ALK Signaling Pathways in NSCLC: From Cell Biology to Therapeutic Insights
A special issue of Cells (ISSN 2073-4409).
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 31 July 2026 | Viewed by 84
Special Issue Editors
Interests: genomic-defined NSCLC; molecular alterations; intrinsic & acquired TKI-resistance mechanisms; oncogenic pathways; biomarkers; data science
2. Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Copenhagen, DK-2200 Copenhagen, Denmark
Interests: non-small cell lung cancer; molecular alterations; novel biomarkers; diagnosis; predictive biomarkers; intrinsic & acquired TKI-resistance
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
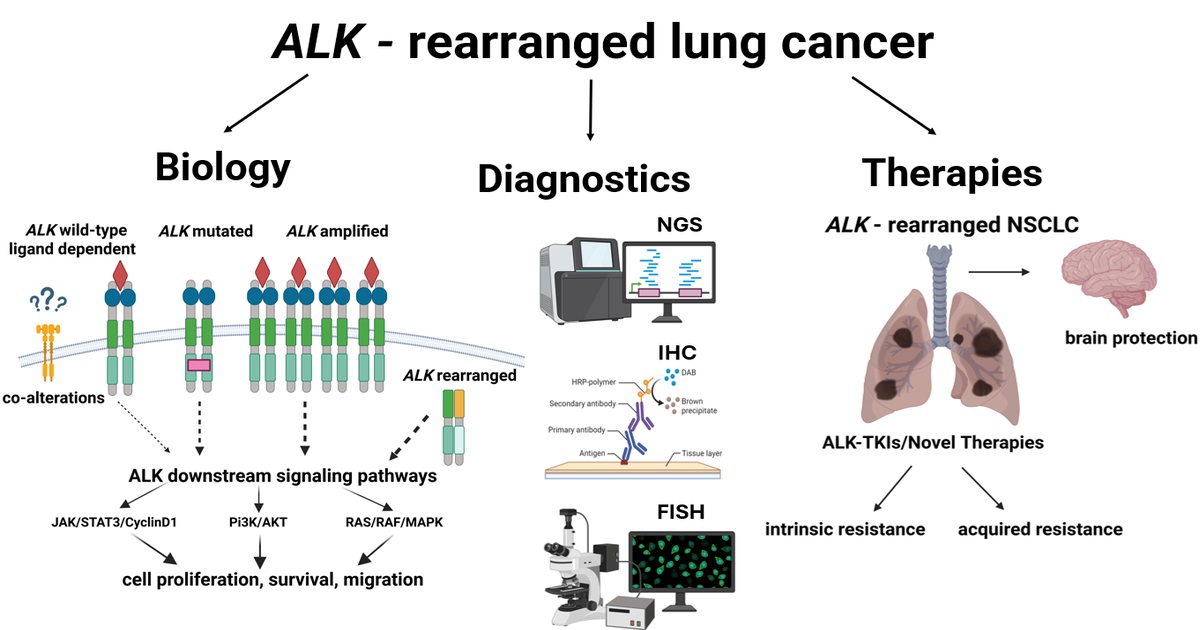
The discovery of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in 2007 led to the development of six ALK-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) that are currently approved worldwide, as well as tremendous progress in treatment outcomes, with more than 10 years’ overall survival in the advanced stages, the best ever reported prognosis among patients with oncogene-addicted NSCLC. Each successive generation of ALK-TKIs shows greater potential regarding ALK signal inhibition, improved intracranial efficacy, and a broader coverage of on-target ALK mutations.
Nowadays, the diagnostics of ALK fusions may be performed via IHC, FISH, or NGS; each detects different aspects of this genomic rearrangement and has its advantages and disadvantages. Consequently, concordance among these methods is important in achieving optimal diagnostics and the most accurate prediction of treatment outcomes.
Despite the fact that most NSCLC patients with ALK rearrangement derive significant therapeutic benefit, there are still challenges to overcome, and topics such as mechanisms of ALK-TKI resistance and related novel therapies require further investigation.
In this Special Issue, we will highlight current research trends in signaling pathways in ALK-rearranged NSCLC and real-world diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Therefore, we invite both basic scientists and clinicians interested in ALK-rearranged NSCLC to provide their contribution.
Dr. Edyta Maria Urbanska
Prof. Dr. Eric Santoni-Rugiu
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)
- non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK-TKIs)
- drug resistance
- signal transduction and oncogenic pathways
- molecular diagnostics (IHC, FISH, NGS)
- targeted therapy
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.







