Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New 2-Arylpropanoic Acid-l-Tryptophan Derivatives for Mitigating Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
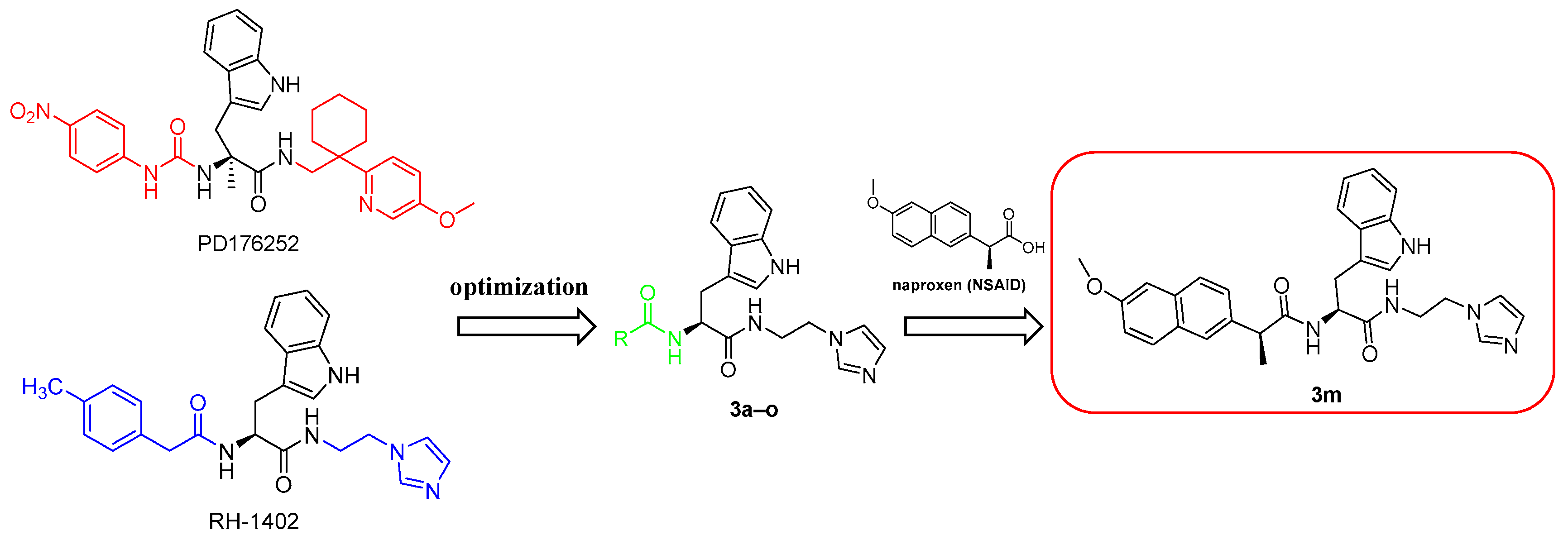
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Compounds 3a–o
2.1.1. Design
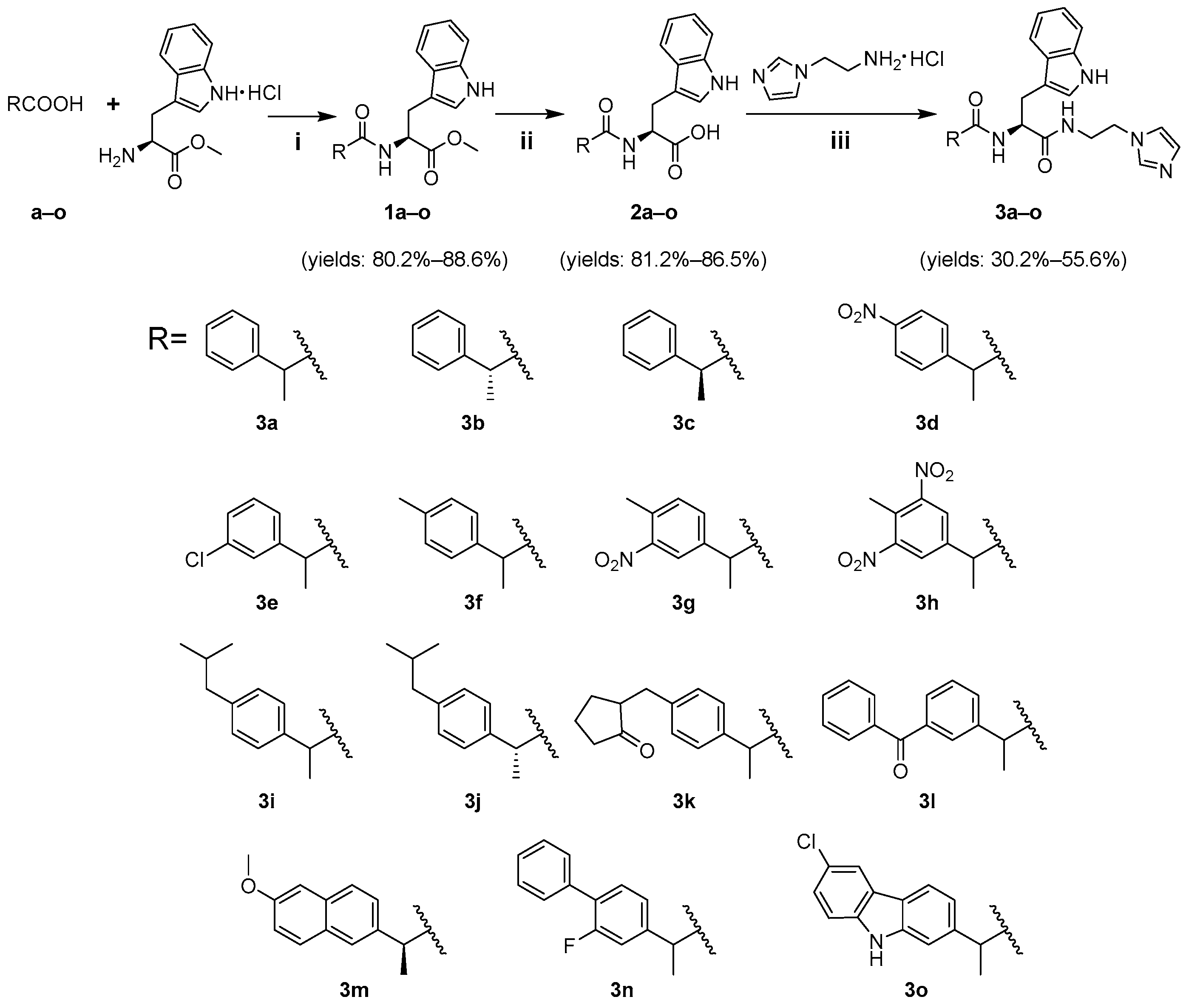
2.1.2. Synthesis
2.2. Biological Activity
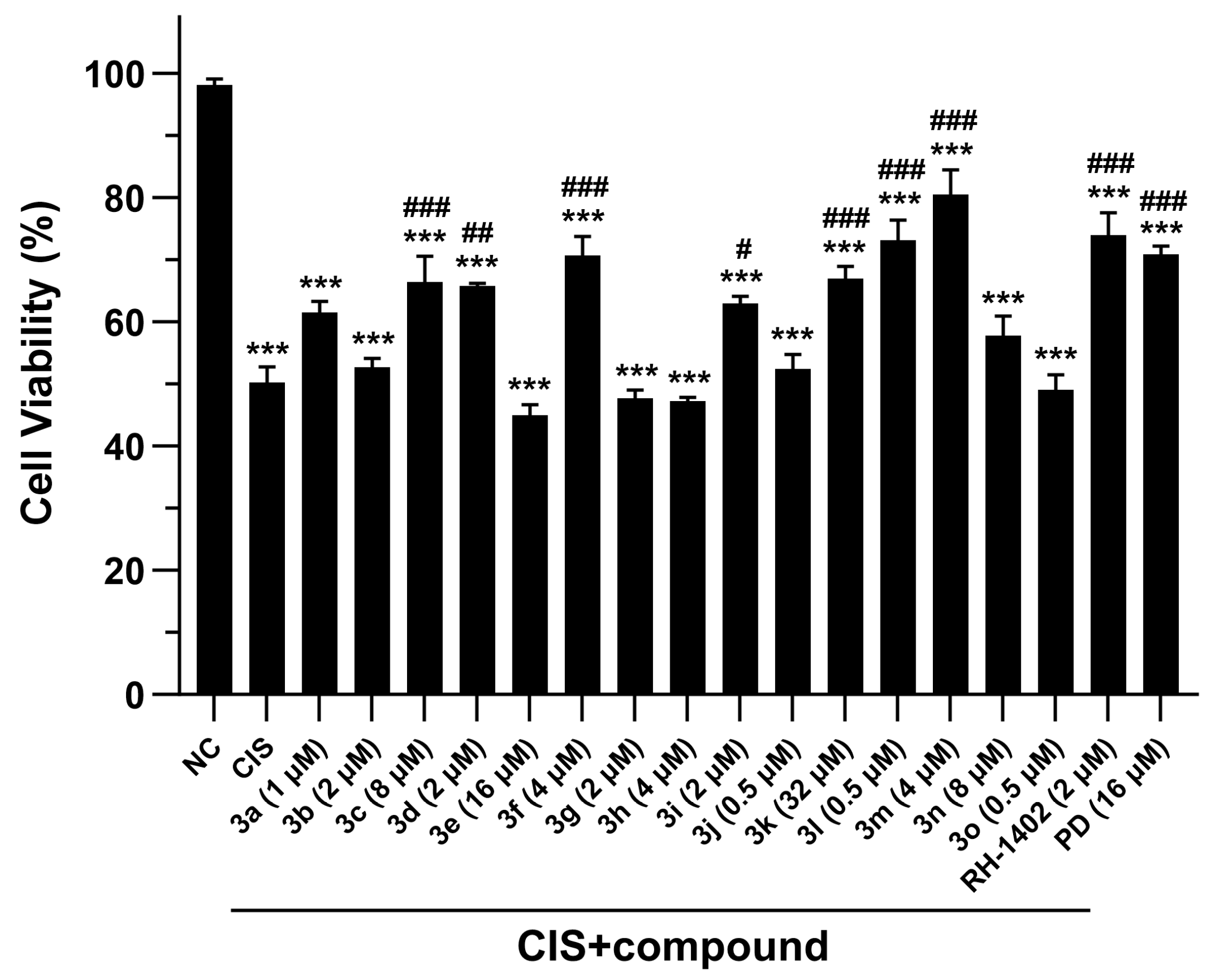
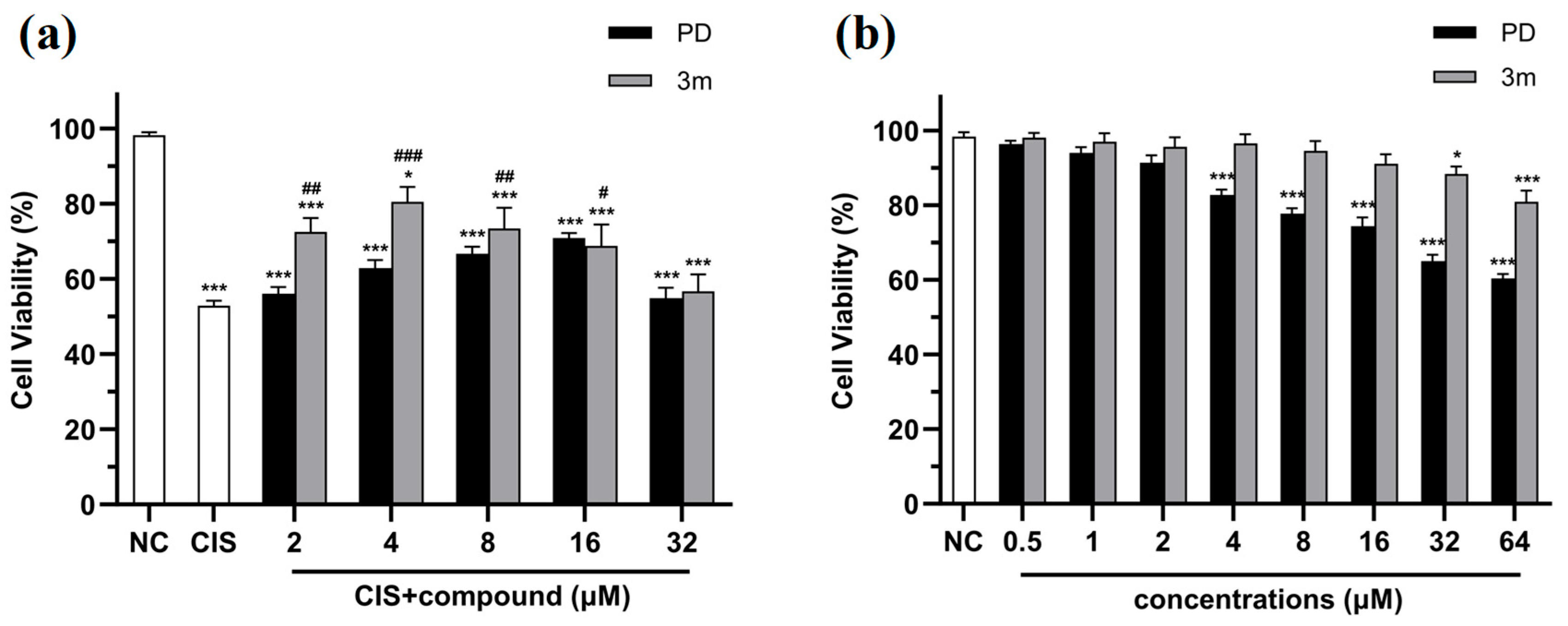
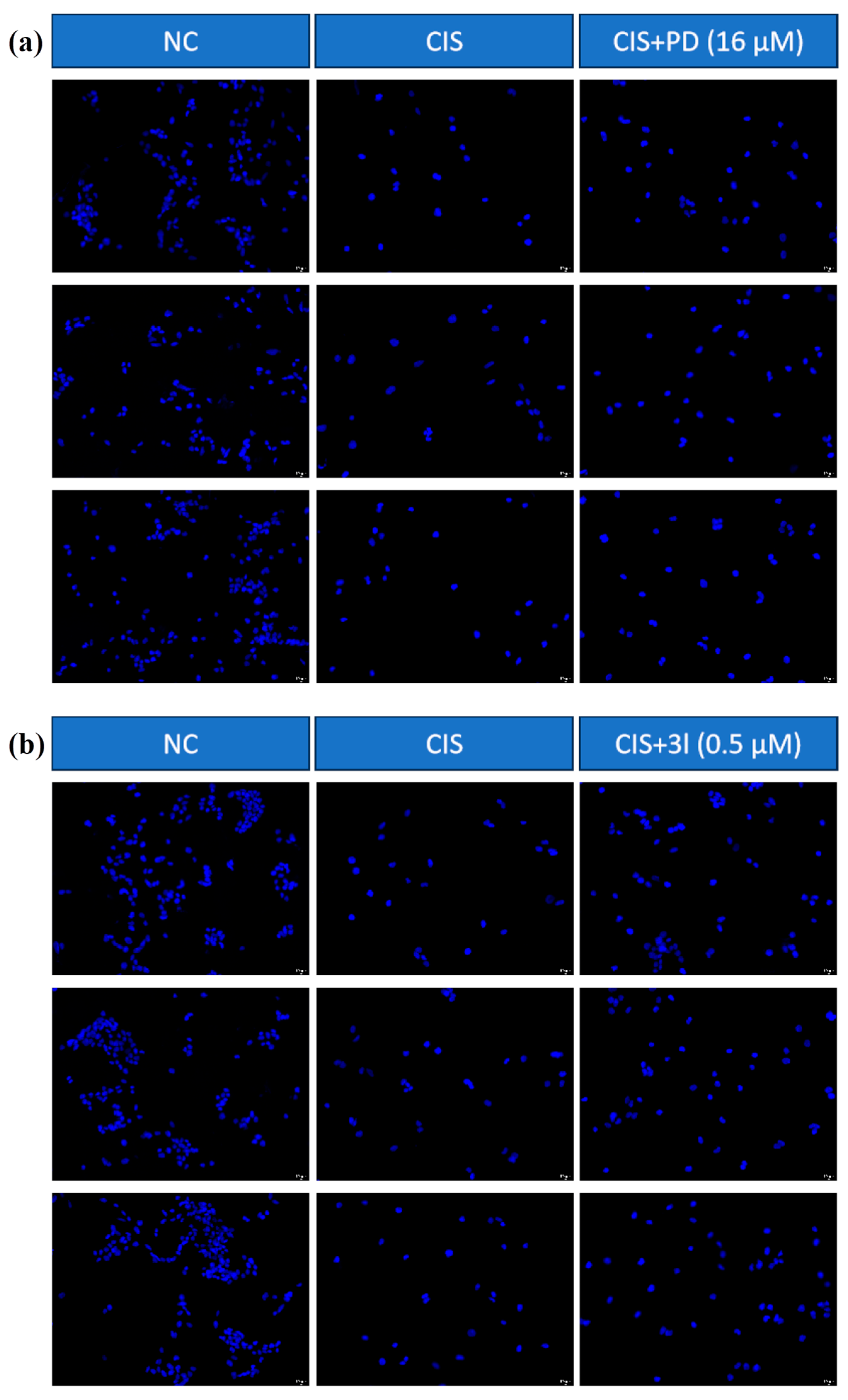
2.2.1. Compounds 3a–o Mitigate CIS-Induced mRTEC Death
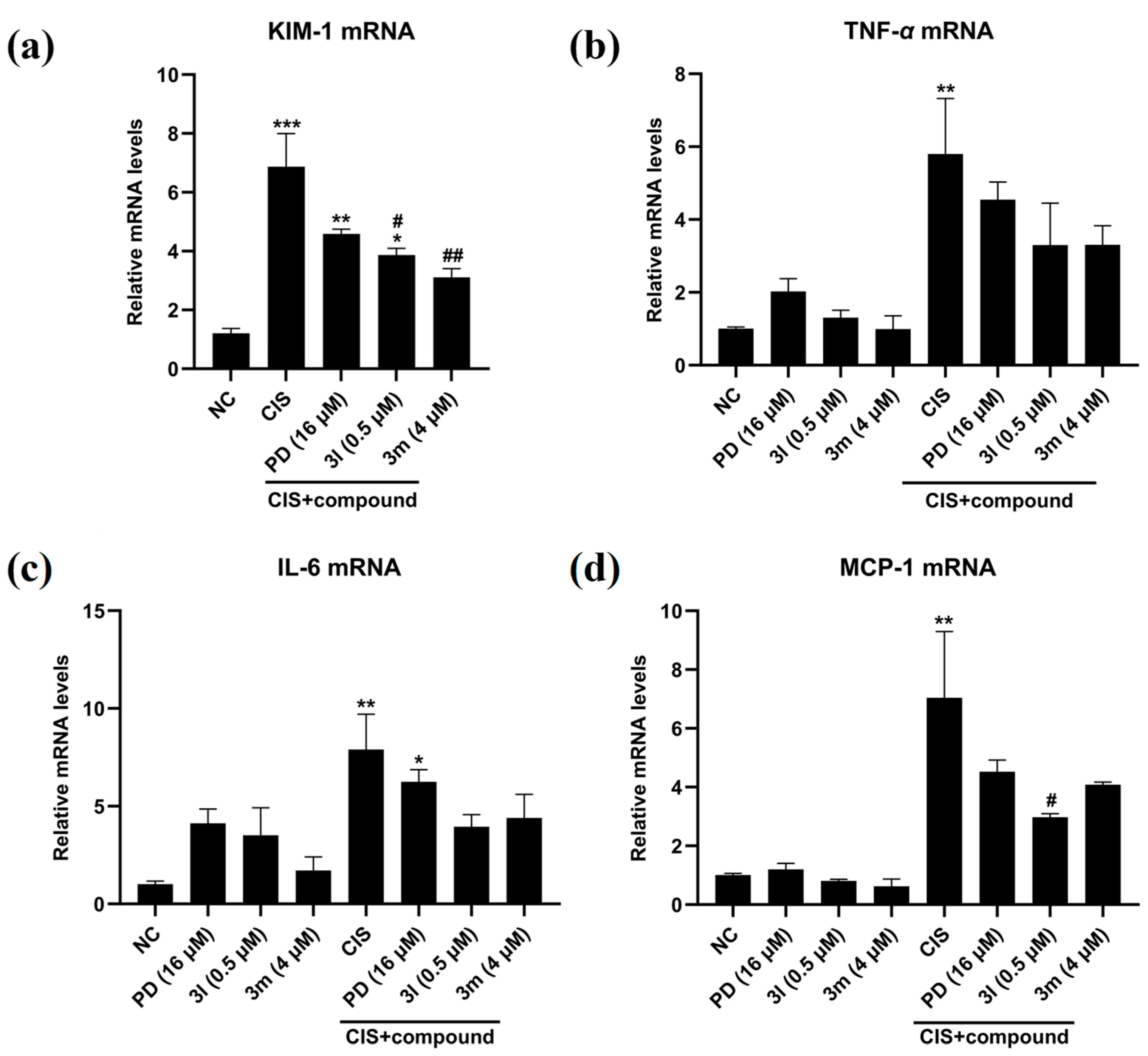
2.2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Compounds 3m and 3l
2.3. SwissADME Predictions
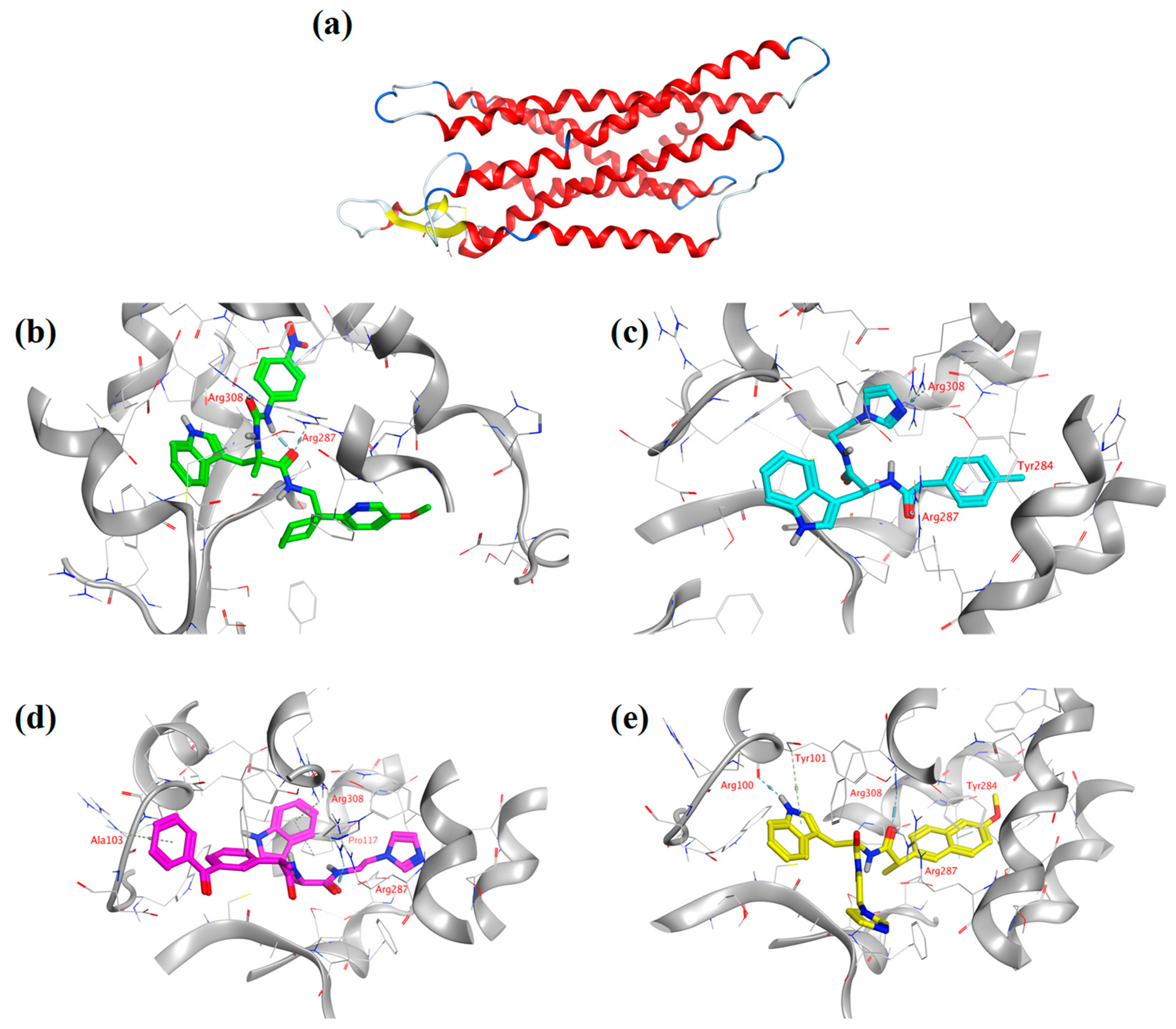
2.4. Analysis of Molecular Docking Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Procedure for Synthesizing Compounds 3a–o (Scheme 1)
3.2.1. Synthesis of Intermediates 1a–o
3.2.2. Synthesis of Intermediates 2a–o
3.2.3. Synthesis of Target Compounds 3a–o
3.3. Structural Characterization of Target Compounds 3a–o
3.4. Cells
3.5. Cell Viability Assay
3.6. DAPI Staining Assay
3.7. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Assay
3.8. Experimental Methods in Molecular Docking
3.9. Experimental Data Processing
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| GRPR | Gastrin-Releasing Peptide Receptor |
| mRTEC | Mouse Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell |
| KIM-1 | Kidney Injury Molecule-1 |
| CIS | Cisplatin |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| GRP | Gastrin-Releasing Peptide |
| NSAIDs | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| EDCI | 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide |
| HOBt | 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| HR-MS | High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry |
| MP | Melting Point |
| MPA | Melting Point Apparatus |
| DIPEA | N,N-Diisopropylethylamine |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| DS | Discovery Studio |
| MOE | Molecular Operating Environment |
Appendix A
| Mouse Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| KIM-1 | CAGGGAAGCCGCAGAAAA | GAGACACGGAAGGCAACCAC |
| TNF-α | CATCTTCTCAAAATTCGAGTGACAA | TGGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| IL-6 | GAGGATACCACTCCCAACAGACC | AAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTCATACA |
| MCP-1 | CTTCTGGGCCTGCTGTTCA | CCAGCCTACTCATTGGGATCA |
References
- Romani, A.M.P. Cisplatin in cancer treatment. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 206, 115323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Dasari, S.; Noubissi, F.K.; Ray, P.; Kumar, S. Advances in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of action of cisplatin in cancer therapy. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 13, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietras, P.; Aulas, A.; Fay, M.M.; Leśniczak-Staszak, M.; Sowiński, M.; Lyons, S.M.; Szaflarski, W.; Ivanov, P. Translation inhibition and suppression of stress granules formation by cisplatin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, X.X.; Lv, W.X.; Xu, Z.J. Inhibition of CXCL1-CXCR2 axis ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by mediating inflammatory response. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, Z.W.; Tew, K.D.; Townsend, D.M. Cisplatin chemotherapy and renal function. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 152, 305–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Guan, Y.J.; Bayliss, G.; Zhao, T.C.; Zhuang, S.G. SET8 inhibition preserves PTEN to attenuate kidney cell apoptosis in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, C.V.; Edwin, S.B.; Szpunar, S.; Forman, J. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in an outpatient setting. Pharmacotherapy 2021, 41, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.C.; Huang, L.F.; Tang, J.X.; Wu, D.; An, N.; Ye, Z.N.; Lan, H.Y.; Liu, H.F.; Yang, C. Asiatic acid alleviates cisplatin-induced renal fibrosis in tumor-bearing mice by improving the TFEB-mediated autophagy-lysosome pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.B.; Cha, M.H.; Won, D.H.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, Y.Y.; Yun, J.W. Transcriptomic analysis of rat kidney reveals a potential mechanism of sex differences in susceptibility to cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 174, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, K.R.; Gadanec, L.K.; Qaradakhi, T.; Ali, B.A.; Zulli, A.; Apostolopoulos, V. Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury: Pathological mechanisms, pharmacological interventions, and genetic mitigations. Cancers. 2021, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, N.X.; Wang, Y.E.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zha, Z.X.; Yang, S.L.; Xu, Q.M.; Liu, Y.L. Anemoside B4 attenuates nephrotoxicity of cisplatin without reducing anti-tumor activity of cisplatin. Phytomedicine. 2019, 56, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.W.; Yang, D.Y.; Zha, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Cai, J.; Chen, G.C.; Dong, Z. The STAT1/HMGB1/NF-κB pathway in chronic inflammation and kidney injury after cisplatin exposure. Theranostics. 2023, 13, 2757–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razak, S.; Afsar, T.; Bibi, N.; Abulmeaty, M.; Bhat, M.A.; Inam, A.; Trembley, J.H.; Almajwal, A.; Shabbir, M.; Alruwaili, N.W.; et al. Sulindac acetohydrazide derivative attenuates against cisplatin induced organ damage by modulation of antioxidant and inflammatory signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dil, E.; Topcu, A.; Mercantepe, T.; Tumkaya, L.; Akyildiz, K.; Saral, S.; Yilmaz, A. Agomelatine on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via oxidative stress and apoptosis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 2753–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Sathyanathan, V.; Salaman, S.D. Molecular mechanisms underlying cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and the potential ameliorative effects of essential oils: A comprehensive review. Tissue Cell. 2024, 88, 102377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Heo, S.C.; Kim, Y.N.; Joo, J.Y.; Hwang, J.J.; Bae, M.K.; Kim, H.J. Gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP) stimulates osteoclastogenesis in periodontitis. Cells. 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.T.; Chen, A.W.; Dai, D.Q.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.F.; Xiong, L.Z. Role of the GRP/GRPR system in regulating brain functions. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 3588–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.J.; Li, C.; He, M.; Zhu, Y.T.; Yang, R.; Deng, S.S.; Meng, X.M.; Yao, R.S. Structure–activity relationship studies on Pd176252 derivatives leading to discovery of novel GRP receptor antagonist with potent anticancer activity. Med. Chem. Res. 2021, 30, 2069–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.L.; Ma, Q.Y.; Bian, H.G.; Meng, X.M.; Jin, J. Novel insight on GRP/GRPR axis in diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, K.J.; Vellaisamy, K.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. Peptide-conjugated long-lived theranostic imaging for targeting GRPr in cancer and immune cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 18053–18058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Wei, B.; Yu, M.J.; Meng, X.M.; He, M.; Yao, R.S. Design, synthesis and evaluation of PD176252 analogues for ameliorating cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. RSC Med. Chem. 2019, 10, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.J.; Li, C.; Deng, S.S.; Meng, X.M.; Yao, R.S. Discovery of a novel GRPR antagonist for protection against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 124, 105794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.B.; Li, W.; Yao, R.; Xu, M.Y.; Dong, W.; Chen, Y.; Ni, W.J.; Xie, S.S.; Sun, Z.H.; Li, C.; et al. Aurantiamide mitigates acute kidney injury by suppressing renal necroptosis and inflammation via GRPR-dependent mechanism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 139, 112745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Y.; Li, X.M.; Wu, W.B.; Hou, M.J.; Yin, G.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Du, Z.Y.; Ma, Y.F.; Lou, Q.; Wei, Y.X. Tim-3 protects against cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, I.; Altayb, H.N.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Alharbi, K.S.; Almalki, N.A.R.; Moglad, E.; Al-Qahtani, S.D.; Bawadood, A.S.; Sayyed, N. Rosiridin prevents cisplatin-induced renal toxicity by inhibiting caspase-3/NF-κB/Bcl-2 signaling pathways in rats and in silico study. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 5895–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhamdi, H.W.; Fayad, E.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Katouah, H.A.; Alshaya, D.S.; Shati, A.A.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Elshaarawy, R.F.M.; Serag, W.M. Chitosan-Ascorbate Nanocapsules for Sustained Cisplatin Release: Minimizing Nephrotoxicity via Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 109, 106968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, Q.Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Li, H.D.; Yu, M.J.; Xie, S.S.; Ma, W.X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.N.; He, R.B.; et al. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of GRPR protects against acute kidney injury via attenuating renal inflammation and necroptosis. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 2734–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisignano, M.; Geisslinger, G. Rethinking the use of NSAIDs in early acute pain. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Gou, S.H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of antitumor platinum(II) agents conjugated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug species. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 120, 105633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, M.; Zanellato, I.; Gabano, E.; Perin, E.; Rangone, B.; Coppola, M.; Osella, D. Antiproliferative activity of Pt (IV) conjugates containing the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) ketoprofen and naproxen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Hou, X.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Shi, Y.F.; Xu, L.Q.; Zheng, X.Q.; Liu, N.; Qiu, A.D.; Zhuang, S.G. 3-deazaneplanocin A protects against cisplatin-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis and acute kidney injury by restoration of E-cadherin expression. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Jiang, K.; Luo, H.J.; Wu, C.; Yu, W.M.; Cheng, F. Novel lncRNA XLOC_032768 alleviates cisplatin-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response of renal tubular epithelial cells through TNF-α. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.P.; Hao, X.G.; Li, X.X.; Li, Q.J.; Fang, X.X. Effects of ginsenoside Rh2 on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in renal tubular epithelial cells by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxic. 2024, 38, 23768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Zhong, Y.P.; Wang, D.; Lu, Z.T. A simple colorimetric method for viable bacteria detection based on cell counting Kit-8. Anal. Methods. 2021, 13, 5211–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokura, K.; Kuromi, Y.; Endo, T.; Anzai, N.; Kazuki, Y.; Oshimura, M.; Ohbayashi, T. A kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1) gene reporter in a mouse artificial chromosome: The responsiveness to cisplatin toxicity in immortalized mouse kidney S3 cells. J. Gene. Med. 2016, 18, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Ren, G.L.; Gao, L.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.D.; Wu, W.F.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Li, J. NADPH oxidase 4 promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via ROS-mediated programmed cell death and inflammation. Lab. Invest. 2018, 98, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Li, M.T.; Li, C.Q.; Li, X.T.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Lu, H.T.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Liu, W.R. Protective Effect of Mangiferin on Cisplatin Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Vivo. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2025, 20, 1934578X251325035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, N.; Raza, S.A.; Alamgeer; Khalil-Ur-Rehman, M.; Anwar, R.; Ahmed, A.; Irfan, H.M. Amelioration of pain and adjuvant-induced arthritis by syringic acid via modulation of behavioral parameters and inflammatory mediators i.e. TNF-α, Interleukins, MCP-1, NF-kB and COX-2. Inflammopharmacololy 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyatip, P.; Nunthaboot, N.; Puthongking, P. In silico ADME, metabolism prediction and hydrolysis study of melatonin derivatives. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2020, 13, 1178646920978245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzaffar, S.; Shahid, W.; Riaz, N.; Saleem, M.; Ashraf, M.; Aziz-Ur-Rehman; Bashir, B.; Kaleem, A.; Al-Rashida, M.; Baral, B.; et al. Probing phenylcarbamoylazinane-1, 2, 4-triazole amides derivatives as lipoxygenase inhibitors along with cytotoxic, ADME and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 107, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyar, S.; Alyar, H.; Özmen, Ü.Ö.; Aktaş, O.; Erdem, K. Biochemical properties of Schiff bases derived from FDA-approved sulfa drugs: Synthesis, ADME/molecular docking studies, and anticancer activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1293, 136167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Entry | GI Absorption a | BBB Permeant b | Bioavailability Score c | AMES Toxicity d | log Po/w e | Lipinski Rules f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD176252 | Low | No | 0.17 | 0.918 | 5.43 | No |
| RH-1402 | High | No | 0.55 | 0.859 | 2.76 | Yes |
| 3l | High | No | 0.55 | 0.393 | 4.24 | Yes |
| 3m | High | No | 0.55 | 0.800 | 4.17 | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, M.; Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Yao, S.; Yao, R. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New 2-Arylpropanoic Acid-l-Tryptophan Derivatives for Mitigating Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Molecules 2025, 30, 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112400
Yuan M, Wang H, Yu M, Yao S, Yao R. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New 2-Arylpropanoic Acid-l-Tryptophan Derivatives for Mitigating Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Molecules. 2025; 30(11):2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112400
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Ming, Huai Wang, Mingjun Yu, Sen Yao, and Risheng Yao. 2025. "Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New 2-Arylpropanoic Acid-l-Tryptophan Derivatives for Mitigating Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity" Molecules 30, no. 11: 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112400
APA StyleYuan, M., Wang, H., Yu, M., Yao, S., & Yao, R. (2025). Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New 2-Arylpropanoic Acid-l-Tryptophan Derivatives for Mitigating Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Molecules, 30(11), 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30112400









