Intermittent Cold Exposure Induces Distinct Proteomic Signatures in White Adipose Tissue of Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
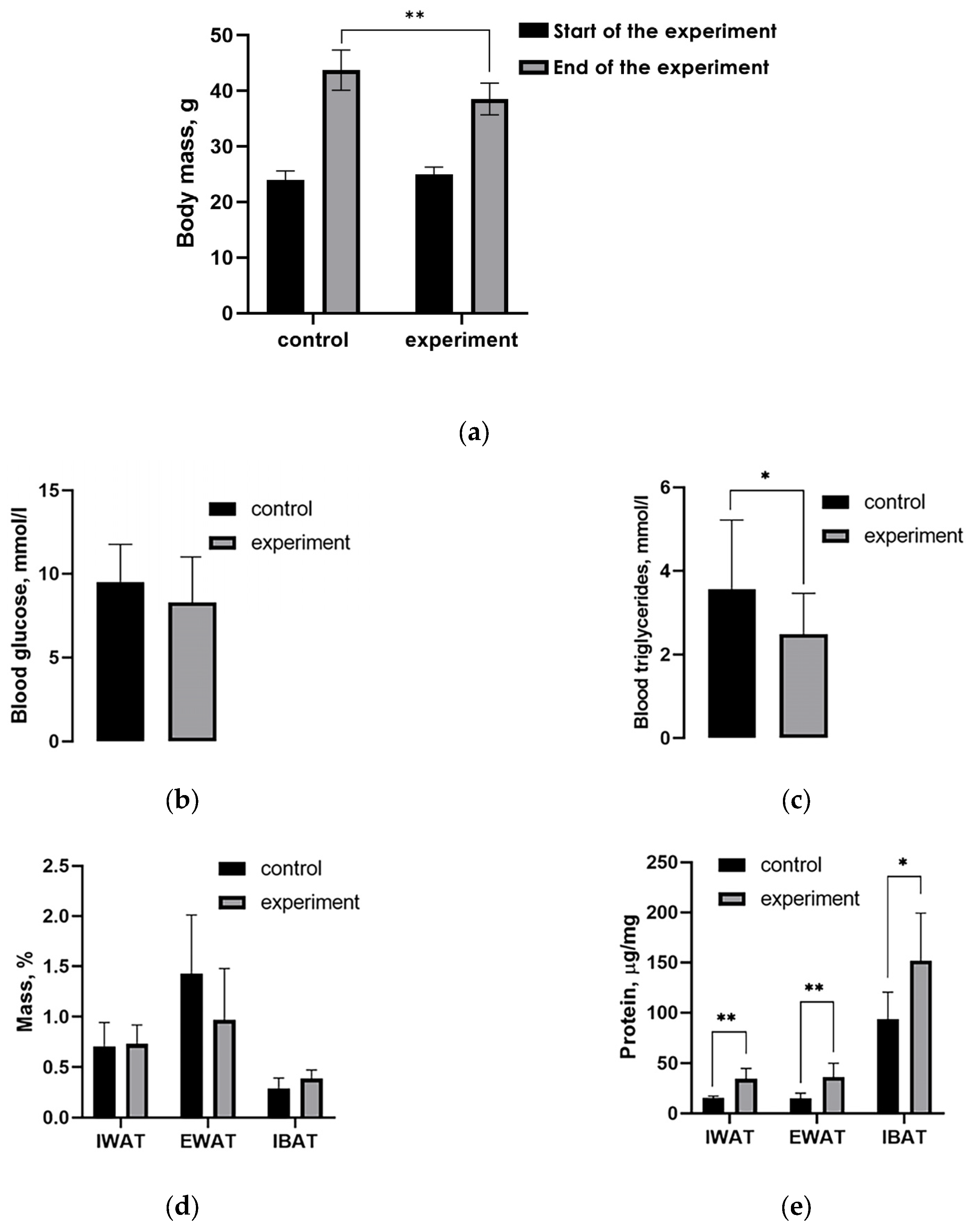
2.1. Effect of Intermittent Cold Exposures on Body Weight and Adipose Tissues
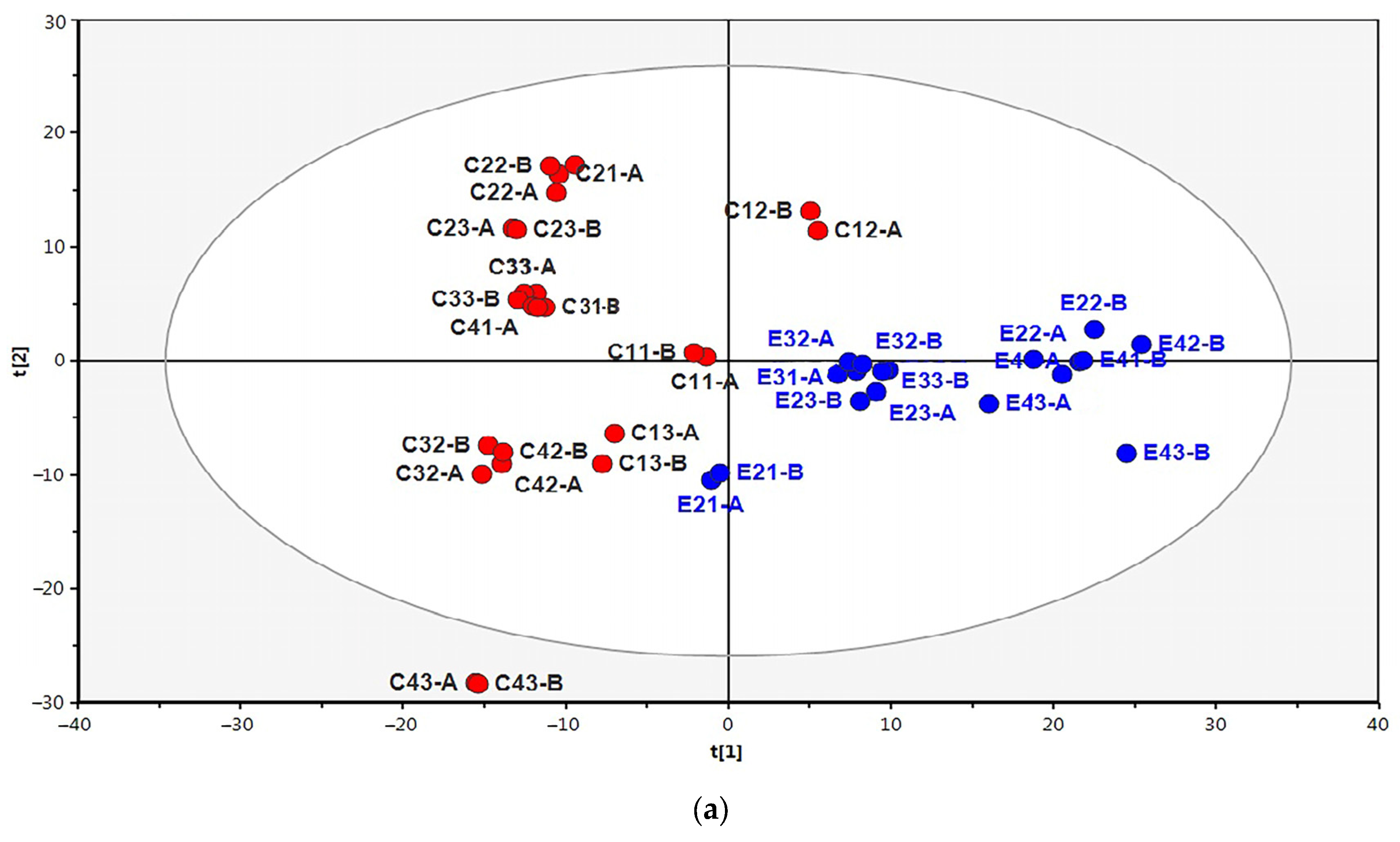
2.2. Proteomic Analysis of IWAT
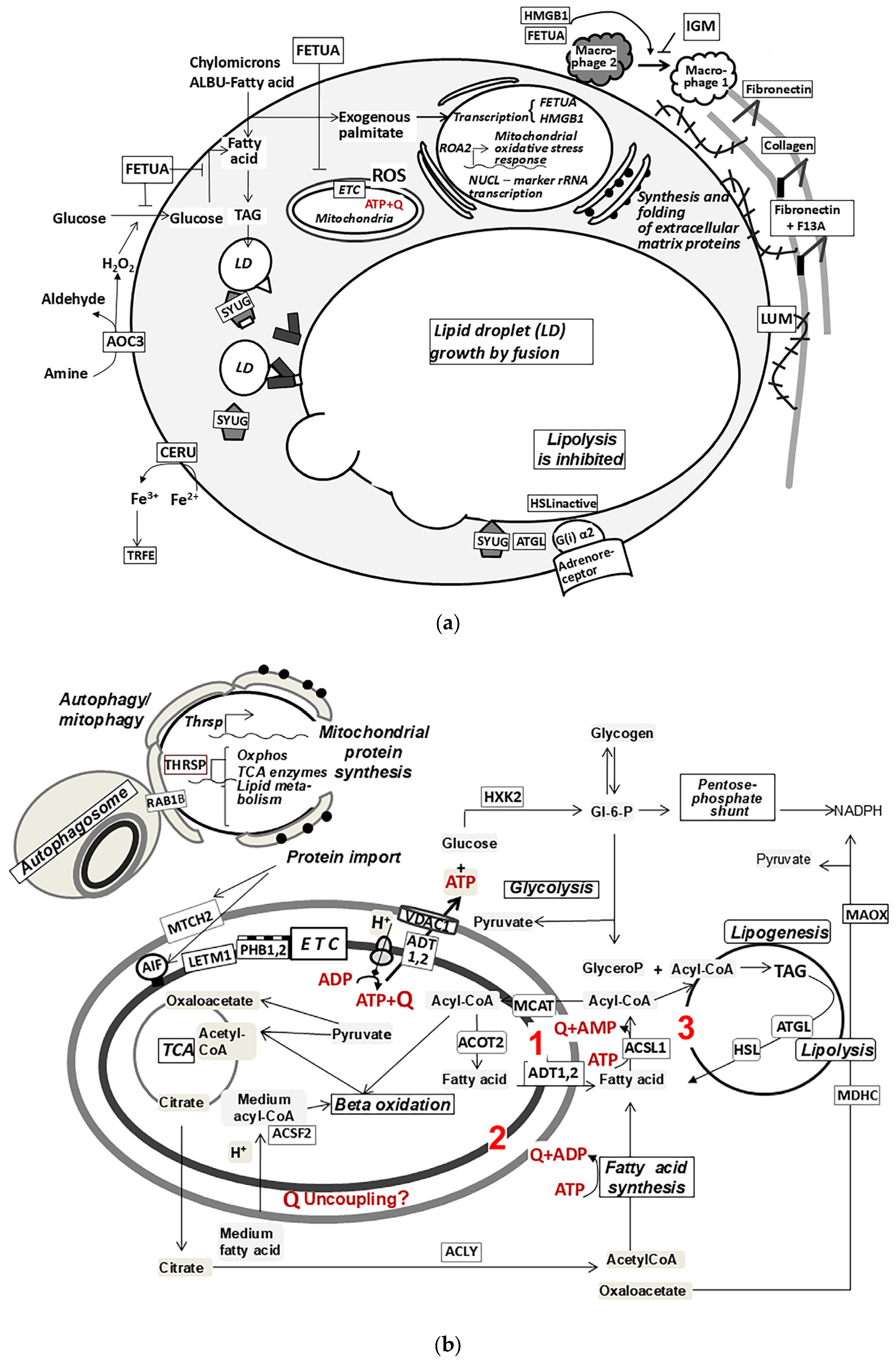
2.2.1. Functional Analysis of Up-Regulated Proteins
2.2.2. Functional Analysis of Down-Regulated Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
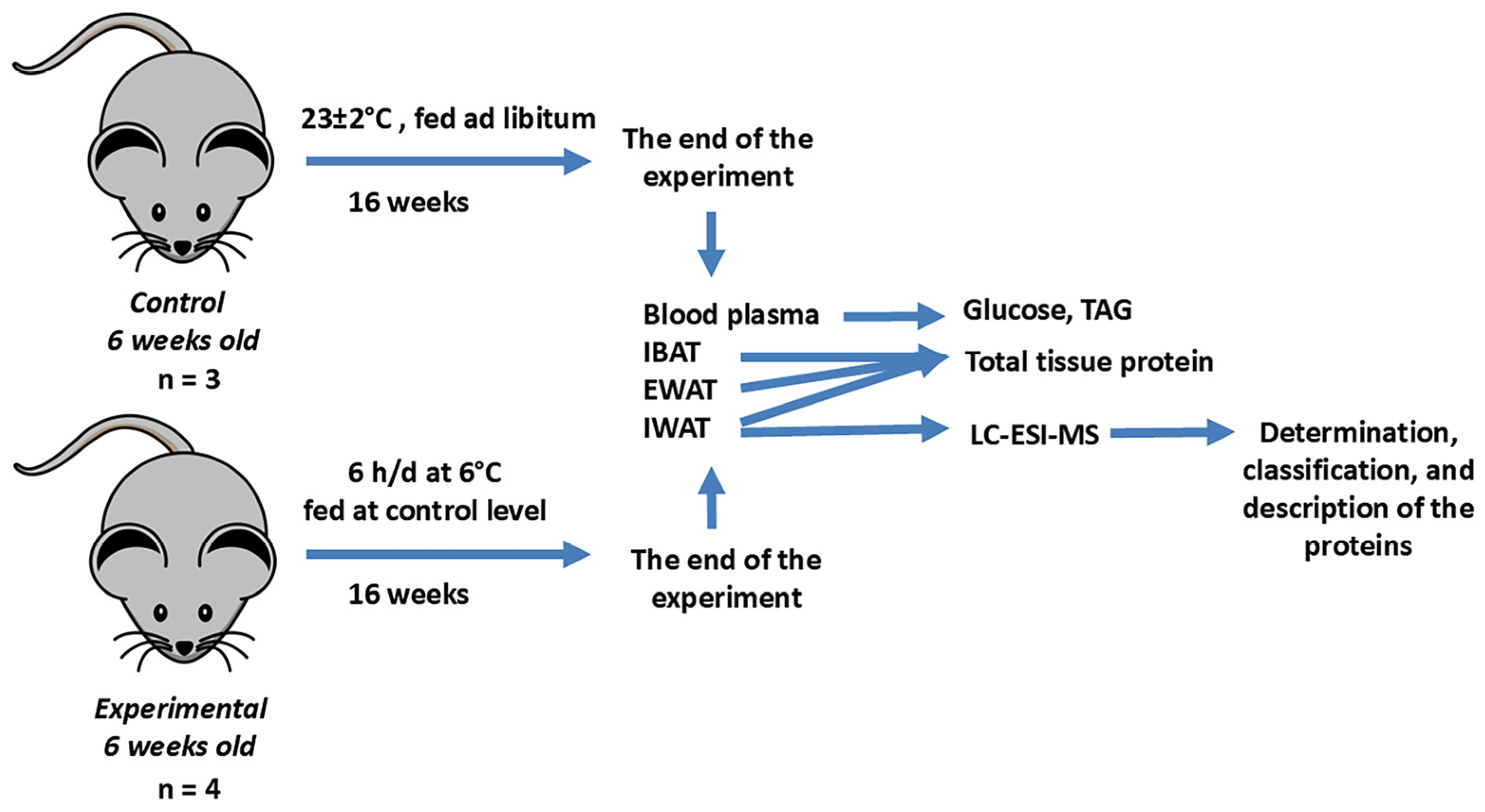
4.1. Animals and Study Design of Intermittent Cold Exposures
4.2. Total Protein Assay in Adipose Tissues
4.3. Proteomic Analysis of Inguinal Adipose Tissue
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICE | Intermittent cold exposure |
| IWAT | Inguinal white adipose tissue |
| EWAT | Epididymal white adipose tissue |
| IBAT | Interscapular brown adipose tissue |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid |
| ICR | Institute of Cancer Research |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| PMSF | Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| TBST | Tris-buffered saline solution containing Tween 20 |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| LFQ | Label-free quantification |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| PANTHER | Protein Analysis through Evolutionary Relationships |
| TAG | Triacylglycerol |
| ETC | Electron transport chain |
| EPR | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
References
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. What We Talk About When We Talk About Fat. Cell 2014, 156, 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Long, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wu, W.; Lin, Z.; Sun, W.; Gu, P.; Deng, T.; Loomes, K.M.; Wu, D.; et al. Cold-Induced Reprogramming of Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue Assessed by Single-Cell and Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing. Research 2023, 6, 0182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sárvári, A.K.; Van Hauwaert, E.L.; Markussen, L.K.; Gammelmark, E.; Marcher, A.-B.; Ebbesen, M.F.; Nielsen, R.; Brewer, J.R.; Madsen, J.G.S.; Mandrup, S. Plasticity of Epididymal Adipose Tissue in Response to Diet-Induced Obesity at Single-Nucleus Resolution. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 437–453.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalina, I.G.; Petrovic, N.; de Jong, J.M.A.; Kalinovich, A.V.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. UCP1 in Brite/Beige Adipose Tissue Mitochondria Is Functionally Thermogenic. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, A.; Murano, I.; Zingaretti, M.C.; Frontini, A.; Ricquier, D.; Cinti, S. The adipose organ of obesity-prone C57BL/6J mice is composed of mixed white and brown adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, N.H.; Landa, A.; Park, S.; Smith, R.G. Aging leads to a programmed loss of brown adipocytes in murine subcutaneous white adipose tissue. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, M.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Tan, P.-C.; Zhou, S.-B.; Li, Q.-F. Adipose tissue aging: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaum, N.; Lehallier, B.; Hahn, O.; Pálovics, R.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Lee, S.E.; Sit, R.; Lee, D.P.; Losada, P.M.; Zardeneta, M.E.; et al. Ageing hallmarks exhibit organ-specific temporal signatures. Nature 2020, 583, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, A.K.; Espelage, L.; Chadt, A. Many Ways to Rome: Exercise, Cold Exposure and Diet—Do They All Affect BAT Activation and WAT Browning in the Same Manner? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, A.; Sun, Q. Intermittent cold exposure improves glucose homeostasis associated with brown and white adipose tissues in mice. Life Sci. 2015, 139, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, Y.; Xiao, C.; Gavrilova, O.; Reitman, M.L. Effect of Intermittent Cold Exposure on Brown Fat Activation, Obesity, and Energy Homeostasis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.S.; Qiao, L.; Bosco, C.; Leong, L.-H.; Lytle, N.; Feng, G.-S.; Chi, N.-W.; Shao, J. Intermittent Cold Exposure Enhances Fat Accumulation in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ping, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, T.; Chen, G.; Ma, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, L. Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Cold Exposure and β3-AR Agonist CL316,243-Induced Browning of White Fat. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 667698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Pan, J.; Cao, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, K.; Tao, C.; Wang, Y. Transcriptional Response of Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue to Acute Cold Exposure in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, M.; Kaforou, M.; Frontini, A.; Okolo, A.; Chan, Y.-W.; Nikolopoulou, E.; Millership, S.; Fenech, M.E.; MacIntyre, D.; Turner, J.O.; et al. Brown and white adipose tissues: Intrinsic differences in gene expression and response to cold exposure in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E945–E964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; You, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Shan, T. Cold-induced lipid dynamics and transcriptional programs in white adipose tissue. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, A.; Plucińska, K.; Isidor, M.S.; Brown, E.L.; Tozzi, M.; Sidoli, S.; Petersen, P.S.S.; Agueda-Oyarzabal, M.; Torsetnes, S.B.; Chehabi, G.N.; et al. White adipose remodeling during browning in mice involves YBX1 to drive thermogenic commitment. Mol. Metab. 2021, 44, 101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinovich, A.V.; de Jong, J.M.A.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. UCP1 in adipose tissues: Two steps to full browning. Biochimie 2017, 134, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PANTHER. Available online: https://www.pantherdb.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Dewulf, J.P.; Gerin, I.; Rider, M.H.; Veiga-da-Cunha, M.; Van Schaftingen, E.; Bommer, G.T. The synthesis of branched-chain fatty acids is limited by enzymatic decarboxylation of ethyl- and methylmalonyl-CoA. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 2427–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tran, Q.; Shrestha, R.; Piao, L.; Park, S.; Park, J.; Park, J. LETM1 is required for mitochondrial homeostasis and cellular viability (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3367–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, C.; Arena, G.; Nedara, K.; Edwards, R.; Brenner, C.; Tokatlidis, K.; Modjtahedi, N. AIF meets the CHCHD4/Mia40-dependent mitochondrial import pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.J.; Miyamoto, S. Hexokinase II integrates energy metabolism and cellular protection: Akting on mitochondria and TORCing to autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guna, A.; Stevens, T.A.; Inglis, A.J.; Replogle, J.M.; Esantsi, T.K.; Muthukumar, G.; Shaffer, K.C.L.; Wang, M.L.; Pogson, A.N.; Jones, J.J.; et al. MTCH2 is a mitochondrial outer membrane protein insertase. Science 2022, 378, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, K.; Mookerjee, S.; Le Vasseur, M.; Gibbs, E.; Lerner, C.; Nunnari, J. The modified mitochondrial outer membrane carrier MTCH2 links mitochondrial fusion to lipogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202103122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millership, S.; Ninkina, N.; Guschina, I.A.; Norton, J.; Brambilla, R.; Oort, P.J.; Adams, S.H.; Dennis, R.J.; Voshol, P.J.; Rochford, J.J.; et al. Increased lipolysis and altered lipid homeostasis protect γ-synuclein–null mutant mice from diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20943–20948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Nagata, K. Biology of Hsp47 (Serpin H1), a collagen-specific molecular chaperone. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 62, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.-Y.; Hu, D.; Matsumoto, K.; Takeda, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yamamoto, K. Malectin Forms a Complex with Ribophorin I for Enhanced Association with Misfolded Glycoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38080–38089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Kuroda, A.; Kusama, K.; Matsutani, T.; Matsuda, A.; Tamura, K. Impact of serine protease inhibitor alpha1-antitrypsin on expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced proinflammatory factors in adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 100967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voong, C.K.; Goodrich, J.A.; Kugel, J.F. Interactions of HMGB Proteins with the Genome and the Impact on Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, M.; Pan, H.; Fang, J.-K.; Avadhani, N.G. Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A2 Is a Common Transcriptional Coactivator in the Nuclear Transcription Response to Mitochondrial Respiratory Stress. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 4107–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Ruiz, R.; Tercero-Alcázar, C.; López-Alcalá, J.; Sánchez-Ceinos, J.; Malagón, M.M.; Gordon, A. The potential role of the adipokine HMGB1 in obesity and insulin resistance. Novel effects on adipose tissue biology. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 536, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiss, V.; Schönsiegel, A.; Gnad, T.; Kerner, J.; Kaur, J.; Sartorius, T.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Birnbaumer, L.; Häring, H.-U.; et al. Lack of Gαi2 proteins in adipocytes attenuates diet-induced obesity. Mol. Metab. 2020, 40, 101029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, N.; Lizcano, J.M.; Fontana, E.; Marti, L.; Smih, F.; Rouet, P.; Prévot, D.; Zorzano, A.; Unzeta, M.; Carpéné, C. Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase substrates stimulate glucose transport and inhibit lipolysis in human adipocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, G.; Taranko, A.E.; Meln, I.; Weinmann, J.; Sijmonsma, T.; Lerch, S.; Heide, D.; Billeter, A.T.; Tews, D.; Krunic, D.; et al. Diet-dependent function of the extracellular matrix proteoglycan Lumican in obesity and glucose homeostasis. Mol. Metab. 2019, 19, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, V.D.; Mousa, A.; Kaartinen, M.T. Factor XIII-A transglutaminase deficient mice show signs of metabolically healthy obesity on high fat diet. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, W.C.; Schwartlander, R.; Smith, M.L.; Gourdon, D.; Vogel, V. Stretched Extracellular Matrix Proteins Turn Fouling and Are Functionally Rescued by the Chaperones Albumin and Casein. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4158–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Ruiz, R.; Tercero-Alcázar, C.; Rabanal-Ruiz, Y.; Díaz-Ruiz, A.; El Bekay, R.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.A.; Navarro-Ruiz, M.C.; Molero, L.; Membrives, A.; Ruiz-Rabelo, J.F.; et al. Adipose tissue depot-specific intracellular and extracellular cues contributing to insulin resistance in obese individuals. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7520–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekol Abebe, E.; Tilahun Muche, Z.; Behaile, T.; Mariam, A.; Mengie Ayele, T.; Mekonnen Agidew, M.; Teshome Azezew, M.; Abebe Zewde, E.; Asmamaw Dejenie, T.; Asmamaw Mengstie, M. The structure, biosynthesis, and biological roles of fetuin-A: A review. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 945287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; He, H.; Bai, Y. PPIA is a novel adipogenic factor implicated in obesity. Obesity 2015, 23, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Seal, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Kundu, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Ray, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Majumdar, S.S.; Bhattacharya, S. Adipocyte Fetuin-A Contributes to Macrophage Migration into Adipose Tissue and Polarization of Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28324–28330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, A.K.; Huang, Y.; Hertzel, A.V.; Bernlohr, D.A. Adipose oxidative stress and protein carbonylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, G.; Xu, E.; Chen, H. Ablation of hephaestin and ceruloplasmin results in iron accumulation in adipocytes and type 2 diabetes. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Ruiz, R.; Ortega, F.; Rodríguez, A.; Vázquez-Martínez, R.; Díaz-Ruiz, A.; Garcia-Navarro, S.; Giralt, M.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Cobo-Padilla, D.; Tinahones, F.J.; et al. Alarmin high-mobility group B1 (HMGB1) is regulated in human adipocytes in insulin resistance and influences insulin secretion in β-cells. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Li, X.; Scherer, P.E. Extracellular Matrix (ECM) and Fibrosis in Adipose Tissue: Overview and Perspectives. In Comprehensive Physiology; Prakash, Y.S., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 4387–4407. ISBN 978-0-470-65071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Srikakulapu, P.; McNamara, C.A. B Lymphocytes and Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, G.; McGahee, A.; Ntambi, J.M.; Simcox, J. Lipid Transport in Brown Adipocyte Thermogenesis. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 787535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markan, K.R.; Jurczak, M.J.; Brady, M.J. Stranger in a strange land: Roles of glycogen turnover in adipose tissue metabolism. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 318, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckl, J.; Janovska, P.; Adamcova, K.; Bardova, K.; Brunner, S.; Dieckmann, S.; Ecker, J.; Fromme, T.; Funda, J.; Gantert, T.; et al. Loss of UCP1 function augments recruitment of futile lipid cycling for thermogenesis in murine brown fat. Mol. Metab. 2022, 61, 101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeova, C.; Anderson-Pullinger, L.; Boye, K.; Boos, F.; Sharpadskaya, Y.; Herrmann, J.M.; Seifert, E.L. Multiple mitochondrial thioesterases have distinct tissue and substrate specificity and CoA regulation, suggesting unique functional roles. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 19034–19047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samartsev, V.N.; Rybakova, S.R.; Dubinin, M.V. Interaction of free fatty acids with mitochondria during uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. Biophysics 2013, 58, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ježek, P.; Jabůrek, M.; Porter, R.K. Uncoupling mechanism and redox regulation of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1). Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Bioenerg. 2019, 1860, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönfeld, P.; Wojtczak, L. Short- and medium-chain fatty acids in energy metabolism: The cellular perspective. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakuta, S.; Yamaguchi, J.; Suzuki, C.; Sasaki, M.; Kazuno, S.; Uchiyama, Y. Small GTPase Rab1B is associated with ATG9A vesicles and regulates autophagosome formation. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3757–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.T.; Brock, K.; Musselman, L.P. Meep, a Novel Regulator of Insulin Signaling, Supports Development and Insulin Sensitivity via Maintenance of Protein Homeostasis in Drosophila melanogaster. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020, 10, 4399–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinlaw, W.B.; Church, J.L.; Harmon, J.; Mariash, C.N. Direct Evidence for a Role of the “Spot 14” Protein in the Regulation of Lipid Synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16615–16618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahonen, M.A.; Höring, M.; Nguyen, V.D.; Qadri, S.; Taskinen, J.H.; Nagaraj, M.; Wabitsch, M.; Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liebisch, G.; et al. Insulin-inducible THRSP maintains mitochondrial function and regulates sphingolipid metabolism in human adipocytes. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, Y.; Halabi, N.; Madani, A.Y.; Engelke, R.; Bhagwat, A.M.; Abdesselem, H.; Agha, M.V.; Vakayil, M.; Courjaret, R.; Goswami, N.; et al. SIRT1 promotes lipid metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis in adipocytes and coordinates adipogenesis by targeting key enzymatic pathways. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, J.R.; Puthillathu, N.; Vengilote, R.; Jaworski, D.M.; Namboodiri, A.M. Acetate Revisited: A Key Biomolecule at the Nexus of Metabolism, Epigenetics, and Oncogenesis—Part 2: Acetate and ACSS2 in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 580171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlanmerini, M.; Carpenter, B.J.; Remsberg, J.R.; Aubert, Y.; Peed, L.C.; Richter, H.J.; Lazar, M.A. Circadian lipid synthesis in brown fat maintains murine body temperature during chronic cold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18691–18699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2025).

| Protein ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | p-Value | Corrected p-Value * | LFQE/LFQC Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9Z2I0 | LETM1 | Mitochondrial proton/calcium exchanger protein | 1.27 × 10−3 | 4.53 × 10−3 | 15.11 |
| Q9Z0X1 | AIFM1 | Apoptosis-inducing factor 1, mitochondrial | 9.68 × 10−5 | 6.53 × 10−4 | 14.5 |
| P67778 | PHB | Prohibitin | 3.25 × 10−8 | 4.38 × 10−6 | 14.13 |
| Q9D6Y9 | GLGB | 1,4-alpha-glucan-branching enzyme | 1.60 × 10−8 | 3.23 × 10−6 | 14.09 |
| O35129 | PHB2 | Prohibitin-2 | 4.18 × 10−5 | 4.03 × 10−4 | 12.63 |
| Q9CR68 | UCRI | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit Rieske, mitochondrial | 3.62 × 10−7 | 2.01 × 10−5 | 12.19 |
| Q9QZA0 | CAH5B | Carbonic anhydrase 5B, mitochondrial | 4.46 × 10−5 | 4.20 × 10−4 | 11.54 |
| Q9QYR9 | ACOT2 | Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 2, mitochondrial | 3.98 × 10−7 | 2.01 × 10−5 | 11.27 |
| Q9DC69 | NDUA9 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 9, mitochondrial | 1.73 × 10−3 | 5.90 × 10−3 | 11.18 |
| P97450 | ATP5J | ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial | 2.51 × 10−6 | 5.65 × 10−5 | 9.74 |
| Q8VCW8 | ACSF2 | Medium-chain acyl-CoA ligase ACSF2, mitochondrial | 1.33 × 10−4 | 7.84 × 10−4 | 9.45 |
| Q9D6J6 | NDUV2 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 2, mitochondrial | 1.07 × 10−4 | 6.97 × 10−4 | 9.33 |
| P06745 | G6PI | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase | 9.27 × 10−5 | 6.36 × 10−4 | 8.59 |
| Q91ZJ5 | UGPA | UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridylyl transferase | 3.13 × 10−7 | 2.01 × 10−5 | 7.46 |
| Q9DB20 | ATPO | ATP synthase subunit O, mitochondrial | 3.13 × 10−3 | 9.26 × 10−3 | 7.34 |
| Q91V76 | CK054 | Ester hydrolase C11orf54 homolog | 3.13 × 10−3 | 9.26 × 10−3 | 6.7 |
| P12787 | COX5A | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5A, mitochondrial | 5.61 × 10−6 | 9.47 × 10−5 | 6.53 |
| Q91YT0 | NDUV1 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 1, mitochondrial | 2.36 × 10−4 | 1.23 × 10−3 | 6.24 |
| Q9WUM5 | SUCA | Succinate-CoA ligase [ADP/GDP-forming] subunit alpha, mitochondrial | 1.55 × 10−5 | 1.96 × 10−4 | 6.1 |
| O08528 | HXK2 | Hexokinase-2 | 2.26 × 10−5 | 2.52 × 10−4 | 5.92 |
| Q9D1G1 | RAB1B | Ras-related protein Rab-1B | 3.62 × 10−4 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 5.65 |
| P70404 | IDHG1 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit gamma 1, mitochondrial | 4.13 × 10−6 | 7.40 × 10−5 | 5.46 |
| Q62425 | NDUA4 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit NDUFA4 | 3.42 × 10−4 | 1.67 × 10−3 | 5.46 |
| Q9QXG4 | ACSA | Acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase, cytoplasmic | 8.35 × 10−6 | 1.30 × 10−4 | 5.32 |
| Q64521 | GPDM | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 2.76 × 10−6 | 5.88 × 10−5 | 5.28 |
| Q8BKZ9 | ODPX | Pyruvate dehydrogenase protein X component, mitochondrial | 5.20 × 10−4 | 2.29 × 10−3 | 5.01 |
| P56391 | CX6B1 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B1 | 4.68 × 10−4 | 2.08 × 10−3 | 4.93 |
| Q9DBB8 | DHDH | Trans+G100dehydrogenase | 5.71 × 10−4 | 2.46 × 10−3 | 4.9 |
| Q91VD9 | NDUS1 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 75 kDa subunit, mitochondrial | 3.49 × 10−6 | 7.08 × 10−5 | 4.47 |
| Q60597 | ODO1 | 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 1.31 × 10−5 | 1.77 × 10−4 | 4.46 |
| Q921G7 | ETFD | Electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase, mitochondrial | 4.99 × 10−5 | 4.39 × 10−4 | 4.38 |
| Q8BMF4 | ODP2 | Dihydrolipoyl lysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial | 1.44 × 10−6 | 4.17 × 10−5 | 4.34 |
| P47934 | CACP | Carnitine O-acetyltransferase | 8.30 × 10−5 | 6.01 × 10−4 | 4.2 |
| P12382 | PFKAL | ATP-dependent 6-phosphofructokinase, liver type | 7.79 × 10−5 | 5.84 × 10−4 | 4.07 |
| Q9DCT2 | NDUS3 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 3, mitochondrial | 5.76 × 10−5 | 4.58 × 10−4 | 3.81 |
| P35486 | ODPA | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, somatic form, mitochondrial | 2.47 × 10−5 | 2.63 × 10−4 | 3.78 |
| Q60932 | VDAC1 | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 | 2.46 × 10−7 | 2.01 × 10−5 | 3.71 |
| Q9D2G2 | ODO2 | Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase component of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial | 6.63 × 10−4 | 2.71 × 10−3 | 3.6 |
| Q91VR2 | ATPG | ATP synthase subunit gamma, mitochondrial | 6.27 × 10−4 | 2.62 × 10−3 | 3.55 |
| Q8JZU2 | TXTP | Tricarboxylate transport protein, mitochondrial | 1.43 × 10−6 | 4.17 × 10−5 | 3.38 |
| Q91ZA3 | PCCA | Propionyl-CoA carboxylase alpha chain, mitochondrial | 3.32 × 10−3 | 9.67 × 10−3 | 3.29 |
| Q00612 | G6PD1 | Glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase X | 4.99 × 10−5 | 4.39 × 10−4 | 3.09 |
| Q8CGN5 | PLIN1 | Perilipin-1 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 7.80 × 10−4 | 2.99 |
| P50544 | ACADV | Very long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 8.94 × 10−7 | 3.62 × 10−5 | 2.97 |
| Q9ET01 | PYGL | Glycogen phosphorylase, liver form | 7.49 × 10−4 | 2.97 × 10−3 | 2.97 |
| P52825 | CPT2 | Carnitine O-palmitoyl transferase 2, mitochondrial | 2.16 × 10−3 | 6.99 × 10−3 | 2.76 |
| P06801 | MAOX | NADP-dependent malic enzyme | 2.30 × 10−5 | 2.52 × 10−4 | 2.74 |
| Q8BMS1 | ECHA | Trifunctional enzyme subunit alpha, mitochondrial | 1.07 × 10−5 | 1.58 × 10−4 | 2.68 |
| P97807 | FUMH | Fumarate hydratase, mitochondrial | 3.98 × 10−5 | 3.94 × 10−4 | 2.59 |
| Q9D051 | ODPB | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit beta, mitochondrial | 8.30 × 10−6 | 1.30 × 10−4 | 2.51 |
| P51881 | ADT2 | ADP/ATP translocase 2 | 1.10 × 10−6 | 4.05 × 10−5 | 2.5 |
| Q99MN9 | PCCB | Propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta chain, mitochondrial | 2.33 × 10−3 | 7.42 × 10−3 | 2.49 |
| Q91V92 | ACLY | ATP-citrate synthase | 4.67 × 10−10 | 1.90 × 10−7 | 2.46 |
| Q99JY0 | ECHB | Trifunctional enzyme subunit beta, mitochondrial | 3.48 × 10−5 | 3.59 × 10−4 | 2.44 |
| P00405 | COX2 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2 | 5.85 × 10−5 | 4.58 × 10−4 | 2.38 |
| P51174 | ACADL | Long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 9.29 × 10−4 | 3.58 × 10−3 | 2.38 |
| Q07417 | ACADS | Short-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 5.88 × 10−5 | 4.58 × 10−4 | 2.37 |
| Q9D9V3 | ECHD1 | Ethylmalonyl-CoA decarboxylase | 8.08 × 10−5 | 5.95 × 10−4 | 2.35 |
| P54310 | LIPS | Hormone-sensitive lipase | 1.09 × 10−3 | 4.07 × 10−3 | 2.35 |
| Q9D6R2 | IDH3A | Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit alpha, mitochondrial | 1.20 × 10−5 | 1.68 × 10−4 | 2.28 |
| Q61425 | HCDH | Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 1.04 × 10−3 | 3.94 × 10−3 | 2.17 |
| Q9CZU6 | CISY | Citrate synthase, mitochondrial | 1.36 × 10−5 | 1.78 × 10−4 | 2.12 |
| Q9D0M3 | CY1 | Cytochrome c1, heme protein, mitochondrial | 1.27 × 10−4 | 7.84 × 10−4 | 2.11 |
| Q9CZ13 | QCR1 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 1, mitochondrial | 9.15 × 10−5 | 6.36 × 10−4 | 2.1 |
| Q5SWU9 | ACACA | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 | 4.20 × 10−6 | 7.40 × 10−5 | 2.09 |
| Q8K2B3 | SDHA | Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein subunit, mitochondrial | 6.89 × 10−4 | 2.77 × 10−3 | 2.04 |
| P14152 | MDHC | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic | 1.32 × 10−3 | 4.65 × 10−3 | 2.03 |
| Q99KI0 | ACON | Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial | 1.65 × 10−5 | 2.02 × 10−4 | 2 |
| Q62264 | THRSP | Thyroid hormone-inducible hepatic protein | 3.68 × 10−4 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 1.99 |
| Q9DCD0 | 6PGD | 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating | 1.28 × 10−6 | 4.17 × 10−5 | 1.98 |
| Q9CQ62 | DECR | 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase, mitochondrial | 3.18 × 10−4 | 1.57 × 10−3 | 1.94 |
| P05064 | ALDOA | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A | 4.84 × 10−7 | 2.18 × 10−5 | 1.92 |
| P40142 | TKT | Transketolase | 3.89 × 10−7 | 2.01 × 10−5 | 1.89 |
| P62897 | CYC | Cytochrome c, somatic | 1.34 × 10−3 | 4.68 × 10−3 | 1.89 |
| O08749 | DLDH | Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 2.10 × 10−6 | 5.02 × 10−5 | 1.88 |
| P52480 | KPYM | Pyruvate kinase PKM | 2.11 × 10−6 | 5.02 × 10−5 | 1.84 |
| Q8BWT1 | THIM | 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, mitochondrial | 2.09 × 10−6 | 5.02 × 10−5 | 1.83 |
| P38647 | GRP75 | Stress-70 protein, mitochondrial | 1.57 × 10−4 | 8.59 × 10−4 | 1.81 |
| Q05920 | PYC | Pyruvate carboxylase, mitochondrial | 2.77 × 10−4 | 1.42 × 10−3 | 1.78 |
| P09411 | PGK1 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | 5.91 × 10−5 | 4.58 × 10−4 | 1.77 |
| P45952 | ACADM | Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 3.64 × 10−4 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 1.75 |
| P42125 | ECI1 | Enoyl-CoA delta isomerase 1, mitochondrial | 1.67 × 10−3 | 5.72 × 10−3 | 1.7 |
| Q9DB77 | QCR2 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 2, mitochondrial | 2.69 × 10−3 | 8.25 × 10−3 | 1.69 |
| Q9DBJ1 | PGAM1 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 | 4.03 × 10−4 | 1.83 × 10−3 | 1.61 |
| P08249 | MDHM | Malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 3.97 × 10−6 | 7.40 × 10−5 | 1.52 |
| P56480 | ATPB | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | 5.85 × 10−5 | 4.58 × 10−4 | 1.46 |
| P13707 | GPDA | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [NAD(+)], cytoplasmic | 1.81 × 10−3 | 6.05 × 10−3 | 1.46 |
| P41216 | ACSL1 | Long-chain-fatty-acid-CoA ligase 1 | 1.10 × 10−3 | 4.07 × 10−3 | 1.45 |
| P19096 | FAS | Fatty acid synthase | 1.75 × 10−3 | 5.91 × 10−3 | 1.44 |
| P20108 | PRDX3 | Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase, mitochondrial | 5.60 × 10−4 | 2.44 × 10−3 | 1.43 |
| P16858 | G3P | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 3.05 × 10−3 | 9.16 × 10−3 | 1.43 |
| Q03265 | ATPA | ATP synthase subunit alpha, mitochondrial | 1.34 × 10−4 | 7.84 × 10−4 | 1.42 |
| Q9DCW4 | ETFB | Electron transfer flavoprotein subunit beta | 3.29 × 10−3 | 9.66 × 10−3 | 1.4 |
| Q05816 | FABP5 | Fatty acid-binding protein 5 | 7.89 × 10−4 | 3.10 × 10−3 | 1.36 |
| P63038 | CH60 | 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial | 2.67 × 10−3 | 8.25 × 10−3 | 1.3 |
| P48962 | ADT1 | ADP/ATP translocase 1 | 1.30 × 10−4 | 7.84 × 10−4 | Presented in experimental group only |
| Q9Z2Z6 | MCAT | Mitochondrial carnitine/acylcarnitine carrier protein | 1.46 × 10−4 | 8.20 × 10−4 | |
| Q791V5 | MTCH2 | Mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 | 1.57 × 10−4 | 8.59 × 10−4 | |
| Q6P3A8 | ODBB | 2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase subunit beta, mitochondrial | 8.57 × 10−4 | 3.34 × 10−3 | |
| Q8BJ56 | PLPL2 | Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 2 | 9.55 × 10−4 | 3.65 × 10−3 | |
| Q99LC3 | NDUAA | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 10, mitochondrial | 1.23 × 10−3 | 4.47 × 10−3 |
| Protein ID | Gene Name | Protein Name | p-Value | Corrected p-Value * | LFQC/LFQE Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q91X72 | HEMO | Hemopexin | 1.09 × 10−5 | 1.58 × 10−4 | 1.911 |
| P19324 | SERPH | Serpin H1 | 1.79 × 10−5 | 2.13 × 10−4 | 3.432 |
| Q00896 | A1AT3 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin 1-3 | 1.90 × 10−5 | 2.20 × 10−4 | 2.960 |
| P51885 | LUM | Lumican | 3.55 × 10−5 | 3.59 × 10−4 | 1.360 |
| P20029 | BIP | Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | 4.74 × 10−5 | 3.90 × 10−4 | 1.567 |
| P21614 | VTDB | Vitamin D-binding protein | 5.21 × 10−5 | 4.51 × 10−4 | 2.086 |
| P22599 | A1AT2 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin 1-2 | 5.99 × 10−5 | 5.13 × 10−4 | 2.663 |
| P08113 | ENPL | Endoplasmin | 9.06 × 10−5 | 5.74 × 10−4 | 1.860 |
| P11499 | HS90B | Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta | 8.88 × 10−5 | 6.35 × 10−4 | 1.447 |
| P27773 | PDIA3 | Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 | 9.92 × 10−5 | 6.96 × 10−4 | 1.744 |
| P40124 | CAP1 | Adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 | 1.10 × 10−4 | 7.57 × 10−4 | 1.560 |
| O89053 | COR1A | Coronin-1A | 1.20 × 10−4 | 8.18 × 10−4 | 1.495 |
| P13020 | GELS | Gelsolin | 1.31 × 10−4 | 8.79 × 10−4 | 2.033 |
| Q60605 | MYL6 | Myosin light polypeptide 6 | 1.41 × 10−4 | 9.40 × 10−4 | 1.557 |
| P06728 | APOA4 | Apolipoprotein A-IV | 1.52 × 10−4 | 1.00 × 10−3 | 3.061 |
| P09405 | NUCL | Nucleolin | 1.62 × 10−4 | 1.06 × 10−3 | 1.345 |
| Q921I1 | TRFE | Serotransferrin | 1.73 × 10−4 | 1.12 × 10−3 | 1.754 |
| P07724 | ALBU | Albumin | 1.83 × 10−4 | 1.18 × 10−3 | 1.708 |
| P18760 | COF1 | Cofilin-1 | 1.93 × 10−4 | 1.25 × 10−3 | 1.370 |
| O08677 | KNG1 | Kininogen-1 | 2.04 × 10−4 | 1.31 × 10−3 | 1.526 |
| O88569 | ROA2 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1 | 2.14 × 10−4 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 1.478 |
| P09103 | PDIA1 | Protein disulfide-isomerase | 2.25 × 10−4 | 1.43 × 10−3 | 1.542 |
| P63158 | HMGB1 | High mobility group protein B1 | 2.35 × 10−4 | 1.49 × 10−3 | 3.579 |
| P63101 | 1433Z | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | 2.46 × 10−4 | 1.55 × 10−3 | 1.413 |
| P07901 | HS90A | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | 2.56 × 10−4 | 1.61 × 10−3 | 1.343 |
| P63017 | HSP7C | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein | 2.67 × 10−4 | 1.67 × 10−3 | 1.235 |
| P60710 | ACTB | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | 2.77 × 10−4 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 1.407 |
| Q8BH61 | F13A | Coagulation factor XIII A chain | 2.88 × 10−4 | 1.80 × 10−3 | 2.652 |
| P29699 | FETUA | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | 2.98 × 10−4 | 1.86 × 10−3 | 2.498 |
| O70423 | AOC3 | Membrane primary amine oxidase | 3.09 × 10−4 | 1.92 × 10−3 | 1.375 |
| P08752 | GNAI2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-2 | 3.19 × 10−4 | 1.98 × 10−3 | 1.309 |
| P16015 | CAH3 | Carbonic anhydrase 3 | 3.30 × 10−4 | 2.04 × 10−3 | 1.424 |
| P17742 | PPIA | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A | 3.40 × 10−4 | 2.10 × 10−3 | 1.374 |
| Q00623 | APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I | 2.13 × 10−3 | 6.96 × 10−3 | 0.447 |
| Q9Z0F7 | SYUG | Gamma-synuclein | 3.50 × 10−4 | 2.16 × 10−3 | Presented in control group only |
| P01872 | IGHM | Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu | 3.61 × 10−4 | 2.22 × 10−3 | 16.667 |
| Q91YQ5 | RPN1 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide-protein glycosyltransferase subunit 1 | 3.71 × 10−4 | 2.29 × 10−3 | 10.145 |
| Q61147 | CERU | Ceruloplasmin | 3.82 × 10−4 | 2.35 × 10−3 | 10.653 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsukova, E.; Zamay, T.; Kichkailo, A.; Yakunenkov, A.; Veprintsev, D.V.; Minic, Z.; Berezovski, M.V.; Glazyrin, Y. Intermittent Cold Exposure Induces Distinct Proteomic Signatures in White Adipose Tissue of Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167898
Elsukova E, Zamay T, Kichkailo A, Yakunenkov A, Veprintsev DV, Minic Z, Berezovski MV, Glazyrin Y. Intermittent Cold Exposure Induces Distinct Proteomic Signatures in White Adipose Tissue of Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167898
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsukova, Elena, Tatiana Zamay, Anna Kichkailo, Andrey Yakunenkov, Dmitry V. Veprintsev, Zoran Minic, Maxim V. Berezovski, and Yury Glazyrin. 2025. "Intermittent Cold Exposure Induces Distinct Proteomic Signatures in White Adipose Tissue of Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167898
APA StyleElsukova, E., Zamay, T., Kichkailo, A., Yakunenkov, A., Veprintsev, D. V., Minic, Z., Berezovski, M. V., & Glazyrin, Y. (2025). Intermittent Cold Exposure Induces Distinct Proteomic Signatures in White Adipose Tissue of Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167898











