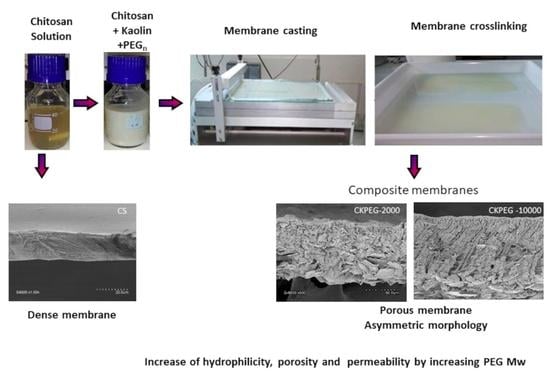
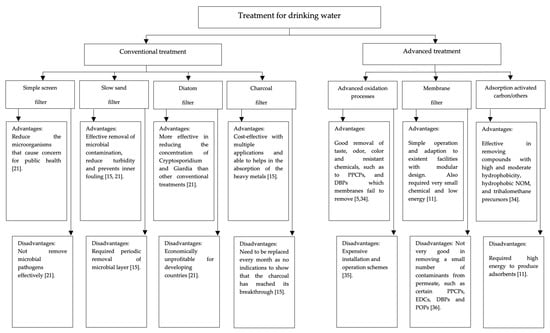
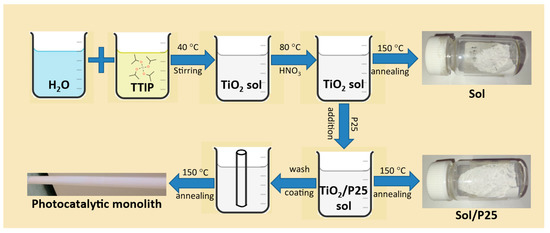
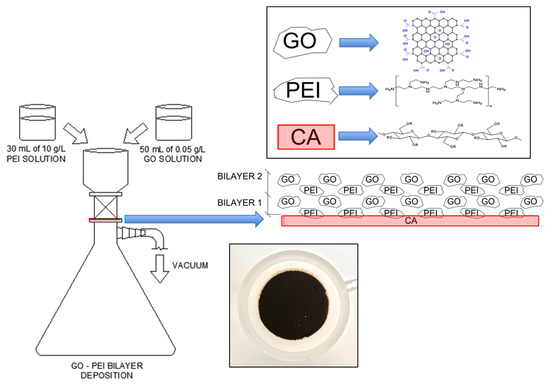
New Challenges in Membranes for Water and Wastewater Application
A topical collection in Membranes (ISSN 2077-0375). This collection belongs to the section "Membrane Applications for Water Treatment".
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 104472Editor
Interests: water and wastewater treatment; membrane processes; fouling; modified membranes; recycle and reuse membrane; new materials
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Water is an essential molecule for life as we know it and for our environment. The composition and structure of this molecule determine its exceptional characteristics, which make it widely employed in several applications. For example, it is used as an energy storage, refrigerant fluid, dissolution medium, and elimination vehicle in the industry. Furthermore, it is used in agriculture, investigation, and many other fields.
It can be classified according to different criteria, such as its use, composition, and origin. Its quality may be affected by several factors (physical, chemical, and biological) and therefore, water quality criteria are defined depending on its expected use. As a result, to reach those objectives, it must be previously conditioned.
Many water treatments have been developed to achieve the required quality levels. Among the different available treatments, “membrane technology” is one the most viable alternatives, as it achieves high removal fields with low costs. For this reason, membrane processes play an essential role in the conditioning of water and industrial streams with applications in different fields.
Different membrane processes, microfiltration (MF), ultrafiltration (UF), nanofiltration (NF), reverse osmosis (RO), electrodialysis (ED), and pervaporation, among others, have been used to treat water and wastewater. In the last decade, new materials and fabrication processes have been developed to improve performance in membrane synthesis and membrane-modification processes.
This Topical Collection aims to cover the new challenges in membranes for water conditioning with different applications and use. Recent developments and advances on all the aspects related to membrane application for water and wastewater treatment are welcome: membrane processes, hybrid processes (including one membrane step), modified membranes, new materials, the possibility of recycling and reusing membranes, and new technologies to reduce fouling and to improve the efficiency of enhanced processes.
Both research and review papers are welcome.
Prof. Dr. Asuncion Maria Hidalgo
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Membranes is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.