The Current State and Future Prospects of Auricularia auricula’s Polysaccharide Processing Technology Portfolio
Abstract
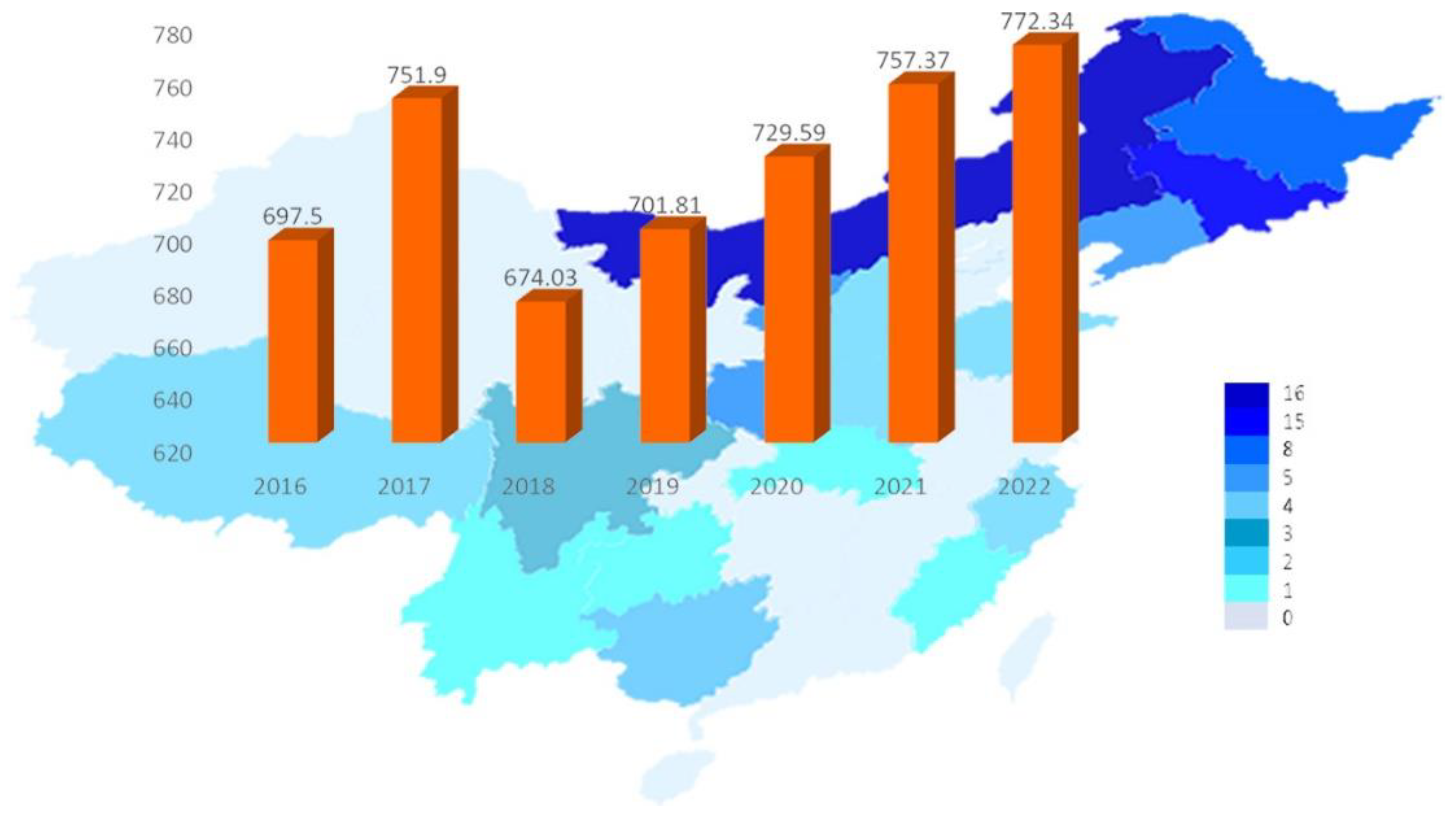
1. Introduction
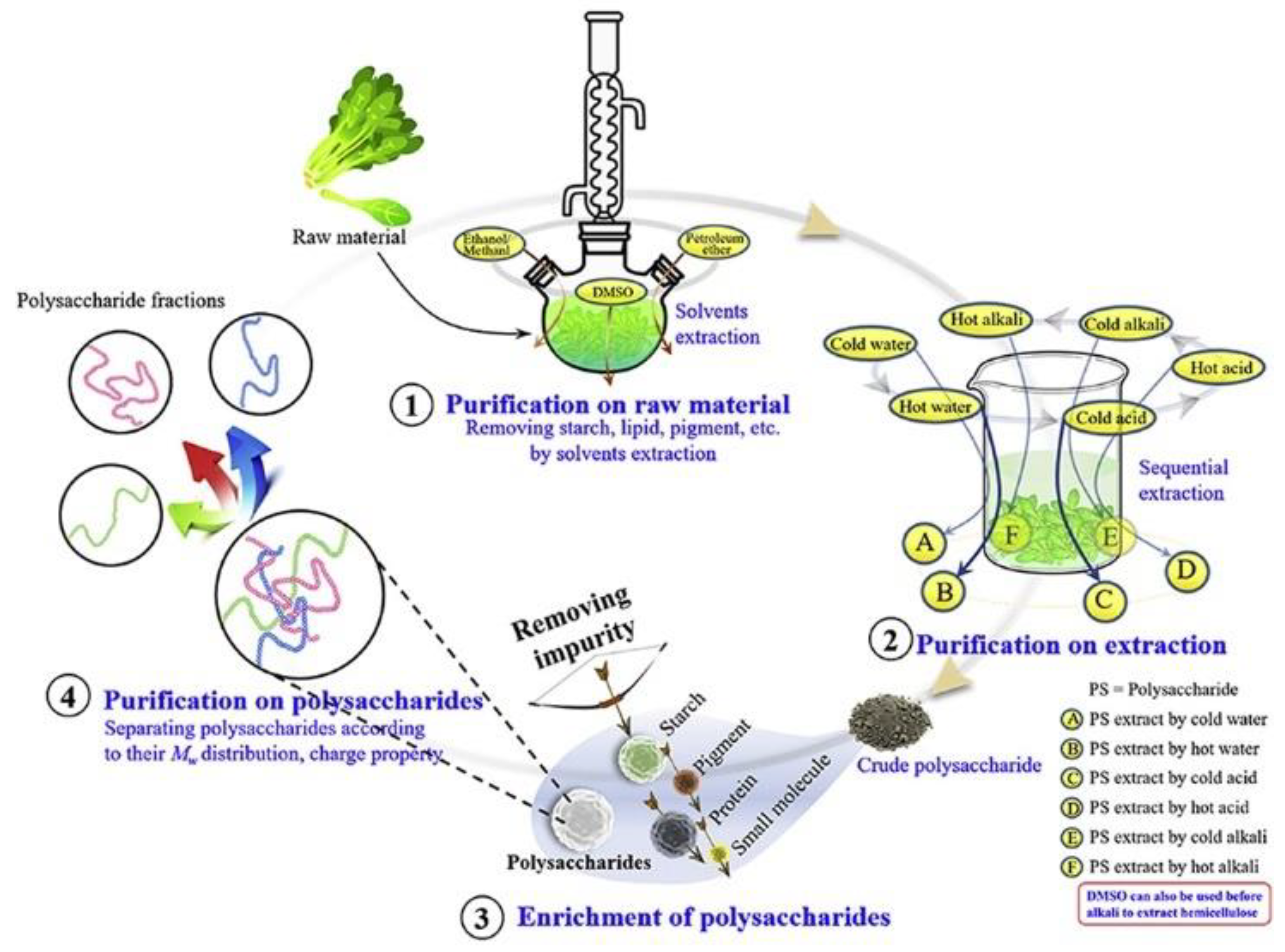
2. Pretreatment of Auricularia auricula and Extraction Technology
3. Separation and Purification
3.1. Concentration Grading Method
3.2. Column Chromatography Method
3.2.1. Macroporous Resin
3.2.2. Cellulose Column Chromatography
3.2.3. Gel Column Chromatography
4. Physiological Activity and Product Development of Polysaccharides of Auricularia auricula
4.1. Physiological Activity of Auricularia auricula
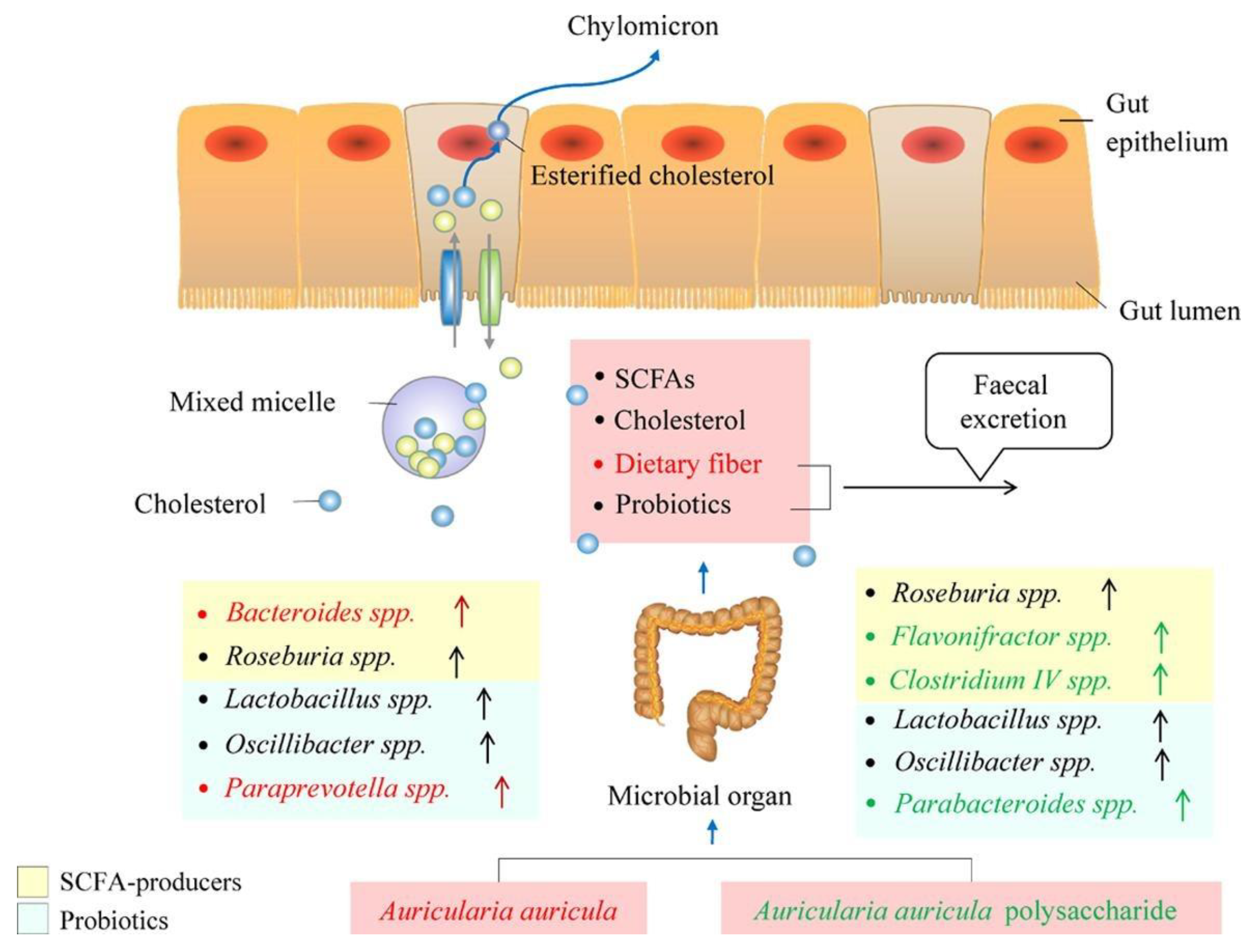
4.1.1. Regulation of Intestinal Flora
4.1.2. Anti-High Cholesterol
4.1.3. Hypoglycemic Effect
4.1.4. Anti-Cancer
4.1.5. Anti-Oxidation and Anti-Aging
4.1.6. Anti-Viral
4.2. Practical Application of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharide
4.2.1. Biological Anticorrosive Film
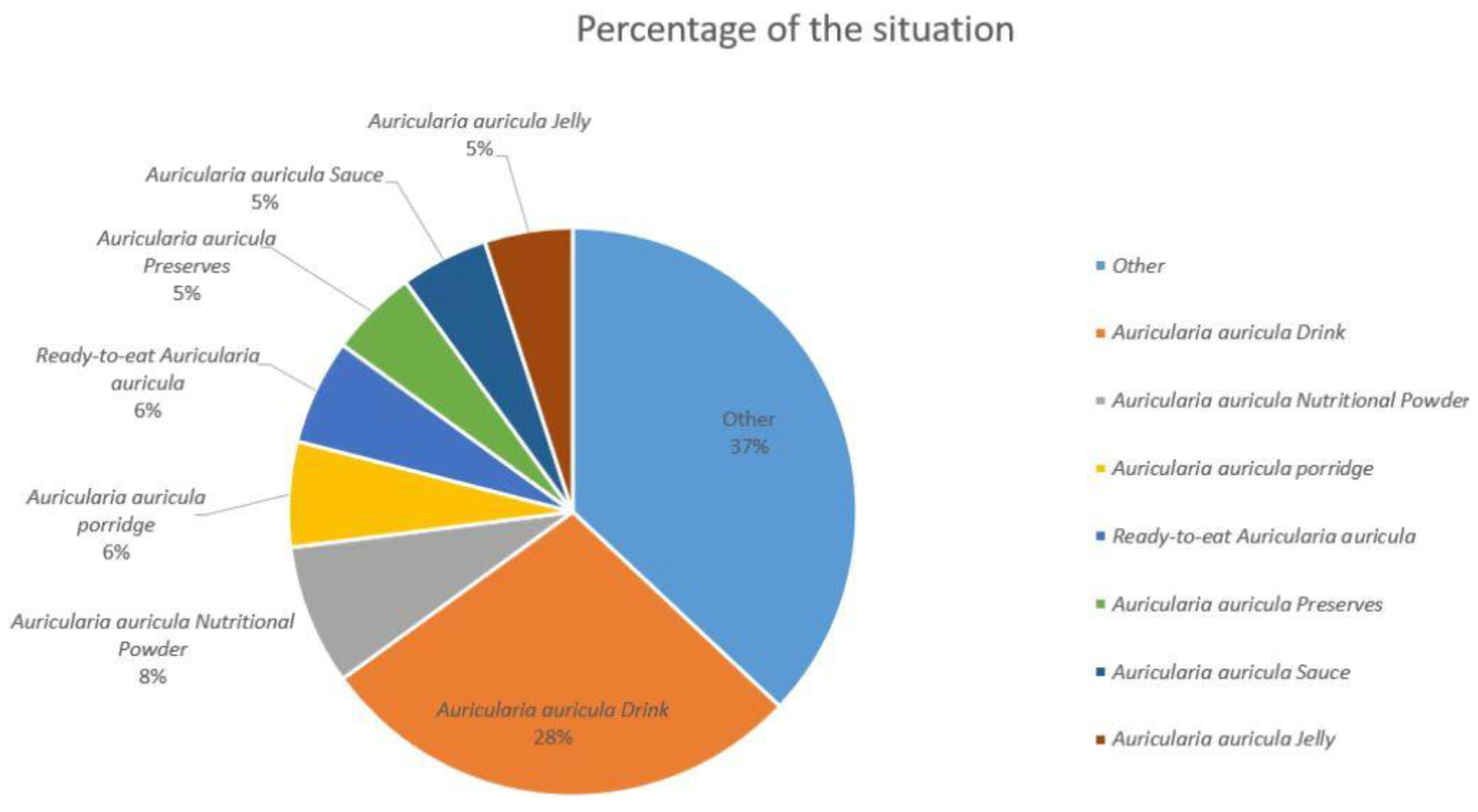
4.2.2. Edible Products
5. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, R.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wong, G.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H.J.S.R. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals relationship of three major domesticated varieties of Auricularia auricula-judae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Xie, L.; Yong, C.; Zhang, H. Purification, characterization and anticoagulant activity of the polysaccharides from green tea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, C.; Wang, Z.; Molecules, S.J. Extraction Optimization, Structural Characterization, and Anticoagulant Activity of Acidic Polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula-judae. Molecules 2020, 25, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Regenstein, J.M.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Isolation, structural characterization and bioactivities of polysaccharides and its derivatives from Auricularia—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Rong, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, S.; Duan, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, X. Extraction of a soluble polysaccharide from Auricularia polytricha and evaluation of its anti-hypercholesterolemic effect in rats. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Qin, D.; Cao, H.; Bai, Y. Enzymatic hydrolysis of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula and characterization of the degradation product. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, H.; Zong, X.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. Polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula: Preparation, structural features and biological activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, W.; Xie, B.; Liu, H. Effects of Auricularia auricula and its polysaccharide on diet-induced hyperlipidemia rats by modulating gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhang, X.; Lin, S. Isolation, purification, characterization, and immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula on RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Purification, characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity of a polysaccharide AAP–3–1 from Auricularia auricula—ScienceDirect. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, K. Antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of the polysaccharides from different varieties of Auricularia auricula. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3868–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Geng, L.; Wang, Z.; Regenstein, J.M. Structure and radio-protective effects of sulfated Auricularia auricula polysaccharides. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Chen, S.; Huang, Q.; Tan, J.; Zeng, J.; Yao, J.; Feng, T.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. The lipid lowering and antioxidative stress potential of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula prepared by enzymatic method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, D.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Abula, S.; Zhang, J.; Qin, T.; Chen, X.; et al. In vitro antiviral activity of sulfated Auricularia auricula polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Jiang, W.; Yao, J.; Zeng, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of the chemical composition and antioxidant stress ability of polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula under different drying methods. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2938–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Xiao, B.; Chen, S.; Zeng, J.; Yao, J.; Tan, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Effect of Enzyme-Assisted Extraction on the Chemical Properties and Antioxidant Activities of Polysaccharides Obtained from the Wood Ear Mushroom, Auricularia auricula (Agaricomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2022, 24, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrinčić, A.; Zorić, Z.; Pedisić, S.; Repajić, M.; Roje, M.; Herceg, Z.; Čož-Rakovac, R.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. Application of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Non-Thermal Plasma for Fucus virsoides and Cystoseira barbata Polysaccharides Pre-Treatment and Extraction. Processes 2022, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F.; Ao, H.; Zhu, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, X. High-Efficiency Production of Auricularia polytricha Polysaccharides Through Yellow Slurry Water Fermentation and Its Structure and Antioxidant Properties. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 811275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Su, Y.; Feng, Y.; Hong, R. A comparison study on digestion, anti-inflammatory and functional properties of polysaccharides from four Auricularia species. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Bi, H. Current Situation and Countermeasures of Auricularia auricula Industry in China. North. Hortic. 2021, 7, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yanfang, L.I.; Zang, F.; Miao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, X.; Shi, C. Disinfection Technology for Auricularia auricula in Bag Cultivation: Problems and Countermeasures. Asian J. Agric. Res. 2021, 12, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Song, W.; Zhou, D.; Wang, J.; Ding, T. The Present Situation and Prospect of Auricularia auricula Mechanized Harvesting in China. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2022, 43, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F. Analysis of Auricularia auricula industry based on spot market and e-commerce sales data. China Veg. 2022, 5, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Guo, C.; Ma, J.; Kong, P.; Fang, B. Research Status of Auricularia auricula Products in China. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Li, F. Investigation and Analysis Report on the Market and Industry of Auricularia auricula in China. Farm Prod. Mart 2021, 50–53, 1009–8070. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Cong, Y.; Li, T.; Meng, X.; Zhang, F. Enhancement of nutritional, sensory and storage stability by lactic fermentation of Auricularia auricula. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 5172–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Zhao, L.; Yang, W.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, Q. Enrichment of bread with nutraceutical-rich mushrooms: Impact of Auricularia auricula (Mushroom) flour upon quality attributes of wheat dough and bread. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillapachaiyaporn, C.; Chuchawankul, S.; Nilkhet, S.; Moungkote, N.; Sarachana, T.; Ung, A.T.; Baek, S.J.; Tencomnao, T. Ergosterol isolated from cloud ear mushroom (Auricularia polytricha) attenuates bisphenol A-induced BV2 microglial cell inflammation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, M. Effects of Ultrasound Treatment on Extraction and Rheological Properties of Polysaccharides from Auricularia Cornea var. Li. Molecules 2019, 24, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.C.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, H.; Jia, L.R.; Chen, W.Y. Characterization of antioxidant polysaccharides from Auricularia auricular using microwave-assisted extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mao, X.; Xu, B. Pulsed electric field extraction enhanced anti-coagulant effect of fungal polysaccharide from Jew’s ear (Auricularia auricula). Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 24, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Yin, H.; Liu, R.; Liang, W.; Yu, M.; Zhang, R. Optimization of Extraction Technology of Auricularia Auricularia Polysaccharides by Strong Electric Field. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2014, 42, 5. [Google Scholar]
- ZZhang, L.; Wang, M. PEG-based ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from superfine ground Auricularia auricular. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 2, e13445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Ye, Z.; Feng, T.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Ultrasonic–assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula and effects of its acid hydrolysate on the biological function of Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Yao, J.; Zeng, J.; Shen, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y. Comparison on chemical features and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula by three different enzymes. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Z.; Ye, P.; Zhou, L.; Fu, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Pasteurization of Salmonella spp. in black fungus (Auricularia auricula) powder by radio frequency heating. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 10820132221123437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.Q.; Zhang, L.M. Chemical structural and chain conformational characterization of some bioactive polysaccharides isolated from natural sources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liu, D.; Yin, J.-Y.; Nie, S.-P. Consecutive and progressive purification of food-derived natural polysaccharide: Based on material, extraction process and crude polysaccharide. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, S.A.; Omara, E.; Abdel-Salam, O.; Zahran, H.G. Mushroom insoluble polysaccharides prevent carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 3184–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W., Jr.; Heldreth, B.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; et al. Safety Assessment of Galactomannans as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 35S–65S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.B. Critical problems stalling progress in natural bioactive polysaccharide research & development. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4581–4583. [Google Scholar]
- Tziveleka, L.-A.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V. Ulvan, a bioactive marine sulphated polysaccharide as a key constituent of hybrid biomaterials: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Willför, S.; Xu, C. A review of bioactive plant polysaccharides: Biological activities, functionalization, and biomedical applications. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2015, 5, 31–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Yan, L.; Li, S.; Ye, X.; Liu, D.; Ding, T.; Linhardt, R.J.; Orfila, C.; et al. Extraction and characterization of RG-I enriched pectic polysaccharides from mandarin citrus peel. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 79, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colodel, C.; Vriesmann, L.C.; Petkowicz, C.L.D.O. Cell wall polysaccharides from Ponkan mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Ponkan) peel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L. Bioactivities, isolation and purification methods of polysaccharides from natural products: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Yao, K.; Jia, D. Physicochemical and rheological properties of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide fractions by ethanol precipitation. CyTA J. Food 2021, 19, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yuan, D.; Li, C.; Fu, X. Physicochemical properties and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Sargassum pallidum by fractional ethanol precipitation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3536–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Liu, X.-Y.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, Y.-F.; Liu, B. Antioxidant activities of polysaccharides obtained from Chlorella pyrenoidosa via different ethanol concentrations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Yue, P.; Luo, H.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, F. Physicochemical Properties and Skin Protection Activities of Polysaccharides from Usnea longissima by Graded Ethanol Precipitation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25010–25018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Huang, Q.; Shen, X.; Hu, J.; Yi, X.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Deproteinization of four macroporous resins for rapeseed meal polysaccharides. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Guo, Q.-S.; Wang, G.-S. Preparative separation and purification of the total flavonoids in Scorzonera austriaca with macroporous resins. Molecules 2016, 21, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Jin, S.; Xiang, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, Q.; Yang, M.; Ji, S.; Huang, R.; Song, C. Enrichment and Cytotoxic Activity of Curcuminoids from Turmeric Using Macroporous Resins. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2024–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Han, Y.; Tao, Y.; Fan, S.; Chu, D.-T.; Ye, X.; Ye, M.; Xie, G. Ultrasound assisted adsorption and desorption of blueberry anthocyanins using macroporous resins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 48, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.-S.; Fang, J. Two acidic polysaccharides from the flowers of Chrysanthemum morifolium. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, L. Leukaemia Infection Diagnosis and Intestinal Flora Disorder. Curr. Mol. Med. 2022, 22, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X. A mini-review of advances in intestinal flora and necrotizing enterocolitis. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Kong, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y. Ischemic stroke and intestinal flora: An insight into brain-gut axis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Li, S.; Li, R. An Investigation into the Correlation of Intestinal Flora with Obesity and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 5677073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; An, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Y.; Niu, H.; Ma, R.; Zhao, H.; Cao, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Effects of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharides on Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Phenotype in Mice. Foods 2022, 11, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiong, C.; Huang, W. Gamma-Irradiation-Induced Degradation of the Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Auricularia polytricha and Its Anti-Hypercholesterolemic Activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Song, X.; Wang, W.; Jia, L.; Zhang, J. Antioxidation, anti-hyperlipidaemia and hepatoprotection of polysaccharides from Auricularia auricular residue. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 333, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Chen, X.; Song, J.; Chen, M.; Gong, P.; Jia, W.; Li, G. Hypoglycemic effects of Auricularia auricula polysaccharides on high fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice using metabolomics analysis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9994–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Cui, C. Hypoglycemic polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula and Auricularia polytricha inhibit oxidative stress, NF-κB signaling and proinflammatory cytokine production in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.; Chang, Y. Auricularia auricula-judae (Bull.) polysaccharides improve type 2 diabetes in HFD/STZ-induced mice by regulating the AKT/AMPK signaling pathways and the gut microbiota. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 5479–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, X.; Feng, Y.; Meng, X. The effects of polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula (Huaier) in adjuvant anti-gastrointestinal cancer therapy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 132, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, M.; Chen, Y.; Lou, Y.; Luo, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, W. Optimization of the polysaccharide hydrolysate from Auricularia auricula with antioxidant activity by response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Qamar, S.A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Bio-based active food packaging materials: Sustainable alternative to conventional petrochemical-based packaging materials. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shui, D.; Li, S.; Lin, X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ji, C. Complexation behavior of Auricularia auricula polysaccharide and whey protein isolate: Characterization and potential beverage application. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Origin | Extraction Method | Time (min) | Solid-Liquid Ratio | Temperature (°C) | Other Conditions | Yield (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinlin County, Jilin Province | Ultrasonic Assist | 40 | 1:70 | 70 °C | Particle size of 150–200 mesh | 29.29 ± 1.41% | [29] |
| Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province | MAE | 25 | 1:25 | 95 °C | Microwave power of 860 W, pH 7.0 | 10.52% | [30] |
| Jiaohe County, Jilin Province | Pulsed Electric Field | 1.5 | 1:30 | Room temperature | HIPEF strength at 24 kV/cm, pulse number at 6, pH 8 | 14.79% | [31,32] |
| Jinan | PEG-based ultrasound-assisted | 32.44 | 1:39.27 | 91.948 °C | PEG concentration of 0.30 g/mL | 21.58% | [33] |
| Greater Khingan Mountains, Helongjiang | Neutral protease | / | 1:75 | 50 °C | E/S at 8% | 12.96% | [13] |
| Greater Khingan Mountains, Heilongjiang Province | Ultrasonic Assist Alkali method | 90 | 1:48 | 70 °C | 2.0% of NaOH concentration | 15.53% | [34] |
| Greater Khingan Mountains, Heilongjiang Province | Mannanase, β-dextranase, and cellulase | 60 | 1:80 | 83.17 °C | pH at 2.1 | 26.42% ± 0.87% | [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, T.; Wu, Q.; Liang, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Shang, X. The Current State and Future Prospects of Auricularia auricula’s Polysaccharide Processing Technology Portfolio. Molecules 2023, 28, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020582
Yu T, Wu Q, Liang B, Wang J, Wu D, Shang X. The Current State and Future Prospects of Auricularia auricula’s Polysaccharide Processing Technology Portfolio. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020582
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Te, Qiong Wu, Bin Liang, Jiaming Wang, Di Wu, and Xinzhu Shang. 2023. "The Current State and Future Prospects of Auricularia auricula’s Polysaccharide Processing Technology Portfolio" Molecules 28, no. 2: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020582
APA StyleYu, T., Wu, Q., Liang, B., Wang, J., Wu, D., & Shang, X. (2023). The Current State and Future Prospects of Auricularia auricula’s Polysaccharide Processing Technology Portfolio. Molecules, 28(2), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020582







