- Article
Automated Malaria Ring Form Classification in Blood Smear Images Using Ensemble Parallel Neural Networks
- Pongphan Pongpanitanont,
- Naparat Suttidate and
- Penchom Janwan
- + 3 authors
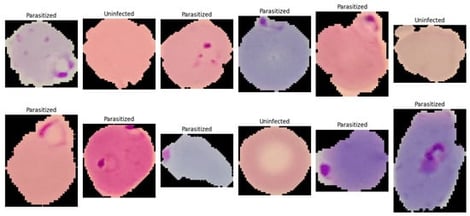
Manual microscopy for malaria diagnosis is labor-intensive and prone to inter-observer variability. This study presents an automated binary classification approach for detecting malaria ring-form infections in thin blood smear single-cell images using a parallel neural network framework. Utilizing a balanced Kaggle dataset of 27,558 erythrocyte crops, images were standardized to 128 × 128 pixels and subjected to on-the-fly augmentation. The proposed architecture employs a dual-branch fusion strategy, integrating a convolutional neural network for local morphological feature extraction with a multi-head self-attention branch to capture global spatial relationships. Performance was rigorously evaluated using 10-fold stratified cross-validation and an independent 10% hold-out test set. Results demonstrated high-level discrimination, with all models achieving an ROC–AUC of approximately 0.99. The primary model (Model#1) attained a peak mean accuracy of 0.9567 during cross-validation and 0.97 accuracy (macro F1-score: 0.97) on the independent test set. In contrast, increasing architectural complexity in Model#3 led to a performance decline (0.95 accuracy) due to higher false-positive rates. These findings suggest that moderate-capacity feature fusion, combining convolutional descriptors with attention-based aggregation, provides a robust and generalizable solution for automated malaria screening without the risks associated with over-parameterization. Despite a strong performance, immediate clinical use remains limited because the model was developed on pre-segmented single-cell images, and external validation is still required before routine implementation.
12 March 2026