SALL2-Mediated Suppression of WNT Signaling Through Transcriptional Control of AXIN2 in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
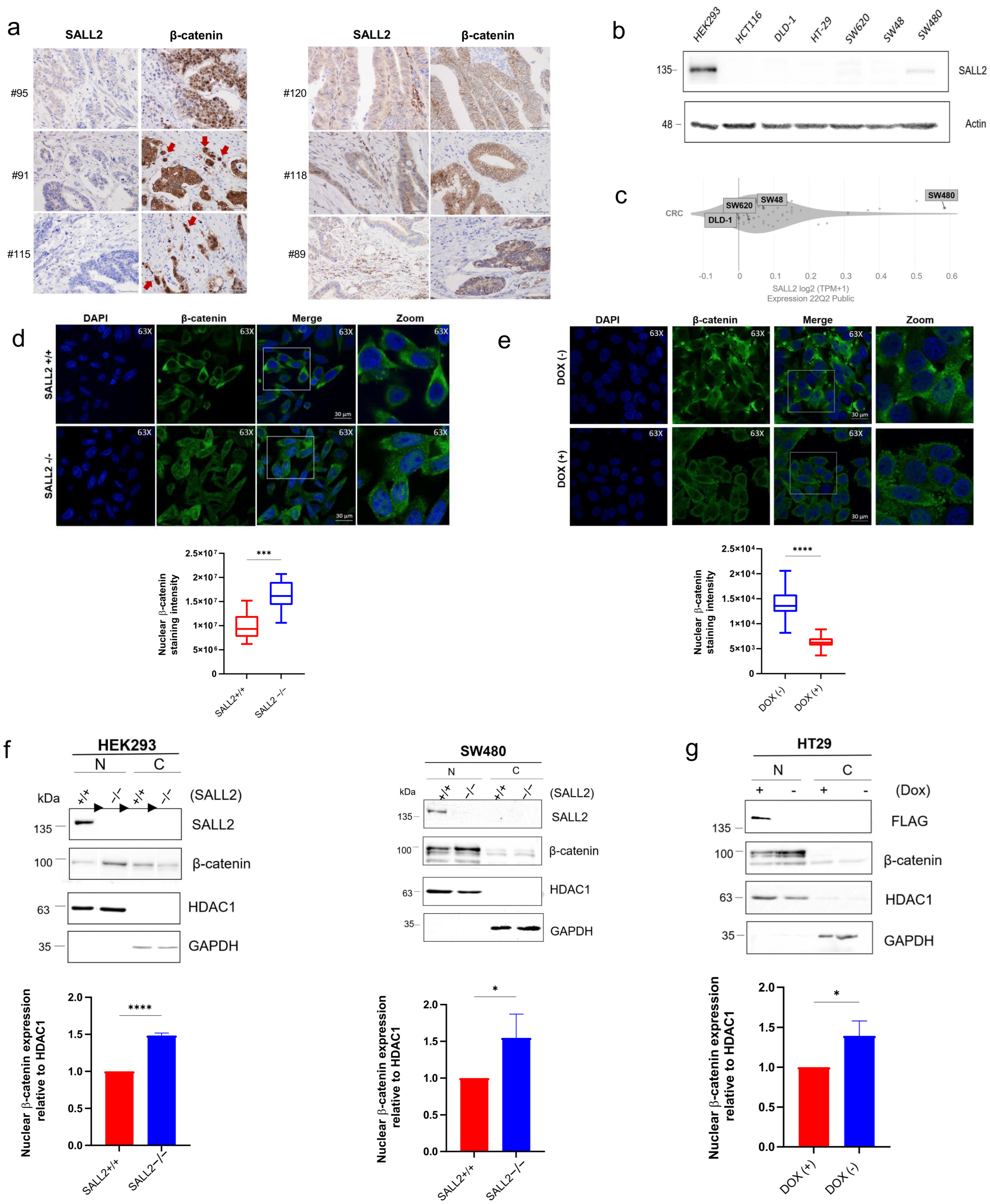
2.1. SALL2 Is Expressed in Normal Colon but Is Downregulated in Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
2.2. The Loss of SALL2 Is Associated with an Increase in Nuclear β-Catenin in CRC Cells and Tissue Samples
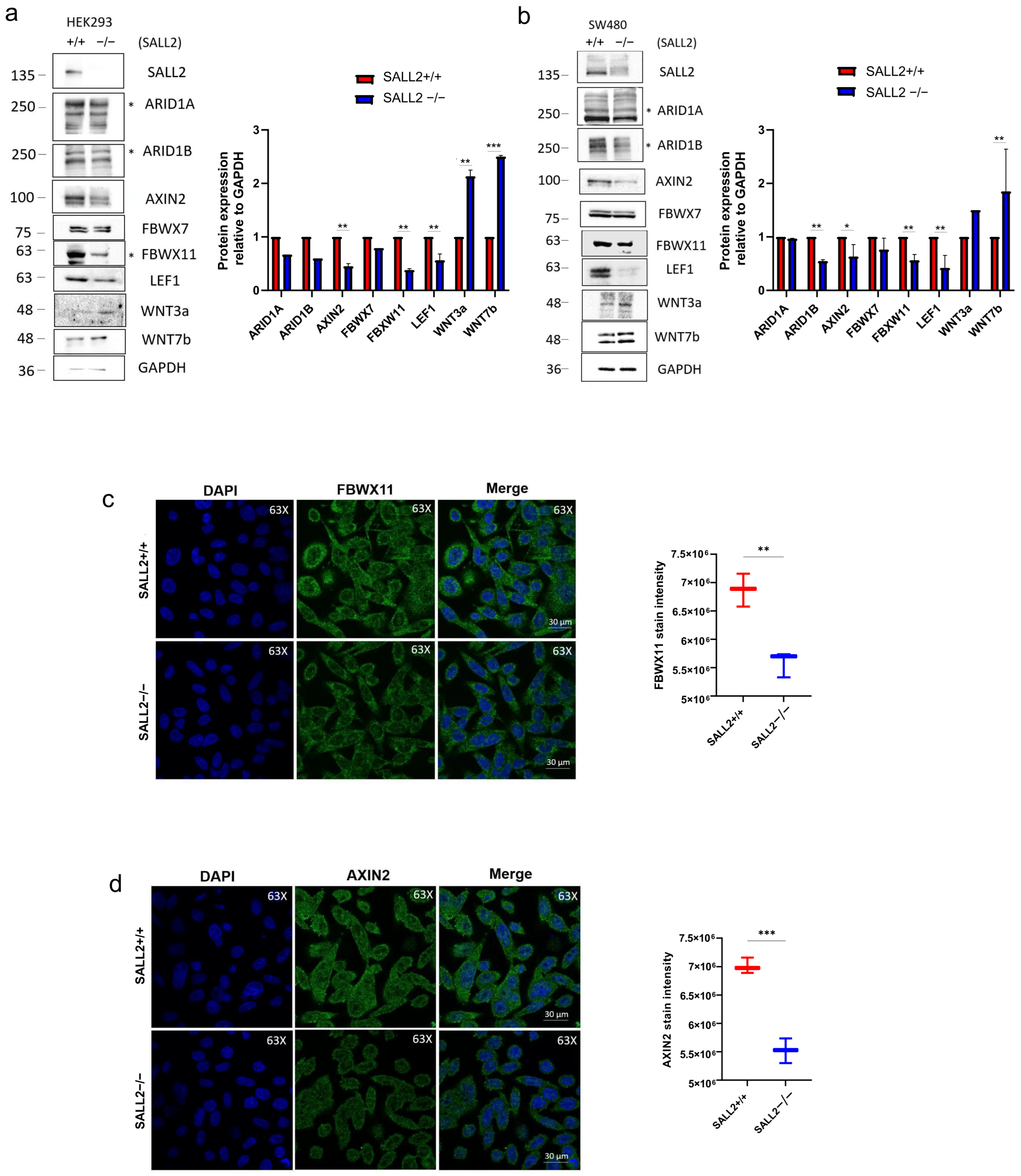
2.3. SALL2 Is an Antagonistic Mediator of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in CRC Cells
2.4. The Expression of the Wnt/β-Catenin Regulator AXIN2 Depends on SALL2 Expression
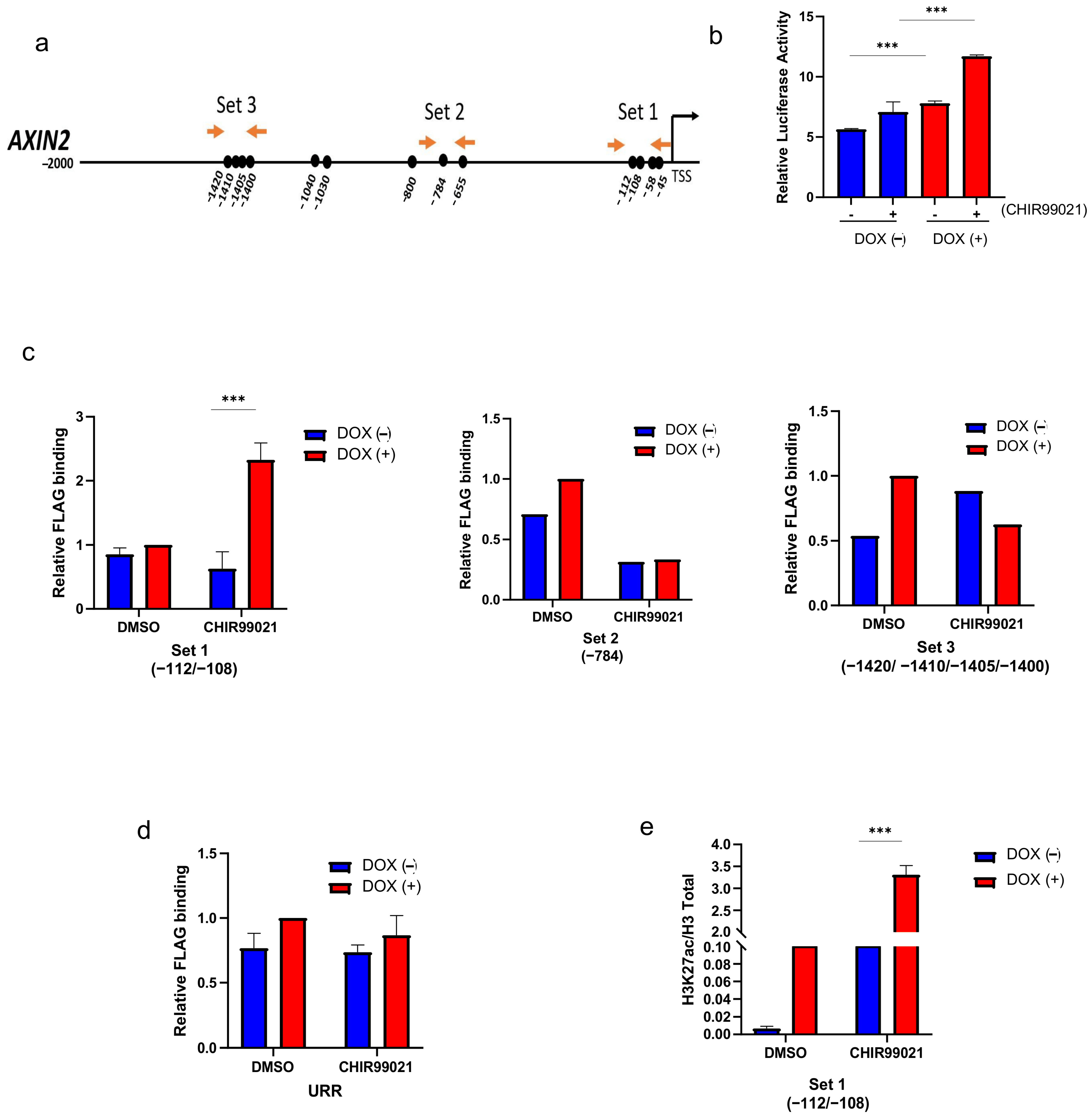
2.5. SALL2 Attenuates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling by Directly Transactivating the AXIN2 Promoter in CRC Cells
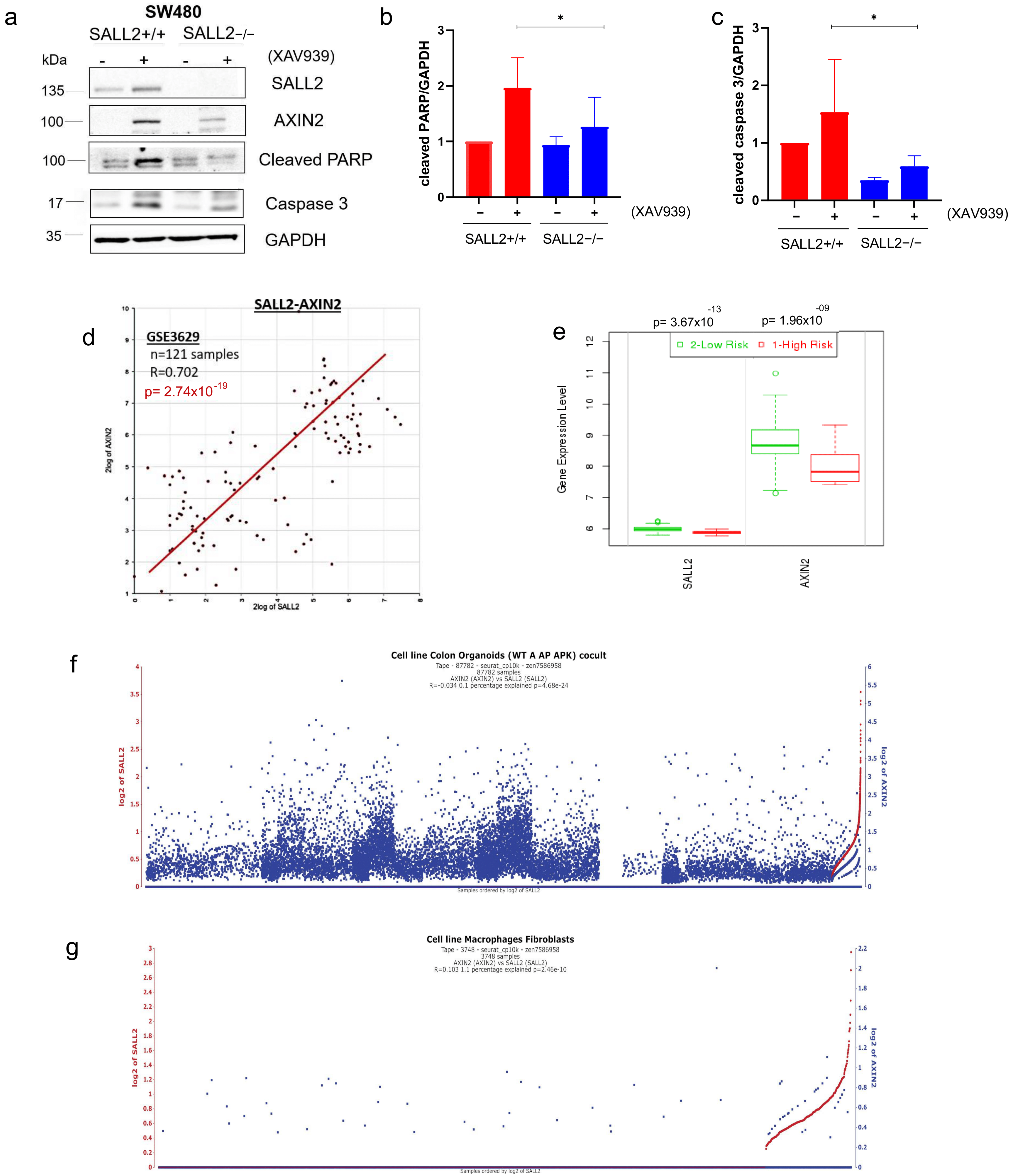
2.6. Suppression of Wnt Signaling by XAV939 Increased CRC Apoptosis in a SALL2-Dependent Manner
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.2. Patients and Tissue Microarray Construction
4.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.4. Multiplexed Immunofluorescence (mIF)
4.5. IHC Analysis
4.6. Agar-Cyto IHC
4.7. Cell Culture and Lentiviral Transduction
Generation of pCW57 Tet-On FLAGSALL2E1A
4.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.9. Subcellular Fractionation
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription
4.12. Luciferase Reporter Gene
4.13. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay (ChIP Assay)
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, J.; Eycken, E.V.; Rous, B.A.; Giuliani, M.; O’Sullivan, B. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; ISBN 1394216858. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.H.; Lin, J.K.; Chang, S.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Chang, H.M.; Liu, J.H.; Li, L.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Tsai, S.F.; Chen, W.S. Molecular profile and copy number analysis of sporadic colorectal cancer in Taiwan. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Cui, B. Comprehensive Analysis of Subtype-Specific Molecular Characteristics of Colon Cancer: Specific Genes, Driver Genes, Signaling Pathways, and Immunotherapy Responses. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 758776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menter, D.G.; Davis, J.S.; Broom, B.M.; Overman, M.J.; Morris, J.; Kopetz, S. Back to the Colorectal Cancer Consensus Molecular Subtype Future. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2019, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanki, K.; Nicholls, M.E.; Gomez, G.; Gajjar, A.; Senagore, A.J.; Rashidi, L.; Qiu, S.; Szabo, C.; Hellmich, M.R.; Chao, C. Consensus Molecular Subtypes of Colorectal Cancer and their Clinical Implications. Int. Biol. Biomed. J. 2017, 3, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrckulak, D.; Kolar, M.; Strnad, H.; Korinek, V. TCF/LEF transcription factors: An update from the internet resources. Cancers 2016, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiheisel, A.; Kaur, M.; Ma, N.; Havard, P.; Shenoy, A.K. Wnt pathway modulators in cancer therapeutics: An update on completed and ongoing clinical trials. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, V.E.; Hepp, M.I.; Escobar, D.; Farkas, C.; Riffo, E.N.; Castro, A.F.; Pincheira, R. Developmental SALL2 transcription factor: A new player in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, C.; Quiroz, A.; Alvarez, C.; Hermosilla, V.; Aylwin, C.F.; Lomniczi, A.; Castro, A.F.; Hepp, M.I.; Pincheira, R. Characterization of SALL2 Gene Isoforms and Targets Across Cell Types Reveals Highly Conserved Networks. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 613808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.K.; Li, D.; Andrews, E.; Drapkin, R.; Benjamin, T. Promoter methylation of the SALL2 tumor suppressor gene in ovarian cancers. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Lin, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, X.; Shi, D.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of SALL 2 confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. EMBO J. 2019, 11, e10638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, C.; Quiroz, A.; Benítez-Riquelme, D.; Pincheira, R.; Riffo, E.; Castro, A.F. SALL proteins; common and antagonistic roles in cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, V.; Salgado, G.; Riffo, E.; Escobar, D.; Hepp, M.I.; Farkas, C.; Galindo, M.; Morín, V.; García-Robles, M.A.; Castro, A.F.; et al. SALL2 represses cyclins D1 and E1 expression and restrains G1/S cell cycle transition and cancer-related phenotypes. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1026–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tian, Y.; Ma, Y.; Benjamin, T. p150 (Sal2) is a p53-independent regulator if p21 (WAF/CIP). Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 3885–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, K.; Shi, L.; Li, Z.; Negi, H.; Gao, G.; Kamle, S.; Li, D. Sal-like protein 2 upregulates p16 expression through a proximal promoter element. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, D.; Hepp, M.I.; Farkas, C.; Campos, T.; Sodir, N.M.; Morales, M.; Álvarez, C.I.; Swigart, L.; Evan, G.I.; Gutiérrez, J.L.; et al. Sall2 is required for proapoptotic Noxa expression and genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis by doxorubicin. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvà, M.L.; Rheinbay, E.; Gillespie, S.M.; Patel, A.P.; Wakimoto, H.; Rabkin, S.D.; Riggi, N.; Chi, A.S.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; et al. Reconstructing and reprogramming the tumor-propagating potential of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cell 2014, 157, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onai, T.; Sasai, N.; Matsui, M.; Sasai, Y. Xenopus XsalF: Anterior neuroectodermal specification by attenuating cellular responsiveness to Wnt signaling. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Xiao, G.; Hu, J. Regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by posttranslational modifications. Cell Biosci. 2014, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermosilla, V.E.; Gyenis, L.; Rabalski, A.J.; Armijo, M.E.; Sepúlveda, P.; Duprat, F.; Benítez-Riquelme, D.; Fuentes-Villalobos, F.; Quiroz, A.; Hepp, M.I.; et al. Casein kinase 2 phosphorylates and induces the SALL2 tumor suppressor degradation in colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnerts, M.E.; Kim, K.-A.; Bright, J.M.; Patel, S.M.; Tran, K.; Zhou, M.; Leung, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Lomas, W.E.; Dixon, M.; et al. R-Spondin1 regulates Wnt signaling by inhibiting internalization of LRP6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14700–14705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, G.; Goessling, W.; North, T.E.; Xavier, R.; Zon, L.I.; Yajnik, V. Molecular association between β-catenin degradation complex and Rac guanine exchange factor DOCK4 is essential for Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5845–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkopf, D.B.; Brückner, M.; Hadjihannas, M.V.; Behrens, J. An aggregon in conductin/axin2 regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and holds potential for cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jho, E.; Zhang, T.; Domon, C.; Joo, C.-K.; Freund, J.-N.; Costantini, F. Wnt/β-Catenin/Tcf Signaling Induces the Transcription of Axin2, a Negative Regulator of the Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, C.; Piemontese, M.; Lumetti, S.; Manfredi, E.; Macaluso, G.M.; Passeri, G. GSK3b-inhibitor lithium chloride enhances activation of Wnt canonical signaling and osteoblast differentiation on hydrophilic titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Khan, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Tu, X. A Highly Selective GSK-3β Inhibitor CHIR99021 Promotes Osteogenesis by Activating Canonical and Autophagy-Mediated Wnt Signaling. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 926622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makola, R.T.; Kgaladi, J.; More, G.K.; van Vuren, P.J.; Paweska, J.T.; Matsebatlela, T.M. Lithium inhibits NF-κB nuclear translocation and modulate inflammation profiles in Rift valley fever virus-infected Raw 264.7 macrophages. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, H.H.; Yong, T.-S.; Jeon, S.-H. Lithium chloride inhibits the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by blocking nuclear translocation of phospho-Erk. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 581, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riffo, E.; Palma, M.; Hepp, M.I.; Benítez-Riquelme, D.; Torres, V.A.; Castro, A.F.; Pincheira, R. The Sall2 transcription factor promotes cell migration regulating focal adhesion turnover and integrin β1 expression. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1031262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Li, D.; Sung, C.K.; Yim, H.; Troke, P.; Benjamin, T. DNA-binding and regulatory properties of the transcription factor and putative tumor suppressor p150Sal2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2011, 1809, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.Y.; Kolligs, F.T.; Wu, R.; Zhai, Y.; Kuick, R.; Hanash, S.; Cho, K.R.; Fearon, E.R. Activation of AXIN2 expression by β-catenin-T cell factor: A feedback repressor pathway regulating Wnt signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21657–21665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantzali, E.; Schulz, H.; Hummel, O.; Hubner, N.; Hatzopoulos, A.K.; Kretsovali, A. Histone deacetylase inhibition accelerates the early events of stem cell differentiation: Transcriptomic and epigenetic analysis. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, D.; Malatesta, M.; Jung, H.R.; Walfridsson, J.; Willer, A.; Olsson, L.; Skotte, J.; Wutz, A.; Porse, B.; Jensen, O.N.; et al. Characterization of an antagonistic switch between histone H3 lysine 27 methylation and acetylation in the transcriptional regulation of Polycomb group target genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 4958–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Christova, T.; Song, S.; Angers, S.; Yan, X.; Attisano, L. Inhibition of Tankyrases Induces Axin Stabilization and Blocks Wnt Signalling in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.M.A.; Mishina, Y.M.; Liu, S.; Cheung, A.; Stegmeier, F.; Michaud, G.A.; Charlat, O.; Wiellette, E.; Zhang, Y.; Wiessner, S.; et al. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature 2009, 461, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Deng, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, D.; Yu, Q.-X.; Yang, X.; Lei, T.-Y.; Han, J.; Pan, M.; Zhen, L.; et al. AXIN2 gene silencing reduces apoptosis through regulating mitochondria-associated apoptosis signaling pathway and enhances proliferation of ESCs by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Luo, F.; Li, J.; Zhong, X.; Liu, K. Tankyrase 1 inhibitior XAV939 increases chemosensitivity in colon cancer cell lines via inhibition of the Wnt signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Rodriguez, F.C.; Sufi, J.; Vlckova, P.; Claus, J.; Tape, C.J. An oncogenic phenoscape of colonic stem cell polarization. Cell 2023, 186, 5554–5568.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Arman, B.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, C.K.; Yim, H.; Gu, H.; Li, D.; Andrews, E.; Duraisamy, S.; Li, C.; Drapkin, R.; Benjamin, T. The Polyoma Virus Large T Binding Protein p150 Is a Transcriptional Repressor of c-MYC. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincheira, R.; Baerwald, M.; Dunbar, J.D.; Donner, D.B. Sall2 is a novel p75NTR-interacting protein that links NGF signalling to cell cycle progression and neurite outgrowth. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Shi, S.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Xu, D.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Xi, Y. A pan-cancer study of spalt-like transcription factors 1/2/3/4 as therapeutic targets. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 711, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.C.d.M.e.; Faletti, A.; Veríssimo, C.P.; Stelling, M.P.; Borges, H.L. p53 Signaling on Microenvironment and Its Contribution to Tissue Chemoresistance. Membranes 2022, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Dannappel, M.; Wan, C.; Firestein, R. Transcriptional Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Kishida, S.; Tanaka, T.; Kikuchi, A.; Kodama, T.; Asashima, M.; Nishinakamura, R. Sall1, a causative gene for Townes–Brocks syndrome, enhances the canonical Wnt signaling by localizing to heterochromatin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 319, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, L.; Zheng, P.S. SALL4 promotes the tumorigenicity of cervical cancer cells through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway via CTNNB1. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2794–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, F.; Han, B.; Zhong, X.; Si, F.; Ye, J.; Hsueh, E.C.; Robbins, L.; Kiefer, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. SALL1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by regulating cancer cell senescence and metastasis through the NuRD complex. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yi, K.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z. The Invasion and Metastasis of Colon Adenocarcinoma (COAD) Induced by SALL4. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkopf, D.B.; Hadjihannas, M.V.; Behrens, J. Negative feedback regulation of the Wnt pathway by conductin/AXIN2 involves insensitivity to upstream signalling. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 128, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelberman, D.; Islam, L.; Lakowski, J.; Bacchelli, C.; Chanudet, E.; Lescai, F.; Patel, A.; Stupka, E.; Buck, A.; Wolf, S.; et al. Mutation of SALL2 Causes Recessive Ocular Coloboma in Humans and Mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 2511–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koinuma, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Liu, W.; Hatanaka, H.; Kurashina, K.; Wada, T.; Takada, S.; Kaneda, R.; Choi, Y.L.; Fujiwara, S.-I.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of AXIN2 in colorectal carcinoma with microsatellite instability. Oncogene 2006, 25, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.; Chen, H.; Wong, C.C.; Peng, Y.; Gou, H.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, D.; Lin, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. ALKBH5 Drives Immune Suppression Via Targeting AXIN2 to Promote Colorectal Cancer and Is a Target for Boosting Immunotherapy. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, D.; Sun, X.; Yang, K.; Yao, J.; Cheng, C.; Wang, C.; Zheng, J. CDX2 inhibits the proliferation and tumor formation of colon cancer cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling via transactivation of GSK-3β and Axin2 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.-K.; Mashima, T.; Seimiya, H. Tankyrase Inhibitors Target Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells via AXIN-Dependent Downregulation of c-KIT Tyrosine Kinase. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Lavrijsen, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, S.; van de Geer, W.S.; van de Werken, H.J.G.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Smits, R. Evaluation of AXIN1 and AXIN2 as targets of tankyrase inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-Q.; Brabletz, T.; Fearon, E.; Willis, A.L.; Hu, C.Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Weiss, S.J. Canonical Wnt suppressor, Axin2, promotes colon carcinoma oncogenic activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11312–11317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaal, U.; Grenz, S.; Merkel, S.; Rau, T.T.; Hadjihannas, M.V.; Kremmer, E.; Chudasama, P.; Croner, R.S.; Behrens, J.; Stürzl, M.; et al. Expression and localization of axin 2 in colorectal carcinoma and its clinical implication. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2013, 28, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennoll, S.A.; Konsavage, W.M.; Yochum, G.S. Nuclear AXIN2 represses MYC gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stakheev, D.; Taborska, P.; Strizova, Z.; Podrazil, M.; Bartunkova, J.; Smrz, D. The WNT/β-catenin signaling inhibitor XAV939 enhances the elimination of LNCaP and PC-3 prostate cancer cells by prostate cancer patient lymphocytes in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorvaldsen, T.E.; Pedersen, N.M.; Wenzel, E.M.; Stenmark, H. Differential roles of AXIN1 and AXIN2 in tankyrase inhibitor-induced formation of degradasomes and β-catenin degradation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waaler, J.; Machon, O.; Tumova, L.; Dinh, H.; Korinek, V.; Wilson, S.R.; Paulsen, J.E.; Pedersen, N.M.; Eide, T.J.; Machonova, O.; et al. A novel tankyrase inhibitor decreases canonical Wnt signaling in colon carcinoma cells and reduces tumor growth in conditional APC mutant mice. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2822–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Talbot, C.C.; Liu, Q.; Jing, Z.-C.; Damico, R.L.; Tuder, R.; Barnes, K.C.; Hassoun, P.M.; Gao, L. Identifying microRNAs targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in end-stage idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joanito, I.; Wirapati, P.; Zhao, N.; Nawaz, Z.; Yeo, G.; Lee, F.; Eng, C.L.P.; Macalinao, D.C.; Kahraman, M.; Srinivasan, H.; et al. Single-cell and bulk transcriptome sequencing identifies two epithelial tumor cell states and refines the consensus molecular classification of colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, M.I.; Escobar, D.; Farkas, C.; Hermosilla, V.E.; Álvarez, C.; Amigo, R.; Gutiérrez, J.L.; Castro, A.F.; Pincheira, R. A Trichostatin A (TSA)/Sp1-mediated mechanism for the regulation of SALL2 tumor suppressor in Jurkat T cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2018, 1861, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereceda, K.; Bravo, N.; Jorquera, R.; González-Stegmaier, R.; Villarroel-Espíndola, F. Simultaneous and Spatially-Resolved Analysis of T-Lymphocytes, Macrophages and PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint in Rare Cancers. Cancers 2022, 14, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Morilla, S.; Villarroel-Espindola, F.; Wong, P.F.; Toki, M.I.; Aung, T.N.; Pelekanou, V.; Bourke-Martin, B.; Schalper, K.A.; Kluger, H.M.; Rimm, D.L. Biomarker discovery in patients with immunotherapy-treated melanoma with imaging mass cytometry. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1987–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galera-Ruiz, H.; Ríos, M.J.; González-Cámpora, R.; de Miguel, M.; Carmona, M.I.; Moreno, A.M.; Galera-Davidson, H. The cadherin–catenin complex in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2011, 268, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palma, M.; Riffo, E.N.; Suganuma, T.; Washburn, M.P.; Workman, J.L.; Pincheira, R.; Castro, A.F. Identification of a nuclear localization signal and importin beta members mediating NUAK1 nuclear import inhibited by oxidative stress. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16088–16107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quiroz, A.; Escalona, E.; Farkas, C.; Benítez-Riquelme, D.; Sepúlveda, P.; Palma, M.; Medina, P.; Delgado, C.; Hepp, M.I.; Villarroel-Espindola, F.; et al. SALL2-Mediated Suppression of WNT Signaling Through Transcriptional Control of AXIN2 in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167896
Quiroz A, Escalona E, Farkas C, Benítez-Riquelme D, Sepúlveda P, Palma M, Medina P, Delgado C, Hepp MI, Villarroel-Espindola F, et al. SALL2-Mediated Suppression of WNT Signaling Through Transcriptional Control of AXIN2 in Colorectal Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167896
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuiroz, Aracelly, Emilia Escalona, Carlos Farkas, Diego Benítez-Riquelme, Paulina Sepúlveda, Mario Palma, Paula Medina, Carolina Delgado, Matías I. Hepp, Franz Villarroel-Espindola, and et al. 2025. "SALL2-Mediated Suppression of WNT Signaling Through Transcriptional Control of AXIN2 in Colorectal Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167896
APA StyleQuiroz, A., Escalona, E., Farkas, C., Benítez-Riquelme, D., Sepúlveda, P., Palma, M., Medina, P., Delgado, C., Hepp, M. I., Villarroel-Espindola, F., Castro, A. F., & Pincheira, R. (2025). SALL2-Mediated Suppression of WNT Signaling Through Transcriptional Control of AXIN2 in Colorectal Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167896





