Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Honey
A special issue of Antibiotics (ISSN 2079-6382). This special issue belongs to the section "The Global Need for Effective Antibiotics".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (15 October 2023) | Viewed by 79558
Special Issue Editors
Interests: honey; bee products; authenticity; quality control; bioactivity; functional food; environmental contamination; adulteration; apitherapy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: essential oils; antimicrobial activity; medicinal plants; mass spectrometry; bacteriology; food microbiology; food safety
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
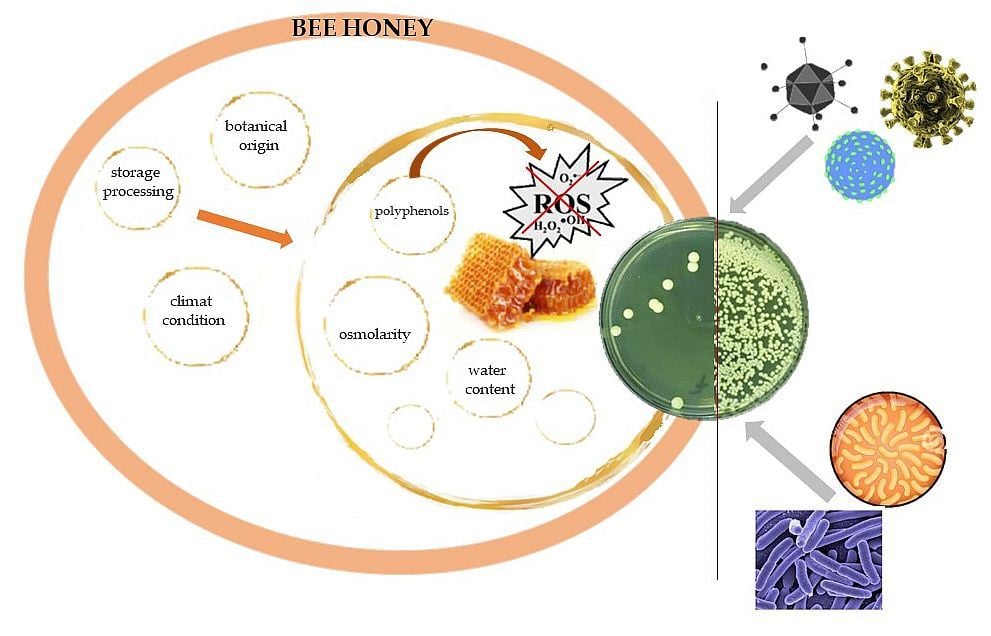
The excessive use of antibiotics can promote bacteria that were originally sensitive to become resistant, so there is a great need to find natural antibacterial agents. One of the considered products is honey, which has been known for its antimicrobial properties, showing a broad spectrum of potential against microorganisms including bacteria. However, the effectiveness of honey against microorganisms depends on the type of the honey produced, which is contingent on its botanical origin (nectar source), the health of bees, climate condition, the storage and processing. The antibacterial activity of honey is attributed to its low water content (low water activity), high viscosity, osmolarity, low pH and acidity, and occurrence of phytochemicals, mainly polyphenols. Currently, many studies confirm the efficacy of honey therapy, but there are still some controversies, mainly regarding the honey-variety dependent action, as well as honey authentication.
Therefore, the main subject of this Special Issue includes the identify of antioxidant and antibacterial properties of varietal honey, the underlying factors that influence its antibacterial efficacy, and its potential medical applications. The manuscripts concerning all honey antibacterial-related activity areas of interest are welcome:
- The impact of botanical origin of honey on its antioxidant activity,
- The key-antioxidant components of honey responsible for their antibacterial action,
- The mechanism of honey polyphenols action against various bacteria and bacteriophages,
- Antibiotics synergism with honey against bacterial biofilms,
- Therapeutic potential of honey in the medical setting,
- The effect of honey processing on its antibacterial properties,
- The necessity of honey authentication and detection of adulterated honey.
Dr. Malgorzata Dzugan
Prof. Dr. Miroslava Kačániová
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Antibiotics is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- honey
- botanical origin
- antioxidant
- antibacterial
- mechanisms
- efficacy
- treatment
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.







