Journal Description
Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology
Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on ophthalmology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 42.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology is a companion journal of JCM.
Latest Articles
Impact of Attending Surgeon Experience on Resident-Performed Cataract Surgery Outcomes
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2026, 4(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto4010005 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Purpose: This study evaluates the association between supervising attending surgeons’ post-residency experience and complication rates during resident-performed phacoemulsification (cataract extraction) surgeries, and to determine whether this relationship changes as the academic year progresses. Methods: A retrospective analysis of 1263 cataract surgeries performed by
[...] Read more.
Purpose: This study evaluates the association between supervising attending surgeons’ post-residency experience and complication rates during resident-performed phacoemulsification (cataract extraction) surgeries, and to determine whether this relationship changes as the academic year progresses. Methods: A retrospective analysis of 1263 cataract surgeries performed by eight PGY-4 residents under 14 board-certified attendings was conducted at a New York City residency program over two years. Attendings were divided into four groups based on years of post-residency experience. Primary complications included posterior capsule (PC) tears, anterior vitrectomy (AV), capsulorrhexis extensions (CE), and inability to place a one-piece intraocular lens (IOL). Chi-square analyses compared complication rates between attending groups overall, and between the first and second halves of the academic year. Results: A total of 167 primary complications (13.2%) were identified. Attendings with the fewest years of experience (Group 1) supervised significantly more cases with PC tears (χ2 = 8.173, p = 0.004), AV usage (χ2 = 7.748, p = 0.005), and inability to place a one-piece IOL (χ2 = 4.753, p = 0.029), particularly during the first half of the academic year. Notably, supervising attending experience was not correlated with resident complications in the second half of the academic year. Conclusions: Early in the academic year, less experienced attendings supervised cases with higher complication rates, underscoring the critical role of strategic case assignment and targeted mentorship during early surgical training. These findings suggest that aligning resident progression with appropriate supervision can enhance outcomes and support skill development, optimizing both education and patient safety.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Comparison of Visual Acuity and Strabismus Pre- and Post-Baerveldt 350 Glaucoma Drainage Device Placement in Refractory Childhood Glaucomas
by
Adam Jacobson, Elizabeth M. Bolton and Brenda L. Bohnsack
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2026, 4(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto4010004 - 19 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: Assess visual acuity (VA) and strabismus changes in children after Baerveldt 350 (BV350) device placement. Methods and Analysis: Retrospective cohort study of children (<21 years of age) who had superotemporal BV350 placement (2011–2023) and >6-month follow-up. Ocular diagnoses, surgical details,
[...] Read more.
Objective: Assess visual acuity (VA) and strabismus changes in children after Baerveldt 350 (BV350) device placement. Methods and Analysis: Retrospective cohort study of children (<21 years of age) who had superotemporal BV350 placement (2011–2023) and >6-month follow-up. Ocular diagnoses, surgical details, and preoperative and final follow-up exam findings were collected. In bilateral cases, first eye implanted was included in analysis. Results: Ninety-seven patients underwent BV350 surgery with median age of 6.7 (interquartile (IQR) 3.1, 11.2) years and with a median of 4.2 (IQR 1.8, 6.8) years of follow-up. Most common glaucomas were secondary to non-acquired ocular anomaly (n = 31) or primary congenital glaucoma (n = 21). There was no difference in preoperative and final VA (p = 0.6583). Twenty-seven (28%) and twenty-five (26%) patients were orthophoric preoperatively and at final follow-up, respectively. Orthophoria at final follow-up was associated with preoperative (odds ratio (OR)1.8 [1.2, 2.9]) and final VA (OR1.5 [1.1, 2.3]). At final follow-up, 13 patients (13%) and 19 patients (20%) showed worsened or improved horizontal deviation (>10 prism diopter (PD) change), respectively. No patients reported postoperative diplopia. Only four patients, all with esotropia, underwent subsequent strabismus surgery. Conclusions: Children who underwent BV350 placement did not have significant change in VA, and a high percentage of patients had strabismus prior to (72%) and following (74%) glaucoma surgery. Orthophoria was associated with better VA. The majority of patients did not show worsening of strabismus postoperatively, and none reported diplopia.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Inaugural Sixth Nerve Palsy in a Patient with Neuroborreliosis: A Case Report
by
Yasmine Lahrichi, Jean-Marie Rakic and Anne-Catherine Chapelle
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2026, 4(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto4010003 - 17 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: We report an uncommon presentation of Lyme disease and highlight the importance of a detailed history in a patient with new-onset sixth nerve palsy. Methods: Case report and literature review. Results: A 46-year-old man receiving infliximab presented to the ophthalmology emergency department
[...] Read more.
Background: We report an uncommon presentation of Lyme disease and highlight the importance of a detailed history in a patient with new-onset sixth nerve palsy. Methods: Case report and literature review. Results: A 46-year-old man receiving infliximab presented to the ophthalmology emergency department with horizontal binocular diplopia. History revealed a diffuse headache that had begun three weeks earlier. Ophthalmologic examination demonstrated a left sixth cranial nerve palsy. The workup showed positive Borrelia serum IgG, which was interpreted as a likely false-positive result given the limited specificity of serologic testing. At follow-up, the patient reported left-sided peripheral facial palsy, and worsening headache and diplopia. Further history revealed prior erythema migrans treated with doxycycline four months earlier. Considering these new findings, a lumbar puncture was performed and demonstrated intrathecal production of Borrelia antibodies. Neuroborreliosis, a neurologic involvement secondary to systemic infection by the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi, was diagnosed. The patient was treated with oral doxycycline for 28 days with complete resolution of symptoms. Conclusions: Lyme disease may present with progressive neuro-ophthalmologic symptoms, underscoring the crucial role of ophthalmologists in its diagnosis. Moreover, immunosuppression may delay diagnosis and allow neurological progression, highlighting the need for careful history taking and close follow-up.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Difluprednate and Loratadine in the Treatment of Pachychoroid Disease Spectrum
by
Emile R. Vieta-Ferrer, Adrian Au, Jeeyun Ahn and Michael B. Gorin
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2026, 4(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto4010002 - 29 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: The recently defined pachychoroid disease spectrum (PDS), which includes central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR), is a group of retinal disorders that share the common characteristic of a thick, dilated, hyperpermeable choroid. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of difluprednate and loratadine in
[...] Read more.
Background: The recently defined pachychoroid disease spectrum (PDS), which includes central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR), is a group of retinal disorders that share the common characteristic of a thick, dilated, hyperpermeable choroid. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of difluprednate and loratadine in the treatment of pachychoroid disease spectrum (PDS). Methods: A retrospective study of 27 eyes from 19 patients with macular edema secondary to chronic PDS were treated with topical difluprednate and oral loratadine at a tertiary medical center. Visual acuity and optical coherence tomography (OCT) images were analyzed at baseline, 1-, 2-, 3-, 6-, 12-month, and final follow-up. Baseline was defined as the initiation of topical difluprednate. Patients with neovascularization or who had other concurrent treatments for PDS were excluded. Subfoveal choroidal thickness was measured at each time point. Response was defined as eyes that showed a reduction in intra- or subretinal fluid. Results: All 27 eyes studied responded to treatment. Of these, 70.4% resolved by 4 months and 81.5% by 6 months, with 52.2% of these patients having recurrences related to cessation or tapering of topical steroids. Visual acuity remained stable (p > 0.05) while subfoveal choroidal thickness decreased compared to baseline (p < 0.001) across all time points. Eleven (40.7%) of the eyes developed increased intraocular pressure, for which seven (25.9%) required incisional surgery. Conclusions: Chronic PDS can be treated with a combination of topical difluprednate and oral antihistamines to reduce retinal edema and subfoveal choroidal thickness. The effectiveness of therapy could be linked to the regulation of mast cell degranulation, necessitating a well-powered prospective randomized clinical trial.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Retinal Diseases: Recent Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Retrospective Review of Dual-Focus MiSight Contact Lenses and 0.05% Atropine for Myopia Management
by
Noreen Shaikh, Magdalena Stec, Huizi Yin and Brenda L. Bohnsack
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2026, 4(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto4010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of low-dose atropine and dual-focus MiSight contact lenses on myopia control. Methods: This study included a retrospective review of patients (5–13 years old) started on MiSight contacts or 0.05% atropine with a
[...] Read more.
Objective: The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of low-dose atropine and dual-focus MiSight contact lenses on myopia control. Methods: This study included a retrospective review of patients (5–13 years old) started on MiSight contacts or 0.05% atropine with a ≥1-year follow-up. Outcomes included cycloplegic refraction, axial length measurement, and side effects. The right eyes were included in analyses. Results: One hundred children were treated with MiSight lenses (n = 55) or 0.05% atropine (n = 45) at an average age of 10.4 ± 2.1 years and 8.4 ± 2.5 years, respectively. At the 1-year follow-up, there was no difference from baseline in spherical equivalent or axial length in the MiSight group (p = 0.61, p = 0.98) or in the atropine group (p = 0.78, p = 0.97). Further, subgroup analysis based on age at treatment initiation (<9.5 years vs. ≥9.5 years) showed no age difference in baseline or final spherical equivalent and axial length in either the MiSight group or the atropine group. Linear regression analysis demonstrated no association between initial age and baseline spherical equivalent, baseline axial length, or the change in spherical equivalent in either the MiSight or atropine group. Conclusions: There was no significant difference in spherical equivalent or axial length after 1 year of treatment with either the MiSight contact lenses or 0.05% atropine eye drops. However, the limited sample size, the difference in age and ethnicity, and baseline refraction prevent a direct comparison between the two treatment groups.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Balancing Pressure and Pills: Short-Term Outcomes of Goniotomy vs. Trabeculectomy in Adult Glaucoma
by
Sunny Kahlon and John Steven Jarstad
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040027 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Trabeculectomy and minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) such as goniotomy aim to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) and medication burden but are often performed in patients with differing disease severity. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 100 eyes from 76 adults with glaucoma that underwent
[...] Read more.
Background: Trabeculectomy and minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) such as goniotomy aim to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) and medication burden but are often performed in patients with differing disease severity. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 100 eyes from 76 adults with glaucoma that underwent either goniotomy (n = 50; Kahook Dual Blade = 42, OMNI = 8) or trabeculectomy ab externo (n = 50) at a tertiary center between May 2022 and June 2023, with at least six months of follow-up. Baseline and six-month IOP, number of medications, and postoperative complications were recorded. Eyes undergoing trabeculectomy had higher preoperative IOP than those undergoing goniotomy (22.6 ± 7.7 vs. 19.1 ± 5.9 mmHg). Results: At six months, trabeculectomy achieved a greater absolute IOP reduction (8.8 ± 0.8 vs. 5.4 ± 0.8 mmHg; p = 0.004), likely reflecting higher baseline IOP, while goniotomy yielded a larger medication reduction (1.47 ± 0.30 vs. 0.72 ± 0.20; p = 0.041). Hyphema occurred more often after trabeculectomy, and the small number of OMNI cases precluded device comparison. Conclusions: In this short-term retrospective series, trabeculectomy achieved larger absolute IOP reduction whereas goniotomy offered greater medication reduction, highlighting the need to individualize surgical choice and confirm these findings in larger prospective studies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Incidence and Outcomes of Dropped Nucleus After Phacoemulsification Cataract Surgery Between 2020 and 2024
by
Jonathan Halim, Eleonora Micheletti, Maria-Laura Dari, Nakul Mandal and Sharmina R. Khan
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040026 - 30 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: This study evaluates the incidence and outcomes of patients with dropped nucleus/nuclear fragment during phacoemulsification surgery; Methods: Retrospective review of continuous cases with dropped nucleus/nuclear fragment during phacoemulsification cataract surgery from January 2020 to December 2024. Demographic and perioperative data were collected
[...] Read more.
Background: This study evaluates the incidence and outcomes of patients with dropped nucleus/nuclear fragment during phacoemulsification surgery; Methods: Retrospective review of continuous cases with dropped nucleus/nuclear fragment during phacoemulsification cataract surgery from January 2020 to December 2024. Demographic and perioperative data were collected and analysed. A good visual outcome was defined as a postoperative best-distance visual acuity of ≥6/12; Results: A total of 91,883 cases of planned phacoemulsification cataract surgery were identified, of which 175 (0.19%) were complicated by a dropped nucleus/lens fragment. Mean age was 71 years and median number of days from primary procedure to secondary fragmatome was 5 days. Good visual outcomes were achieved in 127 cases (73%). Median final intraocular pressure was 13 mmHg. Most patients required two (63%) or three (29%) operations in total and none developed endophthalmitis. Hypermature cataracts were present in 70 cases (40%) and were significantly associated with poor visual outcomes (p = 0.003). Surgeon grade and other pre-existing ocular co-pathologies known to increase posterior capsular rupture risk were not significantly associated with poor visual outcomes; Conclusions: Overall incidence and outcomes of cases complicated with dropped nucleus/fragment were favourable despite the presence of pre-existing risk factors. Emergent management is paramount to ensure good outcomes in patients.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating a Multi-Modal Large Language Model for Ophthalmology Triage
by
Caius Goh, Jabez Ng, Wei Yung Au, Clarence See, Alva Lim, Jun Wen Zheng, Xiuyi Fan and Kelvin Li
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040025 - 30 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Purpose: Ophthalmic triage is challenging for non-specialists due to limited training and rising global eye disease burden. This study evaluates a multimodal framework integrating clinical text and ophthalmic imaging with large language models (LLMs). Textual consistency filtering and chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning were incorporated
[...] Read more.
Background/Purpose: Ophthalmic triage is challenging for non-specialists due to limited training and rising global eye disease burden. This study evaluates a multimodal framework integrating clinical text and ophthalmic imaging with large language models (LLMs). Textual consistency filtering and chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning were incorporated to improve diagnostic accuracy. Methods: A dataset of 56 ophthalmology cases from a Singapore restructured hospital was pre-processed with acronym expansion, sentence reconstruction, and textual consistency filtering. To address dataset size limitations, 100 synthetic cases were generated via one-shot GPT-4 prompting, validated by semantic checks and ophthalmologist review. Three diagnostic approaches were tested: Text-Only, Image-Assisted, and Image with CoT. Diagnostic performance was quantified using a novel SNOMED-CT-based dissimilarity score, defined as the shortest path distance between predicted and reference diagnoses in the ontology, which was used to quantify semantic alignment. Results: The synthetic dataset included anterior segment (n = 40), posterior segment (n = 35), and extraocular (n = 25) cases. The text-only approach yielded a mean dissimilarity of 6.353 (95% CI: 4.668, 8.038). Incorporation of image assistance reduced this to 5.234 (95% CI: 3.930, 6.540), while CoT prompting provided further gains when imaging cues were ambiguous. Conclusions: The multimodal pipeline showed potential in improving diagnostic alignment in ophthalmology triage. Image inputs enhanced accuracy, and CoT reasoning reduced errors from ambiguous features, supporting its feasibility as a pilot framework for ophthalmology triage.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Ophthalmic Imaging in Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema: Key Findings and Advancements
by
Akanksha Malepati, Edmund Arthur and Maria B. Grant
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040024 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a debilitating chronic disorder that results in ocular microvascular complications, including diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME). Early detection and timely intervention for DR and DME are crucial for improving visual outcomes in affected patients. Ophthalmic imaging
[...] Read more.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a debilitating chronic disorder that results in ocular microvascular complications, including diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME). Early detection and timely intervention for DR and DME are crucial for improving visual outcomes in affected patients. Ophthalmic imaging plays a vital role in the screening, diagnosis, and management of DR and DME. In this review, a comprehensive overview of the imaging modalities frequently utilized in the assessment of DR and DME, encompassing both structural and functional imaging techniques are presented. The key imaging findings that are associated with the various stages of DR and DME are underscored and their diagnostic utility in assessing disease progression and visual function are evaluated. Additionally, we discuss emerging imaging biomarkers that are currently under investigation, which hold significant potential for improving the diagnostic and prognostic capabilities of imaging for DR and DME patients. Finally, the advent of new imaging methods, such as ultrawide-field imaging (UWFI) and deep learning models, which have markedly improved the detection of retinal pathologies are considered.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Application of Smartphone-Based Fundus Cameras and Telemedicine in the Brazilian Amazon Forest
by
Josmar Sabage, Luís Expedito Sabage, João Vitor Mota Lanzarin, Leonardo Resende de Sousa, Isabela Ussifati Negrine, Carolina Poltronieri Chiaroni, Ana Claudia Ferreira de Almeida, Alessandra Mazzo, Ênio Luís Damaso and Luiz Fernando Manzoni Lourençone
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040023 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Smartphone-based fundus cameras and telemedicine are an opportunity for accessing ocular health inequalities in under-resourced areas. The objective of this study is to evaluate the prevalence of retinal findings in a community in the Amazon and propose strategies to enhance ocular health. A
[...] Read more.
Smartphone-based fundus cameras and telemedicine are an opportunity for accessing ocular health inequalities in under-resourced areas. The objective of this study is to evaluate the prevalence of retinal findings in a community in the Amazon and propose strategies to enhance ocular health. A retrospective study was conducted in a riverside community. Retinal photos from the posterior pole and optic disc were captured using a portable fundus camera. All photos and data were analyzed remotely by a retina specialist. The final sample was 107 participants, aged 52 ± 17. Retinal findings were detected in 37.4% (95%CI 28.7–46.8) of the sample; the three main retinal findings were epithelial changes (10.3%, 95%CI 5.6–17.1), chorioretinal scars (8.4%, 95%CI 4.2–14.8), and dry age-related macular degeneration (7.5%, 95%CI 3.6–13.6). This study detected retinal alterations in a similar prevalence to that of other under-resourced areas. Telemedicine is an opportunity to address health inequities, especially in ophthalmology, through relatively low-cost portable devices, supporting clinical decisions in areas with low health access; however, maintaining assistance after implementation is a challenge. Enhancing medical education and training local non-specialized health professionals in risk assessment, device handling, and data base use is reasonable to ensure follow-up.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Multiple Sclerosis-Associated Uveitis Therapy: Is Modern Better than Old Reliable?
by
Wesley Burrow, Armand Ceniza, Brian Kan, Skyler Colwell and Jorge Cervantes
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040022 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Uveitis, although a rare complication of multiple sclerosis (MS), poses a significant challenge in clinical management. Traditional treatments like corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and surgical interventions often provide limited efficacy. Treatment for MS-associated uveitis involves a combination of traditional and emerging therapies, with a
[...] Read more.
Background: Uveitis, although a rare complication of multiple sclerosis (MS), poses a significant challenge in clinical management. Traditional treatments like corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and surgical interventions often provide limited efficacy. Treatment for MS-associated uveitis involves a combination of traditional and emerging therapies, with a growing emphasis on monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). While there is an increasing use of disease-modifying therapies for MS such as interferon-beta (IFN-β), mAbs are gaining attention for their potential to address both neurological and ophthalmological symptoms. Methods: We conducted a systematic review of the existing literature and analyzed the clinical effect of IFN-β and mAb therapies in the context of MS-associated uveitis, assessing their efficacy in reducing inflammation, maintaining visual acuity (VA), and minimizing steroid dependency. Results: MS-associated uveitis had improved or maintained VA in 95% (35/37) of eyes (21 patients) after an average of 34.7 months (range of 7.9 to 78.7 months) of IFN-β treatment. One hundred percent (10/10) of patients (19/19 eyes) had improved or maintained VA after a mean of 25 months (range 8 to 43 months) of mAb treatment. We also found that IFN-β effect on MS-associated uveitis is comparable to mAbs. Conclusions: We outline the need for further research through human data to strengthen current findings and guide evidence-based clinical practice.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Optogenetics as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Ocular Disease
by
Enzo Maria Vingolo, Simona Mascolo, Mattia Calabro, Filippo Miccichè and Mirko Barresi
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040021 - 20 Oct 2025
Abstract
Optogenetics is a field that emerged with the goal of studying the physiology of nerve cells by selectively expressing opsins—channel proteins that can be activated by light exposure. Once the methodology was established, several research groups sought to express these proteins in damaged
[...] Read more.
Optogenetics is a field that emerged with the goal of studying the physiology of nerve cells by selectively expressing opsins—channel proteins that can be activated by light exposure. Once the methodology was established, several research groups sought to express these proteins in damaged nerve tissue to restore proper signal transmission. Over the years, numerous efforts have been made to restore vision in patients with chronic degenerative diseases, particularly retinitis pigmentosa, with clinical trials yielding encouraging results. However, significant challenges remain, such as the difficulty of delivering the signal to specific retinal cells and the complexity of replicating the physiological activation of the target cells. As research continues, optogenetics remains a promising yet evolving field. This review aims to highlight the therapeutic advantages of optogenetics over currently available strategies and to promote further scientific exploration of this emerging discipline.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
MIGS, Cataract Surgery, or Both? An Analysis of Clinical Trial Data to Compare Efficacy and Outcomes on Glaucoma Patients
by
Jeremy Appelbaum, Abdullah Virk, Deepkumar Patel and Karen Allison
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040020 - 28 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness around the world and is characterized as a group of irreversible optic neuropathies with multiple risk factors such as age, race/ethnicity, sex, and intraocular pressure (IOP), amongst many others that play a role in
[...] Read more.
Background: Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness around the world and is characterized as a group of irreversible optic neuropathies with multiple risk factors such as age, race/ethnicity, sex, and intraocular pressure (IOP), amongst many others that play a role in disease etiology. However, IOP is the only modifiable risk factor, with higher IOP often causing increased damage to the optic nerve, resulting in the vast majority of medical and surgical treatments aiming to reduce IOP. There are a number of interventions available to treat glaucoma including micro-invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS), whose usage has drastically increased due to its safety and efficacy. Studies also highlight the IOP-reducing effect of cataract surgery, which is the most common procedure performed globally. However, other, more targeted therapies and surgeries have been shown to have a more significant effect on IOP reduction. The objective of this study is to compare the IOP and medication reduction between cataract surgery (CS), MIGS, and MIGS and cataract surgery (MACS) clinical trials. Methods: This analysis consisted of publicly available data on CS, MIGS, and MACS clinical trials from 2005 to 2017 using ClinicalTrials.gov. Data reporting and synthesis adhered to PRISMA guidelines. MIGS interventions studied in this analysis include iStent®, CyPass® Micro-Stent, Ex-PRESS®, Hydrus®, PRESERFLO™ MicroShunt, and XEN® Gel Stent. The main variables of interest are the mean IOP and mean number of glaucoma medications used. The primary outcomes were the baseline, post-procedure, and reduction in IOP and glaucoma medication use. Cohorts were further subdivided by the follow-up period (6, 12, and 24 months), as well as their medicated or unmedicated status for pre-op IOP measurement. PROSPERO CRD42025102892. Results: A total of 21 trials were included in this review, comprising 3330 clinical trial participants: 7 CS trials (N = 570), 13 MIGS trials (N = 1577), and 9 MACS trials (N = 1183). All interventions studied resulted in a decrease in both the IOP and medication usage with varying degrees. At 12 months, the wash-out baseline IOP reduction (mmHg) was 6.9 (27.5%) for CS, 8.8 (34.0%) for MIGS, and 8.2 (32.6%) for MACS. The medication reduction was 0.8 (56.1%) following CS, 1.0 (39.5%) for MIGS, and 1.3 (86.4%) for MACS. At 24 months, the wash-out baseline IOP reduction was 6.3 (25.1%) for CS, 8.4 (33.1%) for MIGS, and 7.6 (30.1%) for MACS. At 24 months, the medication reduction was 0.9 (58.3%) for CS, 1.5 (79.8%) for MIGS, and 1.3 (86.1%) for MACS. Conclusions: The results indicate that CS, MIGS, and MACS all result in a decrease in the IOP and glaucoma medications; however, MIGS and MACS outperform CS in IOP and medication reduction. Adopting MIGS and MACS for patients with ocular hypertension or mild-to-moderate glaucoma will help improve patient outcomes through reducing the IOP and medication burden. Given that glaucoma affects certain populations to a greater degree, future research analyzing racial representation is critical in ensuring the appropriate applicability of clinical trial results toward diverse populations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing Eye Care Needs Among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease on Hemodialysis
by
Priya Agrawal, Ami Patel, Janet Alexander and Ramya Swamy
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040019 - 27 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The prevalence of vision impairment and eye disease is higher among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), yet there are no standardized guidelines for this vulnerable population. We hypothesized that there are self-reported unmet ophthalmic care needs among patients receiving hemodialysis. We also
[...] Read more.
The prevalence of vision impairment and eye disease is higher among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), yet there are no standardized guidelines for this vulnerable population. We hypothesized that there are self-reported unmet ophthalmic care needs among patients receiving hemodialysis. We also hypothesized that limited awareness of the connection between eye health and CKD is a significant barrier to receiving eye care. Methods: From June 2022 to July 2022, patients on dialysis were recruited in-person at two Independent Dialysis Foundation sites in Baltimore, Maryland. Participants completed a survey assessing recent eye exam history, barriers to care, and health literacy. Results: Of 82 participants, 43 (52%) had not received a complete eye exam within the past year. The most common reasons were scheduling conflicts (15 [35%]), not wanting an eye exam (12 [28%]), and costs (6 [14%]). Less than half of respondents (40, 41%) were unaware of a relationship between kidney disease and eye health. Conclusions: Results suggest potential unmet eye care needs and low awareness of CKD-related ocular risks among dialysis patients. Interventions to enhance provider recommendations, improve health literacy, and reduce logistical barriers may help prevent avoidable vision loss in this high-risk population.
Full article
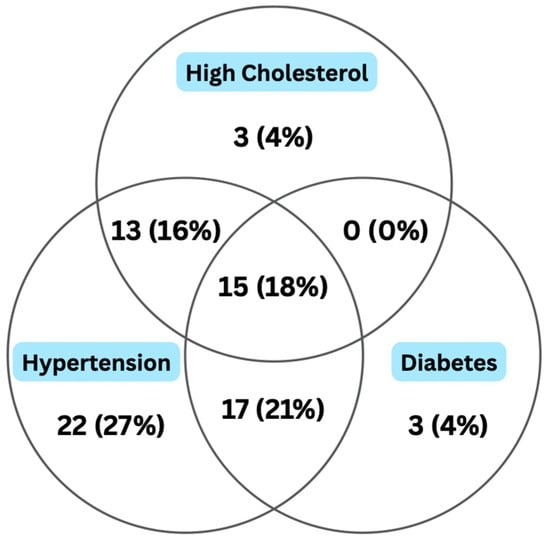
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lens with Butterfly-Shaped Central Area Implanted in a Large Angle Kappa Patient: A Case Report
by
Camille Bosc, Sandra Delaunay, Anne Barrucand and Irene Martínez-Alberquilla
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030018 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Intraocular lens (IOL) alignment is crucial for optimal performance in presbyopia-correcting designs. The aim was to report a case of a patient with a high angle kappa implanted with the continuous transitional focus (CTF) Precizon Prebyopic NVA IOL. Case presentation: A 51-year-old
[...] Read more.
Background: Intraocular lens (IOL) alignment is crucial for optimal performance in presbyopia-correcting designs. The aim was to report a case of a patient with a high angle kappa implanted with the continuous transitional focus (CTF) Precizon Prebyopic NVA IOL. Case presentation: A 51-year-old patient presenting large angle kappa values (0.6/0.8 mm) was implanted with the Precizon Prebyopic NVA IOL and followed-up 1 and 10 months post-surgery. This IOL is designed with a butterfly-shaped central area that allows the orientation of the lens so that the visual axis passes through the wider diameter of the optic zone. Postoperative refraction was −0.25D of cyl at 80° for the right eye and +0.25D −0.50D cyl at 170°. Corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA) at the last visit was −0.1 logMAR monocularly and −0.2 logMAR binocularly. Binocular uncorrected distance (UDVA), intermediate (UIVA) and near visual acuities (UNVA) were −0.1, 0.1 and 0.1 logMAR, respectively. The corrected binocular defocus curve exhibited outstanding vision at the 0.00D defocus level and showed a continuous range of functional vision from distance to near. Overall excellent satisfaction was reported, along with low levels of photopic phenomena. Conclusions: Precizon Presbyopic NVA IOL provided satisfactory vision and low levels of photic phenomena in a high angle kappa patient who would potentially be excluded from presbyopia-correcting IOL implantation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Effect of Netarsudil 0.02% on a Patient with Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy and Radial Keratotomy
by
Praneetha Thulasi, Shae Chambers and Soroosh Behshad
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030017 - 15 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study reports an unusual case of dramatic change in visual acuity, pachymetry, and corneal topography in a patient with a history of Fuchs dystrophy and radial keratotomy following the use of Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor. A patient with a history of 8-cut radial
[...] Read more.
This study reports an unusual case of dramatic change in visual acuity, pachymetry, and corneal topography in a patient with a history of Fuchs dystrophy and radial keratotomy following the use of Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor. A patient with a history of 8-cut radial keratotomy (RK), astigmatic keratotomy (AK), and Fuchs dystrophy showed dramatic changes in visual acuity, pachymetry, and corneal topography after using one drop of netarsudil 0.02%. The dramatic effect of netarsudil in our patient may be due to increased penetration of a rho-kinase inhibitor from the corneal incisions, facilitating the effect on corneal endothelium, resulting in a dramatic improvement in corneal pachymetry. This suggests a potential role for corneal incisions to improve the effectiveness of rho-kinase inhibitors in patients with Fuchs dystrophy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Racial and Gender Disparities in Clinical Trial Representation for Age-Related Macular Degeneration Treatments: A Scoping Review
by
Amirmohammad Shafiee, Taylor Juran, Iza Zabaneh, Deepkumar Patel and Karen Allison
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030016 - 13 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background/Objective: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of irreversible vision loss. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy is the primary treatment for neovascular AMD. This study aimed to assess racial, ethnic, and gender representation in U.S.-based randomized controlled trials (RCTs)
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of irreversible vision loss. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy is the primary treatment for neovascular AMD. This study aimed to assess racial, ethnic, and gender representation in U.S.-based randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of anti-VEGF therapies. Methods: A systematic PubMed search identified 19 eligible RCTs. Titles and abstracts were screened, and demographic data were independently extracted and cross-verified. Chi-squared analysis was used to evaluate disparities in participant representation. Risk of bias was assessed using the ROBIS checklist. Results: Among 8003 participants across 19 trials, 92.3% were Caucasian. Asian, African American, Hispanic/Latino, and American Indian participants collectively comprised just over 5%. This underrepresentation of non-Caucasian groups was statistically significant (p < 0.01, df = 4) and not associated with study sponsorship. Gender analysis showed 59% female and 41% male participation, which was not statistically significant (p = 0.83, df = 1). Conclusions: Non-Caucasian populations remain significantly underrepresented in anti-VEGF RCTs for AMD. This raises concerns about the generalizability of trial findings to diverse populations. Future clinical trials must prioritize inclusive recruitment to ensure equitable, evidence-based care for all patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Retinal Diseases: Recent Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
An Insight into Current and Novel Treatment Practices for Refractory Full-Thickness Macular Hole
by
Chin Sheng Teoh
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030015 - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Refractory full-thickness macular holes (rFTMHs) present a significant challenge in vitreoretinal surgery, with reported incidence rates of 4.2–11.2% following standard vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling and gas tamponade. Risk factors include large hole size (>400 µm), chronicity (>6 months), high myopia,
[...] Read more.
Refractory full-thickness macular holes (rFTMHs) present a significant challenge in vitreoretinal surgery, with reported incidence rates of 4.2–11.2% following standard vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling and gas tamponade. Risk factors include large hole size (>400 µm), chronicity (>6 months), high myopia, incomplete ILM peeling, and post-operative noncompliance. Multiple surgical techniques exist, though comparative evidence remains limited. Current options include the inverted ILM flap technique, autologous ILM transplantation (free flap or plug), lens capsular flap transplantation (autologous or allogenic), preserved human amniotic membrane transplantation, macular subretinal fluid injection, macular fibrin plug with autologous platelet concentrates, and autologous retinal transplantation. Closure rates range from 57.1% to 100%, with selection depending on hole size, residual ILM, patient posturing ability, etc. For non-posturing patients, fibrin plugs are preferred. Residual ILM cases may benefit from extended peeling or flap techniques, while large holes often require scaffold-based (lens capsule, amniotic membrane) or fibrin plug approaches. Pseudophakic patients should avoid posterior capsular flaps due to lower success rates. Despite promising outcomes, the lack of randomized trials necessitates further research to establish evidence-based guidelines. Personalized surgical planning, considering anatomical and functional goals, remains crucial in optimizing visual recovery in rFTMHs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seven-Year Outcomes of Aflibercept in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration in a Teaching Hospital Setting
by
Antoine Barloy, Florent Boulanger, Benjamin Jany and Thi Ha Chau Tran
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030014 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: In clinical practice, visual outcomes with anti-VEGF therapy may be worse than those observed in clinical trials. In this study, we aim to investigate the long-term outcomes of neovascularization treated with intravitreal aflibercept injections (IAI) in a teaching hospital setting. Methods: This
[...] Read more.
Background: In clinical practice, visual outcomes with anti-VEGF therapy may be worse than those observed in clinical trials. In this study, we aim to investigate the long-term outcomes of neovascularization treated with intravitreal aflibercept injections (IAI) in a teaching hospital setting. Methods: This is a retrospective, single-center study including 81 nAMD patients (116 eyes), those both newly diagnosed and switched from ranibizumab. All patients had a follow-up duration of at least seven years. Treatment involved three monthly injections followed by either a pro re nata (PRN) or treat and extend regimen. Follow-up care was primarily conducted by training physicians. The primary endpoint was the change in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) over seven years. Secondary endpoints included central retinal thickness changes, qualitative OCT parameters, macular atrophy progression, injection frequency, and treatment adherence. Results: Among the 116 eyes, 52 (44.8%) completed the seven-year follow-up. Visual acuity improved by +2.1 letters in the overall population (+6.3 letters in treatment-naive eyes) after the loading phase but gradually declined, resulting in a loss of −12.3 letters at seven years. BCVA remained stable (a loss of fewer than 15 letters) in 57.7% of eyes. Central retinal thickness (CRT) decreased significantly during follow-up in both naive and switcher eyes. Macular atrophy occurred in 94.2% of eyes, progressing from 1.42 mm2 to 8.55 mm2 over seven years (p < 0.001). The mean number of injections was 4.1 ± 1.8 during the first year and 3.7 per year thereafter. Advanced age at diagnosis was a risk factor for loss to follow-up, with bilaterality being a protective factor against loss to follow-up (p < 0.05). Conclusions: This study highlights the challenges faced by a retina clinic in a teaching hospital. Suboptimal functional and anatomical outcomes in real life may derive from insufficient patient information and inconsistent monitoring, which contributes to undertreatment and affects long-term visual outcomes. It also raises concerns about supervision in a teaching hospital which needs to be improved.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multimodal Ophthalmic Imaging and Therapeutic Advances in Retinal Diseases: Real-World Insights and Clinical Outcomes)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis of Cycloplegic and Non-Cycloplegic Refraction in Children and Adolescents: Implications for Accurate Assessment of Refractive Errors
by
Ana Maria Varošanec, Leon Marković and Zdenko Sonicki
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030013 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Purpose: This retrospective study aimed to compare the efficacy of cycloplegic (CR) versus non-cycloplegic refraction (NCR) methods in detecting refractive errors among children and adolescents. Methods: Electronic data from pediatric ophthalmology clinics at the University Hospital “Sveti Duh”; Zagreb, Croatia, from January 2008
[...] Read more.
Purpose: This retrospective study aimed to compare the efficacy of cycloplegic (CR) versus non-cycloplegic refraction (NCR) methods in detecting refractive errors among children and adolescents. Methods: Electronic data from pediatric ophthalmology clinics at the University Hospital “Sveti Duh”; Zagreb, Croatia, from January 2008 to July 2023, were analyzed. Comprehensive eye examinations, including Logarithmic Visual Acuity tests, subjective refraction, cycloplegic retinoscopy, slit lamp, and fundus examinations, were conducted. Results: The dataset included 1075 individuals, with 180 undergoing NCR and 895 undergoing CR. In premyopes, the NCR group had a longer follow-up (5.04 vs. 3.45 years; p < 0.001) with similar SE progression. In low myopia, NCR showed more negative first visit SE (−1.86 D vs. −1.35 D; p < 0.001) and faster progression (p = 0.01). In high myopia, follow-up was longer in NCR (5.08 vs. 2.08 years; p = 0.03) with no other significant differences. SE progression was highest in 4–6-year-olds and significantly faster in NCR (−0.61 vs. −0.40 D/year; p = 0.05). Conclusions: Cycloplegic refraction is essential for accurately assessing refractive status, especially in cases of low myopia, as it prevents misclassification and ensures precise evaluation in children and adolescents, thereby facilitating the appropriate diagnosis and treatment of refractive errors.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Special Issues
Special Issue in
JCTO
Clinical Implications of Pupil Function: Optical Quality, Visual Performance, and Neurological Biomarkers
Guest Editors: Pablo De Gracia, Héctor Soriano BaronDeadline: 20 March 2026
Special Issue in
JCTO
Advances in Oculoplastic Surgery: From Eyelid Reconstruction to Innovative Techniques
Guest Editor: Argyrios TzamalisDeadline: 20 April 2026
Special Issue in
JCTO
Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Ocular Surface Tumors and Diseases
Guest Editors: Sotiria Palioura, Carolina L. Mercado, Jaime D. MartinezDeadline: 30 May 2026









