Development of Compounded Surfactant Foam and Its Application in Emergency Control of Piping in Dikes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Development of Compounded Surfactant Formulation
2.1.1. Initial Selection of Single-Component Surfactant
2.1.2. Selection of Compounded Surfactant Formulation
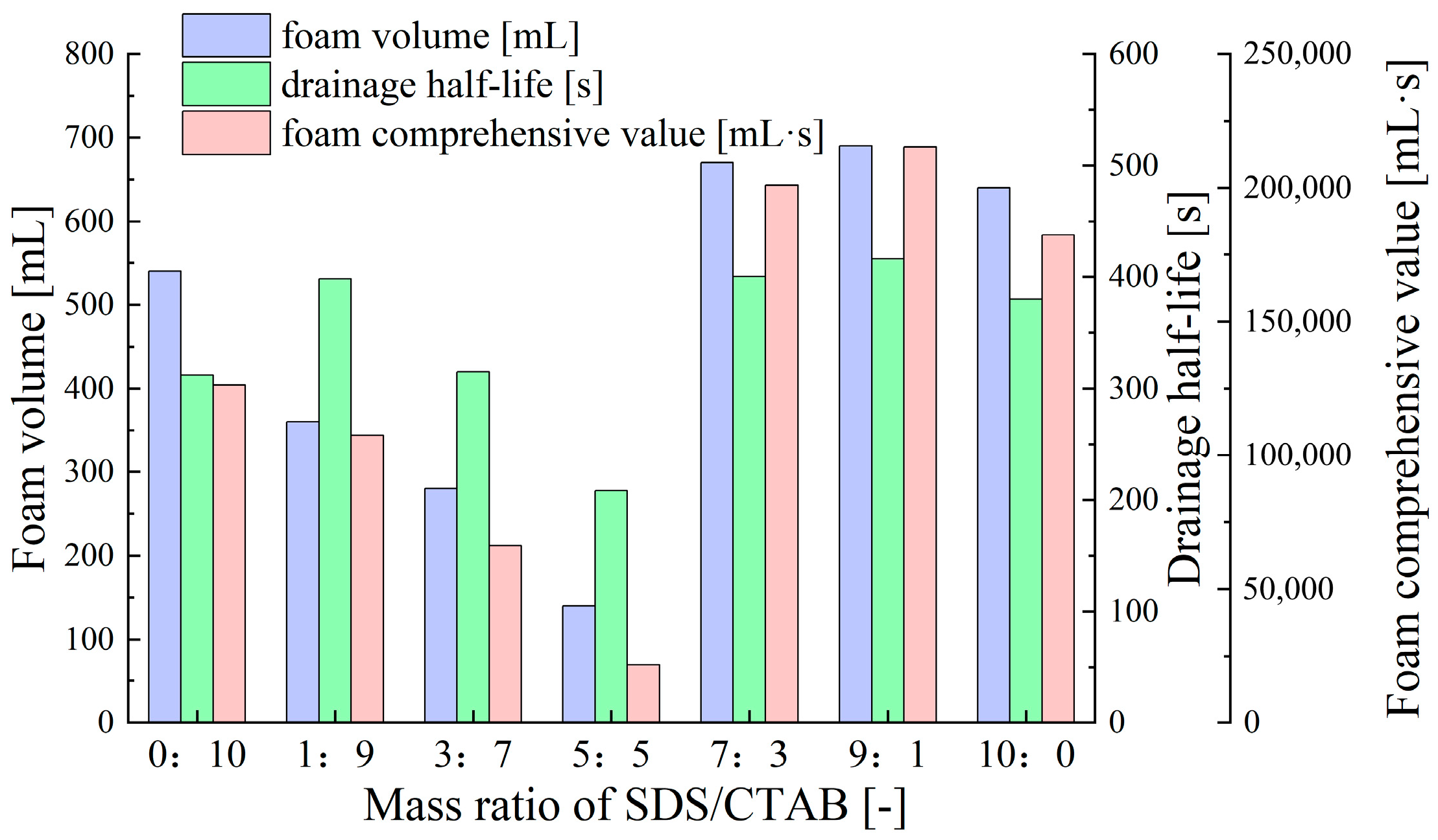
- Synergistic Effects of Anionic–Cationic Surfactant Mixtures
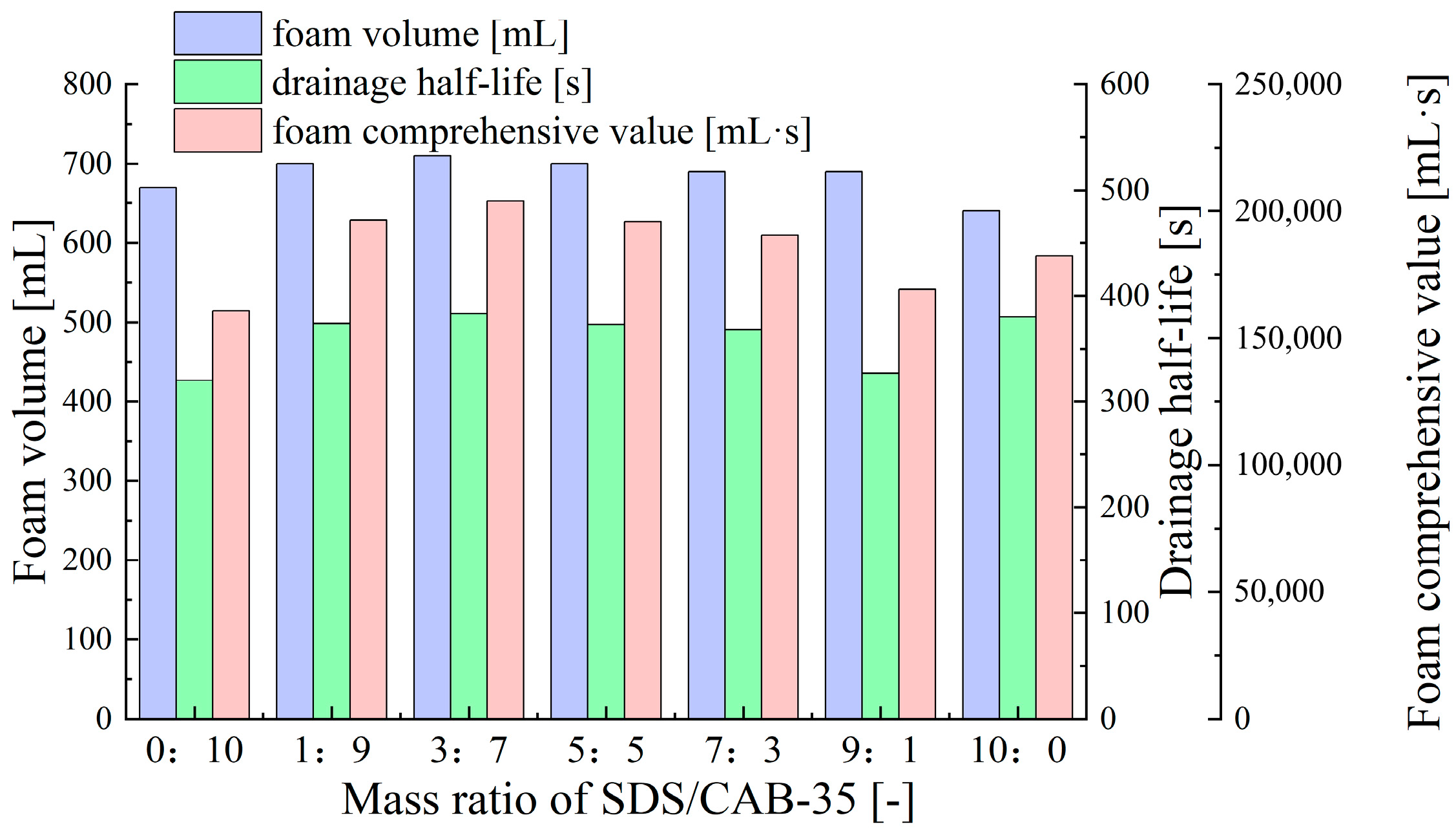
- Synergistic Effects of Anionic–Zwitterionic Surfactant Mixtures
- Synergistic Effects of Anionic–Nonionic Surfactant Mixtures
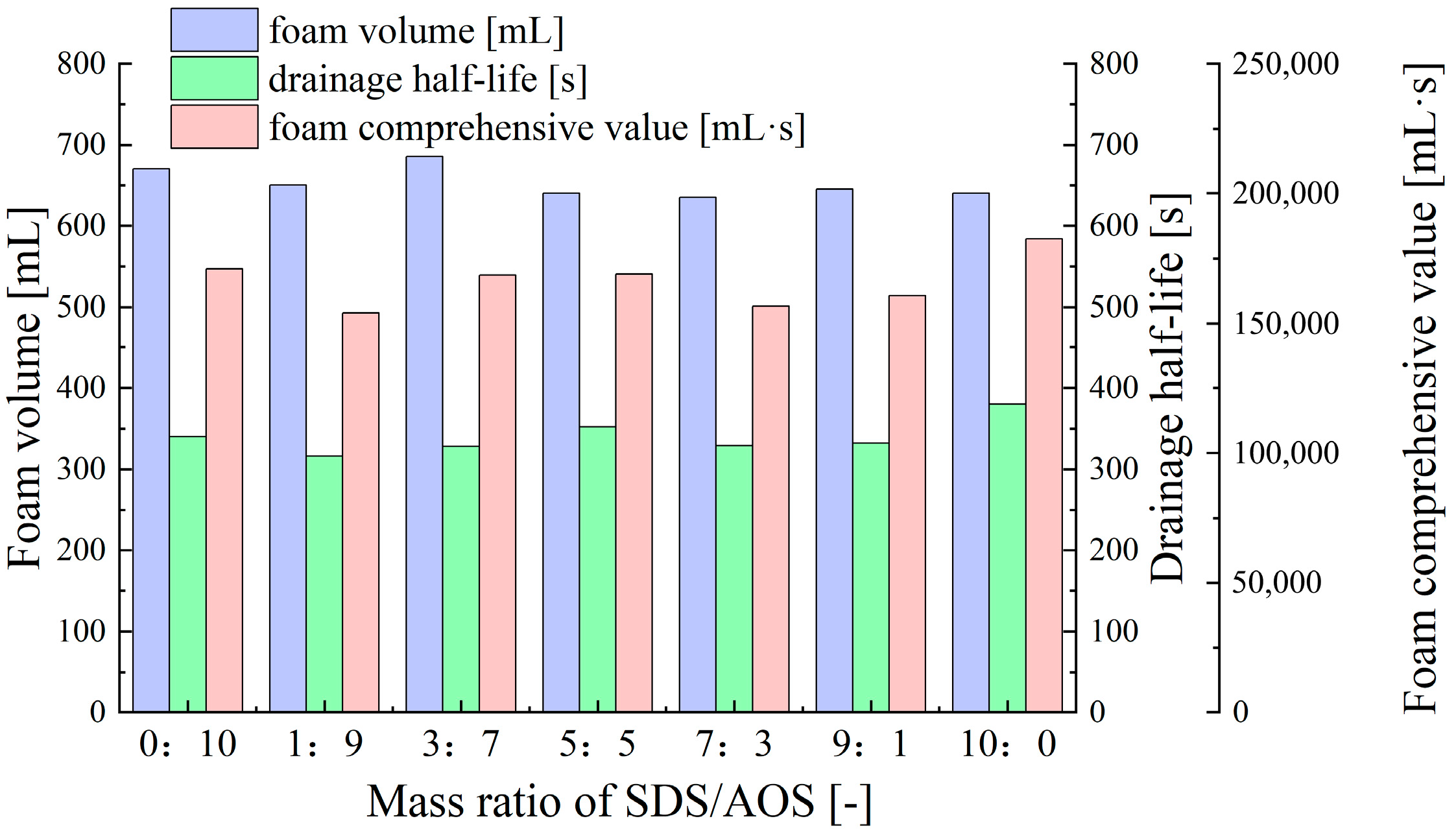
- Synergistic Effects of Anionic–Anionic Surfactant Mixtures
2.1.3. Determination of the Newly Developed Compounded Surfactant Formulation
2.2. Effect of Newly Developed Surfactant Foam in Restraining Piping
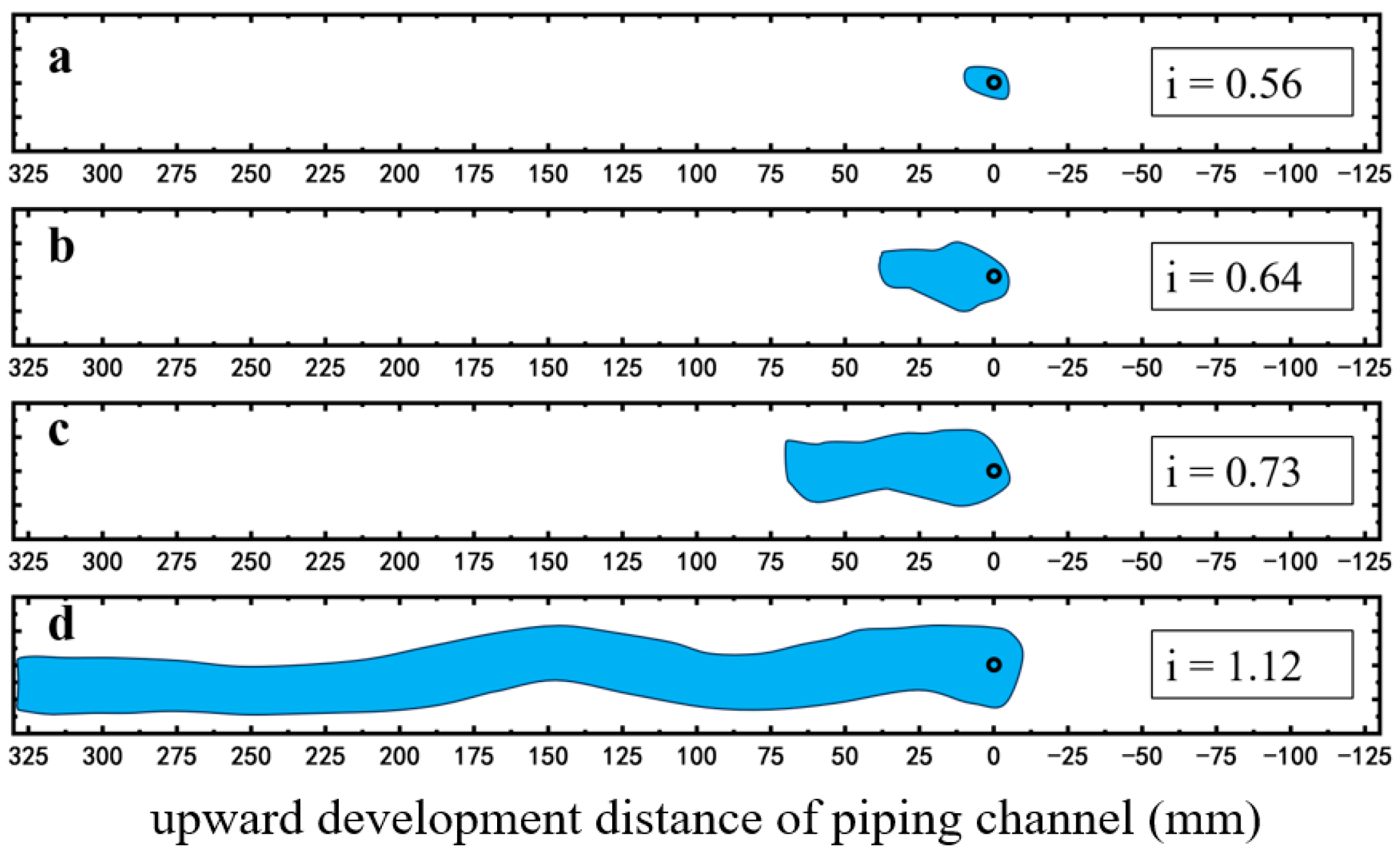
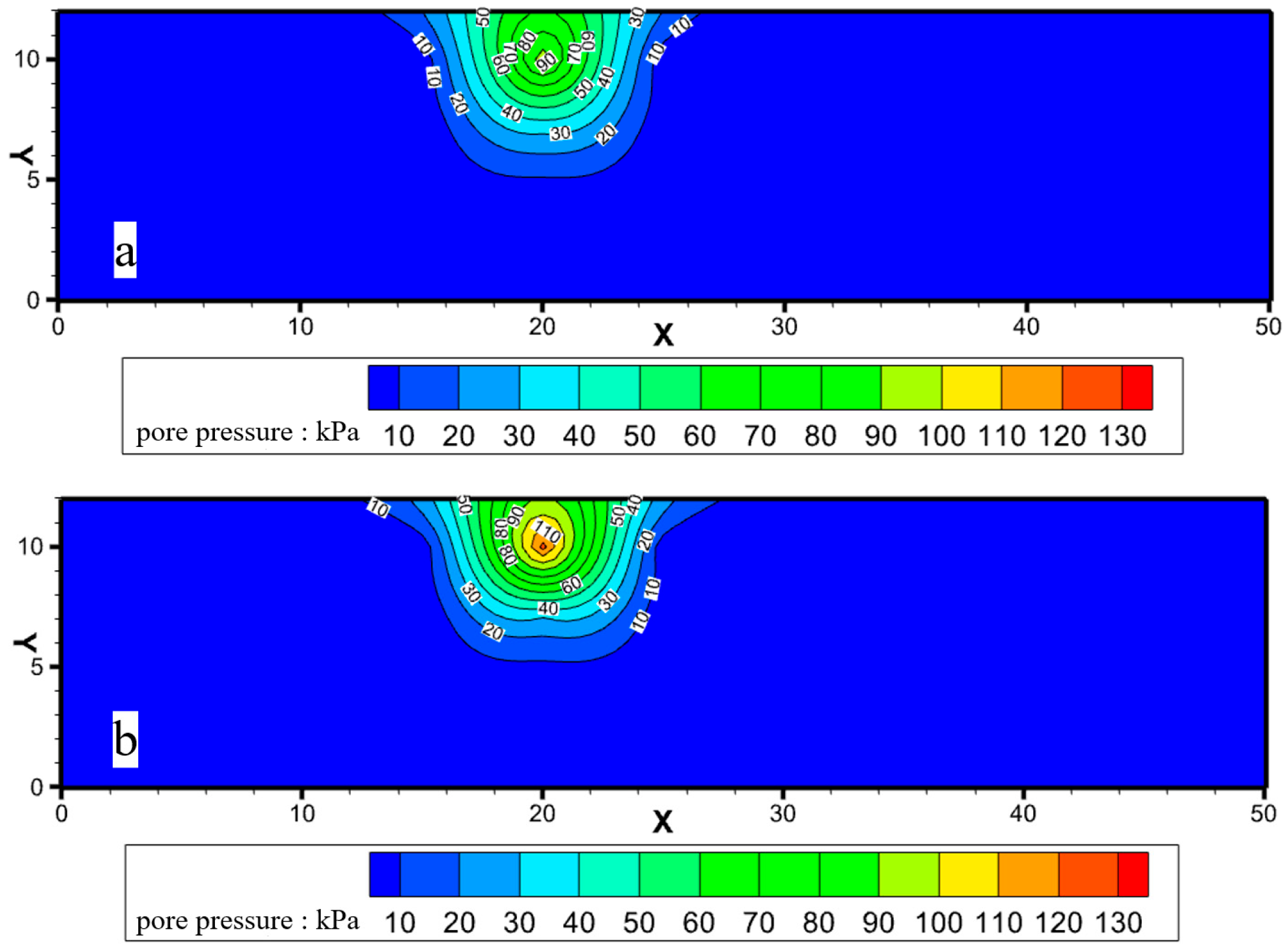
2.2.1. Enhancing the Initiation and Critical Hydraulic Gradient of Piping
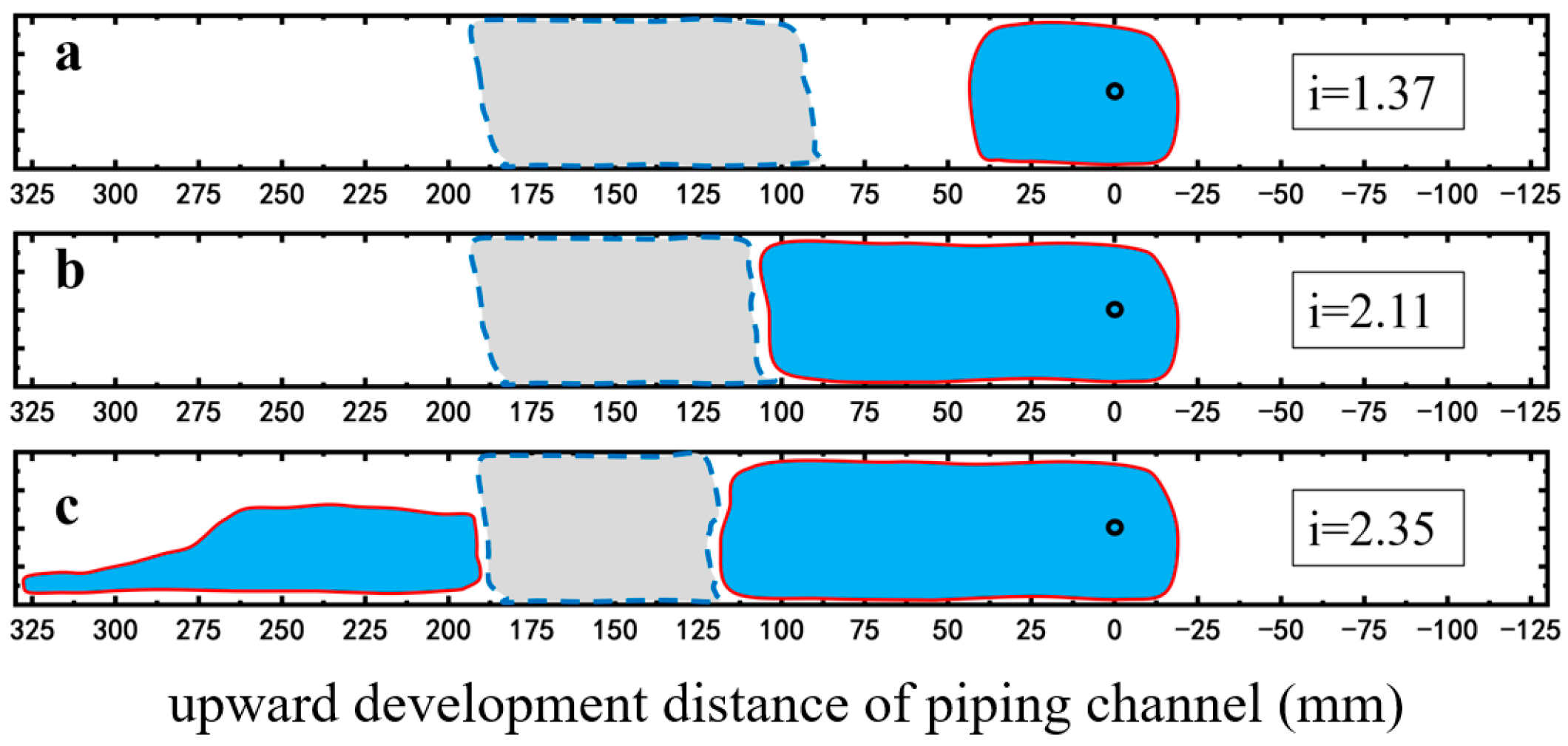
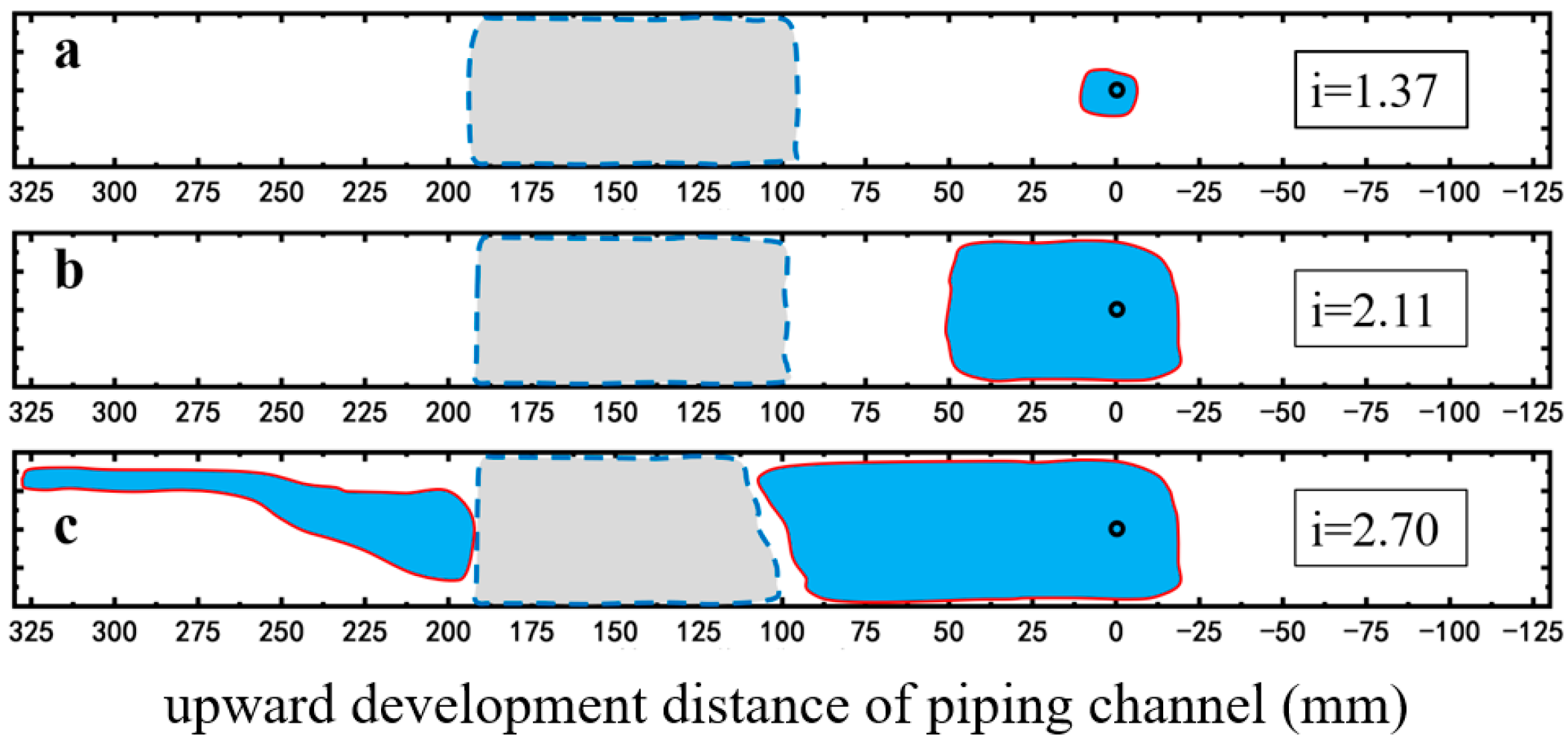
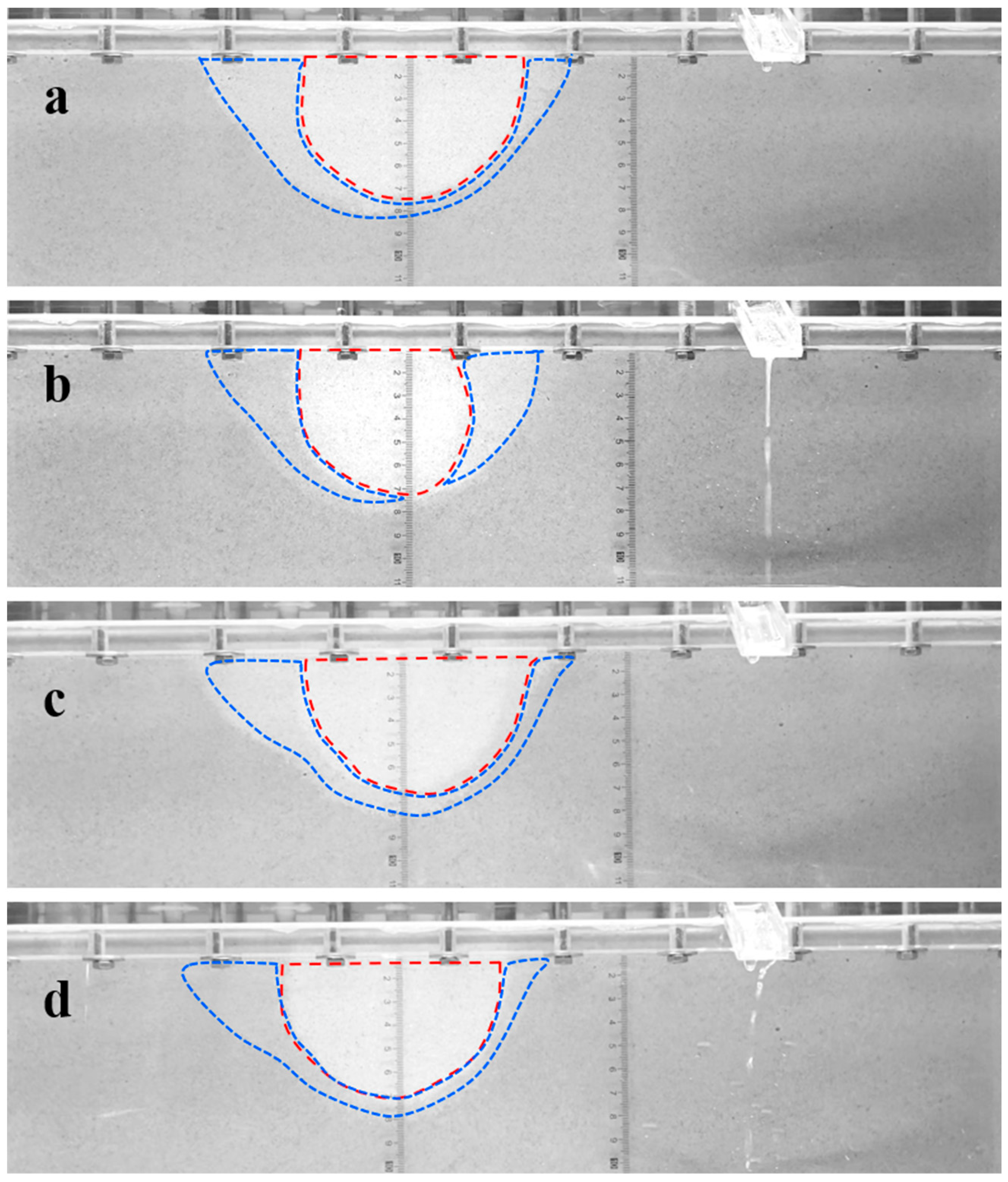
2.2.2. Restraining Piping Channel Extension
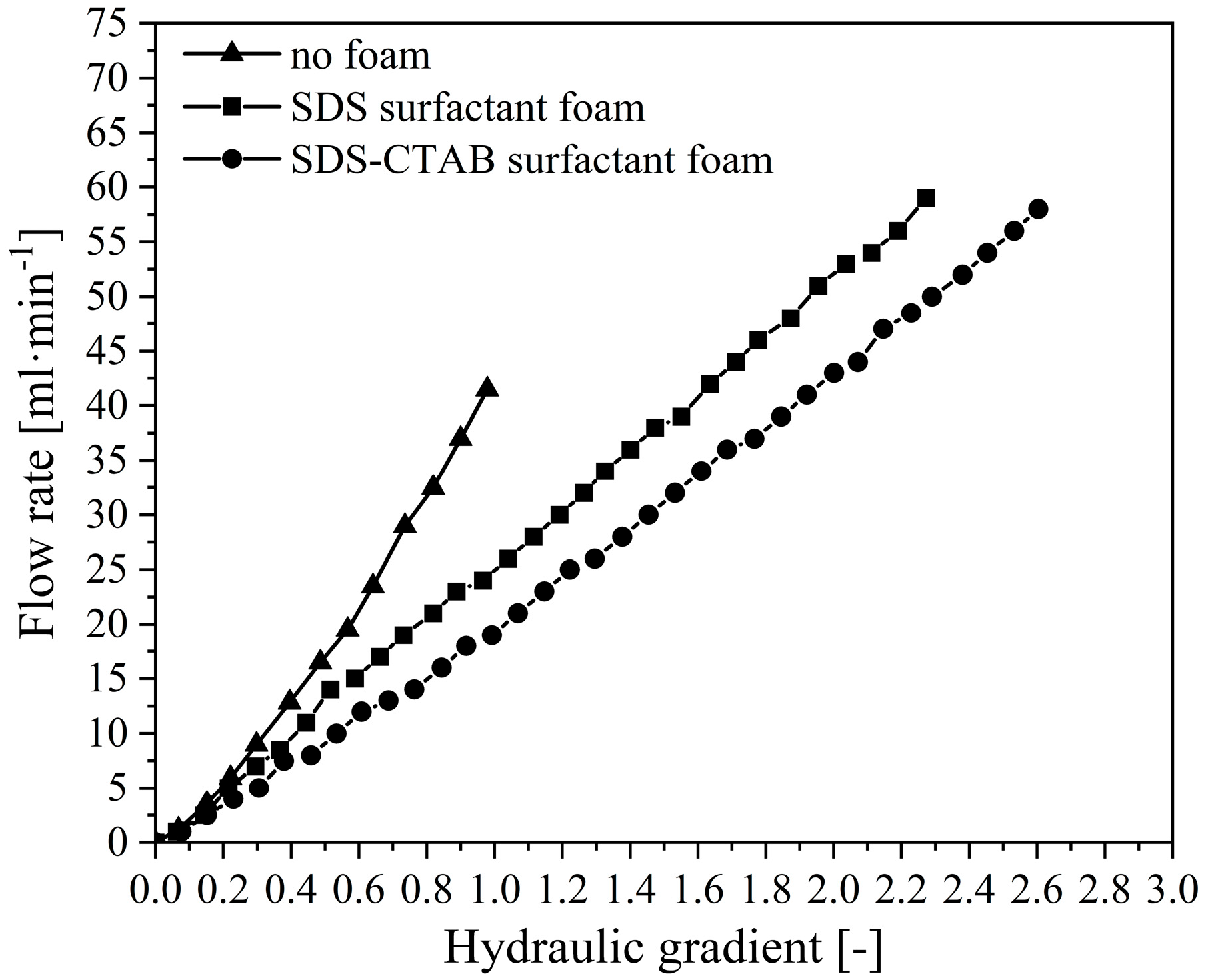
2.2.3. Reducing Flow Rate at Outlet
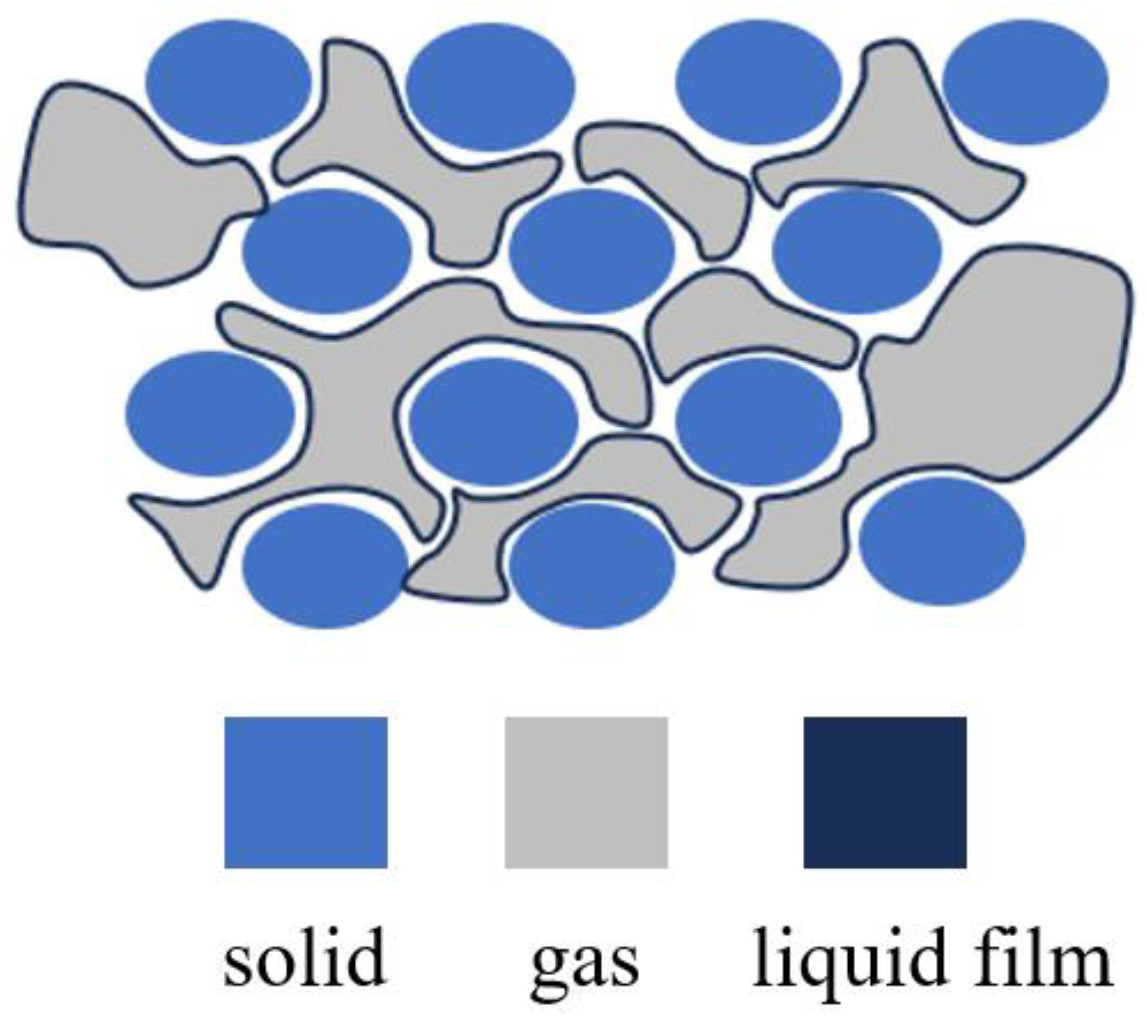
2.3. Mechanisms of Compounded Surfactant Foam Enhancing Capability in Restraining Piping Development
2.3.1. Enhancement of Foam Strength
2.3.2. Enhancement of Foam Stability
- Electrostatic Interaction
- Hydrophobic Interaction
- Hydrogen Bond
2.3.3. Enhancement of Scour Resistance of Foam
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Materials
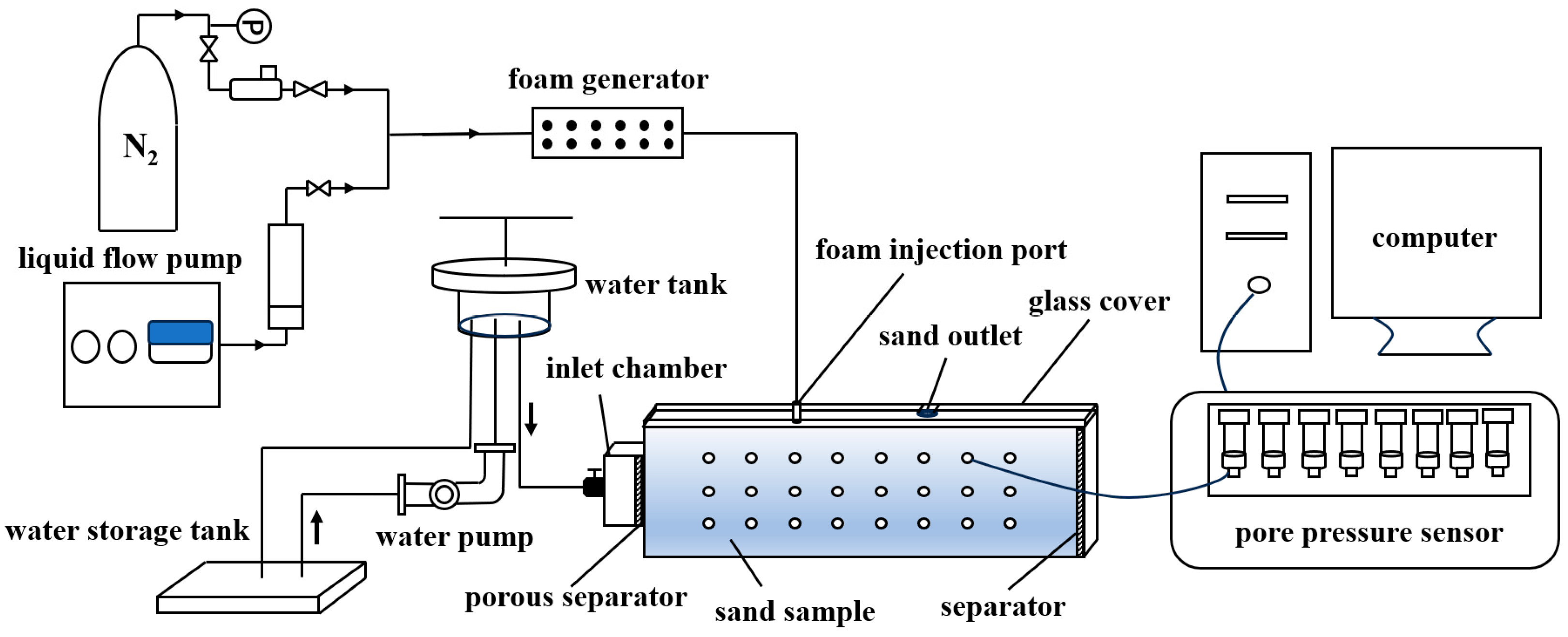
3.2. Experimental Apparatus
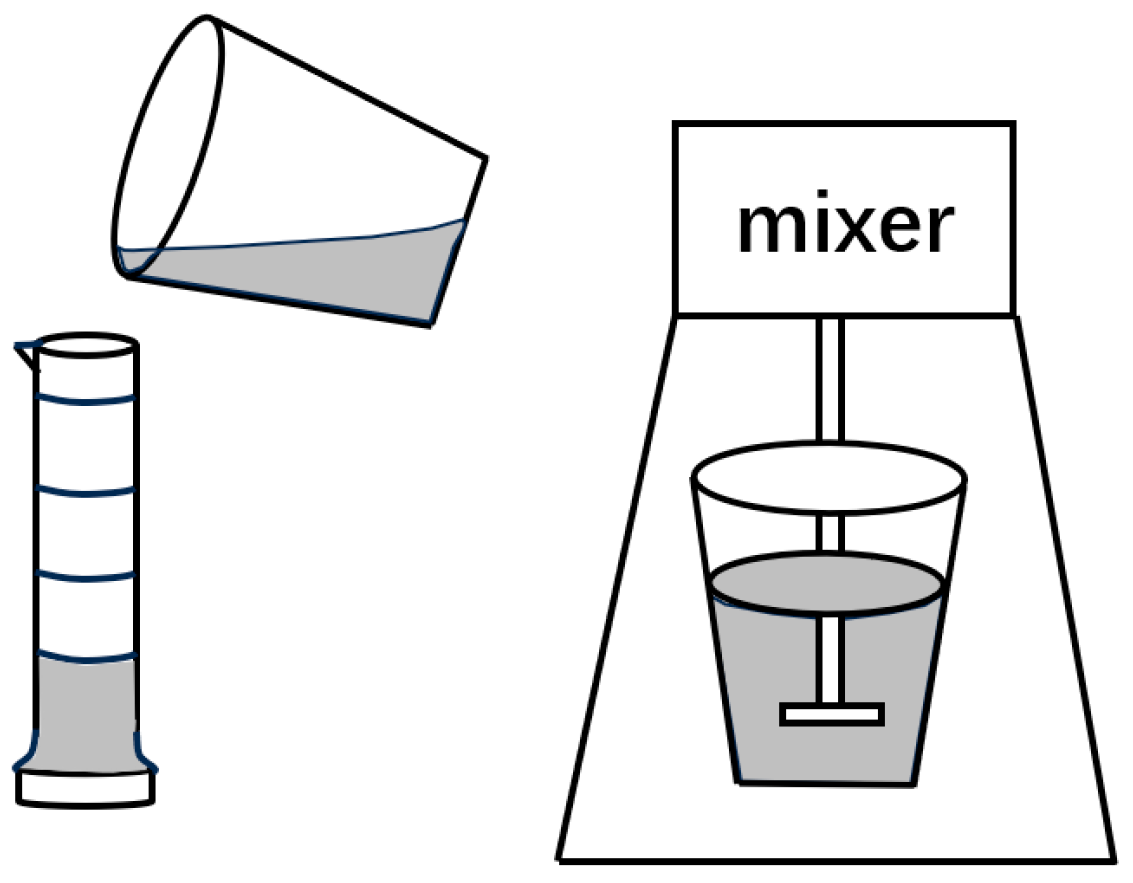
3.2.1. Apparatus for Foam Static-Property Characterization
3.2.2. Apparatus for Foam Plugging Capacity Assessment
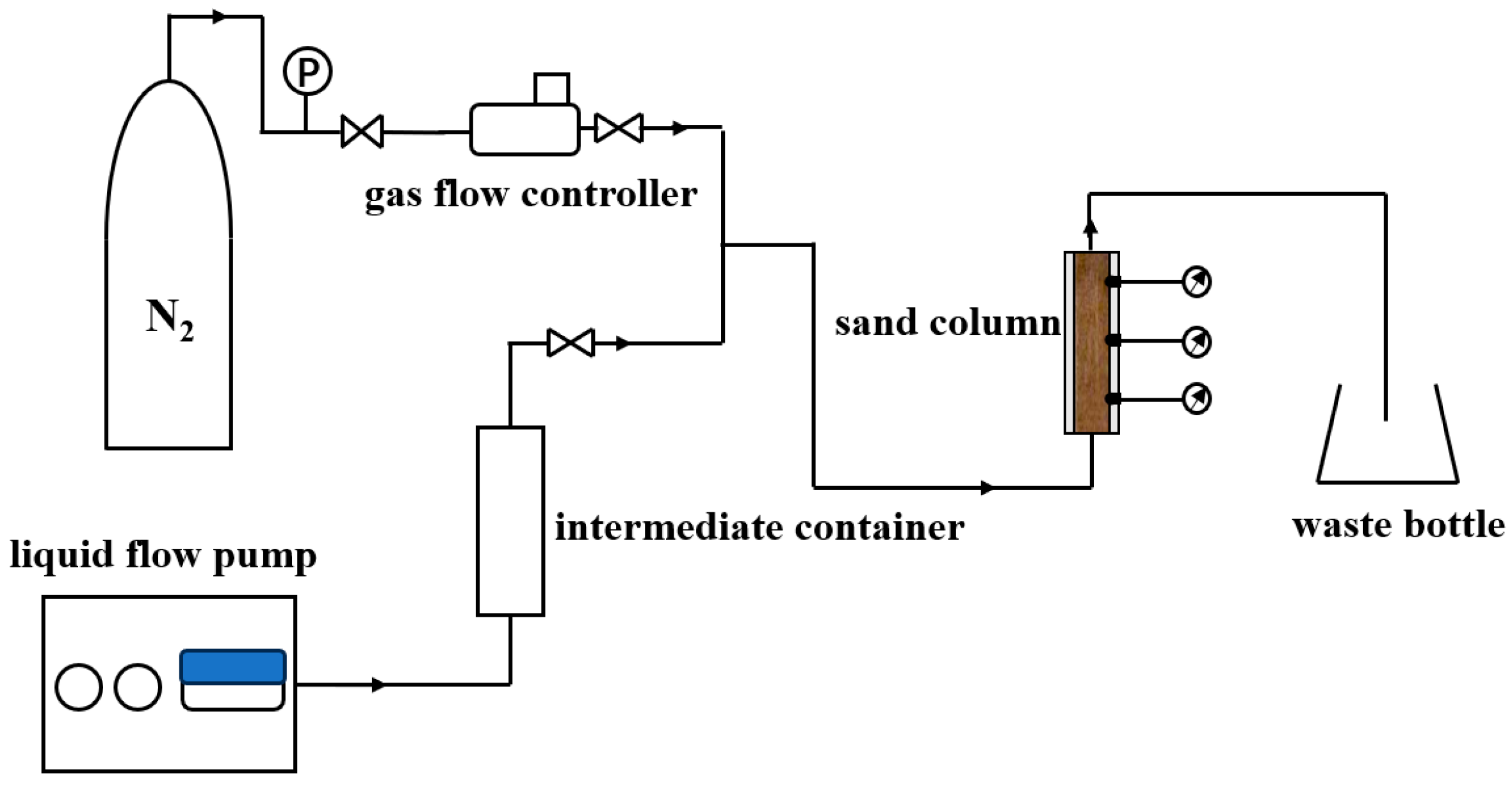
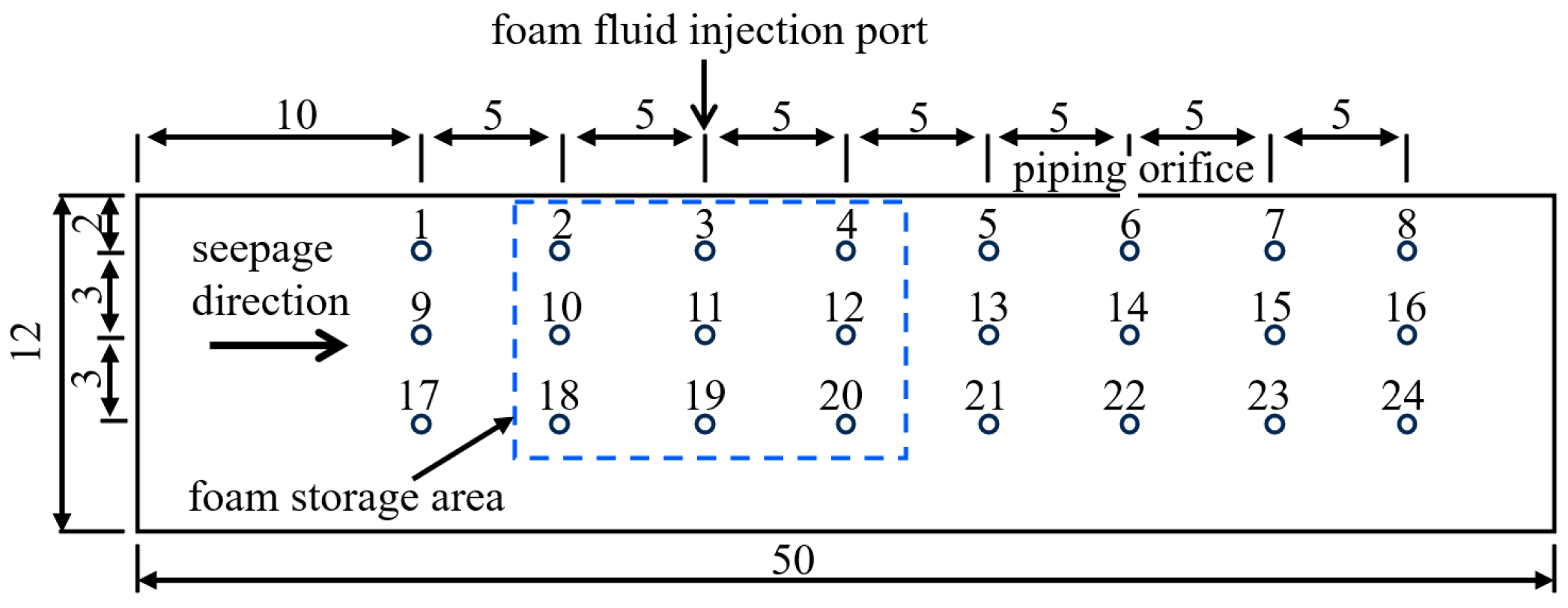
3.2.3. Apparatus for Foam Restraining Piping Experiment
3.3. Experimental Method
3.3.1. Foam Static-Property Characterization Experiment
3.3.2. Foam Plugging Capacity Assessment Experiment
3.3.3. Experiment of Foam Restraining the Piping
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, W.; Wu, J.; Tang, R.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y. A Review of Flood Risk in China during 1950–2019: Urbanization, Socioeconomic Impact Trends and Flood Risk Management. Water 2022, 14, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. China Water Development Report; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Xu, K.; Watanabe, M. Flood disaster monitoring and evaluation in China. Glob. Environ. Change Part B Environ. Hazards 2002, 4, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, P.; Dey, A. Hydraulic failures of earthen dams and embankments. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2019, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, V.M.; Yao, Q.L.; Van, M.A. Backward Erosion Piping Model Verification Using Cases in China and The Netherlands. In Proceedings of the 7th Conference of the International Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering, Chicago, IL, USA, 29 April–4 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Li, C. Research Progress of Dike Leak Rescue Technology. Water 2023, 15, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omofunmi, O.E.; Kolo, J.G.; Oladipo, A.S.; Diabana, P.D.; Ojo, A.S. A Review on Effects and Control of Seepage through Earth-fill Dam. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, J.; Qiu, H.; Qi, T. Experimental study on application of foam fluids in restraining seepage failure of soils. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 46, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wang, Y.; Gong, J.; Qi, T.; Zhang, S. Effect of foam fluid on seepage characteristic in embankment foundation. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2023, 51, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Tewari, R.D.; Kamarul Bahrim, R.-Z.B.; Rossen, W. Effect of Gas Composition on Surfactant Injectivity in a Surfactant-Alternating-Gas Foam Process. Molecules 2024, 29, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.T.G.; Mutawa, A.S.; Pilus, R.M.; Zitha, P.L.J. Foam-Assisted Chemical Flooding for Enhanced Oil Recovery: Effects of Slug Salinity and Drive Foam Strength. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 4951–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, R.; Andrianov, A.; Krastev, R.; Hirasaki, G.J.; Rossen, W.R. Foam-oil interaction in porous media: Implications for foam assisted enhanced oil recovery. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 183–184, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Voskov, D.; Tang, J.; Rossen, W.R. Simulation of Foam Enhanced-Oil-Recovery Processes Using Operator-Based Linearization Approach. SPE J. 2021, 26, 2287–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mulligan, C.N. An evaluation of surfactant foam technology in remediation of contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, C.K.; Rong, J.G.; Kam, S.I.; Liljestrand, H.M.; Rossen, W.R. Simulating use of foam in aquifer remediation. Dev. Water Sci. 2002, 47, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portois, C.; Boeije, C.S.; Bertin, H.J.; Atteia, O. Foam for Environmental Remediation: Generation and Blocking Effect. Transp. Porous Media 2018, 124, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, W.R.; Farajzadeh, R.; Hirasaki, G.J.; Amirmoshiri, M. Potential and challenges of foam-assisted CO2 sequestration. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 239, 212929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Føyen, T.; Brattekås, B.; Fernø, M.A.; Barrabino, A.; Holt, T. Increased CO2 storage capacity using CO2-foam. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2020, 96, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, A.; Hamalian, M.; Acharya, P.V.; Bahadur, V. Ultrafast Formation of Carbon Dioxide Hydrate Foam for Carbon Sequestration. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 11013–11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Bezuijen, A.; Thewes, M. An experimental study on foam infiltration into saturated sand and its consequence for EPB shield tunneling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 111, 103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Dai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, A.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, M. Enhanced foam stability by adding comb polymer gel for in-depth profile control in high temperature reservoirs. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakore, V.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.-A.; Polsky, Y.; Ren, F. Stability study of aqueous foams under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions relevant to Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS). Geothermics 2024, 116, 102862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, P.; Miller, R.; Javadi, A.; Firouzi, M. Pickering foams and parameters influencing their characteristics. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 301, 102606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Pokalai, K.; Johnson, R.; Gonzalez, M.; Haghighi, M. Experimental and simulation study of foam stability and the effects on hydraulic fracture proppant placement. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 46, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ye, H.; Yang, L.; Luo, D.; Peng, B. Nanoparticles as foam stabilizer: Mechanism, control parameters and application in foam flooding for enhanced oil recovery. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 202, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, N.R.; Maurya, N.K. Keys to enhancing efficiency in nanoparticle-based foam EOR: Experimental insights into different types of surfactant-nanoparticle interactions. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 422, 126927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.; Ramesh, D.N.; Prakash, S.; Saw, R.K.; Maurya, N.K.; Rathi, K.B.; Mitra, S.; Sinha, O.P.; Bikkina, P.K.; Mandal, A. Formulation and characterisation of polymer and nanoparticle-stabilized anionic surfactant foam for application in enhanced oil recovery. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 56, 105615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Ge, J.; Rahman, M.A.; Economou, I.G.; Guérillot, D. Polymer enhanced foam for improving oil recovery in oil-wet carbonate reservoirs: A proof of concept and insights into the polymer-surfactant interactions. Energy 2023, 264, 126256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, M.; Mushtaq, M.; Al-Shalabi, E.W.; Alameri, W.; Karanikolos, G.; Iglauer, S. Polymer-Enhanced Foam Formulation Design for CO2-Sequestration and Mobility Control in Carbonate Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the ADIPEC 2024, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 4–7 November 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Hanamertani, A.S.; Elraies, K.A.; Bt Mohd Shafian, S.R. Enhanced CO2 trapping by hydrophobically modified polymer stabilized foam: Significance for CO2 geo-storage. Energy 2025, 314, 133839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiertel-Pochopien, A.; Batys, P.; Zawala, J.; Kowalczuk, P.B. Synergistic Effect of Binary Surfactant Mixtures in Two-Phase and Three-Phase Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 3855–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Ju, H.; Wang, Y. Synergistic effect of binary mixtures contained newly cationic surfactant: Interaction, aggregation behaviors and application properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 232, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, A.; Ojha, K.; Mandal, A. Synergistic Effect of Mixed Surfactant Systems on Foam Behavior and Surface Tension. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2013, 16, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Fan, Z.; Wei, X. Hydrophobic mesoporous silicon dioxide for improving foam stability. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 18565–18571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.; Pu, W.; Sun, L.; Pu, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, Y. Role of water-soluble polymer on foam-injection process for enhancing oil recovery. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 65, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, H.; Cao, A.; Wang, F. Effect of surfactant concentration on foam texture and flow characteristics in porous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, N.; Joshi, T. A Concise Review on Surfactants and Its Significance. Int. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 13, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Goual, L.; Piri, M. Synergistic effects of surfactant mixtures on the displacement of nonaqueous phase liquids in porous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Hua, X.Y. Surface concentrations and molecular interactions in binary mixtures of surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1982, 86, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Gu, B.; Murphy, D.S.; Zhu, Z.H. Synergism in binary mixtures of surfactants: 9. N-alkyl-2-pyrrolidone-anionic mixtures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 129, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Kong, B.; Puerto, M.; Bao, X.; Sha, O.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, S.; et al. Mixtures of Anionic/Cationic Surfactants: A New Approach for Enhanced Oil Recovery in Low-Salinity, High-Temperature Sandstone Reservoir. SPE J. 2016, 21, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Somasundaran, P. Adsorption of mixtures of nonionic sugar-based surfactants with other surfactants at solid/liquid interfaces: I. Adsorption of n-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside with anionic sodium dodecyl sulfate on alumina. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 302, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Somasundaran, P. Study of mixtures of n-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside with anionic, cationic, and nonionic surfactant in aqueous solutions using surface tension and fluorescence techniques. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 278, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tah, B.; Pal, P.; Mahato, M.; Talapatra, G.B. Aggregation Behavior of SDS/CTAB Catanionic Surfactant Mixture in Aqueous Solution and at the Air/Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 8493–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Chang, W. Evaluation of Foaming Chemical Composition and Performance of Commonly Used Detergents. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2023, 7, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoyomi, O.; Jide, I.; Akanni, M.; Soriyan, O.; Morakinyo, M.K. Interactions between sodium dodecylsulphate and Triton X-100: Molecular properties and kinetics investigations. J. Appl. Sci. 2005, 5, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liang, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Geng, T. Synergistic effects of nonionic surfactants ethoxylated alkylamines and sodium dodecyl sulfate in mixed systems. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 694, 134192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, C. Synergistic interactions in the mixed micelles of anionic amino acid surfactant with cationic gemini surfactant. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2021, 162, 106568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Shah, S.; Chakraborty, G.; Bhattarai, A.; De, R. Synergistic and antagonistic effects in micellization of mixed surfactants. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, P.; Hei, Y.; Shi, D.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Leng, W.; Lv, Q.; Sun, W. Synergistic mechanism in anionic/zwitterionic and anionic/nonionic surfactant mixtures on improving the thermal stability of emulsions: An experimental and simulation study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 289, 119824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Cui, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Husein, M.M. Assessing the performance of foams stabilized by anionic/nonionic surfactant mixture under high temperature and pressure conditions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, R.; Krastev, R.; Zitha, P.L.J. Foam films stabilized with alpha olefin sulfonate (AOS). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 324, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo Estrada, E.; Bertin, H.; Atteia, O. Experimental Study of Foam Flow in Sand Columns: Surfactant Choice and Resistance Factor Measurement. Transp. Porous Media 2015, 108, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, V.; Sellmeijer, J.B.; Barends, F.B.J.; Bezuijen, A. Initiation of backward erosion piping in uniform sands. Géotechnique 2014, 64, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riha, J.; Petrula, L. Experimental Research on Backward Erosion Piping Progression. Water 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbub, S.; Molla, M.R.; Saha, M.; Shahriar, I.; Hoque, M.A.; Halim, M.A.; Rub, M.A.; Khan, M.A.; Azum, N. Conductometric and molecular dynamics studies of the aggregation behavior of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) in aqueous and electrolytes solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 283, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, A.; Niraula, T.; Chatterjee, S. Sodium dodecyl sulphate: A very useful surfactant for Scientific Invetigations. J. Knowl. Innov. 2014, 2, 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Naskar, B. Micellization and Physicochemical Properties of CTAB in Aqueous Solution: Interfacial Properties, Energetics, and Aggregation Number at 290 to 323 K. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubenrauch, C.; Hamann, M.; Preisig, N.; Chauhan, V.; Bordes, R. On how hydrogen bonds affect foam stability. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 247, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Luo, D.; Peng, B. Ultra-Low Interfacial Tension Foam System for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenboer, K.; van Beek, V.M.; Bezuijen, A. 3D character of backward erosion piping. Geotechnique 2017, 68, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Niu, R.; Cao, S.; Liu, L.; Song, Y. Features of nanoparticle composite-enhanced CO2 foam-flooding systems for low-permeability reservoirs. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 10, 1060356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Song, G. Study on enhanced oil recovery by multi-component foam flooding. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 177, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

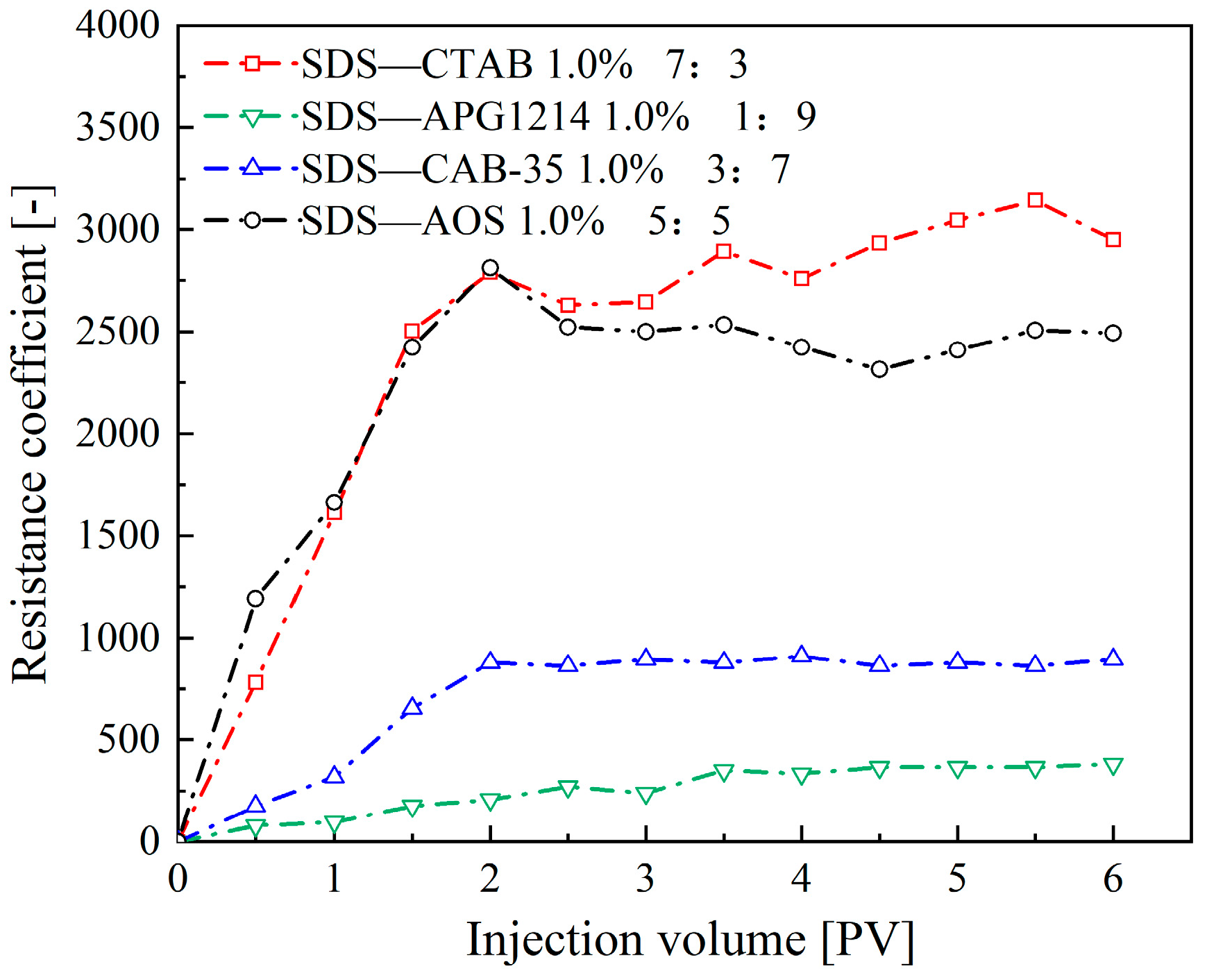
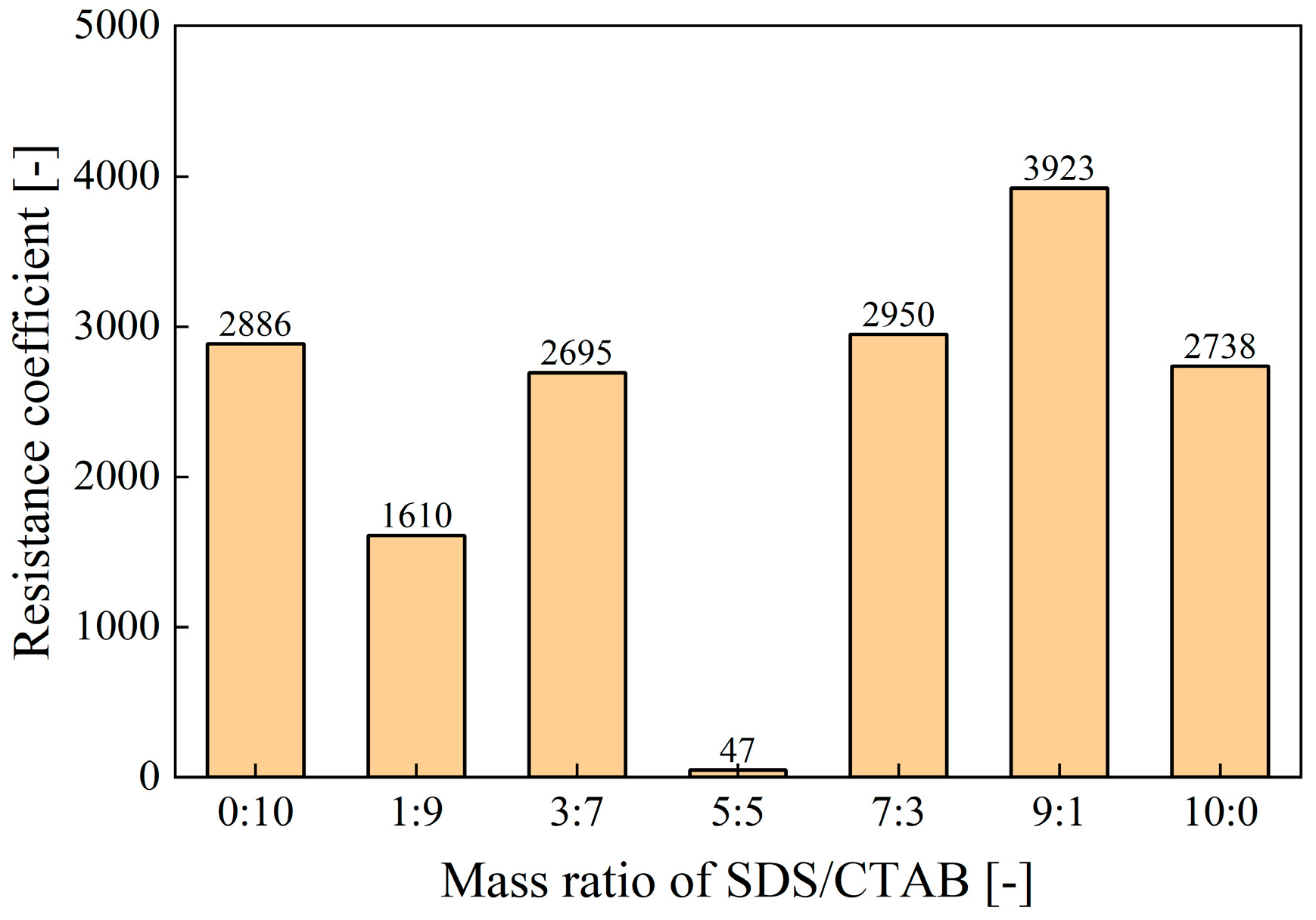
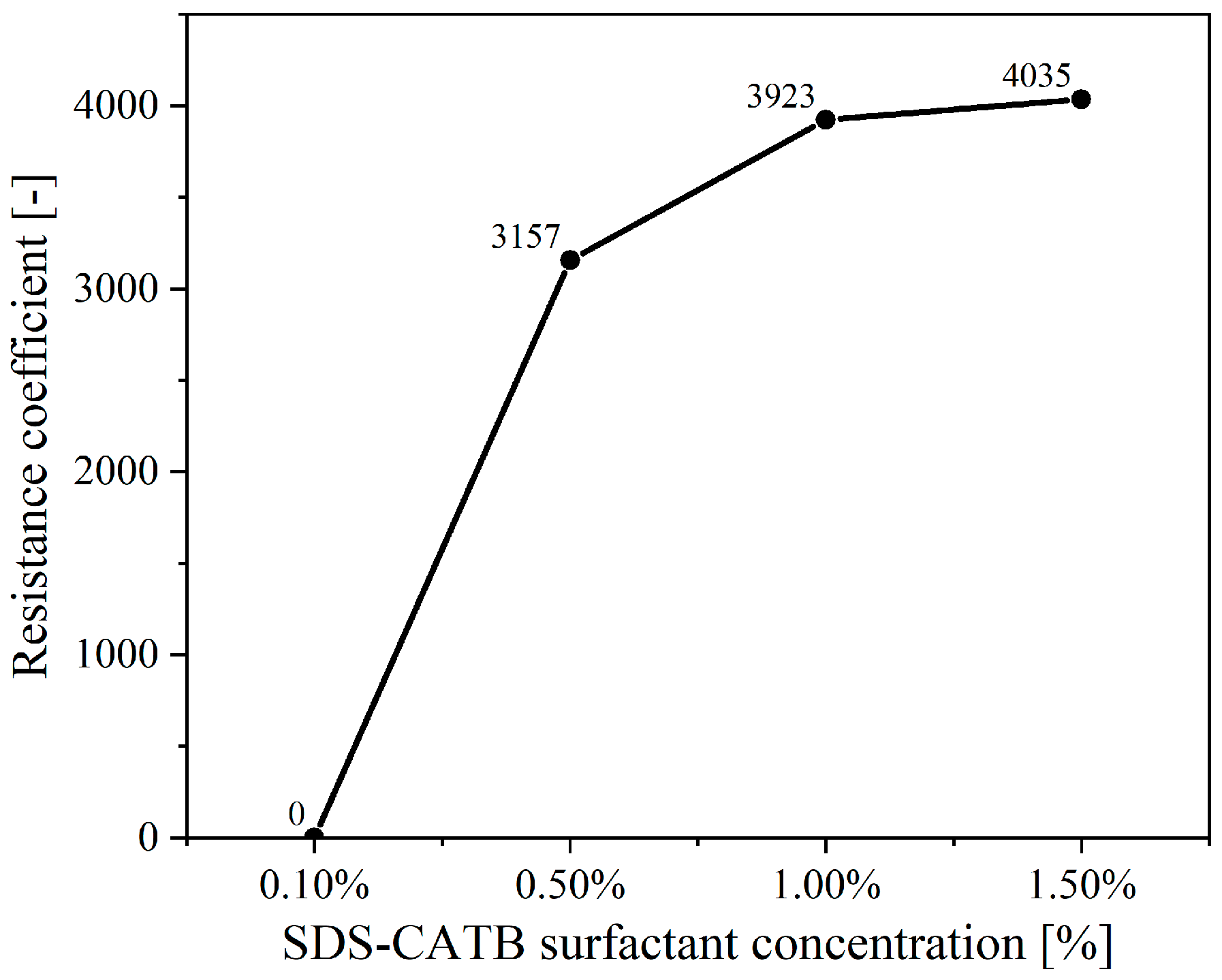


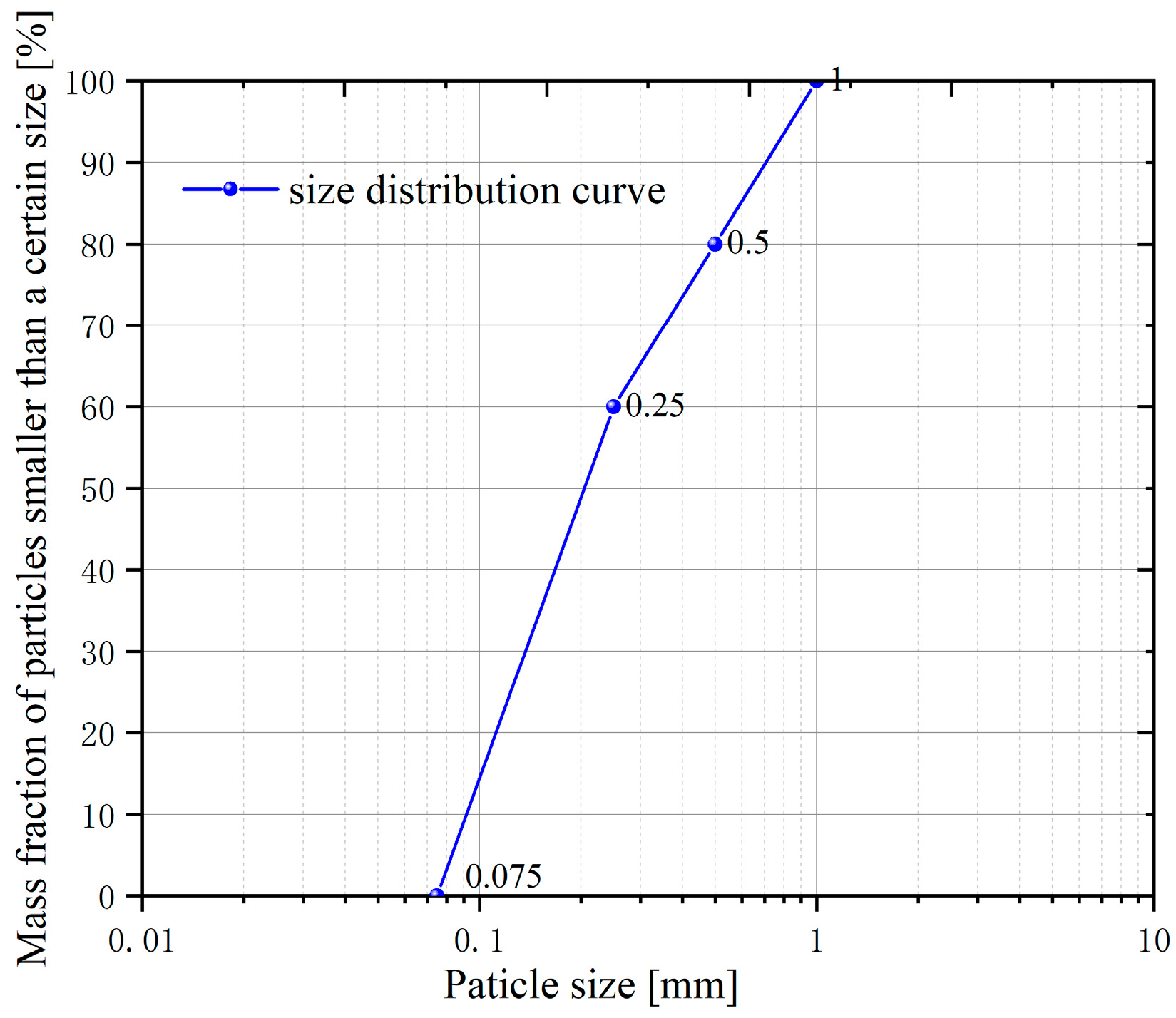
| Surfactant Types | Surfactants | Concentration | V0 | t1/2 | FCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anionic surfactant | Sodium alpha olefin sulfonate (AOS, 92% purity, Tianjin Xienci Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China) | 0.1% | 615 | 329 | 151751 |
| 0.3% | 645 | 353 | 170763 | ||
| 0.5% | 630 | 369 | 174352 | ||
| 0.7% | 650 | 344 | 167700 | ||
| 0.9% | 665 | 326 | 162592 | ||
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, 99% purity, Tianjin Xienci Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 600 | 330 | 148500 | |
| 0.3% | 630 | 363 | 171517 | ||
| 0.5% | 640 | 369 | 177120 | ||
| 0.7% | 635 | 354 | 168592 | ||
| 0.9% | 630 | 375 | 177187 | ||
| Disodium sulfosuccinate monoester (MES-30, 30% active content, Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., Linyi, China) | 0.1% | 530 | 254 | 100965 | |
| 0.3% | 600 | 310 | 139500 | ||
| 0.5% | 620 | 280 | 130200 | ||
| 0.7% | 630 | 315 | 148837 | ||
| 0.9% | 650 | 272 | 132600 | ||
| Sodium fatty alcohol ether sulfate (AES, 70% active content, Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 540 | 248 | 100440 | |
| 0.3% | 610 | 229 | 104767 | ||
| 0.5% | 630 | 265 | 125212 | ||
| 0.7% | 620 | 238 | 110670 | ||
| 0.9% | 620 | 254 | 118110 | ||
| Zwitterionic surfactant | Cocoamidopropyl betaine (CAB-35, 35% active content, Tianjin Xienci Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 590 | 273 | 120802 |
| 0.3% | 650 | 263 | 128212 | ||
| 0.5% | 650 | 290 | 141375 | ||
| 0.7% | 660 | 271 | 134145 | ||
| 0.9% | 660 | 318 | 157410 | ||
| Lauryl propyl betaine (LAB-35, 35% active content, Tianjin Xienci Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 430 | 190 | 61275 | |
| 0.3% | 570 | 268 | 114570 | ||
| 0.5% | 650 | 290 | 141375 | ||
| 0.7% | 640 | 275 | 132000 | ||
| 0.9% | 630 | 282 | 133245 | ||
| Lauramidopropyl hydroxy sulfobetaine (LHSB, 35% active content, Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 470 | 182 | 64155 | |
| 0.3% | 600 | 230 | 103500 | ||
| 0.5% | 600 | 257 | 115650 | ||
| 0.7% | 600 | 276 | 124200 | ||
| 0.9% | 610 | 270 | 123525 | ||
| Dodecyl dimethyl amine oxide (OB-2, 98% purity, Tianjin Xienci Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 620 | 271 | 126015 | |
| 0.3% | 640 | 234 | 112320 | ||
| 0.5% | 630 | 190 | 89775 | ||
| 0.7% | 630 | 194 | 91665 | ||
| 0.9% | 620 | 158 | 73470 | ||
| Nonionic surfactant | Coconut diethanolamide (CDEA, 70% active content, Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 120 | 310 | 27900 |
| 0.3% | 590 | 307 | 135847 | ||
| 0.5% | 670 | 325 | 163312 | ||
| 0.7% | 600 | 381 | 171450 | ||
| 0.9% | 330 | 1052 | 260370 | ||
| Alkyl glycoside (APG1214, 50% active content, Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 380 | 266 | 75810 | |
| 0.3% | 510 | 392 | 149940 | ||
| 0.5% | 550 | 427 | 176137 | ||
| 0.7% | 560 | 561 | 235620 | ||
| 0.9% | 530 | 668 | 265530 | ||
| Polysorbate 80 (Tween 80, 99% purity, Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 80 | 275 | 16500 | |
| 0.3% | 120 | 376 | 33840 | ||
| 0.5% | 350 | 147 | 38587 | ||
| 0.7% | 400 | 195 | 58500 | ||
| 0.9% | 450 | 209 | 70537 | ||
| Primary alcohol ethoxylate (AEO-9, 99% purity, Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 300 | 129 | 29025 | |
| 0.3% | 470 | 195 | 68737 | ||
| 0.5% | 520 | 224 | 87360 | ||
| 0.7% | 550 | 243 | 100237 | ||
| 0.9% | 590 | 236 | 104430 | ||
| Cationic surfactant | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 98% purity, Tianjin Xienci Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 475 | 290 | 103312 |
| 0.3% | 470 | 271 | 95527 | ||
| 0.5% | 515 | 297 | 114716 | ||
| 0.7% | 500 | 299 | 112125 | ||
| 0.9% | 550 | 300 | 123750 | ||
| Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (DTAC, 30% active content, Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Co., Ltd.) | 0.1% | 420 | 201 | 63315 | |
| 0.3% | 475 | 267 | 95118 | ||
| 0.5% | 620 | 234 | 108810 | ||
| 0.7% | 600 | 229 | 103050 | ||
| 0.9% | 600 | 224 | 100800 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, J.; Pang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Qi, T.; Bezuijen, A. Development of Compounded Surfactant Foam and Its Application in Emergency Control of Piping in Dikes. Molecules 2025, 30, 2583. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122583
Gong J, Pang Z, Wang Y, Ren J, Qi T, Bezuijen A. Development of Compounded Surfactant Foam and Its Application in Emergency Control of Piping in Dikes. Molecules. 2025; 30(12):2583. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122583
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Jiakun, Zuopeng Pang, Yuan Wang, Jie Ren, Tian Qi, and Adam Bezuijen. 2025. "Development of Compounded Surfactant Foam and Its Application in Emergency Control of Piping in Dikes" Molecules 30, no. 12: 2583. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122583
APA StyleGong, J., Pang, Z., Wang, Y., Ren, J., Qi, T., & Bezuijen, A. (2025). Development of Compounded Surfactant Foam and Its Application in Emergency Control of Piping in Dikes. Molecules, 30(12), 2583. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30122583






