Journal Description
Future
Future
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal focused on the research areas of growth and development and school health published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 52.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 7.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
From Pilot to Practice: Developing a Family-Based Nutrition, Literacy, and Parenting Protocol for the Books & Cooks Education Intervention
Future 2026, 4(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/future4010006 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Families with low income are faced with various intertwined public health issues, including low literacy levels and nutrition insecurity. Although numerous studies have detailed effective methodologies for delivering literacy or nutrition education in silos, there is no protocol for developing, implementing, and evaluating
[...] Read more.
Families with low income are faced with various intertwined public health issues, including low literacy levels and nutrition insecurity. Although numerous studies have detailed effective methodologies for delivering literacy or nutrition education in silos, there is no protocol for developing, implementing, and evaluating a brief, interdisciplinary literacy and nutrition education program for parent–child dyads. Books & Cooks, a seven-week literacy and nutrition education program aimed at improving families’ literacy and nutrition capacities by providing parents with strategies to assist their child, facilitating interactive education lessons, and providing take-home reflection activities, was piloted during the 2023–2024 school year. Results informed the protocol for current and future cohorts in efforts to further enhance outcomes. Family literacy capacity is addressed using evidence-based, grade-appropriate literacy techniques and evaluated using validated and internally developed instruments. Family nutrition capacity is addressed through education and cooking lessons based on the 2020–2025 Dietary Guidelines and MyPlate and evaluated using validated instruments. Results will be analyzed by assessing change from baseline to post-program completion, addressing potential confounding factors, and utilizing randomization. By detailing the development, implementation, and evaluation of this study, we anticipate that this protocol will provide guidance for cross-functional collaborators who seek to address various public health concerns in at-risk populations.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Non-Invasive Neuromodulation for Pain Management in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
by
Gabrielly Santos Pereira, Marcelo Lourenço da Silva, Ana Beatriz Oliveira and Luciano Maia Alves Ferreira
Future 2026, 4(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/future4010005 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pain in children and adolescents remains an underestimated and undertreated condition, with long-term physical and psychosocial consequences. Non-invasive neuromodulation has emerged as a promising, low-risk approach for managing acute and chronic pain by modulating central and peripheral neural pathways. This systematic review followed
[...] Read more.
Pain in children and adolescents remains an underestimated and undertreated condition, with long-term physical and psychosocial consequences. Non-invasive neuromodulation has emerged as a promising, low-risk approach for managing acute and chronic pain by modulating central and peripheral neural pathways. This systematic review followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and clinical applicability of non-invasive neuromodulation techniques in pediatric pain. Searches were conducted in PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane CENTRAL, and ScienceDirect for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published between 2015 and 2025. Six RCTs met the inclusion criteria, encompassing percutaneous electrical nerve field stimulation (PENFS), transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS), transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation (TEAS), and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Four trials reported significant reductions in pain intensity alongside improvements in functional outcomes and quality of life, particularly in functional abdominal pain and postoperative contexts. Most studies showed low or moderate risk across domains, with appropriate randomization and blinded assessment. No serious adverse events were reported, confirming an excellent safety profile. These findings support non-invasive neuromodulation as a feasible and well-tolerated adjunct to conventional pediatric pain management. Further high-quality trials are warranted to standardize protocols and explore mechanisms of neuroplasticity in the developing nervous system. PROSPERO (CRD420251170866).
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProtocol
School Nurse Interventions for Children with Special Health Care Needs: A Scoping Review Protocol
by
Fernanda Pombal, Lia Sousa, Alexandra Pereira, Marta Catarino and Constança Festas
Future 2026, 4(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/future4010004 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Children with special health care needs require health and related services beyond those required by children in general, which may affect their participation and inclusion in school. School nurses play a key role in supporting these children through a range of health-related interventions
[...] Read more.
Children with special health care needs require health and related services beyond those required by children in general, which may affect their participation and inclusion in school. School nurses play a key role in supporting these children through a range of health-related interventions within the school setting. However, evidence on school nurse–led interventions for this population remains fragmented. This scoping review will follow the JBI methodology and aims to map the nature and extent of interventions developed by school nurses for children with special health care needs in school settings worldwide. The review will provide an overview of current practices and may inform the development of school health policies and evidence-informed nursing interventions. This research is registered on the Open Science Framework platform since 10 June 2024, with data updated on 26 August 2025.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Risk and Protective Factors of Smoking, Drinking, and Drug Use in a Sample of Hungarian Adolescents
by
Bettina F. Piko
Future 2026, 4(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/future4010003 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
Adolescence is a critical life period connected with the initiation of substance use. Exploring the prevalence of and contributors to adolescents’ smoking, drinking, and drug use is essential for developing effective health education programs. This study aims to detect prevalence rates of adolescent
[...] Read more.
Adolescence is a critical life period connected with the initiation of substance use. Exploring the prevalence of and contributors to adolescents’ smoking, drinking, and drug use is essential for developing effective health education programs. This study aims to detect prevalence rates of adolescent substance use and their association with sociodemographics and a set of psychological, social, and school-related variables. Participants were high school students (9th graders, N = 1590; 694 males, 896 females) in Békés county, Hungary. The lifetime prevalence rates were the following: smoking (47.2%), alternative smoking (49.2%), drinking (85.7%), cannabis use (7.6%), sedative use (7.0%), and designer drug (herbal) use (3.7%), with gender differences (a surplus of girls) found only in smoking and sedative use. Using bivariate logistic regression analyses, depressive and psychosomatic symptoms and internet addiction increased the odds of all types of substance use, life satisfaction, future orientation, and social support from the family, while school achievement and school satisfaction showed odds-reducing effects. In multivariate analyses, the various types of substance use were predicted by different variables, while psychosomatic symptoms, social support from the family, and school achievement seemed to be the most relevant contributors. Health education programs should also incorporate fostering mental health to prevent adolescent substance use.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Perfectionism, Family Climate and Emotion Regulation in Childhood
by
Katerina Antonopoulou, Nikolaos Anastasopoulos, Dimitrios A. Alexopoulos and Sofia Kouvava
Future 2026, 4(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/future4010002 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
While perfectionism is recognized as a complex personality trait with both adaptive and maladaptive facets in adults, the specific developmental and contextual factors that influence its emergence in children are poorly understood. This study addresses this critical gap by examining associations between children’s
[...] Read more.
While perfectionism is recognized as a complex personality trait with both adaptive and maladaptive facets in adults, the specific developmental and contextual factors that influence its emergence in children are poorly understood. This study addresses this critical gap by examining associations between children’s perceptions of family climate and emotion regulation strategies. A sample of 191 children (94 boys, Mage = 11.27 years, SD = 0.97) completed standardized measures of perfectionism, family environment, and emotion regulation. Results indicated that both family climate and emotion regulation significantly predict perfectionism in children (R2 = 0.36). Specifically, children’s perceptions of high parental control, a strong achievement family orientation, and reliance on expressive suppression (hiding emotions) emerged as moderate, significant predictors. These findings clarify the developmental factors underlying perfectionism, providing actionable targets—particularly around adaptive parenting and emotion coping—for child and family support programs and preventative interventions focused on promoting long-term well-being.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Safety of Children with Food Allergies in Public Schools: Gaps, Challenges, and Strategies for Improvement
by
Alexandra Ribeiro, Sara Diogo Gonçalves, Maria Monteiro and Ana Caramelo
Future 2026, 4(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/future4010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
Food allergies in school-aged children are a growing public health concern, requiring coordinated strategies to ensure safety in educational settings. This study aimed to evaluate the safety conditions for children and young people with food allergies in public schools of the municipality of
[...] Read more.
Food allergies in school-aged children are a growing public health concern, requiring coordinated strategies to ensure safety in educational settings. This study aimed to evaluate the safety conditions for children and young people with food allergies in public schools of the municipality of Matosinhos, Portugal. A descriptive, cross-sectional, quantitative study was conducted during the 2022/2023 academic year, targeting coordinating teachers from all public schools. Data were collected using a structured questionnaire based on national guidelines for managing food allergies in schools. Results revealed significant gaps in preparedness: 35.99% of respondents reported the absence of a formal document on food allergies, 66.01% indicated no school training plan on the topic, and bar and canteen staff were often excluded from training (50.00% and 42.00%, respectively). Furthermore, 83.02% stated that preventive measures were not consistently adopted, and 49.99% felt insufficiently trained to act in emergencies. Based on these findings, an intervention project with tailored training sessions for coordinating teachers was proposed to improve safety and inclusion for students with food allergies. The study highlights the urgent need for standardized protocols, inclusive training, and preventive measures in schools to mitigate risks and foster a safe learning environment for children with food allergies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Sociocultural Factors Impacting Substance Misuse and Treatment: A Latent Class Analysis of Youths Undergoing Combined Treatment
by
Hayley D. Seely, Luke Still, Emily Weinberger, Eileen Chen, Kalyn Holmes, Ryan Loh and Christian Thurstone
Future 2025, 3(4), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3040025 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Adolescent mental health and substance misuse is a growing issue, disproportionately affecting diverse youth and those in low-resourced, high-stress environments. Yet, despite recent advances in evidence-based practices for adolescent substance use, perpetuating factors remain under-explored and marginalized, and underserved groups continue to
[...] Read more.
Background: Adolescent mental health and substance misuse is a growing issue, disproportionately affecting diverse youth and those in low-resourced, high-stress environments. Yet, despite recent advances in evidence-based practices for adolescent substance use, perpetuating factors remain under-explored and marginalized, and underserved groups continue to be underrepresented. The current study aimed to investigate sociocultural factors impacting substance misuse and treatment outcomes. Methods: Data from adolescents receiving combined mental health and substance misuse treatment at a regional safety-net hospital were analyzed. Using Latent Class Analysis (LCA), demographic variables including insurance coverage, area deprivation, race, ethnicity, age, gender, court involvement, and primary mental health diagnoses were used to identify unique adolescent subgroups based on these different sociocultural risk factors. Identified classes were tested as predictors of treatment engagement, length of treatment, future service utilization, substance misuse, and urine drug screen results. Results: Five unique subgroups were identified, differentially impacting substance misuse, future service utilization, and treatment outcomes. Conclusions: These results highlight the need for improved access to resources for adolescents who have been marginalized and traditionally underserved. Furthermore, the identified subgroups can inform future research and practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Future)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Parents’ Perceptions of Screens, Addiction and the Impact on Teenagers’ Sleep
by
Laetitia Gomes, Frederica Simplício, Anna Litvinchuck, Amélia Rica and Elisabete Cioga
Future 2025, 3(4), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3040024 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to analyze parents’ perceptions regarding adolescents’ screen use, signs of screen dependency, and its impact on sleep among 10- to 16-year-olds in the district of Leiria, Portugal. A descriptive–correlational, cross–sectional study was conducted in April 2024 using an online
[...] Read more.
Objective: This study aimed to analyze parents’ perceptions regarding adolescents’ screen use, signs of screen dependency, and its impact on sleep among 10- to 16-year-olds in the district of Leiria, Portugal. A descriptive–correlational, cross–sectional study was conducted in April 2024 using an online questionnaire completed by a non-probabilistic accidental sample of 616 parents or legal guardians. Nearly half of the respondents (48.2%) perceived adolescents as dependent on screens, while 68.7% believed that their screen time was excessive. Several behavioural signs consistent with digital dependence were reported. Increased screen use was significantly associated with shorter sleep duration, daytime sleepiness, and difficulties initiating sleep. Although many adolescents still achieved the recommended number of hours of sleep, those perceived as screen-dependent were more likely to experience compromised sleep quality and quantity. These findings reinforce the growing concern about adolescents’ digital habits and underscore the importance of implementing targeted health promotion strategies focused on responsible screen use and sleep hygiene among school-aged youth.
Full article
Open AccessCommentary
Towards Gender-Inclusive HPV Vaccination in England: Addressing Misconceptions and Missed Opportunities for Boys
by
Daniel Gaffiero, Amelia Dytham, Rebecca Cotton, Rahim Hussein, Michaela E. Christodoulaki and Stephanie A. Davey
Future 2025, 3(4), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3040023 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination is a cornerstone of cancer prevention across genders. In the United Kingdom (UK), the programme now includes boys, yet uptake remains below target, with persistent disparities by gender and region. This commentary examines the drivers of these gaps, including
[...] Read more.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination is a cornerstone of cancer prevention across genders. In the United Kingdom (UK), the programme now includes boys, yet uptake remains below target, with persistent disparities by gender and region. This commentary examines the drivers of these gaps, including the historical framing of the HPV vaccine as a vaccine for girls, limited public awareness of boys’ eligibility, and challenges in school-based delivery. Gendered misconceptions, cultural norms, and inadequate communication continue to limit uptake in boys, while healthcare professionals, including general practitioners, dentists, and pharmacists, remain underused in supporting vaccine access and tackling parental hesitancy. Schools are central to equitable delivery, but teachers often lack training and possess low-to-moderate knowledge of HPV-related topics, including HPV vaccination availability for boys and HPV-related cancers affecting men. Drawing on health behaviour theory, we propose evidence-informed, multi-level recommendations to improve uptake, from gender-inclusive messaging and more efficient consent processes to digital engagement tools that support parents. We also highlight our ongoing research into parental attitudes toward HPV vaccination for boys aged 9–12 in England, which will inform future targeted interventions and policy development.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Integrating Plant-Based Diets into Schools for a Healthier and More Sustainable Future: A Contemporary Overview
by
Alejandro Borrego-Ruiz and Juan J. Borrego
Future 2025, 3(4), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3040022 - 23 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Schools constitute strategic settings for shaping eating behaviors among youth. Given the profound environmental, health, and social challenges associated with current food systems, there is an urgent need to explore dietary patterns that simultaneously support human well-being, ecological sustainability, and ethical principles. This
[...] Read more.
Schools constitute strategic settings for shaping eating behaviors among youth. Given the profound environmental, health, and social challenges associated with current food systems, there is an urgent need to explore dietary patterns that simultaneously support human well-being, ecological sustainability, and ethical principles. This comprehensive review provides a contemporary overview of the role of plant-based diets as an instrumental pathway to a healthier and more sustainable future by examining (i) environmental and social impacts of current food systems; (ii) the effects of plant-based diets on health; (iii) determinants of plant-based diet implementation in schools, including barriers and facilitators to their adoption; and (iv) the development of future-oriented dietary guidelines. Transitioning to plant-based diets, combined with sustainable agricultural practices, can reduce resource use and promote ecological sustainability. Promoting plant-based diets can also encourage the development of a more responsible and equitable social culture. Plant-based diets consistently provide metabolic, cardiovascular, and anti-inflammatory benefits across diverse populations, contributing to healthy weight and glycemic regulation. Well-planned plant-based diets may also improve cognitive function and promote psychological well-being. The integration of plant-based diets in schools is limited by barriers such as children’s food preferences, habitual eating patterns, peer influence, time and resource constraints, limited knowledge, cultural attachment to meat, and low family involvement. Conversely, facilitators including experiential learning, nutrition education, teacher and family engagement, social norms, ethical or environmental motivations, and institutional support promote acceptance and implementation. Ongoing research is required to refine dietary recommendations, assess long-term health outcomes, and ensure nutritional adequacy across pediatric populations. Continued evaluation of school-based interventions and policy frameworks will be essential to optimize the integration of plant-based diets and to monitor their health, ethical, and environmental impacts.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Navigating Controversial Topics: Discussion-Based Pedagogy in Health Education
by
Emily Lockhart, Jennie Bickmore-Brand and Phil Doecke
Future 2025, 3(4), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3040021 - 21 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: Health education is critical in imparting health literacy to children and developing community health and wellbeing. The effectiveness of the teaching–learning interaction in health education classes depends on the teacher employing effective teaching methods, facilitating students’ deep understanding, critical thinking, and
[...] Read more.
Objective: Health education is critical in imparting health literacy to children and developing community health and wellbeing. The effectiveness of the teaching–learning interaction in health education classes depends on the teacher employing effective teaching methods, facilitating students’ deep understanding, critical thinking, and the development of skills, beliefs and attitudes that will be needed for them to cultivate healthy behaviours throughout their lives. Health education teaching differs from other learning areas as it addresses controversial and sensitive topics in class. Little research has been conducted regarding the preferred teaching methods of health educators and their ability to employ these teaching methods effectively in the classroom. Methods: In this paper, we present findings from a doctoral grounded theory study to explain the preferred teaching methods of teachers as they work with young people in the important learning area of health education. The study was conducted using a Chamazian constructivist grounded theory approach with the data being analysed using an inductive process, beginning with open codes and progressing to high-level categories. Main Results: This study determined that the preferred teaching method of the teachers delivering health education in Western Australia was discussion-based teaching. We examine the literature regarding discussion-based teaching methods, particularly in health education. Our findings evidence that teachers report preferring a discussion-based teaching approach, even though the health curriculum advises a critical inquiry approach and many schools in Australia currently promote an explicit teaching method. Conclusions: Teachers have expressed uncertainty as to how to effectively employ a discussion-based approach in class and have sought further clarification as they lead class discussions. Effective teaching practices need to be interrogated to support teachers, so how do we do this in a way that provides clarity for teachers and ultimately produces the best outcomes for young people?
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Parenting Style and Adolescents’ Cyberbullying Behaviors: Restrictive Parental Internet Intervention as a Moderator in Macau
by
Shu-Wen Liu and Ka Long Hoi
Future 2025, 3(4), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3040020 - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study examined the effects of perceived parenting styles and restrictive parental internet intervention on adolescents’ cyberbullying behaviors in Macau. A survey conducted in 2023 gathered responses from 708 secondary school students aged 12 to 18. The findings indicated that fathers’ authoritative and
[...] Read more.
This study examined the effects of perceived parenting styles and restrictive parental internet intervention on adolescents’ cyberbullying behaviors in Macau. A survey conducted in 2023 gathered responses from 708 secondary school students aged 12 to 18. The findings indicated that fathers’ authoritative and permissive parenting styles were positively associated with adolescents’ experiences of cyberbullying, both as perpetrators and victims. Mothers’ authoritative style was significantly associated with increased cyber-victimization. Notably, when mothers used an authoritative style and also applied restrictive internet intervention strategies—such as time or content controls—adolescents reported higher levels of cyber-victimization. These results suggest that rigid control, if not combined with open communication, may heighten risk. This study highlights the importance of involving both parents—particularly fathers—in adolescent media education and calls for increased awareness in social work, education, and family policy to prevent and mitigate cyberbullying in the digital age.
Full article
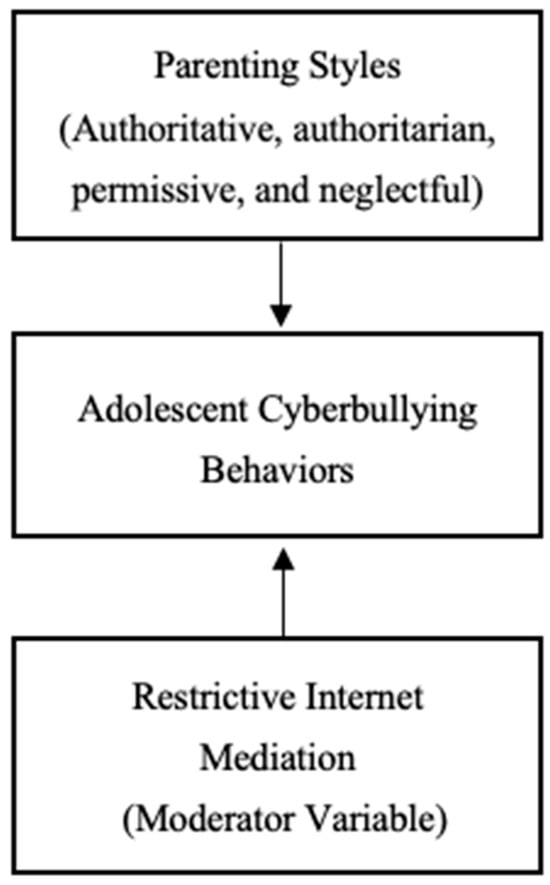
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Associations Between Preschool Bedroom Television and Subsequent Psycho-Social Risks Amplified by Extracurricular Childhood Sport
by
Béatrice Necsa, Kianoush Harandian, Caroline Fitzpatrick, Eric F. Dubow and Linda S. Pagani
Future 2025, 3(4), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3040019 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Preschool bedroom television placement represents an established risk factor for negative psychological and behavioral outcomes in adolescence. Girls and boys have different risk factors for developmental psychopathology. It is unclear if childhood sport participation can act as a protective factor for the
[...] Read more.
Background: Preschool bedroom television placement represents an established risk factor for negative psychological and behavioral outcomes in adolescence. Girls and boys have different risk factors for developmental psychopathology. It is unclear if childhood sport participation can act as a protective factor for the potential maladaptive behaviors associated with having a bedroom television in early childhood. Methods: This study aims to evaluate the impact of having a bedroom television in early childhood on later externalizing behaviors while examining the potential beneficial role of extracurricular sport participation in middle childhood using the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Child Development (Canada). We examine subsequent teacher-reported psycho-social outcomes by the end of sixth grade. Linear regression is used to examine the interaction between child-reported bedroom television placement (age 4 years) and parent-reported childhood sport participation trajectories (ages 6 to 10 years) in predicting behavioral outcomes at age 12 years. Results: For boys, extracurricular sport amplified the relationship between having a preschool bedroom television and subsequent physical aggression (b = 0.95, SE = 0.32, p < 0.001) and ADHD symptoms (b = 0.59, SE = 0.30, p ≤ 0.05), beyond individual and family characteristics. No interaction results were found for girls; however, consistent sport participation between ages 6 and 10 years resulted in a decrease in ADHD symptoms in girls (b = −0.329, SE = 0.102, p ≤ 0.001). Conclusion: Unexpectedly, for boys exposed to early bedroom television, consistently participating in extracurricular sport in childhood exacerbated long-term behavioral risks. Social unpreparedness from bedroom television placement countered the intended benefits of sport. This private access to screens might influence sedentary, unsupervised, isolated activity that increases the chances of viewing violence and reduces opportunities for social interaction.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Thyroid Disorder in Obese Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangladesh
by
Farzana Sharmin, Anika Tasneem Chowdhury, Mosharop Hossian, Shaima Rafiquzzaman, Dhiraj C. Biswas, Fatema Hashem Rupa and Suraiya Begum
Future 2025, 3(4), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3040018 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Childhood obesity is becoming an increasingly pressing issue on a global scale. This study aimed to explore the relationship between thyroid hormone levels and body mass index (BMI) in obese children and adolescents, an area with limited research, particularly in Bangladesh. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background: Childhood obesity is becoming an increasingly pressing issue on a global scale. This study aimed to explore the relationship between thyroid hormone levels and body mass index (BMI) in obese children and adolescents, an area with limited research, particularly in Bangladesh. Methods: This cross-sectional study was undertaken in Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University, Bangladesh, from August 2018 to January 2020. We included 105 participants aged 10–18 years, divided into obese (n = 69) and normal-weight (n = 36) groups based on the CDC BMI percentiles. We conducted chi-square tests, Pearson correlation, and linear regression analyses. Results: Obese participants exhibited significantly higher mean levels of TSH (4.40 ± 3.20 µIU/mL vs. 2.26 ± 0.97 µIU/mL, p-value 0.0002) and FT3 (3.52 ± 0.71 pg/mL vs. 3.02 ± 0.48 pg/mL, p-value < 0.001) and lower FT4 levels (1.23 ± 0.21 ng/dL vs. 1.38 ± 0.30 ng/dL, p-value 0.0002) compared to normal-weight participants. We observed a positive correlation between BMI and TSH (p-value 0.002) and FT3 (p-value < 0.001), and a negative correlation between BMI and FT4 (p-value 0.003). Most of the obese children were euthyroid (71.01%), with 27.54% showing subclinical hypothyroidism and 1.45% showing overt hypothyroidism. Multivariable linear regression analysis revealed that with a one unit increase in BMI, FT3 increased by 0.032 ± 0.011 pg/mL (p-value 0.004), FT4 decreased by 0.010 ± 0.004 (p-value 0.017 ng/dL, and TSH increased by 0.104 ± 0.044 µIU/mL (p-value 0.020). Conclusions: The significant association between BMI and thyroid hormone levels underscores the necessity for routine thyroid function monitoring in obese paediatric populations. The early detection and management of thyroid dysfunction may enhance health and well-being outcomes in obese children and adolescents.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Parents and Athletes’ Perceptions of Parental Involvement Practices in Youth Basketball
by
Maria V. Lopes, Andreas Ihle, Élvio Rúbio Gouveia, Adilson Marques, Fahri Safa Cinarli and Cíntia França
Future 2025, 3(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3030017 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Parental involvement in youth sports is an increasingly relevant topic because of its key implications for children’s development in youth sports. This study’s aims are threefold: (1) to investigate parental involvement practices based on parents’ previous sports experiences, (2) to examine athletes’ and
[...] Read more.
Parental involvement in youth sports is an increasingly relevant topic because of its key implications for children’s development in youth sports. This study’s aims are threefold: (1) to investigate parental involvement practices based on parents’ previous sports experiences, (2) to examine athletes’ and parents’ perceptions on parental involvement practices across different age categories, and (3) to compare the athletes’ and parents’ overall perceptions on parental involvement practices. In total, 423 participants (151 youth players and 272 parents) completed the Parental Behaviors in Sports (PBSP) questionnaire. The PBSP includes separate versions for parents and athletes, each assessing five key dimensions: (1) sports support, (2) competition attendance, (3) technical influence, (4) performance pressure, and (5) sports expectations. In the parents’ group, 154 participants (56.6%) reported previous sports experience. No statistically significant differences were observed in the PBSP dimensions between parents with and without previous sports experience. Parents’ years of sports experience negatively correlated with performance pressure (r = −0.155, p = 0.013) and expectations (r = −0.149, p = 0.017). Age group analysis showed lower competition attendance in the U18 group and higher expectations in the U12 group. When comparing parents’ and athletes’ responses, statistically significant differences emerged in all PBSP dimensions except for performance pressure. These findings underscore the importance of aligning parental involvement with children’s experiences to foster enjoyment, reduce pressure, and support sustained engagement in youth sports.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Appearance of Disordered Eating Behaviors in Adulthood Through Low Self-Esteem and Mental Health in Childhood
by
Anna Papadimitriou and Eirini Karakasidou
Future 2025, 3(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3030016 - 13 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to explore the extent to which self-esteem, depression, anxiety, and stress experienced during childhood may contribute to the development of disordered eating behaviors in adulthood. The existing literature indicates that disordered eating habits are positively associated with
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this study is to explore the extent to which self-esteem, depression, anxiety, and stress experienced during childhood may contribute to the development of disordered eating behaviors in adulthood. The existing literature indicates that disordered eating habits are positively associated with symptoms of anxiety, stress, depression, and low self-esteem. However, most research focuses on the concurrent relationships among these variables rather than examining whether low self-esteem and poor mental health in childhood can influence the emergence of disordered eating behaviors later in life. An online quantitative survey was conducted using questionnaires completed by 135 participants aged between 30 and 70 years. The results revealed that low self-esteem and high levels of depression, anxiety, and stress during childhood were associated with increased disordered eating behaviors in adulthood. These findings suggest that negative self-perceptions and poor mental health in childhood have lasting effects that extend into adulthood. This knowledge can be valuable for psychologists, mental health professionals, parents, and schools in designing intervention programs aimed at enhancing children’s and adolescents’ self-esteem, promoting good mental health, and fostering healthy eating habits.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Changes in Alcohol, Cannabis, and Tobacco Use Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic in Adolescents in Catalonia: A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study
by
Judit Rogés, Katherine Pérez, Xavier Continente, Juan Miguel Guerras, Brenda Robles, Inmaculada Mateo, Carmen Vives-Cases, Marina Bosque-Prous, Helena Gonzalez-Casals, Cinta Folch, Montse Bartroli, María José López, Esteve Fernández and Albert Espelt
Future 2025, 3(3), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3030015 - 8 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study analyzes the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on alcohol, cannabis, and tobacco use among adolescents aged 14–19 in Central Catalonia across three periods. Data were obtained from two waves of the DESKcohort project. The first wave (n = 4641) was
[...] Read more.
This study analyzes the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on alcohol, cannabis, and tobacco use among adolescents aged 14–19 in Central Catalonia across three periods. Data were obtained from two waves of the DESKcohort project. The first wave (n = 4641) was pre-COVID-19 and the second wave was divided into two phases: post-COVID-19 with restrictions (n = 3478) and post-COVID-19 without restrictions (n = 2900). The prevalence of monthly binge drinking, cannabis use in the last 30 days, and daily tobacco use was calculated. Poisson regression models estimated adjusted prevalence ratios (aPR) comparing two post-pandemic phases to the pre-pandemic baseline. Binge drinking increased during the restrictions among girls [aPR = 1.5 (95%CI: 1.1–2.1)] and boys [aPR = 1.7 (95%CI: 1.3–2.3)]. Cannabis use decreased during restrictions and remained low post-pandemic, especially among girls [aPR = 0.6 (95%CI: 0.5–0.8)] and boys in the 4th Compulsory Secondary Education (CSE) [aPR = 0.4 (95%CI: 0.3–0.6)], and girls in the 2nd Post-Compulsory Secondary Education/Intermediate-Level Training Cycles (PCSE/ILTC) [aPR = 0.7 (95%CI: 0.6–0.9)]. Daily tobacco use also dropped among boys in the 4th year of CSE [aPR = 0.5 (95%CI: 0.3–0.7)] and girls in the 2nd year of PCSE/ILTC [aPR = 0.7 (95%CI: 0.6–0.9)]. The COVID-19 pandemic has created a unique opportunity to reassess patterns of adolescent substance use in a context of sudden social disruption. The findings highlight the need to denormalize alcohol and tobacco use and promote healthier adolescent behavior through education.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Professional Development Pilot Program for Paraprofessionals in a Special Education Setting: A Qualitative Exploration of Their Experiences
by
Keisha McCoy and Chana S. Max
Future 2025, 3(3), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3030014 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
Paraprofessionals play a crucial role in supporting both teachers and students within a classroom, even though the specifics of their duties vary. While their responsibilities involve supporting student achievement, research has shed light that many paraprofessionals feel unprepared for their responsibilities in the
[...] Read more.
Paraprofessionals play a crucial role in supporting both teachers and students within a classroom, even though the specifics of their duties vary. While their responsibilities involve supporting student achievement, research has shed light that many paraprofessionals feel unprepared for their responsibilities in the classroom. This study aimed to address a gap in the existing literature by exploring how a professional development program that mirrors the trainings special education teachers receive would impact paraprofessionals and help them feel more prepared for their responsibilities in the classroom. Employing a generic qualitative methodology, this study sought to capture the experiences of 43 paraprofessionals. Data collection involved an online open-ended questionnaire at the start and conclusion of the school year. The study’s outcomes revealed five patterns in the data: (a) paraprofessionals struggled with collaborating with classroom teams at the start of the school year, (b) paraprofessionals struggled with managing student behavior at the start of the school year, (c) professional development was helpful to most of the paraprofessionals, (d) professional development led to better preparedness to address challenging behavior, and (e) professional development led to better preparedness to address the instructional needs of students with disabilities. Following a thorough analysis and synthesis, these patterns were condensed into two general themes: the importance of professional development for paraprofessionals and the importance of presenting the professional development that teachers receive on a continuous basis to paraprofessionals as well. These findings are significant for school leaders and educators, as they highlight the importance of providing professional development to paraprofessionals while supporting students with disabilities.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Caregiving for Children and Youth with CHARGE Syndrome: Impact of Family Caregiver Quality of Life and Coping Strategies
by
Afeez A. Hazzan, Lauren J. Lieberman, Pamela Beach and Jonathan Ferrer
Future 2025, 3(3), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3030013 - 20 Jun 2025
Abstract
Individuals with CHARGE syndrome often experience motor delays impacting their balance, flexibility, and hand–eye coordination. Due to the medical complications associated with CHARGE syndrome, 40% of children will not develop functional communication skills and many more will have difficulty with speech and oral
[...] Read more.
Individuals with CHARGE syndrome often experience motor delays impacting their balance, flexibility, and hand–eye coordination. Due to the medical complications associated with CHARGE syndrome, 40% of children will not develop functional communication skills and many more will have difficulty with speech and oral communication. Family caregivers play a critical role in the care of children and youths with disabilities, especially CHARGE syndrome. However, there is minimal research on the parental experiences of children and youth with CHARGE syndrome. The purpose of this study was to understand the family caregiver experiences and needs of parents of children and youth with CHARGE syndrome and related disabilities. Six family caregivers of children and youth living with CHARGE syndrome in the United States were interviewed to understand their current quality of life, factors influencing their quality of life, and the coping strategies they use. The interviews were transcribed verbatim and then analyzed using qualitative content analysis. The themes generated from the qualitative analyses of interviews showed that family caregivers experienced significant challenges in their quality of life and faced barriers as they navigated a complex system of care. However, family caregivers described robust approaches such as social support for coping with some of the stresses.
Full article
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Overview and Methods for Chinese National Surveillance on Students’ Common Diseases and Risk Factors, 2022
by
Yi Xing, Qi Ma, Mengjie Cui, La Mang, Peijin Hu, Bin Dong, Yanhui Dong, Li Chen, Jun Ma and Yi Song
Future 2025, 3(2), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/future3020012 - 19 Jun 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Child and adolescent health plays a critical role in shaping future public health and intergenerational outcomes. In China, rising rates of myopia, obesity, mental health issues, and other common conditions highlight the need for continuous monitoring. Since 2016, the Chinese National Surveillance on
[...] Read more.
Child and adolescent health plays a critical role in shaping future public health and intergenerational outcomes. In China, rising rates of myopia, obesity, mental health issues, and other common conditions highlight the need for continuous monitoring. Since 2016, the Chinese National Surveillance on Students’ Common Diseases and Risk Factors (CNSSCDRF) has provided comprehensive, nationwide data on student health. By 2022, the system had expanded to nearly all counties, tracking key indicators such as vision problems, overweight/obesity, dental caries, and health-risk behaviors across multiple administrative levels. This review outlines the surveillance methodology, including sampling, data collection, and analysis. Findings have directly informed school health policies and technical guidelines, supporting national goals such as those in the Healthy China 2030 Plan.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Children, Disabilities, Future, Healthcare, IJERPH, Sports
Health, Physical Activity, and Recreation of Children with Sensory Impairments
Topic Editors: Lauren Lieberman, Pamela BeachDeadline: 30 June 2027








