- Article
Extracellular Small RNAs in Human Milk: Molecular Profiles, Stability and Fragment-Specific Responses in Cell-Based Assays
- Clara Claus,
- Carla Borini Etichetti and
- Silvana V. Spinelli
- + 4 authors
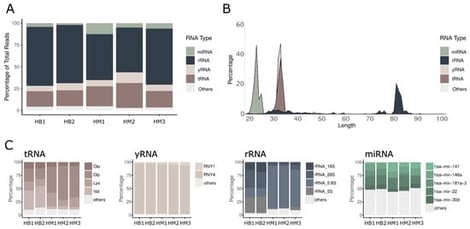
Background/Objectives: Human milk is a complex biological fluid containing not only macro- and micronutrients but also diverse bioactive molecules, including extracellular RNAs. Although RNA has been detected in milk for decades, only a subset of RNA species has been characterized in detail, and abundant families such as tRNA-, yRNA-, and rRNA-derived fragments remain underexplored. This study aimed to define the composition, fragmentation patterns, stability, and exploratory functional activity of these highly abundant RNAs in human milk. Methods: We performed small RNA sequencing on skim milk samples and analyzed the resulting profiles in comparison with publicly available milk and biofluid datasets. RNA stability assays, Northern blotting, and RT-qPCR were conducted to validate RNA abundance and degradation kinetics. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) and non-vesicular fractions were analyzed to determine the subcellular distribution of RNA species. Exploratory functional assays using synthetic RNA fragments were carried out to assess their ability to modulate cellular responses in vitro. Results: Human milk was found to be highly enriched in small RNA fragments derived from tRNA, yRNA, and rRNA, dominated by a limited set of discrete sequences. These profiles were highly reproducible across independent datasets and distinct biofluids. Orthologal validation assays confirmed their abundance and stability, with RNA levels exceeding those of serum by over two orders of magnitude. Full-length transcripts were enriched in EVs, whereas shorter fragments predominated in the non-vesicular fraction. Synthetic milk-derived exRNAs showed detectable pro-survival activity under stress conditions in vitro. Conclusions: This study reveals that human milk carries a limited set of highly abundant stable sRNA molecules, primarily derived from tRNAs, yRNAs, and rRNAs. These findings provide new insights into the RNA cargo of human milk and offer preliminary evidence that selected sRNA fragments can modulate cellular stress responses in in vitro models.
9 February 2026



![miRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II as primary transcripts (pri-miRNAs), which are then processed in the nucleus by the enzyme Drosha along with its cofactor DGCR8 into precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs). These pre-miRNAs are transported to the cytoplasm via exportin 5, where they associate with the Dicer/TRBP complex and are cleaved into short double-stranded RNA molecules. One strand of this miRNA duplex is then incorporated into the Argonaute protein to form the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). RISC then binds to specific target mRNAs, leading to their degradation, destabilization, or inhibition of translation. In addition to the canonical pathway, miRNAs can be generated through non-canonical biogenesis routes, including Drosha-independent mechanisms (where pri-miRNAs are processed by the spliceosome) as well as Dicer-independent pathways. Abbreviations: Ago2: Argonaute 2, DGCR8: DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8, RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex, TRBP: Transactivation response element RNA-binding protein. Created in https://BioRender.com (accessed on 8 July 2025). Modified from Seyhan, Attila 2023 [51].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/ncrna/ncrna-12-00002/article_deploy/html/images/ncrna-12-00002-g001-550.jpg)
