European Health Technology Assessment (EU HTA)
A topical collection in Journal of Market Access & Health Policy (ISSN 2001-6689).
Viewed by 40870Editors
2. European Access Academy, 4059 Basel, Switzerland
Interests: health economic; health technology assessment; health services; health outcomes and management
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The Health Technology Assessment (HTA) process in Europe has been emerging over the past two decades, with various pilot projects and joint actions paving the way for a unified approach.
The EU-HTA initiative aims to establish a harmonized framework for assessing the clinical and economic value of health technologies, make innovative health technologies more widely available to patients, reduce the duplication of efforts by national HTA bodies, and ensure resource efficiency across member states. This process is expected to significantly shape market access strategies in Europe over the next decade.
While the EU-HTA process differs from the drug regulatory process overseen by the EMA, the latter’s experience can serve as a valuable benchmark for the future evolution of EU-HTA. Like the EMA, the EU-HTA initiative is likely to go through various phases, including conception, initiation, positioning, and maturation, before establishing itself as a well-respected international organization advising Member States and informing the European Commission.
We are now setting the foundation of the EU-HTA that will shape the future. It has become a pivotal topic in the field of HTA, as it has the potential to streamline the evaluation process, promote transparency, and facilitate harmonized access to innovative healthcare solutions for patients across Europe.
While a wealth of information is available through various sources, such as the EU’s official website, scientific publications, blogs, conferences, and webinars, there is a need for a comprehensive resource that consolidates relevant information and diverse perspectives on the EU-HTA. By gathering insights from multiple stakeholders, we can gain a deeper understanding of the current status, challenges, opportunities, and future prospects of this initiative.
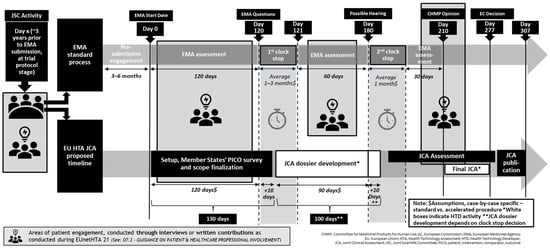
With the EU HTA Assessments starting from January 2025, we believe that it is the right time to make a pause and consider a multi-stakeholder perspective on this status, an analysis of challenges and opportunities, and some prospective views about EU-HTA. We are pleased to announce that the European Access Academy (EAA) and the Market Access Society (MAS) have joined forces to edit a Collection of the Journal of Market Access and Health Policy focused on the EU-HTA.
We encourage you to consider contributing to this Collection and sharing your expertise and/or perspective with the broader market access and HTA communities. Your role and insights are invaluable in shaping the discourse around this transformative regulation. Please feel free to reach out to us with any questions or to discuss potential contribution ideas. We look forward to receiving your valuable contributions.
Prof. Dr. Jörg Ruof
Prof. Dr. Mondher Toumi
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Journal of Market Access & Health Policy is an international peer-reviewed open access quarterly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1500 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- EU HTA regulation
- EU HTA process
- innovative health technologies
- patient access
- European Access Environment
- HTA procedures
- EU HTA initiative
- HTA bodies
- European Access Academy
- Market Access Society
- HTA community