- Article
A Digital Twin Approach Integrating IoT and AI for Monitoring and Assessing Roof Degradation in Historic Buildings
- Margherita Valentini,
- Paolo Brotto and
- Rita Vecchiattini
- + 6 authors
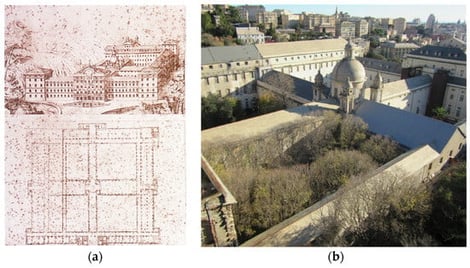
The EN-HERITAGE project aims to define and prototype an integrated digital platform for the management of virtual models of buildings belonging to the historic built heritage, with a particular focus on slate roofing systems. The platform integrates IoT technologies for environmental monitoring, architectural surveys carried out using laser scanning and photogrammetry, HBIM models, and artificial intelligence algorithms for the analysis of degradation phenomena. The pilot application was conducted on the Albergo dei Poveri complex in Genoa, providing a replicable methodology for the planned conservation of the historic built environment. Preliminary results highlight the effectiveness of the platform in integrating heterogeneous data, providing stakeholders involved in the management of extensive architectural heritage with concrete support for decision-making processes and greater efficiency in planning maintenance and restoration interventions on historic buildings.
13 January 2026



![Fissure-Filled Highly Expansive Soil. Reproduced from [17]. Note: The typical width of the filled fissure is approximately 10 cm.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/iic/iic-01-00009/article_deploy/html/images/iic-01-00009-g001-550.jpg)