Fluorescent-Dye-Labeled Amino Acids for Real-Time Imaging in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Fluorescent-Dye-Labeled Amino Acid Derivatives
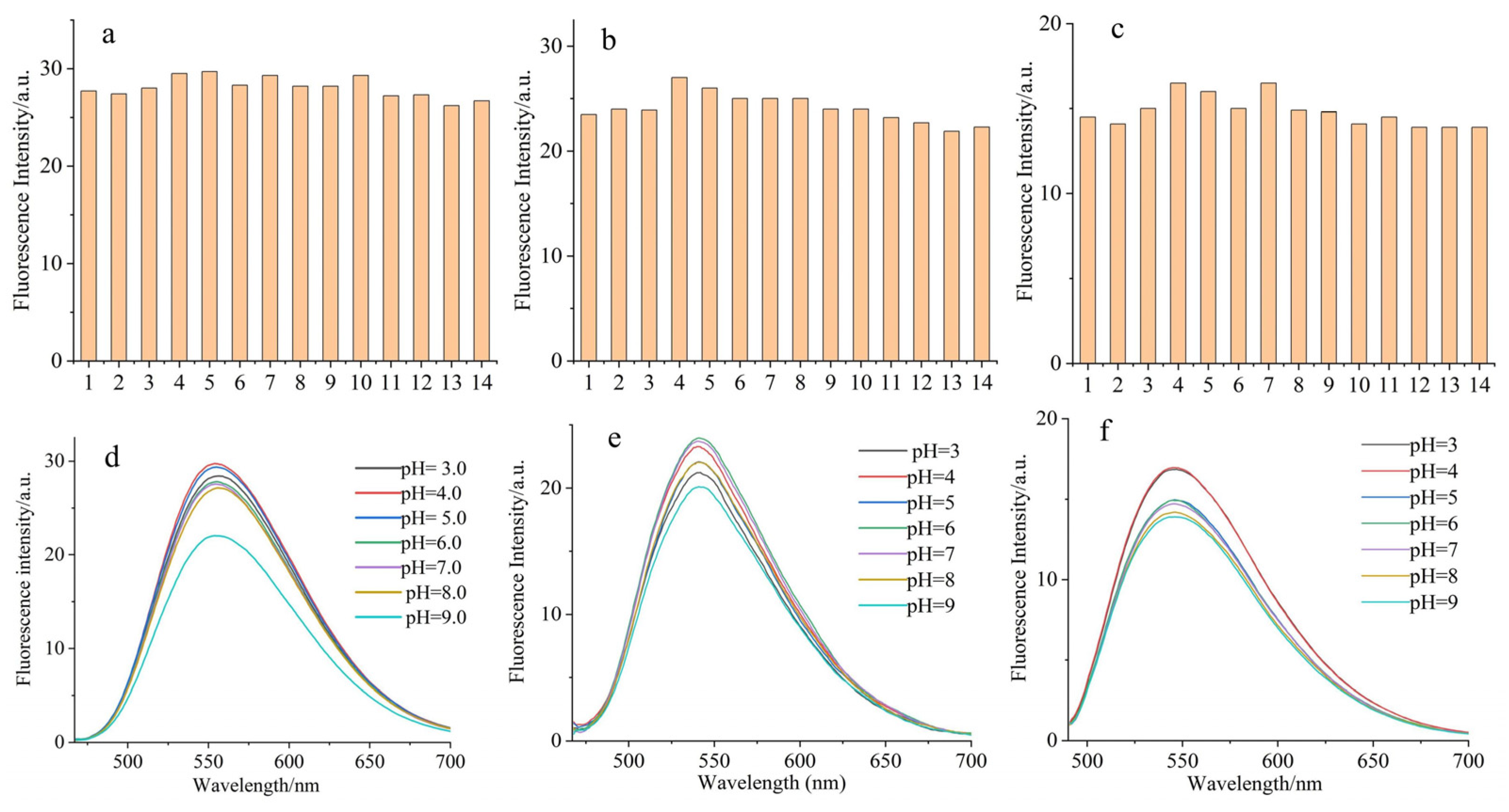
2.2. Interference and Effect of pH Value on Fluorescent-Dye-Labeled Amino Acid Derivatives
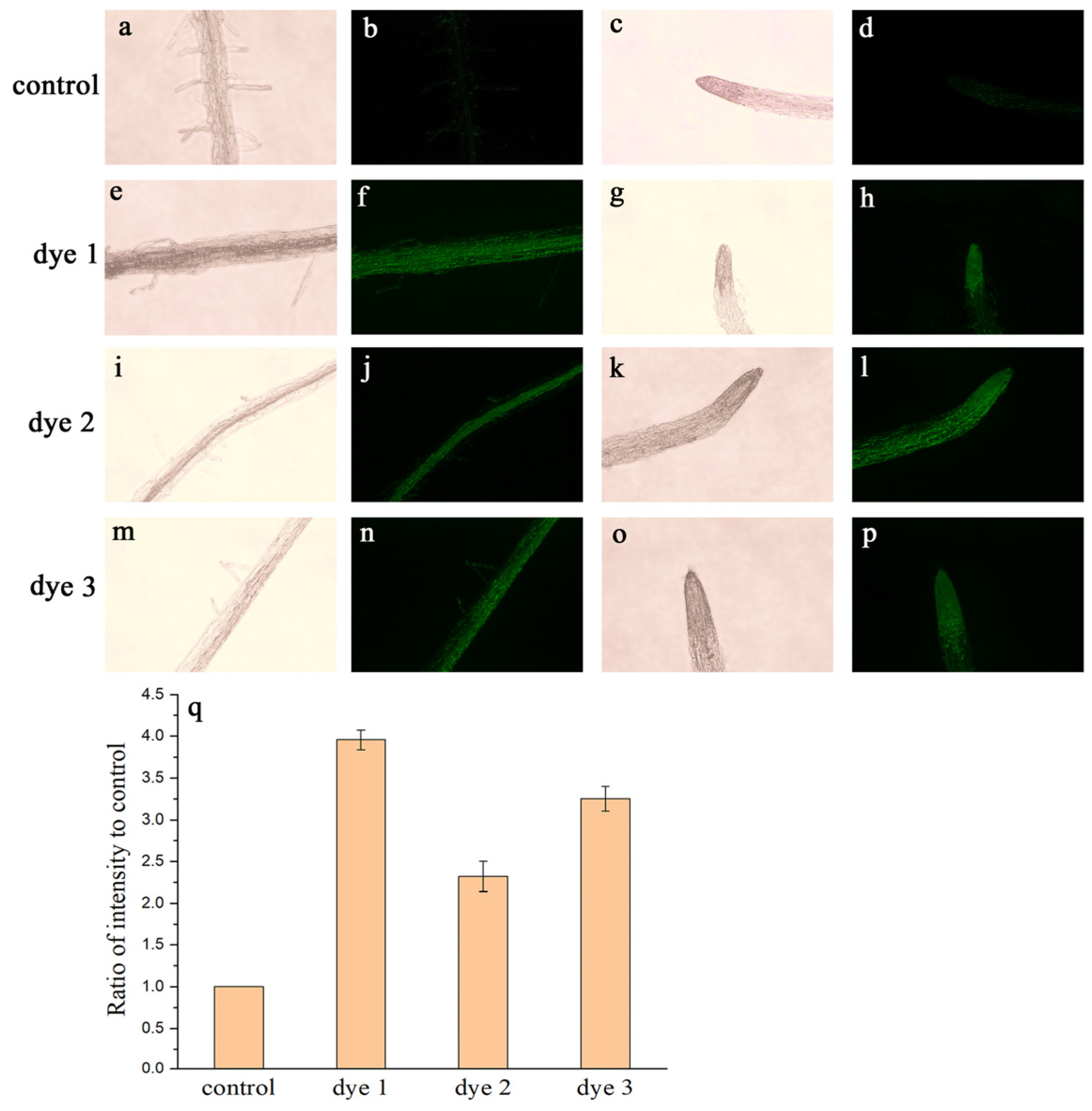
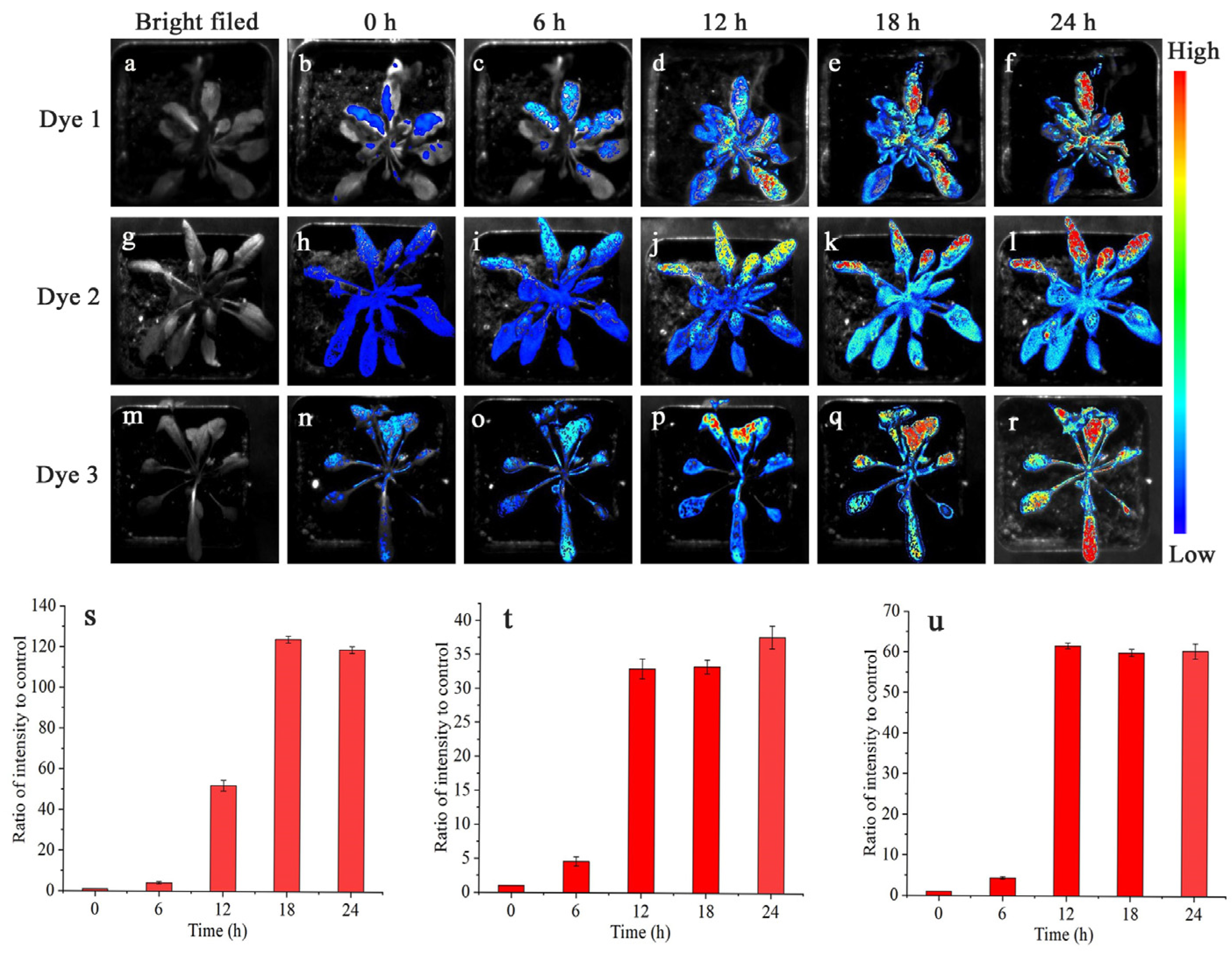
2.3. Tissues and Whole-Plant Fluorescence Imaging
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Instruments
3.2. Synthesis of the Dye-Labeled Fluorescent Amino Acids
3.3. Quantum Yield (QY) Estimation
3.4. Interference and Effect of pH Value on Fluorescent Amino Acids
3.5. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
3.6. Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Investigations
3.7. Imaging Analysis of the Whole Plant
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kristyna, B.; Barbora, P.; Martin, K.; Alexandra, H.; Martin, K.; Ma, Q.; Michaela, S.; Stéphanie, R.; Karel, D.; Miroslav, S. New fluorescently labeled auxins exhibit promising anti-auxin activity. New Biotechnol. 2019, 48, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, D.P.; Shiratori, I.; Shimizu, A.; Kato, K.; Mii, M.; Waga, I. Generation of brilliant green fluorescent petunia plants by using a new and potent fluorescent protein transgene. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichman, Y.; Miller, G.; Mittler, R. Whole-plant live imaging of reactive oxygen species. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Villasante, C.; Burén, S.; Blázquez-Castro, A.; Barón-Sola, Á.; Hernández, L.E. Fluorescent in vivo imaging of reactive oxygen species and redox potential in plants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 122, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, R.; Lu, C.; Baluška, F.; Wan, Y. Di-4-ANEPPDHQ, a fluorescent probe for the visualisation of membrane microdomains in living Arabidopsis thaliana cells. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 87, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Lei, B. Pollen derived blue fluorescent carbon dots for bioimaging and monitoring of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium uptake in Brassica parachinensis L. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33459–33465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegeder, M.; Rentsch, D. Uptake and partitioning of amino acids and peptides. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perchlik, M.; Foster, J.; Tegeder, M. Different and overlapping functions of Arabidopsis LHT6 and AAP1 transporters in root amino acid uptake. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5193–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegeder, M.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perchlik, M.; Tegeder, M. Leaf amino acid supply affects photosynthetic and plant nitrogen use efficiency under nitrogen stress. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Wu, B.; Ji, Y. The amino acid transporter OsAAP4 contributes to rice tillering and grain yield by regulating neutral amino acid allocation through two splicing variants. Rice 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentsch, D.; Schmidt, S.; Tegeder, M. Transporters for uptake and allocation of organic nitrogen compounds in plants. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirner, A.; Ladwig, F.; Stransky, H.; Okumoto, S.; Keinath, M.; Harms, A.; Frommer, W.B.; Koch, W. Arabidopsis LHT1 is a high-affinity transporter for cellular amino acid uptake in both root epidermis and leaf mesophyll. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerstam, H.; Jämtgård, S.; Ahmad, I.; Huss-Danell, K.; Torgny, N.; Ganeteg, U. Transporters in Arabidopsis roots mediating uptake of amino acids at naturally occurring concentrations. New Phytol. 2011, 191, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, C.R. Post-uptake metabolism affects quantification of amino acid uptake. New Phytol. 2011, 193, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran-Zuloaga, D.; Dippold, M.; Glaser, B.; Kuzyakov, Y. Organic nitrogen uptake by plants: Reevaluation by position-specific labeling of amino acids. Biogeochemistry 2015, 125, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Shinozaki, K. Polyamine Transport Systems in Plants. In Polyamines; Kusano, T., Suzuki, H., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; pp. 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, J.L.; Wang, C.W.; Yu, A.X.; Liu, N.; Chen, L.; Lin, F.; Xu, H.H. Glycinergic-fipronil uptake is mediated by an amino acid carrier system and induces the expression of amino acid transporter genes in Ricinus communis seedlings. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3810–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, N.; Holzgrabe, U. Stability and assessment of amino acids in parenteral nutrition solutions. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 147, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Sun, L.; Yao, X.; Pimpl, P.; Jiang, L. Organelle pH in the Arabidopsis endomembrane system. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1419–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratelli, R.; Boyd, S.; Pilot, G. Analysis of amino acid uptake and alocation in Arabidopsis with a low-cost hydroponic system. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2016, 179, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegeder, M.; Hammes, U.Z. The way out and in: Phloem loading and unloading of amino acids. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 43, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L. Autofluorescence in Plants. Molecules 2020, 25, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, B.M.; Oh, G.G.K.; Lee, C.P.; Millar, A.H. Metabolite regulatory interactions control plant respiratory metabolism via target of rapamycin (TOR) kinase activation. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Cao, X.; Wu, L.; Mi, W.; Feng, Y. Light intensity affects the uptake and metabolism of glycine by pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Xiao, H.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yang, D. Effects of cadmium stress on growth and amino acid metabolism in two Compositae plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 158, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurack, K.; Spieles, M. Fluorescence quantum yields of a series of red and near-infrared dyes emitting at 600–1000 nm. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Cao, F.; Yuan, G. Fluorescent-Dye-Labeled Amino Acids for Real-Time Imaging in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecules 2023, 28, 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073126
Yuan Y, Cao F, Yuan G. Fluorescent-Dye-Labeled Amino Acids for Real-Time Imaging in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073126
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yao, Fuxiang Cao, and Guangming Yuan. 2023. "Fluorescent-Dye-Labeled Amino Acids for Real-Time Imaging in Arabidopsis thaliana" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073126
APA StyleYuan, Y., Cao, F., & Yuan, G. (2023). Fluorescent-Dye-Labeled Amino Acids for Real-Time Imaging in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecules, 28(7), 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073126





