Review Papers of Fibers
A topical collection in Fibers (ISSN 2079-6439).
Viewed by 111709
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Martin J. D. Clift
Prof. Dr. Martin J. D. Clift
 Prof. Dr. Martin J. D. Clift
Prof. Dr. Martin J. D. Clift
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
In Vitro Toxicology Group, Institute of Life Sciences 1, Swansea University Medical School (SUMS), Swansea SA2 8PP, Wales, UK
Interests: nanotoxicology; genotoxicology; immunology; inflammation; cancer; cell signalling; in vitro analysis; cellular entry mechanisms; protein-nanoparticle interactions; nanoparticle-cell interactions; nanofibers; nanoparticles
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Fiber is a natural or human-made substance that is significantly longer than it is wide, which plays an important role in daily life. In plants and animals, fibers play an important role in maintaining tissue. Fibers are widely used and can be woven into thin threads, thread ends and hemp ropes, and can also be woven into fiber layers when making paper or weaving felt. It is also commonly used to manufacture other materials, and to form composite materials together with other materials. Fiber filling can effectively improve the strength and stiffness of plastics. The application of fiber is ubiquitous in life, and it contains high technology, high temperature resistance of missiles, collapse of river embankments, and prevention of cracking of cement, all of which are inseparable from fibers.
This Topical Collection aims to collect scientific and technological developments and the latest research hot topics in the field of “fibers”. The main article type will be focused on “review”. The following topics are welcomed, but not limited to:
- Polymer fibers;
- Carbon fibers;
- Nanofibers;
- Optical fibers;
- Glass fibers;
- Nanotubes;
- Plant fibers;
- Cellulose;
- Animal fibers;
- Mineral fibers;
- Synthetic fibers;
- Textile fibers;
- Fibers reinforcement;
- Other topics related to fibers.
Prof. Dr. Martin J. D. Clift
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Fibers is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2000 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (13 papers)
Open AccessReview
Advanced Peptide Nanofibers in Delivery of Therapeutic Agents: Recent Trends, Limitations, and Critical Properties
by
Razieh Taghizadeh Pirposhteh, Omolbani Kheirkhah, Shamsi Naderi, Fatemeh Borzouee, Masoume Bazaz and Mazeyar Parvinzadeh Gashti
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1431
Abstract
Peptide nanofibers (PNFs) have emerged as versatile platforms for delivering therapeutic agents due to their biocompatibility, tunable characteristics, and ability to form well-ordered nanostructures. The primary goal of this review is to elaborate on the key features of common PNF fabrication strategies, including
[...] Read more.
Peptide nanofibers (PNFs) have emerged as versatile platforms for delivering therapeutic agents due to their biocompatibility, tunable characteristics, and ability to form well-ordered nanostructures. The primary goal of this review is to elaborate on the key features of common PNF fabrication strategies, including both spontaneous and non-spontaneous methods, while exploring how the amino acid sequences of these peptides influence their secondary structure and fiber formation. Additionally, we have compiled studies on PNFs that investigate various delivery approaches, such as systemic delivery, localized delivery, controlled delivery, stimuli-responsive delivery, and targeted delivery. This analysis aims to guide researchers in selecting the most suitable fabrication strategy for specific delivery applications and provide insights into choosing optimal amino acids for rational peptide design. We also focused on the applications of PNFs in delivering various therapeutic agents, including drugs, functional peptides, diagnostic and imaging agents, genes, viral vectors, and vaccines, demonstrating their significant potential in biomedical applications. The synergy between nanofiber fabrication strategies and peptide chemistries offers new avenues for advancing therapeutic products. Overall, this review serves as an important reference for the design and development of advanced PNFs for the effective delivery of various therapeutic agents.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Comprehensive Review of Vertical Forest Buildings: Integrating Structural, Energy, Forestry, and Occupant Comfort Aspects in Renovation Modeling
by
Vachan Vanian, Theodora Fanaradelli and Theodoros Rousakis
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1873
Abstract
This current review examines modeling approaches for renovating reinforced concrete (RC) buildings for vertical forest (VF) application, taking into account structural retrofitting, energy systems, forestry integration, and occupant comfort. The study assesses research conducted with an advanced 3D finite element analysis and the
[...] Read more.
This current review examines modeling approaches for renovating reinforced concrete (RC) buildings for vertical forest (VF) application, taking into account structural retrofitting, energy systems, forestry integration, and occupant comfort. The study assesses research conducted with an advanced 3D finite element analysis and the use of retrofitting modeling techniques, including textile-reinforced mortar (TRM), fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP), seismic joints, and green concrete applications. The energy system modeling methods are reviewed, taking into account the complexity of incorporating vegetation and seasonal variations. During forestry integration, three main design parameters are identified, namely, root systems, trunks, and crowns, for their critical role in the structural stability and optimal environmental performance. The comfort models are identified evolving from static to adaptive models incorporating thermal, acoustic, visual and air quality parameters. The current review consists of more than one hundred studies indicating that the integration of natural systems to buildings requires a multidimensional and multidisciplinary approach with sophisticated systems. The findings of this review provide the basis for implementing VF models to RC buildings, while highlighting areas requiring further research and validation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Use of Asbestos and Its Consequences: An Assessment of Environmental Impacts and Public Health Risks
by
António Curado, Leonel J. R. Nunes, Arlete Carvalho, João Abrantes, Eduarda Lima and Mário Tomé
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 6712
Abstract
The use of asbestos, once celebrated for its versatility and fire-resistant properties, has left a lasting legacy of environmental degradation and public health risks. This paper provides a comprehensive assessment of the environmental impacts and health risks associated with asbestos, highlighting its widespread
[...] Read more.
The use of asbestos, once celebrated for its versatility and fire-resistant properties, has left a lasting legacy of environmental degradation and public health risks. This paper provides a comprehensive assessment of the environmental impacts and health risks associated with asbestos, highlighting its widespread use, environmental persistence, and adverse effects on human health. Through a literature review, this study examines the historical context of asbestos use, its adverse environmental effects and the mechanisms by which exposure to asbestos poses significant health risks, including the development of asbestos-related diseases such as mesothelioma, lung cancer, asbestosis, etc. It also assesses the current regulatory framework and provides a methodological analysis of the strategy for recycling end-of-life materials containing asbestos fibers, proposing the inclusion of asbestos-containing materials (ACMs) in the rock wool industry to reduce Greenhouse Gasses (GHG) emissions. Drawing on interdisciplinary insights from environmental science, public health, and regulatory analysis, this paper concludes with recommendations for improving asbestos management strategies, promoting safer alternatives and mitigating the long-term environmental and human health impacts of asbestos.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Sustainable and Naturally Derived Wet Spun Fibers: A Systematic Literature Review
by
Cristiana Pereira, Tânia V. Pinto, Raquel M. Santos and Nuno Correia
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 6404
Abstract
Increasing economic and environmental concerns arising from the extensive exploration and dependence on fossil fuel-based materials have encouraged the search for eco-friendly alternatives. Fibers based on biomass-derived materials have been attracting growing interest. Among other features, the mechanical performance of bio-based fibers needs
[...] Read more.
Increasing economic and environmental concerns arising from the extensive exploration and dependence on fossil fuel-based materials have encouraged the search for eco-friendly alternatives. Fibers based on biomass-derived materials have been attracting growing interest. Among other features, the mechanical performance of bio-based fibers needs to be improved to effectively compete with their counterparts and emerge as viable substitutes. This review presents scientific advancements in the development of naturally derived fibers, and strategies for their production with tailored mechanical properties. The potential of natural precursor-based fibers for their conversion into high-performance carbon fibers is also emphasized. Studies reporting the mechanical properties of bio-based fibers developed by wet spinning are identified, analyzed, and discussed. These studies show that cellulose is the most studied material, while Ioncell technology is identified as the most suitable method for producing cellulose-based fibers with the highest tensile strength. Studies have also demonstrated that silk fibroin exhibits tensile strength and elongation at break ranging from 300 to 600 MPa and 30 to 50%. Although several novel processes have been explored, there are still challenges that need to be addressed for bio-based fibers to become feasible options, and to boost their usage across industries.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Potential Valorization of Banana Production Waste in Developing Countries: Bio-Engineering Aspects
by
Robert Waraczewski and Bartosz G. Sołowiej
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 10638
Abstract
Plant food production generates a lot of by-products (BPs). These BPs are majorly discarded into the environment, polluting it, or into landfills where they just decompose, providing no benefit and taking up storage space, causing financial costs. These plant BPs are biodegradable, but
[...] Read more.
Plant food production generates a lot of by-products (BPs). These BPs are majorly discarded into the environment, polluting it, or into landfills where they just decompose, providing no benefit and taking up storage space, causing financial costs. These plant BPs are biodegradable, but reusing them may provide a better outcome and profit. The vast majority of plant-based food BPs are polysaccharide polymers like gums, lignin, cellulose, and their derivatives. It is possible to utilize plant food production waste, like banana peels, leaves, pseudostems, and inflorescences, to produce bioethanol, single-cell protein, cellulase, citric acid, lactic acid, amylase, cosmetics, fodder additives, fertilizers, biodegradable fibers, sanitary pads, bio-films, pulp and paper, natural fiber-based composites, bio-sorbents, bio-plastic, and bio-electricity in the agro-industry, pharmaceutical, bio-medical, and bio-engineering fields. Moreover, the use of banana BPs seems to be a way of dealing with many issues in underdeveloped countries, providing a clean and ecological solution. The suggested idea might not only reduce the use of plastic but also mitigate waste pollution.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Production of Nanofibers by Electrospinning as Carriers of Agrochemical
by
Julia Colín-Orozco, Elena Colín-Orozco and Ricardo Valdivia-Barrientos
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4148
Abstract
Agrochemicals can now be protected from harsh environments like pH, light, temperature, and more with the help of a drug-loading system. This has allowed the creation of targeted and continuous release functions for pesticides and fertilizers, as well as the precise application, reduction,
[...] Read more.
Agrochemicals can now be protected from harsh environments like pH, light, temperature, and more with the help of a drug-loading system. This has allowed the creation of targeted and continuous release functions for pesticides and fertilizers, as well as the precise application, reduction, and efficiency of agrochemicals. All of these benefits have been made possible by the recent advancements in the field of nanomaterials. A simple procedure known as electrospinning can be used to create nanofibers from natural and synthetic polymers. Nanofibers have come to be recognized as one of the sustainable routes with enormous applicability in different fields. In agriculture, a promising strategy may entail plant protection and growth through the encapsulating of numerous bio-active molecules as pesticides and fertilizers for intelligent administration at the desired places. Owing to their permeability, tiny dimensions, and large surface area, nanofibers can regulate the rate at which agrochemicals are released. This slows down the rate at which the fertilizer dissolves and permits the release of coated fertilizer gradually over time, which is more effectively absorbed by plant roots, as well as the efficiency of pesticides. Thus, modern agriculture requires products and formulations that are more efficient and environmentally friendly than traditional agrochemicals. In addition to highlighting the significance and originality of using nanofibers and offering a brief explanation of the electrospinning technology, the review article’s main goal is to provide a thorough summary of the research leading to breakthroughs in the nanoencapsulation of fertilizers and pesticides.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Utilization of Novel Basalt Fiber Pellets from Micro- to Macro-Scale, and from Basic to Applied Fields: A Review on Recent Contributions
by
Tasnia Ahmed, Ahmed Bediwy, Ahmed Azzam, Riham Elhadary, Ehab El-Salakawy and Mohamed T. Bassuoni
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3406
Abstract
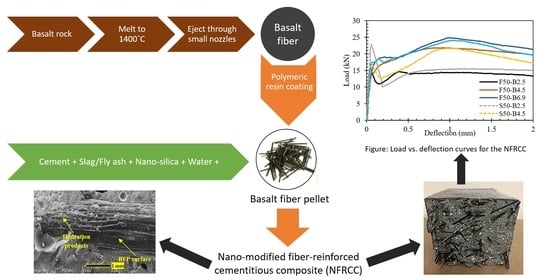
Fiber-reinforced cementitious composites (FRCC) are one of the leading engineering materials in the 21st century, as they offer proficiency in enhancing strength, ductility, and durability in structural engineering applications. Because the recently developed basalt fiber pellets (BFP) offer combined strands of fibers encased
[...] Read more.
Fiber-reinforced cementitious composites (FRCC) are one of the leading engineering materials in the 21st century, as they offer proficiency in enhancing strength, ductility, and durability in structural engineering applications. Because the recently developed basalt fiber pellets (BFP) offer combined strands of fibers encased in a polymer matrix, they are being prevalently studied to explore new possibilities when used in brittle materials such as mortar and concrete. Hence, this paper synthesizes the intensive research efforts and contributions to this novel class of fibers conducted by the authors. Specifically, it reviews the fresh, mechanical, and durability properties of FRCC incorporating single BFP or hybrid with polyvinyl alcohol fibers and modified with slag/fly ash and nano-materials and its suitability for different field applications. In addition, the nano- and meso-scale modeling of such matrices are described. BFP significantly contributes to improving post-cracking flexural behavior by toughening the cementitious matrix and minimizing strength losses when exposed to harsh environments. All results show promising progress in the development of high-performance FRCC comprising BFP, with potential success for structural and pavement applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
A Review of Fibre Reinforced Polymer Bridges
by
Jawed Qureshi
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 21911
Abstract
Fibre-reinforced polymer composites (FRPs) offer various benefits for bridge construction. Lightweight, durability, design flexibility and fast erection in inaccessible areas are their unique selling points for bridge engineering. FRPs are used in four bridge applications: (1) FRP rebars/tendons in concrete; (2) repair and
[...] Read more.
Fibre-reinforced polymer composites (FRPs) offer various benefits for bridge construction. Lightweight, durability, design flexibility and fast erection in inaccessible areas are their unique selling points for bridge engineering. FRPs are used in four bridge applications: (1) FRP rebars/tendons in concrete; (2) repair and strengthening of existing bridges; (3) new hybrid–FRP bridges with conventional materials and (4) all–FRP composite new bridges made entirely of FRP materials. This paper reviews FRP bridges, including all–FRP and hybrid–FRP bridges. FRP bridges’ history, materials, processes and bridge components—deck, girder, truss, moulded parts and cables/rebars are considered. This paper does not discuss the use of FRP as an architectural element and a strengthening system. While lack of design codes, material specifications and recycling are the major challenges, the high cost of FRPs still remains the most critical barrier to the progress of FRPs in bridges.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperEditor’s ChoiceReview
Nanofibres in Drug Delivery Applications
by
Samia Farhaj, Barbara R. Conway and Muhammad Usman Ghori
Cited by 80 | Viewed by 15106
Abstract
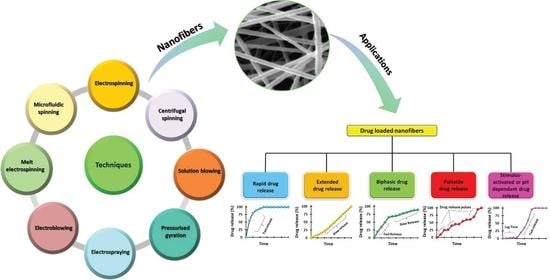
Over the years, scientists have been continually striving to develop innovative solutions to design and fabricate medicines with improved therapeutic potential. Conventional dosage forms, such as tablets, capsules, and injections, are limited when exploited for advanced therapeutics, such as drug targeting. To cater
[...] Read more.
Over the years, scientists have been continually striving to develop innovative solutions to design and fabricate medicines with improved therapeutic potential. Conventional dosage forms, such as tablets, capsules, and injections, are limited when exploited for advanced therapeutics, such as drug targeting. To cater to these limitations, nanofibres have emerged as novel nanomaterials to provide enhanced bioavailability, targeted drug release, extended drug release profile, minimum toxicity, and reduced dosage frequency, which has indisputably improved patient adherence and compliance. This review will concern understanding the potential of drug-loaded nanofibres in drug delivery while comprehending a detailed description of their different production methods. The literature has been thoroughly reviewed to appreciate their potential in developing nanofibrous-based pharmaceutical formulations. Overall, this review has highlighted the importance, versatility, and adaptability of nanofibres in developing medicines with varied drug release kinetics. Several problems must be resolved for their full commercial realisation, such as the drug loading, the initial burst effect, the residual organic solvent, the stability of active agents, and the combined usage of new or existing biocompatible polymers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Evaluation of the Tensile Characteristics and Bond Behaviour of Steel Fibre-Reinforced Concrete: An Overview
by
Mohammed A. Mujalli, Samir Dirar, Emad Mushtaha, Aseel Hussien and Aref Maksoud
Cited by 42 | Viewed by 9327
Abstract
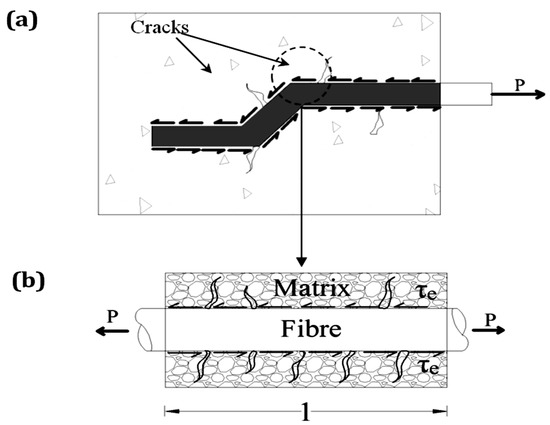
Conventional concrete is a common building material that is often ridden with cracks due to its low tensile strength. Moreover, it has relatively low shear strength and, unless reinforced, undergoes brittle failure under tension and shear. Thus, concrete must be adequately reinforced to
[...] Read more.
Conventional concrete is a common building material that is often ridden with cracks due to its low tensile strength. Moreover, it has relatively low shear strength and, unless reinforced, undergoes brittle failure under tension and shear. Thus, concrete must be adequately reinforced to prevent brittle tensile and shear failures. Steel fibres are commonly used for this purpose, which can partially or fully replace traditional steel reinforcement. The strength properties and bond characteristics between reinforcing steel fibres and the concrete matrix are crucial in ensuring the effective performance of the composite material. In particular, the quality of the bond has a significant impact on crack development, crack spacing, and crack width, among other parameters. Hence, the proper application of steel fibre-reinforced concrete (SFRC) requires a thorough understanding of the factors influencing its bond behaviour and strength properties. This paper offers a comprehensive review of the main factors controlling the bond behaviour between concrete and steel fibres in SFRC. In particular, we focus on the effects of the physical and mechanical properties of steel fibres (e.g., geometry, inclination angle, embedded length, diameter, and tensile strength) on the bond behaviour. We find that the addition of up to 2% of steel fibres into concrete mixtures can significantly enhance the compressive strength, tensile strength, and flexural strength of concrete components (by about 20%, 143%, and 167%, respectively). Furthermore, a significant enhancement in the pull-out performance of the concrete is observed with the addition of steel fibres at various dosages and geometries.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Invasive Alien Plant Species for Use in Paper and Packaging Materials
by
Urška Vrabič-Brodnjak and Klemen Možina
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 7509
Abstract
Invasive plant species can impede the establishment and growth of native plants and affect several ecosystem properties. These properties include soil cover, nutrient cycling, fire regimes, and hydrology. Controlling invasive plants is therefore a necessary, but usually expensive, step in restoring an ecosystem.
[...] Read more.
Invasive plant species can impede the establishment and growth of native plants and affect several ecosystem properties. These properties include soil cover, nutrient cycling, fire regimes, and hydrology. Controlling invasive plants is therefore a necessary, but usually expensive, step in restoring an ecosystem. The sustainability of materials with an emphasis on the use of local resources plays an important role in the circular economy. The use of alternative fibers from invasive plants promotes local production in smaller paper mills that offer the protection of local species and the reduction of waste and invasive plants. A synthesis of the literature is needed to understand the various impacts of invasive plants and their practical control in the context of papermaking applications and to identify associated knowledge gaps. To improve our understanding of the practical application of invasive species in the paper industry, we reviewed the existing literature on invasive plant species in the area of fiber production, printability, coating solution production, dyes, and extracts, and collected information on the major invasive plant species in Europe and the methods used for various applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Nanotubes: Carbon-Based Fibers and Bacterial Nano-Conduits Both Arousing a Global Interest and Conflicting Opinions
by
Silvana Alfei and Gian Carlo Schito
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3656
Abstract
Nanotubes (NTs) are mainly known as materials made from various substances, such as carbon, boron, or silicon, which share a nanosized tube-like structure. Among them, carbon-based NTs (CNTs) are the most researched group. CNTs, due to their nonpareil electrical, mechanical, and optical properties,
[...] Read more.
Nanotubes (NTs) are mainly known as materials made from various substances, such as carbon, boron, or silicon, which share a nanosized tube-like structure. Among them, carbon-based NTs (CNTs) are the most researched group. CNTs, due to their nonpareil electrical, mechanical, and optical properties, can provide tremendous achievements in several fields of nanotechnology. Unfortunately, the high costs of production and the lack of unequivocally reliable toxicity data still prohibit their extensive application. In the last decade, a significant number of intriguing nanotubes-like structures were identified in bacteria (BNTs). The majority of experts define BNTs as membranous intercellular bridges that connect neighboring bacterial cell lying in proximity. Despite recent contrasting findings, most evidence suggested that bacteria exploit NTs to realize both antagonistic and cooperative intercellular exchanges of cytoplasmic molecules and nutrients. Among other consequences, it has been proposed that such molecular trade, including even plasmids, can facilitate the emergence of new non-heritable phenotypes and characteristics in multicellular bacterial communities, including resistance to antibiotics, with effects of paramount importance on global health. Here, we provide an enthralling comparison between CNTs, which are synthetically producible and ubiquitously exploitable for improving the quality of human life, and BNTs biosynthetically produced by prokaryotes, whose functions are not still fully clarified, but whose greater knowledge could be crucial to better understand the mechanisms of pathogenesis and combat the phenomenon of resistance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Factors of Weave Estimation and the Effect of Weave Structure on Fabric Properties: A Review
by
Most. Setara Begum and Rimvydas Milašius
Cited by 46 | Viewed by 16151
Abstract
This paper provides a review of recent studies on the weave factor along with the effect of weave parameters and particularly the weave structure on various properties of woven fabric. The weave structure can be considered as one of the prime parameters that
[...] Read more.
This paper provides a review of recent studies on the weave factor along with the effect of weave parameters and particularly the weave structure on various properties of woven fabric. The weave structure can be considered as one of the prime parameters that contributes to the dominant physical and qualitative properties of the woven fabric. This study analyzed not only the parameters that significantly influence the properties of the woven fabric, but also the weave factors for the estimation of the weave that were proposed by earlier scientists. This review paper highlights the impact of weave structure on the physical and mechanical, thermo-physiological and comfort properties, and some special application properties of woven fabrics. This work seeks to serve as a future reference for related research.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures