Abstract
Soluble adenylyl cyclase (sAC) is molecularly and biochemically distinct from other mammalian nucleotidyl cyclases. It is uniquely regulated directly by bicarbonate (HCO3−) and calcium (Ca2+) ions and is responsive to physiologic fluctuations in levels of its substrate, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Our initial in vitro biochemical studies suggested two mechanisms for HCO3−-dependent elevation of sAC activity: increasing catalytic rate and relieving inhibition observed in the presence of supraphysiological levels of substrate, ATP. Structural and mutational studies revealed that HCO3− increases catalytic rate via the disruption of a salt bridge that facilitates productive interactions with the substrate. Here, we demonstrate that the HCO3− stimulation observed under supraphysiological ATP concentrations is due to the mitigation of ATP-dependent acidification. Therefore, we conclude that the sole physiologically relevant mechanism of HCO3− regulation of sAC is through its pH-independent effect facilitating productive substrate binding to the catalytic site.
1. Introduction
Many intracellular signal transduction pathways are mediated by the ubiquitous second messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Adenylyl cyclases (ACs) produce cAMP by cyclizing adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In mammalian cells, there are 10 known AC isoforms encoded by the genes ADCY1-10, which can be divided into two classes: transmembrane adenylyl cyclases (tmAC) and soluble adenylyl cyclases (sAC). The nine tmACs (ACDY1-9) are regulated by heterotrimeric G proteins and mediate cAMP responses downstream from hormone and neurotransmitter signaling via G protein-coupled receptors [1,2]. Conversely, sAC (ACDY10) is not bound to the cell membrane and instead is localized to various intracellular compartments including the cytosol, mitochondria, and nucleus [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. As with other Class III nucleotidyl cyclases, sAC activity requires the intramolecular dimerization of two related catalytic domains (C1 and C2) [10]. Regulation of sAC occurs directly through HCO3− and Ca2+ ions [11,12,13], and its activity is sensitive to physiologically relevant ATP fluctuations [11,14].
While Ca2+ ions stimulate sAC activity by increasing the apparent affinity for the substrate ATP [11], HCO3− stimulates both Mg2+-dependent and Mg2+/Ca2+-dependent cyclase activity with an EC50 within the physiologic intracellular range of HCO3− in cells (i.e., 10–25 mM) [11,13]. Initial in vitro cyclase assays on purified sAC protein suggested that HCO3− activation occurred via direct binding and was independent of changes in pH [13]. Subsequent kinetic studies predicted two mechanisms for HCO3− activation of sAC activity, increasing max velocity (Vmax) and relieving a putative substrate inhibition observed under conditions with supraphysiological levels of ATP [11]. Structural, mutational, and biochemical studies of human sAC identified the bicarbonate binding site (BBS) and revealed the molecular mechanism for the HCO3−-dependent elevation of the enzyme’s kcat [10,15,16]. The BBS is adjacent to the ATP-binding catalytic site, and both sites include residues from C1 and C2. Two important residues in the BBS are Lys95 and Arg176. In apo human sAC, a salt bridge is formed between Arg176 and a residue essential for ATP conversion, Asp99. The Arg176–Asp99 salt bridge creates an inhibitory interaction. HCO3− binding engages Arg176, breaking the salt bridge and releasing Asp99, which allows it to flip towards the active site, facilitating ion site formation and ATP binding and turnover. Arg176 acts as a “switch” connecting the active site and the BBS, meaning its movement dictates whether the enzyme is in the active or inactive conformation. Thus, direct binding of HCO3− to the BBS favors productive ATP binding elevating the enzyme’s Vmax [10,15].
In contrast, structural and kinetic studies provided no insight into the molecular basis for the substrate inhibition observed at supraphysiological ATP levels (>7.5 mM) and the hypothesized second HCO3−-dependent activation mechanism via mitigation of this inhibitory effect. Here, we investigate this second mechanism of HCO3−-dependent stimulation of sAC in vitro activity.
2. Results
Our previous studies exploring sAC sensitivity to pH focused exclusively on the effects of basic pH and its possible role in HCO3−-induced sAC activation [13]. Here, we expanded these studies to ask how sAC in vitro activity is affected by acidic pH. When assayed at a physiologic or slightly basic pH, the cyclase activity of sAC is unchanged. However, as the pH becomes more acidic, cyclase activity decreases until there is almost no measurable cyclase activity at a pH of 5.5 (Figure 1). This acid sensitivity is consistent with the catalytic roles of several acidic residues [10,15]. With the appreciation that the cyclase activity of sAC is highly acid-sensitive, we revisited whether the previously used assay conditions supplied sufficient buffering capacity to neutralize the pH of solutions containing supraphysiological levels of ATP, whose disodium salt (the form used in all our assays) is a weak polyacid. Our previous kinetic experiments were performed in the presence of 50 mM of Tris at pH 7.5 [11]. The pH of 10 mM of disodium ATP dissolved in water in the presence of 50 mM of Tris proved to be acidic, at ~6.1. In contrast, 100 mM of Tris (pH 7.5) was adequate to buffer 10 mM of disodium ATP to remain at ~7.2 (Figure 2). Interestingly, an addition of 40 mM of HCO3−, a concentration which had successfully mitigated the previously observed substrate inhibition [11], neutralized the pH of 10 mM of ATP solution in 50 mM of Tris to ~6.8 (Figure 2). These data suggested that the substrate inhibition observed at high levels of ATP, which was mitigated by HCO3− in previous experiments, may be due to inadequate buffering by 50 mM of Tris.
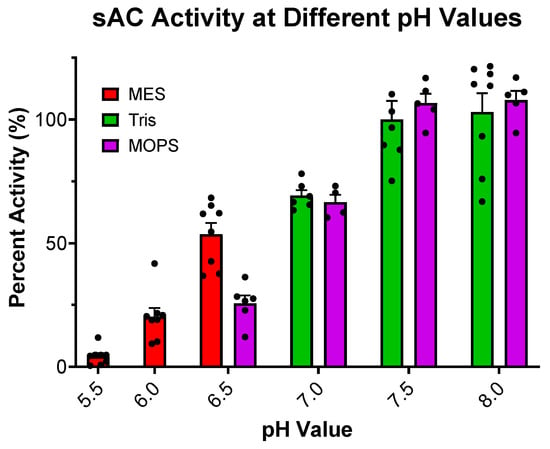
Figure 1.
Effect of pH on sAC cyclase activity: In vitro cyclase activity assay of recombinant sACt, in the presence of 10 mM of Mn2+, 2 mM of ATP, and 50 mM of respective buffer to maintain the pH indicated. Mn2+ was used in this experiment for full catalytic activity. All data were normalized to activity at pH 7.5, the standard pH used previously.. Bars represent averages, with each dot representing individual replicates and errors bars indicating standard errors of the means. The addition of 75 mM of MES or 75 mM of MOPS had no effect on sAC activity when tested in the presence of 75 mM of Tris at pH 7.5 (Supplemental Figure S1).
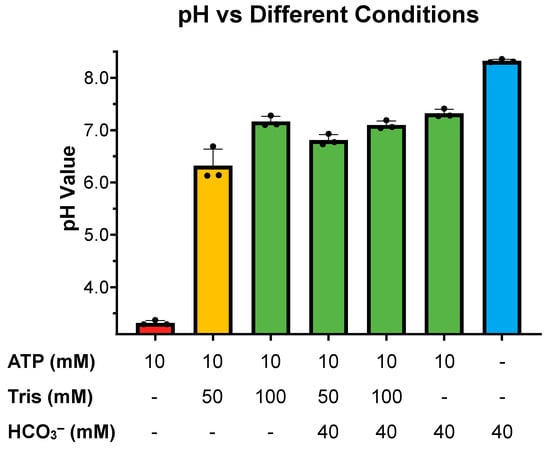
Figure 2.
pH of different cyclase reaction components: Final pH of different concentrations of Tris pH 7.5, ATP, and HCO3− as indicated. Bars represent the averages of 3 independent pH measurements taken at room temperature (~22 °C) with each dot representing individual replicates and error bars indicating standard error of the mean.
We tested this hypothesis by measuring cyclase activity of sAC in the presence of two concentrations of ATP (2 and 10 mM), two concentrations of Tris (50 and 100 mM), and in the presence and absence of HCO3−. At physiological ATP levels (2 mM), there was no significant difference between the activity observed in the presence of 50 mM of Tris relative to 100 mM of Tris, and at both pHs, HCO3− stimulated sAC activity to a similar degree (Figure 3A). In contrast, when measured in the presence of supraphysiological levels of ATP (10 mM), there was a stark difference between the assays buffered with 50 mM of Tris, where the pH decreased to ~6.1, compared with the assays buffered with 100 mM of Tris, which remained at pH ~7.5. In the assay with 50 mM of Tris, the acidity caused by high levels of ATP reduced sAC activity considerably (Figure 3B). However, when sAC activity was measured in the presence of 10 mM of ATP and 40 mM of HCO3−, which mitigated the acidifying effects of 10 mM of ATP in 50 mM of Tris (Figure 2), the activity was indistinguishable between 50 mM and 100 mM of Tris (Figure 3B).
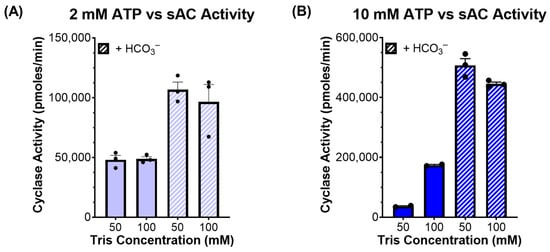
Figure 3.
sAC activity in the presence of different cyclase reaction components: In vitro cyclase activity assay of recombinant sACt, in the presence of Mg2+ and Ca2+, the absence and presence of 40 mM of HCO3−, the presence of either 50 mM or 100 mM of Tris, and either (A) 2 mM of ATP or (B) 10 mM of ATP. Bars represent the average of triplicate determinations with each dot representing individual replicates and error bars indicating standard error of the mean, from a representative experiment which was repeated 3 independent times.
Finally, we directly compared ATP kinetics in 50 mM of Tris (pH 7.5) with that in 150 mM of Tris (pH 7.5). These experiments were performed at 150 mM of Tris pH 7.5 to ensure adequate buffering for the highest levels of ATP tested (15 mM). Since Ca2+ stimulates sAC by decreasing the enzyme’s KM for substrate ATP, Ca2+ and HCO3− work synergistically [11]. In the absence of HCO3− (i.e., Mg2+/Ca2+ ATP alone), we observed inhibition at high ATP levels (>5 mM) only in the reactions buffered by 50 mM of Tris; in the reactions buffered by 150 mM of Tris, the KM for ATP was ~1 mM, as previously reported, and importantly, there was no evidence of substrate inhibition even at the highest ATP concentrations tested (Figure 4A). In contrast, in the presence of 40 mM of HCO3−, there was no discernable difference in the kinetics measured in the presence of 50 mM of Tris compared with 150 mM of Tris. In both cases, the measured KM was between 1 and 2 mM (Figure 4B), consistent with previous reports [11]. These observations reveal that the substrate inhibition observed in 50 mM of Tris in the absence of HCO3− is due to the acid sensitivity of the enzyme, and the previously hypothesized HCO3−-dependent stimulation of activity at supraphysiological levels of ATP was merely due to its ability to mitigate the acidification due to the insufficient buffering capacity of 50 mM of Tris.
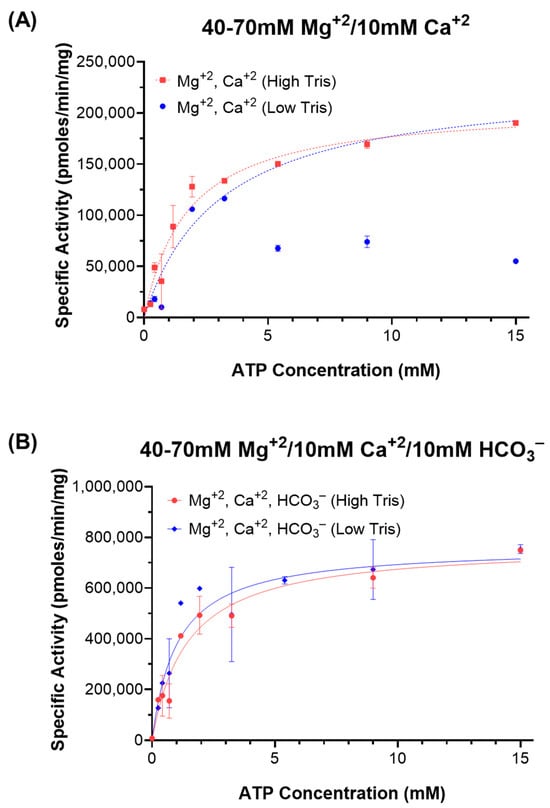
Figure 4.
ATP kinetics of sAC in different Tris concentrations: In vitro cyclase activity of recombinant sACt, in the presence of Mg2+, Ca2+, HCO3−, and either 50 mM (blue lines; “Low Tris”) or 150 mM (red lines; “High Tris”) of Tris (pH 7.5). Activity was assayed as a function of substrate [Mg2+-ATP] in the presence of either (A) 40–70 mM of Mg2+ and 10 mM of Ca2+ (dotted lines) or (B) 40–70 mM of Mg2+, 10 mM of Ca2+, and 40 mM of HCO3− (solid lines). Data points represent averages of duplicate determinations with standard error of the mean indicated, from a representative experiment which was repeated 3 independent times. The dotted blue curve was generated excluding the inhibited points at higher values of ATP.
In conclusion, the data presented in this paper reveal that the buffering capacity used previously was insufficient at very high levels of ATP and updates the mechanism for HCO3− activation of sAC. The previous hypothesized ATP inhibition was in fact due to a decrease in cyclase activity at pH values less than 6.5. Therefore, the only known mechanism for HCO3− activation of sAC is through direct binding to the enzyme, which breaks an inhibitory salt bridge (Figure 5) [10,15]. Moreover, moving forward, the optimal conditions for ATP kinetics of sAC to properly control pH are higher concentrations of Tris or ATP stock solutions with pre-adjusted pH to avoid pH shifts in the assay solution.
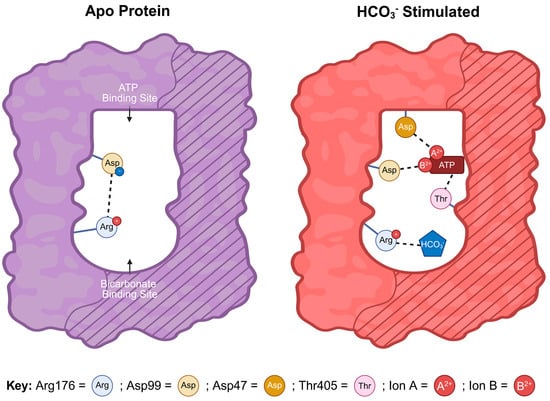
Figure 5.
Current model for HCO3– activation of sAC: Cartoon representation of the mechanism of HCO3—-dependent sAC activation. The bicarbonate binding site (BBS) (curved area) and the ATP-binding active site (rectangular area) are formed from the interface of the two related catalytic domains C1 (unshaded) and C2 (striped). In apo human sAC, a salt bridge forms between Arg176 and Asp99, which prevents productive ATP binding. When HCO3— occupies the BBS, it interacts with Arg176 breaking the salt bridge and releasing Asp99. Once released, Asp99 is able to reorient towards the active site facilitating ATP binding and catalysis. Thus, Arg176 acts as a “switch” connecting the active site and the BBS. In the active complex, residues from both catalytic domains participate in ATP binding; Asp99 and Asp47 from C1 each interact with ATP via divalent cations (i.e., Mg2+, Ca2+) and Thr405 from C2 interacts with the adenine group of ATP [10,15]. A previously proposed mechanism whereby HCO3— relieved ATP inhibition was due to acid sensitivity.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2), calcium chloride (CaCl2), manganese (II) chloride (MnCl2), sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), dithiothreitol (DTT), bovine serum albumin (BSA), disodium ATP (non-radioactive), cAMP (non-radioactive), Tris-HCl, MES, and MOPS were all purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). [α-32P]-ATP and [2,8-3H]-cAMP were purchased from PerkinElmer (Waltham, MA, USA).
Heterologously expressed and purified human truncated sAC (sACt) protein was used for all biochemical assays. The sACt protein was N-terminal tagged with GST and purified from Sf9 cells via baculovirus expression [11].
3.2. In Vitro Adenylyl Cyclase Activity Assay
All in vitro adenylyl cyclase activity assays utilized the classical “two-column” method, developed by Salomon [17]. In this assay, conversion of [α-32P]-ATP to [32P]-cAMP is quantified by sequential Dowex and Alumina chromatography resins to purify the generated [32P]-cAMP. Cyclase assays were performed in 100 μL of total reaction volume using 25–600 ng of sACt, 50–150 mM of Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 3 mM of DTT, BSA 0.03%, substrate [α-32P]-ATP, and either MnCl2, or MgCl2, and/or CaCl2, and/or NaHCO3 concentrations as indicated. Reactions were initiated by the addition of 10,000,000–1,000,000 counts/minute of [α-32P]-ATP. Reactions were incubated for 30 min at 30 °C, quenched by adding 200 μL of SDS 2%, and cAMP was quantified following sequential Dowex and Alumina chromatography. An internal standard of ~10,000 counts/minute of [3H]-cAMP was added to each reaction.
3.3. Statistical Analysis
Plotting data, curve fitting, and statistical analyses were performed using the GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad, version 10.2.3, San Diego, CA, USA). All data are shown as the mean ± SD or SEM.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26136401/s1.
Author Contributions
J.F., C.S., J.B. and L.R.L. conceptualized and designed this study; J.F. and H.B. performed all experiments; J.F. prepared figures; J.F., J.B. and L.R.L. wrote and edited the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Health (P50 HD113015 and R01 HD111549 to L.R.L. and J.B.; and F31 HD105363 to J.F.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Levin/Buck laboratory for helpful advice and all the support during this work.
Conflicts of Interest
L.R.L., J.B. and C.S. are co-inventors of a panel of in vivo, validated sAC inhibitors and are co-founders of Sacyl Pharmaceuticals Inc., which licensed the sAC inhibitors for development into contraceptives.
References
- Krupinski, J.; Coussen, F.; Bakalyar, H.A.; Tang, W.J.; Feinstein, P.G.; Orth, K.; Slaughter, C.; Reed, R.R.; Gilman, A.G. Adenylyl cyclase amino acid sequence: Possible channel- or transporter-like structure. Science 1989, 244, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunahara, R.K.; Dessauer, C.W.; Gilman, A.G. Complexity and diversity of mammalian adenylyl cyclases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 36, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkimmiatis, K.; Leronni, D.; Hofer, A.M. The inner and outer compartments of mitochondria are sites of distinct cAMP/PKA signaling dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, G.; Scalzotto, E.; Mongillo, M.; Pozzan, T. Mitochondrial Ca2+ Uptake Induces Cyclic AMP Generation in the Matrix and Modulates Organelle ATP Levels. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsecchi, F.; Konrad, C.; Manfredi, G. Role of soluble adenylyl cyclase in mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842 Pt B, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccolo, M.; Zerio, A.; Lobo, M.J. Subcellular Organization of the cAMP Signaling Pathway. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 278–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzoni, A.; Zhang, X.; Altschuler, D.L. From membrane to nucleus: A three-wave hypothesis of cAMP signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 105497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkimmiatis, K.; Zaccolo, M. cAMP signaling in subcellular compartments. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, A.; Lobingier, B.T.; Stoeber, M.; Tsvetanova, N.G. Chemical biology approaches to resolve the subcellular GPCR signaling landscape. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steegborn, C. Structure, mechanism, and regulation of soluble adenylyl cyclases—similarities and differences to transmembrane adenylyl cyclases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842 Pt B, 2535–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvin, T.N.; Kamenetsky, M.; Zarifyan, A.; Buck, J.; Levin, L.R. Kinetic properties of “soluble” adenylyl cyclase. Synergism between calcium and bicarbonate. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 15922–15926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, B.S.; Conti, M. Calcium regulation of the soluble adenylyl cyclase expressed in mammalian spermatozoa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10676–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cann, M.J.; Litvin, T.N.; Iourgenko, V.; Sinclair, M.L.; Levin, L.R.; Buck, J. Soluble adenylyl cyclase as an evolutionarily conserved bicarbonate sensor. Science 2000, 289, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zippin, J.H.; Chen, Y.; Straub, S.G.; Hess, K.C.; Diaz, A.; Lee, D.; Tso, P.; Holz, G.G.; Sharp, G.W.; Levin, L.R.; et al. CO2/HCO3(-)- and calcium-regulated soluble adenylyl cyclase as a physiological ATP sensor. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33283–33291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinboelting, S.; Diaz, A.; Moniot, S.; van den Heuvel, J.; Weyand, M.; Levin, L.R.; Buck, J.; Steegborn, C. Crystal structures of human soluble adenylyl cyclase reveal mechanisms of catalysis and of its activation through bicarbonate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3727–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saalau-Bethell, S.M.; Berdini, V.; Cleasby, A.; Congreve, M.; Coyle, J.E.; Lock, V.; Murray, C.W.; O’Brien, M.A.; Rich, S.J.; Sambrook, T.; et al. Crystal structure of human soluble adenylate cyclase reveals a distinct, highly flexible allosteric bicarbonate binding pocket. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, Y. Adenylate cyclase assay. Adv. Cycl. Nucleotide Res. 1979, 10, 35–55. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).