Abstract
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) with 0.1 and 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 cathode catalyst loadings were separately contaminated with seven organic species: Acetonitrile, acetylene, bromomethane, iso-propanol, methyl methacrylate, naphthalene, and propene. The lower catalyst loading led to larger cell voltage losses at the steady state. Three closely related electrical equivalent circuits were used to fit impedance spectra obtained before, during, and after contamination, which revealed that the cell voltage loss was due to higher kinetic and mass transfer resistances. A significant correlation was not found between the steady-state cell voltage loss and the sum of the kinetic and mass transfer resistance changes. Major increases in research program costs and efforts would be required to find a predictive correlation, which suggests a focus on contamination prevention and recovery measures rather than contamination mechanisms.
1. Introduction
Vehicles propelled by proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are already commercially available. However, opportunities still exist to improve the technology because it is not expected to mature within the foreseeable future [1]. For instance, research activities are still ongoing to reduce cost while maintaining durability with a lower amount of Pt catalyst [2]. Contaminants in air jeopardize PEMFC operation by increasing the cell voltage degradation rate [3] if the intake filter [4] is saturated or damaged. Therefore, risks associated with contamination of low Pt loaded PEMFCs need to be assessed to support commercialization. Furthermore, fuel cell design robustness could be improved by integrating additional mitigation approaches derived from contamination mechanisms.
Only a few publications discuss the impact of the anode catalyst loading during PEMFC exposures to reformate fuel contaminants, such as CO, CO2, H2S, NH3, and halogenated compounds. All of these species are included in the hydrogen fuel standard [5]. For CO and H2S, a lower Pt or PtRu catalyst loading generally leads to an increase in the anode overpotential [6,7,8,9,10]. However, it was reported that for H2S, the catalyst loading effect disappears for values equal to or below 25 μg cm−2 [10]. An effect was not observed with the weak contaminant CO2, which is attributed to a concentration that was substantially lower (1%) [7] than in a typical reformate (10–20%) [11]. The same situation was noted for NH3, which is assigned to a rapid conversion to NH4+ in the presence of protons or water [12,13], followed by ion exchange with ionomer H+ and transport to the cathode away from the anode under the influence of the electric field [14,15]. For halogenated compounds, a decrease in the Pt catalyst loading of both electrodes led to a faster degradation rate in the presence of HCl in both reactant stream humidifiers [16]. The effect of the anode Pt catalyst loading was exploited to develop sensor cells that are more sensitive to contamination by CO, H2S, and NH3 in H2. These sensors were either based on a PEMFC [17] or a H2 pump [18] design. Only two PEMFC contamination documents focusing on the cathode catalyst loading effect were found [19,20]. However, contamination data in [19] are not directly comparable because both the catalyst layer design and catalyst loading were concurrently altered. The authors also refer to 10 ppb SO2 data obtained by another group that showed more severe fuel cell damage with a catalyst loading decrease from 0.4 to 0.3 mg Pt cm−2. In contrast, the effect of 2,6-diaminotoluene, a species that leaches out of the fuel cell system balance of plant materials, was more impactful after the Pt catalyst loading was lowered from 0.4 to 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 [20]. In comparison to the anode, the higher cathode potential is expected to affect the contamination mechanism with, for example, a different Pt surface charge, altered contaminant adsorbates and reaction intermediates, catalyst coverage, and cell voltage loss. This situation is exacerbated with a catalyst loading change, which affects the overpotential of the irreversible oxygen reduction reaction and the cathode potential. Information about chemical and electrochemical reactions for specific contaminants may be available in the literature. However, the presence of relevant cathode reactants, oxygen and water, may not be considered. For instance, novel intermediates or products were not detected with chlorobenzene in air [21]. However, the presence of acetylene in air led to small amounts of methane [22] that were not expected based on acetylene chemistry and electrochemistry. Therefore, tests completed under these significantly different operating conditions are needed in part because contaminant reactions are not currently predictable in assessing catalyst coverage and cell voltage loss.
This report documents the impact of the cathode Pt catalyst loading effect for PEMFCs contaminated with seven model organic airborne species, which were previously evaluated and selected from a larger pool of 21 contaminants [23]: Acetonitrile (nitrile), acetylene (alkyne), bromomethane (halocarbon), iso-propanol (alcohol), methyl methacrylate (ester), naphthalene (polycyclic aromatic), and propene (alkene). Cell voltage transients obtained under galvanostatic conditions were recorded for this analysis. Additionally, impedance spectroscopy data were acquired to facilitate the development of predictive correlations and contamination mechanisms.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cell Voltage Transients
Figure 1a depicts voltage transients for cells temporarily exposed to 20 ppm CH3CN. The cell voltage for the first 5 h is constant and higher for the 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading. This observation is consistent with previously published data for Gore catalyst coated membranes with the same cathode catalyst loadings and gas diffusion layers (Sigracet 25 BC) [24]. After approximately 5 h of operation, acetonitrile was injected into the cell, which led to a rapid cell voltage decrease that progressively slowed until a steady state was reached. For acetonitrile, the cell voltage loss was larger for the 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading. Subsequently, the acetonitrile injection was interrupted, which quickly initiated a voltage recovery that gradually decelerated until a new steady state was reached. For acetonitrile, the cell voltage after recovery coincided with the value before contaminant injection. Acetonitrile contamination and recovery transients are qualitatively and quantitatively consistent with prior results [23,25,26,27,28]. At irregular intervals and during all baseline, contamination, and recovery stages, cell voltage transients were minimally disrupted for a short period by impedance spectroscopy measurements and the superimposition of a current signal of a small amplitude and variable frequency.
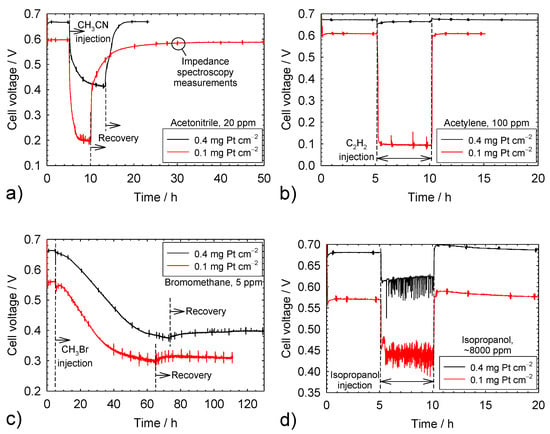
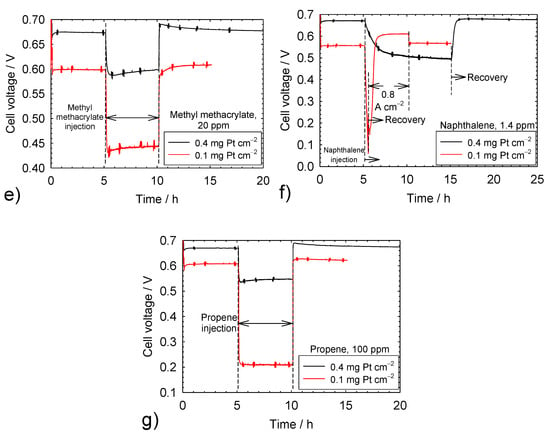
Figure 1.
Cell voltage transients resulting from a temporary contaminant injection. (a) Acetonitrile; (b) acetylene; (c) bromomethane; (d) isopropanol; (e) methyl methacrylate; (f) naphthalene; (g) propene.
Figure 1b–g illustrates voltage transients for the other contaminants. Most of these transients share common features, including a similar initial baseline voltage, a relatively rapid voltage decrease until a steady state is reached, and a complete voltage recovery after contaminant injection was stopped. However, bromomethane transients were significantly slower and only a small fraction of the voltage loss was recovered (Figure 1c). This behavior is the result of a rapid bromomethane hydrolysis within the cell, producing methanol and bromide [28,29,30]. The effective bromomethane concentration is lower than the nominal value, whereas bromide is prevented from penetrating the ionomer by Donnan exclusion [12]. This situation delays the stronger and inhibiting adsorption of bromomethane and bromide on the catalyst surface. The removal of bromide from the catalyst surface is equally hindered due to an unfavorable cathode potential that is significantly higher than the potential of zero charge, preventing bromide desorption and Donnan exclusion, which explains the incomplete voltage recovery. During isopropanol contamination, the voltage is characterized by rapid fluctuations (Figure 1d), which were not observed for lower isopropanol concentrations [23,31]. These fluctuations are attributed to isopropanol, a surfactant commonly used to disperse Pt/C catalyst particles in solution [32], which adsorbs on carbon materials (gas diffusion layer, catalyst support) [33] and modifies liquid water management (buildup and release of liquid water drops), as previously proposed for acetylene [34]. A higher number of buildup and release events of water drops and a higher voltage fluctuation frequency for the lower catalyst loading (Figure 1d) may be related to the lower cathode potential (cell voltage compensated by a similar ohmic drop), which leaves a higher proportion of isopropanol surfactant unoxidized (oxidation initiated at a potential above 0.32 V vs. the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) [35]) and more hydrophilic carbon surfaces. The effect of naphthalene was rapid and severe for the 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading (Figure 1f). As a result, the current density was temporarily lowered and the contaminant injection was interrupted before a steady state was obtained to avoid an automatic test station shutdown. Contamination and recovery transients are qualitatively and quantitatively consistent with the prior results for acetylene [23,36,37,38,39], bromomethane [23,28,29,30], isopropanol [23,31], methyl methacrylate [23,31], naphthalene [23,40], and propene [23,28,31,41].
Table 1 summarizes steady-state cell voltages before, during, and after contamination as well as the cell voltage change during and after contamination for both catalyst loadings. The cell voltage decrease during the contamination period is generally higher for the 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading (23% to 89% in comparison to 1.2% to 43%). After the recovery period, the cell voltage change is minimal and independent of the catalyst loading, varying from −1.7% to 2%, with the exception of bromomethane (−40% to −45%). The larger cell voltage loss during contamination for the low catalyst loading is an important consideration for the selection of tolerance limits for commercially relevant catalyst loadings. Data obtained with a 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading were used to derive tolerance limits [42]. The data of Table 1 suggest that these tolerance limits require a revision for a 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading and additional tests carried out over a range of concentrations. In contrast, International Organization for Standardization (ISO) tolerance limits for hydrogen contaminants [5,43], which do not take account of the catalyst loading effect, were deemed too strict for formaldehyde and formic acid, a low anode catalyst loading of 0.05 mg Pt cm−2, and automotive operating conditions (high fuel utilization, fuel recirculation) [44]. The formaldehyde tolerance limit was recently modified from 10 [43] to 200 ppb [5].

Table 1.
Steady-state cell voltages at the end of each contamination period, and steady-state cell voltage changes during and after contamination.
The magnitude of the cell voltage change during contamination (Table 1) with catalyst loading is species-dependent. For instance, the catalyst loading hardly affected the cell voltage loss for bromomethane (−43% and −47%), whereas for acetylene, the cell voltage loss substantially increased from −1.2% to −85% with a catalyst loading decrease. This observation is attributed to different contamination mechanisms. Impedance spectroscopy data obtained during contamination by all Table 1 species and with a 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading revealed that kinetic, ohmic, and mass transport overpotentials were impacted [42]. These and additional impedance spectroscopy data acquired with a 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading were analyzed to evaluate the existence of a correlation between these resistances and the cell voltage loss due to contamination at the steady state.
2.2. Impedance Spectra
Figure 2a shows impedance spectra (Nyquist representation) for a 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading, before, during, and after acetonitrile contamination. All three spectra share the same features and have two main loops that are respectively attributed to oxygen reduction (medium frequencies) and oxygen mass transfer (low frequencies) [45]. A third loop ascribed to hydrogen oxidation is barely visible as a hump at high frequencies [45]. The high-frequency intercept represents the ohmic resistance, which is mostly caused by the poorly conducting membrane [45]. Multiple explanations were proposed for the inductive impedance values at the lowest and highest frequencies, including electrical cables [46,47] for high frequencies, and processes involving side reactions with intermediate species [47], oxide growth [48], or a slow ionomer water uptake/release [49] for low frequencies. Most of these considerations were either ignored because they did not focus on relevant aspects (electrical cables) or were easily dismissed because, in the absence of contaminants, the cathode potential was too low for Pt oxidation and the sub-saturated air stream did not yield an inductive behavior. For the 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading, the average cell voltage of 0.671 V (Table 1) compensated with an ohmic loss of 0.1 V for a worst-case scenario (1 A cm−2 × 0.1 Ω cm2 from the high-frequency intercepts in Figure 2a) leads to a cathode potential of 0.771 V vs. RHE, which is lower than the smallest Pt oxidation potential of 0.837 V vs. RHE [50]. Acetonitrile contamination causes an increase in the high-frequency intercept and a diameter increase for both main loops (Figure 2a). An increase in ohmic loss was only observed with acetonitrile, owing to the production of ammonium cations by hydrolysis, which displace protons as the main charge carriers in the ionomer [28,51]. In relative terms, this effect is significantly smaller than the kinetic and mass transfer effects, with an approximate doubling of both oxygen reduction and transport loop diameters. However, because the effect is cumulative, a larger change is observed for a longer exposure duration [26]. After contamination, the high-frequency intercept returns to its original value, and both main loops decrease in size to a diameter that is smaller than the original value. These impedance spectra agree with prior results [25,26,27,28]. However, smaller kinetic and mass transfer loops are inconsistent with a complete cell voltage recovery (Figure 1a, Table 1). This observation is possibly due to subtle structural or other changes that are not detectable by cell voltage measurements, such as Pt surface reconstruction in the presence of foreign species [52,53]. The oxygen reduction and mass transfer resistances before, during, and after contamination were generally obtained by curve-fitting an equivalent circuit developed for a PEMFC contaminated with SO2 (Figure 3a) [54]. Resistances during contamination for acetonitrile and a 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading were derived using a modified equivalent circuit that accounts for the inductive behavior at low frequencies (Figure 3b) [55,56]. Resistances during contamination for acetonitrile (0.4 mg Pt cm−2) and propene (0.1 mg Pt cm−2) were obtained using a modified version of the Figure 3b equivalent circuit by omitting the cathode resistance Rk (Figure 3b) to limit the number of parameters (Figure 3c). The impedance spectra are accurately represented by the equivalent circuit models (Figure 2a–f). The resistance values are discussed later in this section.
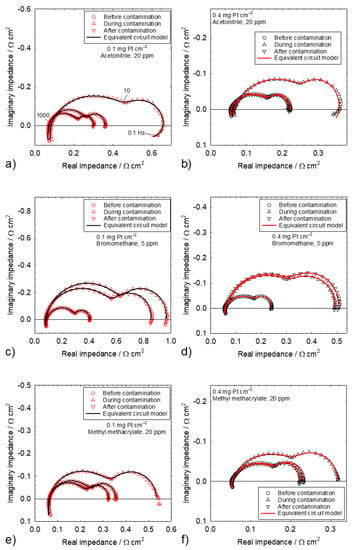
Figure 2.
Impedance spectra before, during, and after contamination by acetonitrile in (a) and (b), bromomethane in (c) and (d), and methyl methacrylate in (e) and (f) for Pt catalyst loadings of 0.1 mg cm−2 in (a), (c), and (e), and 0.4 mg cm−2 in (b), (d), and (f).
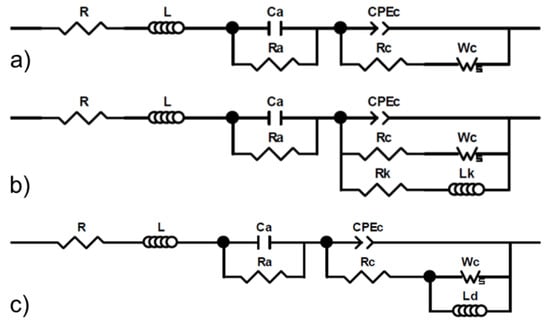
Figure 3.
Equivalent circuit models for a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC). (a) The model previously derived for SO2 contamination and used for all 7 organic contaminants investigated in this work; (b) the model previously derived to capture low-frequency inductive data in the absence of contaminants and used to fit data during acetonitrile contamination (0.1 mg Pt cm−2); (c) the modified model (b) to capture low-frequency inductive data obtained during acetonitrile (0.4 mg Pt cm−2) and propene (0.1 mg Pt cm−2) contamination.
Most of the other impedance spectra for both catalyst loadings and all contaminants are equally well represented by the equivalent circuits shown in Figure 3a,c. For this reason, only a selection is given in Figure 2. A few spectra could not be fitted with any of the equivalent circuits in Figure 3a–c for a few 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading cases. For acetylene, the impedance spectrum during contamination was approximately a single loop of a large diameter that could not be fitted to a two-loop equivalent circuit. For isopropanol, cell voltage fluctuations during contamination (Figure 1d) created a low frequency artefact that also prevented the use of the equivalent circuits of Figure 3a or Figure 3c. For naphthalene, the cell voltage transient was interrupted before a steady state was obtained (Figure 1f), which also led to a low-frequency artefact that could not be fitted to the equivalent circuits of Figure 3a–c. The impedance spectra agree with the prior results for acetonitrile [25,26,27,28], acetylene [36,37,38], bromomethane [28,29,30], isopropanol [31], methyl methacrylate [31], naphthalene [40], and propene [28,31,41].
Table 2 collects kinetic and mass transfer resistances before, during, and after contamination for both catalyst loadings. Dimensionless kinetic and mass transfer resistances during and after contamination are also given in Table 2. The dimensionless kinetic and mass transfer resistances concurrently increase during contamination and are ≥1.05, with the exception of the 0.93 dimensionless mass transfer resistance for isopropanol and a 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading. The isopropanol anomaly may be related to water management, as discussed in the previous section. A hypothesized connection between kinetic and mass transfer resistances during contamination [34] was recently substantiated [57]. Contaminant adsorbates covering the catalyst surface increase the effective current density closer to the limiting value and mass transfer losses in the ionomer layer covering the catalyst. This situation is similar to a decrease in catalyst loading, which has been shown to also increase mass transfer losses [58,59]. The dimensionless kinetic and mass transfer resistances after recovery, with the exception of bromomethane, indicate an incomplete recovery that is less extensive for the lower catalyst loading. For the dimensionless kinetic resistance, values are ≥0.832 and ≥0.95 for, respectively, 0.1 and 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loadings. For the dimensionless mass transfer resistance, values are ≥0.842 and ≥0.88 for, respectively, 0.1 and 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loadings. These results are in contrast with the data of Figure 1 and Table 1, showing a complete recovery within experimental error, with the exception of bromomethane. The discrepancy between the recovery extents of cell voltage and kinetic and mass transfer resistances is due to the higher sensitivity of impedance measurements and the movement of the reaction front (current density and catalyst layer effectiveness redistributions over the catalyst layer thickness). The hydrogen peroxide yield is enhanced in the presence of acetonitrile, acetylene, methyl methacrylate, naphthalene, and propene [60,61,62,63]. The elevated level of hydrogen peroxide in turn promotes ionomer degradation [64] and structural modifications to the catalyst layer that are relatively more impactful for the lower catalyst loading. Therefore, in view of the lower cell voltage and cathode potential for a lower catalyst loading (Figure 1, Table 1), a higher hydrogen peroxide yield [60,61,62,63] and ionomer degradation are expected. Tafel plots obtained before and after contamination with acetylene (Figure 4) support this hypothesis, with a larger cell voltage loss for the 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading (7.9 mV in comparison to 2.9 mV).

Table 2.
Steady-state kinetic and mass transfer resistances at the end of each contamination period, and steady-state dimensionless resistances during and after contamination.
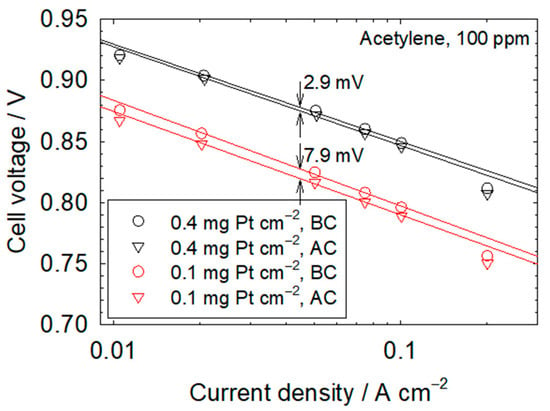
Figure 4.
Tafel plots before contamination (BC) and after contamination (AC) with 100 ppm acetylene for 0.1 and 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loadings. The change in cell voltage between plots at a current density of 0.0447 A cm−2, a value located in the middle of the range used to correlate data (0.02 to 0.1 A cm−2), ignores the slight change in slope.
2.3. Contaminant Effect Prediction
The steady-state cell voltage loss during contamination was correlated with the sum of the kinetic and mass transfer resistance changes during contamination (Figure 5). A significant correlation was not identified, as significant deviations from Ohm’s law were noted. Furthermore, it is difficult to argue that there is a catalyst loading effect because the two data sets largely overlap. The absence of a correlation is not surprising, considering the effects of cell design and operating conditions on contamination. Several parameters were mentioned in an earlier attempt to correlate the effect of contaminants on oxygen reduction kinetics [65], including contaminant partial pressure and temperature, exposed Pt surface features (crystal faces, edges), Pt state (reduced or oxidized), phase in contact with the Pt surface (air, ionomer), adsorption isotherms for O2, contaminants, and related intermediates and products, and elementary chemical and electrochemical reactions and associated rate constants for O2 reduction and contaminant oxidation or reduction. This list is enlarged by factors affecting ohmic and mass transfer losses, including cation and neutral molecules’ absorption isotherms influencing ionomer and membrane ionic conductivity and oxygen permeability by swelling and changing the distance between sulfonate groups, and contaminant scavenging by liquid water modifying the effective contaminant concentration [12,13,66,67,68,69,70,71]. Although cell design and operating conditions were maintained as constant as possible, with the exception of catalyst loading and contaminant concentration, the change in cell resistance is insufficiently precise to capture all contamination nuances and accurately predict the cell voltage loss (Figure 5). An accurate correlation for the cell voltage loss would be useful. However, given the amount of information that will be required and the complexity associated with the derivation of a detailed mathematical model of contamination, a focus on preventive and recovery measures may be more fruitful. This suggestion is reinforced by considering practical aspects, contaminant mixtures [28], and long-term effects [26] that increase the number of contamination parameters and the difficulty in predicting contaminant effects.
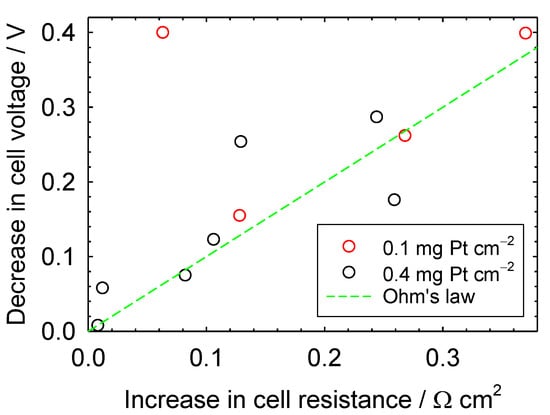
Figure 5.
Cell voltage loss as a function of the sum of the changes in kinetic and mass transfer resistance.
3. Materials and Methods
A single modified Fuel Cell Technologies cell with an active area of 50 cm2 and triple/double serpentine channels for the cathode/anode was used for all experiments. Gore PRIMEA M715 catalyst-coated membranes with a Pt loading of 0.1 or 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 (50 % Pt/C) on each side were inserted between SGL Carbon Sigracet 25 BC gas diffusion layers. The cell was operated with a FCATS™ G050 series test station (Green Light Power Technologies). After cell activation, operating conditions were set to air/H2, 2/2 stoichiometry, 48.3/48.3 kPag outlet pressure, 50%/100% relative humidity, 80 °C, and 1 A cm−2. Contaminant concentrations varied between 1.4 and ~8000 ppm: Acetonitrile (20 ppm), acetylene (100 ppm), bromomethane (5 ppm), isopropanol (~8000 ppm), methyl methacrylate (20 ppm), naphthalene (1.4 ppm), and propene (100 ppm). Contaminant concentrations were individually and empirically adjusted based on prior experience to cause a perceptible to significant cell voltage decrease at the steady state for the 0.4 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading, and to leave a sufficient cell voltage window for an additional decrease induced by the lower 0.1 mg Pt cm−2 catalyst loading. Contaminants were injected after the air humidifier using air-based gas mixtures for most cases. However, isopropanol and naphthalene were respectively evaporated and sublimated by employing a thermally controlled and calibrated liquid/solid holder. Contaminant injection was initiated after 5 h with an exposure that lasted from less than 1 to ~70 h until a steady state was achieved. After the contamination injection was interrupted, the self-induced recovery was recorded until a steady state was obtained, which necessitated between 5 and ~60 h.
During the galvanostatic experiments, impedance spectra were acquired at irregular intervals by superimposing 0.1 Hz to 10 kHz (10 points per decade) current perturbations that caused a voltage change of ~5 mV. The Solartron SI1260 impedance/gain-phase analyzer was operated with ZPlot® software (Version 2.9c, Scribner Associates, Southern Pines, NC, USA). Measurement accuracy was improved by utilizing Stanford Research SR560 low-noise preamplifiers and by winding up both load-bank cables, which have an equal length, to reduce their inductance. The ZView® software (Version 3.5e, Scribner Associates) was employed for fitting impedance spectra to equivalent circuit models. Polarization curves were only recorded before and after acetylene contamination. Polarization curves were measured by decreasing the current density from 2 to 0 (open circuit voltage) A cm−2 in a stepwise fashion, allowing a stabilization time of 15 min at each stage, and otherwise using contamination test operating conditions.
4. Conclusions
The effect of Pt catalyst loading on the steady-state cell voltage loss was characterized for seven organic airborne contaminants. Impedance spectroscopy was used to gain mechanistic insight. The steady-state cell voltage loss is mostly attributed to a concurrent increase in both kinetic and mass transfer resistances that is reminiscent of the effect of a decrease in catalyst loading in the absence of a contaminant. Low Pt catalyst loadings generally lead to a larger steady-state cell voltage loss. A significant correlation between the steady-state cell voltage loss and the sum of the kinetic and mass transfer resistance changes was not found, and would only be improved with major increases in cost and effort. For this reason, it is proposed to focus activities on contamination prevention and recovery measures.
For a commercially relevant cathode catalyst loading of 0.1 mg Pt cm−2, it would be advantageous to expand the current database to other contaminants and contaminant concentrations for the derivation of tolerance limits to support the design of air filters. Although tolerance limits were previously derived for single contaminants rather than for more practically relevant mixtures [42], for very low contaminant concentrations, tolerance limits may still prove useful because the catalyst surface coverage by contaminant adsorbates may be so small that the different species may not interact. In other words, the effects of all contaminants may be additive. It would also be useful to verify this hypothesis with diluted, single, and multiple contaminant mixtures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S.-P. and Y.Z.; methodology, Y.Z.; formal analysis, J.S.-P. and Y.Z.; investigation, Y.Z.; resources, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.-P.; writing—review and editing, J.S.-P. and Y.Z.; visualization, J.S.-P.; supervision, J.S.-P.; project administration, J.S.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the United States Department of Energy, grant number DE-EE0000467, and the Office of Naval Research, grant number N00014-17-1-2206. The APC was funded by the Office of Naval Research.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Hawaiian Electric Company for their ongoing support of the operations of the Hawaii Sustainable Energy Research Facility.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Nagula, M. Forecasting of Fuel Cell Technology in Hybrid and Electric Vehicles Using Gompertz Growth Curve. J. Stat. Manag. Syst. 2016, 19, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Kajikawa, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of Trends and Emerging Technologies in All Types of Fuel Cells Based on a Computational Method. Sustainability 2018, 10, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J. Air Impurities. In Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Durability; Büchi, F.N., Inaba, M., Schmidt, T.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 289–321. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, D.M.; Cahela, D.R.; Zhu, W.H.; Westrom, K.C.; Nelms, R.M.; Tatarchuk, B.J. Fuel Cell Cathode Air Filters: Methodologies for Design and Optimization. J. Power Sources 2007, 168, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrogen Fuel Quality—Product Specification, ISO 14687:2019(E), 1st ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Gasteiger, H.A.; Panels, J.E.; Yan, S.G. Dependence of PEM Fuel Cell Performance on Catalyst Loading. J. Power Sources 2004, 127, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, R.K.; Wang, X. Effect of CO and CO2 Impurities on Performance of Direct Hydrogen Polymer-Electrolyte Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 180, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimasa, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Imamura, D.; Akai, M. PEFC Power Generation Performance Degradation by Hydrogen Sulfide and Ammonia—Effects of Lowering Platinum Loading. Electrochemistry 2011, 79, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafttananian, M.; Ramiar, A.; Shabani, B.; Ranjbar, A.A. Nonlinear Algorithm of PEM Fuel Cell Catalyst Poisoning Progress in the Presence of Carbon Monoxide in Anode Fuel: A Computational Study Using OpenFOAM. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 246, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prass, S.; Friedrich, K.A.; Zamel, N. Tolerance and Recovery of Ultralow-Loaded Platinum Anode Electrodes upon Carbon Monoxide and Hydrogen Sulfide Exposure. Molecules 2019, 24, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, F.A.; Papageorgopoulos, D.C.; Sitters, E.F.; Janssen, G.J.M. The Influence of Carbon Dioxide on PEM Fuel Cell Anodes. J. Power Sources 2002, 110, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J. PEMFC Contamination Model: Foreign Cation Exchange with Ionomer Protons. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 6274–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J. PEMFC Contaminant Tolerance Limit—Foreign Cations in Ionomers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 5527–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.Z.; Delacourt, C. Mathematical Modelling of Cation Contamination in a Proton-Exchange Membrane. Fuel Cells 2008, 8, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienitz, B.L.; Baskaran, H.; Zawodzinski, T.A., Jr. Modeling the Steady-State Effects of Cationic Contamination on Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, A.J.; Hamilton, C.V., Jr.; Debe, M.K. Impact of Micromolar Concentrations of Externally-Provided Chloride and Sulfide Contaminants on PEMFC Reversible Stability. Electrochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 11, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Z.; Hirata, K.; Hayashi, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Nakazato, N.; Seo, A.; Yasuda, I.; Ariura, S.; Shinkai, H.; Sasaki, K. PEFC-Type Impurity Sensors for Hydrogen Fuels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 16256–16263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Z.; Hirata, K.; Hayashi, A.; Takahashi, T.; Nakazato, N.; Saigusa, K.; Seo, A.; Suzuki, K.; Ariura, S.; Shinkai, H.; et al. Hydrogen Pump-Type Impurity Sensors for Hydrogen Fuels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 3281–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talke, A.; Misz, U.; Konrad, G.; Heinzel, A.; Klemp, D.; Wegener, R. Influence of Urban Air on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Vehicles - Long Term Effects of Air Contaminants in an Authentic Driving Cycle. J. Power Sources 2018, 400, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabadi, B.A.T.; Dinh, H.N.; Bender, G.; Weidner, J.W. Effect of System Contaminants on the Performance of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F1527–F1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Baturina, O.; Ramaker, D.; Farquhar, E.; St-Pierre, J.; Swider-Lyons, K. Chlorobenzene Poisoning and Recovery of Platinum-Based Cathodes in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 20328–20338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; St-Pierre, J. Acetylene Contamination Mechanisms in the Cathode of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Zhai, Y.; Angelo, M.S. Effect of Selected Airborne Contaminants on PEMFC Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 161, F280–F290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Bonville, L.; Maric, R. Analysis of H2/Air Polarization Curves: The Influence of Low Pt Loading and Fabrication Process. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F272–F284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; St-Pierre, J. Acetonitrile Contamination in the Cathode of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells and Cell Performance Recovery. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Ge, J.; Qi, J.; St-Pierre, J. Effect of Acetonitrile Contamination on Long-Term Degradation of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F3191–F3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.V.; St-Pierre, J. Study of the Acetonitrile Poisoning of Platinum Cathodes on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Spatial Performance Using a Segmented Cell System. J. Power Sources 2015, 293, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhai, Y.; St-Pierre, J. Effect of Contaminant Mixtures in Air on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance. J. Power Sources 2019, 413, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.V.; Artyushkova, K.; St-Pierre, J. Spatial Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance Under Bromomethane Poisoning. J. Power Sources 2017, 342, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Baturina, O.; Ramaker, D.; Farquhar, E.; St-Pierre, J.; Swider-Lyons, K. Bromomethane Contamination in the Cathode of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.V.; St-Pierre, J. Effects of Propylene, Methyl Methacrylate and Isopropanol Poisoning on Spatial Performance of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. J. Power Sources 2018, 378, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Park, J.H.; Kabir, S.; Neyerlin, K.C.; Kariuki, N.N.; Lv, H.; Stamenkovic, V.R.; Myers, D.J.; Ulsh, M.; Mauger, S.A. Impact of Catalyst Ink Dispersing Methodology on Fuel Cell Performance Using in-Situ X-ray Scattering. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 6417–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.M.K.; Krushnamurty, K.; Subrahmanyam, C. Surface Modification of Carbon Fabric for Isopropanol Removal from Gas Stream. Microelectron. Eng. 2014, 126, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Ge, J.; Zhai, Y.; Reshetenko, T.V.; Angelo, M. PEMFC Cathode Contamination Mechanisms for Several VOCs—Acetonitrile, Acetylene, Bromomethane, Iso-propanol, Methyl Methacrylate, Naphthalene and Propene. Electrochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 58, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-G.; Umeda, M.; Uchida, I. Cyclic Voltammetric Analysis of C1-C4 Alcohol Electrooxidations with Pt/C and Pt-Ru/C Microporous Electrodes. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; St-Pierre, J. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Cathode Contamination—Acetylene. J. Power Sources 2015, 279, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.V.; St-Pierre, J. Study of Acetylene Poisoning of Pt Cathode on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Spatial Performance Using a Segmented Cell System. J. Power Sources 2015, 287, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; St-Pierre, J. Impact of Operating Conditions on the Acetylene Contamination in the Cathode of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 372, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; St-Pierre, J. Tolerance and Mitigation Strategies of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Subject to Acetylene Contamination. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 17475–17479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.V.; St-Pierre, J. Study of the Aromatic Hydrocarbons Poisoning of Platinum Cathodes on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Spatial Performance Using a Segmented Cell System. J. Power Sources 2016, 333, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Virji, M.B.V. Cell Performance Distribution in a Low-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Stack during Propene Contamination. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2016, 46, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Zhai, Y.; Ge, J.; Angelo, M.; Reshetenko, T.; Molter, T.; Bonville, L.; Pasaogullari, U.; Collins, W.; Wessel, S. The Effect of Airborne Contaminants on Fuel Cell Performance and Durability. In DOE Hydrogen and Fuel Cells Program—2013 Annual Progress Report; DOE/GO-102013-4260; United States Department of Energy: Washington DC, USA, 2013; pp. V-1–V-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hydrogen Fuel—Product Specification—Part 2: Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell Applications for Road Vehicles, ISO 14687-2:2012(E), 1st ed.; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Viitakangas, J.; Ihonen, J.; Koski, P.; Reinikainen, M.; Aarhaug, T.A. Study of Formaldehyde and Formic Acid Contamination Effect on PEMFC. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F718–F727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malevich, D.; Halliop, E.; Peppley, B.A.; Pharoah, J.G.; Karan, K. Investigation of Charge-Transfer and Mass-Transport Resistances in PEMFCs with Microporous Layer Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, B216–B224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Manzo, S.; Chen, R.; Rama, P. Inductive Effect on the Fuel Cell Cathode Impedance Spectrum at High Frequencies. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivac, I.; Barbir, F. Inductive Phenomena at Low Frequencies in Impedance Spectra of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells—A Review. J. Power Sources 2016, 326, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setzler, B.P.; Fuller, T.F. A Physics-Based Impedance Model of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Exhibiting Low-Frequency Inductive Loops. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F519–F530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, I.A.; Bayer, M.H.; Wokaun, A.; Scherer, G.G. Impedance Response of the Proton Exchange Membrane in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, B783–B792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; St-Pierre, J.; Joly, A.; Goeke, R.; Datye, A.; Atanassov, P. Aging Studies of Pt/Glassy Carbon Model Electrocatalysts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, B485–B492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Ge, J.; St-Pierre, J. The Ionic Conductivity and Catalyst Activity Effects of Acetonitrile on Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 66, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, D.R.; Zhu, Z.; Mao, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Salmeron, M.; Somorjai, G.A. Mobility on the Reconstructed Pt(100)-hex Surface in Ethylene and in its Mixture with Hydrogen and Carbon Monoxide. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6903–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Dag, S.; Wang, L.-W.; Liu, Z.; Butcher, D.R.; Bluhm, H.; Salmeron, M.; Somorjai, G.A. Break-Up of Stepped Platinum Catalyst Surfaces by High CO Coverage. Science 2010, 327, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Bethune, K.; Bender, G.; Rocheleau, R. Analysis of the SO2 Contamination Effect on the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in PEMFCs by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, B524–B530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hsing, I.-M.; Leng, Y.-J.; Yue, P.-L. Model Interpretation of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Polarization Behavior of H2/CO Mixture Oxidation in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 4397–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.; Gülzow, E. Change of Electrochemical Impedance Spectra (EIS) with Time during CO-Poisoning of the Pt-Anode in a Membrane Fuel Cell. J. Power Sources 2004, 127, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethune, K.; St-Pierre, J.; LaManna, J.M.; Hussey, D.S.; Jacobson, D.L. Contamination Mechanisms of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Fells—Mass Transfer Overpotential Origin. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. In preparation.
- Weber, A.Z.; Kusoglu, A. Unexplained Transport Resistances for Low-Loaded Fuel-Cell Catalyst Layers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17207–17211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkanand, A.; Mathias, M.F. The Priority and Challenge of High-Power Performance of Low-Platinum Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; St-Pierre, J.; Zhai, Y. PEMFC Cathode Catalyst Contamination Evaluation with a RRDE—Acetylene. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 133, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; St-Pierre, J.; Zhai, Y. PEMFC Cathode Catalyst Contamination Evaluation with a RRDE—Acetonitrile. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 134, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; St-Pierre, J.; Zhai, Y. PEMFC Cathode Catalyst Contamination Evaluation with a RRDE—Methyl Methacrylate. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18351–18361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; St-Pierre, J.; Zhai, Y. PEMFC Cathode Catalyst Contamination Evaluation with a RRDE—Propene and Naphthalene. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 138, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatoń, M.; Rozière, J.; Jones, D.J. Current Understanding of Chemical Degradation Mechanisms of Perfluorosulfonic Acid Membranes and their Mitigation Strategies: A Review. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 409–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Zhai, Y.; Ge, J. Relationships between PEMFC Cathode Kinetic Losses and Contaminants’ Dipole Moment and Adsorption Energy on Pt. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F247–F254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J. PEMFC Contamination Model: Neutral Species Sorption by Ionomer. Electrochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 41, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Dale, J.; Ayato, Y.; Asbjørnsen, O.A.; Yuasa, M.; Sekine, I. Unprecedented Effect of Impurity Cations on the Oxygen Reduction Kinetics at Platinum Electrodes Covered with Perfluorinated Ionomer. Langmuir 1999, 15, 8490–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Ayato, Y.; Dale, J.; Yuasa, M.; Sekine, I.; Asbjornsen, O.A. Oxygen Reduction Kinetics at Platinum Electrodes Covered with Perfluorinated Ionomer in the Presence of Impurity Cations Fe3+, Ni2+ and Cu2+. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 3255–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Ayato, Y.; Satou, H.; Yuasa, M.; Sekine, I. The Effect of Impurity Cations on the Oxygen Reduction Kinetics at Platinum Electrodes Covered with Perfluorinated Ionomer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 6980–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Satou, H.; Yuasa, M. Effects of Additives on Oxygen Reduction Kinetics at the Interface between Platinum and Perfluorinated Ionomer. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, J.; Wetton, B.; Zhai, Y.; Ge, J. Liquid Water Scavenging of PEMFC Contaminants. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, E3357–E3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).