The Double Face of Smooth Muscle Cells in Vascular Biology—Friends or Foes, Damage or Regeneration?
A special issue of Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This special issue belongs to the section "Cells of the Cardiovascular System".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (31 December 2024) | Viewed by 3449
Special Issue Editor
Interests: vascular smooth muscle cells; phenotypic modulation; vascular disease; stem cell differentiation; vascular tissue engineering; regenerative medicine
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
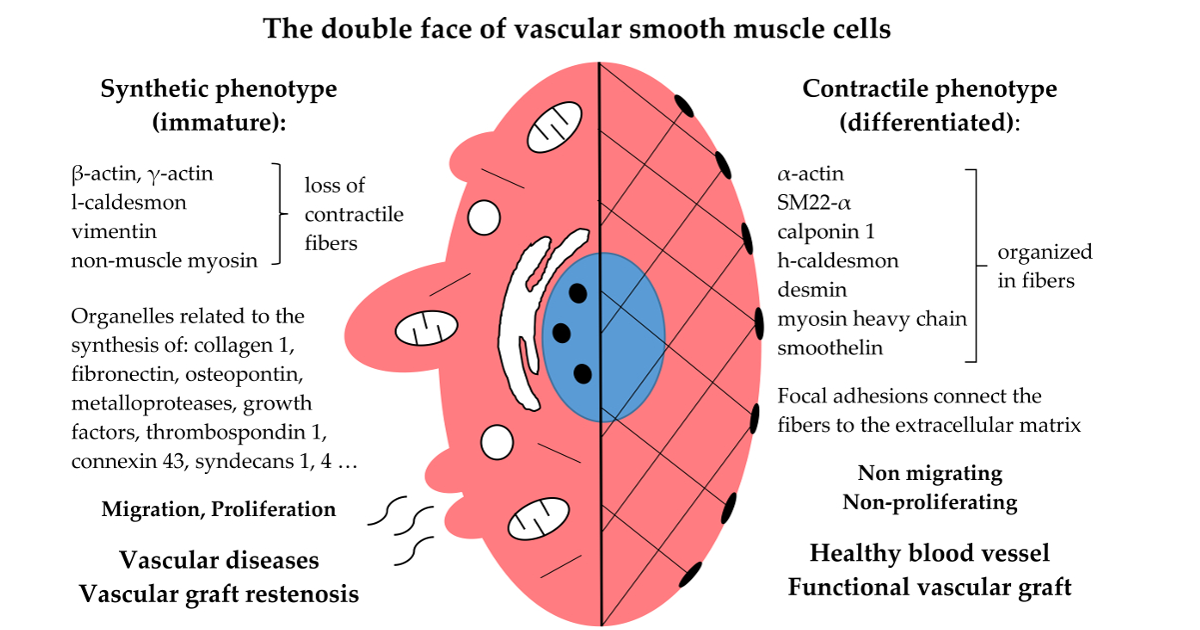
Smooth muscle cells (SMCs) are the most numerous cellular component of the arterial wall, where they form the middle layer called tunica media. They ensure the basic physiological functions of blood vessels, namely contraction, relaxation, and thus regulation of blood flow and pressure. Therefore, in advanced tissue engineering, the layer of SMCs in vascular replacements should always be reconstructed. Nevertheless, tissue engineers have often avoided the presence of SMCs in vascular substitutes. The reason was a high readiness of SMCs for migration and proliferation, which often exceeded the scope of normal regeneration, and led to restenosis of the vascular replacement. A similar mechanism also leads to the formation of atherosclerotic lesions and thickening of the vascular wall in hypertension and other vascular disorders. SMCs undergo a so-called phenotypic modulation, i.e., a transition from a resting, non-proliferative, differentiated contractile phenotype to a less mature, synthetic phenotype, in some ways reminiscent of stem cells. Therefore, during the reconstruction of the vessel wall (whether directly from SMCs or from stem cells), it is necessary to differentiate the cells towards a contractile phenotype via suitable biochemical and mechanical stimuli. These factors include suitable properties of the scaffolds, a suitable composition of the culture medium, suitable mechanical stress in dynamic bioreactors, as well as the presence of a mature semipermeable endothelial cell layer.
In this Special Issue of Cells, I invite you to contribute with original research articles, reviews, or communication articles on all aspects related to the theme of “The double face of smooth muscle cells in vascular biology – from blood vessel damage to regeneration”. Expert articles describing mechanistic, functional, biochemical, cellular, molecular, or genetic aspects of the role of SMCs in blood vessel wall damage or regeneration are highly welcome. Relevant topics include but are not limited to:
- Role of SMCs in vascular diseases;
- Phenotypic switching;
- Contractile phenotype and its achieving/maintaining;
- Synthetic phenotype and its potential reversal;
- Role of extracellular matrix and scaffolds;
- Role of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and hormones;
- Role of oxidative damage and inflammation;
- Vascular replacements and vascular tissue engineering;
- Differentiation of SMCs from stem cells;
- Genetic and RNA modifications of stem cells and SMCs;
- In vitro SMC-based models of the vascular wall or vascular diseases;
- Differences in SMC behavior related to gender, age, species, and localization in the vascular bed, etc.
Dr. Lucie Bacakova
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- vascular smooth muscle cells
- phenotypic modulation
- vascular disease
- stem cell differentiation
- vascular tissue engineering
- regenerative medicine
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






