate synergistic anti-inflammatory effects while simplifying pharmacy logistics. Parallel capacity-building efforts should expand pharmacogenomic screening, particularly for SLCO1B15 alleles, in high-prevalence regions to reduce avoidable toxicity and improve trust in generic formulations. Collectively, these avenues herald a shift from cholesterol-centric usage towards a precise and inflammation-modifying paradigm that positions statins as foundational agents across cardiometabolic, rheumatologic, pulmonary, and neoplastic spectra.
Author Contributions
S.K.: Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Selection of articles for review, Figure conceptualization, and Data collation. B.H.: Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Selection of articles for review, Development of figures, and Literature synthesis. F.B.: Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Selection of articles for review, Preparation of graphical elements, and Figure legend drafting. R.P.: Writing—original draft, Supervision, Writing—review and editing, and Critical content validation. Y.B.: Conceptualization, Writing—review and editing, Scientific oversight, and Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work did not receive external funding for its conception, design, or authorship.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Office of the Dean of Research and Graduate Studies at Mohammed Bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences–Dubai Health (MBRU) for generously covering the article processing charges. Y.B. extends heartfelt gratitude to Aida Azar and Tom Looney, coordinators of the Student Research Project course within the MD programme at Mohammed Bin Rashid University for Medicine and Health Sciences—Dubai Health (MBRU), for their exemplary academic stewardship and commitment to fostering a culture of scholarly inquiry among medical students. Their unwavering support and mentorship created an enabling framework through which B.H. and F.B. were able to engage in the critical analysis of literature and conceptual development that underpin this review. This manuscript, in part, reflects the fruits of MBRU’s sustained commitment to cultivating early research competencies and intellectual curiosity among its students, translating structured academic exercises into a meaningful scholarly contribution. The collaborative ethos of the Student Research Project course has thus served as a cornerstone for the conceptual and analytical depth of this review.
Conflicts of Interest
Y.B. received research support from Pfizer, Amgen and BlueNotes Global. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Randomised trial of cholestesrol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: The Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 1994, 344, 1383–1389.
- Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 360, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Moye, L.A.; Rouleau, J.L.; Rutherford, J.D.; Cole, T.G.; Brown, L.; Warnica, J.W.; Arnold, J.M.; Wun, C.C.; et al. The effect of pravastatin on coronary events after myocardial infarction in patients with average cholesterol levels. Cholesterol and Recurrent Events Trial investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIPID Study Group. Long-term effectiveness and safety of pravastatin in 9014 patients with coronary heart disease and average cholesterol concentrations: The LIPID trial follow-up. Lancet 2002, 359, 1379–1387, Erratum in Lancet 2002, 360, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, C.M.; Pride, Y.B.; Hochberg, C.P.; Sloan, S.; Sabatine, M.S.; Cannon, C.P.; Group, T.S. Effect of intensive statin therapy on clinical outcomes among patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndrome. PCI-PROVE IT: A PROVE IT-TIMI 22 (Pravastatin or Atorvastatin Evaluation and Infection Therapy-Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction 22) Substudy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2290–2295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Danielson, E.; Fonseca, F.A.; Genest, J.; Gotto, A.M., Jr.; Kastelein, J.J.; Koenig, W.; Libby, P.; Lorenzatti, A.J.; MacFadyen, J.G.; et al. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J. The West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study: A trial of cholesterol reduction in Scottish men. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995, 76, 113C–117C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjekshus, J.; Apetrei, E.; Barrios, V.; Bohm, M.; Cleland, J.G.; Cornel, J.H.; Dunselman, P.; Fonseca, C.; Goudev, A.; Grande, P.; et al. Rosuvastatin in older patients with systolic heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2248–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sever, P.S.; Dahlof, B.; Poulter, N.R.; Wedel, H.; Beevers, G.; Caulfield, M.; Collins, R.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Kristinsson, A.; McInnes, G.T.; et al. Prevention of coronary and stroke events with atorvastatin in hypertensive patients who have average or lower-than-average cholesterol concentrations, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial–Lipid Lowering Arm (ASCOT-LLA): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Lietzau, G.; Sienkiewicz, W.; Karwacki, Z.; Dziewiatkowski, J.; Kaleczyc, J.; Kowianski, P. The Effect of Simvastatin on the Dynamics of NF-kappaB-Regulated Neurodegenerative and Neuroprotective Processes in the Acute Phase of Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 4935–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, E.; Broncel, M.; Niedzielski, M.; Wozniak, A.; Gorzelak-Pabis, P. The effect of lipid-lowering therapies on the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory properties of vascular endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, I.; Oz, F.; Arkaya, S.C.; Altun, I.; Bilge, A.K.; Umman, B.; Turkoglu, U.M. Effect of statins on endothelial function in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A prospective study using adhesion molecules and flow-mediated dilatation. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2014, 6, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels da Silva, D.; Langer, H.; Graf, T. Inflammatory and Molecular Pathways in Heart Failure-Ischemia, HFpEF and Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Hu, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, G.; Hong, Z.; Ren, J.; Lab for Trauma and Surgical Infections; Surgical, I. Mitochondrial DNA in liver inflammation and oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2019, 236, 116464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, J.; Abreu, M.T. The Microbiota and the Immune Response: What Is the Chicken and What Is the Egg? Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Deng, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Tan, X.; Cao, G. Cancer Evo-Dev: A Theory of Inflammation-Induced Oncogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 768098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkiz, H.; Simsek, H.; Balci, D.; Ulger, Y.; Onan, E.; Akcaer, N.; Delik, A. Inflammation and cancer: Molecular mechanisms and clinical consequences. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1564572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Y. Impact of statin use on cancer-specific mortality and recurrence: A meta-analysis of 60 observational studies. Medicine 2020, 99, e19596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, M.Y.; Fan, C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.F. Unraveling the Anticancer Potential of Statins: Mechanisms and Clinical Significance. Cancers 2023, 15, 4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatiwada, N.; Hong, Z. Potential Benefits and Risks Associated with the Use of Statins. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, F.; Ray, K.K.; Wiklund, O.; Corsini, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Bruckert, E.; De Backer, G.; Hegele, R.A.; Hovingh, G.K.; Jacobson, T.A.; et al. Adverse effects of statin therapy: Perception vs. the evidence—Focus on glucose homeostasis, cognitive, renal and hepatic function, haemorrhagic stroke and cataract. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2526–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; de Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, e1082–e1143. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, F.C.; Huffman, M.; Ebrahim, S. Statin therapy for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. JAMA 2013, 310, 2451–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, R.; Cantor, A.; Dana, T.; Wagner, J.; Ahmed, A.Y.; Fu, R.; Ferencik, M. Statin Use for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2022, 328, 754–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, B.S.; Saseen, J.J.; Page, R.L., 2nd; Reed, B.N.; Sneed, K.; Kostis, J.B.; Lanfear, D.; Virani, S.; Morris, P.B.; American Heart Association Clinical Pharmacology Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology. Recommendations for Management of Clinically Significant Drug-Drug Interactions with Statins and Select Agents Used in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, e468–e495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.B.; Preiss, D.; Tobert, J.A.; Jacobson, T.A.; Page, R.L., 2nd; Goldstein, L.B.; Chin, C.; Tannock, L.R.; Miller, M.; Raghuveer, G.; et al. Statin Safety and Associated Adverse Events: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e38–e81, Correction in Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Maideen, N.M.P. HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) and their Drug Interactions Involving CYP Enzymes, P-glycoprotein and OATP Transporters-An Overview. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 328–341. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, T.; Fujita, Y.; Ieiri, I. An updated review of pharmacokinetic drug interactions and pharmacogenetics of statins. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasim, R.; Ansari, T.M.; Ahsan, F.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Singh, A.; Shariq, M.; Parveen, S. Pleiotropic Benefits of Statins in Cardiovascular Diseases. Drug Res. 2022, 72, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, D.; Hegarty, B.; Bossard, P.; Ferre, P.; Foufelle, F. SREBP transcription factors: Master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie 2004, 86, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daemen, S.; Kutmon, M.; Evelo, C.T. A pathway approach to investigate the function and regulation of SREBPs. Genes Nutr. 2013, 8, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S.; Kodaka, M.; Kikuchi, A.; Matsunaga, Y.; Shoji, K.; Kuan, Y.C.; Iwase, M.; Takeda, K.; Katsuta, R.; Ishigami, K.; et al. Sulforaphane suppresses the activity of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) by promoting SREBP precursor degradation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.L.; Shiu, S.W.; Cheung, C.L.; Yu-Hung Leung, A.; Tan, K.C. Effects of statins on the inducible degrader of low-density lipoprotein receptor in familial hypercholesterolemia. Endocr. Connect. 2022, 11, e220019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wu, M.; Li, H.; Kraemer, F.B.; Adeli, K.; Seidah, N.G.; Park, S.W.; Liu, J. Strong induction of PCSK9 gene expression through HNF1alpha and SREBP2: Mechanism for the resistance to LDL-cholesterol lowering effect of statins in dyslipidemic hamsters. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagace, T.A. PCSK9 and LDLR degradation: Regulatory mechanisms in circulation and in cells. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2014, 25, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Tsubakio-Yamamoto, K.; Ohama, T.; Nakagawa-Toyama, Y.; Nishida, M. Molecular mechanisms of HDL-cholesterol elevation by statins and its effects on HDL functions. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colhoun, H.M.; Betteridge, D.J.; Durrington, P.N.; Hitman, G.A.; Neil, H.A.; Livingstone, S.J.; Thomason, M.J.; Mackness, M.I.; Charlton-Menys, V.; Fuller, J.H.; et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with atorvastatin in type 2 diabetes in the Collaborative Atorvastatin Diabetes Study (CARDS): Multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 364, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, J.A.; Gotto, A.M., Jr. The Heart Protection Study: Expanding the boundaries for high-risk coronary disease prevention. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 92, 3i–9i. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, J.R.; Clearfield, M.; Weis, S.; Whitney, E.; Shapiro, D.R.; Beere, P.A.; Langendorfer, A.; Stein, E.A.; Kruyer, W.; Gotto, A.M., Jr. Primary prevention of acute coronary events with lovastatin in men and women with average cholesterol levels: Results of AFCAPS/TexCAPS. Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study. JAMA 1998, 279, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerli, A.W.; Aronow, H.D.; Sprecher, D.L. The Lescol Intervention Prevention Study (LIPS): Start all patients on statins early after PCI. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2003, 70, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.; Shao, L.; Tomlinson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.M. An evaluation of pitavastatin for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.P.; Alaeiilkhchi, N.; Wright, J.M. Pitavastatin for lowering lipids. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, CD012735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Mizuma, H.; Kuwabara, Y.; Sato, Y.; Shindo, S.; Kotooka, N.; Fujimatsu, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Inoue, T.; Node, K.; et al. Effects of pitavastatin in Japanese patients with chronic heart failure: The Pitavastatin Heart Failure Study (PEARL Study). Circ. J. 2013, 77, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiro, T.; Kimura, T.; Morimoto, T.; Miyauchi, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Yamagishi, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Kimura, K.; Saito, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; et al. Effect of intensive statin therapy on regression of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A multicenter randomized trial evaluated by volumetric intravascular ultrasound using pitavastatin versus atorvastatin (JAPAN-ACS [Japan assessment of pitavastatin and atorvastatin in acute coronary syndrome] study). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak, R.C.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Bairey-Merz, C.N.; Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Lenfant, C.; American College of Cardiology; American Heart Association; National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. ACC/AHA/NHLBI Clinical Advisory on the Use and Safety of Statins. Stroke 2002, 33, 2337–2341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeiser, R. Immune modulatory effects of statins. Immunology 2018, 154, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeganeh, B.; Wiechec, E.; Ande, S.R.; Sharma, P.; Moghadam, A.R.; Post, M.; Freed, D.H.; Hashemi, M.; Shojaei, S.; Zeki, A.A.; et al. Targeting the mevalonate cascade as a new therapeutic approach in heart disease, cancer and pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefieva, T.I.; Filatova, A.Y.; Potekhina, A.V.; Shchinova, A.M. Immunotropic Effects and Proposed Mechanism of Action for 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A Reductase Inhibitors (Statins). Biochemistry 2018, 83, 874–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Xiang, X.D.; Sun, F.; Xiao, B.W.; Yan, M.Y.; Peng, B.; Liu, D. Simvastatin Reduces NETosis to Attenuate Severe Asthma by Inhibiting PAD4 Expression. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2023, 2023, 1493684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Cho, J.H.; Jeong, A.R.; Kim, E.J.; Park, D.K.; Kwon, K.A.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of simvastatin in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-induced small bowel injury. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, N.N.; Lingaraju, M.C.; Balaganur, V.; Kant, V.; More, A.S.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, D.; Tandan, S.K. Anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects of atorvastatin in a cartilage explant model of osteoarthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Ning, Z.; Li, Z. The beneficial effects of Rosuvastatin in inhibiting inflammation in sepsis. Aging 2024, 16, 10424–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.K.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, E.K.; Park, D.K.; Kwon, K.A.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, K.O.; Kim, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of rosuvastatin by regulation of oxidative stress in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis model. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4559–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Du, H.P.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.L.; You, S.J.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Cao, Y.J.; Liu, C.F.; et al. Statins upregulate cystathionine gamma-lyase transcription and H2S generation via activating Akt signaling in macrophage. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 87, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Ni, Z.; Qian, J.; Tomino, Y. Pravastatin inhibits carboxymethyllysine-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 expression in podocytes via prevention of signalling events. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2007, 106, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Z.; Sun, J.; Han, J.J.; Qian, Z.J. Anti-inflammation of simvastatin by polarization of murine macrophages from M1 phenotype to M2 phenotype. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2013, 93, 2071–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, S.; Nakamura, H.; Seki, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Furuuchi, M.; Nakajima, T.; Tsujimura, S.; Shirahata, T.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Reversal of elastase-induced pulmonary emphysema and promotion of alveolar epithelial cell proliferation by simvastatin in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L882–L890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.; Shen, L.H.; Hu, L.H.; Pu, J.; Jing, Q.; He, B. Atorvastatin suppresses inflammatory response induced by oxLDL through inhibition of ERK phosphorylation, IkappaBalpha degradation, and COX-2 expression in murine macrophages. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhova, G.K.; Williams, J.K.; Libby, P. Statins reduce inflammation in atheroma of nonhuman primates independent of effects on serum cholesterol. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.J.; Prowell, T.M.; Blackford, A.L.; Byrne, C.; Khouri, N.F.; Slater, S.A.; Jeter, S.C.; Armstrong, D.K.; Davidson, N.E.; Emens, L.A.; et al. A short-term biomarker modulation study of simvastatin in women at increased risk of a new breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 131, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, S.; Schwartz, E.J.; Jensen, K.; Lipson, J.; Alli, E.; McPherson, L.; Fernandez, A.M.; Sharma, V.B.; Staton, A.; Mills, M.A.; et al. A clinical trial of lovastatin for modification of biomarkers associated with breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 142, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Linden, K.G.; Leachman, S.A.; Zager, J.S.; Jakowatz, J.G.; Viner, J.L.; McLaren, C.E.; Barr, R.J.; Carpenter, P.M.; Chen, W.P.; Elmets, C.A.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II clinical trial of lovastatin for various endpoints of melanoma pathobiology. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukamm, A.; Hoiseth, A.D.; Einvik, G.; Lehmann, S.; Hagve, T.A.; Soyseth, V.; Omland, T. Rosuvastatin treatment in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (RODEO): A randomized controlled trial. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kater, A.L.; Batista, M.C.; Ferreira, S.R. Synergistic effect of simvastatin and ezetimibe on lipid and pro-inflammatory profiles in pre-diabetic subjects. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2010, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaro, A.E.; Serrano, C.V., Jr.; Katz, M.; Marti, L.; Fernandes, J.L.; Parra, P.R.; Campos, A.H. Increasing doses of simvastatin versus combined ezetimibe/simvastatin: Effect on circulating endothelial progenitor cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 18, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Pereira, E.N.G.; Franco, R.L.C.; Santos, R.; Daliry, A. Statins and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A concise review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 183, 117805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappegard, K.T.; Pop-Purceleanu, M.; van Heerde, W.; Sexton, J.; Tendolkar, I.; Pop, G. Improved neurocognitive functions correlate with reduced inflammatory burden in atrial fibrillation patients treated with intensive cholesterol lowering therapy. J. Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, N.C.; Watts, G.F.; Eckel, R.H. Statin Toxicity. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 328–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methe, H.; Kim, J.O.; Kofler, S.; Nabauer, M.; Weis, M. Statins decrease Toll-like receptor 4 expression and downstream signaling in human CD14+ monocytes. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.L.; Hsiao, F.Y.; Dong, Y.H.; Shen, L.J.; Wu, F.L. Statins and the risk of liver injury: A population-based case-control study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2014, 23, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbs, S.; Beck, E.B.; Linke, A.; Adams, V.; Gielen, S.; Krankel, N.; Mobius-Winkler, S.; Hollriegel, R.; Thiele, H.; Hambrecht, R.; et al. High-dose rosuvastatin in chronic heart failure promotes vasculogenesis, corrects endothelial function, and improves cardiac remodeling–results from a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 146, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grip, O.; Janciauskiene, S. Atorvastatin reduces plasma levels of chemokine (CXCL10) in patients with Crohn’s disease. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Interplay of Cholesterol and Actin in Neurotransmitter GPCR Signaling: Insights from Chronic Cholesterol Depletion Using Statin. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 3855–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, R.H.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Fish, B.; Dowdy, A.; Twaddell, B.; Nguyen, T.; Paramsothy, P. The SLIM Study: Slo-Niacin(R) and Atorvastatin Treatment of Lipoproteins and Inflammatory Markers in Combined Hyperlipidemia. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2009, 3, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ljung, R.; Koster, M.; Bjorkenstam, E.; Salmi, P. Associations between statin use and suicidality, depression, anxiety, and seizures. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abulhul, E.; McDonald, K.; Martos, R.; Phelan, D.; Spiers, J.P.; Hennessy, M.; Baugh, J.; Watson, C.; O’Loughlin, C.; Ledwidge, M. Long-term statin therapy in patients with systolic heart failure and normal cholesterol: Effects on elevated serum markers of collagen turnover, inflammation, and B-type natriuretic peptide. Clin. Ther. 2012, 34, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka-Dabrowa, A.; Goch, J.H.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Rysz, J.; Maciejewski, M.; Banach, M. The influence of atorvastatin on parameters of inflammation and function of the left ventricle in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, MS12–MS23. [Google Scholar]
- Sposito, A.C.; Santos, S.N.; de Faria, E.C.; Abdalla, D.S.; da Silva, L.P.; Soares, A.A.; Japiassu, A.V.; Quinaglia e Silva, J.C.; Ramires, J.A.; Coelho, O.R. Timing and dose of statin therapy define its impact on inflammatory and endothelial responses during myocardial infarction. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T.; Naruse, K.; Arakawa, T.; Nakao, M.; Yokoi, K.; Oguri, M.; Marui, N.; Amano, T.; Ichimiya, S.; Ohashi, T.; et al. Impact of pitavastatin on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and adiponectin in hypercholesterolemic patients with the metabolic syndrome: The PREMIUM Study. J. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puurunen, J.; Piltonen, T.; Puukka, K.; Ruokonen, A.; Savolainen, M.J.; Bloigu, R.; Morin-Papunen, L.; Tapanainen, J.S. Statin therapy worsens insulin sensitivity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4798–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena-Evangelista, K.C.; Pedrosa, L.F.; Paiva, M.S.; Dias, P.C.; Ferreira, D.Q.; Cozzolino, S.M.; Faulin, T.E.; Abdalla, D.S. The hypolipidemic and pleiotropic effects of rosuvastatin are not enhanced by its association with zinc and selenium supplementation in coronary artery disease patients: A double blind randomized controlled study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Inciardi, R.M.; Rossi, A.; Temporelli, P.L.; Lucci, D.; Gonzini, L.; Marchioli, R.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Tavazzi, L.; Investigators, G.-H. Prognostic effects of rosuvastatin in patients with co-existing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic heart failure: A sub-analysis of GISSI-HF trial. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 44, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles-Schoeman, C.; Khanna, D.; Furst, D.E.; McMahon, M.; Reddy, S.T.; Fogelman, A.M.; Paulus, H.E.; Park, G.S.; Gong, T.; Ansell, B.J. Effects of high-dose atorvastatin on antiinflammatory properties of high density lipoprotein in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot study. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.J.; Tseng, Y.F.; Yen, C.H.; Lin, P.T. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation (300 mg/day) on antioxidation and anti-inflammation in coronary artery disease patients during statins therapy: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Chalmers, J.D.; Graham, C.; Harley, C.; Sidhu, M.K.; Doherty, C.; Govan, J.W.; Sethi, T.; Davidson, D.J.; Rossi, A.G.; et al. Atorvastatin as a stable treatment in bronchiectasis: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyeux-Faure, M.; Tamisier, R.; Baguet, J.P.; Dias-Domingos, S.; Perrig, S.; Leftheriotis, G.; Janssens, J.P.; Trzepizur, W.; Launois, S.H.; Stanke-Labesque, F.; et al. Response to statin therapy in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 423120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, M.E.; Cockcroft, J.R.; McKeever, T.M.; Coward, W.R.; Shale, D.J.; Johnson, S.R.; Thornton, J.G.; Harrison, T.W.; Knox, A.J.; Bolton, C.E. Cardiovascular and inflammatory effects of simvastatin therapy in patients with COPD: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2015, 10, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vincenzi, B.; Stock, S.; Borba, C.P.; Cleary, S.M.; Oppenheim, C.E.; Petruzzi, L.J.; Fan, X.; Copeland, P.M.; Freudenreich, O.; Cather, C.; et al. A randomized placebo-controlled pilot study of pravastatin as an adjunctive therapy in schizophrenia patients: Effect on inflammation, psychopathology, cognition and lipid metabolism. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 159, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.L.; Bedient, T.J.; Kozlowski, J.; Rosenbluth, D.B.; Isakow, W.; Ferkol, T.W.; Thomas, B.; Mintun, M.A.; Schuster, D.P.; Walter, M.J. [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for lung antiinflammatory response evaluation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.; Shukrullah, I.; Veledar, E.; Bloom, H.L.; Jones, D.P.; Dudley, S.C. Statin therapy for the prevention of atrial fibrillation trial (SToP AF trial). J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2011, 22, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, R.L.; Brown, J.; Buck, S.; Redline, W.; Doyle, J.; Plutzky, J.; Creager, M.A. Association of monocyte tumor necrosis factor alpha expression and serum inflammatory biomarkers with walking impairment in peripheral artery disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 61, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.Y.; Howarth, S.P.; Miller, S.R.; Graves, M.J.; Patterson, A.J.; U-King-Im, J.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Walsh, S.R.; Brown, A.P.; Kirkpatrick, P.J.; et al. The ATHEROMA (Atorvastatin Therapy: Effects on Reduction of Macrophage Activity) Study. Evaluation using ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in carotid disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Os, H.A.; Rollefstad, S.; Gerdts, E.; Kringeland, E.; Ikdahl, E.; Semb, A.G.; Midtbo, H. Preclinical cardiac organ damage during statin treatment in patients with inflammatory joint diseases: The RORA-AS statin intervention study. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3700–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svanteson, M.; Rollefstad, S.; Klow, N.E.; Hisdal, J.; Ikdahl, E.; Semb, A.G.; Haig, Y. Associations between coronary and carotid artery atherosclerosis in patients with inflammatory joint diseases. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikdahl, E.; Rollefstad, S.; Hisdal, J.; Olsen, I.C.; Pedersen, T.R.; Kvien, T.K.; Semb, A.G. Sustained Improvement of Arterial Stiffness and Blood Pressure after Long-Term Rosuvastatin Treatment in Patients with Inflammatory Joint Diseases: Results from the RORA-AS Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikdahl, E.; Hisdal, J.; Rollefstad, S.; Olsen, I.C.; Kvien, T.K.; Pedersen, T.R.; Semb, A.G. Rosuvastatin improves endothelial function in patients with inflammatory joint diseases, longitudinal associations with atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis: Results from the RORA-AS statin intervention study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollefstad, S.; Ikdahl, E.; Hisdal, J.; Olsen, I.C.; Holme, I.; Hammer, H.B.; Smerud, K.T.; Kitas, G.D.; Pedersen, T.R.; Kvien, T.K.; et al. Rosuvastatin-Induced Carotid Plaque Regression in Patients with Inflammatory Joint Diseases: The Rosuvastatin in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis and Other Inflammatory Joint Diseases Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1718–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatelli, P.; Carnevale, R.; Pastori, D.; Cangemi, R.; Napoleone, L.; Bartimoccia, S.; Nocella, C.; Basili, S.; Violi, F. Immediate antioxidant and antiplatelet effect of atorvastatin via inhibition of Nox2. Circulation 2012, 126, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, N.; Kai, H.; Yamagishi, S.; Mizoguchi, M.; Nakaura, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Kaida, H.; Baba, K.; Hayabuchi, N.; Imaizumi, T. Vascular inflammation evaluated by [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography is associated with the metabolic syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, N.; Kai, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakaura, H.; Kaida, H.; Baba, K.; Hayabuchi, N.; Imaizumi, T. Simvastatin attenuates plaque inflammation: Evaluation by fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, H.; Vucic, E.; Subramanian, S.; Abdelbaky, A.; Fayad, Z.A.; Du, S.; Roth, E.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Mohler, E.R.; Farkouh, M.E.; et al. The effect of BMS-582949, a P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (P38 MAPK) inhibitor on arterial inflammation: A multicenter FDG-PET trial. Atherosclerosis 2015, 240, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Agarwal, V.; Baronia, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Poddar, B.; Azim, A. The Effects of Atorvastatin on Inflammatory Responses and Mortality in Septic Shock: A Single-center, Randomized Controlled Trial. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 21, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute ARDS Clinical Trials Network; Truwit, J.D.; Bernard, G.R.; Steingrub, J.; Matthay, M.A.; Liu, K.D.; Albertson, T.E.; Brower, R.G.; Shanholtz, C.; Rock, P.; et al. Rosuvastatin for sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Needham, D.M.; Colantuoni, E.; Dinglas, V.D.; Hough, C.L.; Wozniak, A.W.; Jackson, J.C.; Morris, P.E.; Mendez-Tellez, P.A.; Ely, E.W.; Hopkins, R.O. Rosuvastatin versus placebo for delirium in intensive care and subsequent cognitive impairment in patients with sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: An ancillary study to a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinglas, V.D.; Hopkins, R.O.; Wozniak, A.W.; Hough, C.L.; Morris, P.E.; Jackson, J.C.; Mendez-Tellez, P.A.; Bienvenu, O.J.; Ely, E.W.; Colantuoni, E.; et al. One-year outcomes of rosuvastatin versus placebo in sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: Prospective follow-up of SAILS randomised trial. Thorax 2016, 71, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Y.; Ge, Z.Z.; Xiang, J.; Gao, Y.X.; Lu, X.; Walline, J.H.; Qin, M.B.; Zhu, H.D.; Li, Y. Is rosuvastatin protective against sepsis-associated encephalopathy? A secondary analysis of the SAILS trial. World J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 13, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, C.; Kuypers, F.; Larkin, S.; Hagar, W.; Vichinsky, E.; Styles, L. A pilot study of the short-term use of simvastatin in sickle cell disease: Effects on markers of vascular dysfunction. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 153, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braganza, G.; Chaudhuri, R.; McSharry, C.; Weir, C.J.; Donnelly, I.; Jolly, L.; Lafferty, J.; Lloyd, S.M.; Spears, M.; Mair, F.; et al. Effects of short-term treatment with atorvastatin in smokers with asthma—A randomized controlled trial. BMC Pulm. Med. 2011, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, P.; Chalmers, J.D.; Graham, C.; Clarke, A.; Donaldson, S.; Doherty, C.; Govan, J.R.W.; Davidson, D.J.; Rossi, A.G.; Hill, A.T. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Atorvastatin in Patients with Bronchiectasis Infected With Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: A Proof of Concept Study. Chest 2017, 152, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, G.P.; Choudhary, N.; Bravo-Jaimes, K.; Smotherman, C.; Sherazi, S.; Kraemer, D.F. Effect of atorvastatin on lipogenic, inflammatory and thrombogenic markers in women with the metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnino, M.W.; Cocchi, M.N.; Salciccioli, J.D.; Kim, D.; Naini, A.B.; Buettner, C.; Akuthota, P. Coenzyme Q10 levels are low and may be associated with the inflammatory cascade in septic shock. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, A.R.; Szymonifka, J.D.; Rondina, M.T.; Bogardus, M.; Scott, M.G.; Woller, S.C.; Stevens, S.M.; Eby, C.; Merritt, K.; Valle, A.G.D.; et al. Postoperative Myocardial Injury and Inflammation Is Not Blunted by a Trial of Atorvastatin in Orthopedic Surgery Patients. HSS J. 2018, 14, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gautam, S.; Desai, M.; Steen, H.; Warren, W.P.; Xavier, S.S.; Lima, J.A. Aortic plaque regression as determined by magnetic resonance imaging with high-dose and low-dose statin therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 9, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.; Lu, M.T.; Ihenachor, E.J.; Wei, J.; Looby, S.E.; Fitch, K.V.; Oh, J.; Zimmerman, C.O.; Hwang, J.; Abbara, S.; et al. Effects of statin therapy on coronary artery plaque volume and high-risk plaque morphology in HIV-infected patients with subclinical atherosclerosis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet HIV 2015, 2, e52–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- deFilippi, C.; Christenson, R.; Joyce, J.; Park, E.A.; Wu, A.; Fitch, K.V.; Looby, S.E.; Lu, M.T.; Hoffmann, U.; Grinspoon, S.K.; et al. Brief Report: Statin Effects on Myocardial Fibrosis Markers in People Living with HIV. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2018, 78, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, A.S.; Vengrenyuk, Y.; Shameer, K.; Maehara, A.; Purushothaman, M.; Yoshimura, T.; Matsumura, M.; Aquino, M.; Haider, N.; Johnson, K.W.; et al. Intracoronary Imaging, Cholesterol Efflux, and Transcriptomes After Intensive Statin Treatment: The YELLOW II Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilipovitz, D.T.; Bryson, G.L.; Taljaard, M. STAR VaS–Short Term Atorvastatin Regime for Vasculopathic Subjects: A randomized placebo-controlled trial evaluating perioperative atorvastatin therapy in noncardiac surgery. Can. J. Anaesth. 2012, 59, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovou, G.; Giannakopoulou, V.; Kalogeropoulos, P.; Anagnostopoulou, K.; Goumas, G.; Kazianis, G.; Limberi, S.; Perrea, D.; Mihas, C.; Kolovou, V.; et al. Hellenic Postprandial Lipemia Study (HPLS): Rationale and design of a prospective, open-label trial to determinate the prevalence of abnormal postprandial lipemia as well as its interaction with statins in patients at high- and very high-risk for cardiovascular disease. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2019, 82, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Negredo, E.; Jimenez, M.; Puig, J.; Loste, C.; Perez-Alvarez, N.; Urrea, V.; Echeverria, P.; Bonjoch, A.; Clotet, B.; Blanco, J.; et al. A randomized pilot trial to evaluate the benefit of the concomitant use of atorvastatin and Raltegravir on immunological markers in protease-inhibitor-treated subjects living with HIV. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negredo, E.; Estrada, V.; Domingo, P.; Gutierrez, M.D.; Mateo, G.M.; Puig, J.; Bonjoch, A.; Ornelas, A.; Echeverria, P.; Estany, C.; et al. Switching from a ritonavir-boosted PI to dolutegravir as an alternative strategy in virologically suppressed HIV-infected individuals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giorgi, R.; Quinton, A.M.G.; Waters, S.; Cowen, P.J.; Harmer, C.J. An experimental medicine study of the effects of simvastatin on emotional processing, reward learning, verbal memory, and inflammation in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.N.R.; Bittner, Z.A.; Shankar, S.; Liu, X.; Chang, T.H.; Jin, T.; Tapia-Abellan, A. Recent insights into the regulatory networks of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs248344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiler, S.; Winkels, H.; Kelm, M.; Gerdes, N. IL-1 family cytokines in cardiovascular disease. Cytokine 2019, 122, 154215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschermann, H.; Schuster, D.; Parviz, B.; Haberbosch, W.; Tillmanns, H.; Muth, H. Statins prevent NF-kappaB transactivation independently of the IKK-pathway in human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2006, 185, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousoulis, D.; Psarros, C.; Demosthenous, M.; Patel, R.; Antoniades, C.; Stefanadis, C. Innate and adaptive inflammation as a therapeutic target in vascular disease: The emerging role of statins. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koushki, K.; Shahbaz, S.K.; Mashayekhi, K.; Sadeghi, M.; Zayeri, Z.D.; Taba, M.Y.; Banach, M.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. Anti-inflammatory Action of Statins in Cardiovascular Disease: The Role of Inflammasome and Toll-Like Receptor Pathways. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 60, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Tsao, S.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Yang, A.J.; Huang, C.T.; Huang, K.C.; Lin, W.W. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors activate caspase-1 in human monocytes depending on ATP release and P2X7 activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, J.; Roy, P. Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in vascular diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 110241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck-Hansen, M.; Kassiteridi, C.; Monaco, C. Toll-like receptors in atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14008–14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannati, S.; Patel, A.; Patnaik, R.; Banerjee, Y. Oleocanthal as a Multifunctional Anti-Cancer Agent: Mechanistic Insights, Advanced Delivery Strategies, and Synergies for Precision Oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiak, A.; Brady, G. Bifurcation of signalling in human innate immune pathways to NF-kB and IRF family activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 205, 115246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortego, M.; Gomez-Hernandez, A.; Vidal, C.; Sanchez-Galan, E.; Blanco-Colio, L.M.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; Tunon, J.; Diaz, C.; Hernandez, G.; Egido, J. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors reduce I kappa B kinase activity induced by oxidative stress in monocytes and vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylonas, K.S.; Peroulis, M.; Schizas, D.; Kapelouzou, A. MYD88 and Proinflammatory Chemokines in Aortic Atheromatosis: Exploring Novel Statin Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, X.; Lei, T.; Zhang, K.; Lai, B.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, Y.; Mao, G.; Xiao, L.; Wang, N. Statins Attenuate Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome by Oxidized LDL or TNFalpha in Vascular Endothelial Cells through a PXR-Dependent Mechanism. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 92, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.K. Isoprenoids as mediators of the biological effects of statins. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadeghi, M.; Khayati, S.; Dehnavi, S.; Almahmeed, W.; Sukhorukovi, V.N.; Sahebkar, A. Regulatory impact of statins on macrophage polarization: Mechanistic and therapeutic implications. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2024, 76, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, S.; Iacobini, C.; Vitale, M.; Pugliese, G. The Inflammasome in Chronic Complications of Diabetes and Related Metabolic Disorders. Cells 2020, 9, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Alabdullah, M.; Grossmann, J.; Spieler, F.; Abdosh, R.; Lutz, V.; Kalies, K.; Knopp, K.; Rieckmann, M.; Koch, S.; et al. The differential statin effect on cytokine production of monocytes or macrophages is mediated by differential geranylgeranylation-dependent Rac1 activation. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordbar, M.; de Mutsert, R.; Cevval, M.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Jukema, J.W.; Lijfering, W.M. Differential effect of statin use on coagulation markers: An active comparative analysis in the NEO study. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lu, D.; Fan, M.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Sun, A.; et al. Rosuvastatin protects against coronary microembolization-induced cardiac injury via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Lei, S.Y.; Zhang, D.H.; He, Q.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Zhu, H.J.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, S.Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. The pleiotropic effects of statins: A comprehensive exploration of neurovascular unit modulation and blood-brain barrier protection. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.A.; Liao, J.K. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of statin pleiotropic effects. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1529–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.S.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pereira, A.P. Regulation of IL-6-type cytokine responses by MAPKs. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeldine, J.; Hampson, P.; Opoku, F.A.; Foster, M.; Lord, J.M. N-Formyl peptides drive mitochondrial damage associated molecular pattern induced neutrophil activation through ERK1/2 and P38 MAP kinase signalling pathways. Injury 2015, 46, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksbo, B.D.; Tamrakar, A.K.; Phulka, J.S.; Barra, N.G.; Schertzer, J.D. Statins activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and impair insulin signaling via p38 and mTOR. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E110–E116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogiatzi, G.; Oikonomou, E.; Siasos, G.; Tsalamandris, S.; Briasoulis, A.; Androulakis, E.; Latsios, G.; Papaioannou, S.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. Statins and inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 7027–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satny, M.; Hubacek, J.A.; Vrablik, M. Statins and Inflammation. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anannya, O.; Huang, W.; August, A. The kinase ITK controls a Ca2+-mediated switch that balances T(H)17 and T(reg) cell differentiation. Sci. Signal. 2024, 17, eadh2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, D.S.; Cattley, R.T.; Shipman, C.W.; Happe, C.; Lee, M.; Boggess, W.C.; MacDonald, M.L.; Hawse, W.F. Synergistic and additive interactions between receptor signaling networks drive the regulatory T cell versus T helper 17 cell fate choice. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Spolski, R.; Liao, W.; Leonard, W.J. Complex interactions of transcription factors in mediating cytokine biology in T cells. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 261, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gu, Y.; Dai, X.; Li, B. Transcriptional and posttranslational regulation of Th17/Treg balance in health and disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 2137–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wan, Y.Y. Intricacies of TGF-beta signaling in Treg and Th17 cell biology. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diller, M.L.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Delman, K.A.; Lawson, D.H.; Ford, M.L. Balancing Inflammation: The Link between Th17 and Regulatory T Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 6309219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, A.; Kuchroo, V.K. Th17 cells: From precursors to players in inflammation and infection. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Eizenberg-Magar, I.; Reich-Zeliger, S.; Rimer, J.; Zaretsky, I.; Reshef, D.; Kopitman, E.; Friedman, N.; Antebi, Y.E. Independent and temporally separated dynamics for RORgammat and Foxp3 during Th17 differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1462045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Menn, G.; Jablonska, A.; Chen, Z. The effects of post-translational modifications on Th17/Treg cell differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, E.; Leon, B.; Barber, D.F.; Jimenez-Baranda, S.; Goya, I.; Almonacid, L.; Marquez, G.; Zaballos, A.; Martinez, A.C.; Stein, J.V.; et al. Statins induce regulatory T cell recruitment via a CCL1 dependent pathway. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3524–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntolkeras, G.; Barba, C.; Mavropoulos, A.; Vasileiadis, G.K.; Dardiotis, E.; Sakkas, L.I.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; Bogdanos, D.P. On the immunoregulatory role of statins in multiple sclerosis: The effects on Th17 cells. Immunol. Res. 2019, 67, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivieri, C.; Baldari, C.T. Statins: From cholesterol-lowering drugs to novel immunomodulators for the treatment of Th17-mediated autoimmune diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 88, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, D.M.; Alon, R.; Ginsberg, M.H. Integrin modulation and signaling in leukocyte adhesion and migration. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 218, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, K.; Laudanna, C.; Cybulsky, M.I.; Nourshargh, S. Getting to the site of inflammation: The leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.A. How endothelial cells regulate transmigration of leukocytes in the inflammatory response. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnavi, S.; Sohrabi, N.; Sadeghi, M.; Lansberg, P.; Banach, M.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. Statins and autoimmunity: State-of-the-art. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 214, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C. Humoral Innate Immunity and Acute-Phase Proteins. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, A.S.; Ghoreschi, K. The Interleukin-1 Family. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 941, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pyrillou, K.; Burzynski, L.C.; Clarke, M.C.H. Alternative Pathways of IL-1 Activation, and Its Role in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 613170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.H.; Schroder, K. Inflammasome signaling and regulation of interleukin-1 family cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Overview of the IL-1 family in innate inflammation and acquired immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, M.; Aab, A.; Altunbulakli, C.; Azkur, K.; Costa, R.A.; Crameri, R.; Duan, S.; Eiwegger, T.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Ferstl, R.; et al. Interleukins (from IL-1 to IL-38), interferons, transforming growth factor beta, and TNF-alpha: Receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 984–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, F.; Torzewski, J.; Kamenz, J.; Veit, K.; Hombach, V.; Dedio, J.; Ivashchenko, Y. Interleukin-1beta stimulates acute phase response and C-reactive protein synthesis by inducing an NFkappaB- and C/EBPbeta-dependent autocrine interleukin-6 loop. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2678–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, A.; Suazo, K.F.; Wood, W.G.; Distefano, M.D.; Li, L. Isoprenoids and protein prenylation: Implications in the pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention of Alzheimer’s disease. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 279–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, I.; Masoodi, S.R.; Mir, S.A.; Nabi, M.; Ghazanfar, K.; Ganai, B.A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: From a metabolic disorder to an inflammatory condition. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.L.; Garrie, K.; Turner, M.D. Type 2 diabetes—An autoinflammatory disease driven by metabolic stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3805–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, L.; Liang, H.; Duan, W.; Hu, J.; Zhi, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Liu, J. GPER inhibits diabetes-mediated RhoA activation to prevent vascular endothelial dysfunction. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 95, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, K.P.; Rigsby, C.S.; Webb, R.C. RhoA/Rho-kinase and vascular diseases: What is the link? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 3823–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Komuro, R.; Yamamoto, A.; Miyata, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Matsuda, M.; Fukuhara, A.; Shimomura, I. RhoA induces expression of inflammatory cytokine in adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylow, L.; Jensen, T.E.; Kleinert, M.; Hojlund, K.; Kiens, B.; Wojtaszewski, J.; Prats, C.; Schjerling, P.; Richter, E.A. Rac1 signaling is required for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and is dysregulated in insulin-resistant murine and human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Fukumoto, Y.; Nochioka, K.; Minami, T.; Kudo, S.; Shiba, N.; Takai, Y.; Williams, C.L.; Liao, J.K.; Shimokawa, H. Statins exert the pleiotropic effects through small GTP-binding protein dissociation stimulator upregulation with a resultant Rac1 degradation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchione, C.; Gentile, M.T.; Aretini, A.; Marino, G.; Poulet, R.; Maffei, A.; Passarelli, F.; Landolfi, A.; Vasta, A.; Lembo, G. A novel mechanism of action for statins against diabetes-induced oxidative stress. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Callera, G.; Montezano, A.C.; Antunes, T.T.; He, Y.; Cat, A.N.; Ferreira, N.S.; Barreto, P.A.; Olivon, V.C.; Tostes, R.C.; et al. Renoprotective Effects of Atorvastatin in Diabetic Mice: Downregulation of RhoA and Upregulation of Akt/GSK3. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Shoelson, S.E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnop, M.; Welsh, N.; Jonas, J.C.; Jorns, A.; Lenzen, S.; Eizirik, D.L. Mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Many differences, few similarities. Diabetes 2005, 54 (Suppl. S2), S97–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB in inflammation and cancer. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 811–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Cardozo, A.K.; Cnop, M. The role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, S.V.; Kulkarni, Y.A. NF-kappabeta: A Potential Target in the Management of Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Cai, R.; Gao, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Kang, M.; Jia, H.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. Atorvastatin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through inhibiting oxidative stress and ferroptosis signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 976, 176699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lu, M.; Wang, H.; Tang, F.; Zhang, Y. Simvastatin Improves Cardiac Hypertrophy in Diabetic Rats by Attenuation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Induced by Calpain-1-Mediated Activation of Nuclear Factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.P.; Huang, P.H.; Lai, C.F.; Chen, J.W.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, J.S. Simvastatin Attenuates Oxidative Stress, NF-kappaB Activation, and Artery Calcification in LDLR-/- Mice Fed with High Fat Diet via Down-regulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha and TNF Receptor 1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo Barbagallo, F.; Bosco, G.; Di Marco, M.; Scilletta, S.; Miano, N.; Musmeci, M.; Martedi, M.; Gonzalez-Lleo, A.M.; Ibarretxe, D.; De Francesco, E.M.; et al. Evaluation of glycemic status and subclinical atherosclerosis in familial hypercholesterolemia subjects with or without LDL receptor mutation. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scicali, R.; Di Pino, A.; Urbano, F.; Ferrara, V.; Marchisello, S.; Di Mauro, S.; Scamporrino, A.; Filippello, A.; Rabuazzo, A.M.; Purrello, F.; et al. Analysis of steatosis biomarkers and inflammatory profile after adding on PCSK9 inhibitor treatment in familial hypercholesterolemia subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A single lipid center real-world experience. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Li, Z.; Shi, W.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L. Causal impact of statins on susceptibility to osteoarthritis: Insights from a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2024, 46, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Sun, Z.; Xiong, X.; Tan, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, C. Exploring the causal link among statin drugs and the osteoarthritis risk based on Mendelian randomization research. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1390387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, B.; Babaei, M.; Yosefghahri, B. Prevention of Osteoarthritis Progression by Statins, Targeting Metabolic and Inflammatory Aspects: A Review. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 32, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinc, M.; Bilgen, M.S.; Kucukalp, A.; Bilgen, O.F. An assessment of the chondroprotective effects of intra-articular application of statin and tetracycline on early-stage experimental osteoarthritis. ISRN Orthop. 2012, 2012, 182097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van der Kraan, P.M.; van den Berg, W.B. Anabolic and destructive mediators in osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2000, 3, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Hirano, M.; Akiyama, Y.; Mimura, T. Simvastatin inhibits production of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and IL-8 and cell proliferation induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lazzerini, P.E.; Lorenzini, S.; Selvi, E.; Capecchi, P.L.; Chindamo, D.; Bisogno, S.; Ghittoni, R.; Natale, M.R.; Caporali, F.; Giuntini, S.; et al. Simvastatin inhibits cytokine production and nuclear factor-kB activation in interleukin 1beta-stimulated synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2007, 25, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Thuren, T.; Everett, B.M.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J.; Group, C.T. Effect of interleukin-1beta inhibition with canakinumab on incident lung cancer in patients with atherosclerosis: Exploratory results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Gong, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Yi, J.; Liu, X. Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Promote the Occurrence and Development of Colitis-associated Colorectal Cancer by Inhibiting miR-615-5p. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 1854–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, D.N.; Boldeanu, M.V.; Serban, R.E.; Florescu, L.M.; Serbanescu, M.S.; Ionescu, M.; Streba, L.; Constantin, C.; Vere, C.C. Correlation of the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha, Inflammatory Markers, and Tumor Markers with the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Life 2023, 13, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klampfer, L. Cytokines, inflammation and colon cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibabaw, T.; Teferi, B.; Ayelign, B. The role of Th-17 cells and IL-17 in the metastatic spread of breast cancer: As a means of prognosis and therapeutic target. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1094823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habanjar, O.; Bingula, R.; Decombat, C.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Caldefie-Chezet, F.; Delort, L. Crosstalk of Inflammatory Cytokines within the Breast Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, L.; Lan, M.; Zou, T.; Kong, Z.; Cai, T.; Wu, X.Y.; Cai, Y. Key Factor Regulating Inflammatory Microenvironment, Metastasis, and Resistance in Breast Cancer: Interleukin-1 Signaling. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 7785890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, S.; Maddukuri, M.; Yamauchi, S.; Geshow, G.; Delk, N.A. Interleukin-1 and Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Promote Breast Cancer Progression and Treatment Resistance. Cells 2022, 11, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matanic, D.; Beg-Zec, Z.; Stojanovic, D.; Matakoric, N.; Flego, V.; Milevoj-Ribic, F. Cytokines in patients with lung cancer. Scand. J. Immunol. 2003, 57, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.M.; Mariano, V.S.; Pastrez, P.R.A.; Pinto, M.C.; Castro, A.G.; Syrjanen, K.J.; Longatto-Filho, A. High systemic IL-6 is associated with worse prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Zhou, S.J.; Xiao, N.; Li, Y.S.; Zhen, D.Z.; Su, C.Y.; Liu, Z.D. Research on the relationship between serum levels of inflammatory cytokines and non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 4765–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Functional significance of cholesterol metabolism in cancer: From threat to treatment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1982–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, M.; Salman, H.; Djaldetti, M.; Bessler, H. Statins as modulators of colon cancer cells induced cytokine secretion by human PBMC. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 54, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malicki, S.; Winiarski, M.; Matlok, M.; Kostarczyk, W.; Guzdek, A.; Konturek, P.C. IL-6 and IL-8 responses of colorectal cancer in vivo and in vitro cancer cells subjected to simvastatin. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. The role of statins in the regulation of breast and colorectal cancer and future directions. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1578345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Uppal, H.; Demaria, M.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J.; Kapahi, P. Simvastatin suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation induced by senescent cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galland, S.; Martin, P.; Fregni, G.; Letovanec, I.; Stamenkovic, I. Attenuation of the pro-inflammatory signature of lung cancer-derived mesenchymal stromal cells by statins. Cancer Lett. 2020, 484, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, L.; Falcone, D.; Scaramuzzino, M.; Pelaia, G.; D’Agostino, B.; Mesuraca, M.; Terracciano, R.; Spaziano, G.; Maselli, R.; Navarra, M.; et al. Effects of simvastatin on cell viability and proinflammatory pathways in lung adenocarcinoma cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 15, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, A.; Shirai, R.; Ishii, H.; Kushima, H.; Otani, S.; Hashinaga, K.; Umeki, K.; Kishi, K.; Tokimatsu, I.; Hiramatsu, K.; et al. Inhibitory effect of statins on inflammatory cytokine production from human bronchial epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 168, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabeel, S.; Motaung, B.; Nguyen, K.A.; Ozturk, M.; Mukasa, S.L.; Wolmarans, K.; Blom, D.J.; Sliwa, K.; Nepolo, E.; Gunther, G.; et al. Impact of statins as immune-modulatory agents on inflammatory markers in adults with chronic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0323749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Eisenhut, M.; Kronbichler, A.; van der Vliet, H.J.; Hong, S.H.; Shin, J.I.; Gamerith, G. Effect of Statin on Cancer Incidence: An Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, K.M.; Coleman, C.I.; Henyan, N.N.; Kluger, J.; White, C.M. Statins and cancer risk: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2006, 295, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Jiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Devreotes, P.N.; Zhang, Z. The effects of statins in patients with advanced-stage cancers—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1234713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M. From C-Reactive Protein to Interleukin-6 to Interleukin-1: Moving Upstream To Identify Novel Targets for Atheroprotection. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Tian, W.; Wang, T.; Jia, J.; Lai, R.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Song, L.; Ju, J.; et al. The effect of various types and doses of statins on C-reactive protein levels in patients with dyslipidemia or coronary heart disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 936817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostadal, P.; Alan, D.; Hajek, P.; Vejvoda, J.; Mates, M.; Blasko, P.; Veselka, J.; Kvapil, M.; Kettner, J.; Wiendl, M.; et al. Fluvastatin in the therapy of acute coronary syndrome: Rationale and design of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (The FACS Trial)[ISRCTN81331696]. CuZrr. Control Trials Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, J.; Park, S.H.; Park, J.O.; Park, Y.S.; Lim, H.Y.; Hwang, I.G.; Lee, S.C.; Park, K.W.; et al. Simvastatin plus capecitabine-cisplatin versus placebo plus capecitabine-cisplatin in patients with previously untreated advanced gastric cancer: A double-blind randomised phase 3 study. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, N.J.; Hyung, L.S.; Moon, Y.J.; Yun, T.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, J.S. A randomized phase II study of gefitinib plus simvastatin versus gefitinib alone in previously treated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, G.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, K.Y.; Joo, J.; Go, Y.J.; Lee, J.S.; Han, J.Y. Randomized Phase II Study of Afatinib Plus Simvastatin Versus Afatinib Alone in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Nonadenocarcinomatous Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 49, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarfi, H.; Youssef, L.A.; Salamoon, M. A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Combination of Simvastatin and Chemotherapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 4174395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Mortaja, M.; Son, H.G.; Zhao, X.; Sloat, L.M.; Azin, M.; Wang, J.; Collier, M.R.; Tummala, K.S.; Mandinova, A.; et al. Statin prevents cancer development in chronic inflammation by blocking interleukin 33 expression. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, Y.; Pantea Stoian, A.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Nikolic, D.; Sachinidis, A.; Rizvi, A.A.; Janez, A.; Rizzo, M. Inclisiran: A small interfering RNA strategy targeting PCSK9 to treat hypercholesterolemia. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2022, 21, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo-Barbagallo, F.; Andreychuk, N.; Scicali, R.; Gonzalez-Lleo, A.; Piro, S.; Masana, L.; Ibarretxe, D. Inclisiran, Reasons for a Novel Agent in a Crowded Therapeutic Field. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2025, 27, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Niu, Q.; Wu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, L.; Wang, H. Causal relationship between circulating immune cells and the risk of type 2 diabetes: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1210415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, R.D., Jr.; Thompson, M.A.; Sasse, S.; Pabelick, C.M.; Gerber, A.N.; Prakash, Y.S. Th1 cytokines TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma promote corticosteroid resistance in developing human airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2019, 316, L71–L81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dludla, P.V.; Mabhida, S.E.; Ziqubu, K.; Nkambule, B.B.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Hanser, S.; Basson, A.K.; Pheiffer, C.; Kengne, A.P. Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: Implications of inflammation and oxidative stress. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhumitha, H.; Mohan, V.; Deepa, M.; Babu, S.; Aravindhan, V. Increased Th1 and suppressed Th2 serum cytokine levels in subjects with diabetic coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coward, W.; Chow, S.C. Effect of atorvastatin on TH1 and TH2 cytokine secreting cells during T cell activation and differentiation. Atherosclerosis 2006, 186, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakamada-Taguchi, R.; Uehara, Y.; Kuribayashi, K.; Numabe, A.; Saito, K.; Negoro, H.; Fujita, T.; Toyo-oka, T.; Kato, T. Inhibition of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase reduces Th1 development and promotes Th2 development. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumeanu, T.D.; Goldstein, R.; Casares, S. Down-regulation of autoreactive T-cells by HMG CoA reductase inhibitors. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 119, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Carrasco, G.; Le Saout, C.; Fontanaud, P.; Stratmann, T.; Mollard, P.; Schaeffer, M.; Hernandez, J. CD4(+) T Helper Cells Play a Key Role in Maintaining Diabetogenic CD8(+) T Cell Function in the Pancreas. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Matoba, K.; Sekiguchi, K.; Nagai, Y.; Yokota, T.; Utsunomiya, K.; Nishimura, R. Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muffova, B.; Kauerova, S.; Paukner, K.; Bartuskova, H.; Poledne, R.; Kralova Lesna, I. Anti-inflammatory effect of fluvastatin on polarized macrophages and its dependence on the mevalonate pathway. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Dong, M.; Yang, J.; An, G.; Qin, W.; Gao, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Statins induce the accumulation of regulatory T cells in atherosclerotic plaque. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mausner-Fainberg, K.; Luboshits, G.; Mor, A.; Maysel-Auslender, S.; Rubinstein, A.; Keren, G.; George, J. The effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on naturally occurring CD4+CD25+ T cells. Atherosclerosis 2008, 197, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberale, L.; Carbone, F.; Montecucco, F.; Sahebkar, A. Statins reduce vascular inflammation in atherogenesis: A review of underlying molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 122, 105735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Perea, A.L.; Montoya, C.J.; Olek, S.; Chougnet, C.A.; Velilla, P.A. Statins increase the frequency of circulating CD4+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in healthy individuals. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 762506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Xu, H.; Qian, W. Macrophage Polarization in the Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Orthop. Surg. 2025, 17, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Qiu, L.; Ye, Z.; Tan, X.; Xu, X.; Lu, M.; Kuang, G. The role of Th/Treg immune cells in osteoarthritis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1393418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.; Steinman, L.; Zamvil, S.S. Statin therapy and autoimmune disease: From protein prenylation to immunomodulation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, E.; Shimizu, A.; Masuda, Y.; Kuwahara, N.; Arai, T.; Nagasaka, S.; Aki, K.; Mii, A.; Natori, Y.; Iino, Y.; et al. Statin attenuates experimental anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis together with the augmentation of alternatively activated macrophages. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkakhan, W.; Farrar, N.; Sikora, V.; Emecen-Huja, P.; Huja, S.S.; Yilmaz, O.; Pandruvada, S.N. Statins Modulate Microenvironmental Cues Driving Macrophage Polarization in Simulated Periodontal Inflammation. Cells 2023, 12, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forero-Pena, D.A.; Gutierrez, F.R. Statins as modulators of regulatory T-cell biology. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 167086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Rajput, A.; Jin, N.; Wang, J. Mechanisms of Immunosuppression in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Huang, S.; Lu, J.; Su, L.; Gao, X.; Chi, H. Unveiling the immune symphony: Decoding colorectal cancer metastasis through immune interactions. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1362709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.C.; Jing, Y.H.; Lu, L.; Ren, S.S.; Ji, G.; Xu, H.C. Mechanisms of myeloid-derived suppressor cell-mediated immunosuppression in colorectal cancer and related therapies. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 16, 1690–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Fang, Y.; Li, M.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Luo, H.Y.; Tian, Y. The regulatory network of the chemokine CCL5 in colorectal cancer. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2205168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, M.; Butti, R.; Panda, V.K.; Malhotra, D.; Das, S.; Mitra, T.; Kapse, P.; Gosavi, S.W.; Kundu, G.C. Modulation of the tumor microenvironment and mechanism of immunotherapy-based drug resistance in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Q. The Resistance Mechanisms of Lung Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 568059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Husein, B.A.; Dawah, B.; Bani-Hani, S.; Al Bashir, S.M.; Al-Sawalmeh, K.M.; Ayoub, N.M. Immunomodulatory effect of statins on Regulatory T Lymphocytes in human colorectal cancer is determined by the stage of disease. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35752–35761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M. The Role of Cholesterol Absorption in Modulating the Immune Response in Colorectal Cancer. Immunome Res. 2024, 20, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Al Dujaily, E.; Baena, J.; Das, M.; Sereno, M.; Smith, C.; Kamata, T.; Officer, L.; Pritchard, C.; Le Quesne, J. Reduced Protumorigenic Tumor-Associated Macrophages With Statin Use in Premalignant Human Lung Adenocarcinoma. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020, 4, pkz101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Cai, Y.; Chen, D.; Jiang, G.; Xu, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. Statin shapes inflamed tumor microenvironment and enhances immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e161940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Hu, Z.; Xiong, F.; Yang, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, D.; Li, X. Lipid metabolism reprogramming in tumor-associated macrophages and implications for therapy. Lipids Health Dis. 2023, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Gao, S.; Lu, X.; Pan, Y.; Tang, W.; Huang, R.; Qiao, K.; Ning, S. Statins inhibit paclitaxel-induced PD-L1 expression and increase CD8+ T cytotoxicity for better prognosis in breast cancer. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 4716–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, W.T. Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular diseases in the physical therapy setting. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plowman, T.J.; Shah, M.H.; Fernandez, E.; Christensen, H.; Aiges, M.; Ramana, K.V. Role of Innate Immune and Inflammatory Responses in the Development of Secondary Diabetic Complications. Curr. Mol. Med. 2023, 23, 901–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, C.A.; La Favor, J.D.; Kim, D.H.; Hickner, R.C. Endothelial Dysfunction: Is There a Hyperglycemia-Induced Imbalance of NOX and NOS? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyr, A.R.; Huckaby, L.V.; Shiva, S.S.; Zuckerbraun, B.S. Nitric Oxide and Endothelial Dysfunction. Crit. Care Clin. 2020, 36, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.L.; Edelstein, D.; Dimmeler, S.; Ju, Q.; Sui, C.; Brownlee, M. Hyperglycemia inhibits endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity by posttranslational modification at the Akt site. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.; Dey, S.; Das, T.; Sarkar, M.; Banerjee, J.; Dash, S.K. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 306–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.Y.; Cheng, C.K.; Gou, L.; He, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lau, C.W.; Xu, A.; Chen, A.F.; et al. Induction of KLF2 by Exercise Activates eNOS to Improve Vasodilatation in Diabetic Mice. Diabetes 2023, 72, 1330–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Eto, M.; Kano, M.R.; Kahyo, T.; Setou, M.; Ogawa, S.; Iijima, K.; Akishita, M.; Ouchi, Y. Induction of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, SIRT1, and catalase by statins inhibits endothelial senescence through the Akt pathway. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ii, M.; Nishimura, H.; Kusano, K.F.; Qin, G.; Yoon, Y.S.; Wecker, A.; Asahara, T.; Losordo, D.W. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase mediates statin-induced restoration of vasa nervorum and reversal of diabetic neuropathy. Circulation 2005, 112, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P.; Corbalan, J.J.; Jacob, R.F.; Dawoud, H.; Malinski, T. Atorvastatin enhanced nitric oxide release and reduced blood pressure, nitroxidative stress and rantes levels in hypertensive rats with diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.Y.; Wong, W.T.; Xu, A.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, L.M.; Lee, V.W.; Lau, C.W.; Yao, X.; Huang, Y. Rosuvastatin improves endothelial function in db/db mice: Role of angiotensin II type 1 receptors and oxidative stress. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.K.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, M.C.; Kong, Y.Y.; Hwang, I.K.; Won, M.H.; Rho, J.; Kwon, Y.G. TNF-related activation-induced cytokine enhances leukocyte adhesiveness: Induction of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 via TNF receptor-associated factor and protein kinase C-dependent NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzioni, A. Adhesion molecules–their role in health and disease. Pediatr. Res. 1996, 39, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Manson, J.E.; Tinker, L.; Rifai, N.; Cook, N.R.; Hu, F.B.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Ridker, P.M.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Margolis, K.L.; et al. Circulating levels of endothelial adhesion molecules and risk of diabetes in an ethnically diverse cohort of women. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie-Majd, A.; Prager, G.W.; Bucek, R.A.; Schernthaner, G.H.; Maca, T.; Kress, H.G.; Valent, P.; Binder, B.R.; Minar, E.; Baghestanian, M. Simvastatin reduces the expression of adhesion molecules in circulating monocytes from hypercholesterolemic patients. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Shouzu, A.; Omoto, S.; Inami, N.; Tanaka, A.; Nanba, M.; Shouda, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Kimura, Y.; Iwasaka, T. Correlation between adiponectin and reduction of cell adhesion molecules after pitavastatin treatment in hyperlipidemic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Thromb. Res. 2008, 122, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, G.K.; Watts, G.F.; Chan, D.C.; Stanton, K. Statin therapy improves brachial artery vasodilator function in patients with Type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Nakanishi, N.; Akimoto, K.; Yoshida, M.; Kasai, K. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor increases GTP cyclohydrolase I mRNA and tetrahydrobiopterin in vascular endothelial cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, P.; Daiber, A.; Oelze, M.; Brandt, M.; Closs, E.; Xu, J.; Thum, T.; Bauersachs, J.; Ertl, G.; Zou, M.H.; et al. Mechanisms underlying recoupling of eNOS by HMG-CoA reductase inhibition in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2008, 198, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landmesser, U.; Bahlmann, F.; Mueller, M.; Spiekermann, S.; Kirchhoff, N.; Schulz, S.; Manes, C.; Fischer, D.; de Groot, K.; Fliser, D.; et al. Simvastatin versus ezetimibe: Pleiotropic and lipid-lowering effects on endothelial function in humans. Circulation 2005, 111, 2356–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, H.S.; Tuvdendorj, D.R.; Jialal, I.; Chandalia, M.; Abate, N. Therapeutic lifestyle change intervention improved metabolic syndrome criteria and is complementary to amlodipine/atorvastatin. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2020, 34, 107480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimikas, S.; Witztum, J.L.; Miller, E.R.; Sasiela, W.J.; Szarek, M.; Olsson, A.G.; Schwartz, G.G.; Myocardial Ischemia Reduction with Aggressive Cholesterol Lowering (MIRACL) Study Investigators. High-dose atorvastatin reduces total plasma levels of oxidized phospholipids and immune complexes present on apolipoprotein B-100 in patients with acute coronary syndromes in the MIRACL trial. Circulation 2004, 110, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, D.; Sellam, J.; Berenbaum, F.; Guicheux, J.; Boutet, M.A. The role of the immune system in osteoarthritis: Mechanisms, challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2025, 21, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Munter, W.; van der Kraan, P.M.; van den Berg, W.B.; van Lent, P.L. High systemic levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: Fuel to the flames in inflammatory osteoarthritis? Rheumatology 2016, 55, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, P.L.; Raschi, E.; Testoni, C.; Tincani, A.; Balestrieri, G.; Molteni, R.; Khamashta, M.A.; Tremoli, E.; Camera, M. Statins prevent endothelial cell activation induced by antiphospholipid (anti-beta2-glycoprotein I) antibodies: Effect on the proadhesive and proinflammatory phenotype. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2870–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, U.; Canavan, M.; Biniecka, M.; Veale, D.J. Hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction and synovial invasiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, U.; Hanlon, M.M.; Floudas, A.; Veale, D.J. Cellular metabolic adaptations in rheumatoid arthritis and their therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksandrowicz, M.; Konop, M.; Rybka, M.; Mazurek, L.; Stradczuk-Mazurek, M.; Kciuk, M.; Badzynska, B.; Dobrowolski, L.; Kuczeriszka, M. Dysfunction of Microcirculation in Atherosclerosis: Implications of Nitric Oxide, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinderlerer, A.R.; Steinberg, R.; Johns, M.; Harten, S.K.; Lidington, E.A.; Haskard, D.O.; Maxwell, P.H.; Mason, J.C. Statin-induced expression of CD59 on vascular endothelium in hypoxia: A potential mechanism for the anti-inflammatory actions of statins in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, M.; Heeschen, C.; Glassford, A.J.; Cooke, J.P. Statins have biphasic effects on angiogenesis. Circulation 2002, 105, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhab, L.J.B.; Saber-Ayad, M.M.; Al-Hakm, R.; Nair, V.A.; Paliogiannis, P.; Pintus, G.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M. Chronic Inflammation and Cancer: The Role of Endothelial Dysfunction and Vascular Inflammation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2156–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Z.; Jiang, J.X.; Yu, X.Y.; Xia, W.J.; Yu, P.X.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.G. Endothelial cells in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 11, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiabi, P.; Jiang, J.; Pasquier, J.; Maleki, M.; Abu-Kaoud, N.; Rafii, S.; Rafii, A. Endothelial cells provide a notch-dependent pro-tumoral niche for enhancing breast cancer survival, stemness and pro-metastatic properties. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zou, J.; Li, L.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, W. Elevated serum Cripto-1 and VEGF levels in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. FASEB BioAdvances 2022, 4, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulak, J.; Jozkowicz, A. Anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory effects of statins: Relevance to anti-cancer therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2005, 5, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, I.; Lee, J.; Park, C.; Kang, W.K. Statins, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors, potentiate the anti-angiogenic effects of bevacizumab by suppressing angiopoietin2, BiP, and Hsp90alpha in human colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Lin, J.A.; Chen, W.M.; Shia, B.C.; Wu, S.Y. Statin Therapy Reduces Radiation-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Patients With Breast Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Radiotherapy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e036411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Yuan, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; An, Y.; Tie, L.; Pan, Y.; Li, X. Atorvastatin reduces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in human non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLCs) via inhibition of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, A.K.; Zhu, X. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: Metabolic Regulation and Contribution to Inflammaging. Cells 2020, 9, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, D.T.; de Paula Souza, J.; Donath, M.Y. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome-IL-1beta pathway in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Diabetologia 2025, 68, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, V.; Chain, M.; Majie, A.; Ghosh, A.; Sengupta, P.; Dutta, S.; Mazumder, P.M.; Gorain, B. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome as a novel therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2025, 33, 461–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in MPhis-CRC Crosstalk Promotes Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2022, 52, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, H.; Zeng, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, W. Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome enhances the proliferation and migration of A549 lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, B.; Jin, K.; Dai, J.; Jiang, G. Effect of NLRP3 Inflammasome on Lung Cancer Immune Microenvironment Activation and Its Mechanism. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2024, 30, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ershaid, N.; Sharon, Y.; Doron, H.; Raz, Y.; Shani, O.; Cohen, N.; Monteran, L.; Leider-Trejo, L.; Ben-Shmuel, A.; Yassin, M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome in fibroblasts links tissue damage with inflammation in breast cancer progression and metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.H.; Phuong, T.A.; Jin, S.J.; Li, X.X.; Xu, M. Protection by simvastatin on hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91291–91305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Li, B.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; An, F. Rosuvastatin alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and MAPK pathways in a type 2 diabetes rat model. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2014, 28, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Koka, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, T.; Li, X. Simvastatin improves lysosome function via enhancing lysosome biogenesis in endothelial cells. Front. Biosci. 2020, 25, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Gao, J.; Xu, M.; Ren, S.; Stefanovic-Racic, M.; O’Doherty, R.M.; Xie, W. PXR ablation alleviates diet-induced and genetic obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1876–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongnak, L.; Pengrattanachot, N.; Promsan, S.; Phengpol, N.; Sutthasupha, P.; Chatsudthipong, V.; Lungkaphin, A. The combination of dapagliflozin and statins ameliorates renal injury through attenuating the activation of inflammasome-mediated autophagy in insulin-resistant rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e22978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksbo, B.D.; Lau, T.C.; Cavallari, J.F.; Denou, E.; Chi, W.; Lally, J.S.; Crane, J.D.; Duggan, B.M.; Foley, K.P.; Fullerton, M.D.; et al. Fluvastatin causes NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated adipose insulin resistance. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3742–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, S.; Hu, S.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Geng, X.; Wang, H. NLRP3 inflammasome expression in peripheral blood monocytes of coronary heart disease patients and its modulation by rosuvastatin. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1826–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, A.; Qu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Lou, D.; Niu, N. NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood monocytes of acute coronary syndrome patients and its relationship with statins. Coron. Artery Dis. 2015, 26, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Xu, K.; et al. Atorvastatin inhibited TNF-alpha induced matrix degradation in rat nucleus pulposus cells by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activity and inducing autophagy through NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 2160–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.F.; Washko, G.R.; Nakahira, K.; Hatabu, H.; Patel, A.S.; Fernandez, I.E.; Nishino, M.; Okajima, Y.; Yamashiro, T.; Ross, J.C.; et al. Statins and pulmonary fibrosis: The potential role of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.; Abd El-Fattah, E.E.; Yahya, G.; Gobba, N.A.; Maghmomeh, A.O.; Khodir, A.E.; Mourad, A.A.E.; Saad, A.S.; Mohammed, H.G.; Nouh, N.A.; et al. A Novel Combination Therapy Using Rosuvastatin and Lactobacillus Combats Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats by Targeting the TXNIP/NLRP3 Interaction and Influencing Gut Microbiome Composition. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, M.; Penson, P.E.; Banach, M.; Sahebkar, A. Statins as anti-pyroptotic agents. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 1414–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, M.T. Protease-activated receptors in hemostasis. Blood 2016, 128, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagota, S.; Maruyama, K.; McGuire, J.J. Characterization and Functions of Protease-Activated Receptor 2 in Obesity, Diabetes, and Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3130496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.J.; Miller, D.L.; Jiang, R.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Tarwater, L.; Williams, R.; Balsara, R.; Sauter, E.R.; Stack, M.S. Protease-activated Receptor-2 (PAR-2)-mediated Nf-kappaB Activation Suppresses Inflammation-associated Tumor Suppressor MicroRNAs in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 6936–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oe, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Fushima, T.; Sato, E.; Kisu, K.; Sato, H.; Ito, S.; Takahashi, N. Coagulation Factor Xa and Protease-Activated Receptor 2 as Novel Therapeutic Targets for Diabetic Nephropathy. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagang, N.; Gupta, K.; Singh, G.; Kanuri, S.H.; Mehan, S. Protease-activated receptors in kidney diseases: A comprehensive review of pathological roles, therapeutic outcomes and challenges. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 377, 110470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfi, C.; Brioschi, M.; Lento, S.; Pirillo, A.; Galli, S.; Cosentino, S.; Tremoli, E.; Mussoni, L. Statins prevent tissue factor induction by protease-activated receptors 1 and 2 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, F.F. Role of protease-activated receptor 2 in joint inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3514–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Chan, Y.K.; Shen, K.; Dervish, S.; March, L.; Sambrook, P.N.; Jackson, C.J. Protease-activated receptor 2, rather than protease-activated receptor 1, contributes to the aggressive properties of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, R.; Riaz, S.; Sivani, B.M.; Faisal, S.; Naidoo, N.; Rizzo, M.; Banerjee, Y. Evaluating the potential of Vitamin D and curcumin to alleviate inflammation and mitigate the progression of osteoarthritis through their effects on human chondrocytes: A proof-of-concept investigation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannati, S.; Patnaik, R.; Banerjee, Y. Beyond Anticoagulation: A Comprehensive Review of Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) in Inflammation and Protease-Activated Receptor Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, C.; Amiable, N.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Fahmi, H.; Duval, N.; Pelletier, J.P. Activation of proteinase-activated receptor 2 in human osteoarthritic cartilage upregulates catabolic and proinflammatory pathways capable of inducing cartilage degradation: A basic science study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 9, R121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, R.; Varghese, R.; Jannati, S.; Naidoo, N.; Banerjee, Y. Targeting PAR2-mediated inflammation in osteoarthritis: A comprehensive in vitro evaluation of oleocanthal’s potential as a functional food intervention for chondrocyte protection and anti-inflammatory effects. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Hempel, D.; Sierko, E.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Protease-activated receptors (PARs)–biology and role in cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 775–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetvicka, D.; Suhaj, P.; Olejar, T.; Sivak, L.; Benes, J.; Pouckova, P. Proteinase-activated Receptor 2: Springboard of Tumors. Anticancer Res. 2024, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.; Hill, T.A.; Lim, J.; Fairlie, D.P. Protease-activated receptor 2 attenuates doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 17, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.R.; Ding, Y.; Ricks, T.K.; Gullapalli, A.; Wolfe, B.L.; Trejo, J. Protease-activated receptor-2 is essential for factor VIIa and Xa-induced signaling, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, M.D.; Lan, Y.J.; Jia, C.Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, K.P.; Liu, H.N.; Sun, S.Z.; Tao, R.C.; Lu, X.D.; et al. PAR2 promotes malignancy in lung adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2024, 16, 7416–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, R.; Varghese, R.L.; Khan, S.; Huda, B.; Bhurka, F.; Amiri, L.; Banerjee, Y. Targeting PAR-2-driven inflammatory pathways in colorectal cancer: Mechanistic insights from atorvastatin and rosuvastatin treatment in cell line models. Transl. Cancer Res. 2025, 14, 1531–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghesmati, Z.; Rashid, M.; Fayezi, S.; Gieseler, F.; Alizadeh, E.; Darabi, M. An update on the secretory functions of brown, white, and beige adipose tissue: Towards therapeutic applications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 279–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Patel, B.M. The burning furnace: Alteration in lipid metabolism in cancer-associated cachexia. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 1709–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pare, M.; Darini, C.Y.; Yao, X.; Chignon-Sicard, B.; Rekima, S.; Lachambre, S.; Virolle, V.; Aguilar-Mahecha, A.; Basik, M.; Dani, C.; et al. Breast cancer mammospheres secrete Adrenomedullin to induce lipolysis and browning of adjacent adipocytes. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Ding, G. Increased UCP1 expression in the perirenal adipose tissue of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, H.H.; Schaffner, F.; Kerver, M.; Ellies, L.G.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Mueller, B.M.; Ruf, W. Protease-activated receptor (PAR) 2, but not PAR1, signaling promotes the development of mammary adenocarcinoma in polyoma middle T mice. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7219–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaz, M.; Becker, A.S.; Balazova, L.; Straub, L.; Muller, J.; Gashi, G.; Maushart, C.I.; Sun, W.; Dong, H.; Moser, C.; et al. Inhibition of Mevalonate Pathway Prevents Adipocyte Browning in Mice and Men by Affecting Protein Prenylation. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 901–916.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Tramper, N.; Zhou, E.; Boon, M.R.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Kooijman, S. Role of thermogenic adipose tissue in lipid metabolism and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Lessons from studies in mice and humans. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atale, N.; Wells, A. Statins as Secondary Preventive Agent to Limit Breast Cancer Metastatic Outgrowth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, V.A.; Parisi, V.; Moschetta, D.; Valerio, V.; Conte, M.; Massaiu, I.; Bozzi, M.; Celeste, F.; Leosco, D.; Iaccarino, G.; et al. Efficacy of cardiometabolic drugs in reduction of epicardial adipose tissue: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checa, J.; Aran, J.M. Reactive Oxygen Species: Drivers of Physiological and Pathological Processes. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 1057–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caturano, A.; D’Angelo, M.; Mormone, A.; Russo, V.; Mollica, M.P.; Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Vetrano, E.; Marfella, R.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes: Impacts from Pathogenesis to Lifestyle Modifications. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 6651–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.; Yang, X.; Franklin, B.S.; Hoelscher, M.; Schmitz, T.; Bedorf, J.; Nickenig, G.; Werner, N. High glucose condition increases NADPH oxidase activity in endothelial microparticles that promote vascular inflammation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 98, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowluru, A.; Kowluru, R.A. Phagocyte-like NADPH oxidase [Nox2] in cellular dysfunction in models of glucolipotoxicity and diabetes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.J.; Xiong, S.Q.; Ding, L.X.; Peng, J.; Xia, X.B. Diabetic retinopathy: Focus on NADPH oxidase and its potential as therapeutic target. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 853, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnaghi, S.; Prasadam, I.; Cai, G.; Friis, T.; Du, Z.; Crawford, R.; Mao, X.; Xiao, Y. Protective effects of mitochondria-targeted antioxidants and statins on cholesterol-induced osteoarthritis. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davignon, J.; Jacob, R.F.; Mason, R.P. The antioxidant effects of statins. Coron. Artery Dis. 2004, 15, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, E.A.; Almeida, D.C.; Roma, L.P.; Ortis, F.; Carpinelli, A.R. Lipotoxicity and beta-Cell Failure in Type 2 Diabetes: Oxidative Stress Linked to NADPH Oxidase and ER Stress. Cells 2021, 10, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.O. NADPH Dynamics: Linking Insulin Resistance and beta-Cells Ferroptosis in Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Kabeer, A.; Abbas, Z.; Siddiqui, H.A.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cho, W.C. Interplay of oxidative stress, cellular communication and signaling pathways in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi-Marjaneh, R.; Hassanian, S.M.; Mehramiz, M.; Rezayi, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Khazaei, M.; Avan, A. Reactive oxygen species in colorectal cancer: The therapeutic impact and its potential roles in tumor progression via perturbation of cellular and physiological dysregulated pathways. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 10072–10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr.; Werner, J.; Bazhin, A.V. Reactive oxygen species and colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5119–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, R.; Surepalli, N.; Farran, B.; Malhotra, S.V.; Nagaraju, G.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS): Critical roles in breast tumor microenvironment. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 160, 103285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johar, R.; Sharma, R.; Kaur, A.; Mukherjee, T.K. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Estrogen Dependant Breast Cancer Complication. Anticancer. Agents. Med. Chem. 2015, 16, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, F.; Quinones-Galvan, A.; Regoli, F.; Ferrannini, E.; Galetta, F. A comparative study of the in vitro antioxidant activity of statins. Int. J. Cardiol. 2003, 90, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos, P.M.F.; Volpe, C.M.O.; Miranda, T.C.; Nogueira-Machado, J.A. Atorvastatin Inhibited ROS Generation and Increased IL-1beta And IL-6 Release by Mononuclear Cells from Diabetic Patients. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 19, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.H.; Kohler, T.; Ruckschloss, U.; Just, I.; Hecker, M. Improvement of nitric oxide-dependent vasodilatation by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors through attenuation of endothelial superoxide anion formation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Chai, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.L. Effect of rosuvastatin on high glucose-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.W.; Kuzuya, M.; Sasaki, T.; Inoue, A.; Hu, L.; Song, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, P.; Takeshita, K.; Hirashiki, A.; et al. Inhibition of mineralocorticoid receptor is a renoprotective effect of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor pitavastatin. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piconi, L.; Corgnali, M.; Da Ros, R.; Assaloni, R.; Piliego, T.; Ceriello, A. The protective effect of rosuvastatin in human umbilical endothelial cells exposed to constant or intermittent high glucose. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2008, 22, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Callera, G.E.; Montezano, A.C.; He, Y.; Antunes, T.T.; Nguyen Dinh Cat, A.; Tostes, R.C.; Touyz, R.M. Vascular injury in diabetic db/db mice is ameliorated by atorvastatin: Role of Rac1/2-sensitive Nox-dependent pathways. Clin. Sci. 2015, 128, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaley-Connell, A.; DeMarco, V.G.; Lastra, G.; Manrique, C.; Nistala, R.; Cooper, S.A.; Westerly, B.; Hayden, M.R.; Wiedmeyer, C.; Wei, Y.; et al. Insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and podocyte injury: Role of rosuvastatin modulation of filtration barrier injury. Am. J. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinen, I.; Shimabukuro, M.; Yamakawa, K.; Higa, N.; Matsuzaki, T.; Noguchi, K.; Ueda, S.; Sakanashi, M.; Takasu, N. Vascular lipotoxicity: Endothelial dysfunction via fatty-acid-induced reactive oxygen species overproduction in obese Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, S.N.; Li, C.N.; Sun, S.J.; Liu, Q.; Lei, L.; Gao, L.H.; Shen, Z.F. Atorvastatin helps preserve pancreatic beta cell function in obese C57BL/6 J mice and the effect is related to increased pancreas proliferation and amelioration of endoplasmic-reticulum stress. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhao, S.P. Simvastatin inhibits ox-LDL-induced inflammatory adipokines secretion via amelioration of ER stress in 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 432, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalata, C.I.; Tefas, L.R.; Achim, M.; Tomuta, I.; Porfire, A.S. Statins in risk-reduction and treatment of cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 11, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Peng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yi, L.; Long, Y. Simvastatin induces pyroptosis via ROS/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway in colon cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Yu, Z.; Gao, X.; Gong, J.; Fan, L.; Liu, F. Simvastatin induces breast cancer cell death through oxidative stress up-regulating miR-140-5p. Aging 2019, 11, 3198–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorand, B.; Lowel, H.; Schneider, A.; Kolb, H.; Meisinger, C.; Frohlich, M.; Koenig, W. C-reactive protein as a predictor for incident diabetes mellitus among middle-aged men: Results from the MONICA Augsburg cohort study, 1984–1998. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, J.C. Inflammation and activated innate immunity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speelman, T.; Dale, L.; Louw, A.; Verhoog, N.J.D. The Association of Acute Phase Proteins in Stress and Inflammation-Induced T2D. Cells 2022, 11, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanimirovic, J.; Radovanovic, J.; Banjac, K.; Obradovic, M.; Essack, M.; Zafirovic, S.; Gluvic, Z.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Role of C-Reactive Protein in Diabetic Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 3706508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipe, J.D. Acute-phase proteins in osteoarthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 25, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Cao, S.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, X. Evaluation of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen in comparison to CEA and CA72-4 as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, B.L.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Bernstein, L.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Wener, M.H.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Gilliland, F.D.; Sorensen, B.E.; McTiernan, A.; et al. Elevated biomarkers of inflammation are associated with reduced survival among breast cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hanlon, D.M.; Lynch, J.; Cormican, M.; Given, H.F. The acute phase response in breast carcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 2002, 22, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Liu, F.; Higuchi, K.; Sawashita, J.; Fu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Fu, L.; Tong, Z.; Higuchi, K. Serum amyloid A expression in the breast cancer tissue is associated with poor prognosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35843–35852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.J.; Ahn, J.M.; Yoon, Y.H.; Rhim, T.Y.; Park, C.S.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, J.Y. Identification and validation of SAA as a potential lung cancer biomarker and its involvement in metastatic pathogenesis of lung cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.A.; Danielson, E.; Rifai, N.; Ridker, P.M.; PRINCE Investigators. Effect of statin therapy on C-reactive protein levels: The pravastatin inflammation/CRP evaluation (PRINCE): A randomized trial and cohort study. JAMA 2001, 286, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaba, G.R.; Phoswa, W.N.; Mokgalaboni, K. The Effect of Statins on Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and C-Reactive Protein in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelouei, T.; Abbasifard, M.; Imani, D.; Aslani, S.; Razi, B.; Fasihi, M.; Shafiekhani, S.; Mohammadi, K.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Reiner, Z.; et al. Effect of Statins on Serum level of hs-CRP and CRP in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 8732360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, H.; Hu, B.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, K. New insights into the therapeutic potentials of statins in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1188926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Amiri, S.; Pecic, S.; Machaj, F.; Rosik, J.; Los, M.J.; Alizadeh, J.; Mahdian, R.; da Silva Rosa, S.C.; Schaafsma, D.; et al. Pleiotropic effects of statins: A focus on cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiawan, B.; Budianto, W.; Sukarnowati, T.W.; Rizky, D.; Pangarsa, E.A.; Santosa, D.; Sudoyo, A.W.; Winarni, T.I.; Riwanto, I.; Setiabudy, R.D.; et al. The efficacy of atorvastatin on inflammation and coagulation markers in high-risk thrombotic cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: A randomized controlled trial. Thromb. J. 2025, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthravadi, S.; Shrestha, A.; Madhusudhana, S. Impact of statin use on cancer recurrence and mortality in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgquist, S.; Bjarnadottir, O.; Kimbung, S.; Ahern, T.P. Statins: A role in breast cancer therapy? J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour Talesh, G.; Trezeguet, V.; Merched, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Statins. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 3393–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaidopoulos, S.; Nikiphorou, E.; Dimitroulas, T.; Kitas, G.D. The Role of Statins in Disease Modification and Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vera, M.A.; Choi, H.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Kopec, J.; Lacaille, D. Impact of statin discontinuation on mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based study. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.M.; Zhao, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.F.; Ma, J.X.; Ma, X.L.; Liu, J. The anti-inflammatory effects of statins on patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systemic review and meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarey, D.W.; McInnes, I.B.; Madhok, R.; Hampson, R.; Scherbakov, O.; Ford, I.; Capell, H.A.; Sattar, N. Trial of Atorvastatin in Rheumatoid Arthritis (TARA): Double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, G.; Chobaz, V.; Talabot-Ayer, D.; Taylor, S.; So, A.; Gabay, C.; Busso, N. Assessment of the efficacy of different statins in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 4051–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranow, C.; Cush, J.; Bolster, M.B.; Striebich, C.C.; Dall’era, M.; Mackay, M.; Olech, E.; Frech, T.; Box, J.; Keating, R.; et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II, randomized study of lovastatin therapy in the treatment of mildly active rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, M.; Liao, J.K. Pleiotropic effects of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, P.S.S.; da Paixao, A.B.F.; da Rocha Junior, L.F.; Branco Pinto Duarte, A.L.; Pereira, M.C.; Barreto de Melo Rego, M.J.; da Rocha Pitta, I.; da Rocha Pitta, M.G. Atorvastatin inhibits IL-17A, TNF, IL-6, and IL-10 in PBMC cultures from patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis. Immunobiology 2020, 225, 151908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.T.; Song, Y.; Ding, Y.J.; Liao, Y.H.; Yu, X.; Du, R.; Xiao, H.; Yuan, J.; Zhou, Z.H.; Liao, M.Y.; et al. Atorvastatin upregulates regulatory T cells and reduces clinical disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki-Petaja, K.M.; Booth, A.D.; Hall, F.C.; Wallace, S.M.; Brown, J.; McEniery, C.M.; Wilkinson, I.B. Ezetimibe and simvastatin reduce inflammation, disease activity, and aortic stiffness and improve endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Yin, Y.F.; Zhao, L.D.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.J.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q.J.; Tang, F.L.; Zhang, F.C.; Shan, G.; et al. Effect of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase inhibitor on disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi, S.; Evans, S.J.; Egger, P.; Carpenter, J. Is there an anti-inflammatory effect of statins in rheumatoid arthritis? Analysis of a large routinely collected claims database. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 69, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Parks, J.S. New roles of HDL in inflammation and hematopoiesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Deng, J.; Huang, L. Effects of atorvastatin in suppressing pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clinics 2023, 78, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, T.; Tasdemir, M.S.; Tunik, S.; Ates, G.; Tekes, S.; Kaplanoglu, I.; Topcu, F.; Akkus, M. Effects of atorvastatin on smoking-induced alveolar injury in rat lungs. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2009, 70, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mroz, R.M.; Lisowski, P.; Tycinska, A.; Bierla, J.; Trzeciak, P.Z.; Minarowski, L.; Milewski, R.; Lisowska, A.; Boros, P.; Sobkowicz, B.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of atorvastatin treatment in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A controlled pilot study. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 111–128. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Wang, M.T.; Lo, Y.W.; Tsai, C.L.; Chang, L.C.; Malone, D.C.; Chu, C.L.; Liou, J.T. Statin use and risk of COPD exacerbation requiring hospitalization. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 598–606.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahousse, L.; Loth, D.W.; Joos, G.F.; Hofman, A.; Leufkens, H.G.; Brusselle, G.G.; Stricker, B.H. Statins, systemic inflammation and risk of death in COPD: The Rotterdam study. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 26, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lv, D.; Zhang, C.; Lai, T.; Li, W.; Shen, H. The effect of statins on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational research. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.J.; Baines, K.J.; Smart, J.M.; Gibson, P.G.; Wood, L.G. Rosuvastatin, lycopene and omega-3 fatty acids: A potential treatment for systemic inflammation in COPD; a pilot study. J. Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2016, 5, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulou, M.; Corsini, A.; Roden, M. The role of mitochondria in statin-induced myopathy. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouitbir, J.; Sanvee, G.M.; Panajatovic, M.V.; Singh, F.; Krahenbuhl, S. Mechanisms of statin-associated skeletal muscle-associated symptoms. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 154, 104201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.; Thoma, A.; Hargreaves, I.P.; Lightfoot, A.P. The Role of Mitochondria in Statin-Induced Myopathy. Drug Saf. 2024, 47, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, T.T.; Jacobson, T.A. Statin-induced myopathy: A review and update. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2011, 10, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, M.; Gazzotti, M.; Bonaiti, F.; OImastroni, E.; Arca, M.; Averna, M.; Zambon, A.; Catapano, A.L.; PROSISA Study Group. Reported muscle symptoms during statin treatment amongst Italian dyslipidaemic patients in the real-life setting: The PROSISA Study. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroes, E.S.; Thompson, P.D.; Corsini, A.; Vladutiu, G.D.; Raal, F.J.; Ray, K.K.; Roden, M.; Stein, E.; Tokgozoglu, L.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; et al. Statin-associated muscle symptoms: Impact on statin therapy-European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel Statement on Assessment, Aetiology and Management. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N. Statins and diabetes: What are the connections? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criner, G.J.; Connett, J.E.; Aaron, S.D.; Albert, R.K.; Bailey, W.C.; Casaburi, R.; Cooper, J.A., Jr.; Curtis, J.L.; Dransfield, M.T.; Han, M.K.; et al. Simvastatin for the prevention of exacerbations in moderate-to-severe COPD. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, N.C. Clinical Studies of Statins in Asthma and COPD. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limburg, P.J.; Mahoney, M.R.; Ziegler, K.L.; Sontag, S.J.; Schoen, R.E.; Benya, R.; Lawson, M.J.; Weinberg, D.S.; Stoffel, E.; Chiorean, M.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of sulindac, atorvastatin, and prebiotic dietary fiber for colorectal cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, B.; Nazer, S.; Masoompour, S.M.; Geramizadeh, B.; Sajadi, S.V. The effect of atorvastatin on inflammatory markers in sulfur mustard gas induced bronchitis: A randomized double-blinded, placebo-control clinical trial. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiati, R.F.; Manchini, M.T.; Jacobsen, O.; dos Santos Batista, J.G.; Silva Junior, J.A.; Nascimento, J.W. Evaluation of the Anti-inflammatory Activity of Atorvastatin and its Effect on Alveolar Diameter in a Model of Elastase-induced Emphysema in Rats. Drug Res. 2015, 65, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Association between statin use and incidence or progression of osteoarthritis: Meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, W.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, S.W.; Suh, C.H. Rosuvastatin treatment alone cannot alleviate lupus in murine model: A pilot study. J. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 30, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.W.; Lin, C.L.; Liao, K.F. Rosuvastatin and risk of acute pancreatitis in a population-based case-control study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 187, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, M.; Mohebbi, M.; Dean, O.M.; Cotton, S.M.; Chanen, A.M.; Dodd, S.; Ratheesh, A.; Amminger, G.P.; Phelan, M.; Weller, A.; et al. Youth Depression Alleviation with Anti-inflammatory Agents (YoDA-A): A randomised clinical trial of rosuvastatin and aspirin. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.B.; Daskalakis, N.; Xu, C.; Paccaly, A.; Miller, B.; Fleischmann, R.; Bodrug, I.; Kivitz, A. Disease-Drug Interaction of Sarilumab and Simvastatin in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Salman, M.; Ghiasi, M.; Farid, A.S.; Taraz, M.; Azizpour, A.; Mahmoudi, H. Oral simvastatin combined with narrowband UVB for the treatment of psoriasis: A randomized controlled trial. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, F.; Liu, A.B.; Li, G.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yang, C.S.; Ju, J. Deleterious effects of high concentrations of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and atorvastatin in mice with colon inflammation. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arian, A.; Mortazavi Moghadam, S.G.; Kazemi, T.; Zardast, M.; Zarban, A. Trial of Atorvastatin on Serum Interleukin-6, Total Antioxidant Capacity, C-Reactive Protein, and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Res. Pharm. Pract. 2018, 7, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration; Emberson, J.R.; Kearney, P.M.; Blackwell, L.; Newman, C.; Reith, C.; Bhala, N.; Holland, L.; Peto, R.; Keech, A.; et al. Lack of effect of lowering LDL cholesterol on cancer: Meta-analysis of individual data from 175,000 people in 27 randomised trials of statin therapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29849. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmeister, M.; Jansen, L.; Rudolph, A.; Toth, C.; Kloor, M.; Roth, W.; Blaker, H.; Chang-Claude, J.; Brenner, H. Statin use and survival after colorectal cancer: The importance of comprehensive confounder adjustment. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochhead, P.; Chan, A.T. Statins and colorectal cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.; Perrem, L.; Khashan, A.S.; Henry, M.T.; Ni Chroinin, M. Statins versus placebo for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 7, CD011959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Li, M. The efficacy of statins in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e35088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, S.H.; Bestwick, J.P.; Wald, D.S. Adherence to drugs that prevent cardiovascular disease: Meta-analysis on 376,162 patients. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 882–887.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, P.P.; Granowitz, C.; Hull, M.; Anderson, A.; Philip, S. Long-term statin persistence is poor among high-risk patients with dyslipidemia: A real-world administrative claims analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Vega, G.L. Statin Intolerance and Noncompliance: An Empiric Approach. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, Y.; Fard, J.K.; Ghafoor, D.; Eid, A.H.; Sahebkar, A. Paradoxical effects of statins on endothelial and cancer cells: The impact of concentrations. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, E.; Benaiges, D.; Pedro-Botet, J. Hydrophilic or Lipophilic Statins? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 687585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.M.; Liakoni, E.; Schneider, C.; Burkard, T.; Jick, S.S.; Krahenbuhl, S.; Meier, C.R.; Spoendlin, J. The Risk of Muscular Events Among New Users of Hydrophilic and Lipophilic Statins: An Observational Cohort Study. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.C.; Khalesi, S.; Fenning, A.S.; Vella, R.K. The effect of lipophilicity and dose on the frequency of statin-associated muscle symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, C. Comparative Muscle Tolerability of Different Types and Intensities of Statins: A Network Meta-Analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trials. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2024, 38, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, F.; Biffi, A.; Ronco, R.; Franchi, M.; Cammarota, S.; Citarella, A.; Conti, V.; Filippelli, A.; Sellitto, C.; Corrao, G. Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality Associated With Discontinuing Statins in Older Patients Receiving Polypharmacy. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2113186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalaf, K.; Johnell, K.; Austin, P.C.; Tyden, P.; Midlov, P.; Perez-Vicente, R.; Merlo, J. Low adherence to statin treatment during the 1st year after an acute myocardial infarction is associated with increased 2nd-year mortality risk-an inverse probability of treatment weighted study on 54 872 patients. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2021, 7, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemes, K.; Aberg, F.; Gylling, H.; Isoniemi, H. Cholesterol metabolism in cholestatic liver disease and liver transplantation: From molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yorke, E. Co-Morbid Hypothyroidism and Liver Dysfunction: A Review. Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes 2024, 17, 11795514241231533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duntas, L.H.; Brenta, G. A Renewed Focus on the Association Between Thyroid Hormones and Lipid Metabolism. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scappaticcio, L.; Longo, M.; Maiorino, M.I.; Pernice, V.; Caruso, P.; Esposito, K.; Bellastella, G. Abnormal Liver Blood Tests in Patients with Hyperthyroidism: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid 2021, 31, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, A.K.; Sarma, D.; Kaimal Saikia, U.; Choudhury, B.K. Grave’s Disease with Severe Hepatic Dysfunction: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Case Rep. Med. 2014, 2014, 790458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorke, E. Hyperthyroidism and Liver Dysfunction: A Review of a Common Comorbidity. Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes 2022, 15, 11795514221074672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourian, A.R. Liver Functional Behavior During Thyrotoxicosis: A Review. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 13, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Castro, J.; Cid-Conde, L. Pharmacokinetic Aspects of Statins. In Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Pathology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Willrich, M.A.; Hirata, M.H.; Hirata, R.D. Statin regulation of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 expression. Pharmacogenomics 2009, 10, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corticosteroids. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oluleye, O.W.; Kronmal, R.A.; Folsom, A.R.; Vaidya, D.M.; Ouyang, P.; Duprez, D.A.; Dobs, A.S.; Yarmohammadi, H.; Konety, S.H. Association Between Statin Use and Sex Hormone in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Cohort. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4600–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chihaoui, M.; Terzi, A.; Hammami, B.; Oueslati, I.; Khessairi, N.; Chaker, F.; Yazidi, M.; Feki, M. Effects of high-intensity statin therapy on steroid hormones and vitamin D in type 2 diabetic men: A prospective self-controlled study. Lipids 2024, 59, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glina, F.P.A.; Lopes, L.; E Silva, R.S.; Barros, E.A.C.; Biselli, B.; Glina, S. Do statins decrease testosterone in men? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2024, 50, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trias, F.; Pinto, X.; Corbella, E.; Suarez-Tembra, M.; Ruiz-Garcia, A.; Diaz-Diaz, J.L.; Sanchez-Ruiz-Granado, E.; Sarasa, I.; Martinez-Porqueras, R.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, M.A.; et al. Differences in the diabetogenic effect of statins in patients with prediabetes. The PRELIPID study. Med. Clin. 2022, 158, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, S.M.; Thekkekara, P.T. Combined Effect of Metformin and Statin. In Metformin—Pharmacology and Drug Interactions; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, R.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, R.; Xia, W.; Wang, S. An investigation into the therapeutic effects of statins with metformin on polycystic ovary syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwar, A.; Nagpure, S. Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Cureus 2022, 14, e30351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Li, R.; Lai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiao, J. Adipose insulin resistance is associated with cardiovascular risk factors in polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Rosales, C.; Portilla-Fernandez, E.; Nano, J.; Wilson, R.; Lehne, B.; Mishra, P.P.; Gao, X.; Ghanbari, M.; Rueda-Ochoa, O.L.; Juvinao-Quintero, D.; et al. Epigenetic Link Between Statin Therapy and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Corres, R.; Candas-Estebanez, B.; Padro-Miquel, A.; Fanlo-Maresma, M.; Pinto, X.; Alia-Ramos, P. Influence of 6 genetic variants on the efficacy of statins in patients with dyslipidemia. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, M.; Pasanen, M.K.; Neuvonen, P.J. Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1: A genetically polymorphic transporter of major importance for hepatic drug uptake. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 157–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preissner, S.C.; Hoffmann, M.F.; Preissner, R.; Dunkel, M.; Gewiess, A.; Preissner, S. Polymorphic cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) and their role in personalized therapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, A.B.; van Lijf, H.J.; Bon, M.A.; van den Bergh, F.A.; Touw, D.J.; Neef, C.; Vermes, I. Association of polymorphism in the cytochrome CYP2D6 and the efficacy and tolerability of simvastatin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 70, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canestaro, W.J.; Austin, M.A.; Thummel, K.E. Genetic factors affecting statin concentrations and subsequent myopathy: A HuGENet systematic review. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, E.; Madura, P.; Grandos, J.; Broncel, M.; Pawlos, A.; Wozniak, E.; Gorzelak-Pabis, P. When the same treatment has different response: The role of pharmacogenomics in statin therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 115966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, S.R.; Bravo, M.; Tootoo, J. Geosocial Factors Associated With Adherence to Statin Medications. Ann. Pharmacother. 2020, 54, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruzs, K.; Juhasz, A.; Nagy, C.; Adany, R.; Biro, K. Relationship between Statin Utilization and Socioeconomic Deprivation in Hungary. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, R.W.; Johnsen, S.P.; Olesen, A.V.; Mortensen, J.T.; Boggild, H.; Olsen, J.; Sorensen, H.T. Socioeconomic gradient in use of statins among Danish patients: Population-based cross-sectional study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 60, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D.; Padhee, S.; Sahoo, C.; Jena, S.; Sahoo, A.; Chandra Panda, P.; Nayak, S.; Ray, A. Integrating network pharmacology and experimental verification to decipher the multitarget pharmacological mechanism of Cinnamomum zeylanicum essential oil in treating inflammation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giorgi, M.; Jarrett, K.E.; Burton, J.C.; Doerfler, A.M.; Hurley, A.; Li, A.; Hsu, R.H.; Furgurson, M.; Patel, K.R.; Han, J.; et al. Depletion of essential isoprenoids and ER stress induction following acute liver-specific deletion of HMG-CoA reductase. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).