Abstract
The gut microbiome (GM) of rheumatic arthritis (RA) patients is often altered in composition and function. Moreover, methotrexate (MTX), one of the most frequently used disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, is known to negatively affect GM composition. The modulation of immune system activity is one of the therapeutic benefits of probiotics. The aim of the current investigation was to determine the impact of MTX therapy combined with one of the Lactobacillus strains, Lactoplantibacillus plantarum LS/07 (LB), on adjuvant arthritis (AA) in rats. Methods focused on biometric and inflammatory parameters in AA, particularly on plasmatic levels of IL-17A, MMP-9, and MCP-1, and the activities of gamma-glutamyl transferase in the spleen and joints were applied. Enhancing the effect of MTX, LB positively influenced all biometric and inflammatory parameters. The findings of the present study may be of help in proposing novel therapeutic strategies for RA patients.
1. Introduction
Production of autoantibodies is involved in chronic joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a systemic autoimmune disease. The lungs, heart, and kidneys have been reported to be also affected by RA [1]. Interaction between the human leukocyte antigen gene (HLA) and environmental factors is one of the triggers leading to RA. Smoking, illness, and recently reported dysbiosis belong to the environmental factors [2,3,4].
Probiotics are live bacteria that, given to host in appropriate doses, provide significant health benefits [5]. As nutrition is an important environmental factor influencing the gut microbiota (GM) function, current research focuses on its involvement in the etiology, development, and activity of many diseases, including rheumatic illnesses [6]. Exogenous bacteria may exert subject-specific impacts on GM via altering dysbiosis-related conditions such as RA, which may be improved [7]. Probiotic bacteria have been suggested as an effective tool to treat gut dysbiosis and/or better the homeostasis of GM; hence, having a potential of positively influencing systemic immune responses, probiotics have been proposed for the use as adjuvant treatment in treating the immune system-related disorders [1,8].
Probiotics have been studied to identify potential beneficial effects in the prevention and treatment of various systemic conditions in both animal studies and human trials. The conditions comprise inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as RA, multiple sclerosis, ulcerative colitis, and hepatic encephalopathy. Positive modulation of immune system activity by specific bacteria strains is of the main benefits of probiotics. Various probiotic strains are being used, and various effects are observed [9]; hence, a suitable strain needs to be chosen each time [10]. Some strains have been shown to stimulate the immune system and enhance immune response, which is desirable for immunodeficient patients [11]. For people with immuno-activating diseases such as RA, other strains have been reported to be beneficial due to inhibiting the immune response [2,12].
Although the benefits of probiotics were typically both disease- and strain-specific, meta-analyses of studies using several strains indicated that some effects are shared by various strains [13]. Probiotics are believed to have various health effects, including the ability to modulate the immune response, support gut barrier integrity, and modulate GM. Probiotics may influence existing bacterial communities either directly through trophic interactions or indirectly by changing the production of molecules derived from the host, or both [14,15,16]. Current studies suggested that drugs and genetic material have a reciprocal relationship in which they can affect one another and impact therapeutic results [17].
The most commonly used strains, whether in a mixed culture or as a single species, are Lactobacilli, Bifidobacteria, and Streptococci. A number of randomized controlled clinical studies and meta-analyses on infectious illnesses, antibiotic-associated diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, abdominal pain, and colitis have recognized and supported their beneficial effects [18,19].
The GM of RA patients has been found to be altered in composition and function [20], with a substantial reduction in microbial diversity compared to healthy controls [21]. Increased disease duration in RA patients was associated with decreased GM diversity [21]. Faecalibacterium is one of the most prevalent butyrate-producing Firmicutes in the human gut. RA patients have been found to have lower levels of Faecalibacterium and other butyrate-producing taxa such as Flavobacterium [22]. Compared to healthy controls, the GM of RA patients exhibited a considerable increase in the order of Lactobacillales [21,22] and a broader range of Lactobacilli [23]. Intriguingly, administration of some Lactobacillus species has been reported to improve RA clinical symptoms, indicating that distinct Lactobacilli may play diverse roles in RA etiology and disease activity control [24,25].
There is a certain inconsistency in studies reporting different effects of probiotics on the activity of RA [26]. Zamani et al. (2016) have reported that probiotic supplementation improved the disease activity scores (looking at 28 joints) in patients suffering from RA compared to placebo group [27]. Chen et al. (2016) examined the gut microbiota profile of 40 RA patients and 32 healthy controls. They observed a lesser diversity of gut microbes in RA patients compared to controls and revealed a close correlation between the severity of the disease and the quantity of rheumatoid factor in serum [21].
An interaction between the GM and local/systemic immunity, as well as activation of joint inflammation, has been pointed out in animal studies [28]. One of the many studies in mice sensitive to collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) has documented an increase in the Lactobacillaceae family and the Lactobacillus genus [29]. In another type of inflammation animal model, in DSS-induced mouse models of ulcerative colitis, L. acidophilus treatment suppressed cell-mediated secretion of proinflammatory cytokines/interleukins (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-17, and IL-23) activated by Th17 and supported secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 [30].
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LS/07 (LB) was studied on animal models and published articles state its potential to exert a preventive effect on colon carcinogenesis [31,32,33,34], mammary carcinogenesis, and immunomodulation [35,36], influencing lipid profiles in rats receiving high-fat diet by improving the lipid profile and therefore contributing to a healthier bowel microbial balance [37]. Other animal studies showed the improvement of intestinal inflammation in rats via the increased production of anti-inflammatory cytokines [38,39,40,41]. LB demonstrated the best results in in vitro testing against pathogenic enterotoxigenic E. Coli; compared to other strains of lactobacilli, it showed the best inhibitory effect against the multiplication (growth) of this pathogenic strain [34].
Methotrexate (MTX), one of the most used disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), has been reported to alter GM composition, partially restoring the microbial balance disrupted due to illness [20,22]. Profound knowledge in GM modifications in patients undertaking complex therapy regimens might help better their outcomes via customized therapeutic approaches [22]. In fact, GM modulation has been indicated for rheumatic disease prevention and control [42].
Considering the occurrence of disrupted GM in the etiology of RA, clinical interest in probiotics to address gut dysbiosis and downregulate the proinflammatory cytokine cascade implicated in inflammatory arthritis has grown [12,43,44]. L. casei has been shown to help reduce RA symptoms and inhibit proinflammatory cytokines in patients taking DMARDs, likely implying a favorable synergistic impact of DMARDs and probiotics [24,45].
Based on the positive influence of the Lactobacillacea family on microbiota in RA patients, we have decided to study in detail the effect of one of the Lactobacillus strains, L. plantarum LS/07, in combination therapy with MTX in adjuvant arthritis in rats. We provide experimental evidence that is supportive for the use of LB in complex therapy of RA, particularly in combination with MTX.
2. Results
2.1. Biometric Parameters in Adjuvant Arthritis
In our experiment with Lewis rats, we chose two biometric parameters for describing the development of experimental arthritis and further for evaluation of the treatment effectiveness. Figure 1 presents the obtained data for the change of hind paw volume (cHPV) (Figure 1a) and the change of body weight (cBW) (Figure 1b). The arthritis was already developed on day 14. For both parameters, we obtained significant differences between arthritis and healthy animals. For cHPV we observed an increase in this parameter for animals suffering from arthritis compared to the healthy control group (Figure 1a). In contrast, for cBW we observed a decrease (Figure 1b). After 1 week, in the case of both parameters, were the differences between healthy and arthritic animals even more profound, which is in accordance with the acute phase of the arthritis development in AA. During the chronic phase of arthritis, which is apparent on experimental day 28, we observed regression of the differences between AA and healthy control animals. The administration of LB to healthy control did not show any effect on monitored biometric parameters. LB administered to arthritic animals slightly improved both parameters, but it had a more visible effect for cHPV than cBW during the whole experiment (Figure 1a,b). The administration of MTX in monotherapy caused significant alleviation of biometric parameters in arthritic animals compared to untreated animals. LB administered in combination with MTX caused improvement in the therapy efficacy for both biometric parameters and all experimental days (Figure 1a,b). Moreover, we measured significant change for cHPV on experimental days 21 and 28 (Figure 1a).
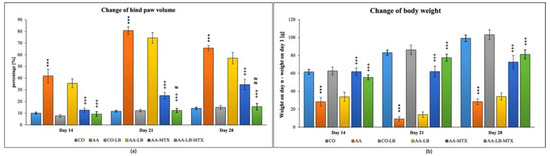
Figure 1.
Change of hind paw volume (cHPV) (a) and change of body weight (cBW) (b) were assessed on experimental days 14, 21, and 28 in rats. CO—healthy control group, AA—group of controls with adjuvant arthritis (AA), CO-LB—a control group of healthy animals administered with L. plantarum (LB), AA-LB—group of animals with AA administered with LB, AA-MTX—rats with AA treated with methotrexate (MTX), AA-LB-MTX—group of rats with AA receiving combinational therapy of MTX and LB. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical significance was evaluated by applying ANOVA for independent variables: *** p < 0.001 vs. CO; +++ p < 0.001 vs. AA; # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 vs. AA-MTX.
2.2. Activity of Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase in Spleen and Joint
At the end of the experiment, we collected relevant tissues to monitor gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) activity. Although the values were elevated differently in the studied tissues (higher values were measured in the spleen compared to joint tissue), significant differences were shown between arthritic and healthy animals (Figure 2a,b) in both analyzed tissues. Again, as for biometric parameters as for the activity of GGT, it did not prove any change in control groups administered with LB compared to untreated healthy controls. In both tissues, we could observe the same pattern in decreasing the GGT activity after administration of LB to arthritic animals in monotherapy as well in combination with MTX: the highest activity was measured in AA-LB group, following AA-MTX. The combination therapy (AA-LB-MTX) decreased the activity of GGT most effectively and significantly.
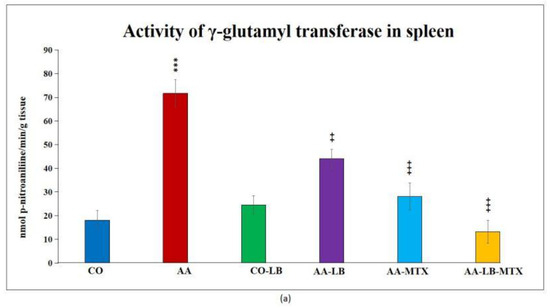
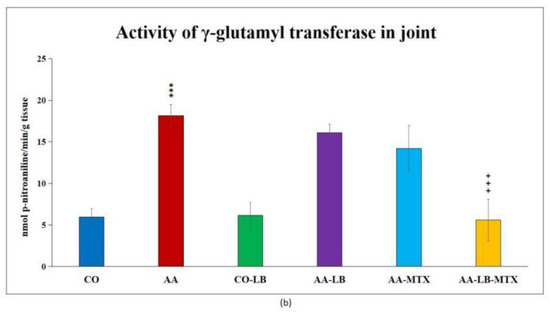
Figure 2.
The effect of L. plantarum administered alone or in combination with MTX on the activity of GGT in the spleen (a) and joint (b) on day 28. CO—healthy control group, AA—group of controls with adjuvant arthritis (AA), CO-LB—a control group of healthy animals administered with L. plantarum (LB), AA-LB—group of animals with AA administered with LB, AA-MTX—rats with AA treated with methotrexate (MTX), AA-LB-MTX—group of rats with AA receiving combinational therapy of MTX and LB. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical significance was evaluated by applying ANOVA for independent variables: *** p < 0.001 vs. CO; +++ p < 0.001 and ++ p <0.01 vs. AA.
2.3. Immunological Parameters in Adjuvant Arthritis and Their Modulation by L. plantarum and Its Combination with Methotrexate
We selected three different inflammatory markers to evaluate the intensity of inflammation and its modulation by the studied therapy. In arthritic animals, the concentration profile for metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) in plasma follows a decreasing trend from day 14 to day 28 (Figure 3b,c). On the other hand, for interleukin-17A (IL-17A), we observed a different pattern with the peak on day 21 and minor differences apparent on day 28 (Figure 3a). All parameters were not changed if we compared the healthy untreated group and the healthy group treated with LB (Figure 3a–c). In the case of IL-17A, the administration of LB improved the elevated concentration in arthritic animals only on day 21 during the acute phase of AA, however the significance was not proved. MTX was effective in lowering the IL-17A concentrations for the first two experimental weeks but not on day 28. The combination with LB significantly lowered IL-17A levels during the whole experiment (Figure 3a). For arthritis, increased concentrations of MMP-9 and MCP-1 in plasma were affected therapeutically mainly at day 14. The increasing efficacy was in this order: AA-LB followed by AA-MTX and AA-LB-MTX. The addition of LB to MTX caused therapeutic improvement, although not significantly between AA-MTX and AA-LB-MTX (Figure 3b,c). MMP-9 was further improved on day 21 by MTX and its combination with LB. However, on day 28, only the combination therapy was effective (Figure 3b). MCP-1 on day 21 was decreased comparable in all treated groups, with significance for AA-MTX and AA-MTX-LB. A slight difference between the healthy control and arthritic group on day 28 was found. Similarly, there were no differences among treated groups of arthritic animals (Figure 3c).
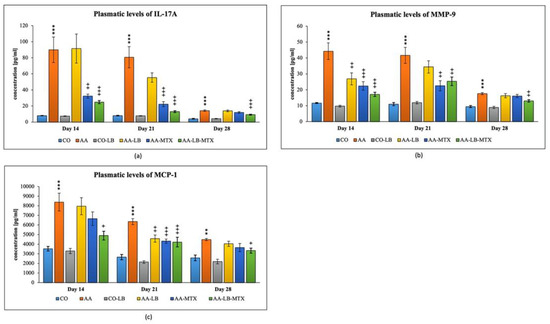
Figure 3.
The effect of L. plantarum on several biochemical markers such as IL-17A (a), MMP-9 (b), and MCP-1 (c), was measured on different experimental days 14, 21, and 28. CO—healthy control group, AA—group of controls with adjuvant arthritis (AA), CO-LB—a control group of healthy animals administered with L. plantarum (LB), AA-LB—group of animals with AA administered with LB, AA-MTX—rats with AA treated with methotrexate (MTX), AA-LB-MTX—group of rats with AA receiving combinational therapy of MTX and LB. Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical significance was evaluated by applying ANOVA for independent variables: *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01 vs. CO group; +++ p < 0.001, ++ p <0.01, + p < 0.05 vs. AA group.
3. Discussion
Probiotics have been recently studied mainly for their modulating effects on the immune system and inflammation. The mechanisms of their action involve downregulation of toll-like receptors (TLRs); alteration of the production of cytokines by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), which trigger adaptive responses; enhancing the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells; competing with pathogens in the intestinal mucosa by entering the lamina propria; and adhering to epithelial cells causing initiation of signaling cascade that leads to immune regulation [46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55]. Probiotic bacteria stimulate cells responsible for innate and acquired immunity, such as epithelial cells and dendritic cells (DCs), natural killer cells (NK), macrophages, and lymphocytes, effectively modifying immune system activity [46,47,48]. Primary response to pathogens mediated by the innate immune system is generated after activation of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that are expressed on immune and non-immune cells, including NK cells, DCs, macrophages, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells [46,48,49]. Most studied PRRs are toll-like receptors (TLRs) responsible for activation of signaling pathways regulating cell proliferation and cytokine production [48,50]. It has been demonstrated that probiotics via downregulation of TLR expression can reduce inflammation [51]. Adaptive immune responses rely mostly on T cells [49]. T-helper as Th1 and Th17 cells mediate inflammatory responses that protect the host from the infection; their overactivation may yet result in harmful inflammation [10]. Probiotics have been shown to modulate production of cytokines by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), triggering adaptive responses [52]. Beyond the immunomodulatory capabilities of DCs and T cells, specific probiotic strains enhance the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells resulting in increased secretion of IgA [53]. Secretory IgA protects against infections by blocking bacterial adhesion to the epithelium hence preventing host tissue penetration [52,53]. Competitive exclusion, where probiotics cling to the intestinal mucosa and prevent pathogens from entering the lamina propria, is an essential mechanism by which probiotics compete in the host environment [53,54]. Additionally, probiotic microbe adherence to epithelial cells may initiate a signaling cascade leading to improved immune regulation [55].
The gut epithelium, immune system, and commensal bacteria interact together in modulating systemic inflammatory status [53]. RA pathogenesis is characterized by an imbalance between anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory cytokines (interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interferon (IFN)-y, IL-6, IL-12, and IL-17), all playing a significant role in the inflammatory processes involved in the pathology [56,57,58].
The proposed gut-joint axis mechanism of inflammatory arthritis is linked to the gut wall’s hyperpermeability, which can expose the immune system to microorganisms, triggering a systemic immune response that initiates a local inflammatory process within the joints [59,60]. In their clinical study, Alipour et al. (2014) showed that L. casei 01 supplementations decreased serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, reduced tender and swollen joint counts, and improved global health scores (p < 0.05), and compared to controls, levels of interleukins (IL-10, IL-12) and TNF-α in the circulation were improved in the probiotic group [24]. Based on meta-analysis of randomized clinical studies covering effects of Lactobacillus as a single species or in mixed cultures with Bifidobacterium species, the probiotic supplementation lowered serum levels of IL-6 [12]. Another systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the effectiveness of L. casei supplementation in RA revealed that this specific strain significantly reduced CRP levels [61].
Numerous animal studies have pointed out an interaction between the GM and local/systemic immunity as well as the activation of joint inflammation [28]. Some studies focusing on Lactobacilli effects were performed using collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in rats or mice. In mice sensitive to CIA, an increase in the Lactobacillaceae family and the Lactobacillus genus has been reported [29]. Therapy with L. casei or L. acidophilus in a preclinical model of CIA in rats for 28 days was as effective as treatment with the standard antiarthritic drug indomethacin in terms of downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines in serum. The administration of L. casei and L. acidophilus significantly decreased parameters of oxidative stress in synovial effusate and ameliorated the arthritis score, hence pointing out the Lactobacillus’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties [62]. The anti-inflammatory effects of L. casei in the CIA rat model were demonstrated by inhibiting COX-2 enzyme and downregulating proinflammatory cytokines [58].
In CIA in female Wistar rats, several Lactobacillus spp. including L. plantarum were examined. Mainly L. casei, L. reuteri, L. fermentum and L. rhamnosus helped to attenuate arthritis in this model by inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines and anti-CII-antibodies and through rebalancing of GM and metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids. L. reuteri and L. casei slowed down the Th1 immune response, while L. rhamnosus and L. fermentum impaired Th17 responses. However, L. plantarum did not alleviate arthritis even though it suppressed Th1 and Th17 immune responses, while L. salivarius only prolonged the onset of arthritis without influencing the immune response. Lactobacilli protect against CIA through both common and individual pathways [63].
Evaluation of Lactobacilli in adjuvant arthritis (AA) is rarely documented. Pan et al. (2019) used AA for the evaluation of L. casei effect in comparison to MTX. Administration of L. casei at the beginning phase of AA in Sprague-Dawley rats slowed down the development of arthritis in a way that was comparable to MTX, with normalization of GM, providing relief of arthritis symptoms, thus improving the arthritis score, and preventing bone destruction and further causing an increase in the population of L. acidophilus [45].
In addition to our AA study, the efficacy of LB was evaluated only in a few studies. One study [41] was conducted in a model of induced acute colitis by dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) in male Sprague-Dawley rats. LB was added to the diet of a group with DSS-induced inflammatory processes, and results showed inhibition of the production of IL-6, IL-8, the activity of NF-κB and myeloperoxidase (MPO), and stimulation of IL-13 production. This probiotic strain also reduced the activity of β-glucuronidase (p < 0.05), increased counts of Lactobacilli, and decreased the number of coliform bacteria, indicating beneficial immunomodulatory and preventive effects in a model of acute colitis [41]. Further, in a rat model of colitis induced by DSS, LB attenuated the DSS-induced signs of an inflammatory process in the colon such as weight loss, diarrhea, infiltration of inflammatory cells associated with decreased colon weight/length ratio, and inhibited gut mucosa destruction and the depletion of goblet cells. Moreover, the strain increased the concentration of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in mucosal tissue. The protective effects of LB in the DSS-induced colitis model were related to the stimulation of IL-10 and the restoration of goblet cells and indicated it as an excellent candidate to prevent and treat diseases associated with inflammation [39].
Another study showed the preventive administration of LB alone or in combination with prebiotic inulin to rats with N,N-dimethylhydrazine-induced chronic inflammation. The LB administration reduced inflammatory process in the jejunal and colon mucosa, probably indirectly, and involved downregulation of the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines and suppression of NF-κB activity in mucosal cells [38].
In our experiment with Lewis rats, we evaluated two biometric parameters for describing the development of experimental arthritis and for investigating the treatment effectivity. Both inflammatory and arthritic changes occurring in rats with AA are reflected by hind paw swelling and weight loss in the experimental animals. For both parameters, change of HPV (cHPV) as well as change of body weight (cBW), we have found significant differences between arthritic and healthy animals on day 14, which indicates that the arthritis was already fully developed. After one week (experimental day 21), in the case of both parameters, the differences between healthy and arthritic animals were even more profound, as could be expected in the acute phase of AA. During the chronic phase of arthritis (experimental day 28), we observed regression of the differences between the AA and healthy control animals. According to our findings, the changes in biometric parameters typical for the animal model of AA are also described elsewhere [64,65]. LB administered to arthritic animals improved both parameters. During the experiment, it had a more visible effect for cHPV than cBW. LB administered in combination with MTX helped alleviate the swelling of hind paws and loss of body weight during the whole experiment. The combination therapy was more effective in decreasing inflammation causing hind paw swelling than MTX alone. This finding was proved on days 21 and 28 also by statistical analysis. Similar results were observed for arthritic cachexia suppression but without showing significance. Combinational therapy of L. casei with MTX proved decreasing of HPV and improving of the arthritic symptoms similarly [45].
Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) is an enzyme present on the cell surfaces of many bodily tissues and is thought to be one of the pathogenic elements contributing to the inflammatory processes. Increased GGT expression and activity in joint tissue is a reliable experimental indicator of synovial inflammation in experimental arthritis, as in the CIA model. Anti-GGT antibodies are suggested as innovative therapeutic agents for reducing joint deterioration and osteoclast formation in RA patients by neutralizing GGT [66,67]. In addition, Ishizuka, et al. (2007) described the therapeutic effect of neutralizing antibodies against GGT on joint destruction using a CIA in mice [66]. We studied the changes in GGT activity in the spleen and joint tissues in our studies, for example, with bioflavonoid-robinin [68]. As previously shown by Tsiklauri et al. (2021), results from present study also show that the values were elevated differently in the examined tissues (higher values were measured in the spleen compared to joint tissue), and significant differences were shown between arthritic and healthy animals. In this study we also achieved regression of the GGT activity for monotherapy and combination therapy. The highest decrease was seen with combinational therapy in both tissues.
Inflammation causes a release of variable inflammatory mediators and chemokines from damaged blood cells, for example, Il-1β or TNF-α [69]. Inflammatory symptoms, such as edema and hyperalgesia, as well as joint damage and auto-inflammatory illnesses, are mediated mainly by IL-1β [70]. Despite many other studies with probiotics focused on IL-1 β expression during treatment in AA, we have chosen to focus on IL-17A instead, as this cytokine is specific for autoimmune diseases. Like IL-1β, IL-17A is produced by activated adaptive and innate immune cells [71,72], and IL-17 contributes to inflammatory changes seen during RA. Various studies showed the enhancing effect of IL-17 on IL-1β and TNF-α in inducing the production of IL-6 and IL-8, which are proinflammatory cytokines [73,74]. Therefore, we studied IL-17 plasmatic levels in experimental arthritis and its pharmacological modulation with plant compounds such as robinin [68], Fatsiphloginum™ [75], or N-feruloylserotonin [76]. The concentrations of IL-17A in plasma were determined on days 14, 21, and 28. In AA animals, the changes in IL-17A on days 14 and 21 compared to healthy animals are noticeable in all experiments mentioned above. However, on day 28, at the end of the experiment, there were no differences among experimental groups in levels of IL-17A. A significant effect has been shown in reducing the levels of the proinflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-17, and IL-6) in a group of AA rats treated with L. casei [45]. In this experiment, we also observed an effect in reducing levels of IL-17A in plasma by LB at day 21 (not significantly). However, combinational therapy significantly reduced levels of IL-17A during all experimental days. Thus, the addition of LB to MTX caused an enhancing effect on the treatment of AA. Similarly, the combination therapy of MTX with natural compounds proved to be more effective in our previous experiments as well [68,75,76,77].
In the present study with LB, we chose to follow the changes in levels of MCP-1 and MMP-9 caused by arthritis. Joint synovium produces MCP-1 in several inflammatory joint diseases. Synovial release of MCP-1 was implicated in the monocyte recruitment during RA-associated inflammation, with synovium macrophages being the primary source of this cytokine [78]. In RA patients, MCP-1 was indicated as a potent chemotactic agent for monocytes/macrophages and implicated in inducing MMPs secretion [79]. MMPs are enzymes produced in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 and TNF-α by activated macrophages and fibroblasts. They were shown to be involved in the destruction of articular tissues in RA [80,81]. Similarly, to the findings of the present study, in our previous studies, while evaluating MMP-9 plasmatic levels [77,82], we found its increased levels mainly in the acute phase of AA. In the chronic state of AA, significant differences between healthy and AA animals have also been found [77,82]. To our knowledge, no experimental results have been published evaluating both the MCP-1 and MMP-9 levels in adjuvant arthritis or CIA so far. In the present study, the concentration profiles for MMP-9 and MCP-1 in arthritic animals showed a decreasing trend from day 14 to day 28. As for the positive anti-inflammatory effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LS/07 observed in our study, these findings are in good agreement with those reported by Tarapatzi et al. (2022) and Wang et al. (2022) [83,84].
In conclusion, we found the combination treatment to be significantly more effective in improving cHPV compared to MTX alone on days 21 and 28. All three immunological parameters monitored (IL-17A, MMP-9, and MCP-1) did not change by the application of LB in healthy groups of animals. We could thus assume that LB unlikely affected the basal levels of these inflammatory markers. On the other hand, the administration of LB to the AA rats improved their elevated concentration of IL-17A on day 21, although not significantly. MTX was effective in lowering the IL-17A concentrations on days 14 and 21. Finally, the combination of MTX with LB was found to be more effective in treatment of AA rats than that of MTX alone. As for the time course, the increased plasma concentrations of MMP-9 and MCP-1 in AA rats were effectively influenced by the applied combinational therapy at day 14. Overall, the efficacy of the treatment tested under our experimental conditions increased in the following order AA-LB < AA-MTX < AA-LB-MTX. Regarding the efficacy of LB monotherapy, we observed a significant decrease of MMP-9 (day 14) and MCP-1 (day 21) compared to the untreated AA group. The combinational therapy showed an effect in decreasing the activity of GGT in joint tissue. In the spleen tissue, GGT activity was significantly decreased by LB in monotherapy as well as in combination with MTX. Concluding, the findings of the present study indicated a beneficial action of the combinational therapy over the methotrexate therapeutic activity in experimental arthritis with no apparent negative effect of LB in monotherapy on inflammation parameters studied. Particular mechanisms involved in the modulation of immune processes involved in RA pathology need to be further elucidated.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
Lewis male rats were bred and purchased for this experiment from the Department of Toxicology and Laboratory Animal Breeding, Centre of Experimental Medicine, SAS, Dobrá Voda, Slovak Republic (SK CH 24016) at the age of 5 weeks. The Ethics Committee of the Institute of Experimental Pharmacology and Toxicology, Center of Experimental Medicine SAS in Bratislava, Slovakia (SK UCH 01017) and State Veterinary and Food Administration of Slovak Republic, Bratislava (3144/16-221/3) authorized the protocol for this experiment. Animals were, upon arrival, submitted to quarantine, which lasted 7 days. Housing conditions were standard, 12 h/12 h light/dark regime, humidity 55%, 21–24 °C. Animals had ad libitum access to a standard pallet diet and tap water. The animal housing agrees with EU Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals Used for Experimental and Other Purposes. Animals were sacrificed at the end of the experiment under deep general anesthesia.
4.2. Induction of Adjuvant Arthritis
Adjuvant arthritis (AA), based on its characteristics, is a well-established model of inflammation [85]. To induce AA, animals weighting 160–180 g were injected with 0.1 mL suspension of heat-killed Mycobacterium butyricum in incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (Difco, Tucker, GA, USA) intradermally at the base of the tail as previously described [68,86].
4.3. Bacterial Cultivation
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LS/07 (LB) was grown in MRS broth (de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe broth, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) at 37 °C. The concentration of viable bacteria was assessed using plate counting on MRS agar (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). The assay was performed in triplicate. In addition, a stationary overnight culture containing 4 × 109 CFU/mL viable bacteria and bacterial metabolites was used for further experiments. Viable bacteria and bacterial metabolites were applied directly perorally in a volume of 100 μL to experimental animals, and thus each rat received a suspension of LB (0.4 × 109 CFU; see Table 1).
4.4. Experimental Design and Treatment
Rats were randomly divided into six experimental groups: 1. a control group of healthy animals (CO); 2. a control group of healthy animals administered with LB daily (100 μL suspension per rat, CO-LB); 3. a group of untreated animals with AA (AA); 4. a group of animals with AA administered with LB daily (100 μL suspension per rat, AA-LB); 5. a group of animals with AA, which was administered MTX twice a week 0.3 mg/kg (AA-MTX); and 6. a group of animals with AA, which received a combination of MTX and LB in the same doses and regimen as in monotherapies (AA-LB-MTX) (Table 1). In our experiment, we used the following number of rats in each group: CO: n = 10, AA: n = 9, CO-LB: n = 11, AA-LB: n = 11, AA-MTX: n = 11, AA-LB-MTX: n = 10. The probiotic strain and the drug were administered perorally during the experiment (28 days). On days 14 and 21, blood samples were taken from the retro-orbital plexus under light Zoletil®/Xylazine anesthesia. On the 28th day, animals were sacrificed under deep Zoletil®/Xylazine anesthesia and blood for plasma preparations was withdrawn. In addition, tissues such as spleen and joints were collected from each rat for further analysis. All samples were stored at −70 °C until analysis.

Table 1.
Experimental design of animal groups with their treatment.
Table 1.
Experimental design of animal groups with their treatment.
| Group | Treatment |
|---|---|
| CO | vehiculum, daily |
| CO-LB | 100 μL suspension of LB, daily |
| AA | vehiculum, daily |
| AA-LB | 100 μL suspension of LB, daily |
| AA-MTX | MTX 0.3 mg/kg, twice a week, vehiculum, daily |
| AA-LB-MTX | MTX 0.3 mg/kg, twice a week + 100 μL suspension of LB, daily |
CO—control group, AA—adjuvant arthritis, LB—Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LS/07, MTX—methotrexate, vehiculum—MRS broth without LB.
4.5. Evaluation of Experimental Arthritis
Biometrical parameters such as volume of hind paws and body weight were measured to evaluate changes during the progression of the disease on the 14th, 21st, and 28th day after initial immunization with M. butyricum. Change of hind paw volume (cHPV) was expressed as the average of the elevation of percentage (%) of the hind paw volume of each rat, compared with HPV measured at day 1 using a water plethysmometer (UGO BASILE, Comerio-Varese, Italy). The measured HPV on the selected day was divided by the HPV on day 1 and expressed in percentage according to the following formula:
([n Day]/[Day 1]) × 100 − 100 = value [%]
The change of body weight (cBW) of the animals was assessed daily. The changes in body weight are shown as the average of weight gain [g]. Weight measured on the day (n—day 14, 21, and 28) minus weight measured on day 1. The mathematical formula we used, as described before [68], is as follows:
[n Day] − [Day 1] = value [g]
4.6. Biochemical Evaluation of Markers of Inflammation in Plasma
All markers of inflammation in plasma were measured by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). For plasmatic concentrations analysis of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and interleukin-17A (IL-17A), we used kits by eBioscience® (Waltham, MA, USA), and for metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) we applied kit by R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA). The assay procedures were applied as described in the product manuals.
4.7. The Determination of Gamma-glutamyl Transferase Activity in the Hind Paw Joint and Spleen Tissue
To measure the activity of γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT) on day 28 in the spleen and hind paw joint tissue homogenates, the method of Orlowski and Meister (1970) [87] and modified by Ondrejickova et al. (1993) [88] was used as in our previous protocol [68]. The tissues were homogenized in a buffer (2.6 mM of NaH2PO4, 50 mM of Na2HPO4, 68 mM of NaCl, 15 mM of EDTA; pH 8.1) at 1:9 (w/v) by Ultra Turax TP 18/10 (Janke and Kunkel) for 1 min at 0 °C. The biochemical substrates (44 mM of methionine and 8.7 mM of L-γ-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide) were then dissolved in isopropyl alcohol (65%) to final concentrations of 2.5 mM and 12.6 mM, respectively. The samples were incubated for one hour at 37 °C, and then we added 2.3 mL of cold methanol to stop the reaction. Tubes were centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 20 min (Centrifuge Eppendorf). The supernatant’s absorbance (product p-nitroaniline) was measured on a spectrophotometer Specord 40 (Analytikjena, Jena, Germany) at 406 nm. Solution mixes without or without substrate or acceptor were used as blanks. The activity was calculated based on absorbance measurement using a calibration coefficient.
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Mean and SEM values were calculated for each parameter in each group (from 6 to 11 animals in each experimental group). Statistically significant differences among treated, untreated, and control groups were tested using parametric analysis of variance (ANOVA). Post-hoc tests (Tukey-Kramer) were applied in situations where differences among groups were significant at the level of significance α = 0.05. After post-hoc testing, the following significance levels were specified: extremely significant (p < 0.001; ***/+++/###, very significant (p < 0.01; **/++/##), significant (p < 0.05; */+/#), and not significant (p > 0.05). The untreated healthy controls (CO) were compared to treated healthy controls (CO-LB). The untreated arthritis group (AA) was compared with healthy control animals (CO) (*) and with the treated arthritis groups (AA-LB, AA-MTX, and AA-LB-MTX) (+)). The Group of arthritic animals treated with MTX (AA-MTX) was compared to the treated arthritis group also receiving L. plantarum (AA-LB-MTX) (#).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.B.; data curation, K.P., M.C. and S.P.; funding acquisition, K.B. and I.J.; formal analysis, M.C.; investigation, Ľ.A., L.S. (Ladislav Strojný), S.P., F.D. and L.S. (Lukáš Slovák); methodology, Ľ.A. and K.Š.; project administration, K.B.; resources, L.S. (Ladislav Strojný); supervision, K.B.; writing—original draft, K.P. and Ľ.A.; writing—review and editing, I.J., K.P., F.D, S.P. and K.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Slovak Grant Agency: VEGA No. 2/0136/20 and VEGA No. 2/0166/20, Bratislava, Slovakia, and by APVV-15-0308, Bratislava, Slovakia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Ethics Committee of the Institute of Experimental Pharmacology and Toxicology, Center of Experimental Medicine SAS in Bratislava, Slovakia (SK UCH 01017) and State Veterinary and Food Administration of Slovak Republic, Bratislava (3144/16-221/3) authorized the protocol for this experiment.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The experimental data are reported here: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/Pruzinska_et_al_Lactobacillus_plantarum_LS07_MTX_xlsx/20715553 (accessed on 13 December 2022).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jana Urgošová and Ing. Danica Mihalová for their technical and administrative support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- De Oliveira, G.L.V.; Leite, A.Z.; Higuchi, B.S.; Gonzaga, M.I.; Mariano, V.S. Intestinal dysbiosis and probiotic applications in autoimmune diseases. Immunology 2017, 152, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, J.; Lydyard, P.M.; Rook, G.A. Rheumatoid arthritis: How well do the theories fit the evidence? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1993, 92, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerola, E.; Möttönen, T.; Hannonen, P.; Luukkainen, R.; Kantola, I.; Vuori, K.; Tuominen, J.; Toivanen, P. Intestinal flora in early rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 33, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusca, S.B.; Abramson, S.B.; Scher, J.U. Microbiome and mucosal inflammation as extra-articular triggers for rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, C.; Lucchino, B.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Iannuccelli, C.; Di Franco, M. Dietary Habits and Nutrition in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Can Diet Influence Disease Development and Clinical Manifestations? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Derrien, M.; Levenez, F.; Brazeilles, R.; Ballal, S.A.; Kim, J.; Degivry, M.-C.; Quéré, G.; Garault, P.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T.; et al. Ecological robustness of the gut microbiota in response to ingestion of transient food-borne microbes. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2235–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareau, M.G.; Sherman, P.M.; Walker, W.A. Probiotics and the gut microbiota in intestinal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butel, M.J. Probiotics, gut microbiota and health. Med. Mal. Infect. 2014, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; Charneca, S.; Dourado, E.; Guerreiro, C.S.; Fonseca, J.E. Probiotic Supplementation for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Promising Adjuvant Therapy in the Gut Microbiome Era. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 711788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, A.; Bi, X.; Nguyen, L.; Matsuda, K.; Pham, H.; Phan, C.; Khu, D.; Ichimura, H. Effects of Short-Term Probiotic Ingestion on Immune Profiles and Microbial Translocation among HIV-1-Infected Vietnamese Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.T.; Khattab, M.; Ahmed, A.M.; Turk, T.; Sakr, N.; Khalil, A.; Abdelhalim, M.; Sawaf, B.; Hirayama, K.; Huy, N.T. The therapeutic effect of probiotics on rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, L.-W.; Yan, B.-L.; Yang, Q.-Y.; Li, M.-M.; Cui, H.-L. Probiotic strategies to prevent necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants: A meta-analysis. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2019, 35, 1143–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T. Fate, activity, and impact of ingested bacteria within the human gut microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.; Pasini, E.; Copeland, J.; Angeli, M.; Husain, S.; Kumar, D.; Renner, E.; Teterina, A.; Allard, J.; Guttman, D.S.; et al. Impact of Immunosuppression on the Metagenomic Composition of the Intestinal Microbiome: A Systems Biology Approach to Post-Transplant Diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, S.; Newberry, S.J.; Maher, A.R.; Wang, Z.; Miles, J.N.V.; Shanman, R.; Johnsen, B.; Shekelle, P.G. Probiotics for the prevention and treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2012, 307, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Lara, M.J.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gil, A. The role of probiotic lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and other related diseases: A systematic review of randomized human clinical trials. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 505878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, D.; Liang, D.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wright, K.; Davis, J.M.; Jeraldo, P.; Marietta, E.V.; Murray, J.; Nelson, H.; Matteson, E.L.; Taneja, V. An expansion of rare lineage intestinal microbes characterizes rheumatoid arthritis. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picchianti-Diamanti, A.; Panebianco, C.; Salemi, S.; Sorgi, M.; Di Rosa, R.; Tropea, A.; Sgrulletti, M.; Salerno, G.; Terracciano, F.; D’Amelio, R.; et al. Analysis of Gut Microbiota in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Disease-Related Dysbiosis and Modifications Induced by Etanercept. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zou, Q.; Zeng, B.; Fang, Y.; Wei, H. Analysis of Fecal Lactobacillus Community Structure in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, B.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Sharif, S.K.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, L.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Nakhjavani, M.R.; Mohtadi-Nia, J. Effects of Lactobacillus casei supplementation on disease activity and inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Alipour, B.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Sharif, S.-K.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Zavvari, S. Probiotic supplementation improves inflammatory status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrition 2014, 30, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakka, K.; Martio, J.; Korpela, M.; Herranen, M.; Poussa, T.; Laasanen, T.; Saxelin, M.; Vapaatalo, H.; Moilanen, E.; Korpela, R. Effects of probiotic therapy on the activity and activation of mild rheumatoid arthritis—A pilot study. Scand J. Rheumatol. 2003, 32, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, B.; Golkar, H.R.; Farshbaf, S.; Emadi-Baygi, M.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Akhavan, R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic supplementation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 19, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorożyńska, I.; Majewska-Szczepanik, M.; Marcińska, K.; Szczepanik, M. Partial depletion of natural gut flora by antibiotic aggravates collagen induced arthritis (CIA) in mice. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Mou, F.; Wang, H.; Zou, Q.; Zhong, B.; Wu, L.; Wei, H.; et al. Role of the Gut Microbiome in Modulating Arthritis Progression in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zou, Y.; Peng, J.; Lu, F.; Yin, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, J. Lactobacillus acidophilus Suppresses Colitis-Associated Activation of the IL-23/Th17 Axis. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertková, I.; Hijová, E.; Chmelarova, A.; Mojzisova, G.; Petrasova, D.; Strojný, L.; Bomba, A.; Zitnan, R. The effect of probiotic microorganisms and bioactive compounds on chemically induced carcinogenesis in rats. Neoplasma 2010, 57, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strojný, L.; Bomba, A.; Hijová, E.; Chmelarova, A.; Mojzisova, G.; Bertková, I.; Koprovičová, J.; Pomfy, M.; Strompfová, V.; Molokáčová, M. Effects of a probiotic in combination with prebiotics on intestinal lactobacilli and coliforms and activities of bacterial enzymes in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine exposed rats. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 56, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čokášová, D.; Bomba, A.; Strojny, L.; Pramuková, B.; Szabados, V.; Salaj, R.; Štofilová, J.; Brandeburová, A.; Supuková, A.; Šoltésová, A.; et al. The effect of new probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum on counts of coliforms, lactobacilli and bacterial enzyme activities in rats exposed to N,N-dimethylhydrazine (chemical carcinogen). Acta Vet. Brno 2012, 81, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strojný, L.; Štofilová, J.; Hijová, E.; Szabados, V.; Salaj, R.; Bertková, I.; Chmelarova, A.; Cokášová, D.; Pramuková, B.; Brandeburová, A.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum LS/07 in combination with flaxseed oil on the microflora, enzymatic activity, and histological changes in the development of chemically induced precancerous growth in the rat colon. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 59, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassayová, M.; Bobrov, N.; Strojný, L.; Kisková, T.; Mikeš, J.; Demečková, V.; Orendáš, P.; Bojková, B.; Péč, M.; Kubatka, P.; et al. Preventive effects of probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus plantarum and dietary fiber in chemically-induced mammary carcinogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2014, 9, 4969–4975. [Google Scholar]
- Kassayová, M.; Bobrov, N.; Strojný, L.; Orendáš, P.; Demečková, V.; Jendželovský, R.; Kubatka, P.; Kisková, T.; Kružliak, P.; Adamkov, M.; et al. Anticancer and Immunomodulatory Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum LS/07, Inulin and Melatonin in NMU-induced Rat Model of Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 6, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar]
- Salaj, R.; Stofilová, J.; Šoltésová, A.; Hertelyová, Z.; Hijová, E.; Bertková, I.; Strojný, L.; Kružliak, P.; Bomba, A. The effects of two Lactobacillus plantarum strains on rat lipid metabolism receiving a high fat diet. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 135142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štofilová, J.; Szabadosová, V.; Hrčková, G.; Salaj, R.; Bertková, I.; Hijová, E.; Strojný, L.; Bomba, A. Co-administration of a probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum LS/07 CCM7766 with prebiotic inulin alleviates the intestinal inflammation in rats exposed to N,N-dimethylhydrazine. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 2, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štofilová, J.; Langerholc, T.; Botta, C.; Treven, P.; Gradišnik, L.; Salaj, R.; Šoltésová, A.; Bertková, I.; Hertelyová, Z.; Bomba, A. Cytokine production in vitro and in rat model of colitis in response to Lactobacillus plantarum LS/07. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijová, E.; Šoltésová, A.; Salaj, R.; Kuzma, J.; Strojný, L.; Bomba, A.; Gregová, K. Preventive use of Lactobacillus plantarum LS/07 and inulin to relieve symptoms of acute colitis. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijová, E.; Bertková, I.; Štofilová, J.; Strojný, L.; Chmelarova, A.; Bomba, A. Anti-inflammatory potential of Lactobacillus plantarum LS/07 in acute colitis in rats. Acta Veterinaria 2018, 68, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Wiele, T.; Van Praet, J.T.; Marzorati, M.; Drennan, M.B.; Elewaut, D. How the microbiota shapes rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Tao, J.-H.; Pan, H.-F. Probiotic bacteria: A viable adjuvant therapy for relieving symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, J.R.; Briggs, A.M.; Whittle, S.; Stephenson, M.D. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Probiotic Administration in Inflammatory Arthritis. Complement Ther. Clin. Pract. 2020, 40, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Guo, R.; Ju, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Lu, L.; et al. A single bacterium restores the microbiome dysbiosis to protect bones from destruction in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Microbiome 2019, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez-Brito, M.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Gómez-Llorente, C.; Gil, A. Probiotic Mechanisms of Action. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fata, G.; Weber, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. Probiotics and the Gut Immune System: Indirect Regulation. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Llorente, C.; Muñoz, S.; Gil, A. Role of Toll-like receptors in the development of immunotolerance mediated by probiotics. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.d.A.K.; Sarker, M.; Wan, D. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics on Cytokine Profiles. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Alookaran, J.J.; Rhoads, J.M. Probiotics in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disorders. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, S.; Cavalcanti, E.; Mastronardi, M.; Jirillo, E.; Chieppa, M. Nutritional Keys for Intestinal Barrier Modulation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, E1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Steiner, G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2003, 2, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.-S.; Kwon, H.-K.; Lee, C.-G.; Yi, H.-J.; Park, J.-A.; Lim, S.-Y.; Hwang, K.-C.; Jeon, Y.H.; Im, S.-H. Lactobacillus casei suppresses experimental arthritis by down-regulating T helper 1 effector functions. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2690–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdekar, S.; Singh, V.; Singh, R.; Sharma, P.; Keshav, P.; Kumar, A. Lactobacillus casei reduces the Inflammatory Joint Damage Associated with Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) by Reducing the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Lactobacillus casei: COX-2 inhibitor. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethwa, H.; Abraham, S. The evidence for microbiome manipulation in inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology 2016, 56, kew374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ting, J.P.; Al-Azzam, S.; Ding, Y.; Afshar, S. Therapeutic Advances in Diabetes, Autoimmune, and Neurological Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudbane, S.; Rahmdel, S.; Abdollahzadeh, M.; Zare, M.; Bazrafshan, A.; Mazloomi, S.M. The efficacy of probiotic supplementation in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amdekar, S.; Singh, V.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, P.; Singh, R. Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus acidophilus Regulate Inflammatory Pathway and Improve Antioxidant Status in Collagen-Induced Arthritic Rats. J. Interferon. Cytokine. Res. 2013, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Yang, B.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. The prophylactic effects of different Lactobacilli on collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3681–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovenský, J.; Stančíková, M.; Švík, K.; Utěšený, J.; Bauerová, K.; Jurčovičová, J. Treatment of adjuvant-induced arthritis with the combination of methotrexate and probiotic bacteria Escherichia coli O83 (Colinfant). Folia Microbiol. 2009, 54, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovenský, J.; Švík, K.; Matha, V.; Istok, R.; Ebringer, L.; Ferenčík, M.; Stančíková, M. The effects of Enterococcus faecium and selenium on methotrexate treatment in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2004, 11, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, Y.; Moriwaki, S.; Kawahara-Hanaoka, M.; Uemura, Y.; Serizawa, I.; Miyauchi, M.; Shibata, S.; Kanaya, T.; Takata, T.; Taniguchi, N.; et al. Treatment with Anti-γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Antibody Attenuates Osteolysis in Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mice. J. Bone. Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feketeová, L.; Jančová, P.; Moravcová, P.; Janegová, A.; Bauerová, K.; Poništ, S.; Mihalová, D.; Janega, P.; Babál, P. Effect of methotrexate on inflammatory cells redistribution in experimental adjuvant arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 3517–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiklauri, L.; Švík, K.; Chrastina, M.; Poništ, S.; Dráfi, F.; Slovák, L.; Alania, M.; Kemertelidze, E.; Bauerova, K. Bioflavonoid Robinin from Astragalus falcatus Lam. Mildly Improves the Effect of Metothrexate in Rats with Adjuvant Arthritis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Vita, J.; Lawrence, T. The resolution of inflammation and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and Inflammatory Functions of the Interleukin-1 Family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffen, S.L. Recent advances in the IL-17 cytokine family. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G.; Dayer, J.-M.; Manger, B. Interleukin-1 function and role in rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, Y.; Nadiv, O.; Beer, Y. Interleukin-17 enhances tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced synthesis of interleukins 1,6, and 8 in skin and synovial fibroblasts: A possible role as a “fine-tuning cytokine” in inflammation processes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2001, 44, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.-L.; Jung, Y.O.; Kim, K.-W.; Park, M.-K.; Oh, H.-J.; Ju, J.-H.; Cho, Y.-G.; Min, J.-K.; Kim, S.-I.; Park, S.-H.; et al. IL-17 induces the production of IL-16 in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2008, 40, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiklauri, L.; Drafi, F.; Poništ, S.; Slovák, L.; Chrastina, M.; Švík, K.; Kemoklidze, Z.; Kemertelidze, E.; Bauerová, K. Study of anti-inflammatory activity of Fatsiphloginum™ (Fatsia japonica) and a new purified triterpene-rich extract of saponins (PS-551) in experimental model of arthritis. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, S75–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuncirova, V.; Ponist, S.; Mihalova, D.; Drafi, F.; Nosal, R.; Acquaviva, A.; Gardi, C.; Harmatha, J.; Hradkova, I.; Bauerova, K. N-feruloylserotonin in preventive combination therapy with methotrexate reduced inflammation in adjuvant arthritis. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 28, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slovák, L.; Švík, K.; Mihalová, D.; Tóth, J.; Czigle, S.; Pašková, Ľ.; Bilka, F.; Bauerová, K. Ferulaldehyde Improves the Effect of Methotrexate in Experimental Arthritis. Molecules 2017, 22, E1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.E.; Kunkel, S.L.; Harlow, L.A.; Johnson, B.; Evanoff, H.L.; Haines, G.K.; Burdick, M.D.; Pope, R.M.; Strieter, R.M. Enhanced production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, K.; Nanki, T.; Girschick, H.; Yavuz, S.; Ochi, T.; Lipsky, P.E. Synovial stromal cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients attract monocytes by producing MCP-1 and IL-8. Arthritis Res. 2001, 3, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenti, M.P.; Clark, I.M.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Using inhibitors of metalloproteinases to treat arthritis. Easier said than done? Arthritis Rheumatol. 1994, 37, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnane, G.; Fitzgerald, O.; Beeton, C.; Cawston, T.E.; Bresnihan, B. Early joint erosions and serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase 1, matrix metalloproteinase 3, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2001, 44, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovák, L.; Poništ, S.; Fedorova, T.; Logvinenko, A.; Levacheva, I.; Samsonova, O.; Bakowsky, U.; Pašková, Ľ.; Čavojský, T.; Tsiklauri, L.; et al. Evaluation of liposomal carnosine in adjuvant arthritis. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2017, 36, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarapatzi, G.; Filidou, E.; Kandilogiannakis, L.; Spathakis, M.; Gaitanidou, M.; Arvanitidis, K.; Drygiannakis, I.; Valatas, V.; Kotzampassi, K.; Manolopoulos, V.G.; et al. The Probiotic Strains Bifidοbacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces boulardii Regulate Wound Healing and Chemokine Responses in Human Intestinal Subepithelial Myofibroblasts. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.F.; Zhou, F.; Xu, S.; Feng, Y.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhu, Q.; He, Q.N.; Zheng, P.F. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum attenuates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by regulating the inflammatory response, T helper 17 immune response, and intestinal permeability. Biologia 2022, 77, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.; Bhatt, L.K.; Prabhavalkar, K.S. Experimental Animal Models for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2018, 40, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponist, S.; Gardi, C.; Paskova, L.; Svik, K.; Slovak, L.; Bilka, F.; Tedesco, I.; Bauerova, K.; Russo, G.L. Modulation of Methotrexate Efficacy by Green Tea Polyphenols in Rat Adjuvant Arthritis. PharmaNutrition 2020, 14, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, M.; Meister, A. The γ-Glutamyl Cycle: A Possible Transport System for Amino Acids*. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 67, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrejickova, O.; Ziegelhoeffer, A.; Gabauer, I.; Sotnikova, R.; Styk, J.; Gibala, P.; Sedlak, J.; Horakova, L. Evaluation of ischemia-reperfusion injury by malondialdehyde, glutathione and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: Lack of specific local effects in diverse parts of the dog heart following acute coronary occlusion. Cardioscience 1993, 4, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).