Multitarget Molecular Hybrids of Cinnamic Acids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
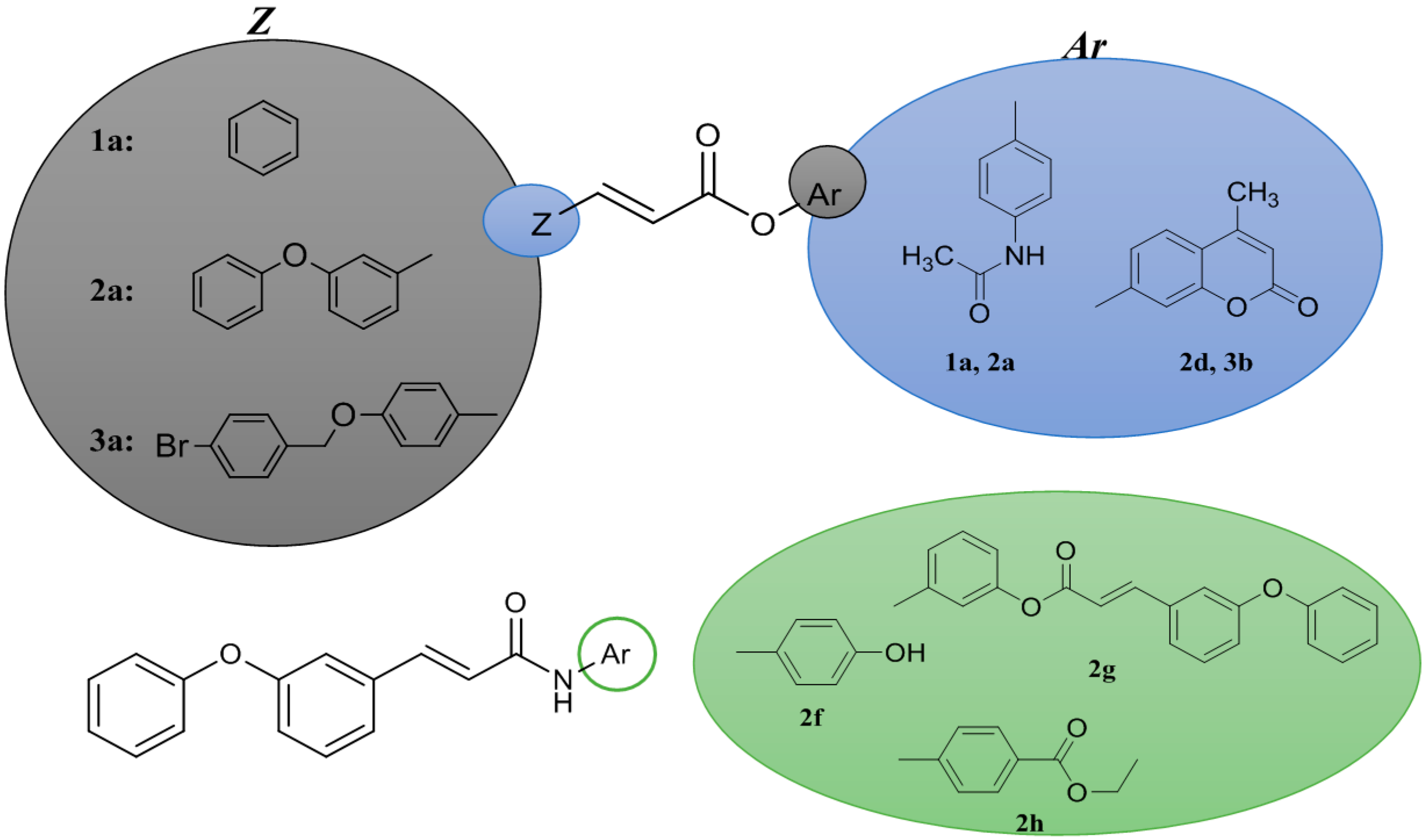
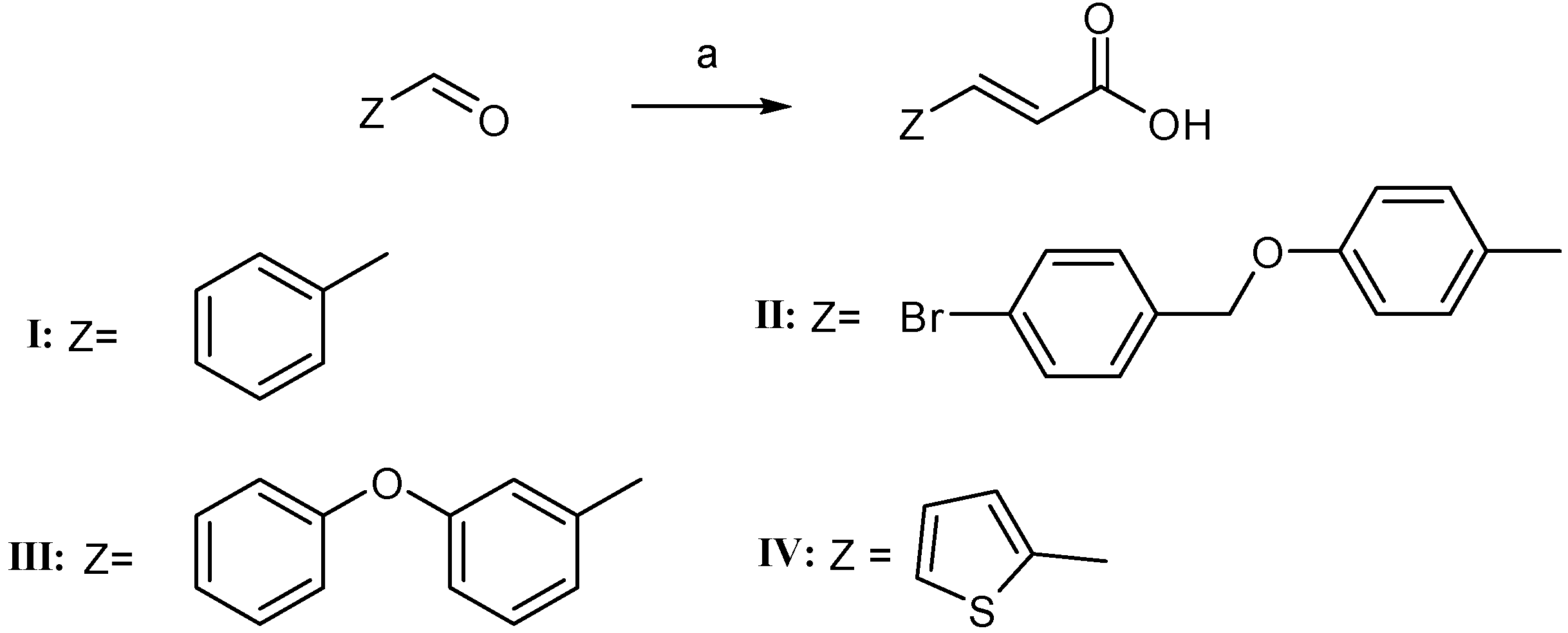

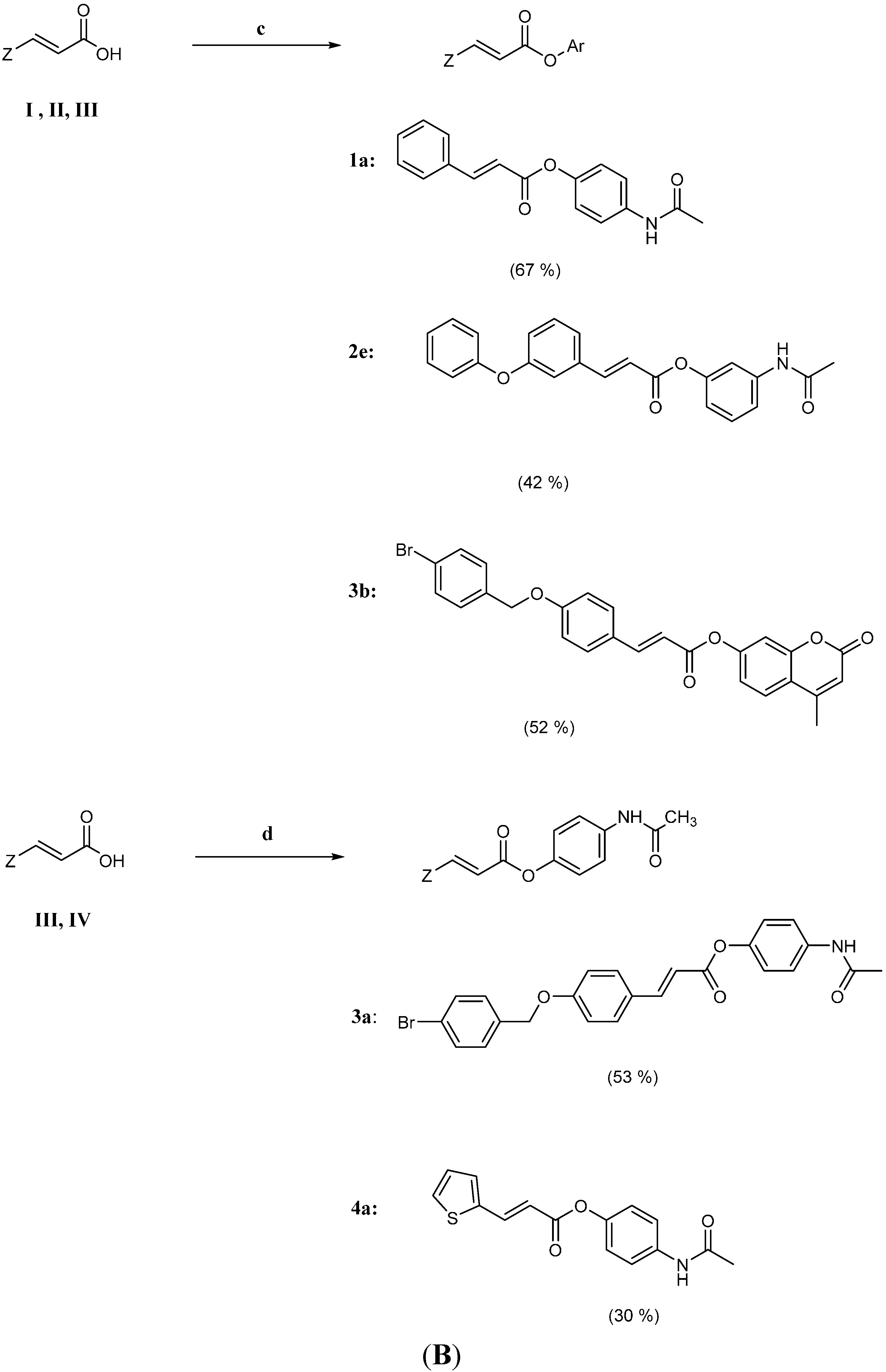
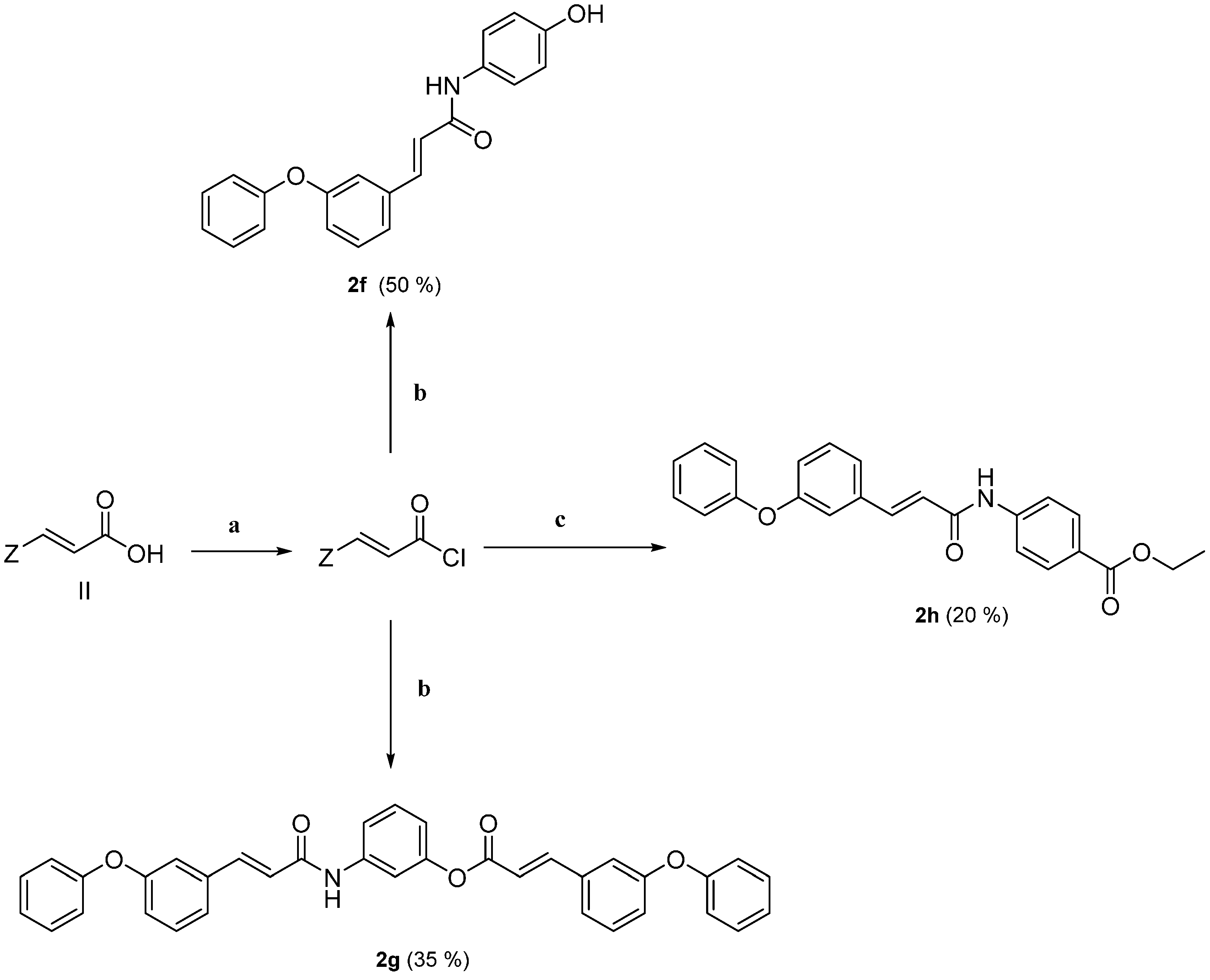
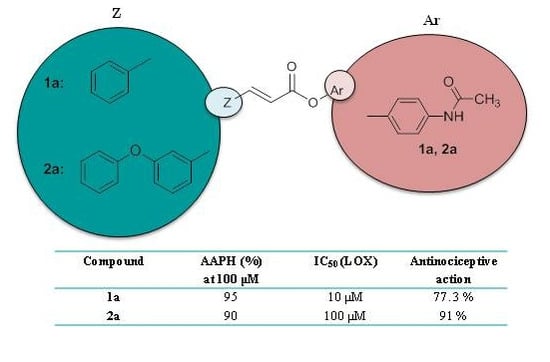
2.2. Physicochemical Studies
n = 9, r = 0.914, r2 = 0.836, q2 = 0.663, s = 0.271, F1,7 = 35.75, α = 0.01
| Compounds | RM (±S.D.) a | AAPH % b,c | IC50 μM c LOX Inh. | IC50 μM/% c Trypsin Inh. | % ANA (0.01 mmol/0.1 kg) d | % ICPE (0.01 mmol/1 kg) e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I [18] | −0.485 ± 0.044 | 78 | 56 μM | 55 μM | 60.2 * | nt |
| II [15] | −0.41 ± 0.026 | 84 | 66 μM | na | 67 * | 41.6 * |
| III [15] | −0.17 ± 0.016 | 84 | 89 μM | na | 15.3 * | 44.4 * |
| IV [13,14,15,16,17] | −0.56 ± 0.019 | 60 | 98 μM | na | nt | 42.7 * |
| 1a | −0.725 ± 0.009 | 95 | 10 μM | 34% b | 77.3 ** | nt |
| 2a | 0.276 ± 0.006 | 90 | 100 μM | 10 μM | 91 ** | 36.5 ** |
| 2b | −0.661± 0.008 | 100 | 100 μM | 100 μM | nt | nt |
| 2c | 0.444 ±0.008 | 93 | 20% b | 10 μM | 70.4 ** | nt |
| 2d | 0.558 ± 0.040 | 97 | 74 μM | 10 μM | 66 ** | nt |
| 2e | 0.407 ± 0.015 | 60 | 0.34 μM | na | 98.1 ** | nt |
| 2f | −0.116 ± 0.003 | 100 | na | 26 μM | nt | nt |
| 2g | 1.092 ± 0.044 | 60 | 72 μM | 43.6 μM | nt | nt |
| 2h | 0.399 ± 0.045 | 64 | 100 μM | 50 μM | nt | nt |
| 3a | −0.24 ± 0.009 | 96 | 55 μM | 100 μM | 52 ** | nt |
| 3b | −0.602 ± 0.01 | 90 | 50 μM | 5 μM | nt | nt |
| 4a | −0.826 ± 0.05 | 95 | 16% b | na | nt | nt |
| NDGA | nt | nt | 51.5 μM | nt | nt | nt |
| Trolox | nt | 63 | nt | nt | nt | nt |
| Coumarin | nt | nt | nt | 13% | nt | nt |
| 4-HC | nt | 100 | nt | na | nt | 62 * |
| 7-HC | nt | 92 | nt | 100 μM | nt | nt |
| Hymechromone | nt | 93 | nt | 60% | nt | nt |
| Salicylic acid | nt | nt | nt | 53.6% | nt | nt |
| Paracetamol | nt | 91 | 82 μM | na | 66 * | 21 * |
| p-AP | nt | 99 | nt | 87% | nt | nt |
| m-AP | nt | 95 | nt | 90% | nt | nt |
| Benzocaine | nt | 25 | nt | 28% | nt | nt |
| Indomethacin | nt | nt | nt | nt | nt | 47 * |
| Compounds | Clog P a | MR-Ar |
|---|---|---|
| I | 2.24 | - |
| II | 3.28 | - |
| III | 4.34 | - |
| IV | 5.38 | - |
| 1a | 3.28 | 3.92 |
| 2a | 5.38 | 3.92 |
| 2b | 6.02 | 4.06 |
| 2c | 5.89 | 4.06 |
| 2d | 6.39 | 4.52 |
| 2e | 5.54 | 4.07 |
| 2f | 5.10 | 2.74 |
| 2g | 10.14 | 9.99 |
| 2h | 6.73 | 4.54 |
| 3a | 5.83 | 3.92 |
| 3b | 6.84 | 4.52 |
| 4a | 2.93 | 3.92 |
2.3. Biological Evaluation Antioxidant, Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity
n = 10, r = 0.972, r2 = 0.946, s = 0.016, F1,8 = 140, α = 0.01
n = 7, r = 0.910, r2 = 0.82, s = 0.601, F1,5 = 3.45, α = 0.1
n = 10, r = 0.858, r2 = 0.736, s = 0.115, F2,7 = 1.94, α = 0.1
| Score | Movement in Hindlimb |
|---|---|
| 0 | No movement |
| 1 | Mild movement |
| 2 | Walking with mild deficit |
| 3 | Nearly normal |
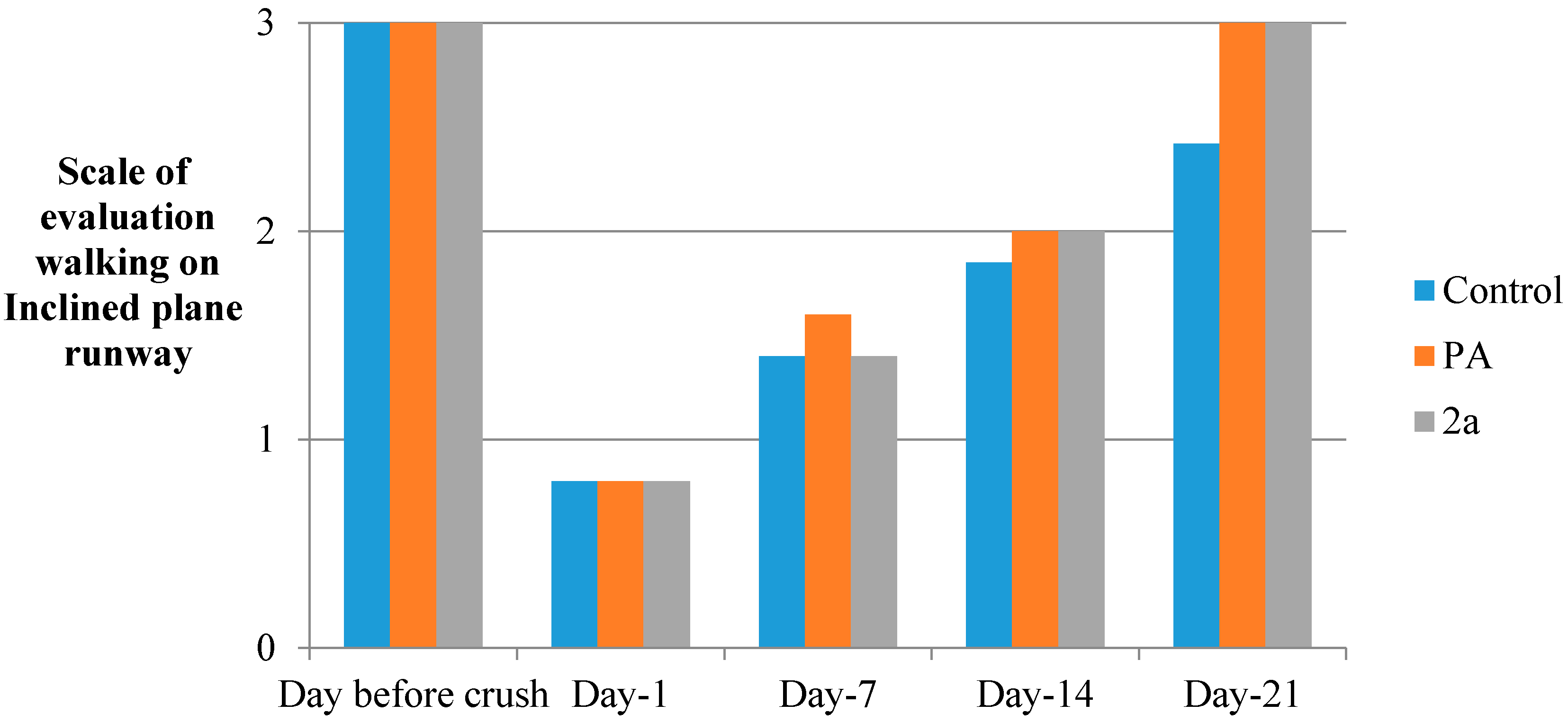
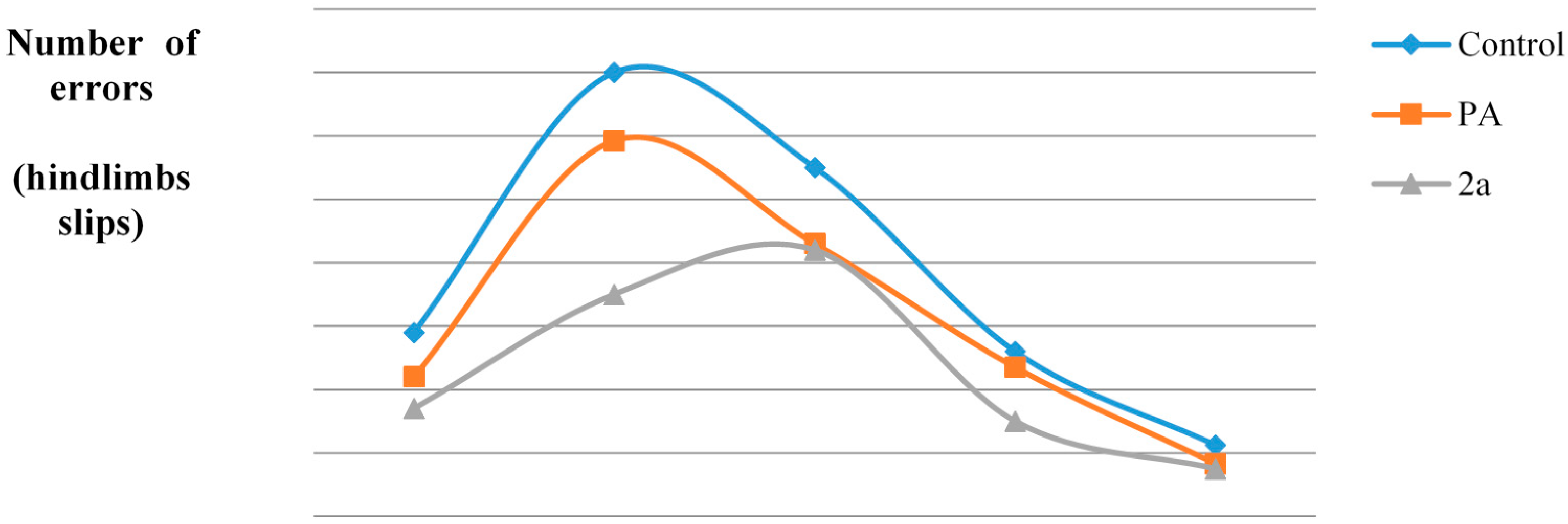
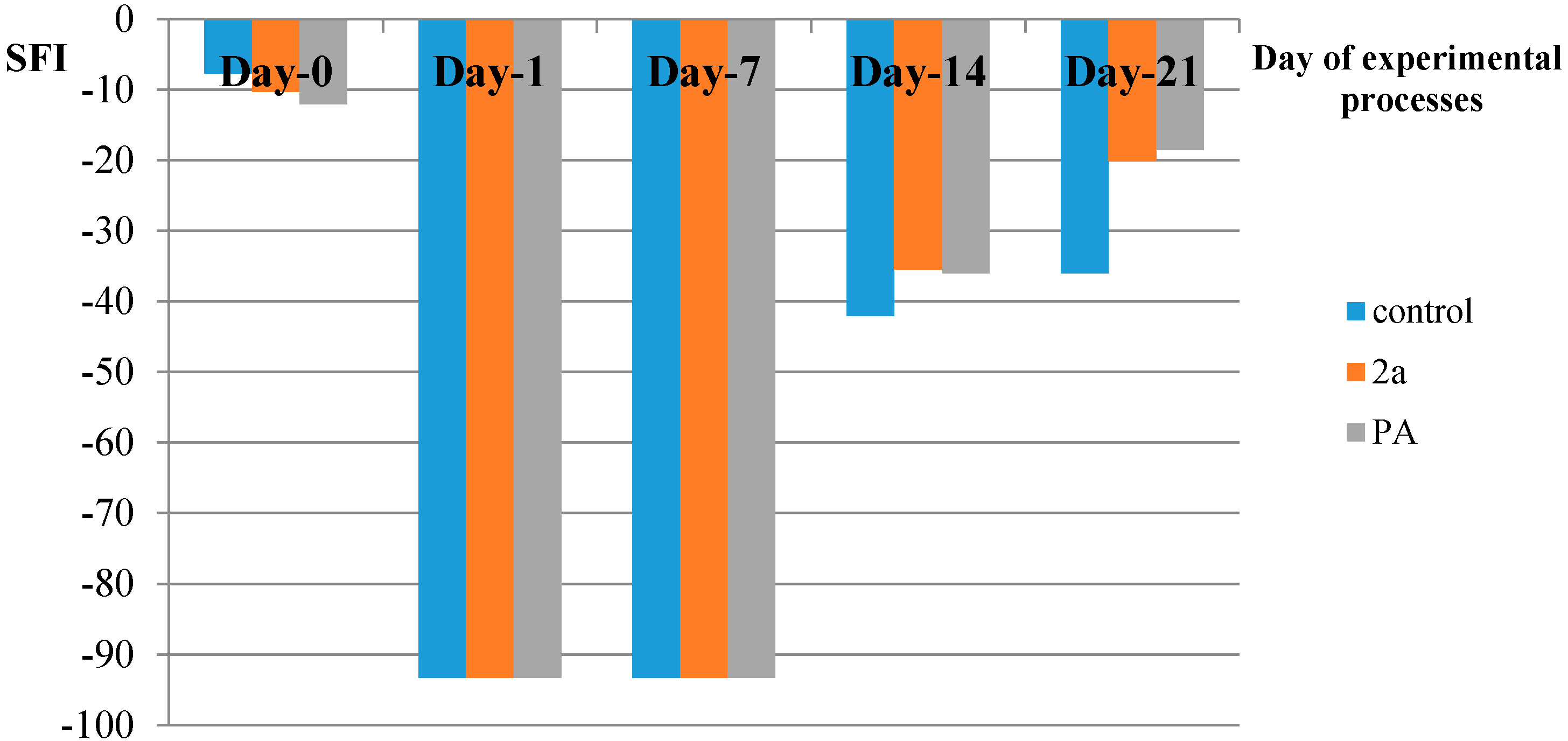
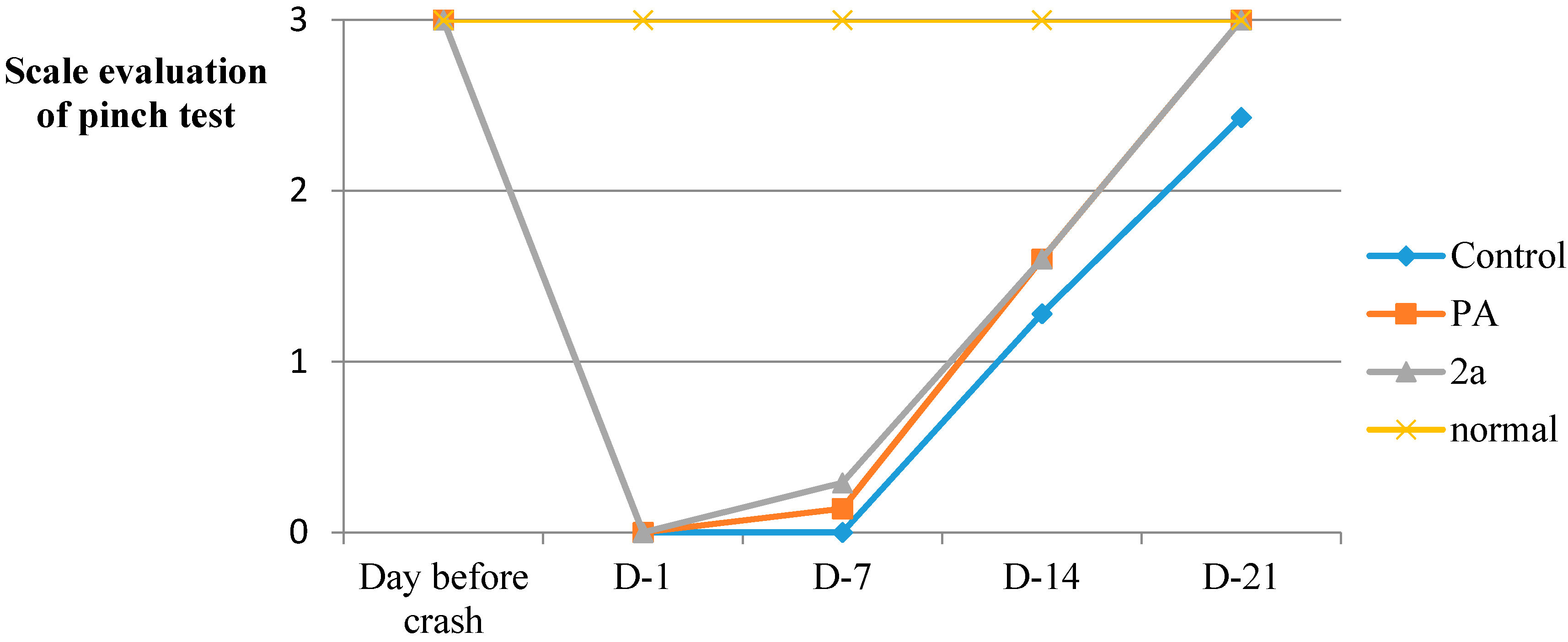
| SFI | Day before Crash | Day-1 | Day-7 | Day-14 | Day-21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | −7.67 | −93.3 | −93.3 | −42 | −36 |
| PA | −12 | −93.3 | −93.3 | −36 | −18.5 |
| 2a | −10.26 | −93.3 | −93.3 | −35.45 | −20.06 |
2.4. Computational Studies
2.4.1. Computational Methods, Docking Simulations
2.4.2. Molecular Docking Studies on Soybean Lipoxygenase
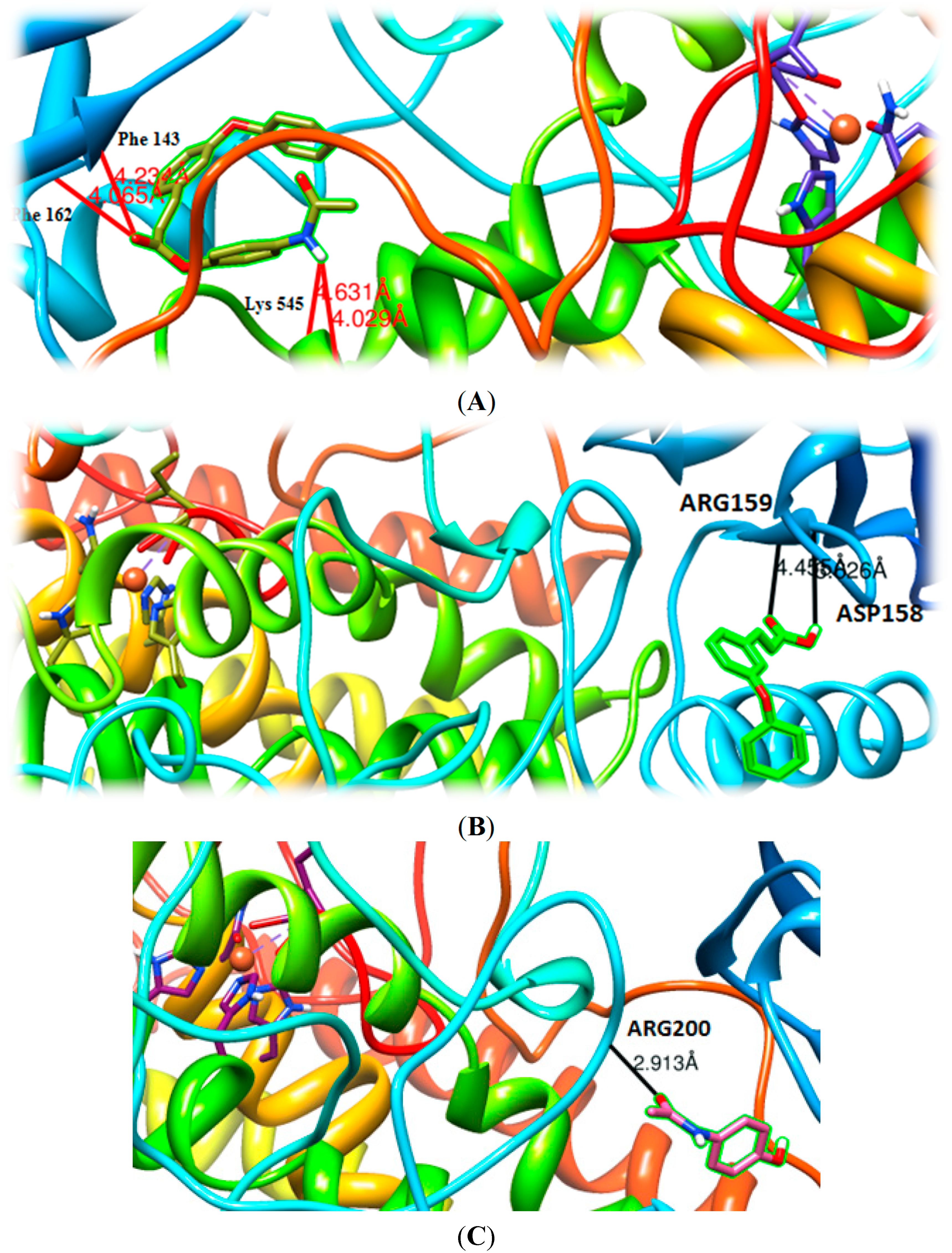
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Chemistry General Procedure
3.2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Hybrid Cinnamic Esters 2a–d (through the Formation of Cinnamoyl Chloride)]
3.2.2. One Pot Synthesis of Hybrid Cinnamic Esters 3a and 4a
3.2.3. One Pot Synthesis of Hybrid Cinnamic Esters 1a, 2e and 3b
3.2.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Hybrid Cinnamic Amides 2f, 2g
3.2.5. Synthesis of Hybrid Cinnamic Amide 2h
3.3. Physicochemical Studies
Determination of RM Values
3.4. Biological in Vitro Assays
3.4.1. TLC Screening for Free Radical Scavengers
3.4.2. Inhibition of Linoleic Acid Lipid Peroxidation
3.4.3. Soybean Lipoxygenase Inhibition Study in Vitro
3.4.4. Inhibition of Trypsin Induced Proteolysis in Vitro
3.4.5. In Vitro Esterase Activity on Hybrids 2a and 2b
3.4.6. In Vitro Stability of Hybrid Molecule 2a under Acidic and Basic Conditions
3.5. In Vivo Assays
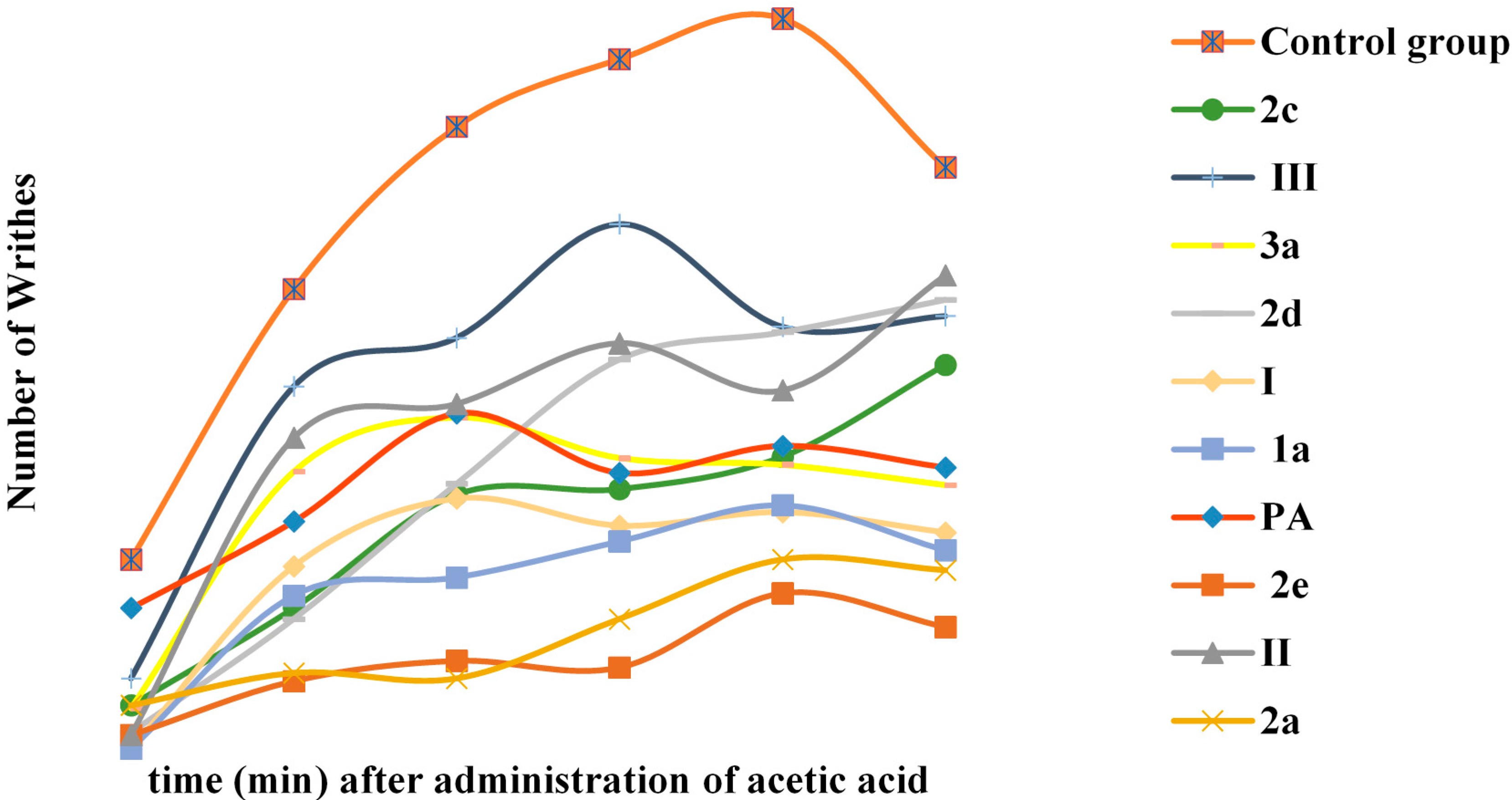
3.5.1. Antinociceptive Screen
3.5.2. Inhibition of the Carrageenin-Induced Edema
3.5.3. Induction of Sciatic Nerve Injury
3.5.4. Drug and Time of Administration
3.5.5. Locomotor Testing
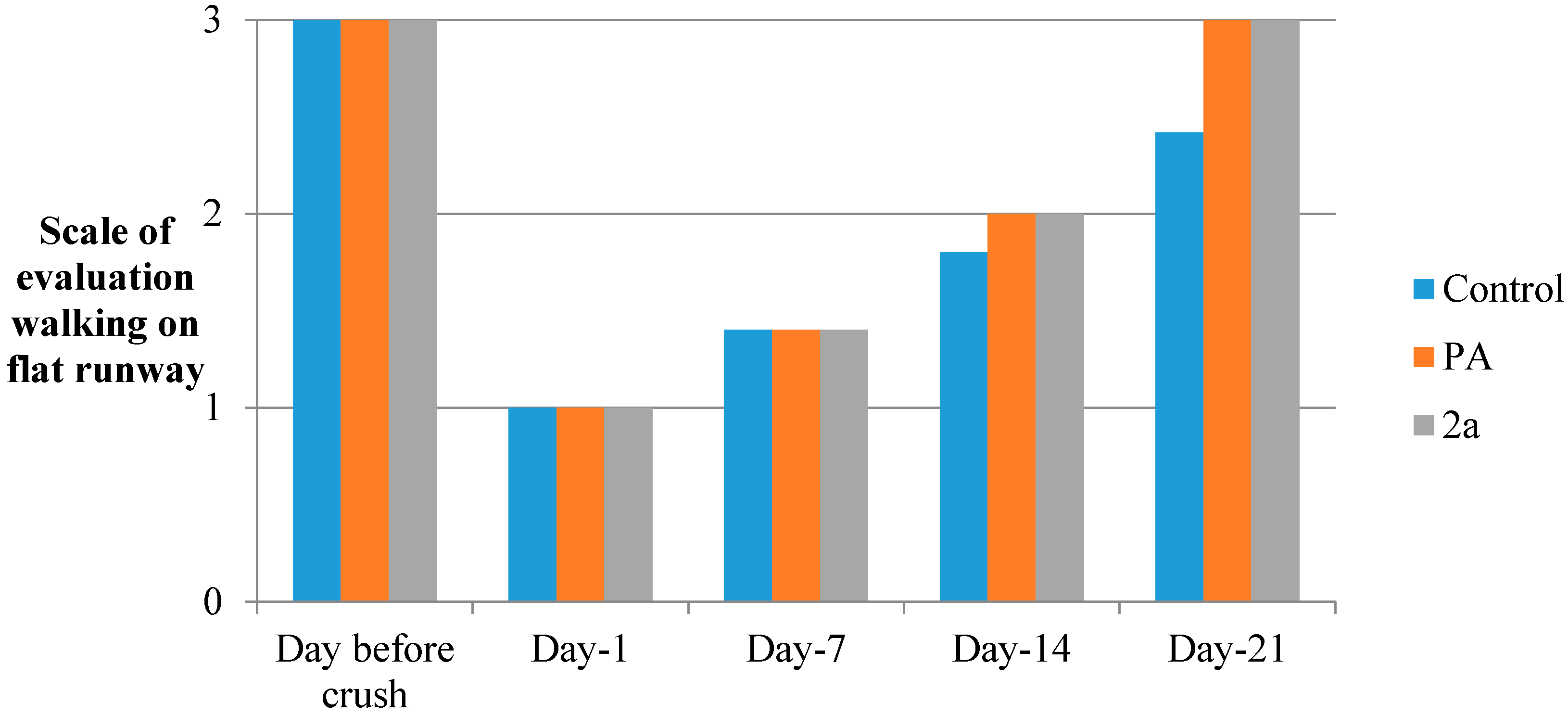
3.5.6. Flat Runway
3.5.7. Inclined Plane Runway
3.5.8. Grid Runway
3.5.9. Sciatic Functional Index (SFI)
- (i)
- print length (PL): distance from the heel to the third toe,
- (ii)
- toe spread (TS) distance from the first to the fifth toe on both sides and
- (iii)
- intermediate toe spread (ITS) the distance between the middle of the second and fourth toe
3.5.10. Sensory Testing Pinch Test
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Abbreviation
| AAPH | 2,2-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride |
| ABTS | 2,2' azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| ACPYPE | AnteChamber PYthon Parser interface |
| BOP | O-(benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N',N''-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate |
| clog P | Theoretically calculated lipophilicity |
| DPPH | 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical |
| ET | electron transfer |
| HAT | hydrogen atom transfer |
| 4-HC | 4-hydroxycoumarin |
| 7-HC | 7-hydroxycoumarin |
| LOX | Lipoxygenase |
| NDGA | nordihydroguaiaretic acid |
| m-AP | m-aminophenol |
| p-AP | p-aminophenol |
| RPTLC | Reverse-phase thin layer chromatography |
| PA | paracetamol |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sova, M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of cinnamic acid derivatives. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernini, R.; Mincione, E.; Barontini, M.; Provenzano, G.; Setti, L. Obtaining 4-vinylphenols by decarboxylation of natural 4-hydroxycinnamic acids under microwave irradiation. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 9663–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.S.; Shin, J.C. Characterization of antioxidant alkaloids and phenolic acids from anthocyanin-pigmented rice (Oryza sativa cv. Heugjinjubyeo). Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, D.P.; Castro, F.O.; Alves, A.P.N.N.; Pessoa, C.; Moraes, M.O.; Silveira, E.R.; Lima, M.A.S.; Elmiro, F.J.M.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. In vivo growth-inhibition of Sarcoma 180 by piplartine and piperine, two alkaloid amides from Piper. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2006, 39, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Ahmad, S.; Ajaz Rasool, S.; Asad Sayeed, S.; Siddiqi, R. Antibacterial activity directed isolation of compounds from Onosma hispidum. Microbiol. Res. 2006, 161, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardini, M.; D’Aquino, M.; Tomassi, G.; Gentili, V.; di-Felice, M.; Scaccini, C. Inhibition of human low-density lipoprotein oxidation by caffeic acid and other hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshihara, Y.; Neichi, T.; Murota, S.; Lao, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Tatsuno, T. Caffeic acid is a selective inhibitor for leukotriene biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 792, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morphy, R.; Kay, C.; Rankovic, Z. From magic bullets to designed multiple ligands. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morphy, R.; Rankovic, Z. Designed multiple ligands. An emerging drug discovery paradigm. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 6523–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of aryl-acetic and hydroxamic acids as novel lipoxygenase inhibitors. Med. Chem. 2006, 2, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Synthesis and pharmacochemical evaluation of novel aryl-acetic acid inhibitors of lipoxygenase, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 5819–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Geromichalos, G.; Papageorgiou, A. Anticancer activity and quantitative-structure activity relationship (QSAR) studies of a series of antioxidant/anti-inflammatory aryl-acetic and hydroxamic acids. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 74, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Litinas, K.; Nicolotti, O.; Carotti, A. Design, synthesis and pharmacobiological evaluation of novel acrylic acid derivatives acting as lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitors with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Litinas, K.; Geromichalos, G. Novel cinnamic acid derivatives as antioxidant and anticancer agents: Design, synthesis and modeling studies. Molecules 2014, 19, 9655–9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontiki, E.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Lipoxygenase inhibitors: A comparative QSAR study review and evaluation of new QSARs. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 39–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNulty, J.; Steere, J.A.; Wolf, S. The ultrasound promoted Knoevenagel condensation. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 8013–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sova, M.; Perdih, A.; Kotnik, M.; Kristan, K.; Rizner, T.L.; Solmajerb, T.; Gobec, S. Flavonoids and cinnamic acid esters as inhibitors of fungal 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: A synthesis, QSAR and modelling study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 7404–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbag, V.R.; Crider, M.A.; Gohkale, R.; Harpalani, A.; Dick, R.M. Ester and amide prodrugs of ibuprofen and naproxen: Synthesis, anti-inflammatory activity, and gastrointestinal toxicity. J. Pharm. Sci. 1992, 81, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.J. Fundamentals and Applications in Chemistry and Biology. In Exploring QSAR; Heller, S.R., Ed.; ACS Professional Reference Book: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- BioByte Home Page. Available online: http://www.biobyte.com/ (accessed on 1 June 2012).
- C-QSAR Database; Biobyte Corp: Claremont, CA, USA. Available online: http://www.biobyte.com (accessed on 1 December 2014).
- Flohe, L.; Beckman, R.; Giertz, H.; Loschen, G. Oxygen-centered free radicals as mediators of inflammation. In Oxidative Stress; Sies, H., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1985; pp. 403–435. [Google Scholar]
- Niki, E. Do antioxidants impair signaling by reactive oxygen species and lipid oxidation products? FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3767–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liegois, C.; Lermusieau, G.; Colin, S. Measuring antioxidant efficiency of wort, malt, and hops against the 2,2-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride-induced oxidation of an aqueous dispersion of linoleic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, S.W.; Stockley, R.A. Leukotriene B4. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 30, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, K. 5-Lipoxygenase and 12-lipoxygenase: Attractive targets for the development of novel antipsoriatic drugs. Arch. Pharm. 1994, 327, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, L.O.; Selitto, J.J. A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1957, 111, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siegmund, E.A.; Cadmus, R.A.; Lu, G. A method for evaluating both non-narcotic and narcotic analgesics. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 1957, 95, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.Y. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents. In Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry; Wolf, M.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Volume 1, pp. 1217–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Flower, R.J.; Moncada, S.; Vane, J.R. Drug therapy of inflammation. In The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 7th ed.; Goodman Gilman, A., Goodman, L.S., Rall, T.W., Murad, F., Eds.; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 674–715. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Hue, J.; Li, S. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs promote axon regeneration via RhoA inhibition. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4154–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara-Lemarroy, C.R.; Cabello-Garcia, A.J.; Guzman-de la Garza, E.J.; Barrera-Oranday, E.A.; Garcia-Tamez, A.; Fernandez-Garza, N.E. Celecoxib accelerates functional recovery after sciatic nerve crush in the rat. J. Brachial Plex. Peripher. Nerve Inj. 2008, 26, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Blough, E.R.; Wu, M. Acetaminophen: beyond pain and fever-relieving. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrone, B.; Polenzani, L.; de Santi, S.; Moreci, W.; Guglielmotti, A. Paracetamol reduces neuropathic pain-like behaviour in rats by potentiating serotonergic neurotransmission. IJIB 2007, 1, 196–205. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoukranidou, D.; Kalamara, T.V.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Effects of acetaminophen on motor and sensory functions in adult rats after sciatic nerve crush. J. Analg. 2013, 1, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lashley, K.S. Basic neural mechanisms in behaviour. Ann. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel-Bagden, E.; Dai, H.N.; Bregman, B.S. Methods to assess the development and recovery of locomotor function after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp. Neurol. 1993, 119, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmalbruch, H. Fiber composition of the rat sciatic nerve. Anat. Rec. 1986, 215, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ChemDraw Ultra_v.12; CambridgeSoft: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986–2009. Available online: http://www.cambridgesoft.com/software/chemDraw/ (accessed on 26 February 2013).
- OpenBabel, version 2.2.3. OELib Cheminformatics. Available online: http://sourceforge.net/projects/openbabel (accessed on 10 February 2010).
- USCF CHIMERA; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1994. Available online: http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera (accessed on 10 February 2010).
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, B.; Kutzner, C.; van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 435–447. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2006, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Autodock Vina, version 1.1.1; The Scripps Research Institute: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010.
- Sargis Pallakyan, PyRx-Python Prescription, version 0.5; The Scripps Research Institute: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008–2010. Available online: http://pyrx.scripps.edu/ (accessed on 10 February 2010).
- Minor, W.; Steczko, J.; Stec, B.; Otwinowski, Z.; Bolin, J.T.; Walter, R.; Axelrod, B. Crystal structure of soybean lipoxygenase L-1 at 1.4 Å resolution. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 10687–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H. Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2003, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsori, A.M.; Chatzopoulou, M.; Dimas, K.; Kontogiorgis, C.; Patsilinakos, A.; Trangas, T.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Curcumin analogues as possible anti-proliferative & anti-inflammatory agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 2722–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittert, L.W.; Caldwell, H.C.; Adams, H.J.; Irwin, G.M.; Swintosky, J.V. Acetamidophen prodrugs I, synthesis, physicochemical properties and analgesic activity. J. Pharm. Sci. 1968, 57, 774–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Bariamis, S.; Militsopoulou, M.; Athanassopoulos, C.M.; Papaioannou, D. Trioxsalen derivatives with lipoxygenase inhibitory activity. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekker, R.F. The Hydrophobic Fragmental Constant; Pharmacochemistry Library; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Michaelidou, A.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Matsini, I.; Tsitsogianni, E. Heterocyclic aryl(phenyl)acetic acid and aryl acetohydroxamic acids as antiinflammatory-antioxidant agents and inhibitors of lipoxygenase and serine proteases. Med. Chem. 2007, 3, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Rekka, E.; Hadjipetrou-Kourounakis, L.; Kourounakis, P. Synthesis and biological studies of some novel antiinflammatory aryl-hydroxy-amino-ketones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1991, 26, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medinaceli, L.; Freed, W.J.; Wyatt, R.J. An index of the functional condition of rat sciatic nerve based on measurements made from walking tracks. Exp. Neurol. 1982, 77, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramoff, M.D.; Magalhaes, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Image processing with Image. J. Biophotonics Int. 2004, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, J.R.; Mackinnon, S.E.; Hunter, D.A. Functional evaluation of complete sciatic, peroneal and posterior tibial nerve lesions in the rat. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1989, 83, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1a, 2a–h, 3a–b and 4a are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peperidou, A.; Kapoukranidou, D.; Kontogiorgis, C.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Multitarget Molecular Hybrids of Cinnamic Acids. Molecules 2014, 19, 20197-20226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220197
Peperidou A, Kapoukranidou D, Kontogiorgis C, Hadjipavlou-Litina D. Multitarget Molecular Hybrids of Cinnamic Acids. Molecules. 2014; 19(12):20197-20226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220197
Chicago/Turabian StylePeperidou, Aikaterini, Dorothea Kapoukranidou, Christos Kontogiorgis, and Dimitra Hadjipavlou-Litina. 2014. "Multitarget Molecular Hybrids of Cinnamic Acids" Molecules 19, no. 12: 20197-20226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220197
APA StylePeperidou, A., Kapoukranidou, D., Kontogiorgis, C., & Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. (2014). Multitarget Molecular Hybrids of Cinnamic Acids. Molecules, 19(12), 20197-20226. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220197