- 3.3Impact Factor
- 6.8CiteScore
- 15 daysTime to First Decision
All Sections
Bacterial Pathogens
Bacteria are ubiquitous in nature, with only a fraction able to cause infection and disease in plants, animals, or humans. But what defines a pathogen? Bacterial species dominate the microbial world, existing in a wide range of environments, from soil, aquatic, or extreme habitats to animal and a...
Emerging Pathogens
Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases
Fungal Pathogens
Fungi cause infections of humans, animals, insects, and plants. These pathogens have a significant impact on global human health and threaten our food supplies by causing widespread infections of plants and animals. In the last half century, the threat of fungal pathogens has become more acute. R...
Immunological Responses and Immune Defense Mechanisms
The immune system detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, playing a key role in protecting the host from infections. The immune system can be divided into two main subsystems: the innate immune system and adaptive immune system. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defen...
Parasitic Pathogens
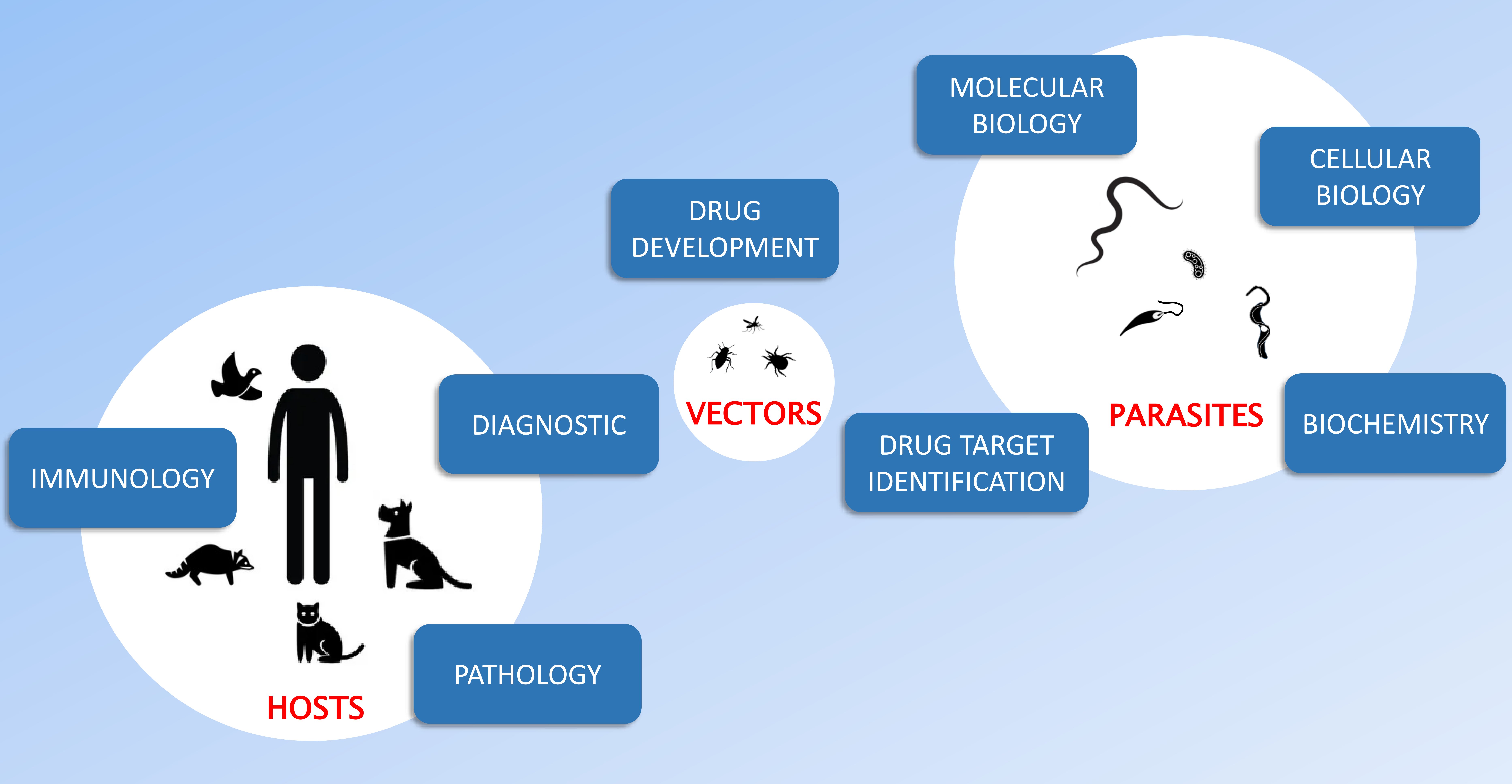
Parasitic diseases are caused by numerous and diverse infectious organisms, ranging from protozoa to helminths. Many of these pathogens have complex life cycles and require trans...
Ticks
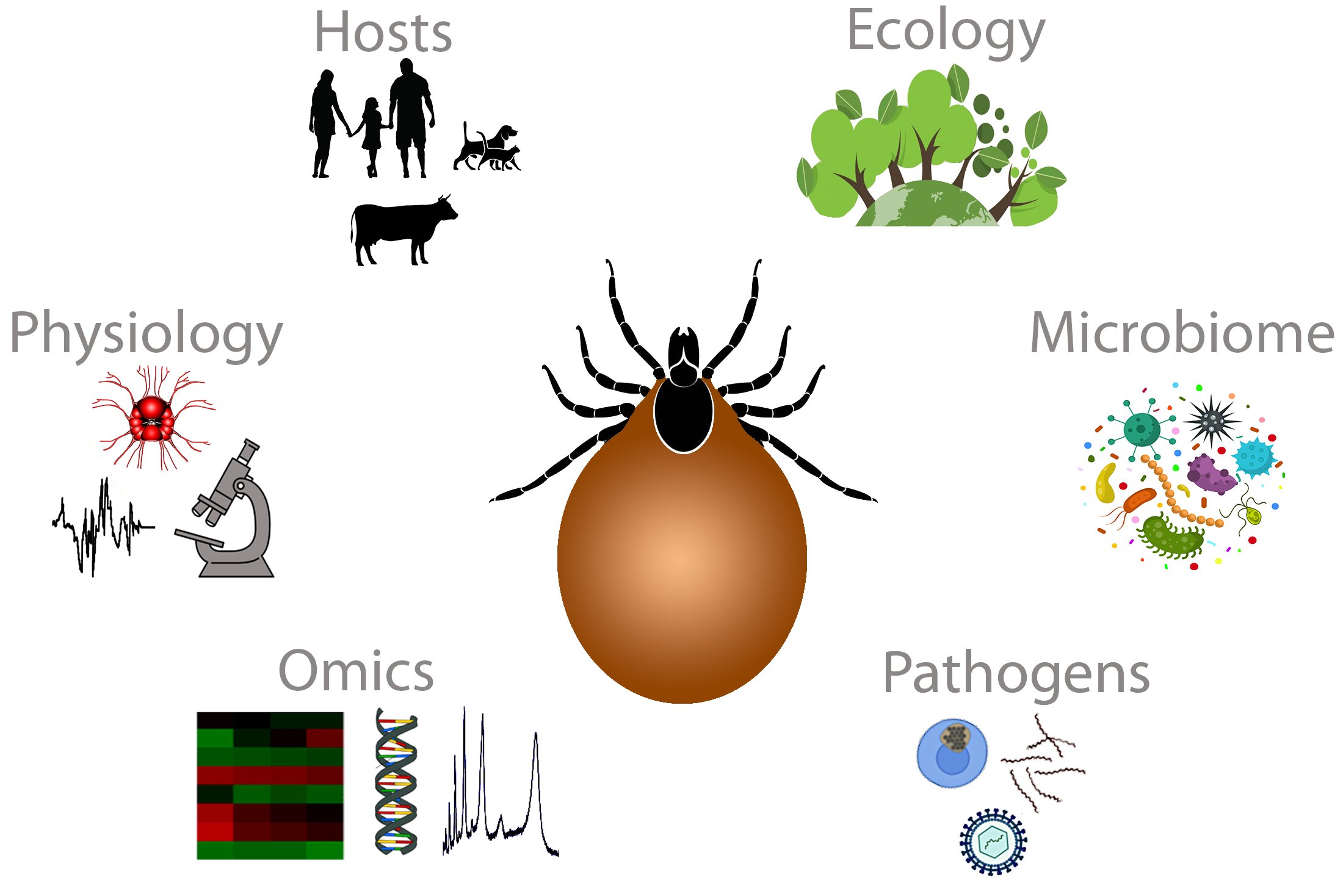
Ticks is a section publishing high quality research ...
Vaccines and Therapeutic Developments
This section is open to research on novel and current vaccines, their mechanism of action and efficacy in the face of emerging variants and new pathogens, as well as traditional, natural, and pharmacologic treatment of infections in different species. AI-assisted methodology and identification of...
Viral Pathogens
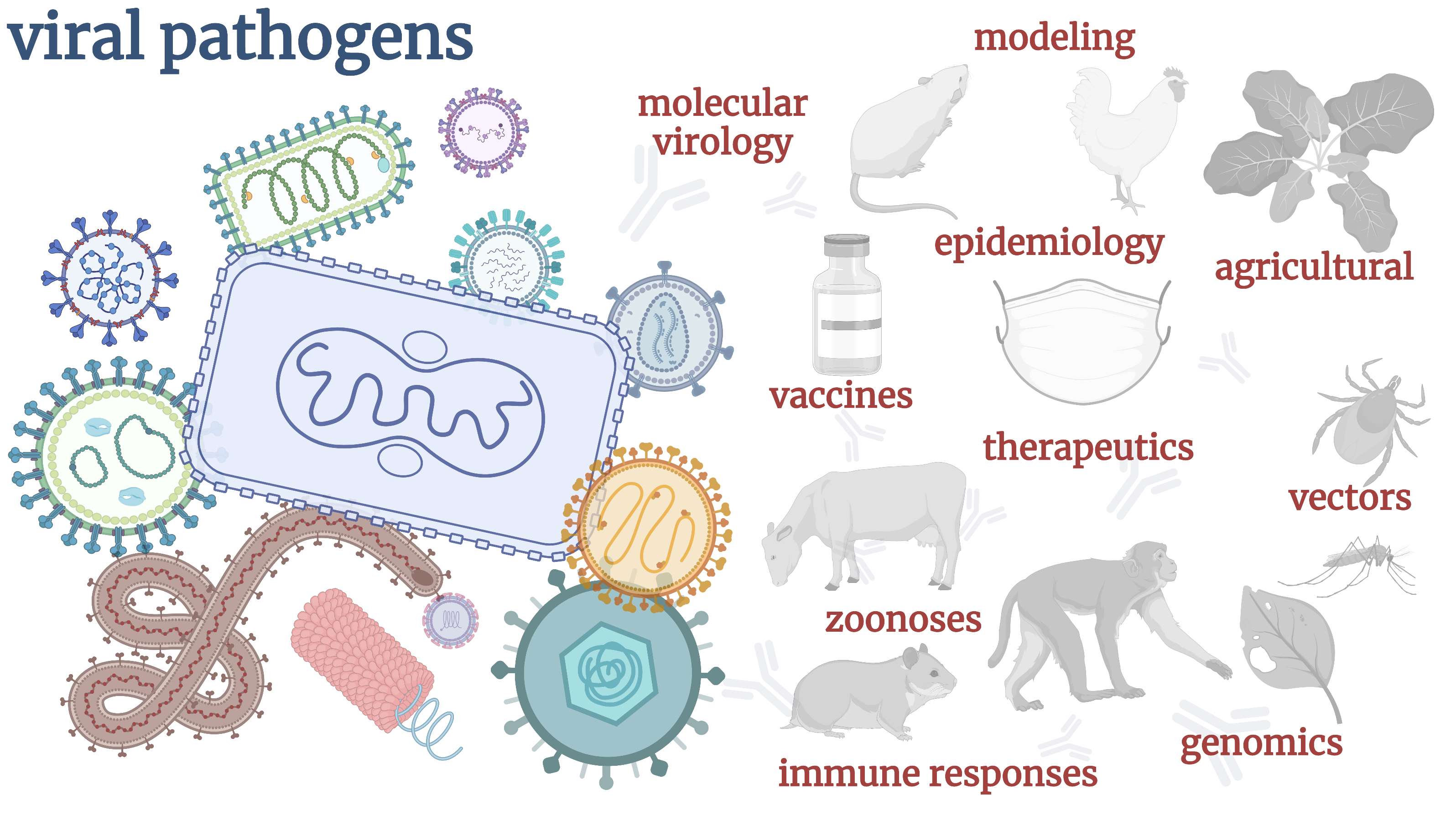
Viruses infect all forms of life, including humans, animals, plants, bacteria, and archaea. Viral infections in humans can cause mild to severe and sometimes fatal diseases, such as the common cold, flu, chickenpo...

