- Article
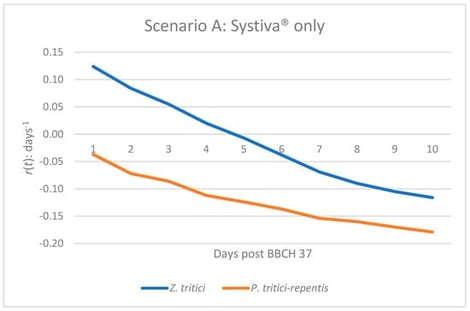
The foliar pathogens of wheat, particularly Zymoseptoria tritici and Pyrenophora tritici-repentis, represent a significant threat to yield. We used a SEIR (Susceptible–Exposed–Infected–Removed) model to quantify epidemic dynamics based on different fungicide application strategies, focusing on the daily dynamic growth rate r(t) (net infection increase) and the removal rate γ(t) (loss infectious tissue) after BBCH 37. In Scenario A (treatment of seed with Systiva®), the r(t) of Z. tritici was positive only during the early phase of the epidemic, followed by progressive suppression over time, while the r(t) for P. tritici-repentis remained negative throughout. Scenario B (seed treatment combined with foliar propiconazole) resulted in uniformly negative r(t) values for both pathogens, indicating stronger and sustained suppression. These findings highlight the practical utility of epidemic growth rate modeling for evaluating fungicide strategies and support integrated seed + foliar applications as a robust approach to disease management in wheat.
4 February 2026