Abstract
This study investigated the genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (Map)—the causative agent of paratuberculosis—isolated from different host species in Germany. A total of 500 isolates from 243 cattle herds and 9 other host species originating from 13 federal states were genotyped. A multi-target approach was applied, comprising IS900-RFLP with BstEII and PstI digestion; MIRU-VNTR; and SSR1, SSR8, and SSR9 analysis. In total, 93 combined genotypes were identified, 84 in cattle and 21 in non-cattle isolates. Ninety genotypes were assigned to the C-type group, and three genotypes (three from sheep and one from cattle) were assigned to the S-type/subtype III group. Cluster analysis divided genotypes into subgroups similar to those shown for WGS-SNP-based phylogenetic trees. New genotypes were revealed, including INMV262–267 and a specific sequence at locus VNTR7. Five genotypes that were predominant in cattle were also detected in sheep, goats, and deer. The majority of genotypes [61%] were identified only once. Polyclonal infections were observed in individual animals and herds, and various potential Map transmission linkages were uncovered. This high genotype richness of Map reflects the long history of paratuberculosis in Germany and intensive nationwide animal movement and international trading activity.
1. Introduction
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (Map)—a member of non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM)—is the causative agent of paratuberculosis or Johne’s disease, a chronic infectious granulomatous enteritis with protein-losing enteropathy and severe weight loss, primarily affecting ruminants [,]. The disease is widespread worldwide, especially in farmed animals, but also in wild animals, and causes considerable economic losses to the livestock industries [,,]. As in many other countries of the world, in Germany, paratuberculosis affects dairy and beef cattle, sheep, goats, feral red deer, fallow deer, and roe deer, as well as exotic ruminants held in zoological gardens or under private ownership [,,,,,]. Map has also been detected in some non-ruminant species, including humans []. A possible role of Map as a zoonotic agent with an etiological relevance for Crohn’s disease in humans is under longstanding discussion [,,,]. Paratuberculosis became a notifiable disease in Germany in 1970.
Map is an evolutionary young organism of clonal nature with a highly monomorphic genome [,]. Based on differences in genotype, genome structure, growth characteristics, and pathogenesis, Map is divided into two major phylogenetic lineages, C (cattle)-type and S (sheep)-type [,,]. Map C-type strains, also designated as subtype II strains, have a broad host range. Although initially isolated almost exclusively from cattle, they have since been isolated from many other ruminants and non-ruminants, including humans []. The S-type group consists of subtypes I and III [,,]. Early isolates of subtype I were mostly from sheep and also from goat [], but more recent systematic surveys have revealed that in regions where beef cattle, deer, and sheep were held in close contact, subtype I strains were also isolated from beef, dairy cattle, and deer []. Subtype III strains were isolated from cattle, sheep, goats, deer, and camels [,,,]. Although there is some evidence for C-type and S-type lineage-specific differences in virulence [], there is not yet any information about differences in the virulence of strains within the main C-type or the S-type lineages in ruminants []. However, there is evidence for S-type sublineage-specific variants of genes associated with virulence in mycobacteria [,]. Monitoring and investigation of Map genotype distribution, diversity, and evolution is crucial for understanding how this organism spreads, for identifying mutations that facilitate enhanced virulence and/or a broadened host range, and for finding effective new control strategies [].
The diversity of Map has been extensively investigated over the last three decades using assays that target different regions in the genome [,,,]. Early studies involved one or two methods, targeting Map-specific or nonspecific genomic regions that were applied to panels of isolates from different hosts from many different countries worldwide [,,,,,,,,,,,,,], including some regions in Germany [,,]. The discriminatory power of Map genotyping was significantly increased by combining two [,,,,] or three complementary typing techniques [,,], and along with additional epidemiological data, it was possible to uncover epidemiological links between Map strains originating from cattle herds and feral red deer in a National Park in Germany [].
In 2009, an overview of Map genotypes originating from different hosts from seven European countries (not including Germany) was presented using a combination of pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), restriction-fragment length-polymorphism analysis based on the insertion sequence IS900 (IS900-RFLP), and mycobacterial interspersed repetitive units-variable-number tandem repeat (MIRU-VNTR) typing []. Despite the limited number of strains per country, this overview was the first major step toward determining the level of diversity of Map within Europe. More recently, single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis based on whole-genome sequence (WGS) data was used to determine the diversity of strains from different hosts of 17 regions or countries worldwide []. SNP analyses allow a very sensitive differentiation of isolates, the calculation of reliable phylogenetic relationships, and the tracking of putative Map transmission between herds and regions [,,,,]. On the other hand, a previous study revealed only a very low number of SNPs within a panel of C-type strains from Australia and worldwide []. The results of WGS-based SNP analysis are very comprehensive, but the bioinformatic tools required are complex and have not been standardized. The method has thus not yet completely replaced conventional genotyping.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the molecular diversity of Map across Germany, to examine the distribution of identified genome variations (genotypes) among different cattle herds and different hosts and federal states, and to compare German genotyping data with that of existing data from other countries. A total of 518 isolates from cattle and nine other hosts from different herds and sources in Germany, as well as from tissue and fecal samples from individual animals, were genotyped using a combination of IS900-RFLP, MIRU-VNTR, and short-sequence-repeat (SSR) analysis. This study provides a comprehensive overview of combined Map genotypes in Germany, their similarity and presumed relationship, information about the most prevalent genotypes and possible inter-herd and inter-species transmissions, and the tendency for co-infections of individual animals with different Map strains.
2. Results
2.1. Genotypes Identified, Origin, and Subdivision of C- and S-Type Strains
A total of 518 Map isolates originating from 243 cattle herds and 25 regional localities (non-cattle isolates) in 13 of the 16 federal states in Germany (Figure 1) were characterized and resulted in 93 combined genotypes (GTs), (Table 1). The results of all included isolates are listed in Table S1 (cattle isolates), Table S2 (non-cattle isolates), and Table S3 (isolates from different tissues of individual animals). Counting only the isolates with different genotypes from one cattle herd or one locality, 311 strains from cattle and 32 strains from other species, i.e., a total of 343 strains from 268 sources, were assessed as independent in this study.
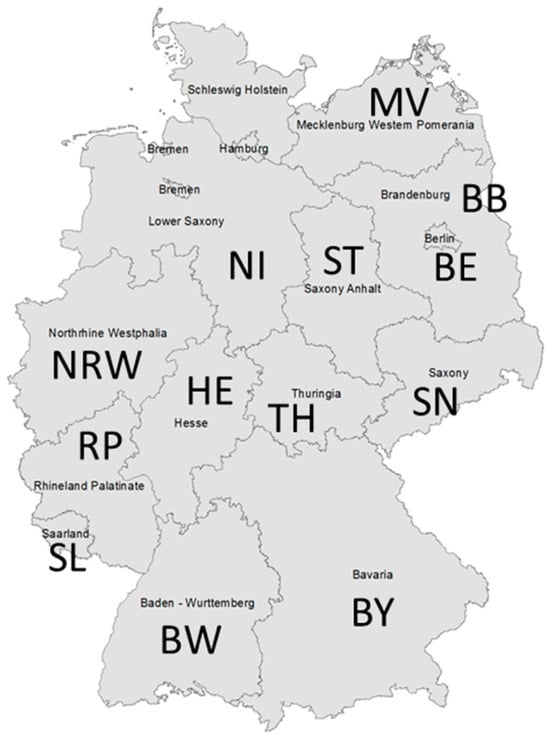
Figure 1.
Federal states in Germany (n = 13), which were the origin of Map isolates characterized for this work. The number of isolates is given in brackets: BB—Brandenburg (n = 21), BE—Berlin (n = 1), BW—Baden-Wuerttemberg (n = 20), BY—Bavaria (n = 11), HE—Hesse (n = 36), MV—Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (n = 19), NI—Lower Saxony (n = 36), NRW—North Rhine-Westphalia (n = 95), RP—Rhineland Palatinate (n = 70), SL—Saarland (n = 6), SN—Saxony (n = 51), ST—Saxony-Anhalt (n = 29), and TH—Thuringia (n = 123).

Table 1.
Combined genotypes (GTs) detected in German Mycobacterium (M.) avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains isolated from different host species between 1993 and 2016.
The majority of the investigated isolates belonged to the C-type group and could be divided into 90 GTs. Eleven isolates were identified as S-type strains of subtype III with three GTs; nine of them originated from sheep (two flocks and two migrating herds) and two from cattle (two herds). Cattle and non-cattle hosts shared 13 GTs. A total of 57 out of 93 GTs (61%) were detected only once, including 9 GTs that were not found in cattle but were detected in a human, a donkey, goats, deer, and sheep.
2.2. Individual Genotypes and Discriminatory Power of RFLP, MIRU-VNTR, and SSR Typing
2.2.1. Previously Detected and Novel Genotypes
The 93 GTs consisted of 39 IS900-RFLP patterns (a combination of 26 and 17 band patterns after BstEII and PstI digestion, respectively), 33 MIRU-VNTR, and 15 SSR profiles. Two novel IS900-RFLP patterns (C45 and P20; see Figure 2) and seven novel INMV profiles (Table 2) were discovered. All IS900-RFLP band patterns are shown as schematic representations and corresponding gel images of Southern blots in Figures S1–S3.
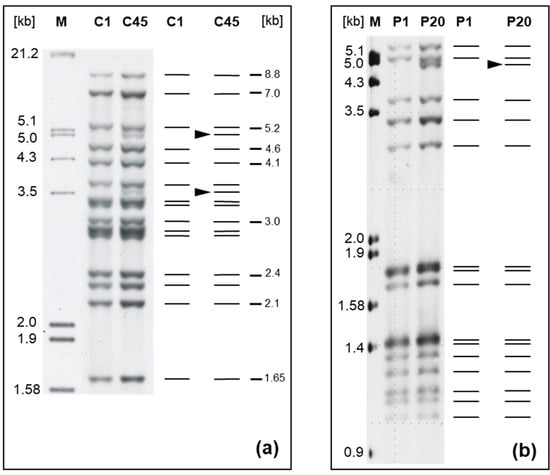
Figure 2.
New IS900-RFLP profiles of M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains from cattle. (a) Profile C45 (strain 06A0169) compared to reference profile C1 (strain 06A0168) after chromosomal DNA digestion with BstEII and (b) profile P20 (strain 12MA1661) compared to reference profile P1 (strain 12MA1602) after chromosomal DNA digestion with PstI. A digoxigenin-labeled specific 453 bp fragment of IS900 was used as probe. The numbers above the lanes are the type designations. The black arrowhead in the schematic diagram shows the difference between type C1 [] and novel type C45, as well as P1 designated according to [] and novel type P20. Lane M represents the molecular weight marker III (Roche Diagnostics). Numbers on the right in (a) indicate sizes of reference bands.

Table 2.
New numerical codes determined by MIRU-VNTR typing of German isolates.
2.2.2. Specific Sequence Pattern at VNTR7
The new MIRU-VNTR profiles include INMV30* (325223*28) with a new sequence pattern at locus 7, identified by sequencing and in silico analysis: in addition to two complete copies of VNTR7 repeat (CGAAATATTCGCCGTGAGAACA), a different sequence of 24 nucleotides was detected. This consisted of an additional imperfect back-flanking sequence region of 12 nucleotides (nt)—(CGTGCGGCGAAG)—followed by an imperfect repeat of 12 nt (GCCGTGAGAACA), (plus CG). The amplicon size appeared like three repeats, and the number of repeats was therefore designated as 3*. Profile INMV30* was found in two isolates from intestinal lymph nodes of two individual cattle in a single herd in Thuringia (Table S1).
2.2.3. Number and Frequency of Individual IS900-RFLP, MIRU-VNTR, and SSR Types
In the following text, the number n (in brackets) represents the number of independent strains originating from different herds or sources and belonging to the individual genotype of the respective typing method.
Typing by IS900-RFLP with BstEII digestion revealed 303 independent strains with the following 4 of 26 patterns identified most frequently: C1 (n = 202, 67%), C17 (n = 22, 7%), C18, and C41 (n = 17, 6%). Typing via IS900-RFLP with PstI digestion revealed 302 independent strains, and 5 of the 17 detected patterns were most often found: P1 (n = 184, 61%), P3 (n = 36, 12%), P16 (n = 16, 5.3%), P7, and P8 (n = 15, 5%). IS900-RFLP typing after BstEII and PstI digestions resulted in 39 combined profiles and 313 independent strains. Type C1-P1 (n = 174, 56%) and C1-P3 (n = 31, 10%) were most frequently detected. A total of 14 profiles were found in multiple (2 to 16) strains, and 23 profiles were found only once. However, the most common IS900-RFLP (BstEII) C1 type was subdivided into 42 combined genotypes in this study.
Using MIRU-VNTR typing, 318 independent strains could be differentiated, exhibiting the following 4 of 33 profiles most frequently: INMV2 (n = 95, 30%), INMV1 (n = 58, 18%), INMV19 (n = 38, 12%), and INMV33 (n = 37, 12%).
Finally, SSR typing revealed 299 independent strains, and the following 3 of 15 profiles were detected most frequently: 7-4-4 (n = 198, 66%), 7-4-5 (n = 39, 13%), and 7-5-5 (n = 20, 7%). The results for each individual genotype identified using the different methods and the number of independent strains with that genotype are listed in Table S4.
2.2.4. Discriminatory Power of Typing
Based on the total of 93 identified genotypes and the resulting 343 independent strains, the discriminatory power of the combined genotyping technique was calculated and showed a DI value of 0.954. IS900-RFLP (BstEII, PstI), MIRU-VNTR, and SSR typing each had a lower discriminatory power, with DI values of 0.67, 0.847, and 0.54, respectively (Table S4).
2.3. Comparison of Combined Genotypes and Phylogeny
The relationship of the identified genotypes is shown in Figure 3. The 93 genotypes were grouped into C-type and S-type, with C-type further divided into the main subgroups A and B, with nine and three clusters, respectively. German strains with genotypes GT59, 37, 2, 4, and 80 (Figure 3), assigned to five clusters within Subgroup A, were included in two previous WGS studies [,], where they were assigned in a SNP-based phylogenetic tree to five clusters within Subgroup A of the C-type group [].
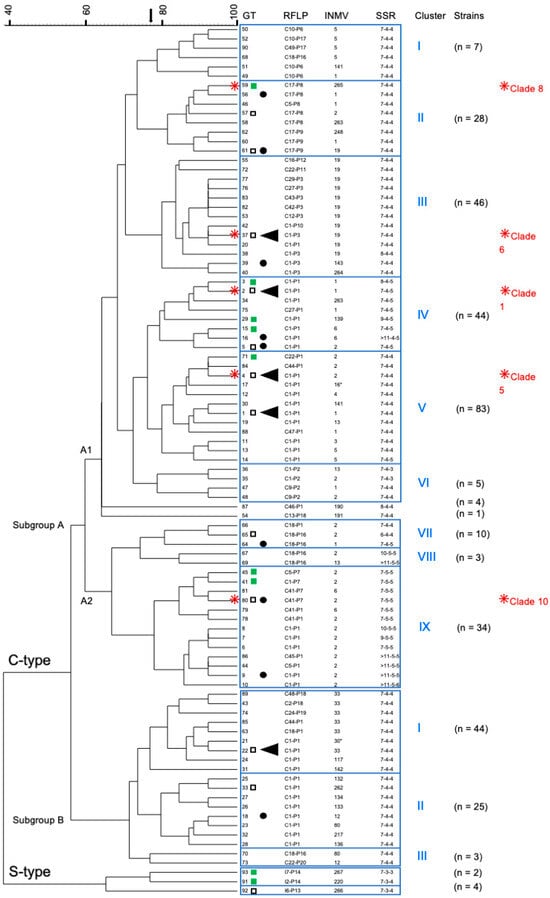
Figure 3.
This dendrogram (UPGMA-tree) shows the similarity of 93 combined genotypes (GTs) of German M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains and their assignment to main groups, subgroups, and clusters. The tree was calculated based on the results of IS900-RFLP (BstEII, PstI), MIRU-VNTR typing (8 loci; only INMV profiles are shown), and SSR analysis (SSR1, 8 and 9). The five most frequently detected GTs 1, 2, 4, 22, and 37 (found in 16–52 independent strains) are highlighted by (◄), and frequently detected GTs (found in 7–14 independent strains) are indicated by (●). The number n of independent strains that belong to the respective clusters is given in parentheses. (□) GT was determined in cattle as well as non-cattle isolates. (■) GT was determined in non-cattle isolates only. All other GTs have so far only been found in cattle isolates.  GTs of five German isolates included in a previous WGS-based SNP analysis [] and a SNP-based assay with assignment to specific phylogenetic clades [] are shown with the respective clade number in red letters.
GTs of five German isolates included in a previous WGS-based SNP analysis [] and a SNP-based assay with assignment to specific phylogenetic clades [] are shown with the respective clade number in red letters.
2.4. Distribution of Map Genotypes Among Different Herds, Hosts, and Federal States
The minimum spanning trees (Figure 4) show the distribution of genotypes among herds/sources, hosts, and federal states. No correlations were found between geographic origins (federal states) and the predominant GTs.
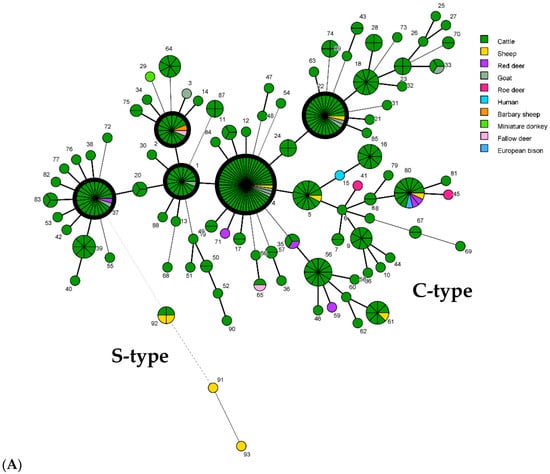
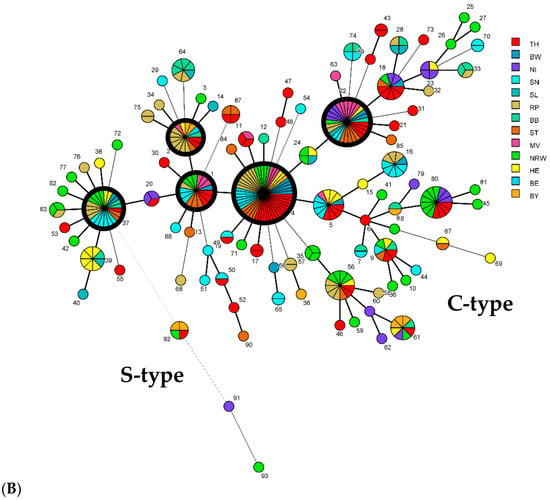
Figure 4.
Minimum spanning tree (MST) based on comparison of 93 combined genotypes of M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolates identified in this study. Each genotype (GT) is displayed as a node, dimensioned proportional to the number of clustered independent strains harboring this specific GT (node numbering = GT, according to Table 1). A combined genotype from each herd/local source was considered only once, regardless of the number of isolates with that GT. In total, the GTs of 343 independent strains from cattle of 243 cattle herds and 32 independent strains from 9 other hosts in 25 other sources in Germany were included. Thick black-bordered circles represent the five most common GTs (GT1, 2, 4, 22, and 37). The distances between nodes (corresponding to GTs) vary depending on the number of typing target regions that differ. Thick lines between two nodes represent a difference at one target region, and thin and dashed lines show a difference at two or more typing targets. (A) Different colors highlight the different host origins of strains. (B) Different colors represent the origin of isolates from the different federal states in Germany (see Figure 1).
2.5. Diversity of Isolates
Altogether, 84 GTs were detected in cattle (83 C-type and 1 S-type), with 49 GTs unique to single herds across all federal states, affecting 20% of herds. A total of 30 GTs were found in 2 to 12 cattle herds and in up to six federal states (Figure 4), and 5 predominant GTs were detected in 14 to 48 cattle herds and in up to 10 federal states (Table 3).

Table 3.
Predominant M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis genotypes in cattle herds.
Non-cattle isolates exhibited 18 C-type and 3 S-type GTs (Table 1, Tables S2 and S7), with 7 C-type and 2 S-type GTs unique to non-cattle. Predominant cattle GTs were also found in sheep (GT2, 4 and 22), goats (GT1, 4, 22, and 37), and deer (GT2 and 37). Ten GTs (all C-type) were detected in isolates from wild living ruminants (red deer, roe deer, fallow deer, and European mouflon), with four unique to them.
2.6. Intra-Herd Diversity of Map
Multiple Map isolates were characterized from 70 herds, detecting one genotype in 22 herds and multiple genotypes in 48 herds, regardless of whether isolates were collected at the same time or at intervals of one to ten years (Table S8). In herds with multiple GTs, two to eight GTs per herd were found. Among these, there were herds in which one genotype predominated (NRW-4) and remained detectable over several years (TH-1, RP-12, and RP-14; see Tables S1 and S8).
In 36 herds, GTs differed at 2 to 8 of the 13 target regions for typing. The remaining 12 herds harbored strains that differed at only one target region (Table S8).
The intra-herd strain type diversity of Map varied. Diversity was calculated for two herds with more than 20 isolates genotyped and was higher in herd NRW-12 (23 isolates with eight GTs) than in herd TH-1 (28 isolates with 4 GTs), exhibiting a Shannon diversity index H = 1.514 versus H = 0.559 and a Simpson index D = 0.265 versus D = 0.733 (Table S9).
2.7. Mixed Genotypes and Co-Infection of Individual Animals
2.7.1. Mixed Genotypes in Individual Isolates
Double PCR-bands observed in the agarose gels at one or two specific MIRU-VNTR loci indicated mixed genotypes in ten cases (Table 4). In three cases, multiple target regions showed genotype differences. The suggested GTs were confirmed in several cases by separate detection of one or both GTs in the same herd (Table S1). All mixed GTs were found in cattle isolates from fecal and intestinal content and boot swab samples (Table S1).

Table 4.
Mixed genotypes in cattle isolates.
2.7.2. Different Genotypes in Isolates from Individual Animals
Two different GTs were identified per animal in isolates from different tissues and fecal samples of 9 out of 22 animals (Table 5 and Table S3).

Table 5.
Different combined genotypes (GT) in various tissues and feces of nine single animals.
2.8. Suspected Epidemiological Linkages
Infection with the same strain was assumed if isolates from a single animal, herd, or other source had the same GT. Shared GTs among different herds or hosts suggested possible epidemiological linkages (Figure 4). Figure 5 and Figure 6 illustrate the genotype distribution in Thuringia and Brandenburg.
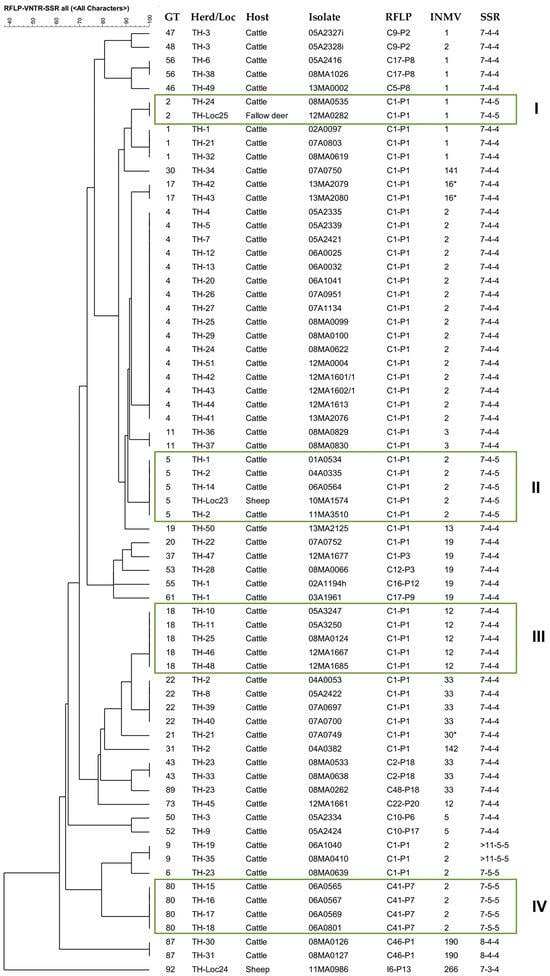
Figure 5.
IS900-RFLP/MIRU-VNTR/SSR based tree of similarity (UPGMA) of 68 independent M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains with 31 genotypes across 51 cattle herds, 2 fallow deer, and 2 sheep (including one European mouflon) in Thuringia. Identical genotypes (GTs) suggest possible epidemiological links: Boxes I and II show isolates with identical GT originating from different hosts; boxes III and IV include identical GTs found in isolates from cattle of 5 or 4 herds, respectively. * INMV16* (323325*28) is a profile with an altered repeat sequence at VNTR locus 7.
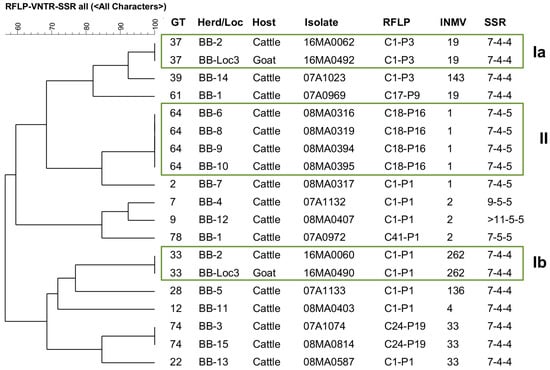
Figure 6.
IS900-RFLP/MIRU-VNTR/SSR based tree of similarity (UPGMA) of 17 M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains from cattle and 2 from goat originating altogether from 15 herds in Brandenburg. Only cattle isolates with different genotypes (GT) from the same herd (independent strains) were included. Boxes Ia and Ib highlight two GTs identified in isolates from cattle and goats from the same herd (BB-2 = BB-Loc3). Box II shows identical GT found in different cattle herds.
In Thuringia (TH), the predominant GT4, GT22, and GT1 suggest links within TH, but also to herds in other federal states. GT2, identified in a cow and fallow deer (Box I), and GT5, found in cattle and a sheep (European mouflon) (Box II), indicate possible interspecies transmission. GT5 was confirmed in isolates of a herd from 2004 to 2011, indicating the persistence of a genotype in a herd over a longer period of time.
In Brandenburg, different GTs were identified in a cattle herd and in a herd keeping cattle and goats (BB-2 = BB-Loc3). The goats were introduced to this herd in 2011 and were temporarily grazed together with cattle on the same pasture. At the time of strain isolation (2016), cattle and goats were suffering from clinical paratuberculosis. Two identical GTs in both species suggest interspecies transmission in this herd. In addition, GT64 was found in four cattle herds, which could indicate transmission by animal movement.
3. Discussion
Paratuberculosis has long been recognized and is widespread worldwide [,,,]. The high diversity of Map revealed in this study reflects, to some extent, the long history of this disease in Germany, including the intensive trading activity within the country and with neighboring countries in Europe (ec.europa.eu/Eurostat/data), as well as direct or indirect Map transmission between livestock and wild living animals [,].
The current study began before the WGS-based SNP analysis for genotyping Map was introduced. IS900-RFLP typing was carried out in the laboratory initially, followed by MIRU-VNTR and SSR analyses. Like other fingerprinting methods, IS900-RFLP is a technically demanding and time-consuming laboratory procedure and was replaced by MIRU-VNTR, multi-locus SSR, and WGS-based SNP analysis in several subsequent studies. Nevertheless, this study presents gel images and schematic overviews of the IS900-RFLP profiles based on BstEII and PstI digestion of German isolates and combines IS900-RFLP with MIRU-VNTR and SSR profiles for individual strains.
3.1. Genotyping Markers and Homoplasy
In general, strain diversity is caused by the plasticity of the Map genomes, which change slowly relative to many other bacterial genera through spontaneous mutations and as a result of changing selective pressures in their microenvironment []. Natural events such as recombination and slipped-strand mispairing during replication lead to VNTRs and SSRs [] with varied repeat numbers, possibly facilitating reversible shutdown or modulation of the function of specific bacterial genes [,]. These changes are in addition to major differences between C- and S-type with gene insertions and deletions and differing genome structure [,,]. Map strains within the main lineages differ genetically in their content of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) or SNPs [,,,], indels, and repeat sequences [,], as summarized in []. Finally, these polymorphisms cause different IS900-RFLP patterns (also based on SNVs or SNPs at restriction sites of digestion enzymes) and different MIRU-VNTR and SSR profiles (based on repetitive mini- and microsatellites) used in this study for genotyping.
The genetic markers of genotyping have varying mutation rates [,,]. SNPs are very stable and therefore useful for phylogenetic studies [], while MIRU-VNTR loci and SSRs may be subject to homoplasy in Map genomes, affecting phylogenetic accuracy [,,,]. MIRU-VNTR typing results were found to both over- and underestimate the phylogenetic relationships between strains compared to WGS-SNP analysis results [,,,,]. In addition, the results of SSR typing at 11 SSR loci did not show any significant correlation with WGS-based SNP clustering [,], probably caused by erroneous sequencing results at SSR1 and 2 with more than 11 mononucleotide repeats [] and a very high mutation rate at SSR2 []. In this study, we excluded SSR2 and used SSR1 up to ≥11 repeats.
However, previous studies have demonstrated the sufficient stability of the genetic markers employed in the current study for revealing Map diversity and performing epidemiological investigations on a limited temporal and spatial scale [,].
3.2. Phylogenetic Grouping and Comparison with WGS-Based SNP Analysis
The phylogenetic relationships of Map strains are currently calculated using WGS-based SNP analyses of the core genomes [,]. However, these analyses, usually based on short-read sequence data, exclude information about genome structure, IS elements, and other repetitive (micro and minisatellite) sequences, which can be detected partly by IS900-RFLP, MIRU-VNTR, and SSR analyses. In the similarity tree of this study (Figure 3), the assignment of combined genotypes in the C-type group to two main subgroups, A and B, and several sub-clusters was very similar to that in two WGS-SNP-based phylogenetic analyses, including a large number of Map strains, originating from different hosts and regions worldwide [,]. As mentioned above (Section 2.3), five German strains analyzed in the present study were also included in these two previous studies. These strains were assigned to five phylogenetic clades in Subgroup A [], which corresponds to their assignment to five sub-clusters in the similarity tree of the present study. These similarities suggest a phylogenetic relevance of the calculated relationships based on combined genotypes, despite the suspected homoplastic properties of some MIRU-VNTRs and SSRs sequences [,,].
In both the similarity tree and the SNP-based phylogenetic tree [], genotypes with INMV1 and INMV2 profiles were only assigned to subgroup A, and only Subgroup B contained strains with INMV33, INMV80, and other individual profiles. The groupings indicate a possible association between certain genomic markers/target regions of the typing approach used, such as INMV profiles, and SNP-based phylogeny, providing validation of both methods for use in classifying Map isolates. A strong statistical association between phylogeny and INMV1, but not INMV2, was previously revealed in another WGS-based study of 200 Map C-type isolates from Western France []. Future studies using WGS-based SNP analysis of the German Map strains will further clarify the phylogenetic relevance of current clustering.
3.3. Genotypes of Map S-Type Strains
Apart from sheep and cattle in Germany, subtype III strains have been previously detected in several countries worldwide in sheep (Canada, South Africa, Spain, and the United States), as well as in goats (Canada, Spain, Switzerland), deer (The Netherlands, Czech Republic), and cattle (Canada, Switzerland) [,,,,], whereas subtype I strains have been mostly reported in sheep (Scotland, England, Hungary, Spain, the Faroe Islands, Morocco, South Africa, New Zealand, and Australia), but also in deer, goat, dairy, and beef cattle (Spain, Hungary, and New Zealand) [,,,,].
In this study, three genotypes belonged to S-type/subtype III, detected in six epidemiologically independent strains. In Germany, there is a significantly lower number of sheep farms compared to cattle farms, and sheep and cattle are usually farmed separately. In addition, sheep in Germany were tested for Map infection less frequently than cattle, which could also explain the paucity of Map S-type stains in this study set. All three genotypes (GT91-93) were isolated from sheep, but GT92 was additionally isolated from two cattle herds without known contact with the two sheep herds with GT92. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of Map S-type isolated from German cattle. Map S-type strains have also been found occasionally in cattle in other countries, e.g., in Scotland [], Australia, Iceland [], Spain [], subtype I in New Zealand [], and subtype III in Canada [] and Switzerland []. Direct or indirect contact of cattle with paratuberculosis-infected sheep was reported as a major reason for transmission of S-type strains between sheep and cattle [,]. No further epidemiological information was available for the Map S-type affected German cattle herds.
Genotype GT91 (I2-P14/INMV220/7-3-4) was isolated from a sheep flock with a chronic paratuberculosis problem. Profile INMV220 was also reported for Map isolates from a sheep (2016) and a goat (2018) in different cantons of Switzerland (Scherrer, personal communication, []). However, the VNTR profile [22331(1.5)18] in INMV220 is identical to that in INMV124, which has already been found in Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis (Mah) isolates from pigs [,], a Tapir [], a dog, a chicken, and other sources (Möbius, personal communication). At the VNTR 7 locus, all S-type strains and strains of the Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) harbor 1.5 repeats [], including Mah strains with profile INMV124 []. However, a specific SNP (C > T) at position 89 bp in the VNTR 7 locus outside the true repeat sequence(s) distinguishes Map from other MAC genomes [], confirmed for Map S-type strains (C) in this study and for different Mah strains (T) with INMV124 (Möbius, personal communication).
3.4. Diversity of Map C-Type Strains
The majority of GTs identified in this work belonged to the C-type group (90 GTs) and were found in 507 isolates from 243 cattle herds and 22 other sources in Germany. Earlier studies by other authors on Map diversity in Germany, conducted from 2009 onwards, examined fewer isolates, mostly cattle isolates, from fewer sources and in only one or three federal states, and used other combinations of typing methods from those employed in the present study [,,]. However, all revealed a relatively high diversity of C-type strains in Germany by applying more than one typing method. Employing our applied typing approach on such a large number of isolates from different herds and regional origins has provided an even greater estimate of diversity within the Map population in Germany than previously determined.
Various combinations of analysis tools have also been applied to reveal the Map diversity in different studies conducted in other countries. Comparing the results of typing from these previous studies to results from this study shows varying diversity of Map in individual regions in the middle of Europe and the detection of several dominant genotypes common to Germany and neighboring countries.
In a study by Stevenson et al. [], the diversity of Map in different hosts from seven European countries (not including Germany) was presented. A total of 44 combined profiles (IS900-RFLP [BstEII] + PFGE multiplex + MIRU-VNTR) were found in 164 isolates from 16 host types, including 15 profiles from 35 cattle and 10 profiles for 13 isolates from wild ruminants. In the present study, significantly more combined profiles (n = 84) were identified in German cattle, perhaps reflecting the higher number of cattle isolates characterized or the different typing approaches applied. There was agreement when diversity from the same methods was compared. About 70% of all isolates in the Stevenson study [] showed IS900-RFLP profile C1, 11% in combination with profile INMV1, and 12% in combination with profile INMV2. In the current study, 76% of all isolates harbored IS900-RFLP profile C1, 10% in combination with INMV1, and 23% with INMV2.
Only 20 combined genotypes were identified in a study from Austria that employed IS900-RFLP [BstEII, PstI] and MIRU-VNTR analysis to type 249 isolates from cattle, goat, sheep, and wild ruminants from different herds and regional origins []. In the present study, 80 genotypes were found, based on both methods, suggesting a higher Map diversity in Germany than in Austria.
Of the 33 INMV profiles identified in German strains, including 29 INMV profiles from cattle, 7 profiles (INMV262–267, and 30*) have not yet been published. INMV30* and 16* with unique sequences at VNTR 7 locus did not correspond to the specifications for the MAC-INMV-SSR database [] and were therefore probably not registered in the database, although special sequences at VNTR 7 locus were also described previously []. INMV2 and INMV1 were the most common profiles in Germany (30% and 18%). These were also the predominant profiles in other countries in Europe, Canada, Argentina, and New Zealand, followed by INMV19 and 33 (12% each), which were found less frequently or not at all outside of Germany [,,,,,,,,] (Price-Carter, personal communication). Apart from the different numbers of isolates, herds, and regional origins, the total number of INMV profiles detected so far in Canada, Austria, Ireland, and Argentina was lower [,,,] than in Germany or France (this study [,]). Furthermore, several INMV profiles appeared more frequently in other countries, e.g., INMV3 in Canada and INMV11 in Argentina [,], and some were not identified in German strains.
The most common SSR typing profiles in Germany, 7-4-4, 7-4-5, and 7-5-5 (three out of 15 profiles), were also the most frequently detected in isolates from France and Ireland, 7-4-4 (combined with INMV1 and 2), 7-4-5 (combined with INMV1), and 7-5-5 (combined with INMV2) [,]. Other SSR profiles were predominant in strains from the United States, including profile 7-6-5 [], which has not yet been detected in Germany, profile 7-5-5, and profile >11-5-5 [].
The marked differences in Map diversity in different countries and regions of the world, discussed above and in [], are related to the history of paratuberculosis and the intensity and direction of global cattle trade, which has increased dramatically over the last century. Differences in Map diversity between continental European territories and Ireland or Canada and the introduction and persistence of only subsets of genotypes in these countries were confirmed by WGS-based SNP-analysis and other bioinformatic tools [,].
3.5. Intra-Herd Diversity of Map and Co-Infections of Herds and Individual Animals
Different studies have shown that the intra-herd variation of Map strains depended on the frequency at which infected animals were introduced into herds from different sources []. The results from the current work also confirm this tendency, as a significantly higher Map diversity was found in a cattle herd with known intensive animal movements than in a cattle herd with one predominant infection strain without intensive cattle movement (Table S9).
Co-infections of herds or individual animals with multiple genotypes of Map were reported in several previous studies [,,,]. In the present study, two to eight GTs were found in 66% of tested cattle herds. In 36 of these 48 herds with multiple GTs, the polymorphisms involved two, but mostly four to eight of the 13 target regions, indicating more distantly related strains and separate infection events caused by different strains. The target sites that varied most frequently included SNPs at digestion sites of restriction enzymes responsible for different RFLP patterns, several VNTR loci (VNTR292, 7, 47, and 25) as well as SSR8 and 9. In 12 of the 48 herds with multiple GTs, the isolates varied in only one, but different target regions (without a preference of a specific genome marker), suggesting spontaneous random mutations of a Map strain within the affected herd rather than co-infection with different strains.
Map infections in wild and domestic ruminant species in general seem to be polyclonal []. In the current study, multiple genotypes of individual animals were identified in mixed isolates and in isolates from different tissues. In seven of ten mixed isolates, only one polymorphism was detected, again suggesting recent mutation rather than a co-infection with different strains.
After multiple infections with different strains and during different infection processes, the bacteria can be disseminated to different sections of the intestinal system and also to different extraintestinal tissues [,], which was also confirmed by the results of this study: Map was isolated also from liver, spleen, muscle, udder, and lung (and genotyped). As described above for individual herds or isolates, and also discussed previously [], multiple genotypes found in tissue and different fecal samples of individual animals varied either in only one target region or in several, again reflecting both within-host/herd evolution and/or multiple introductions.
One sheep was even co-infected with a C-type and an S-type strain, detected by using different culture media. Systematic cultivation of isolates on different culture media could possibly reveal more polyclonal infections, as individual strains or groups favor certain ingredients, as described for Map C-type and S-type strains [,].
3.6. Epidemiological Findings
The results from the current multi-target study provide useful information about the Map distribution and possible epidemiological links of specific Map genotypes in Germany (see Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6). The multi-target approach used in this study provided a value of >0.954 (DI) deemed sufficient for epidemiological studies [].
The five predominant genotypes in German cattle were widespread, perhaps suggesting that present phenotypes have a similar virulence or are highly adaptable. Because these GTs were distributed across a wide range of federal states, it was not possible to draw firm conclusions regarding transmission routes via animal movements. Certain GTs occurred more frequently in individual states, but there was no statistically significant association between the genotypes and the regional origin. This lack of association could be due to a high exchange of cattle between herds in Germany, as has been shown for other European regions—for example, France [] and the West of France [].
Interestingly, the predominant type GT22 (including INMV33) was mostly found in the former Eastern Germany states, in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia, possibly caused by the import of cattle from Lower Saxony after 1989. The rare GT17 (with INMV16*), reported for cattle isolates from Thuringia in this study, was also identified (without RFLP results) in a goat herd in TH [], suggesting a possible epidemiological link between cattle and goats in this federal state.
Only a few isolates from wildlife and domestic non-cattle species were characterized; therefore, our study gives only limited insight into the diversity and epidemiology of Map in non-cattle species. The seven unique C-type GTs, not found in cattle, originated from a donkey born in France [], a healthy human, two wild living red deer, two wild living roe deer, and a goat (from a private husbandry). The eleven other C-type GTs from non-cattle hosts were shared with cattle, including the predominant GTs as well as six others. Ten of them were found in both cattle and non-cattle in the same federal state (Table S7), suggesting interspecies transmission, as discussed in previous studies [,,,].
Ten genotypes were detected in wildlife isolates, four of which had three unique IS900-RFLP patterns and one new INMV profile (INMV265). This could indicate a specific Map population in wildlife, possibly as a result of evolution or immigration of wildlife from neighboring countries []. The other six GTs were shared with cattle, suggesting interspecies transmission of these strains, as described above and discussed before [,].
Wildlife could have become infected through shared pastures contaminated with Map; from farm animals or within their population at feeding sites, especially in winter; or even by contact across national borders [,]. Furthermore, infections can be introduced into zoological gardens through the purchase of sub-clinically infected animals and can be transmitted between zoo animals of different species through shared habitats [].
Nearby Germany, in Austria, ten profiles were detected by MIRU-VNTR in isolates from five species of wild living ruminants []. Apart from INMV1 and INMV2, eight other profiles were identified that do not occur in German wildlife isolates. However, as in Germany, data from studies in Austria show that there are multiple epidemiological links between isolates from wild and farm animals [], and some wild animals appear to be infected by specific Map genotypes.
The comparison of data from Austria [,] with data from this study did not provide evidence of Map transmission between wildlife from the two countries. But because there were only a small number of wildlife isolates characterized in our study, it was not possible to draw firm conclusions. Further studies are required for this purpose.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Map Isolates
The Map field isolates used in this study were collected between 1993 and 2016 and were transferred to the strain collection of the National Reference Laboratory (NRL) for Paratuberculosis, Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut (FLI) in Jena, Germany. The majority of the isolates were submitted from regional veterinary diagnostic laboratories of the German federal states, which obtained the isolates as part of routine diagnostics from fecal or tissue samples of different animal species. Others were directly isolated by the NRL from diagnostic samples or from samples obtained as part of field studies.
Most isolates came from cattle: 438 isolates from individual cattle in 243 herds, mainly dairy herds. Different numbers of cattle isolates (n = 1 to 28) per herd and herds of origin (n = 6 to 51) per federal state were available for genotyping (Table S1). In addition, 46 isolates from 44 individual animals of eight non-cattle host species and from one healthy human were characterized (Table S2). The origin of isolates was indicated by assignment to the numbered source herd (cattle isolates) or the numbered collection site/location (non-cattle isolates) within each federal state. The additional animal species included sheep (domestic sheep [Ovis gmelini aries], European mouflon [Ovis gmelini musimon], and Cameroon sheep [Ovis aries aries]), goat (Capra aegagrus hircus), red deer (Cervus elaphus), roe deer (Capreolus capreolus), fallow deer (Dama dama), Barbary sheep (Ammontragus lervia), European bison (Bos bonasus), and a miniature donkey (Equus asinus f. asinus), which was included as a non-ruminant species. The animals were free living (deer and mouflon) or held in domestic herds (sheep and goat), in zoological gardens, or were privately owned (sheep, goat, bison, and donkey). The only human isolate came from a healthy person. The year in which the individual isolates were collected is also listed in Tables S1 and S2.
Furthermore, 63 isolates (Table S3) originating from two to five tissues and/or fecal samples from 22 animals of 6 host species (cattle, bison, sheep, red deer, roe deer, and goat) were included to identify co-infections at the individual animal level (29 out of these 63 isolates were also included in the strain panels in Tables S1 and S2). Tissue samples originated from the intestinal tract (ileum, intestinal mucosa, jejunum, jejunal lymph node (LN), caecum, ileo-caecal LN, and mesenterial LN) or from extraintestinal tissues (liver, liver LN, spleen, muscle, udder, milk, or lung of fetus).
Some isolates, indicated with references in Tables S1–S3, were also included in previous studies [,,,,].
4.2. Map Strain Isolation, Cultivation, and Subspecies Identification
4.2.1. Strain Isolation, Cultivation, Sub-Cultivation
The Map strains were originally isolated from feces and different tissues of cattle and non-cattle, as well as from boot swabs and slurry collected in cattle barns of individual herds according to the standardized protocol described in the official manual of diagnostic procedures of the National Reference Laboratory (NRL) for Paratuberculosis published by the FLI [], with some modifications. Briefly, feces and slurry (3 g) were decontaminated for 48 h using 30 mL 0.75% hexadecyl pyridinium chloride (HPC) solution (Sigma Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany), and crushed tissue (1 g) was decontaminated for 24 h using 7 mL 0.9% HPC, both at room temperature. After centrifugation (20 min, 1880× g) and discarding of the supernatant, the pellet was resuspended in 1 mL 1 × PBS (phosphate-buffered saline), and 0.2 mL of this solution was inoculated onto slants of Herrold`s egg yolk-medium (FLI, Jena, Germany) with ANV (Amphotericin, nalidixic acid, and Vancomycin), Löwenstein-Jensen Map medium, and Stonebrink Map medium with pyruvate (Artelt-Enclit, Borna, Germany), all supplemented with 2 mg/L of Mycobactin J and incubated at 37 °C for three to twelve months. The Mycobactin J dependence of these isolates was confirmed to exclude other mycobacterial species as sources. Characteristic colonies appeared after four to six weeks at the earliest. Boot swab samples (n = 17) were processed differently [] in different laboratories. Fecal material was either rinsed off with sterile PBS and centrifuged prior to decontamination with 0.75% HPC solution, or about 5 g of cut boot swabs was placed directly in the 0.75% HPC solution and processed further, as described above [].
After confirmation of Map subspecies, as described below, culture material for each Map isolate was cryo-conserved in Middlebrook bouillon (MB 7H9) supplemented with Mycobactin J (Allied Monitor, Inc. Fayette, MO, or IDvet, Grabels, France), glycerol, 10% Middlebrook Oleic acid, Albumin, Dextrose, and Catalase (OADC) enrichment (Becton Dickinson) and PANTA (Polymyxin B, Amphotericin B, nalidixic acid, Trimethoprim, Azlocillin—all SIGMA-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) at −80 °C or was used directly for genotyping.
Map isolates supplied by other German Federal State laboratories and cryo-conserved isolates were sub-cultivated at the FLI in Middlebrook bouillon (MB 7H9) supplemented with Mycobactin J and 10% Middlebrook Oleic acid, Albumin, Dextrose, and Catalase (OADC) enrichment (Becton Dickinson, Sparks, MD, USA), tested for their subspecies identity, and were mass-cultivated on solid media as mentioned above.
4.2.2. DNA Extraction for PCR Reactions
DNA was isolated from several colonies of culture material after decontamination (20 min at 80 °C), followed by ultrasonication (35 kHz, 10 min), heating (10 min at 100 °C in a heating block), and centrifugation for 5 min at 12,000 rpm (15,300× g). The supernatant was centrifuged again for 5 min at 12,000 rpm, and DNA concentration was measured using a NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA). For the IS900-RFLP analysis described below, DNA was isolated using the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method (see Section 4.3.1).
4.2.3. Molecular Map Identification
After 4 to 12 weeks (or longer for sheep and some cattle isolates), DNA was extracted from visible bacterial growth in cultures and characterized using PCR assays that speciate Mycobacterium (M.) avium complex (MAC) bacteria. These assays target the reliable subspecies-specific markers: IS900 [], IS1245 [], and IS901 []. Map was detected (IS900 positive, IS1245 negative, and IS901 negative) and distinguished from Mah (IS900 negative, IS1245 positive, and IS901 negative) and M. avium subsp. avium (IS900 negative, IS1245 positive, and IS901 positive).
4.3. Molecular Genotyping
Map-isolates were differentiated into C- or S-type and within the S-type group into subtype I or III by targeting the gyrA gene (gyrA-2 and gyrA-3) using two different PCR assays with subsequent sequencing []. These assignments were later confirmed by IS900-RFLP-profile analysis [] when a large amount of high-quality DNA was available. Three complementary typing techniques were applied for more detailed sub-typing: IS900-RFLP, MIRU-VNTR, and SSR analysis.
4.3.1. IS900-RFLP Analysis
IS900-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) analysis is a classical Southern blot method used for differentiation of Map strains [] using the Map-specific IS900 element, which is present 16 to 22 times in the genome []. DNA is cut into thousands of fragments by specific restriction enzymes, separated according to their sizes in an agarose gel, and hybridized with a Map-specific IS900 probe. Following immunological detection and visualization, specific IS900 band patterns are revealed for each isolate. The IS900-RFLP patterns differ between the C-type and S-type (subtypes I and III) lineage(s) and within the S-type lineage due to different genome structures and numbers of IS900 elements. Within the C-type lineage, genomes show strong synteny and an identical or nearly identical number of IS elements [,]. Furthermore, it is assumed that the chromosomal localization of the IS900 elements (IS900 loci) within the main Map-lineages is conserved []. Therefore, different IS900 patterns are presumably also based on differences (SNVs/SNPs and epigenetic modifications []) in the DNA of each isolate at the restriction sites of the respective digestion enzyme, leading to associated changes in the DNA fragment lengths in gel.
For IS900-RFLP, genomic DNA of high quality was required. It was extracted using a modification of the standardized CTAB method []. This modified method included treatment of killed bacteria resuspended in 500 µL of TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) with 1 µL of RNAse A (10 mg/mL) and 50 µL of lysozyme (10 mg/mL) and incubation overnight (rather than for 1 h) at 37 °C. In contrast to the standard CTAB method [], the treatment with proteinase K and SDS was followed by the addition of 100 (rather than 80) µL of CTAB/NaCl solution and also 100 µL of 5 M NaCl solution. Three additional wash steps with 70% ethanol and centrifugation at 12,000 rpm (15,300× g) at 4 °C (four wash steps in total) were performed on the DNA pellets, including drying DNA for 20 min at 60 °C (rather than air drying), and dissolving the DNA in EB buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5) (rather than 0.1X TE) for 1 h at 60 °C, which were also part of the modifications. DNA isolation for the other two typing methods was described above.
IS900-RFLP analysis was by Sothern blotting as previously described in []. Briefly, two micrograms of purified genomic DNA from each isolate was digested with BstEII and PstI (New England Biolabs, Frankfurt am Main, Germany). The resulting DNA fragments were separated by horizontal electrophoresis on a 240 mm 1% (w/v) agarose gel at 65 V for 16 h, vacuum blotted onto a HybondTM-N nylon membrane (Amersham Biosciences, Little Chalfont, UK), and hybridized with a digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled DNA probe specific for insertion element IS900 (Southern blotting). The target molecules were subjected to immunological detection with anti-DIG antibodies conjugated to alkaline phosphatase (DIG luminescence detection kit; Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). The CSPD detection system was used to visualize the hybridized probe (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Hyperfilm ECL (GE Healthcare, Freiburg, Germany) was exposed after placement on the nylon membrane and developed for an optimal exposure time of 1 to 30 min.
The probe was prepared by PCR amplification using the forward primer 5′-TGG ACA ATG ACG GTT ACG GAG GTG G-3′ and the reverse primer 5′-GAT CGG AAC GTC GGC TGG TCA GGA T-3′ recommended in the standardized IS900-RFLP protocol [] with genomic DNA of Map strain ATCC 19698 as the source. PCR was conducted with a digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) mixture (DIG DNA labeling mix; Roche Diagnostics) []. The amplification product was purified with a QIAquick gel extraction kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). This probe was a specific IS900 fragment of 453 bp containing no PstI and no BstEII digestion site.
The resulting IS900-RFLP genotypes consisted of two robust band patterns. Known patterns were designated with the nomenclature described previously after BstEII digestion with “C” [cattle type] or with “I” [intermediate type (=subtype III)] and after PstI digestion with P, together with sequential numbers [,,,,,,,,,,]. To simplify the nomenclature, the former IS900-RFLP (BstEII) patterns Cn1-Cn9 [,,] were changed to C41-C49. New patterns were given new designations.
4.3.2. MIRU-VNTR Typing
Mycobacterial interspersed repetitive-unit–variable-number tandem repeat (MIRU-VNTR) typing is based on the Map strain depending on variation in the number of different short tandem repeat structures comprising repetitive nucleotide sequences (minisatellites of 18–58 nt) at multiple conserved (putative intergenic) loci throughout the Map genome [,,].
MIRU-VNTR typing in this study was performed using specific PCR reactions targeting eight mini-satellite regions (loci 292, X3, 25, 47, 3, 7, 10, and 32), []. The PCR conditions and annealing temperatures were updated []. The number of copies of mycobacterial interspersed repetitive units (MIRUs) at loci 292 and X3 and of variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) at loci 25, 47, 3, 7, 10, and 32 were determined according to the sizes of the amplicons after separation by electrophoresis using 1.5% agarose gels (universal agarose, Bio&Sell, Feucht, Germany). Different-sized alleles were classified using an allele-calling table [,]. The numbers of these repeats were arranged according to the mentioned order of loci and assigned to given numerical codes according to the INRA Nouzilly MIRU-VNTR (INMV) nomenclature for MIRU-VNTR patterns, the so-called INMV profiles, available in the freely accessible MAC-INMV-SSR database http://mac-inmv.tours.inra.fr (accessed on 1 September 2024) []. For new numerical codes, new INMV profile numbers were assigned by the database managers upon request. Additionally, to identify polymorphisms at VNTR locus 7 for strains with unusual amplicon sizes, PCR products were purified using the QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and sequenced at Eurofins Genomics GmbH (Konstanz, Germany). Resulting sequence chromatograms were compared with reference sequences []. Furthermore, to analyze unusual or unclear results at other VNTR loci, amplicons of PCRs with these regions were also sequenced. In our analysis, 8.6 tandem repeats (TR) at VNTR32 locus were interpreted as 8 TR.
4.3.3. SSR Analysis
Short-sequence repeat (SSR) analysis of Map is based on microsatellite structures with strain-depending variations in the numbers of mono-, di-, and trinucleotide repeats at specific loci in the genome []. Depending on the number and stability of the selected polymorphic SSR loci analyzed, the method is very useful for distinguishing Map isolates, as well as in combination with other typing methods [,,]. The impact of the copy number of the SSR at the different genome loci on the expression of neighboring genes is not yet known [].
SSR analysis was applied according to the published procedure [,]. The microsatellite structures at SSR locus 1 (G1 repeats), locus 8 (GGT repeats), and locus 9 (TGC repeats) were chosen because these are the most informative SSR loci [,,,]. The same primers were used as published []. For amplification of G1 repeats, a specific polymerase (Herculase II Fusion DNA polymerase; Agilent Technologies, Cedar Creek, TX, USA) was chosen to minimize the risk of polymerase slippage at poly(G) motifs. PCR products were purified using the QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and sequenced at Eurofins Genomics GmbH (Konstanz, Germany).
The number of specific repeats at these loci was given a numerical code. Isolates with 11 or more G1 repeats at locus 1 were designated as ≥11 because of slipping effects of the polymerase described previously [,]. Locus 2 was not included, as it was found to be unreliable in previous studies [,]. The three SSR loci used for this work are referred to below as SSR1, SSR8, and SSR9.
4.3.4. Analysis of Typing Results and Discriminatory Power
Altogether, this complementary genotyping method used 13 different target structures within the Map genome and resulted in two band patterns of IS900-RFLP, repeat numbers at eight specific MIRU-VNTR loci, and repeat numbers at three specific SSR loci. Isolates that differed in at least one or more of these targets/genomic markers were considered to have distinct genotypes.
The discriminatory power of genotyping (IS900-RFLP, MIRU-VNTR, and SSR typing alone and combined) was calculated using the discriminatory index (DI) according to Hunter and Gaston [], as described before []. The DI indicates the probability of each typing approach to discriminate between two epidemiologically unlinked strains of the German Map population in this study. Only epidemiologically unrelated (=independent) strains were included in these calculations. This means that if a genotype occurred in more than one isolate in the same herd, it was only considered once. Therefore, depending on the typing method (separate or combined), the number of independent strains for calculation varied. Isolates with a mixed genotype were included as two individual genotypes.
4.4. Comparison of Strains and Analysis of Phylogeny
Phylogenies were constructed using the unweighted-pair group method with arithmetic averages (UPGMA) to compare categorical values for the combined genotypes. The relationships of all identified genotypes of strains, their distribution in cattle herds and other hosts or federal states, and the pairwise relationships of strains within federal states for epidemiological investigations were visualized with similarity matrice-based dendrograms and minimum spanning trees (MST). The dendrograms and MSTs were generated using BioNumerics software version 7.5 created by Applied Maths NV (St-Martens-Latem, Belgium).
5. Conclusions
This study of isolates spanning 24 years gave an overview of the diversity of 507 Map isolates belonging to the C-type group, and, in addition, 11 isolates of the S-type group originating from a country in the middle of Europe where paratuberculosis is endemic in dairy cattle and has a variable prevalence and long history. This study was based on a very large Map strain collection, started with isolates from 1993. The high discriminatory power of the combined multi-locus genotyping, consisting of IS900-RFLP (BstEII, PstI), MIRU-VNTR, and SSR, enabled the detection of high Map diversity in Germany. Map transmission between cattle herds within or between federal states and between different hosts, including domestic and wildlife animals, was suggested. There were predominant genotypes distributed in cattle herds in most of the federal states that also had infected non-cattle species. Two or more genotypes revealed in isolates from individual animals, single herds, and locations indicated possible polyclonal infections. Similar genotypes with differences at only one typing target in isolates from one origin (single isolates, animals, and herds) suggested divergent evolution. There was no significant association of genotypes with their geographical origin. This study could not match inferences about Map transmission facilitated by WGS-based studies, but the modularity of the method used (RFLP IS900, MIRU-VNTR, and SSR) allowed for comparisons with typing using one or more of these methods carried out by other groups, facilitating comparisons of genotype distributions within and across national boundaries. In comparison to the results of high-resolution WGS-based studies, it would be interesting to find out what role the polymorphisms at the MIRU-VNTR and SSR loci and the SNPs or variable genome structure responsible for the different RFLP patterns play in revealing Map transmission and phylogenetic relationships. Further studies will compare the current combined genotyping results with those of whole-genome core SNP-based analysis of a selection of these Map strains to clarify the validity/importance of the observed clustering of combined genotypes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26115273/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.M. and H.K.; methodology, P.M.; formal analysis, P.M.; investigation, P.M.; resources, P.M. and H.K.; data curation, P.M.; writing—original draft preparation, P.M. and M.P.-C.; writing—review and editing, P.M., M.P.-C. and H.K.; visualization, P.M.; supervision, P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Institutional Review Board Statement was waived because the samples from which the isolates were obtained (feces, tissues, and environmental samples) were collected by field veterinarians, members of German animal health services, and veterinary diagnosticians, respectively, during the investigation of suspected clinical cases and during the examination of dead animals as part of the health monitoring of herds and as part of field studies.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated and analyzed during this study are included in the Supplementary Material. Additionally, data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kerstin Steger for her excellent technical assistance in genotyping, Marcus Pfau for his support with image processing, and the former and present staff of the NRL for Paratuberculosis for the establishment and maintenance of the strain collection (Friedrich Loeffler-Institut, Jena). We are very grateful to the many colleagues from different state laboratories and universities in Germany for providing us with Map isolates or animal samples for Map isolation. This included STUA Aulendorf; CVUA-RRW Krefeld; LAVES Oldenburg; TLLV Bad Langensalza; LALLF MV Rostock; LAV Sachsen-Anhalt; LUA Sachsen; LUA Rheinland-Pfalz; ILAT Berlin; LHL Hessen; TiHo Hannover; the Institute for Food Hygiene at the University of Giessen; Giessen University Hospital; veterinary practitioners; and veterinarians of the animal health services of Thuringia, Saxony, and Bavaria.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Marian Price-Carter was employed by the company AgResearch Ltd. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Glossary
Isolate = the culture of multiple colonies resulting from decontamination, inoculation, and incubation of one specimen of distinct origin on media; genotype = a unique pattern differing at least 1 of 13 different target regions from other known types, as determined by the combined IS900-RFLP, MIRU-VNTR, and SSR genotyping assay used in this study; strain = a specific genotype identified one or more times in one or more herds or locations; independent strain = a specific genotype identified one or more times in one herd or source.
References
- Whitlock, R.H.; Buergelt, C. Preclinical and clinical manifestations of paratuberculosis (including pathology). Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 1996, 12, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windsor, P.A. Paratuberculosis in sheep and goats. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittington, R.; Donat, K.; Weber, M.F.; Kelton, D.; Nielsen, S.S.; Eisenberg, S.; Arrigoni, N.; Juste, R.; Saez, J.L.; Dhand, N.; et al. Control of paratuberculosis: Who, why and how. A review of 48 countries. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, P.; Barkema, H.W.; Mason, S.; Beaulieu, E.; Hall, D.C. Economic losses due to Johne’s disease (paratuberculosis) in dairy cattle. J. Dairy. Sci. 2021, 104, 3123–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardaro, R.; Pieragostini, E.; Rubino, G.; Petazzi, F. Impact of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis on profit efficiency in semi-extensive dairy sheep and goat farms of Apulia, southern Italy. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 136, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, S.; Krieger, M.; Campe, A.; Lorenz, I.; Einax, E.; Donat, K. Herd Prevalence Estimation of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis Burden in the Three Main Dairy Production Regions of Germany (PraeMAP). Animals 2022, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stau, A.; Seelig, B.; Walter, D.; Schroeder, C.; Ganter, M. Seroprevalence of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in small ruminants in Germany. Small Rumin. Res. 2012, 105, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, I.; Luyven, G.; Kohler, H.; Lutz, W.; Mobius, P. Suspicion of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis transmission between cattle and wild-living red deer (Cervus elaphus) by multitarget genotyping. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, M.; Hansen, S.; Knauf-Witzens, T.; Oelemann, W.M.R.; Czerny, C.P.; Abd El Wahed, A.; Goethe, R. Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis Infection in Zoo Animals: A Review of Susceptibility and Disease Process. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 572724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobius, P.; Fritsch, I.; Luyven, G.; Hotzel, H.; Kohler, H. Unique genotypes of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains of Type III. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, L.; Garzelli, C. Genetic diversity and phylogeny of Mycobacterium avium. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, J.W.; Bull, T.J.; Seemann, T.; Bulach, D.M.; Wagner, J.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Michalski, W.P. Exploring the zoonotic potential of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis through comparative genomics. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, R.; Bulte, M.; Gerlach, G.F.; Goethe, R.; Hornef, M.W.; Kohler, H.; Meens, J.; Mobius, P.; Roeb, E.; Weiss, S.; et al. Facts, myths and hypotheses on the zoonotic nature of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruska, K.; Sechi, L.A. Long History of Queries about Bovine Paratuberculosis as a Risk Factor for Human Health. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Aitken, J.; Hamblin, H.; Collins, M.; Borody, T.J. Putting Crohn’s on the MAP: Five Common Questions on the Contribution of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis to the Pathophysiology of Crohn’s Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.M.; Thibault, V.C.; Smith, D.G.; McLuckie, J.; Heron, I.; Sevilla, I.A.; Biet, F.; Harris, S.R.; Maskell, D.J.; Bentley, S.D.; et al. Phylogenomic exploration of the relationships between strains of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlstrom, C.; Barkema, H.W.; Stevenson, K.; Zadoks, R.N.; Biek, R.; Kao, R.; Trewby, H.; Haupstein, D.; Kelton, D.F.; Fecteau, G.; et al. Genome-Wide Diversity and Phylogeography of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in Canadian Dairy Cattle. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.M.; Gabric, D.M.; de Lisle, G.W. Identification of two groups of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis strains by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.J.; Marsh, I.B.; Saunders, V.; Grant, I.R.; Juste, R.; Sevilla, I.A.; Manning, E.J.; Whitlock, R.H. Culture phenotypes of genomically and geographically diverse Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolates from different hosts. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, K. Genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis and the influence of strain type on infection and pathogenesis: A review. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, E.; Aranaz, A.; Romero, B.; de Juan, L.; Alvarez, J.; Bezos, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Stevenson, K.; Mateos, A.; Dominguez, L. Polymorphisms in gyrA and gyrB genes among Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis type I, II, and III isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3439–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biet, F.; Sevilla, I.A.; Cochard, T.; Lefrancois, L.H.; Garrido, J.M.; Heron, I.; Juste, R.A.; McLuckie, J.; Thibault, V.C.; Supply, P.; et al. Inter- and intra-subtype genotypic differences that differentiate Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis strains. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdugo, C.; Pleydell, E.; Price-Carter, M.; Prattley, D.; Collins, D.; de Lisle, G.; Vogue, H.; Wilson, P.; Heuer, C. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolated from sheep, cattle and deer on New Zealand pastoral farms. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 117, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, I.; Garrido, J.M.; Geijo, M.; Juste, R.A. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profile homogeneity of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolates from cattle and heterogeneity of those from sheep and goats. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, S.; Stephan, R.; Zumthor, J.P.; Kipar, A.; Seehusen, F. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of a New Mycobacterium avium Subsp. paratuberculosis S-Type Strain Genotype in Goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machackova, M.; Svastova, P.; Lamka, J.; Parmova, I.; Liska, V.; Smolik, J.; Fischer, O.A.; Pavlik, I. Paratuberculosis in farmed and free-living wild ruminants in the Czech Republic (1999–2001). Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 101, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Hsu, C.; Alyamani, E.J.; Shehata, M.M.; Al-Dubaib, M.A.; Al-Naeem, A.; Hashad, M.; Mahmoud, O.M.; Alharbi, K.B.; Al-Busadah, K.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the emerging infection with Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis in the Arabian camels (Camelus dromedarius). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackintosh, C.G.; Labes, R.E.; Clark, R.G.; de Lisle, G.W.; Griffin, J.F. Experimental infections in young red deer (Cervus elaphus) with a bovine and an ovine strain of Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis. N. Z. Vet. J. 2007, 55, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobius, P.; Liebler-Tenorio, E.; Holzer, M.; Kohler, H. Evaluation of associations between genotypes of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculsis and presence of intestinal lesions characteristic of paratuberculosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 201, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizzi, R.; Timms, V.J.; Price-Carter, M.L.; Gautam, M.; Whittington, R.; Heuer, C.; Biggs, P.J.; Plain, K.M. Comparative Genomics of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Paratuberculosis Sheep Strains. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 637637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibberg, D.; Price-Carter, M.; Ruckert, C.; Blom, J.; Mobius, P. Complete Genome Sequence of Ovine Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Strain JIII-386 (MAP-S/type III) and Its Comparison to MAP-S/type I, MAP-C, and M. avium Complex Genomes. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannantine, J.P.; Li, L.L.; Sreevatsan, S.; Kapur, V. How does a Mycobacterium change its spots? Applying molecular tools to track diverse strains of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 57, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motiwala, A.S.; Li, L.; Kapur, V.; Sreevatsan, S. Current understanding of the genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, E.; de Juan, L.; Dominguez, L.; Aranaz, A. Progress in molecular typing of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 92, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, A.; Zschock, M.; Ewers, C.; Eisenberg, T. Genotyping methods and molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP). Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2018, 6, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.J.; Hope, A.F.; Marshall, D.J.; Taragel, C.A.; Marsh, I. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis: IS900 restriction fragment length polymorphism and IS1311 polymorphism analyses of isolates from animals and a human in Australia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3240–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlik, I.; Bartl, J.; Dvorska, L.; Svastova, P.; du Maine, R.; Machackova, M.; Yayo Ayele, W.; Horvathova, A. Epidemiology of paratuberculosis in wild ruminants studied by restriction fragment length polymorphism in the Czech Republic during the period 1995–1998. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 77, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, I.; Li, L.; Amonsin, A.; Garrido, J.M.; Geijo, M.V.; Kapur, V.; Juste, R.A. Comparative analysis of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolates from cattle, sheep and goats by short sequence repeat and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, V.C.; Grayon, M.; Boschiroli, M.L.; Willery, E.; Allix-Beguec, C.; Stevenson, K.; Biet, F.; Supply, P. Combined multilocus short-sequence-repeat and mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit-variable-number tandem-repeat typing of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 4091–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douarre, P.E.; Cashman, W.; Buckley, J.; Coffey, A.; O’Mahony, J. Molecular characterization of Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis using multi-locus short sequence repeat (MLSSR) and mycobacterial interspersed repetitive units-variable number tandem repeat (MIRU-VNTR) typing methods. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 149, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsmann, H.; Stalder, G.L.; Spergser, J.; Hoelzl, F.; Deutz, A.; Kuebber-Heiss, A.; Walzer, C.; Smith, S. Multiple strain infections and high genotypic diversity among Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis field isolates from diseased wild and domestic ruminant species in the eastern Alpine region of Austria. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronai, Z.; Csivincsik, A.; Gyuranecz, M.; Kreizinger, Z.; Dan, A.; Janosi, S. Molecular analysis and MIRU-VNTR typing of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains from various sources. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioffre, A.; Munoz, M.C.; Pinedo, M.F.A.; Vaca, R.; Morsella, C.; Fiorentino, M.A.; Paolicchi, F.; Ruybal, P.; Zumarraga, M.; Traveria, G.E.; et al. Molecular typing of Argentinian Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis isolates by multiple-locus variable number-tandem repeat analysis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kruijf, M.; Lesniak, O.N.; Yearsley, D.; Ramovic, E.; Coffey, A.; O’Mahony, J. Low genetic diversity of bovine Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis isolates detected by MIRU-VNTR genotyping. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 203, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricchi, M.; Barbieri, G.; Taddei, R.; Belletti, G.L.; Carra, E.; Cammi, G.; Garbarino, C.A.; Arrigoni, N. Effectiveness of combination of Mini-and Microsatellite loci to sub-type Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Italian type C isolates. BMC Vet. Res. 2011, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amonsin, A.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Bannantine, J.P.; Motiwala, A.S.; Sreevatsan, S.; Kapur, V. Multilocus short sequence repeat sequencing approach for differentiating among Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M. Studies on the Strain Differentiation of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Doctoral Dissertation, Freie Universität Berlin, Mensch und Buch Verlag Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Silva, J.A.; Abdulmawjood, A.; Akineden, O.; Drager, K.; Klawonn, W.; Bulte, M. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis at a regional scale in Germany. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, A.; Zschöck, M.; Ewers, C.; Eisenberg, T. Development of a hierarchical typing approach for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP) and characterization of MAP field cultures from Central Germany. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, V.C.; Grayon, M.; Boschiroli, M.L.; Hubbans, C.; Overduin, P.; Stevenson, K.; Gutierrez, M.C.; Supply, P.; Biet, F. New variable-number tandem-repeat markers for typing Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and M. avium strains: Comparison with IS900 and IS1245 restriction fragment length polymorphism typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2404–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodoma, E.; Altmann, S.; Mitterhuemer, S.; Moebius, P.; Duenser, M. First comprehensive study on molecular diversity of Austrian Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis isolates from domestic and wild ruminants. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2017, 131, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobius, P.; Luyven, G.; Hotzel, H.; Kohler, H. High genetic diversity among Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains from German cattle herds shown by combination of IS900 restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis and mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit-variable-number tandem-repeat typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, K.; Alvarez, J.; Bakker, D.; Biet, F.; de Juan, L.; Denham, S.; Dimareli, Z.; Dohmann, K.; Gerlach, G.F.; Heron, I.; et al. Occurrence of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis across host species and European countries with evidence for transmission between wildlife and domestic ruminants. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perets, V.; Allen, A.; Crispell, J.; Cassidy, S.; O’Connor, A.; Farrell, D.; Browne, J.A.; O’Mahony, J.; Skuce, R.; Kenny, K.; et al. Evidence for local and international spread of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis through whole genome sequencing of isolates from the island of Ireland. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 268, 109416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, C.; Theze, J.; Cochard, T.; Rossignol, M.N.; Fourichon, C.; Delafosse, A.; Joly, A.; Guatteo, R.; Schibler, L.; Bannantine, J.P.; et al. Genetic Features of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Strains Circulating in the West of France Deciphered by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e03392-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, A.; Ollier, S.; Tahlan, K.; Biet, F.; Bissonnette, N. Genomic epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis isolates from Canadian dairy herds provides evidence for multiple infection events. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1043598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgeman, R.; Mann, R.; Savin, K.; Djitro, N.; Rochfort, S.; Rodoni, B. Molecular characterisation of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in Australia. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlik, I.; Horvathova, A.; Dvorska, L.; Bartl, J.; Svastova, P.; du Maine, R.; Rychlik, I. Standardisation of restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis for Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 38, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipple, D.; Kapke, P.; Vary, C. Identification of restriction fragment length polymorphisms in DNA from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2561–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leao, C.; Goldstone, R.J.; Bryant, J.; McLuckie, J.; Inacio, J.; Smith, D.G.; Stevenson, K. Novel Single Nucleotide Polymorphism-Based Assay for Genotyping Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johne, H.A.; Frothingham, L. Ein eigenthuemlicher Fall von tuberkulose beim Rind. Dtsch. Z. Tiermed. Path 1895, 21, 438–454. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, E.H.G.; Gill, D.A. Johne’s disease. N. Z. J. Agric. 1937, 54, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini, R.J.; Van Kruiningen, H.J.; Merkal, R.S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne’s disease): The current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984, 74, 218–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P.J.; Walthers, E.A.; Kalif, A.S.; Richmond, K.L.; Adair, D.M.; Hill, K.K.; Kuske, C.R.; Andersen, G.L.; Wilson, K.H.; Hugh-Jones, M.; et al. Characterization of the variable-number tandem repeats in vrrA from different Bacillus anthracis isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Aertsen, A.; Michiels, C.W. The role of variable DNA tandem repeats in bacterial adaptation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Xu, S.; Huang, H. The discovery, function and development of the variable number tandem repeats in different Mycobacterium species. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 738–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semret, M.; Turenne, C.Y.; de Haas, P.; Collins, D.M.; Behr, M.A. Differentiating host-associated variants of Mycobacterium avium by PCR for detection of large sequence polymorphisms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, E.; Aranaz, A.; Gould, K.A.; Linedale, R.; Stevenson, K.; Alvarez, J.; Dominguez, L.; de Juan, L.; Hinds, J.; Bull, T.J. Discovery of stable and variable differences in the Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis type I, II, and III genomes by pan-genome microarray analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannantine, J.P.; Conde, C.; Bayles, D.O.; Branger, M.; Biet, F. Genetic Diversity Among Mycobacterium avium Subspecies Revealed by Analysis of Complete Genome Sequences. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas, I.; Homolka, S.; Niemann, S.; Gagneux, S. Genotyping of genetically monomorphic bacteria: DNA sequencing in Mycobacterium tuberculosis highlights the limitations of current methodologies. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlstrom, C.; Barkema, H.W.; Stevenson, K.; Zadoks, R.N.; Biek, R.; Kao, R.; Trewby, H.; Haupstein, D.; Kelton, D.F.; Fecteau, G.; et al. Limitations of variable number of tandem repeat typing identified through whole genome sequencing of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis on a national and herd level. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasnitz, N.; Kohler, H.; Weigoldt, M.; Gerlach, G.F.; Mobius, P. Stability of genotyping target sequences of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis upon cultivation on different media, in vitro- and in vivo passage, and natural infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, C.A.; Jones-Bitton, A.; Ahlstrom, C.; Mutharia, L.; De Buck, J.; Jansen, J.; Kelton, D.; Menzies, P. Identification of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis strains isolated from dairy goats and dairy sheep in Ontario, Canada. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 81, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rasper-Hossinger, M.; Biggel, M.; Stephan, R.; Seehusen, F.; Scherrer, S. Strain diversity in Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis-positive bovine fecal samples collected in Switzerland. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1154516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, J.A.A. Johne’s disease in a bovine associated with the pigmented strain of Mycobacterium johnei. Vet. Rec. 1954, 66, 387. [Google Scholar]
- Whittington, R.J.; Taragel, C.A.; Ottaway, S.; Marsh, I.; Seaman, J.; Fridriksdottir, V. Molecular epidemiological confirmation and circumstances of occurrence of sheep (S) strains of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in cases of paratuberculosis in cattle in Australia and sheep and cattle in Iceland. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 79, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Juan, L.; Alvarez, J.; Aranaz, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Romero, B.; Bezos, J.; Mateos, A.; Dominguez, L. Molecular epidemiology of Types I/III strains of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis isolated from goats and cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 115, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochard, T.; Branger, M.; Supply, P.; Sreevatsan, S.; Biet, F. MAC-INMV-SSR: A web application dedicated to genotyping members of Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) including Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 77, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, T.; Volmer, R.; Eskens, U.; Moser, I.; Nesseler, A.; Sauerwald, C.; Seeger, H.; Klewer-Fromentin, K.; Mobius, P. Outbreak of reproductive disorders and mycobacteriosis in swine associated with a single strain of Mycobacterium avium subspecies hominissuis. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subangkit, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Ishida, M.; Nomura, A.; Yasiki, N.; Sudaryatma, P.E.; Goto, Y.; Okabayashi, T. Genotyping of swine Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis isolates from Kyushu, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcordes, S.; Lueders, I.; Grund, L.; Sliwa, A.; Maurer, F.P.; Hillemann, D.; Mobius, P.; Barth, S.A. Clinical outcome and diagnostic methods of atypical mycobacteriosis due to Mycobacterium avium ssp. hominissuis in a group of captive lowland tapirs (Tapirus terrestris). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, A.; Zschock, M.; Ewers, C.; Eisenberg, T. New polymorphisms within the variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) 7 locus of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Mol. Cell. Probes 2016, 30, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperiale, B.R.; Moyano, R.D.; AB, D.I.G.; Romero, M.A.; Alvarado Pinedo, M.F.; Santangelo, M.P.; Traveria, G.E.; Morcillo, N.S.; Romano, M.I. Genetic diversity of Mycobacterium avium complex strains isolated in Argentina by MIRU-VNTR. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.K.; Mitchell, R.M.; Kramer, A.J.; Zurakowski, M.J.; Fyock, T.L.; Whitlock, R.H.; Smith, J.M.; Hovingh, E.; Van Kessel, J.A.; Karns, J.S.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in a longitudinal study of three dairy herds. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.B.; Payeur, J.B.; Kapur, V.; Sreevatsan, S. Short-sequence-repeat analysis of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium isolates collected from animals throughout the United States reveals both stability of loci and extensive diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2970–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hulzen, K.J.; Heuven, H.C.; Nielen, M.; Hoeboer, J.; Santema, W.J.; Koets, A.P. Different Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis MIRU-VNTR patterns coexist within cattle herds. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antognoli, M.C.; Garry, F.B.; Hirst, H.L.; Lombard, J.E.; Dennis, M.M.; Gould, D.H.; Salman, M.D. Characterization of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis disseminated infection in dairy cattle and its association with antemortem test results. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 127, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, C.; O’Grady, D.; O’Meara, F.; Egan, J.; Bassett, H. Relationships between clinical signs, pathological changes and tissue distribution of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis in 21 cows from herds affected by Johne’s disease. Vet. Rec. 2008, 162, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, D.V.; Williams, S.N.; Hope, A.; Eamens, G.J. DNA fingerprinting of Australian isolates of Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis using IS900 RFLP. Aust. Vet. J. 2000, 78, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Juan, L.; Alvarez, J.; Romero, B.; Bezos, J.; Castellanos, E.; Aranaz, A.; Mateos, A.; Dominguez, L. Comparison of four different culture media for isolation and growth of type II and type I/III Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis strains isolated from cattle and goats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5927–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, D.S.; Hauser, P.M.; Francioli, P.; Bille, J. Molecular typing methods and their discriminatory power. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 1998, 4, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaunee, G.; Vergu, E.; Ezanno, P. Modelling of paratuberculosis spread between dairy cattle farms at a regional scale. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickrodt, C.; Kohler, H.; Moog, U.; Liebler-Tenorio, E.M.; Mobius, P. Molecular Diversity of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in Four Dairy Goat Herds from Thuringia (Germany). Animals 2023, 13, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stief, B.; Mobius, P.; Turk, H.; Horugel, U.; Arnold, C.; Pohle, D. [Paratuberculosis in a miniature donkey (Equus asinus f. asinus)]. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2012, 125, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glawischnig, W.; Steineck, T.; Spergser, J. Infections caused by Mycobacterium avium subspecies avium, hominissuis, and paratuberculosis in free-ranging red deer (Cervus elaphus hippelaphus) in Austria, 2001–2004. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, H.; Muller, J.; Kloss, E.; Mobius, P.; Barth, S.A.; Sickinger, M.; Gies, N.; Heydel, C.; Peters, M. Paratuberculosis in South American camelids: Two independent cases in alpacas in Germany. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möbius, P.; Nordsiek, G.; Hölzer, M.; Jarek, M.; Marz, M.; Köhler, H. Complete genome sequence of JIII-1961, a bovine Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis field isolate from Germany. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobius, P.; Holzer, M.; Felder, M.; Nordsiek, G.; Groth, M.; Kohler, H.; Reichwald, K.; Platzer, M.; Marz, M. Comprehensive insights in the Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis genome using new WGS data of sheep strain JIII-386 from Germany. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2585–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut. Paratuberkulose (Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis). Available online: https://www.openagrar.de/servlets/MCRFileNodeServlet/openagrar_derivate_00028517/TK18-Paratuberkulose-2023-04-26_bf.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Hahn, N.; Failing, K.; Eisenberg, T.; Schlez, K.; Zschock, P.M.; Donat, K.; Einax, E.; Kohler, H. Evaluation of different diagnostic methods for the detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in boot swabs and liquid manure samples. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englund, S.; Ballagi-Pordany, A.; Bolske, G.; Johansson, K.E. Single PCR and nested PCR with a mimic molecule for detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1999, 33, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, C.; Bernasconi, C.; Burki, D.; Bodmer, T.; Telenti, A. A novel insertion element from Mycobacterium avium, IS1245, is a specific target for analysis of strain relatedness. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, Z.M.; Portaels, F.; McFadden, J.J. Biologically distinct subtypes of Mycobacterium avium differ in possession of insertion sequence IS901. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, C.; Price-Carter, M.; Cochard, T.; Branger, M.; Stevenson, K.; Whittington, R.; Bannantine, J.P.; Biet, F. Whole-Genome Analysis of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis IS900 Insertions Reveals Strain Type-Specific Modalities. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 660002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, B.; Khare, S.; Klein, P.; Roussel, A.; Adams, L.G.; Ficht, T.A.; Rice-Ficht, A.C. Amplified fragment length polymorphism reveals specific epigenetic distinctions between Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis isolates of various isolation types. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2222–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Soolingen, D.; Hermans, P.W.; de Haas, P.E.; Soll, D.R.; van Embden, J.D. Occurrence and stability of insertion sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: Evaluation of an insertion sequence-dependent DNA polymorphism as a tool in the epidemiology of tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2578–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lisle, G.W.; Yates, G.F.; Collins, D.M. Paratuberculosis in farmed deer: Case reports and DNA characterization of isolates of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 1993, 5, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, V.F.; Eamens, G.J.; Turner, M.J.; Jessep, T.M. Identification of a new RFLP type of Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis in epidemiological tracing of bovine Johne’s disease. Aust. Vet. J. 2003, 81, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overduin, P.; Schouls, L.; Roholl, P.; van der Zanden, A.; Mahmmod, N.; Herrewegh, A.; van Soolingen, D. Use of multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis for typing Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 5022–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, T.J.; Sidi-Boumedine, K.; McMinn, E.J.; Stevenson, K.; Pickup, R.; Hermon-Taylor, J. Mycobacterial interspersed repetitive units (MIRU) differentiate Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis from other species of the Mycobacterium avium complex. Mol. Cell. Probes 2003, 17, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.; Kohler, H.; Heenemann, K.; Mobius, P. Mycobacteriosis in Various Pet and Wild Birds from Germany: Pathological Findings, Coinfections, and Characterization of Causative Mycobacteria. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0045222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, E.; Romero, B.; Rodriguez, S.; de Juan, L.; Bezos, J.; Mateos, A.; Dominguez, L.; Aranaz, A. Molecular characterization of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis Types II and III isolates by a combination of MIRU-VNTR loci. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomski, N.; Thibault, V.C.; Karoui, C.; de Cruz, K.; Cochard, T.; Gutierrez, C.; Supply, P.; Biet, F.; Boschiroli, M.L. Determination of genotypic diversity of Mycobacterium avium subspecies from human and animal origins by mycobacterial interspersed repetitive-unit-variable-number tandem-repeat and IS1311 restriction fragment length polymorphism typing methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P.R.; Gaston, M.A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: An application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2465–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).