H3PO4/KOH Activation Agent for High Performance Rice Husk Activated Carbon Electrode in Acidic Media Supercapacitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
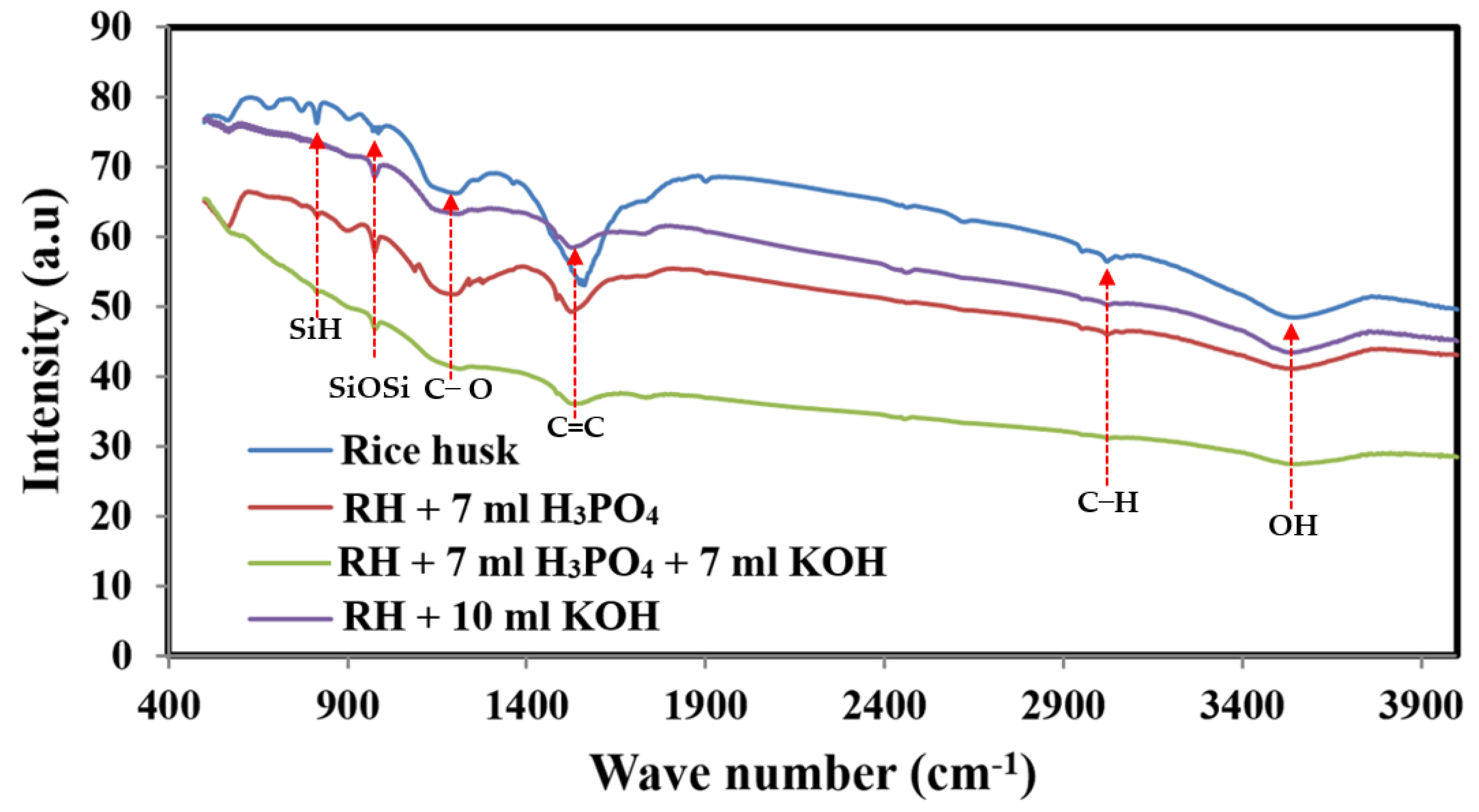
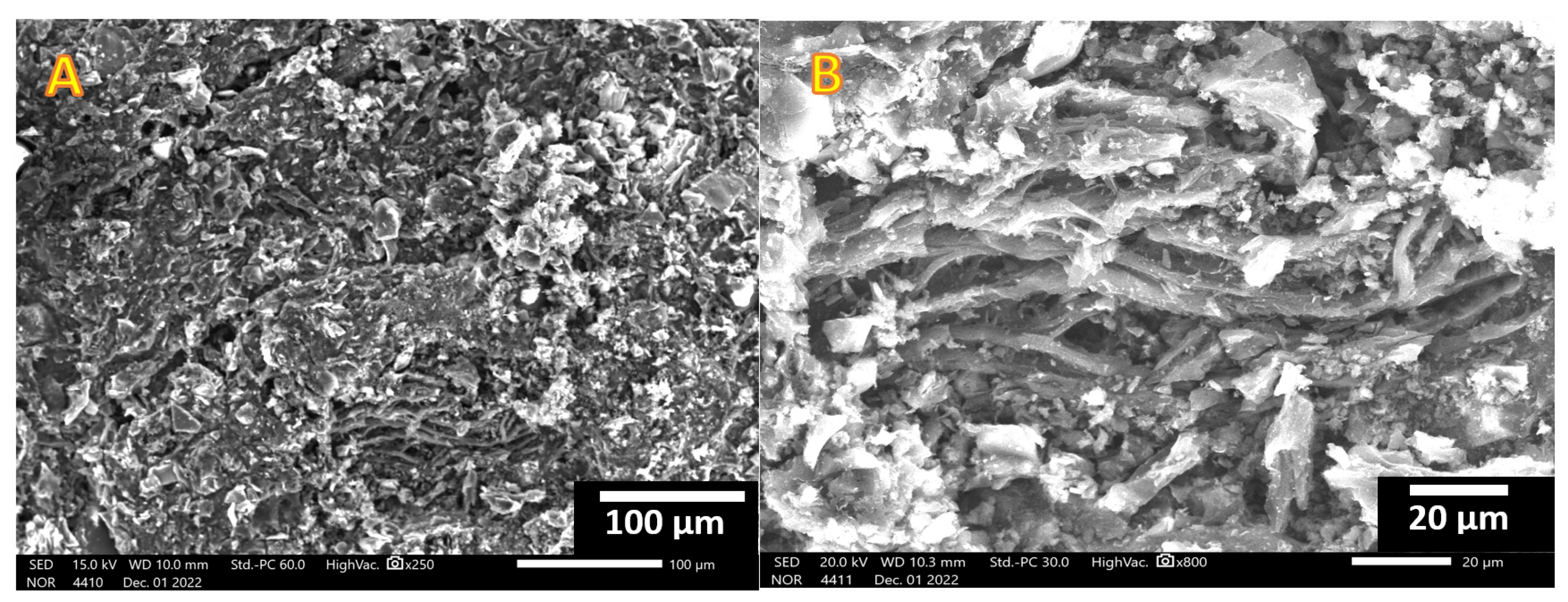
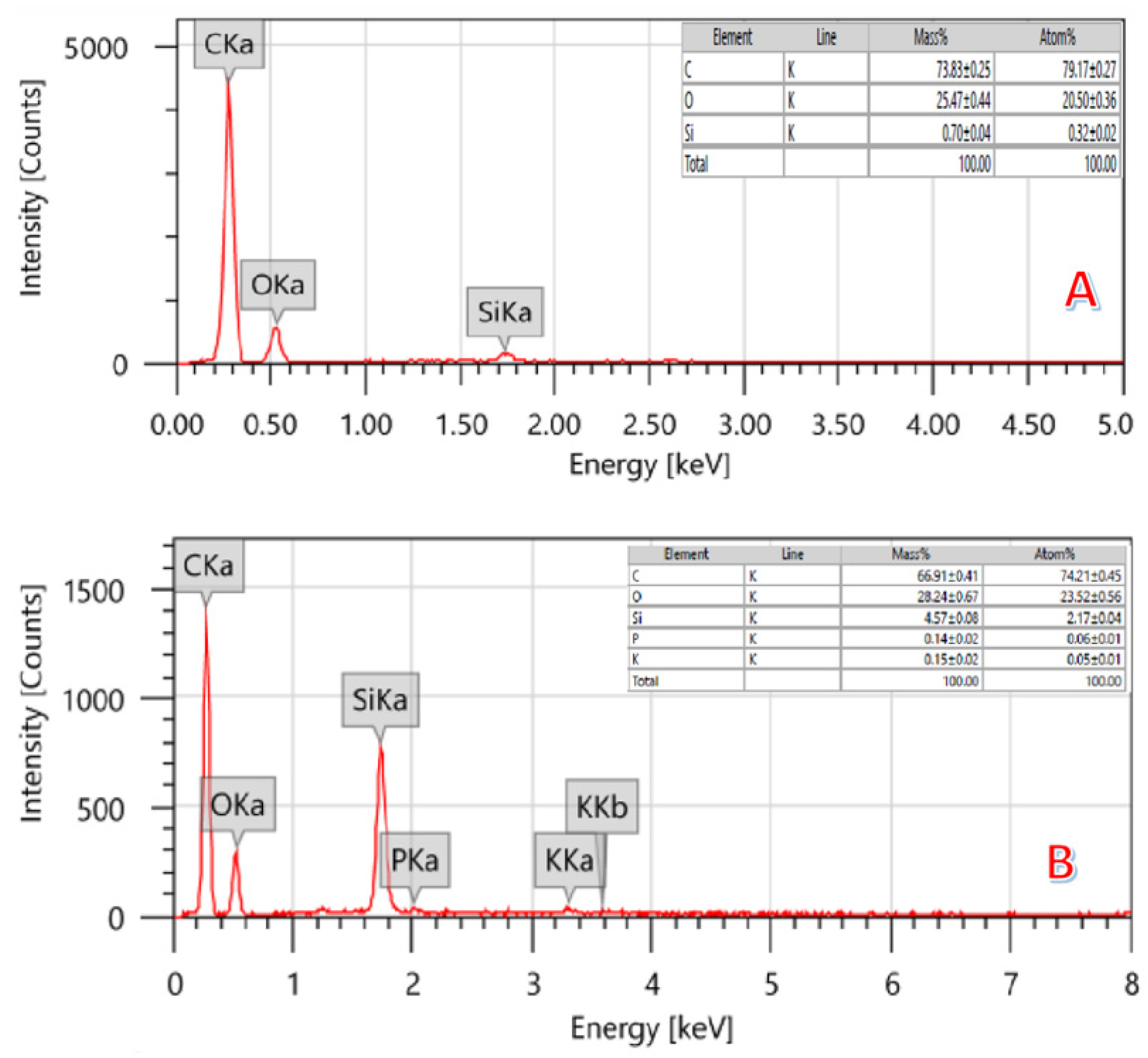
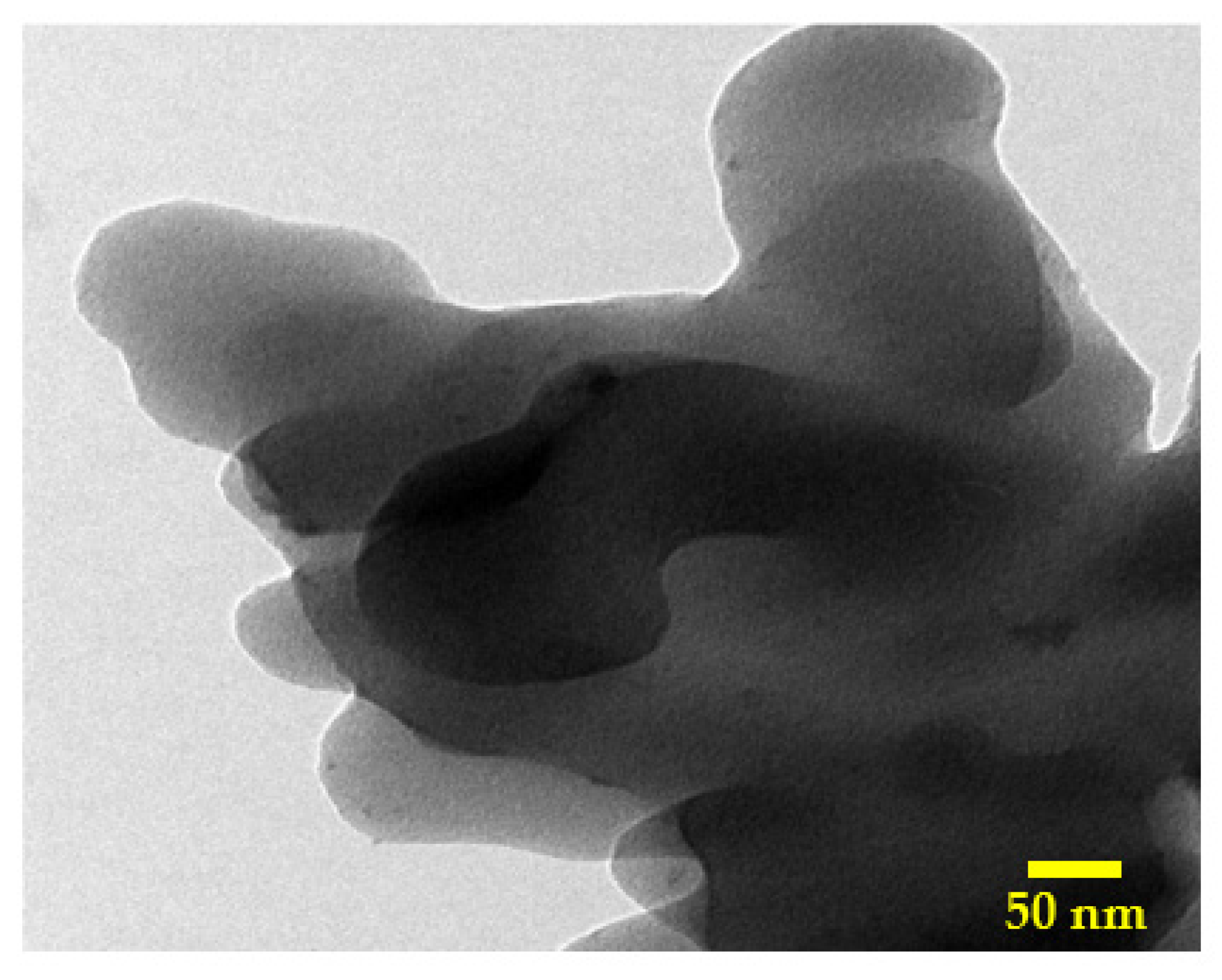
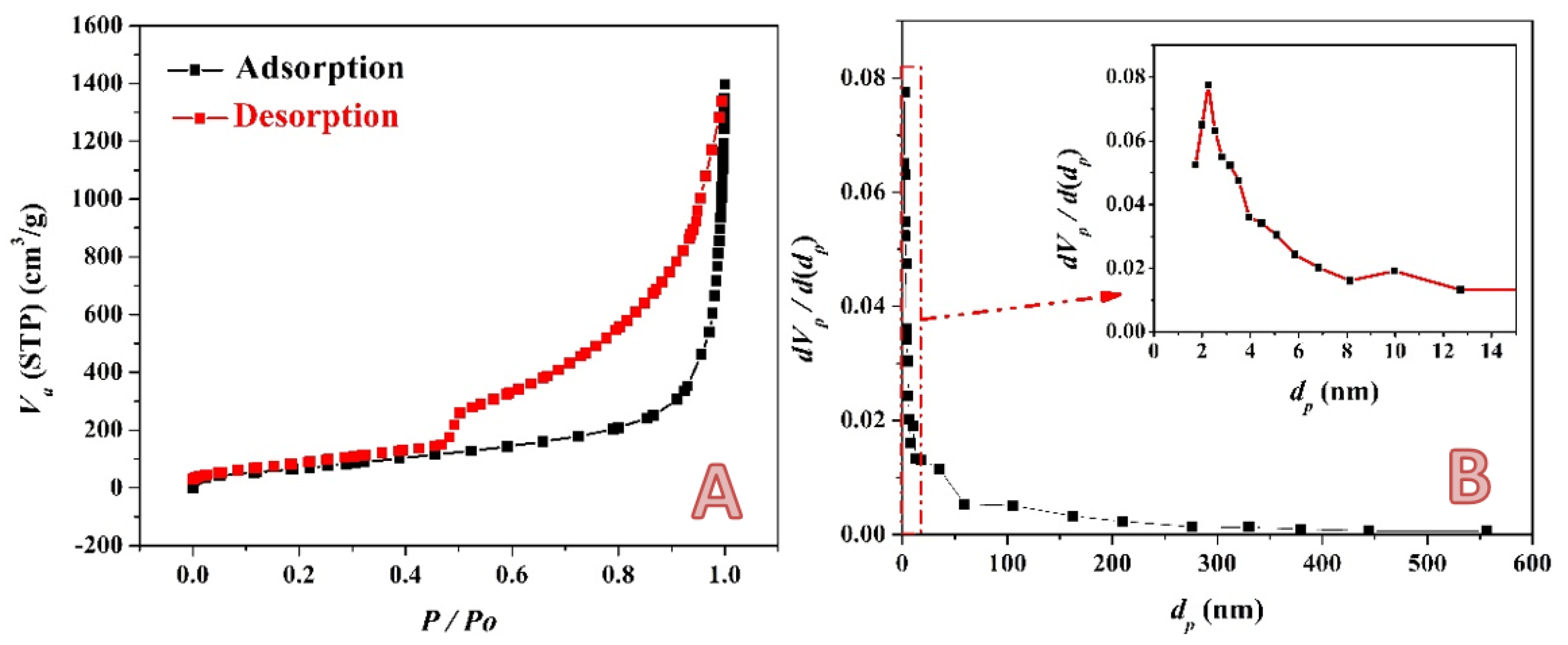
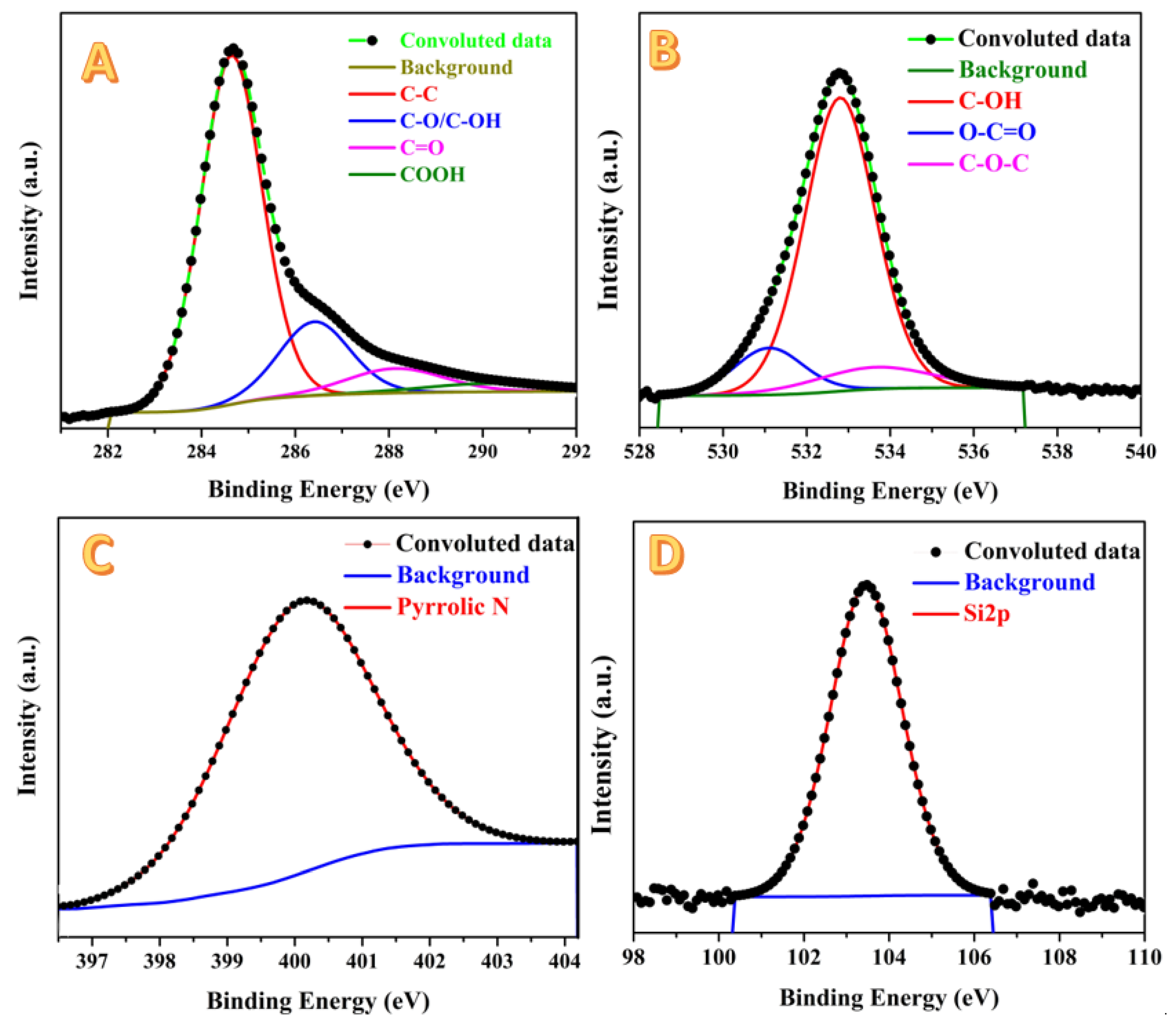
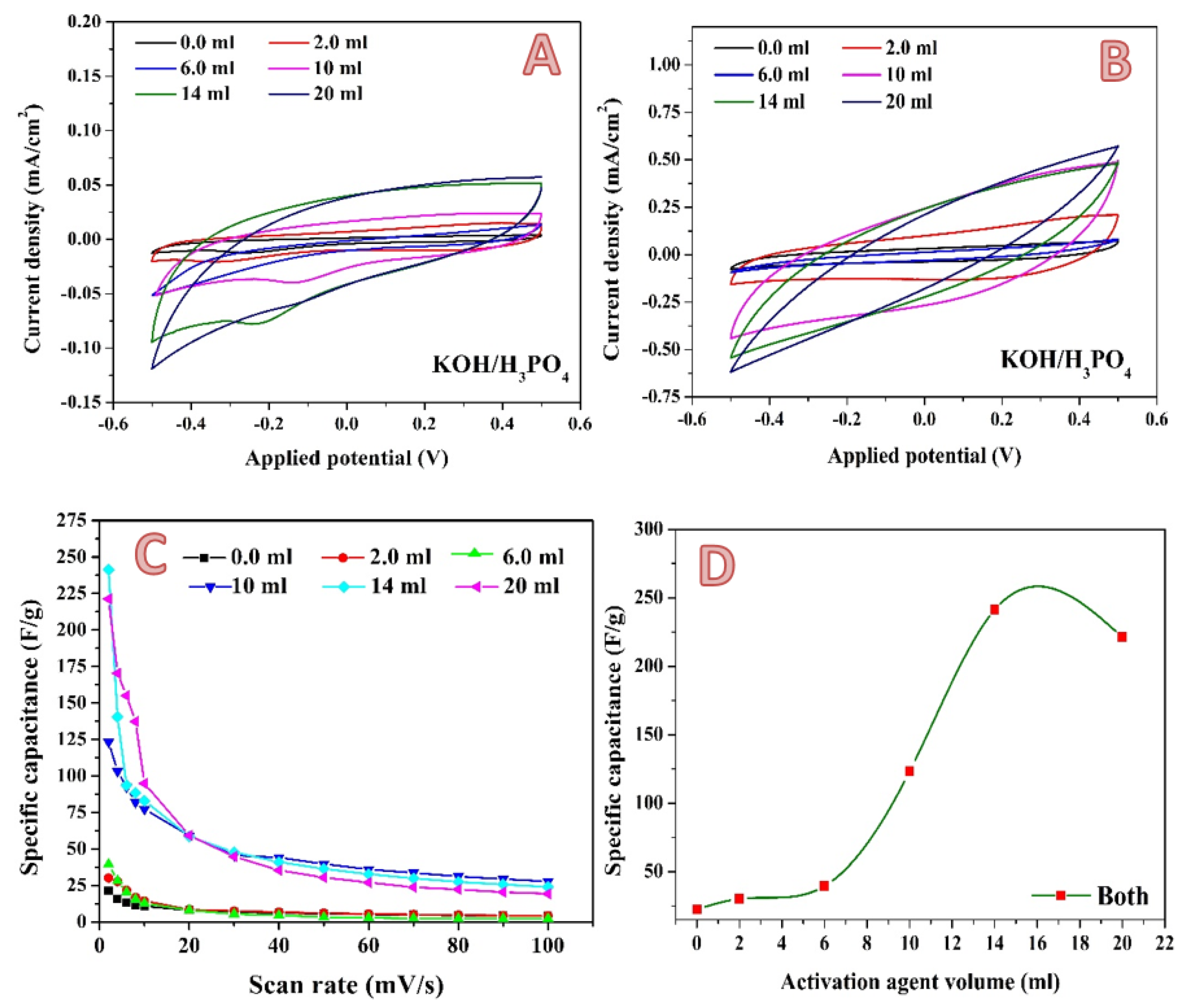
2.1. Activated Carbon Characterization
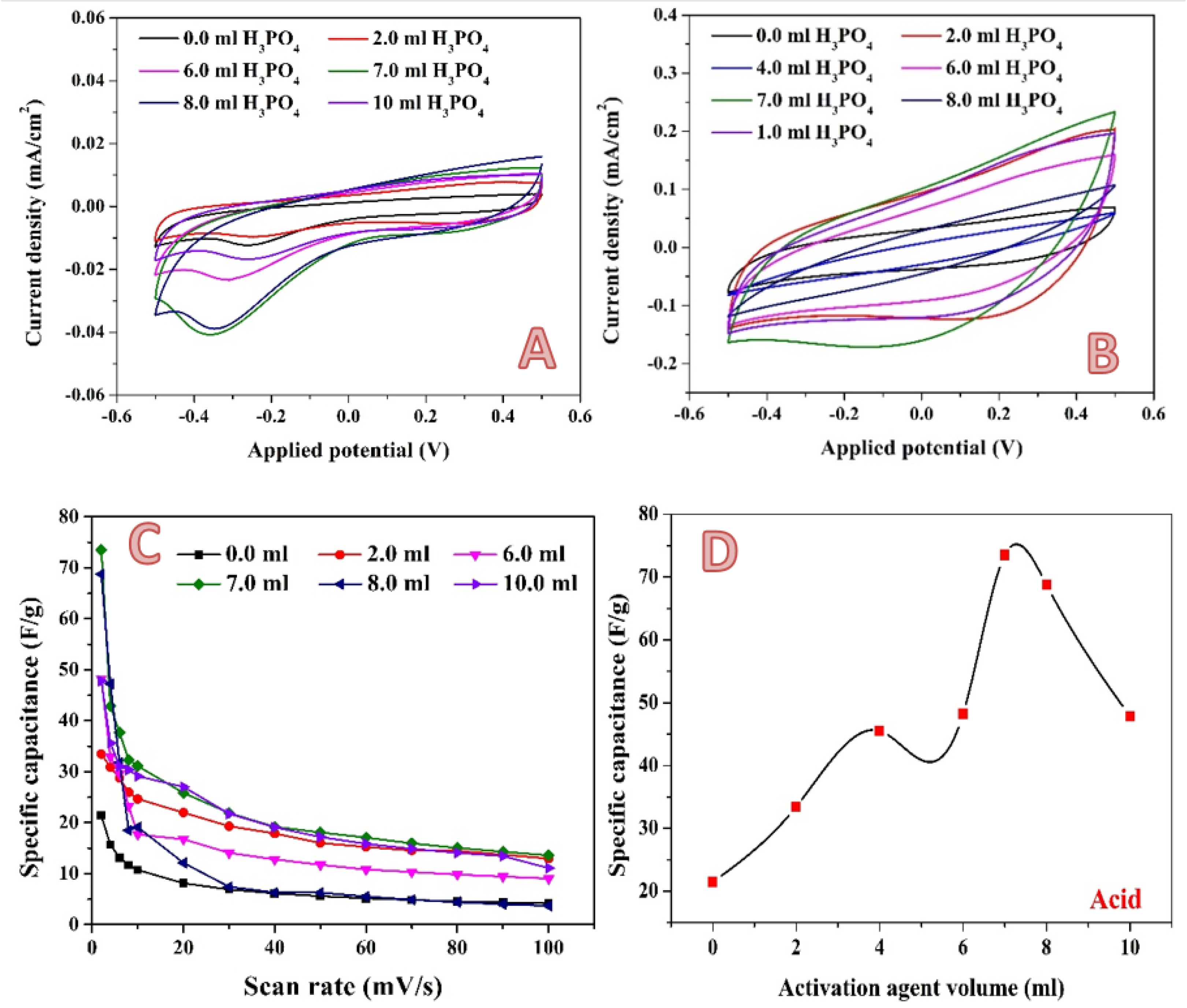
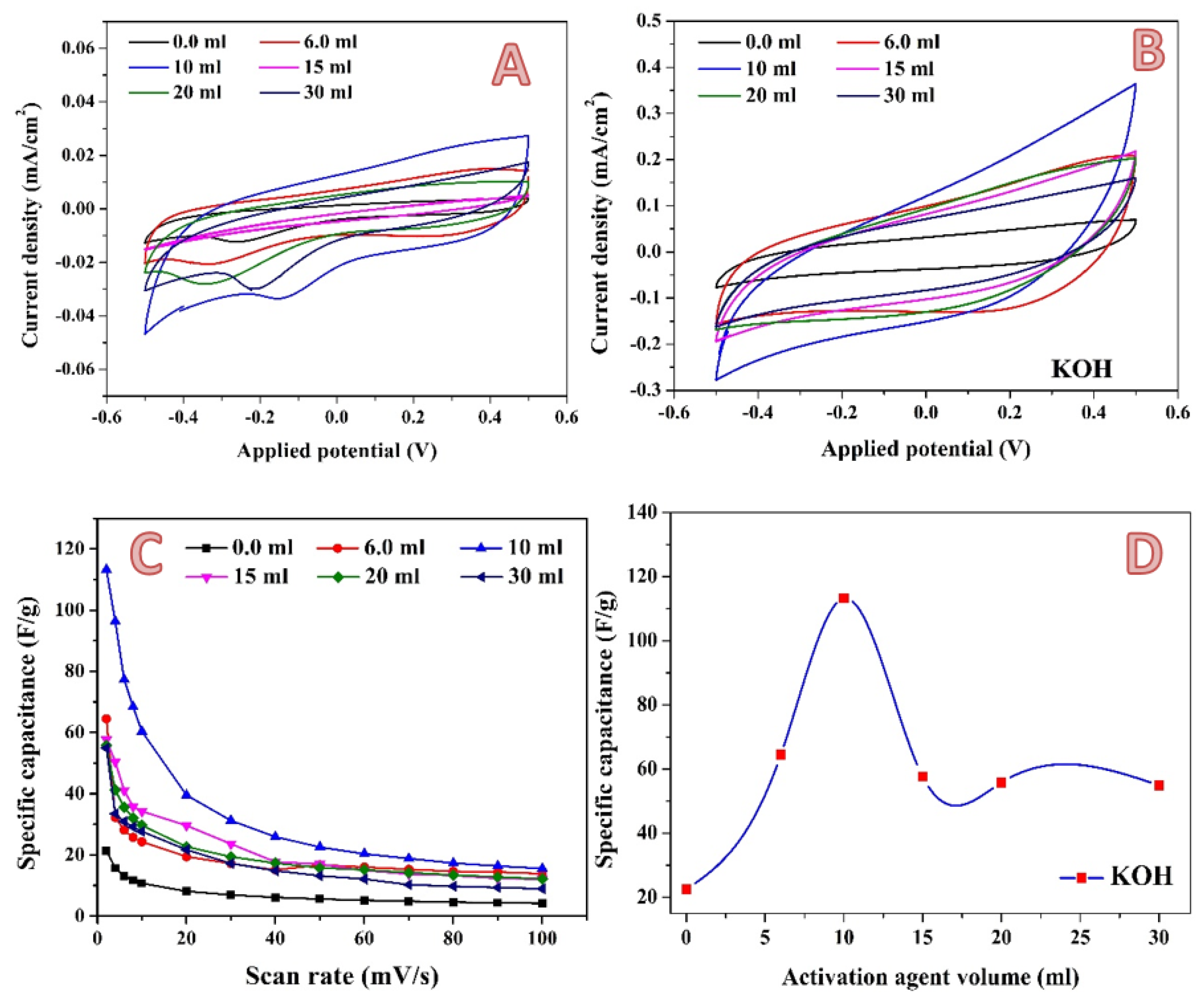
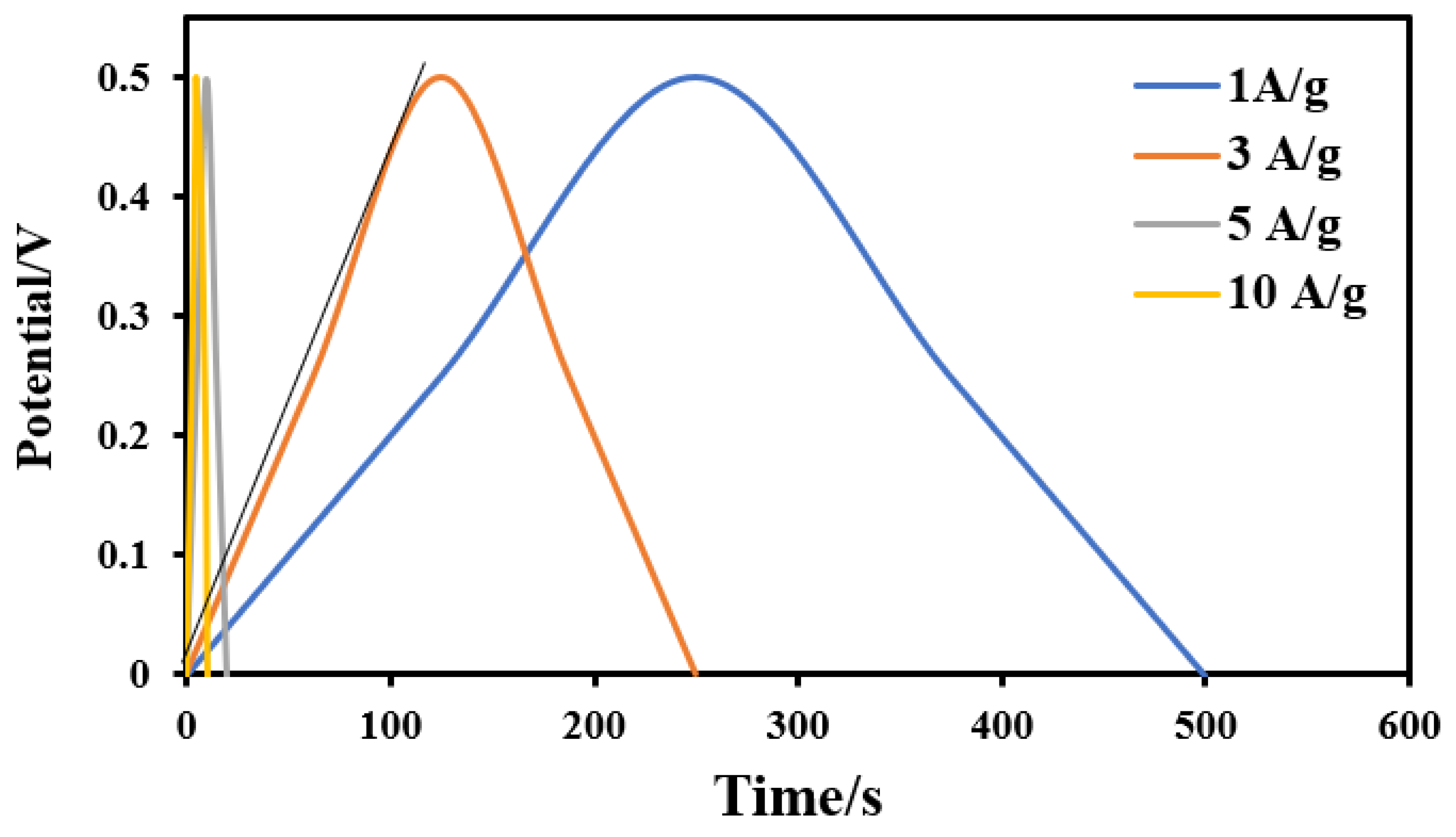
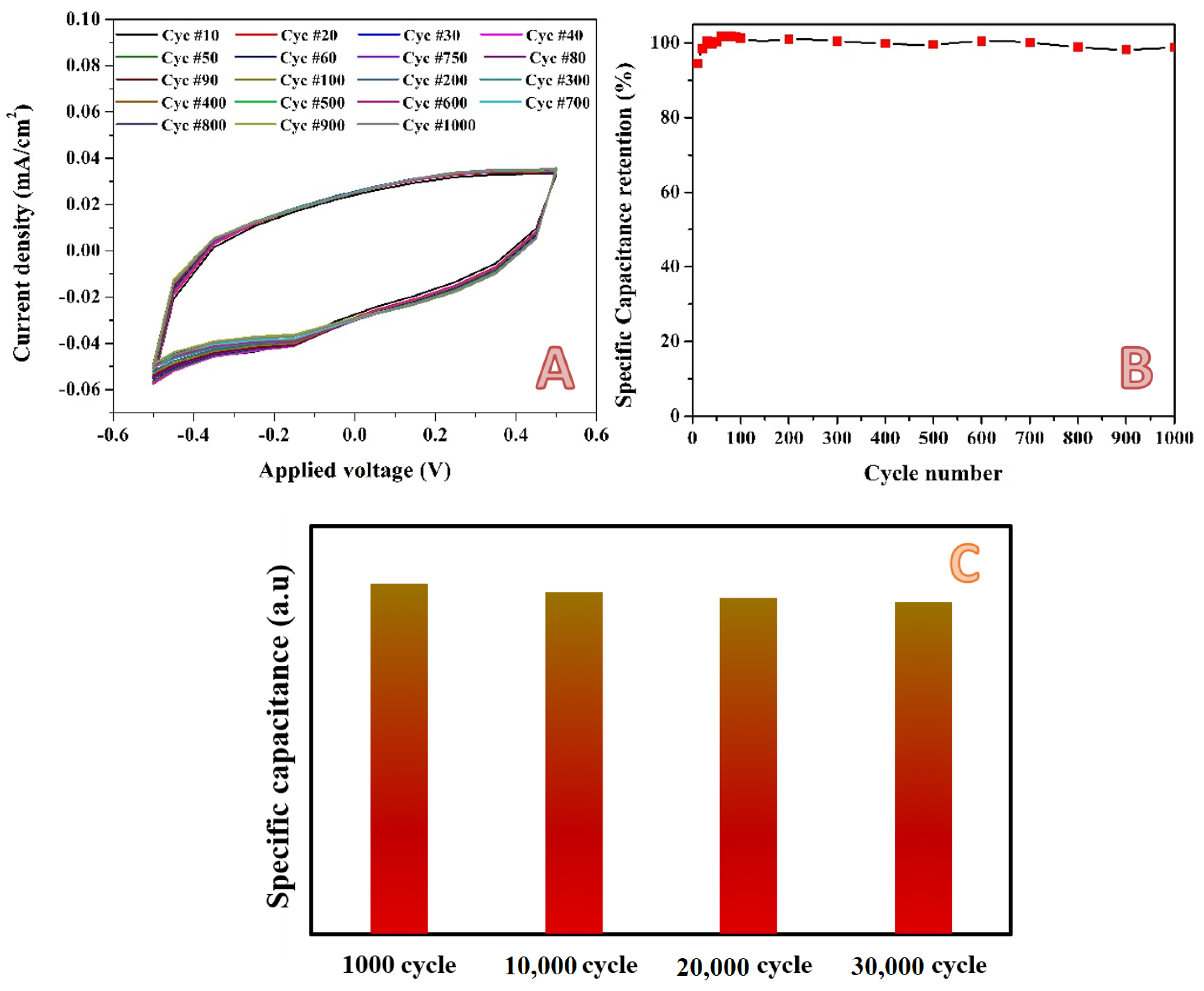
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Activated Carbon from Rice Husk
3.2.1. Carbonization Step
3.2.2. Activation Step
3.3. Characterizations
3.4. Ex Situ of the Synthesized Electrodes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Raza, W.; Ali, F.; Raza, N.; Luo, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Yang, J.; Kumar, S.; Mehmood, A.; Kwon, E.E. Recent advancements in supercapacitor technology. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 441–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araichimani, P.; Prabu, K.M.; Kumar, G.S.; Karunakaran, G.; Surendhiran, S.; Shkir, M.; AlFaify, S. Rice Husk-Derived Mesoporous Silica Nanostructure for Supercapacitors Application: A Possible Approach for Recycling Bio-Waste into a Value-Added Product. Silicon 2022, 14, 10129–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farma, R.; Deraman, M.; Awitdrus, A.; Talib, I.A.; Taer, E.; Basri, N.H.; Manjunatha, J.G.; Ishak, M.M.; Dollah, B.N.M.; Hashmi, S.A. Preparation of highly porous binderless activated carbon electrodes from fibres of oil palm empty fruit bunches for application in supercapacitors. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, P.; Gogotsi, Y. Materials for Electrochemical Capacitors. In Nanoscience and Technology: A Collection of Reviews from Nature Journals; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010; pp. 320–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kavaliauskas, Z.; Marcinauskas, L.; Valatkevicius, P. Formation and characterization of carbon and nickel oxide/carbon composites for supercapacitors. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2011, 119, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abechi, S.E.; Gimba, C.E.; Uzairu, A.; Dallatu, Y.A. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from palm kernel shell by chemical activation. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2013, 3, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Erdemir, F.; Tuzcu, E.; Bilgin, S.; Alver, Ü.; Çanakçı, A. Influence of fluorine doping of zinc oxide on its electrochemical performance in supercapacitors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 259, 124033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arico, A.S.; Bruce, P.; Scrosati, B.; Tarascon, J.M.; Van Schalkwijk, W. Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. In Materials for Sustainable Energy: A Collection of Peer-Reviewed Research and Review Articles from Nature Publishing Group; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2011; pp. 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, N.; Liu, D.; Xu, J.; Sha, J.; Yin, J.; Tan, X.; Yang, H.; Lu, H.; Lin, H. Direct carbonization of rice husk to prepare porous carbon for supercapacitor applications. Energy 2017, 128, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y. A green technology for the preparation of high capacitance rice husk-based activated carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y. Hierarchical porous carbon based on the self-templating structure of rice husk for high-performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 19294–19300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xiao, X.; Cai, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Highly rate and cycling stable electrode materials constructed from polyaniline/cellulose nanoporous microspheres. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 16424–16429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, G.; Shen, J.; Zou, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X. Nanocellulose-derived highly porous carbon aerogels for supercapacitors. Carbon 2016, 99, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Gao, Q.; Qian, W. Interlinked porous carbon nanoflakes derived from hydrolyzate residue during cellulosic bioethanol production for ultrahigh-rate supercapacitors in nonaqueous electrolytes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Lin, H. Hierarchical porous carbon derived from lignin for high performance supercapacitor. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 484, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; Lin, Z.; Yin, J.; Lu, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, M. 3 D Hierarchical Porous Carbon for Supercapacitors Prepared from Lignin through a Facile Template-Free Method. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Smith, A.T.; Wang, W.; Sun, L. Versatile nanostructures from rice husk biomass for energy applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13722–13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, S. Effects of water washing and torrefaction pretreatments on rice husk pyrolysis by microwave heating. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RSaidur, R.; Abdelaziz, E.; Demirbas, A.; Hossain, M.; Mekhilef, S. A review on biomass as a fuel for boilers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2262–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A.; Shaikh, M.A.; Akbar, H. Utilization of rice husk ash as viscosity modifying agent in self compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azat, S.; Korobeinyk, A.V.; Moustakas, K.; Inglezakis, V.J. Sustainable production of pure silica from rice husk waste in Kazakhstan. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kwac, L.K.; Shin, H.K. Characterization of activated carbon paper electrodes prepared by rice husk-isolated cellulose fibers for supercapacitor applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, A.M.; Ani, F.N. Recent development in the production of activated carbon electrodes from agricultural waste biomass for supercapacitors: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcın, N.; Sevinc, V. Studies of the surface area and porosity of activated carbons prepared from rice husk. Carbon 2000, 38, 1943–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Castelló, D.; Lillo-Ródenas, M.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Linares-Solano, A. Preparation of activated carbons from Spanish anthracite: I. Activation by KOH. Carbon 2001, 39, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniandy, L.; Adam, F.; Mohamed, A.R.; Ng, E.P. The synthesis and characterization of high purity mixed microporous/mesoporous activated carbon from rice husk using chemical activation with NaOH and KOH. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S.; Sekar, K.; Gupta, V.K.; Ganesan, S. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous activated carbon from rice husk for adsorption of glycine from alcohol-aqueous mixture. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 177, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, L.J.; Vijaya, J.J.; Kayalvizhi, K.; Sekaran, G. Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions using mesoporous carbon prepared by two-stage process. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kaskel, S. KOH activation of carbon-based materials for energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23710–23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Stoller, M.D.; Ganesh, K.J.; Cai, W.; Ferreira, P.J.; Pirkle, A.; Wallace, R.M.; Cychosz, K.A.; Thommes, M. Carbon-based supercapacitors produced by activation of graphene. Science 2011, 332, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W. Effect of removing silica in rice husk for the preparation of activated carbon for supercapacitor applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.; Hameed, B. Utilization of rice husks as a feedstock for preparation of activated carbon by microwave induced KOH and K2CO3 activation. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9814–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hared, I.A.; Dirion, J.-L.; Salvador, S.; Lacroix, M.; Rio, S. Pyrolysis of wood impregnated with phosphoric acid for the production of activated carbon: Kinetics and porosity development studies. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2007, 79, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palit, D.; Moulik, S.P. Adsorption behaviors of L-histidine and DL-tryptophan on cholesterol, silica, alumina, and graphite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 239, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfer, S.; Fainchtain, R.; Purinson, Y.; Kedem, O. Surface characterization by FTIR-ATR spectroscopy of polyethersulfone membranes-unmodified, modified and protein fouled. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 172, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solum, M.; Pugmire, R.; Jagtoyen, M.; Derbyshire, F. Evolution of carbon structure in chemically activated wood. Carbon 1995, 33, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Peng, H.; Travas-Sejdic, J.; Kilmartin, P.A. Free radical scavenging properties of polypyrrole and poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Curr. Appl. Phys. 2008, 8, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Xue, B.; Li, W.; Ding, Z.; Yang, X.; Qiu, J.; Wang, Z. Rice husk-based hierarchical porous carbon for high performance supercapacitors: The structure-performance relationship. Carbon 2020, 161, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolba, G.M.; Barakat, N.A.; Bastaweesy, A.; Ashour, E.; Abdelmoez, W.; El-Newehy, M.H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Kim, H.Y. Effective and highly recyclable nanosilica produced from the rice husk for effective removal of organic dyes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolba, G.M.; Bastaweesy, A.; Ashour, E.; Abdelmoez, W.; Khalil, K.A.; Barakat, N.A. Effective and highly recyclable ceramic membrane based on amorphous nanosilica for dye removal from the aqueous solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, M.; Tolba, G.M.; Motlak, M.; Fadali, O.A.; Khalil, K.A.; Almajid, A.A.; Kim, B.; Barakat, N.A. Effective polysulfone-amorphous SiO2 NPs electrospun nanofiber membrane for high flux oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartick, B.; Srivastava, S.K. Green synthesis of graphene. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 4320–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puziy, A.M.; Poddubnaya, O.I.; Socha, R.P.; Gurgul, J.; Wisniewski, M. XPS and NMR studies of phosphoric acid activated carbons. Carbon 2008, 46, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidou, O.; Zabaniotou, A. Agricultural residues as precursors for activated carbon production—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1966–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Lim, S.; Song, Y.; Ota, Y.; Qiao, W.; Tanaka, A.; Mochida, I. KOH activation of carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2004, 42, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibril, B.; Houache, O.; Al-Maamari, R.; Al-Rashidi, B. Effects of H3PO4 and KOH in carbonization of lignocellulosic material. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 83, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.; Yan, D.S.; O’Grady, T.M.; Wennerberg, A. Formation of active carbons from cokes using potassium hydroxide. Carbon 1984, 22, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerf, A.; He, H.; Riedl, T.; Forster, M.; Klinowski, J. 13C and 1H MAS NMR studies of graphite oxide and its chemically modified derivatives. Solid State Ion. 1997, 101, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Kido, G.; Hara, K.; Noguchi, H. Characterization of neutralized graphite oxide and its use in electric double layer capacitors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 712, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zięzio, M.; Charmas, B.; Jedynak, K.; Hawryluk, M.; Kucio, K. Preparation and characterization of activated carbons obtained from the waste materials impregnated with phosphoric acid (V). Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 4703–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Takagaki, A.; Toda, M.; Kondo, J.N.; Domen, K.; Tatsumi, T.; Hara, M.; Hayashi, S. Acid-catalyzed reactions on flexible polycyclic aromatic carbon in amorphous carbon. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3039–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Huang, M.; Ma, H.-L.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Gao, J.-M.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Han, X.-J.; Guo, X.-Y. Preparation of a carbon-based solid acid catalyst by sulfonating activated carbon in a chemical reduction process. Molecules 2010, 15, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, J.; Bai, T.; Long, B.; Zhou, X. Facile synthesis of few-layer graphene from biomass waste and its application in lithium ion batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 768, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Cheng, H.M. The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 2012, 50, 3210–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobinski, L.; Lesiak, B.; Malolepszy, A.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Mierzwa, B.; Zemek, J.; Jiricek, P.; Bieloshapka, I. Graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide studied by the XRD, TEM and electron spectroscopy methods. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2014, 195, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Kumar, N.; Panda, K.; Kanan, V.; Joshi, S.; Visoly-Fisher, I. Role of oxygen functional groups in reduced graphene oxide for lubrication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourlier, Y.; Bouttemy, M.; Patard, O.; Gamarra, P.; Piotrowicz, S.; Vigneron, J.; Aubry, R.; Delage, S.; Etcheberry, A. Investigation of InAlN layers surface reactivity after thermal annealings: A complete XPS study for HEMT. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, P329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.; Ahmed, E.; Farghali, A.A.; Nassar, M.M.; Tolba, G.M.; Zaki, A.H. Facile synthesis of Ni-incorporated and nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide as an effective electrode material for tri (ammonium) phosphate electro-oxidation. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 2760–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, T.-H. Preparation and characterization of nano-structured silica from rice husk. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 364, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Wang, F. Electrochemical capacitor performance: Influence of aqueous electrolytes. In Supercapacitors—Theoretical and Practical Solutions; Intech Open: London, UK, 2018; pp. 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- Silvester, D.S. Recent advances in the use of ionic liquids for electrochemical sensing. Analyst 2011, 136, 4871–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchała, K.; Kierzek, K.; Machnikowski, J. Capacitance behavior of KOH activated mesocarbon microbeads in different aqueous electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 86, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, E.Y.L.; Muniandy, L.; Ng, E.-P.; Adam, F.; Mohamed, A.R.; Jose, R.; Chong, K.F. High surface area activated carbon from rice husk as a high performance supercapacitor electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 192, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.; El-Deen, A.G.; Shin, G.; Park, M.; Kim, H.Y. Novel Cd-doped Co/C nanoparticles for electrochemical supercapacitors. Mater. Lett. 2013, 99, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deen, A.G.; El-Newehy, M.; Kim, C.S.; Barakat, N.A. Nitrogen-doped, FeNi alloy nanoparticle-decorated graphene as an efficient and stable electrode for electrochemical supercapacitors in acid medium. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Largeot, C.; Portet, C.; Chmiola, J.; Taberna, P.-L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Simon, P. Relation between the ion size and pore size for an electric double-layer capacitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2730–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, N.; Shinde, S.; Vishwakarma, R.; Kadam, S.; Sharon, M.; Sharon, M. MWCNTs synthesized from waste polypropylene plastics and its application in super-capacitors. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 1538, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, R.; Li, G.; Hu, C. The role of H3PO4 in the preparation of activated carbon from NaOH-treated rice husk residue. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32626–32636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczek, B. Preparation of Active Carbon by Additional Activation with Potassium Hydroxide and Characterization of Their Properties. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5819208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Martin-Gullón, I.; Grulke, E.A. Carbon materials in environmental applications. Chem. Phys. Carbon 2000, 27, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Frackowiak, E. Carbon materials for supercapacitor application. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, E.Y.L.; Lim, H.N.; Jose, R.; Chong, K.F. Aminopyrene functionalized reduced graphene oxide as a supercapacitor electrode. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 38111–38116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.-Y.; Zhang, W.-L.; Lin, H.-B.; Tian, Y.-X.; Li, X.-X.; Tian, Y.-Y.; Lu, H.-Y. Modification of a rice husk-based activated carbon by thermal treatment and its effect on its electrochemical performance as a supercapacitor electrode. New Carbon Mater. 2019, 34, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kader, A.; Ammar, A.; Saleh, S. High-temperature phase transition in potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals. Thermochim. Acta 1990, 167, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, X. Rice Hull-Derived Carbon for Supercapacitors: Towards Sustainable Silicon-Carbon Supercapacitors. Polymers 2021, 13, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocuweang, T.; Aussawasathien, D.; Worasuwannarak, N.; Road, P.; Nueng, K.; Luang, K. Preparation of super-capacitor from soluble produced from rice straw. J. Sustain. Energy Environ. 2020, 11, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sankar, S.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.; Kim, A.; Ahmed, A.T.A.; Inamdar, A.I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Im, H.; Kim, D.Y. Ultrathin graphene nanosheets derived from rice husks for sustainable supercapacitor electrodes. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 13792–13797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Bahadur, J.; Pal, K. One-step one chemical synthesis process of graphene from rice husk for energy storage applications. Graphene 2017, 6, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.; Lin, H.; Lu, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, D. On the cycling stability of the supercapacitive performance of activated carbon in KOH and H2SO4 electrolytes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 511, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wei, Y.; Chen, G.; Ge, J.; Lu, H. Porous carbon made from rice husk as electrode material for electrochemical double layer capacitor. Appl. Energy 2015, 153, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, B.; Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Wu, K.; Sun, L.; Peng, X.; Fu, J. Nanoporous activated carbon derived from rice husk for high performance supercapacitor. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, K.L.; Thi, T.T.L. Activated carbon derived from rice husk by NaOH activation and its application in supercapacitor. Progress Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2014, 24, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Raj, J.; Shaijumon, M.M. Nanoporous rice husk derived carbon for gas storage and high performance electrochemical energy storage. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, H.; Kim, Y.A.; Yang, K.S.; Cruz-Silva, R.; Toda, I.; Yamada, T.; Terrones, M.; Endo, M.; Hayashi, T.; Saitoh, H. Rice husk-derived graphene with nano-sized domains and clean edges. Small 2014, 10, 2766–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Ling, P.; Yu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, M. Rice husk-derived porous carbons with high capacitance by ZnCl2 activation for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 105, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Park, K.H.; Shim, W.G.; Balathanigaimani, M.; Moon, H. Performance of electrochemical double layer capacitors using highly porous activated carbons prepared from beer lees. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Ma, C.; Wu, L.; Wei, C.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Shi, J. Preparation of cellulose acetate derived carbon nanofibers by ZnCl2 activation as a supercapacitor electrode. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 6419–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, K.; Thundat, T. Carbonized nanocellulose sustainably boosts the performance of activated carbon in ionic liquid supercapacitors. Nano Energy 2016, 25, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, H. Supercapacitive performance of hierarchical porous carbon microspheres prepared by simple one-pot method. J. Power Sources 2014, 254, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Presser, V.; Zhang, L.; Niu, J.J.; McDonough, J.K.; Pérez, C.R.; Lin, H.; Fong, H.; Gogotsi, Y. High power supercapacitor electrodes based on flexible TiC-CDC nano-felts. J. Power Sources 2012, 201, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Ye, L.; Huang, Z.-H.; Xu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Kang, F.; Yang, Q.-H. A honeycomb-like porous carbon derived from pomelo peel for use in high-performance supercapacitors. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13831–13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wei, W.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, R.; Chen, J.; Du, C. Nitrogen, sulfur co-doped hierarchically porous carbon from rape pollen as high-performance supercapacitor electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 311, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Activation | Electrolyte | Sp. Cap. (F/g) | Ref/Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH | Thermal 600 | 3 M KOH | 216 | [2] 2022 |
| Act-RH–900 | NaOH | 1 M KOH | 150.8 | [75] 2021 |
| ACP–1100 | KOH | 1 M KOH | 255 | [22] 2020 |
| RS 900 °C was | 1 M KCl 1 M KOH | 46.79 40.91 | [76] 2020 | |
| RHPC | NaOH | 6 M KOH | 263 | [38] 2020 |
| RHAC RHAC-T | Thermal/800 | 1 mol L–1Et4NBF | 115 152 | [73] 2019 |
| RH | KOH | 6 M KOH | 315 | [31] 2019 |
| Graphene/RH | KOH | 1 M Na2SO4 | 115 | [77] 2017 |
| RH/GR | KOH | 1 M (Na2SO4) | 86 | [78] 2017 |
| RHPC | NaOH | 6 M KOH | 97 | [9] 2017 |
| RHC | KOH | 1 M H2SO4 | 225 | [79] 2016 |
| RHC 850 | KOH | 6 M KOH | 143 | [63] 2016 |
| RH 850 | KOH | 6 M KOH | 147 | [63] 2016 |
| RHAC 800 | KOH | 6 M KOH 1.5 M TEA–BF4 | 367 147 | [80] 2015 |
| RHs | KOH | 6 M KOH | 250 | [81] 2014 |
| RHN–800 | NaOH | 0.5 M K2SO4 | 172.3 | [82] 2014 |
| RH | H3PO4 | 1 M H2SO4 | 112 | [83] 2014 |
| Monolayered graphene RH | KOH | 1 M H2SO4 | 80 | [84] 2014 |
| ZnCl2/RH | ZnCl2 | 6 M KOH | 243 | [85] 2013 |
| RH | CO2 | 1 M (Na2SO4) | 112 | [86] 2011 |
| RH | H3PO4/KOH | 0.1 M H2SO4 | 241.3 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barakat, N.A.M.; Irfan, O.M.; Moustafa, H.M. H3PO4/KOH Activation Agent for High Performance Rice Husk Activated Carbon Electrode in Acidic Media Supercapacitors. Molecules 2023, 28, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010296
Barakat NAM, Irfan OM, Moustafa HM. H3PO4/KOH Activation Agent for High Performance Rice Husk Activated Carbon Electrode in Acidic Media Supercapacitors. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010296
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarakat, Nasser A. M., Osama M. Irfan, and Hager M. Moustafa. 2023. "H3PO4/KOH Activation Agent for High Performance Rice Husk Activated Carbon Electrode in Acidic Media Supercapacitors" Molecules 28, no. 1: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010296
APA StyleBarakat, N. A. M., Irfan, O. M., & Moustafa, H. M. (2023). H3PO4/KOH Activation Agent for High Performance Rice Husk Activated Carbon Electrode in Acidic Media Supercapacitors. Molecules, 28(1), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010296





