Sustainable Household Behaviors: Consumption and Mobility
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Urban and Rural Development".
Viewed by 74455Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
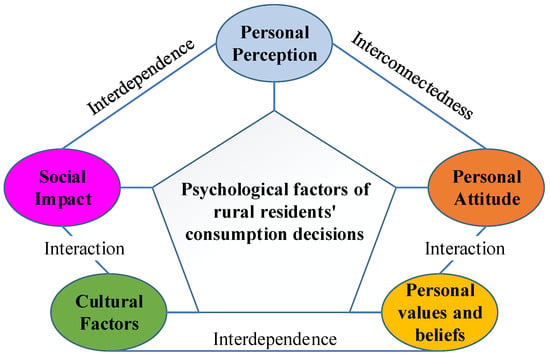
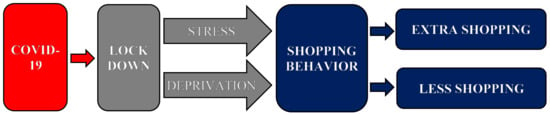
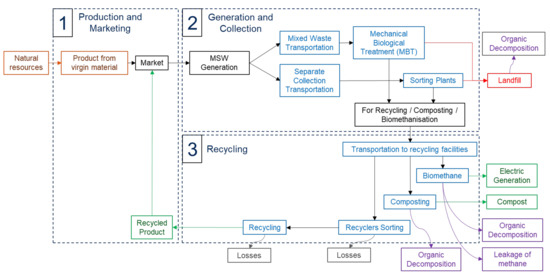
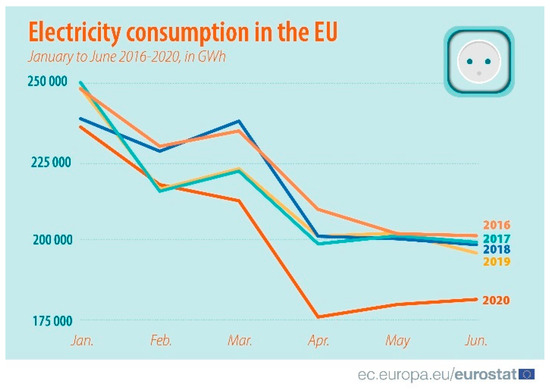
It is clear that environmental impacts from household activities have grown in recent decades and are expected to intensify in the future. Households, as a group, are not the largest contributor to the most sustainable pressures, but their impact is significant and will almost certainly intensify. In this context, it is essential to better understand household environmental behaviors by analyzing the factors underlying households’ choices. This Special Issue is dedicated to the sustainable day-to day actions of households in two specific areas: consumption and mobility. A better understanding of the determinants of both consumption and mobility decisions will provide useful insights for policy makers. In particular, the Special Issue addresses questions such as i) the effects of sociodemographic, attitudinal, and contextual factors in sustainable household behaviors, with respect to consumption (food, energy, water, waste, etc.) and mobility (public and private commuting, school-to-home transportation, recreational mobility, etc.) and ii) households’ responsiveness to various kinds of environmental policy measures, addressed in these two areas. Thus, two crucial aspects in the debate over sustainable consumption and mobility are the importance of behavioral changes, and the role of government in providing essential infrastructure for the population to engage in more sustainable lifestyles. Most countries have implemented policies to reduce the environmental impacts from household activities, but most of these policies have resulted in only limited changes in behavior, with overall results appearing to be modest. Governments are working to help households to reduce their environmental impacts, with policies that promote sustainable behaviors, by examining the efficacy of different types of policy instruments and by identifying combinations of instruments for promoting more sustainable behaviors. This Special Issue intends, from a multidisciplinary approach, to provide new insights to policy makers for the design of environmental policies in consumption and mobility, with the primary objective being to change individual behaviors.
Prof. José Alberto Molina
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- household economics
- population behaviors
- consumption
- mobility