- Review
The Stiff Side of Cancer: How Matrix Mechanics Rewrites Non-Coding RNA Expression Programs
- Alma D. Campos-Parra,
- Jonathan Puente-Rivera and
- Macrina Beatriz Silva-Cázares
- + 4 authors
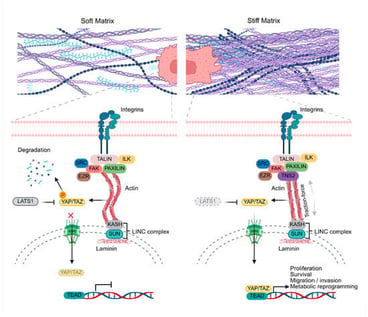
Extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffening is a defining biophysical feature of solid tumors that reshape gene regulation through mechanotransduction. Increased collagen crosslinking and stromal remodeling enhance integrin engagement, focal-adhesion signaling and force transmission to the nucleus, where key hubs such as lysyl oxidase (LOX), focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and the Hippo co-activators YAP1 and TAZ (WWTR1) promote proliferation, invasion, stemness and therapy resistance. Here, we synthesize evidence that quantitative changes in matrix stiffness remodel the miRNome and lncRNome in both tumor and stromal compartments, including extracellular vesicle cargo that reprograms metastatic niches. To address heterogeneity in experimental support, we classify mechanosensitive ncRNAs into studies directly validated by stiffness manipulation (e.g., tunable hydrogels/AFM) versus indirect associations based on mechanosensitive signaling, and we summarize physiological versus pathophysiological stiffness ranges across tissues discussed. We further review competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks converging on mechanotransduction nodes and ECM remodeling enzymes, and discuss translational opportunities and challenges, including targeting mechanosensitive ncRNAs, combining ncRNA modulation with anti-stiffening strategies, delivery barriers in dense tumors, and the potential of circulating/exosomal ncRNAs as biomarkers. Overall, integrating ECM mechanics with ncRNA regulatory circuits provides a framework to identify feed-forward loops sustaining aggressive phenotypes in rigid microenvironments and highlights priorities for validation in physiologically relevant models.
18 February 2026



![(A): Overview of the current understanding of TR evolution in Metazoa (image adapted from [2]). The majority of known TRs in the kingdom of Animalia is of the H/ACA box snoRNA sub-type and transcribed by RNA Polymerase II (RNAP II), indicated in blue. Interestingly, in Arthropoda, and more precisely in the order Hymenoptera, RNA Polymerase III (RNAP III) dependent TRs are reported [1] while in Lepidoptera, RNAP II seems to be responsible for TR transcription [4], indicated in yellow and green, respectively. Corresponding TRs do not contain the H/ACA box feature and are comparably small with respect to other metazoan TRs. (B): Length distribution of recently identified TRs in insects [1] (left) compared to known TRs in other Metazoa (right), based on the Telomerase Database [6], last update August 2025.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/ncrna/ncrna-12-00006/article_deploy/html/images/ncrna-12-00006-g001-550.jpg)