Carbon Dots: A Versatile Platform for Cu2+ Detection, Anti-Counterfeiting, and Bioimaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
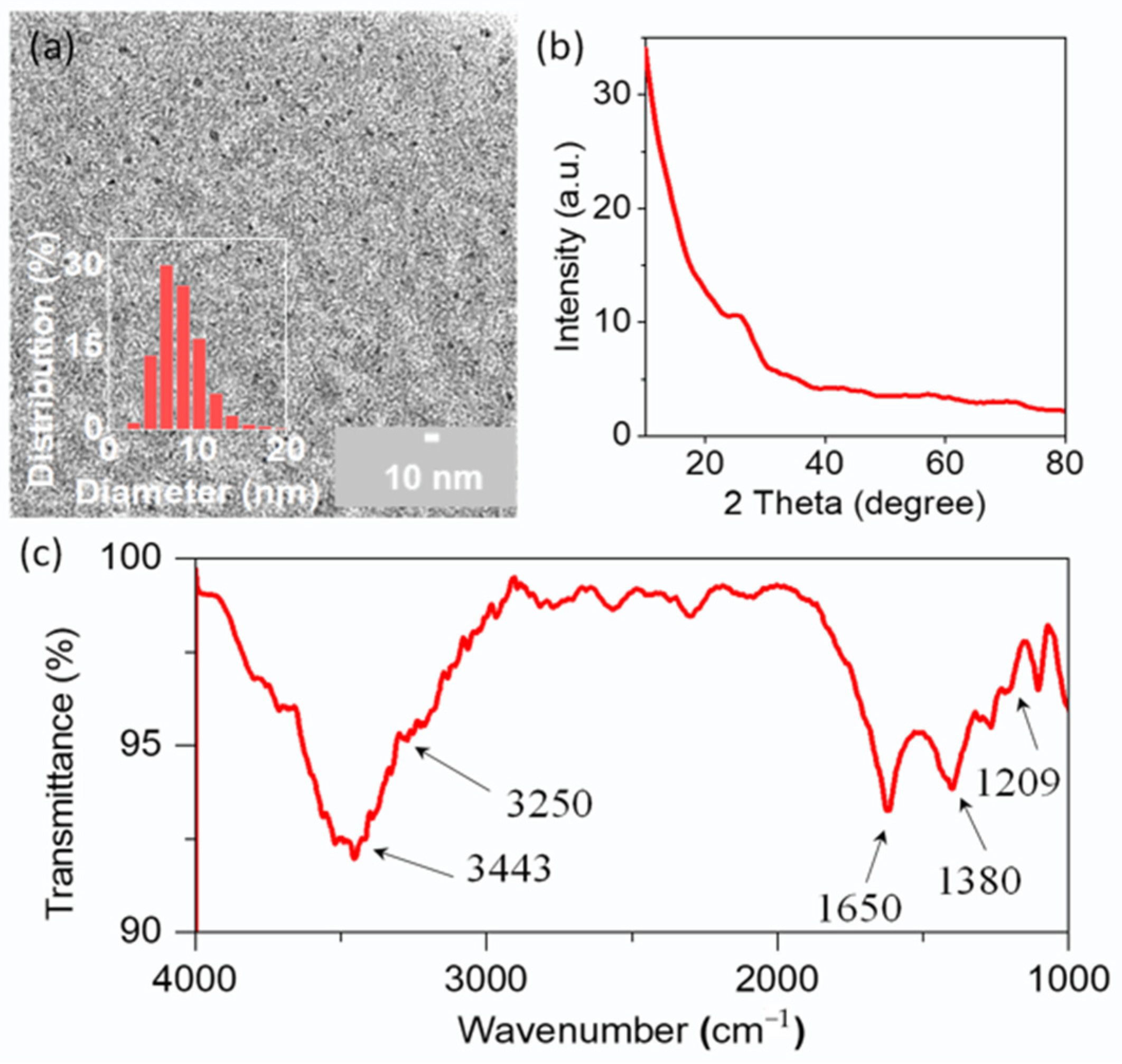
2.1. The Preparation and Characterization of CDs
2.2. Optical Performance of the CDs
2.3. Detection of Cu2+
2.4. CDs for Anti-Counterfeiting
2.5. Cytotoxicity and Cell Imaging of CDs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of CDs
3.3. Material Characterization
3.4. Luminescence Quantum Yield of CDs
3.5. MTT Assays
3.6. Cell Imaging
3.7. Fluorescence Detection of Cu2+
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arumugham, T.; Alagumuthu, M.; Amimodu, R.G.; Munusamy, S.; Iyer, S.K. A sustainable synthesis of green carbon quantum dot (CQD) from Catharanthus roseus (white flowering plant) leaves and investigation of its dual fluorescence responsive behavior in multi-ion detection and biological applications. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 23, e00138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Rafiq, M.; Hanif, M. Organic material based fluorescent sensor for Hg2+: A brief review on recent development. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 31–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.K.; Dey, N.; Kumari, N.; Biswakarma, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Multimodal ion sensing by structurally simple pyridine-end oligo p-phenylenevinylenes for sustainable detection of toxic industrial waste. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12304–12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Min, H.; Shi, W.; Cheng, P. Multicenter metal–organic framework-based ratiometric fluorescent sensors. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1805871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, H.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Ge, B.; Yu, D. Deep-learning-assisted single-molecule tracking on a live cell membrane. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 8810–8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, M.; Shanker, U.; Kaith, B.S.; Sillanpää, M. Green fabrication of fluorescent N-doped carbon quantum dots from Aegle marmelos leaves for highly selective detection of Fe3+ metal ions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 159, 111878. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Du, H.; Tang, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Liu, J.; Sun, K.; Li, Z.; Deng, G. Boron difluoride modified zinc metal–organic framework-based “off–on” fluorescence sensor for tetracycline and Al3+ detection. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendão, R.M.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.; Pinto da Silva, L.J.C. Applications of fluorescent carbon dots as photocatalysts: A Review. Catalysts 2023, 13, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, F.; Song, S.; Ai, G.; Xin, X.; Zhao, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Recent advances in g-C3N4-based materials and their application in energy and environmental sustainability. Molecules 2023, 28, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariminia, S.; Shamsipur, M.; Barati, A. Fluorescent folic acid-chitosan/carbon dot for pH-responsive drug delivery and bioimaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Cai, H.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Qu, X.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Carbon dots in bioimaging, biosensing and therapeutics: A comprehensive review. Small Sci. 2022, 2, 2200012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, R.; Rodrigues, J.; Neto, V.; Monteiro, T.; Gonçalves, G. Carbon Dots: A bright future as anticounterfeiting encoding agents. Small 2024, 20, 2311526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Duan, H.; Tan, K.; Dong, L. One-step solvothermal synthesis of full-color fluorescent carbon dots for information encryption and anti-counterfeiting applications. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 11642–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Qian, Y.; Bao, L.; Wang, W.; Deng, N.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Fu, X.; Fu, W. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for fluorescence sensing, anti-counterfeiting and logic gate operations. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; He, H.; Feng, Z.; Mao, J.; Hu, X.; Wei, X.; Bi, S.; Qin, G.; Wang, X. Carbon dot blinking fingerprint uncovers native membrane receptor organizations via deep learning. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3914–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Xue, M.; Guan, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Qin, G.; He, H. Near-infrared blinking carbon dots designed for quantitative nanoscopy. Nano Lett. 2022, 23, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.L.; Zhou, S.Z.; Ma, Y.H.; Wei, Y.Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.Z.; Yu, S.P. Folic acid functionalized gadolinium-doped carbon dots as fluorescence/magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent for targeted imaging of liver cancer. Colloid Surf. B 2024, 234, 113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Mu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Bai, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, F.; Jing, Y.; Dai, H. Structure, luminescence, and bioimaging of bimetallic CuAu nanoclusters. Opt. Mater. 2018, 86, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.S.; Lee, N.Y. Comprehensive review on fluorescent carbon dots and their applications in nucleic acid detection, nucleolus targeted imaging and gene delivery. Analyst 2024, 149, 4095–4115. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Huang, L.; Li, T.; Song, J.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Ramakrishna, S. Application of carbon dots in dye-sensitized solar cells: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Lin, L.; Zheng, X.; Xu, X.; Du, P.; Xu, H. Synthesis of multicolor carbon dots at room temperature and in atmosphere toward energy-efficient preparation and LEDs application. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 687, 133486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Nau, W.M.; Huang, F. Carbon dot blinking enables accurate molecular counting at nanoscale resolution. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3968–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Chen, X.; Feng, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Bi, S. Nanoscopic imaging of nucleolar stress enabled by protein-mimicking carbon dots. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 5689–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, H.; Ge, B.; Wang, S. High-density super-resolution localization imaging with blinking carbon dots. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11831–11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. One-step synthesis of self-doped carbon dots with highly photoluminescence as multifunctional biosensors for detection of iron ions and pH. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammina, S.K.; Kumar, J.V.; Rhim, J.-W. Detection, detoxification, and anti-counterfeiting applications of pullulan-modified nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 320, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Jian, K.; Han, Y.; Zhao, X. Reaction temperature-controlled synthesis of multicolor aggregation-induced emission carbon dots and their various applications in anti-counterfeiting, fingerprint detection. Microchem. J. 2024, 202, 110765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, Z.; Shen, Y.; Qin, H.; Yuan, H.; Lu, J.; Guo, F.; Li, C.; Shi, W. Efficient photothermal-assisted photocatalytic H2 production using carbon dots-infused g-C3N4 nanoreactors synthesized via one-step template-free thermal polymerization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 488, 151041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, D.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Hocking, R.K.; Fox, B. Properties, synthesis, and applications of carbon dots: A review. Carbon Trends 2023, 12, 100276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhong, X.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; Zou, G.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. A review of carbon dots in synthesis strategy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 498, 215468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Preparation of high quantum yield nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots for sensitive detection of Cu2+. J. Nanophotonics 2024, 18, 016011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ning, J.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, Y. Prepared carbon dots from wheat straw for detection of Cu2+ in cells and zebrafish and room temperature phosphorescent anti-counterfeiting. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 281, 121597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, Z.; Mao, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Wei, X.; Fang, H. Microwave-synthesized fluorescent carbon nanoparticles for nucleolus imaging. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 48, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cao, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Leng, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen and boron doped carbon quantum dots with yellow-green emission for sensing Cr (VI), anti-counterfeiting and cell imaging. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 48386–48393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Wu, P.; Ma, C.; Wu, X.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Liu, S. Hydrothermal synthesis of green fluorescent nitrogen doped carbon dots for the detection of nitrite and multicolor cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1090, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, Y.; Li, K. Hydrothermal synthesis of high-yield red fluorescent carbon dots with ultra-narrow emission by controlled O/N elements. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, Q.; Li, M.; Song, N.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, H.; James, T.D.; Feng, L. Functionalization of cellulose carbon dots with different elements (N, B and S) for mercury ion detection and anti-counterfeit applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Bai, Z.; Xi, X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, Y. Rapid microwave-assisted green synthesis of guanine-derived carbon dots for highly selective detection of Ag+ in aqueous solution. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 248, 119208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Long, R.; Li, T.; Tang, C.; Tong, X.; Guo, Y.; Shi, S.; Xiang, H.; Tong, C. One-pot fabrication of dual-emission and single-emission biomass carbon dots for Cu2+ and tetracycline sensing and multicolor cellular imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 7481–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seesuea, C.; Sangtawesin, T.; Thangsunan, P.; Wechakorn, K. Facile green gamma irradiation of water hyacinth derived-fluorescent carbon dots functionalized thiol moiety for metal ion detection. J. Fluoresc. 2024, 34, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedda, G.; Lee, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wu, H.-F. Green synthesis of carbon dots from prawn shells for highly selective and sensitive detection of copper ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Ding, L.; Zhang, B.; Huang, J. Detection of nitrite based on fluorescent carbon dots by the hydrothermal method with folic acid. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 172149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Simple aqueous solution route to luminescent carbogenic dots from carbohydrates. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 5563–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafiej, A.; Pyrzynska, K. Adsorption of heavy metal ions with carbon nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 58, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Qu, Q.; Shao, X.; Kong, B.; Tian, Y. Carbon-dot-based dual-emission nanohybrid produces a ratiometric fluorescent sensor for in vivo imaging of cellular copper ions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 7185–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, W.; Gai, Q.; Tian, Z.; Ren, S. A carbon-dot-based fluorescent probe for the sensitive and selective detection of Copper (II) Ions. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 2392–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algethami, F.K.; Abdelhamid, H.N. Heteroatoms-doped carbon dots as dual probes for heavy metal detection. Talanta 2024, 273, 125893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Pang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, C.; Ma, C.; Gu, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G. One-step synthesis of the nitrogen and sulfur codoped carbon dots for detection of lead and copper ions in aqueous solution. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 8828456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Chen, Y.; Labidi, A.; Zhao, K.; Xu, X.; Othman, S.I.; Allam, A.A.; Rudayni, H.A.; Wang, C. Transforming bio-waste lignin into amine functionalized carbon quantum dots for selective detection of trace Cu2+ in aqueous system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Mo, F.; Sun, Z.; Luo, J.; Fan, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X. Bright red-emitting P, Br co-doped carbon dots as “OFF-ON” fluorescent probe for Cu2+ and L-cysteine detection. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 897, 162731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Yang, G.; Wan, X. Ultra-high quantum yield nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots and their versatile application in fluorescence sensing, bioimaging and anti-counterfeiting. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 253, 119583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Mo, S.; Fang, B.; Cheng, W.; Yin, M. Dual fluorescence switching of a Rhodamine 6G-naphthalimide conjugate with high contrast in the solid state. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10270–10275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Chemo-Sensors | Starting Materials | QYs (%) | Fluorescence | Linear Range (mM) | LOD (μM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-CDs | p-phenylenediamine, thiosemicarbazone | 28.26 | Greenish | 0.02–0.2 | 4.8 | [31] |
| N, S, O-CDs | L-cysteine | Blue | 0.01–0.0333 | 2.0 | [47] | |
| CDs-SH | Water hyacinth | 13.00 | Blue | 0–0.6 | 31.1 | [40] |
| NS-CDs | L-cysteine | 18.00 | 0–0.5 | 5.0 | [48] | |
| NH2-CQDs | Lignin | 21.10 | Greenish | 0.0005–0.08 | 2.420 | [49] |
| N-CDs | p-phenylenediamine, polyethylene glycol 20000 | 2.16 | Red | 0.045–0.07 | 45.87 | [49] |
| P, Br-CDs | Phenylenediamine, disodium hydrogen phosphate, KBr | 11.30 | Red | 0–0.15 | 4.408 | [50] |
| CDs | Diaminomaleonitrile, Boc-D-2, 3-diaminopropionic acid | 28.2 | Blue | 0.0001–0.009 | 1.34 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; He, X.; Mao, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, F.; Zhao, B.; Chen, G.; et al. Carbon Dots: A Versatile Platform for Cu2+ Detection, Anti-Counterfeiting, and Bioimaging. Molecules 2024, 29, 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174211
Wang Q, He X, Mao J, Wang J, Wang L, Zhang Z, Li Y, Huang F, Zhao B, Chen G, et al. Carbon Dots: A Versatile Platform for Cu2+ Detection, Anti-Counterfeiting, and Bioimaging. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174211
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qian, Xinyi He, Jian Mao, Junxia Wang, Liangliang Wang, Zhongchi Zhang, Yongfei Li, Fenglin Huang, Bin Zhao, Gang Chen, and et al. 2024. "Carbon Dots: A Versatile Platform for Cu2+ Detection, Anti-Counterfeiting, and Bioimaging" Molecules 29, no. 17: 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174211
APA StyleWang, Q., He, X., Mao, J., Wang, J., Wang, L., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Huang, F., Zhao, B., Chen, G., & He, H. (2024). Carbon Dots: A Versatile Platform for Cu2+ Detection, Anti-Counterfeiting, and Bioimaging. Molecules, 29(17), 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174211






