- Article
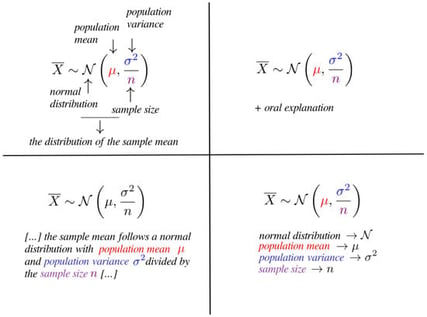
Effective signaling in instructional materials—through cues such as highlights, arrows, and annotations—can guide learner attention, reduce cognitive load, and enhance comprehension in multimedia-rich online courses. While the benefits of signaling are well documented, little is known about how combinations of signaling strategies influence both the average performance and the consistency of student outcomes. In this study, we propose a data-driven approach to evaluate and optimize signaling strategies in online teaching. Using lecture materials from three semesters of introductory and intermediate statistics courses, we extracted multiple features of textual and visual signaling, including highlighted words, annotated formulas, arrows, and notes. Principal Component Analysis identified four distinct signaling strategies employed by the instructor. We then applied a heteroscedastic beta regression model to link these strategies to topic-level exam performance, allowing simultaneous assessment of mean learning outcomes and their variability. Results show that strategies combining formula highlighting with arrows and detailed notes improve both the average proportion of successful learners and the stability of outcomes, while relying solely on formula highlighting increases variability. Our findings provide actionable guidance for instructors to design effective signaling strategies, and demonstrate a flexible framework for data-driven evaluation of teaching practices in online learning environments.
22 January 2026