Advances in MIMO Systems
A special issue of Electronics (ISSN 2079-9292). This special issue belongs to the section "Microwave and Wireless Communications".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 15 July 2026 | Viewed by 6792
Special Issue Editors
Interests: next generation wireless communication; MIMO; NOMA; OCDM; AI for wireless networks
Interests: 5G & beyond radio access technology; wireless communication and network; embedded system; ICT convergence system etc.
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
As the demand for wireless data continues to surge with the global deployment of 5G, research is actively advancing towards 6G to meet even greater performance requirements. A crucial technology at the heart of this evolution is Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems. MIMO, already pivotal in 5G, will play an even more significant role in 6G by enabling higher data rates, lower latency, enhanced energy efficiency, and increased spectral efficiency.
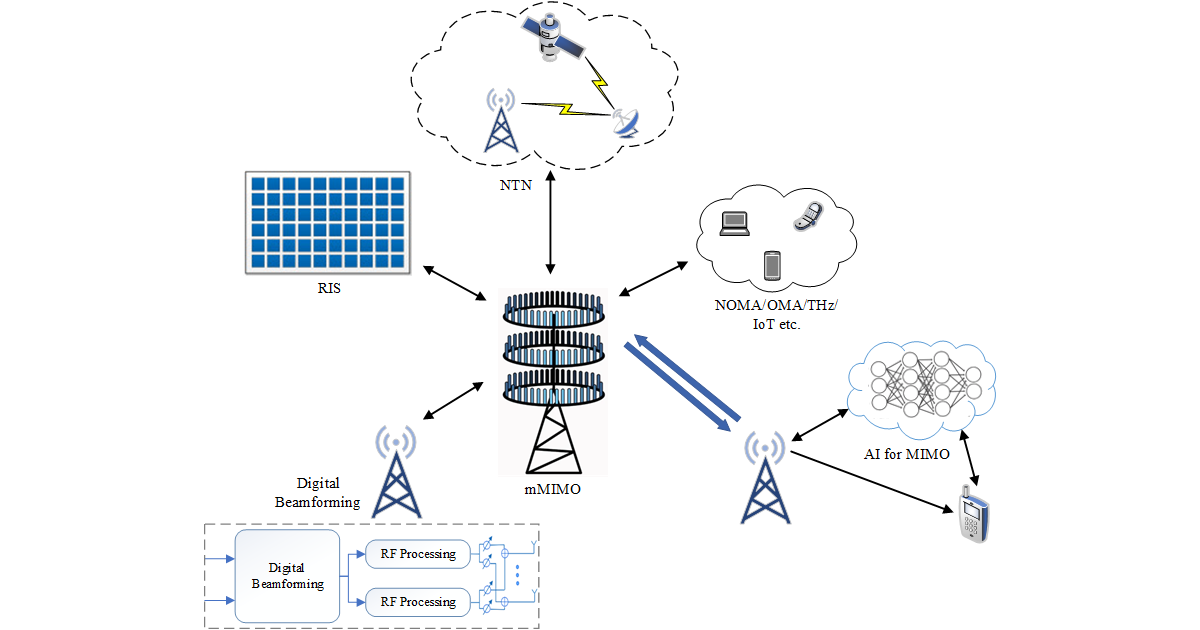
Recent advances in MIMO technology, such as massive MIMO, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), and hybrid beamforming, are shaping the future of wireless communications. These innovations aim to address challenges related to spectrum scarcity, interference, and the massive connectivity demands of IoT, IIoT, and emerging applications like autonomous systems, multisensory extended reality, and holographic rendering. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques into MIMO systems is expected to optimize resource management, beamforming, and signal processing, further pushing the performance boundaries of wireless networks.
This Special Issue will focus on the latest breakthroughs and technical challenges in MIMO systems, particularly in the context of evolving from 5G to 6G. We seek contributions that address cutting-edge developments in MIMO technology, including, but not limited to, novel architectures, AI-enhanced MIMO design, and experimental results from testbeds and field trials. The aim is to gather innovative research that will accelerate the deployment of future MIMO-based wireless networks.
In this Special Issue, original research articles and reviews are welcome. Research areas may include (but need not be limited to) the following:
- Massive MIMO, hybrid beamforming, and distributed MIMO architectures;
- AI and machine learning techniques for MIMO optimization, including resource allocation, beamforming, and interference management;
- Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) for enhancing MIMO systems;
- Energy efficiency and green communication strategies in MIMO networks;
- Advanced modulation and coding schemes for MIMO;
- Security, privacy, and interference management in MIMO systems;
- Full-duplex MIMO and its role in 6G;
- Millimeter-wave and terahertz MIMO technologies;
- Channel modeling and estimation techniques in MIMO for 5G and beyond;
- Multi-user MIMO for dense wireless environments;
- Field trials, testbeds, and real-world applications of advanced MIMO systems;
- Integration of MIMO with edge computing and AI-driven networks.
We look forward to receiving your contributions.
Dr. Muneeb Ahmad
Prof. Dr. Soo Young Shin
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Electronics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- MIMO
- massive MIMO
- hybrid beamforming
- reconfigurable intelligent surfaces
- AI in MIMO
- multi-user MIMO
- millimeter-wave
- terahertz
- full-duplex
- wireless communications
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






