Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment on Pulmonary Hypertension in Newborns and Children
A special issue of Children (ISSN 2227-9067). This special issue belongs to the section "Pediatric Cardiology".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (5 July 2022) | Viewed by 6274
Special Issue Editor
Interests: pediatric cardiology and pediatric pulmonology; investigation on pulmonary hypertension-associated heart failure
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
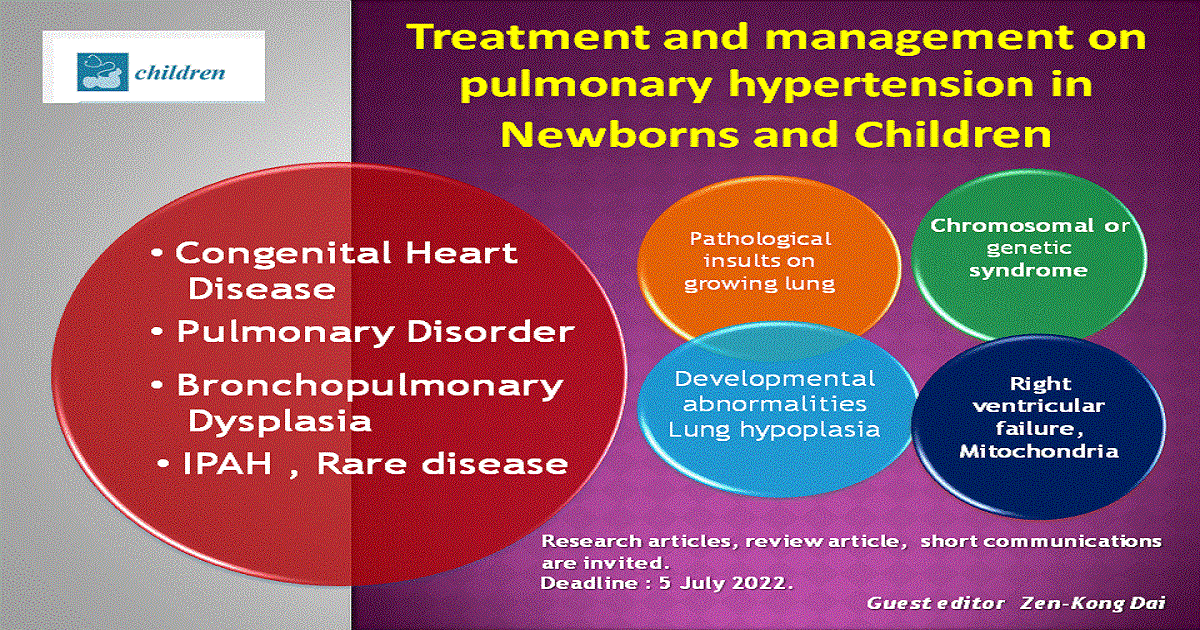
Dear Colleagues,
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is pulmonary vascular disease defined as increased pulmonary artery pressure. Pathologically, pulmonary vascular remodeling occurs with varying severity, resulting in pressure overload in the right ventricle, right ventricular hypertrophy, and even mortality in some cases. Compared with adult patients, PH is characterized by complex heterogeneity in pediatric patients with congential heart disease, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, persisent pulmonary hypertension of newborn (PPHN), collagen disease, etc. The Nice PH classification does not completely characterize or individualize any subgroup of pediatric PH. This is in contrast to the Panama classification, in which prenatal and fetal origins of many pulmonary vascular diseases in neonates and children, perinatal pulmonary vascular maladaptation, prenatal and postnatal pulmonary vascular mal-development, and pulmonary vascular hypoplasia are included. Moreover, it is necessary to develop a more comprehensive algorithm in which multiple specific pediatric risk factors are determined. The critical goal of treatment should be to permit children with PAH to engage in normal activities without the need to self-limit. Beneficial data on diagnosis and targeted pharmacologic interventions are still in the preliminary stages, and large trials are warranted.
In this Special Issue, we invite you to submit interesting and up-to-date articles related to clinical diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension in newborns and children.
Prof. Dr. Zen-Kong Dai
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Children is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- pulmonary hypertension
- vascular remodeling
- premature
- congenital heart disease
- bronchopumonary dysplasia
- vasodilator
- endothelial dysfunction
- idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
- congenital pulmonary abnormality
- pressure overload
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






